Targeted Atherosclerosis Treatment Using Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Targeting Peptide-Engineered Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
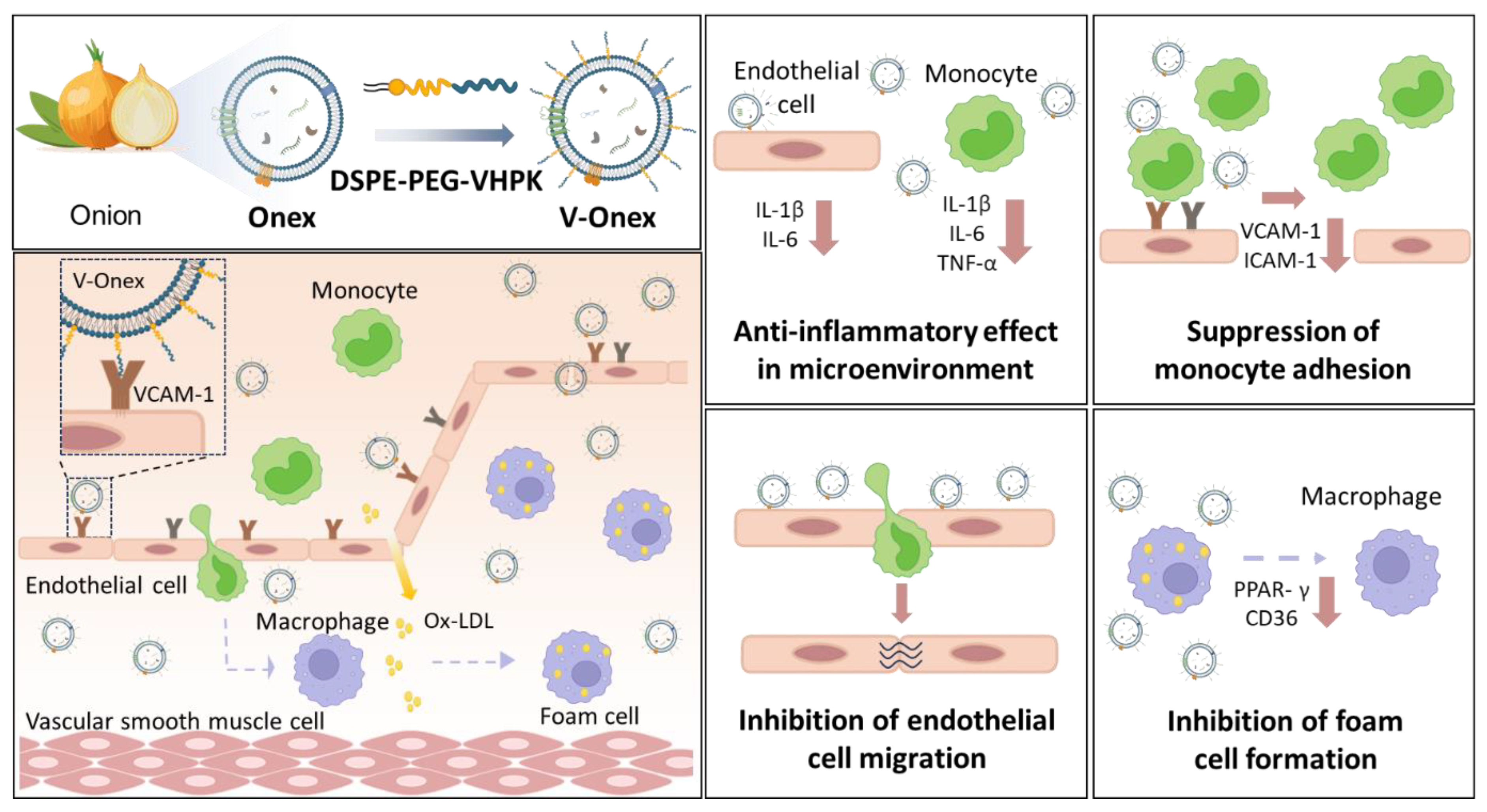
2. Results and Discussion
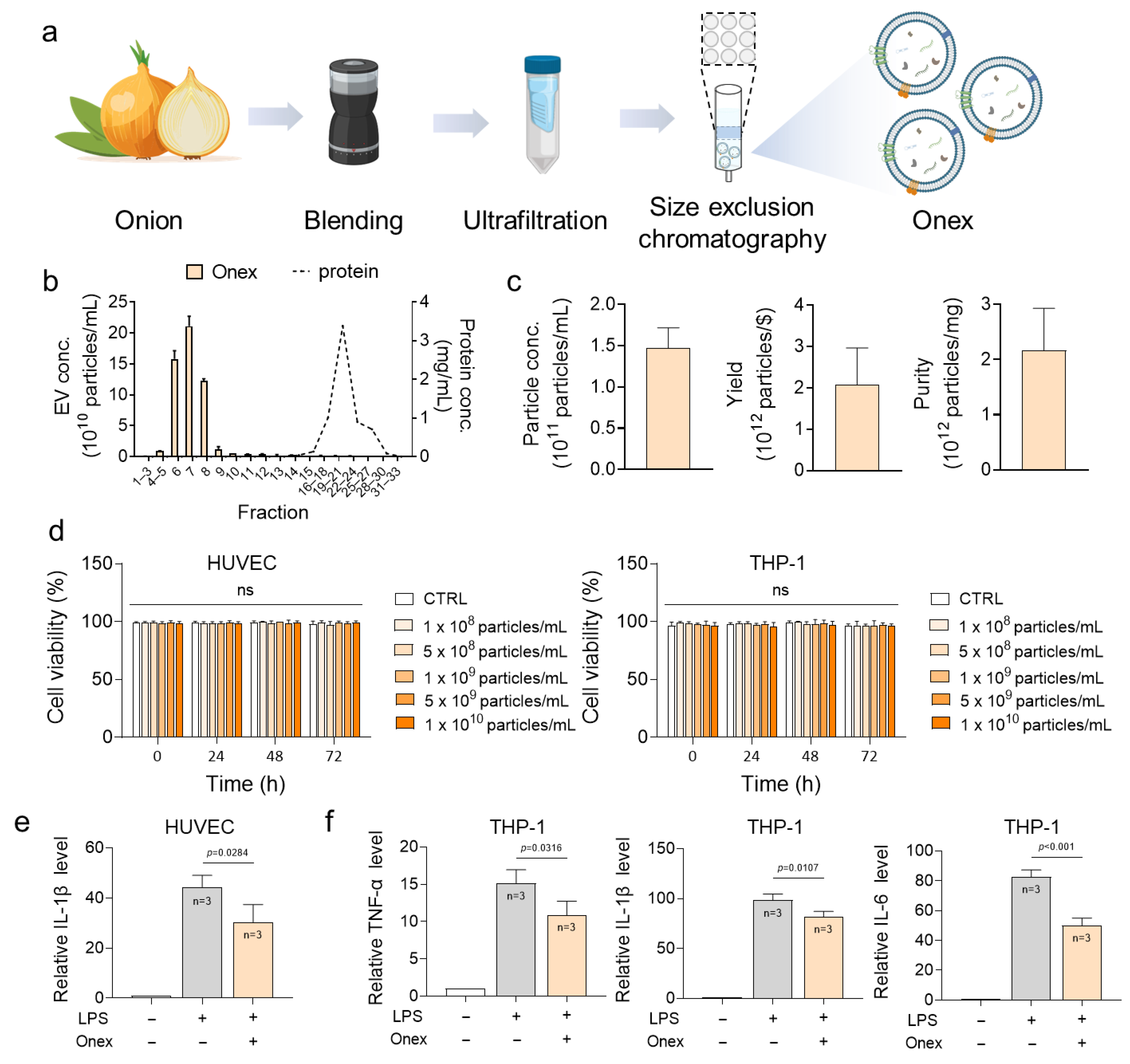
2.1. Characterization and Cytotoxicity Assessment of Onex
2.2. Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Onex in HUVECs and THP-1 Cells
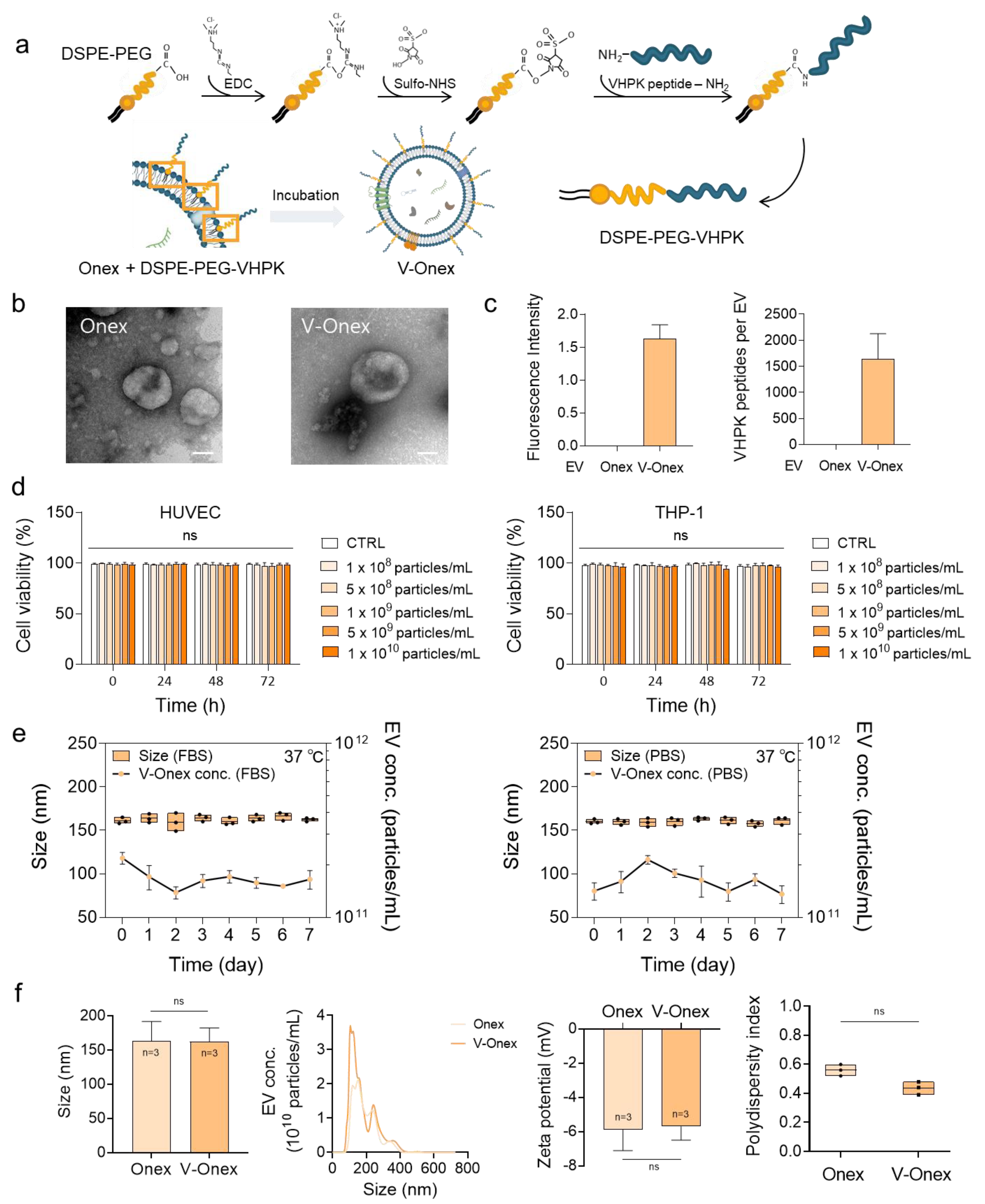
2.3. V-Onex Construction by Surface Engineering of Onex and Their Characterization
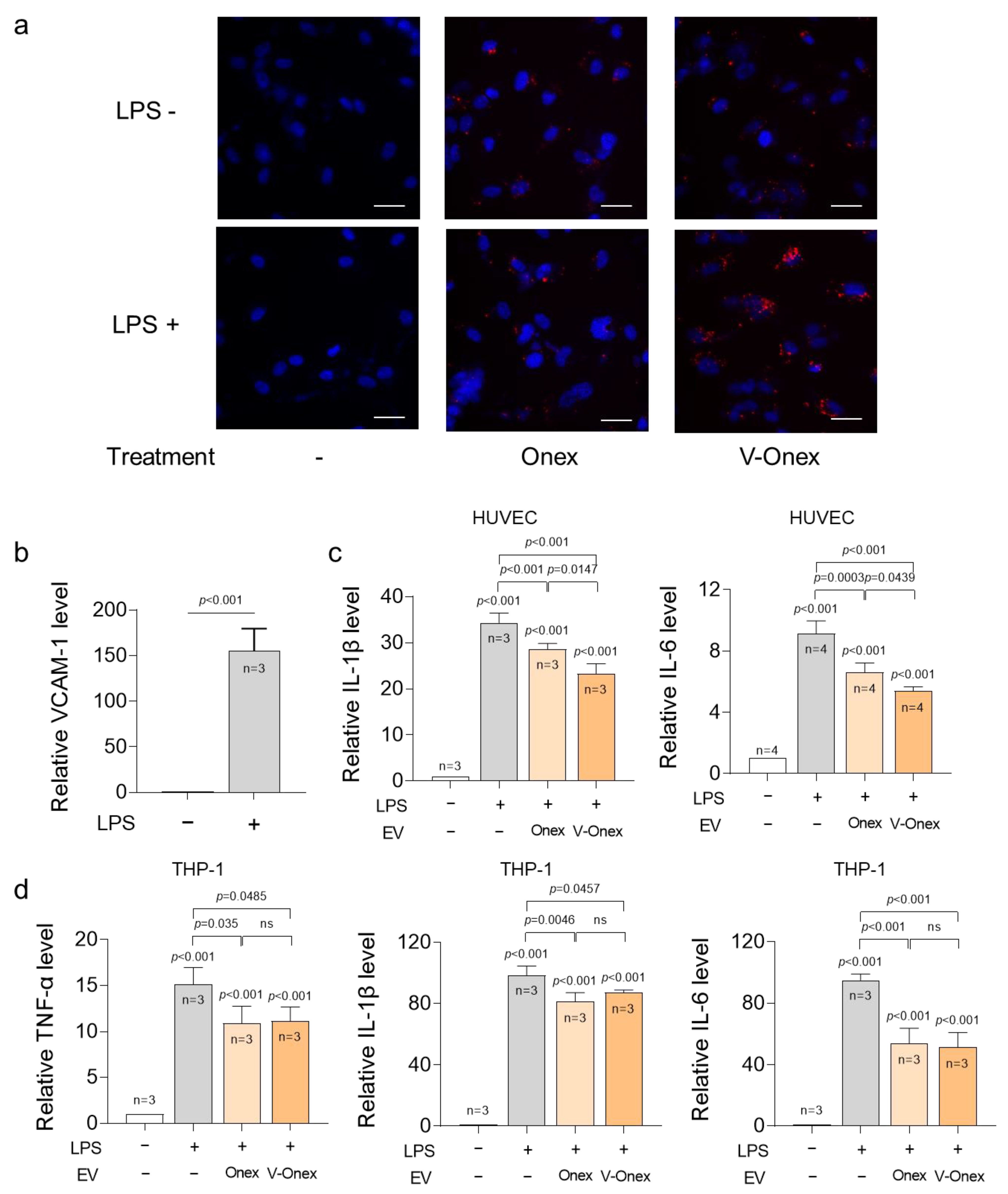
2.4. Targeting Capability of V-Onex in Inflamed Endothelial Cells
2.5. Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Gene Regulations of V-Onex in HUVECs and THP-1 Cells
2.6. Enhanced Suppression Activity of Endothelial Cell Migration by V-Onex
2.7. Enhanced Suppression of Monocyte Adhesion to Endothelial Cells by VCAM-1-Targeting V-Onex
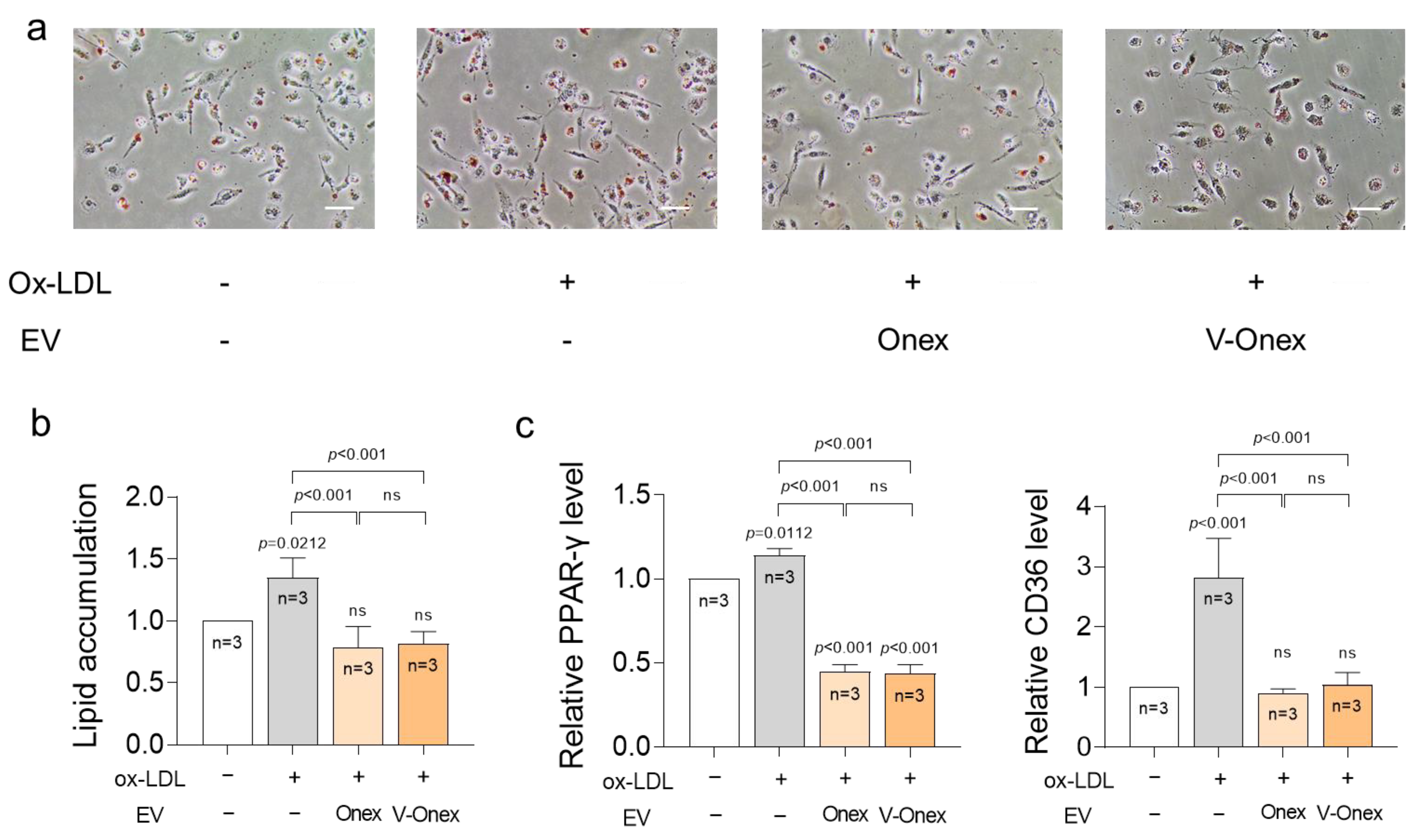
2.8. Suppression of Foam Cell Formation by Onex and V-Onex Function
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Cultures
3.2. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles from Onion
3.3. NTA and Zeta Potential Analysis
3.4. Effects of Onex on Cell Viability
3.5. qRT-PCR Analysis
3.6. Construction of V-Onex
3.7. Targeting Effect Assessment of V-Onex
3.8. Monocyte Adhesion Assay
3.9. Migration Assay
3.10. ORO Staining
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NTA | Nanoparticle tracking analysis |
| ORO | Oil Red O |
| Ox-LDL | Oxidized low-density lipoprotein |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
References
- Barquera, S.; Pedroza-Tobías, A.; Medina, C.; Hernández-Barrera, L.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Lozano, R.; Moran, A.E. Global overview of the epidemiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2015, 46, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, C.; Chimowitz, M.I. Stroke caused by atherosclerosis of the major intracranial arteries. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, M.; Hak, A.E.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Bots, M.L.; Grobbee, D.E.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C.M.; Breteler, M.M.B. Comparison between measures of atherosclerosis and risk of stroke: The Rotterdam Study. Stroke 2003, 34, 2367–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palasubramaniam, J.; Wang, X.; Peter, K. Myocardial infarction—From atherosclerosis to thrombosis: Uncovering new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e176–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, K.J.; Valtonen, V.V.; Nieminen, M.S.; Asikainen, S. Role of infection as a risk factor for atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; García-Cardeña, G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horio, E.; Kadomatsu, T.; Miyata, K.; Arai, Y.; Hosokawa, K.; Doi, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Horiguchi, H.; Endo, M.; Tabata, M.; et al. Role of endothelial cell–derived Angptl2 in vascular inflammation leading to endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis progression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, T.; Xiong, X.; Yang, Q.; Su, Z.; Zheng, M.; Chen, Q. Colchicine delivered by a novel nanoparticle platform alleviates atherosclerosis by targeted inhibition of NF-κB/NLRP3 pathways in inflammatory endothelial cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertic, J.; Slavicek, J.; Bozina, N.; Malenica, B.; Kes, P.; Reiner, Z. Cytokines and growth factors in mostly atherosclerotic patients on hemodialysis determined by biochip array technology. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, F.; Xiang, M. Engineered M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles with platelet membrane fusion for targeted therapy of atherosclerosis. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 35, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, K.; Huo, Y. VCAM-1 is critical in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Gordon, J.L.; Gearing, A.J.; Pigott, R.; Woolf, N.; Katz, D.; Kyriakopoulos, A. The expression of the adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1, PECAM, and E-selectin in human atherosclerosis. J. Pathol. 1993, 171, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybulsky, M.I.; Iiyama, K.; Li, H.; Zhu, S.; Chen, M.; Iiyama, M.; Davis, V.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Connelly, P.W.; Milstone, D.S. A major role for VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1, in early atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-J.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Sharrett, A.R.; Smith, L.C.; Davis, C.; Gotto, A.M., Jr.; Boerwinkle, E. Circulating adhesion molecules VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin in carotid atherosclerosis and incident coronary heart disease cases: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation 1997, 96, 4219–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Kaur, R.; Kumari, P.; Pasricha, C.; Singh, R. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1: Gatekeepers in various inflammatory and cardiovascular disorders. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 548, 117487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Jiang, C.; Song, J.; Bi, Y.; Chen, W.; Lu, C.; Chen, M.; Lv, L.; Yu, R.; Zou, J.; et al. Microenvironment responsive nanoplatform for targeted removal of cholesterol and reshaping inflammatory microenvironment in atherosclerotic plaques. J. Control. Release 2025, 365, 114000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirolomoom, A.; Kim, C.W.; Seo, J.W.; Kumar, S.; Son, D.J.; Gagnon, M.K.J.; Ingham, E.S.; Ferrara, K.W.; Jo, H. Multifunctional nanoparticles facilitate molecular targeting and miRNA delivery to inhibit atherosclerosis in ApoE–/– mice. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8885–8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distasio, N.; Salmon, H.; Dierick, F.; Ebrahimian, T.; Tabrizian, M.; Lehoux, S. VCAM-1-Targeted gene delivery nanoparticles localize to inflamed endothelial cells and atherosclerotic plaques. Adv. Ther. 2021, 4, 2000196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distasio, N.; Dierick, F.; Ebrahimian, T.; Tabrizian, M.; Lehoux, S. Design and development of branched poly(β-aminoester) nanoparticles for Interleukin-10 gene delivery in a mouse model of atherosclerosis. Acta Biomater. 2022, 143, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Bai, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, W.; Shu, M.; Mei, Q.; et al. VCAM-1-binding peptide targeted cationic liposomes containing NLRP3 siRNA to modulate LDL transcytosis as a novel therapy for experimental atherosclerosis. Metabolism 2022, 135, 155274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, S.; Raghunath, A.; Raghunath, S. Statin therapy: Review of safety and potential side effects. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2016, 32, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, S.H.; Rashidijahanabad, Z.; Ramadan, S.; Kauffman, N.; Parameswaran, N.; Zinn, K.R.; Qian, C.; Arora, R.; Agnew, D.; Huang, X. Effective atherosclerotic plaque inflammation inhibition with targeted drug delivery by hyaluronan conjugated atorvastatin nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 9541–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Pradhan, A.D.; Glynn, R.J.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Nissen, S.E.; PROMINENT, REDUCE-IT, and STRENGTH Investigators. Inflammation and cholesterol as predictors of cardiovascular events among patients receiving statin therapy: A collaborative analysis of three randomised trials. Lancet 2023, 401, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, C.J.; Gotto, A.M., Jr.; Basson, C.T. The evolving role of statins in the management of atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscica, M.; Ferri, N.; Banach, M.; Sirtori, C.R.; Corsini, A. Side effects of statins: From pathophysiology and epidemiology to diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 3288–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bełtowski, J.; Wójcicka, G.; Jamroz-Wiśniewska, A. Adverse effects of statins—Mechanisms and consequences. Curr. Drug Saf. 2009, 4, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournadre, A. Statins, myalgia, and rhabdomyolysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2020, 87, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, E.S. Hepatotoxicity of statins and other lipid-lowering agents. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.D.; Zhao, Y.; Quek, R.G.W.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Budoff, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Garg, P.; Sandfort, V.; Tsai, M.; Lopez, J.A.G. Residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in statin-treated adults: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2017, 11, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, C.; Armitage, J. Management of residual risk after statin therapy. Atherosclerosis 2016, 245, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.Y.; Kang, S.J.; Rhee, W.J. Isolation of cabbage exosome-like nanovesicles and investigation of their biological activities in human cells. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4321–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Rhee, W.J. Antioxidative effects of carrot-derived nanovesicles in cardiomyoblast and neuroblastoma cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, W.; Li, J.; Ruan, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yan, A.; Zhu, H. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles as a promising anti-tumor approach: A comprehensive assessment of effectiveness, safety, and mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2024, 130, 155750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, S.; Karimi, H.; Alizadeh, M.; Khazaei, A.H.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Rezakhani, L.; Sharifi, E. Prospects of plant-derived exosome-like nanocarriers in oncology and tissue engineering. Hum. Cell 2024, 37, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, M.; Singh, B.; Mir, R.A.; Nemati, M.; Babaei, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Rasmi, Y.; Gholinejad Golezani, A.; Rezaie, J. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel nanomedicine approach with advantages and challenges. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Kang, S.J.; Rhee, W.J. Perilla-leaf-derived extracellular vesicles selectively inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Shimizu, T.; Alaaeldin, E.; Hussein, A.; Sarhan, H.A.; Szebeni, J.; Ishida, T. PEGylated liposomes: Immunological responses. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.Y.; Kang, S.J.; Kim, G.; Gwak, S.; Baek, G.; Rhee, W.J. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: Current status and challenges for developing a new paradigm in therapeutics development. View 2025, 6, 20240115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.J.; Rhee, W.J. Exploiting spinach-derived extracellular vesicles for anti-obesity therapy through lipid accumulation inhibition. Adv. Ther. 2024, 7, 2400150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, W.-K.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Cha, S.-G.; Park, J.M.; Park, H.J.; Park, C.G.; Han, D.K. Recent advances in extracellular vesicle engineering and its applications to regenerative medicine. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Ye, Z.; Xu, J. Engineering extracellular vesicles as delivery systems in therapeutic applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Schwarz, H.; Nanda, H.S.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Y. Exosomes, a new star for targeted delivery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 751079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Rhee, W.J. Engineered plant-derived extracellular vesicles for targeted regulation and treatment of colitis-associated inflammation. Theranostics 2024, 14, 5643–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Kim, S.E.; Seo, M.J.; Kim, E.; Rhee, W.J. Suppression of inflammatory responses in macrophages by onion-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 115, 287–297, Erratum in J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 142, 753–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.Y.; Hsueh, Y.C.; Cheng, H.L.; Wu, K.K. Cytokine-induced autophagy promotes long-term VCAM-1 but not ICAM-1 expression by degrading late-phase IκBα. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickett, J.R.; Wu, Y.; Zacchi, L.F.; Ta, H.T. Targeting endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in atherosclerosis: Drug discovery and development of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1-directed novel therapeutics. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 2278–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook-Mills, J.M.; Marchese, M.E.; Abdala-Valencia, H. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and signaling during disease: Regulation by reactive oxygen species and antioxidants. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1607–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, C.; Rhee, W.J. Targeted Atherosclerosis Treatment Using Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Targeting Peptide-Engineered Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188884
Choi C, Rhee WJ. Targeted Atherosclerosis Treatment Using Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Targeting Peptide-Engineered Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188884
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Chanwoo, and Won Jong Rhee. 2025. "Targeted Atherosclerosis Treatment Using Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Targeting Peptide-Engineered Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188884
APA StyleChoi, C., & Rhee, W. J. (2025). Targeted Atherosclerosis Treatment Using Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Targeting Peptide-Engineered Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188884






