PAFAH1B3 Exists in Linear Chromosomal and Extrachromosomal Circular DNA and Promotes HCC Progression via EMT
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
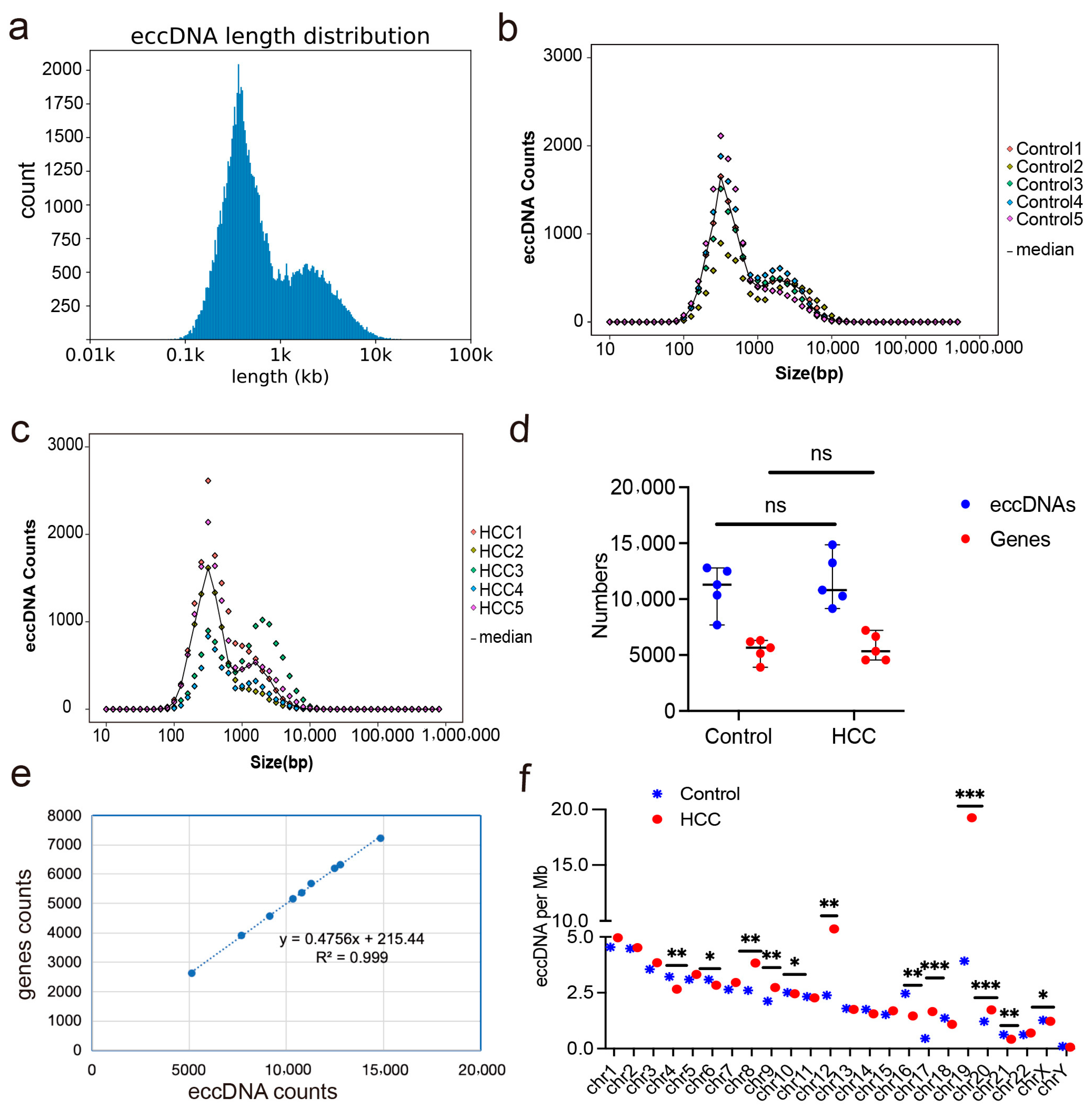
2.1. Expression Profiles of eccDNAs in Liver Cancer and Adjacent Non-Cancerous Tissues
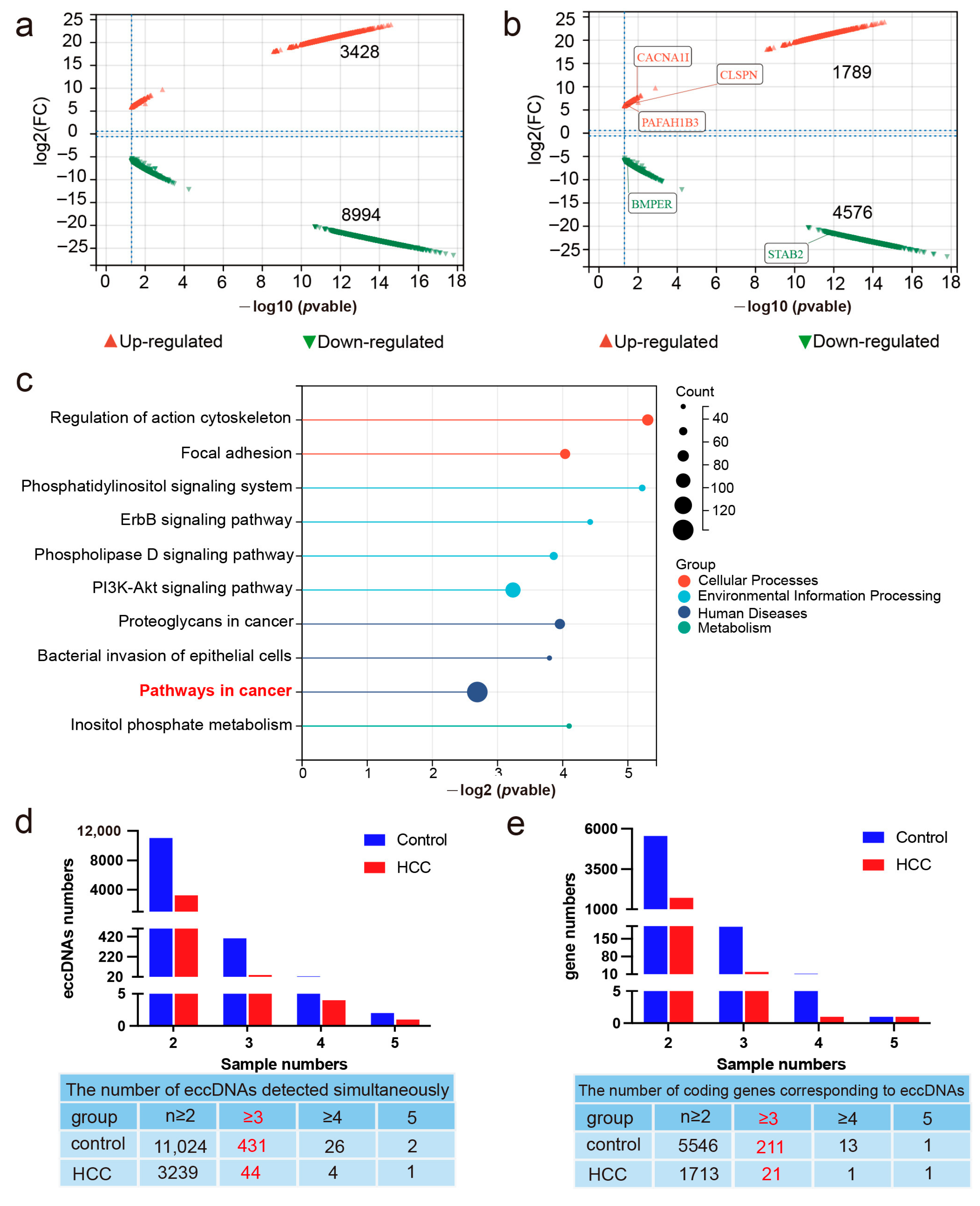
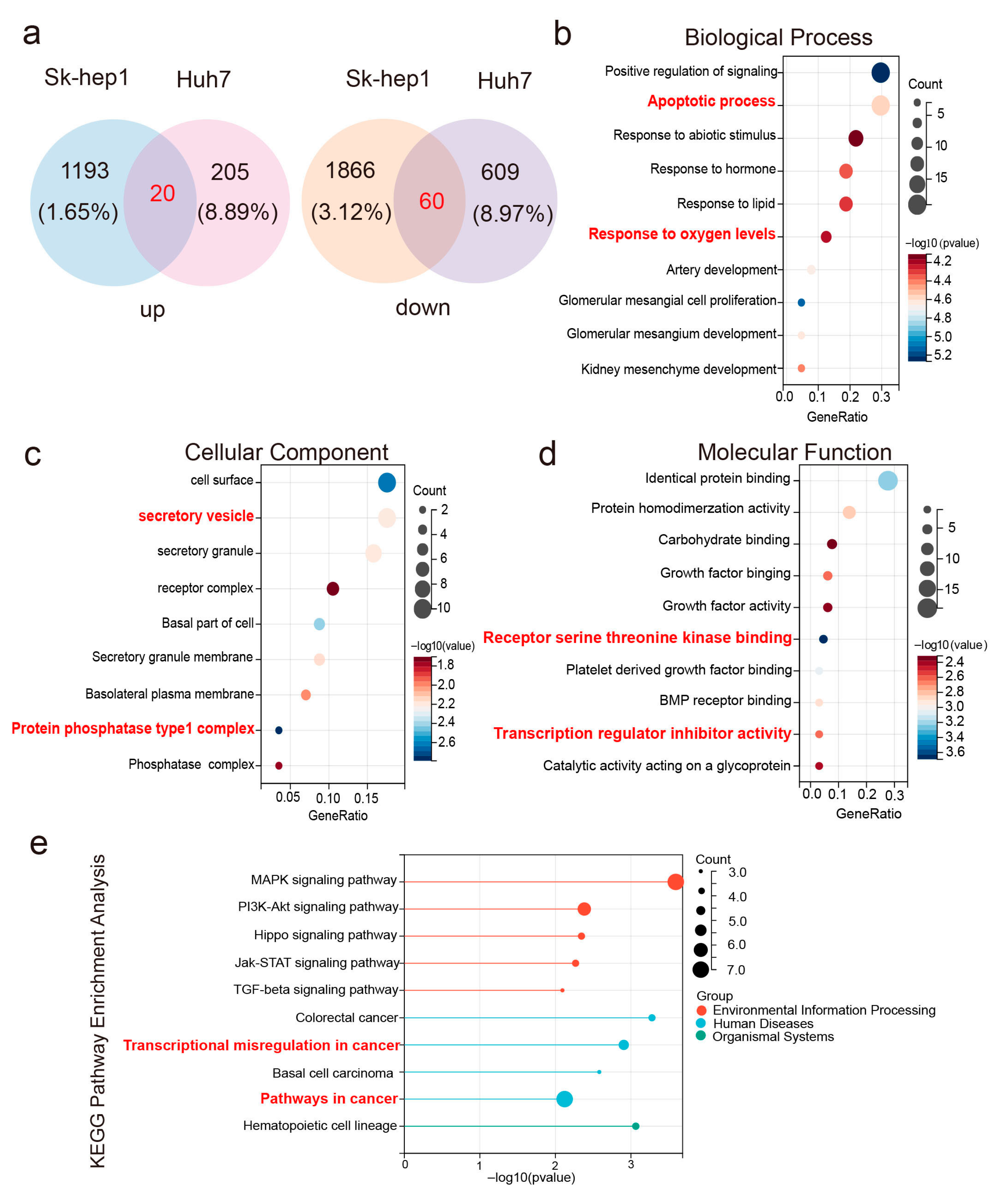
2.2. Differentially Expressed eccDNAs in Liver Cancer and Adjacent Non-Cancerous Tissues
2.3. Expression Quantification and Circularity Verification of eccDNA PAFAH1B3 in Tissues and Cell Lines
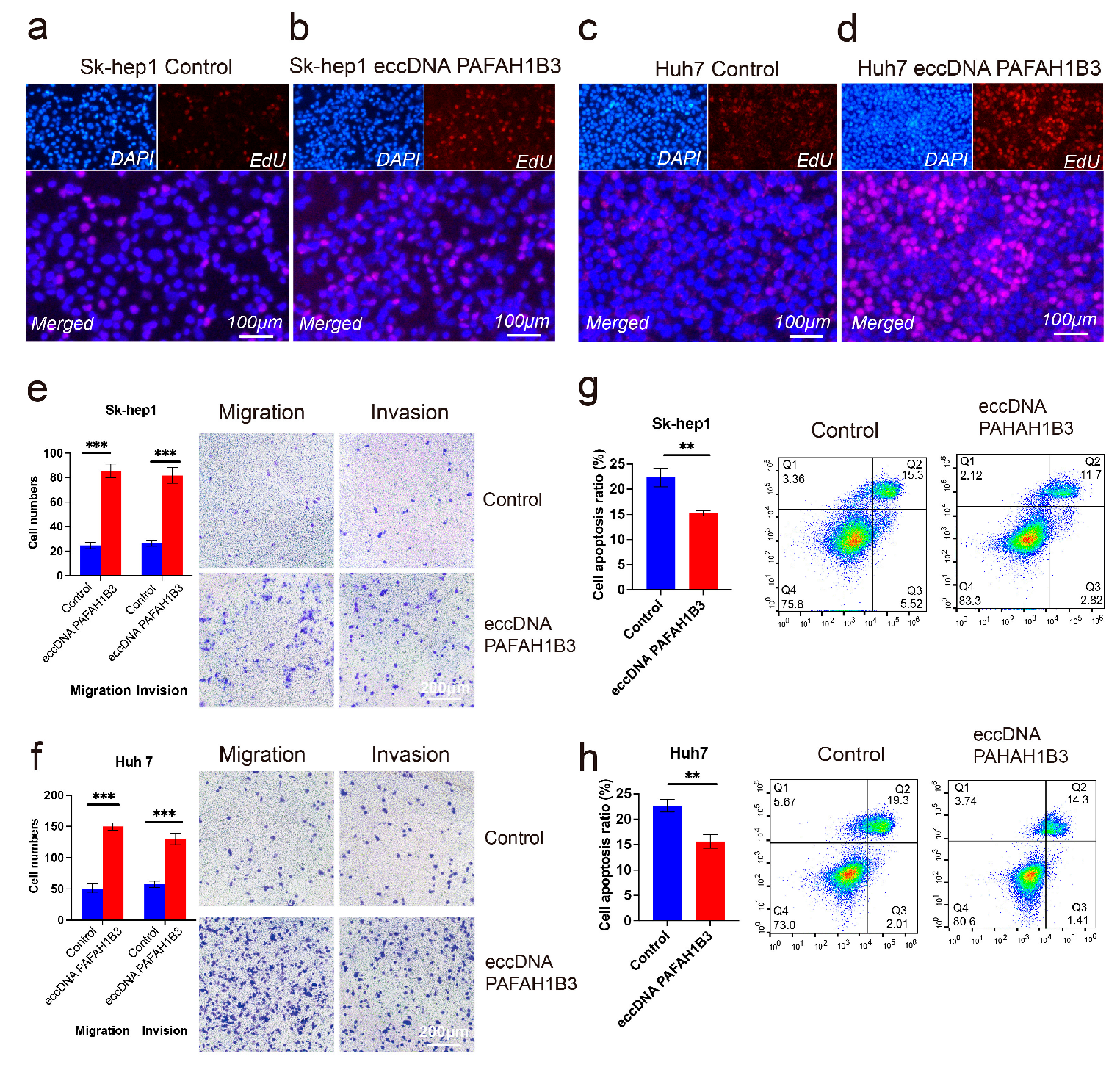
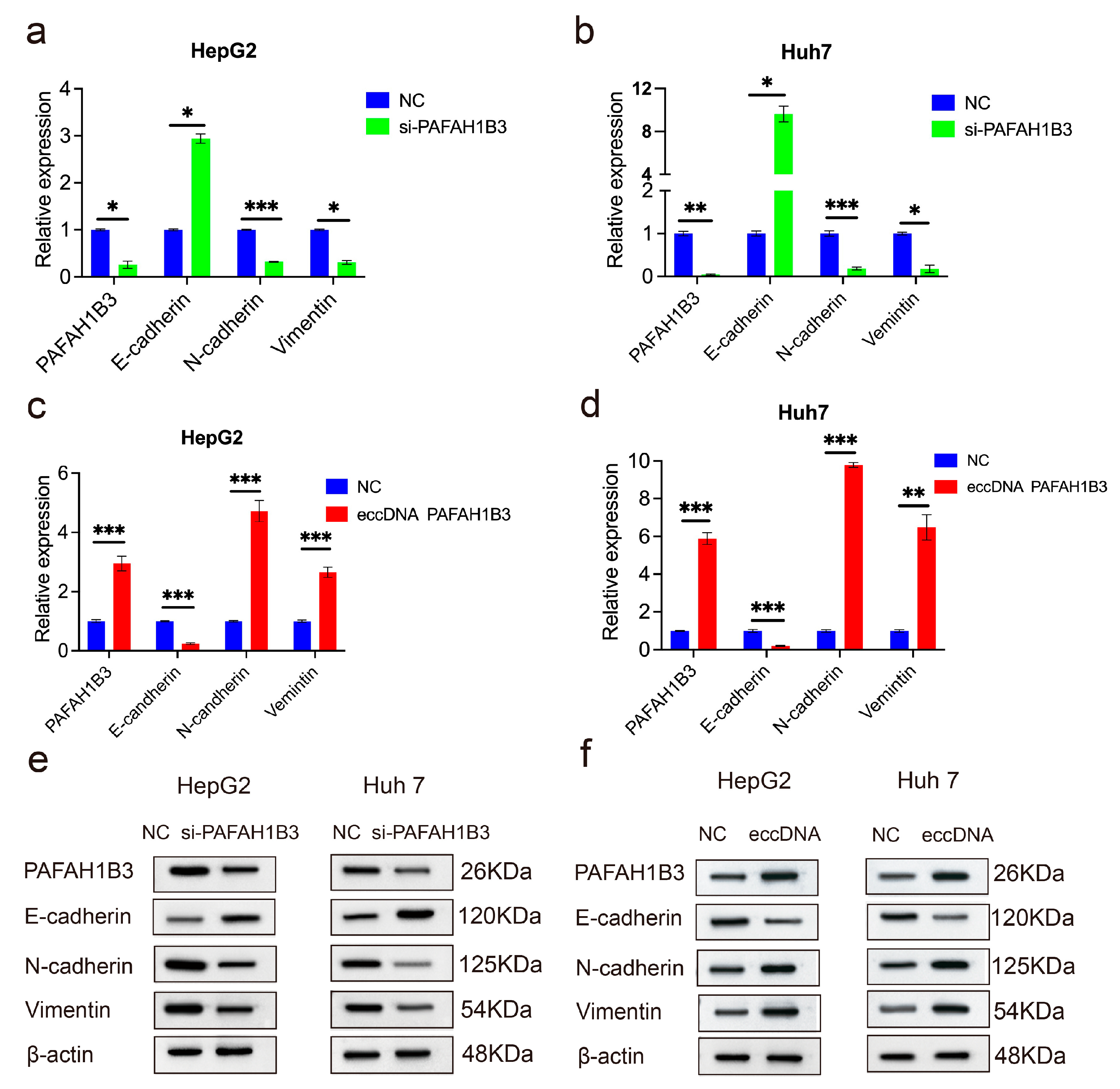
2.4. The Impact of eccDNA PAFAH1B3 on Liver Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Apoptosis
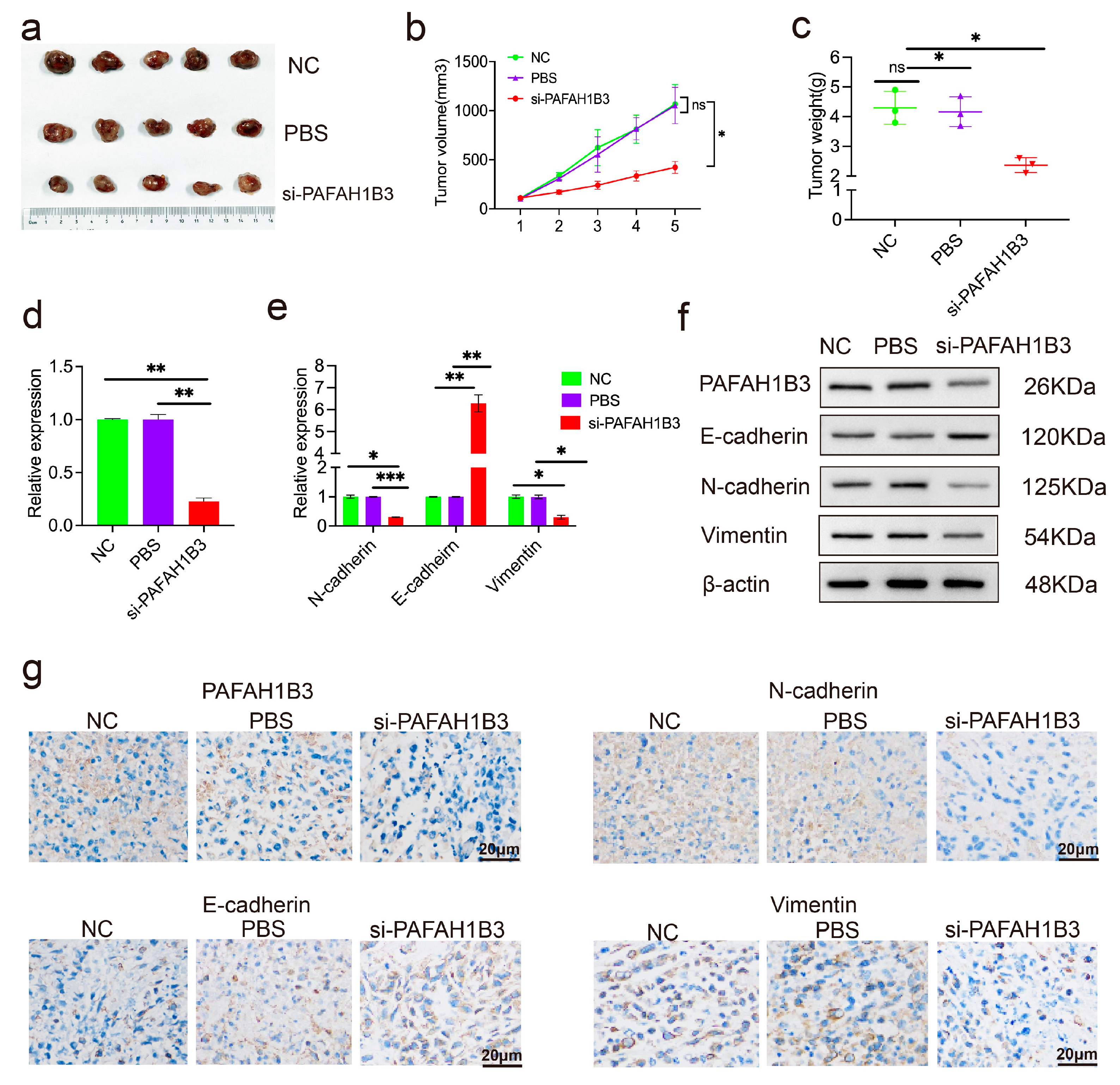
2.5. The si-PAFAH1B3 Inhibited the Malignant Progression of HCC In Vitro and In Vivo by Regulating EMT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Specimens
4.2. Isolation, Purification, and Sequencing of eccDNAs from Liver Cancer Tissues
4.2.1. Isolation and Purification of eccDNAs
4.2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis and Screening of Differentially Expressed eccDNAs in Liver Cancer Tissues
4.2.3. Screening of Differentially Expressed eccDNAs
4.2.4. Quantification of eccDNA PAFAH1B3 Expression in Liver Cancer Tissues and Circularity Validation
4.2.5. Circularity Validation of eccDNA PAFAH1B3
4.2.6. Artificial Circular DNA Synthesis
4.3. EdU Assays
4.4. Transwell Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
4.5. Apoptosis Assays
4.6. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription–Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Xenograft Tumorigenesis
4.9. Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EccDNA | Extrachromosomal circular DNAs |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| PAFAH1B3 | Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 1B3 |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
References
- Yang, L.; Jia, R.; Ge, T.; Ge, S.; Zhuang, A.; Chai, P.; Fan, X. Extrachromosomal circular DNA: Biogenesis, structure, functions and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, Y.; Bassel, A. Molecular Size and Circularity of Dna in Cells of Mammals and Higher Plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1965, 53, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugen-Olsen, R.A.B.; Hariprakash, J.M.; Oestergaard, V.H.; Regenberg, B. Molecular mechanisms of extrachromosomal circular DNA formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, gkaf122, Erratum in Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, gkaf491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA): An emerging star in cancer. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, Y.; Kumar, P.; Layer, R.; Willcox, S.; Gagan, J.R.; Griffith, J.D.; Dutta, A. Extrachromosomal microDNAs and chromosomal microdeletions in normal tissues. Science 2012, 336, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.M.; Deshpande, V.; Beyter, D.; Koga, T.; Rusert, J.; Lee, C.; Li, B.; Arden, K.; Ren, B.; Nathanson, D.A.; et al. Extrachromosomal oncogene amplification drives tumour evolution and genetic heterogeneity. Nature 2017, 543, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Wei, L.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, K.; Mao, F.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, X. Innovative insights into extrachromosomal circular DNAs in gynecologic tumors and reproduction. Protein Cell 2024, 15, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Lv, W.; Han, P.; Sun, K.; Hao, Z.; Gao, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shao, S.; Ma, S.; et al. Plasma extrachromosomal circular DNA as a potential diagnostic biomarker for nodular thyroid disease. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Turner, K.M.; Nguyen, N.; Raviram, R.; Erb, M.; Santini, J.; Luebeck, J.; Rajkumar, U.; Diao, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Circular ecDNA promotes accessible chromatin and high oncogene expression. Nature 2019, 575, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Bafna, V.; Mischel, P.S. Extrachromosomal oncogene amplification in tumour pathogenesis and evolution. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, M.C.; González, R.C.; Brückner, L.; Conrad, T.; Wittstruck, N.; Szymansky, A.; Eggert, A.; Schulte, J.H.; Koche, R.P.; Henssen, A.G.; et al. Intercellular extrachromosomal DNA copy-number heterogeneity drives neuroblastoma cell state diversity. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Xue, R.; Liu, M.; Bai, J.; Bao, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Deep whole-genome analysis of 494 hepatocellular carcinomas. Nature 2024, 627, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Djekidel, M.N.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Alt, F.W.; Zhang, Y. eccDNAs are apoptotic products with high innate immunostimulatory activity. Nature 2021, 599, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Peng, H.; Llauro, C.; Bucher, E.; Mirouze, M. ecc_finder: A Robust and Accurate Tool for Detecting Extrachromosomal Circular DNA From Sequencing Data. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 743742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, K.; Luo, S.; Tang, M.; Liu, N.; Jiang, C.; Fang, J.; Li, S.; Hou, Y.; Guo, C.; et al. Comparative analysis of methodologies for detecting extrachromosomal circular DNA. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qiu, Q.; She, J.; Yu, J. Extrachromosomal circular DNA in colorectal cancer: Biogenesis, function and potential as therapeutic target. Oncogene 2023, 42, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Xu, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, F. Extrachromosomal circular DNA promotes prostate cancer progression through the FAM84B/CDKN1B/MYC/WWP1 axis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2024, 29, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, K.; Cao, G.; Xu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Niu, C.; Wang, X. Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) characteristics in the bile and plasma of advanced perihilar cholangiocarcinoma patients and the construction of an eccDNA-related gene prognosis model. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1379435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, K.; Romero, N.; MacLachlan, J.; Allard, N.; Cowie, B. Modeling Progress Toward Elimination of Hepatitis B in Australia. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Chen, S.; Rao, G.; Zhang, G.; Ma, M.; Peng, B.; Du, X.; Huang, W.; Lin, W.; Tian, Y.; et al. Extrachromosomal circular MiR-17-92 amplicon promotes HCC. Hepatology 2024, 79, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrisani, O. Two important players in poor-prognosis hepatocellular carcinoma: Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) and its passenger, the oncogenic miR-17~92 locus. Hepatology 2024, 79, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Huang, P.; Ma, K.; Zhao, Z.; Hua, T.; Zai, W.; Chen, J.; Fu, X. Genome-Wide Extrachromosomal Circular DNA Profiling of Paired Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adjacent Liver Tissues. Cancers 2023, 15, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livnat, I.; Finkelshtein, D.; Ghosh, I.; Arai, H.; Reiner, O. PAF-AH Catalytic Subunits Modulate the Wnt Pathway in Developing GABAergic Neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Duan, L. Comprehensive Analysis of the Prognostic and Immunological Role of PAFAH1B in Pan-Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 799497, Erratum in Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 1497296. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Quan, R.; Bhandari, A.; Hirachan, S.; Chen, C.; Lv, S.; Zheng, C. PAFAH1B3 Regulates Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Metastasis by Affecting the EMT. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 1152–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Ni, J.; Chen, B.; Sun, F.; Huang, J.; Ni, S.; Tang, Z. PAFAH1B3 predicts poor prognosis and promotes progression in lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Pan, X.; Li, W.; Han, P.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Lv, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of extrachromosomal circular DNA in gastric cancer and its potential role in carcinogenesis and cancer progression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Duan, W.; Cui, J.; Gu, L.; Gao, X.; Ma, J.; Cui, M.; Luo, H.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of extrachromosomal circular DNA in breast cancer and its potential role in carcinogenesis and cancer progression. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Pan, X.; Han, P.; Wu, S.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Xu, M.; Qi, Y.; Deng, L.; et al. Extrachromosomal circular DNA orchestrates genome heterogeneity in urothelial bladder carcinoma. Theranostics 2024, 14, 5102–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, B.; Xie, C.; Song, Y. Encoding gene RAB3B exists in linear chromosomal and circular extrachromosomal DNA and contributes to cisplatin resistance of hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma via inducing autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.D.; Mohiyuddin, M.; Prada-Luengo, I.; Sailani, M.R.; Halling, J.F.; Plomgaard, P.; Maretty, L.; Hansen, A.J.; Snyder, M.P.; Pilegaard, H.; et al. Circular DNA elements of chromosomal origin are common in healthy human somatic tissue. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Su, Q.; Wei, C.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Su, X.; Zhuang, W. Extrachromosomal circular DNAs in prostate adenocarcinoma: Global characterizations and a novel prediction model. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1464145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, T.; Shibata, Y.; Kumar, P.; Dillon, L.; Dutta, A. Small extrachromosomal circular DNAs, microDNA, produce short regulatory RNAs that suppress gene expression independent of canonical promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4586–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Pan, X.; Lv, W.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Dang, Y.; et al. Identification and functional analysis of circulating extrachromosomal circular DNA in schizophrenia implicate its negative effect on the disorder. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yang, Y.; Qian, J.-K.; Zhang, X.; Ji, J.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.-Z.; Yuan, F. Aberrant Expression of PAFAH1B3 Affects Proliferation and Apoptosis in Osteosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 664478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Guo, X.; Wu, D.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. PAFAH1B3 Expression Is Correlated With Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation and Immune Infiltration. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 591545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zang, Y.; Cao, S.; Lei, D.; Pan, X. Aberrant expression of PAFAH1B3 associates with poor prognosis and affects proliferation and aggressiveness in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, L.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Zheng, M.-M.; Qin, C.-T.; Huang, X.-G.; Zhou, L.; Xu, W.-J.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis between tumor tissues and intratumoral exosomes from lung adenocarcinoma patients identifies PAFAH1B3 as an exosomal protein key for initiating metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X.; Huang, K.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X. Identification of PAFAH1B3 as Candidate Prognosis Marker and Potential Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 700700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, L. PAFAH1B3 Exists in Linear Chromosomal and Extrachromosomal Circular DNA and Promotes HCC Progression via EMT. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188801
Li D, Sun H, Wang Y, Yin Y, Zhu Y, Qian X, Wang S, Zhang L, Zhao H, Qiu L. PAFAH1B3 Exists in Linear Chromosomal and Extrachromosomal Circular DNA and Promotes HCC Progression via EMT. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188801
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dandan, Huishan Sun, Yingjie Wang, Yicong Yin, Ying Zhu, Xia Qian, Shanshan Wang, Longhao Zhang, Haitao Zhao, and Ling Qiu. 2025. "PAFAH1B3 Exists in Linear Chromosomal and Extrachromosomal Circular DNA and Promotes HCC Progression via EMT" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188801
APA StyleLi, D., Sun, H., Wang, Y., Yin, Y., Zhu, Y., Qian, X., Wang, S., Zhang, L., Zhao, H., & Qiu, L. (2025). PAFAH1B3 Exists in Linear Chromosomal and Extrachromosomal Circular DNA and Promotes HCC Progression via EMT. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188801






