LINE-1 266/97 and ALU 260/111 Copy Number Ratios in Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Plasma as Potential Biomarkers for the Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
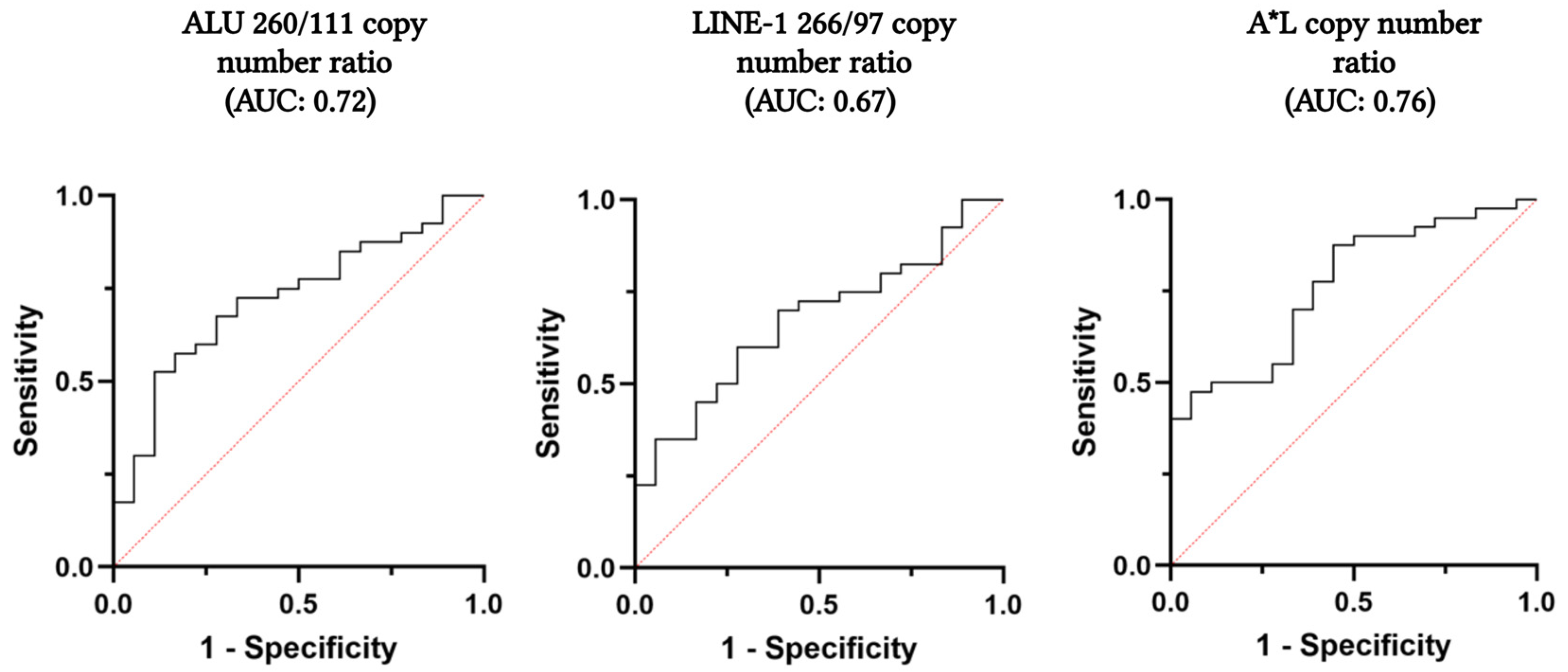
2.2. Evaluation of ALU 260/111 and LINE-1 266/97 Copy Number Ratio and cfDI in the Plasma of Patients’ Cohort
2.3. Evaluation of ccfDNA Quantity by EEF1A2 and ESR1 Copy Number in the Plasma of PCa and BPH Patients
2.4. Correlation of ALU 260/111 and LINE-1 266/97 Copy Number Ratio with the Clinical-Pathological Status of PCa Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Plasma Preparation and ccfDNA Extraction
4.3. ddPCR Analysis on EEF1A2, ESR1 and ccfDNA Quantity
4.4. ddPCR Analysis on ALU 260, ALU 111, LINE-1 266 and LINE-1 97 Fragments
× 618 × 1.7 × 10−15)
× bpn × 618 × 1.7 × 10−15)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Soerjomataram, I. The Ever-Increasing Importance of Cancer as a Leading Cause of Premature Death Worldwide. Cancer 2021, 127, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraju, V.; Ashlyin, P.V.K.; Elango, N.; Devanand, B. Role of Transrectal Ultrasound Elastography in the Diagnosis of Prostate Carcinoma. J. Med. Ultrasound 2020, 28, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, N.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer—2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, P.J.; Bjartell, A.S.; Catto, J.W.F.; Eggener, S.E.; Lilja, H.; Loeb, S.; Schalken, J.; Schlomm, T.; Cooperberg, M.R. Genomic Predictors of Outcome in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Hoon, D.S.B.; Pantel, K. Cell-Free Nucleic Acids as Biomarkers in Cancer Patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ces, A.M.; Rapado-González, Ó.; Salgado-Barreira, Á.; Santos, M.A.; Aroso, C.; Vinhas, A.S.; López-López, R.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Liquid Biopsies Based on Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, N.; Generali, D.; Zanconati, F.; Bortul, M.; Scaggiante, B. Cell-Free DNA Integrity for the Monitoring of Breast Cancer: Future Perspectives? World J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 9, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, N.; Tierno, D.; Pavan, N.; Generali, D.; Grassi, G.; Zanconati, F.; Scaggiante, B. Circulating Cell-Free DNA Integrity for Breast and Prostate Cancer: What Is the Landscape for Clinical Management of the Most Common Cancers in Women and Men? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Zennami, K.; Velarde, E.; Thorek, D.L.J.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; DeWeese, T.L.; Lupold, S.E. Longitudinal Measurement of Subcutaneous and Intratibial Human Prostate Cancer Xenograft Growth and Response to Ionizing Radiation by Plasma Alu and LINE-1 CtDNA: A Comparison to Standard Methods. Prostate 2021, 81, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, E.M.; Ha, S.; Mita, P.; Brittingham, G.; Sciamanna, I.; Spadafora, C.; Logan, S.K. Long Interspersed Nuclear Element-1 Expression and Retrotransposition in Prostate Cancer Cells. Mob. DNA 2018, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavia, P.; Sciamanna, I.; Spadafora, C. An Epigenetic LINE-1-Based Mechanism in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houede, N.; Piazza, P.V.; Pourquier, P. LINE-1 as a Therapeutic Target for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2018, 23, 1292–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, N.; Levanon, E.Y.; Amariglio, N.; Heimberger, A.B.; Ram, Z.; Constantini, S.; Barbash, Z.S.; Adamsky, K.; Safran, M.; Hirschberg, A.; et al. Altered Adenosine-to-Inosine RNA Editing in Human Cancer. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortul, M.; Giudici, F.; Tierno, D.; Generali, D.; Scomersi, S.; Grassi, G.; Bottin, C.; Cappelletti, M.R.; Zanconati, F.; Scaggiante, B. A Case–Control Study by DdPCR of ALU 260/111 and LINE-1 266/97 Copy Number Ratio in Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Plasma Revealed LINE-1 266/97 as a Potential Biomarker for Early Breast Cancer Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrborn, C.G. BPH Progression: Concept and Key Learning from MTOPS, ALTESS, COMBAT, and ALF-ONE. BJU Int. 2008, 101 (Suppl. 3), 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.J.; Coffey, D.S.; Walsh, P.C.; Ewing, L.L. The Development of Human Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Age. J. Urol. 1984, 132, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2025. Atlanta: American Cancer Society. 2025. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/2025-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- Madhavan, D.; Wallwiener, M.; Bents, K.; Zucknick, M.; Nees, J.; Schott, S.; Cuk, K.; Riethdorf, S.; Trumpp, A.; Pantel, K.; et al. Plasma DNA Integrity as a Biomarker for Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer and Potential Marker for Early Diagnosis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Enzo, M.V.; Bedin, C.; Belardinelli, V.; Goldin, E.; Del Bianco, P.; Maschietto, E.; D’Angelo, E.; Izzi, L.; Saccani, A.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA: A Promising Marker of Regional Lymphonode Metastasis in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancer Biomark. 2012, 11, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, N.A.; Mohamed, S.N.; Ahmed, M.A. Plasma ALU-247, ALU-115, and CfDNA Integrity as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Breast Cancer. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 1028–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Feng, G.; Xiao, L.; Tang, J.; Huang, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, G. Plasma Cell-Free DNA and Its DNA Integrity as Biomarker to Distinguish Prostate Cancer from Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Patients with Increased Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, A.; Sweify, K.M.; El-Fayoumy, H.M.; Nofal, N. Quantitative Analysis of Plasma Cell-Free DNA and Its DNA Integrity in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer Using ALU Sequence. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, M.; Hosseini, J.; Mirfakhraie, R.; Habibi, M.; Azargashb, E.; Pouresmaeili, F. The Value of the Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Concentration and Integrity Index as a Clinical Tool for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: A Prospective Case-Control Cohort Study in an Iranian Population. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 4549–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condappa, A.; McGrowder, D.; Aiken, W.; McLaughlin, W.; Gossell-Williams, M. Evaluation of Plasma Circulating Cell Free DNA Concentration and Integrity in Patients with Prostate Cancer in Jamaica: A Preliminary Study. Diseases 2020, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, R.; Rieger-Christ, K.M.; Canes, D.; Emara, N.R.; Shuber, A.P.; Boynton, K.A.; Libertino, J.A.; Summerhayes, I.C. DNA Integrity Assay: A Plasma-Based Screening Tool for the Detection of Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4569–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadio, V.; Calistri, D.; Salvi, S.; Gunelli, R.; Carretta, E.; Amadori, D.; Silvestrini, R.; Zoli, W. Urine Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Marker for Early Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: A Pilot Study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 270457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancks, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H. Active Human Retrotransposons: Variation and Disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2012, 22, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciamanna, I.; Sinibaldi-Vallebona, P.; Serafino, A.; Spadafora, C. LINE-1-Encoded Reverse Transcriptase as a Target in Cancer Therapy. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2018, 23, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.E.; Kaul, T.; Walker, J.N.; Everett, C.; White, T.; Deininger, P. Altered DNA Repair Creates Novel Alu/Alu Repeat-Mediated Deletions. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zong, W.; Ju, S.; Jing, R.; Cui, M. Promising Member of the Short Interspersed Nuclear Elements (Alu Elements): Mechanisms and Clinical Applications in Human Cancers. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 56, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Cuk, K.; Heil, J.; Golatta, M.; Schott, S.; Sohn, C.; Schneeweiss, A.; Burwinkel, B.; Surowy, H. Cell-Free Circulating DNA Integrity Is an Independent Predictor of Impending Breast Cancer Recurrence. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 54537–54547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Su, L.; Sang, J.; Wang, S.; Yao, Y. Plasma Cell-Free DNA Integrity: A Potential Biomarker to Monitor the Response of Breast Cancer to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Yu, C.; Huang, Q. Diagnostic Value of Combined Detection of Plasma CfDNA Concentration and Integrity in NSCLC. Lung Cancer Manag. 2024, 13, LMT64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liang, M.; Ma, G.; Li, L.; Zhou, W.; Xia, T.; Xie, H.; Wang, S. Plasma Cell-Free DNA Integrity plus Circulating Tumor Cells: A Potential Biomarker of No Distant Metastasis Breast Cancer. Neoplasma 2017, 64, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Holland-Letz, T.; Wallwiener, M.; Surowy, H.; Cuk, K.; Schott, S.; Trumpp, A.; Pantel, K.; Sohn, C.; Schneeweiss, A.; et al. Circulating Free DNA Integrity and Concentration as Independent Prognostic Markers in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 169, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, S.; Leal, A.; Phallen, J.; Fiksel, J.; Adleff, V.; Bruhm, D.C.; Jensen, S.Ø.; Medina, J.E.; Hruban, C.; White, J.R.; et al. Genome-Wide Cell-Free DNA Fragmentation in Patients with Cancer. Nature 2019, 570, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.M.D.; Han, D.S.C.; Jiang, P.; Chiu, R.W.K. Epigenetics, Fragmentomics, and Topology of Cell-Free DNA in Liquid Biopsies. Science 2021, 372, eaaw3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, H.; Lubrich, H.; Blum, S.; Antoniadis, S.; Lermann, J.; Ekici, A.; Fasching, P.A.; Beckmann, M.W.; Ruebner, M.; Burghaus, S. Comparison of Methods for Isolation and Quantification of Circulating Cell-Free DNA from Patients with Endometriosis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2021, 43, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehle, S.; Emons, J.; Hack, C.C.; Heindl, F.; Hein, A.; Preuß, C.; Seitz, K.; Zahn, A.L.; Beckmann, M.W.; Fasching, P.A.; et al. Evaluation of Automated Techniques for Extraction of Circulating Cell-Free DNA for Implementation in Standardized High-Throughput Workflows. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, T.; Li, R. Clinical Value of Plasma CfDNA Concentration and Integrity in Breast Cancer Patients. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arko-Boham, B.; Aryee, N.A.; Blay, R.M.; Owusu, E.D.A.; Tagoe, E.A.; Doris Shackie, E.S.; Debrah, A.B.; Adu-Aryee, N.A. Circulating Cell-Free DNA Integrity as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker for Breast and Prostate Cancers. Cancer Genet. 2019, 235–236, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Vafaei, S.; Gu, X.; Zhong, X. The Prognostic Value of Plasma Cell-Free DNA Concentration in the Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 599602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ces, A.M.; Rapado-González, Ó.; Aguín-Losada, S.; Formoso-García, I.; López-Cedrún, J.L.; Triana-Martínez, G.; López-López, R.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Circulating Cell-Free DNA Concentration as a Biomarker in Head and Neck Cancer. Oral Dis. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucedo-Sariñana, A.M.; Lugo-Escalante, C.R.; Barros-Núñez, P.; Marín-Contreras, M.E.; Pineda-Razo, T.D.; Mariscal-Ramírez, I.; Gallegos-Arreola, M.P.; Rosales-Reynoso, M.A. Circulating Cell-Free-DNA Concentration Is a Good Biomarker for Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer in Mexican Patients. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, E.R.; Anwar, M.M.; Kohail, H.M.A.; El-Zoghby, S.M.; Abo-El-Eneen, M.S. Cell-Free DNA Concentration and Integrity as a Screening Tool for Cancer. Indian J. Cancer 2013, 50, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ruocco, F.; Basso, V.; Rivoire, M.; Mehlen, P.; Ambati, J.; De Falco, S.; Tarallo, V. Alu RNA Accumulation Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition by Modulating MiR-566 and Is Associated with Cancer Progression. Oncogene 2018, 37, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.C.; Parfenov, M.; Gorham, J.M. Droplet Digital PCR with EvaGreen Assay: Confirmational Analysis of Structural Variants. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2018, 97, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood-Bouwens, C.; Lau, B.T.; Handy, C.M.; Lee, H.J.; Ji, H.P. Single-Color Digital PCR Provides High-Performance Detection of Cancer Mutations from Circulating DNA. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | PCa Patients (n = 40) | BPH Patients (n = 18) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age median (IQR) | 76.0 (66.8–79.3) | 68.0 (60.3–74.5) | 0.028 * |
| BMI mean (IQR) | 25.6 (23.6–28.5) | 25.6 (24.0–27.3) | 0.942 |
| PSA baseline median (IQR) | 6.8 (4.6–9.5) | 7.5 (5.5–11.6) | 0.542 |
| Tumour Stage number of patients (percentage) | |||
| I–II (early) | 30 (75.0%) | nd | nd |
| III–IV (advanced/metastatic) | 8 (20.0%) | nd | nd |
| Not Available | 2 (5.0%) | nd | nd |
| Variable | PCa Patients (n = 40) | BPH Patients (n = 18) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALU 260/111 copy number ratio median (IQR) | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | 0.05 (0.04–0.05) | 0.006 ** |
| LINE-1 266/97 copy number ratio median (IQR) | 0.10 (0.07–0.14) | 0.14 (0.10–0.17) | 0.037 * |
| ALU 260/111 cfDI (ng/mL) median (IQR) | 0.07 (0.06–0.11) | 0.11 (0.08–0.13) | 0.006 ** |
| LINE-1 266/97 cfDI (ng/mL) median (IQR) | 0.28 (0.19–0.43) | 0.39 (0.29–0.48) | 0.037 * |
| ALU 260/111 Copy Number Ratio | LINE 266/97 Copy Number Ratio | A*L Copy Number Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cut-off | 0.0383 | 0.1326 | 0.0069 |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | 67.5% (50.9–81.4%) | 70.0% (53.5–83.4%) | 87.5% (73.2–95.8%) |
| Specificity (95% CI) | 72.2% (46.5–90.3%) | 61.1% (35.7–82.7%) | 55.6% (30.8–78.5%) |
| PPV (95% CI) | 84.4% (64.4–91.9%) | 80.0% (58.6–89.6%) | 81.4% (60.9–93.5%) |
| NPV (95% CI) | 50.0% (33.3–78.2%) | 47.8% (31.1–73.6%) | 66.7% (43.8–85.4%) |
| FP | 5 | 7 | 8 |
| FN | 13 | 12 | 5 |
| Variable | PCa Patients (n = 40) | BPH Patients (n = 18) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEF1A2 copies/mL plasma median (IQR) | 1925.0 (1250.0–3000.0) | 1202.5 (1106.3–1418.8) | 0.017 * |
| ESR1 copies/mL plasma median (IQR) | 2075.0 (1131.3–3393.8) | 1351.0 (1062.5–1618.8) | 0.024 * |
| EEF1A2/ESR1 median (IQR) | 0.91 (0.76–1.07) | 0.92 (0.86–1.03) | 0.737 |
| ccfDNA (ng/mL) by EEF1A2 copy number median (IQR) | 6.35 (4.12–9.9) | 3.97 (3.65–4.68) | 0.017 * |
| ccfDNA (ng/mL) by ESR1 copy number median (IQR) | 6.85 (3.73–11.20) | 4.45 (3.51–5.34) | 0.024 * |
| Variable | ALU 260/111 Copy Number Ratio | p-Value | LINE-1 266/97 Copy Number Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| <76 (n = 19) | 0.03 (0.02–0.04) | 0.212 | 0.10 (0.08–0.18) | 0.316 |
| ≥76 (n = 21) | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | 0.10 (0.06–0.13) | ||
| BMI | ||||
| <25 (n = 15) | 0.03 (0.02–0.04) | 0.355 | 0.10 (0.08–0.15) | 0.774 |
| ≥25 (n = 23) | 0.03 (0.03–0.05) | 0.10 (0.07–0.16) | ||
| Tumour Stage * | ||||
| I-II (n = 30) | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | 0.322 | 0.11 (0.08–0.17) | 0.235 |
| III-IV (n = 8) | 0.04 (0.03–0.04) | 0.09 (0.03–0.14) | ||
| GLEASON score (ISUP) * | ||||
| Low risk (0–1) (n = 10) | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | 0.159 | 0.10 (0.06–0.13) | 0.515 |
| Intermediate risk (2–3) (n = 18) | 0.03 (0.02–0.03) | 0.11 (0.08–0.18) | ||
| High risk (4–5) (n = 10) | 0.04 (0.03–0.05) | 0.10 (0.08–0.13) | ||
| Recurrence ** | ||||
| Yes (n = 4) | 0.04 (0.03–0.06) | 0.325 | 0.11 (0.08–0.17) | 0.575 |
| No (n = 31) | 0.03 (0.02–0.04) | 0.11 (0.10–0.12) |
| Variable vs. PSA Levels | PCa Patients (n = 38) | BPH Patients (n = 17) |
|---|---|---|
| ALU 260/111 copy number ratio baseline (p-value) | 0.313 (0.06) | 0.167 (0.523) |
| LINE-1 266/97 copy number ratio baseline (p-value) | −0.04 (0.802) | −0.06 (0.823) |
| ALU 260/111 copy number ratio one-year follow-up (p-value) | −0.004 (0.983) | nd |
| LINE-1 266/97 copy number ratio one-year follow-up (p-value) | −0.168 (0.332) | nd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tierno, D.; Pavan, N.; Giudici, F.; Grassi, G.; Valeri, E.; Zanconati, F.; Traunero, F.; Liguori, G.; Scaggiante, B. LINE-1 266/97 and ALU 260/111 Copy Number Ratios in Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Plasma as Potential Biomarkers for the Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Case-Control Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188862
Tierno D, Pavan N, Giudici F, Grassi G, Valeri E, Zanconati F, Traunero F, Liguori G, Scaggiante B. LINE-1 266/97 and ALU 260/111 Copy Number Ratios in Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Plasma as Potential Biomarkers for the Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Case-Control Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188862
Chicago/Turabian StyleTierno, Domenico, Nicola Pavan, Fabiola Giudici, Gabriele Grassi, Eleonora Valeri, Fabrizio Zanconati, Fabio Traunero, Giovanni Liguori, and Bruna Scaggiante. 2025. "LINE-1 266/97 and ALU 260/111 Copy Number Ratios in Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Plasma as Potential Biomarkers for the Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Case-Control Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188862
APA StyleTierno, D., Pavan, N., Giudici, F., Grassi, G., Valeri, E., Zanconati, F., Traunero, F., Liguori, G., & Scaggiante, B. (2025). LINE-1 266/97 and ALU 260/111 Copy Number Ratios in Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Plasma as Potential Biomarkers for the Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Case-Control Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188862







