Current Landscape of the Interrelationship Between Periodontitis, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
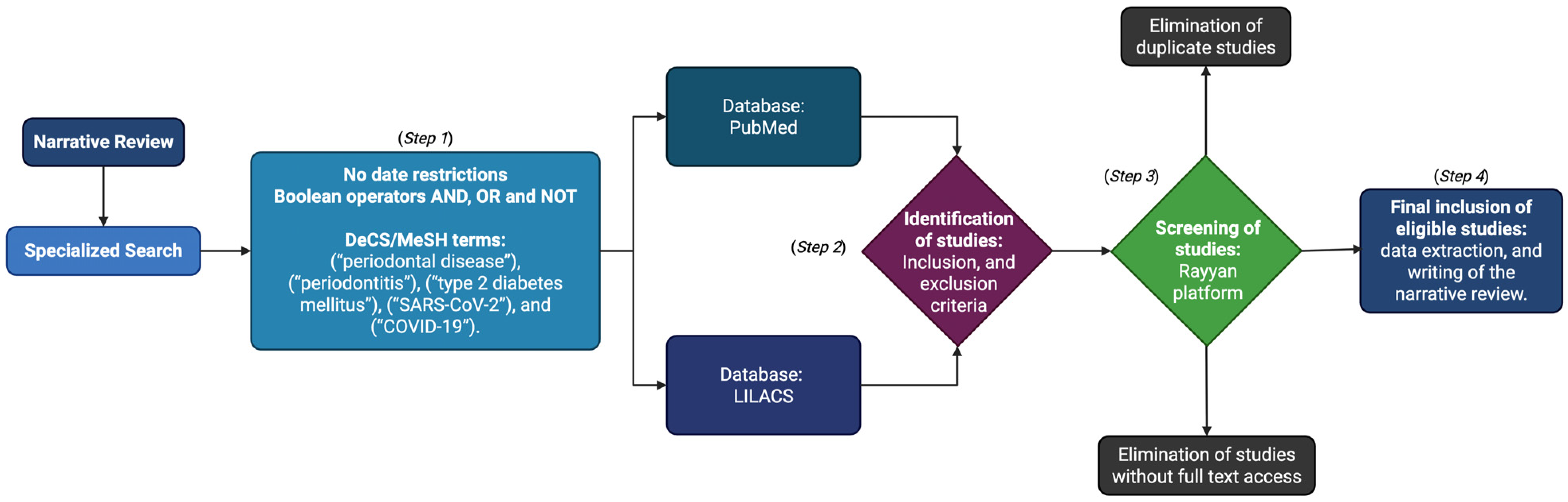
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Step 1: Specialized Search
2.2. Step 2: Identification of Studies
2.3. Step 3: Screening of Studies
2.4. Step 4: Inclusion and Analysis of Studies
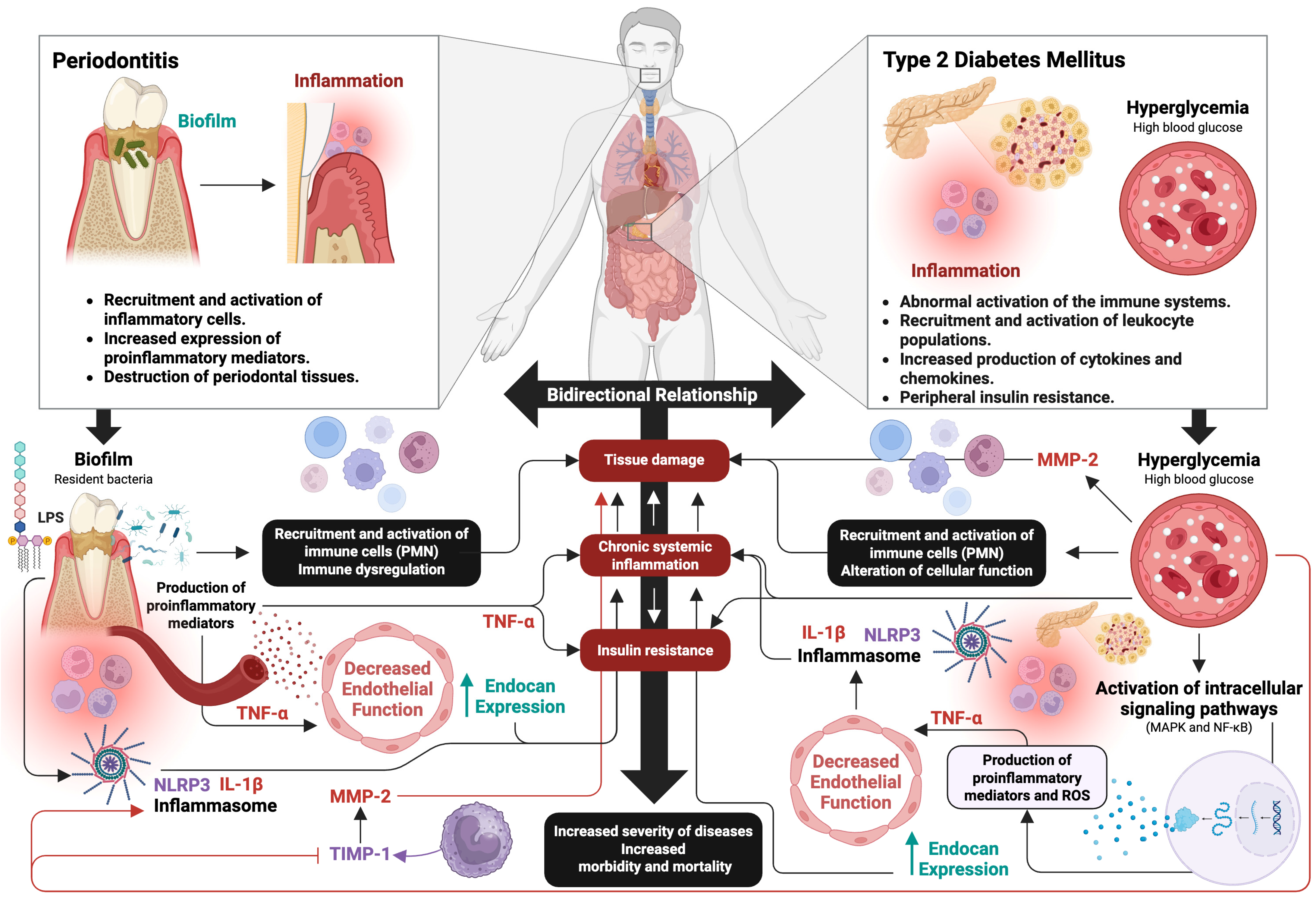
3. Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
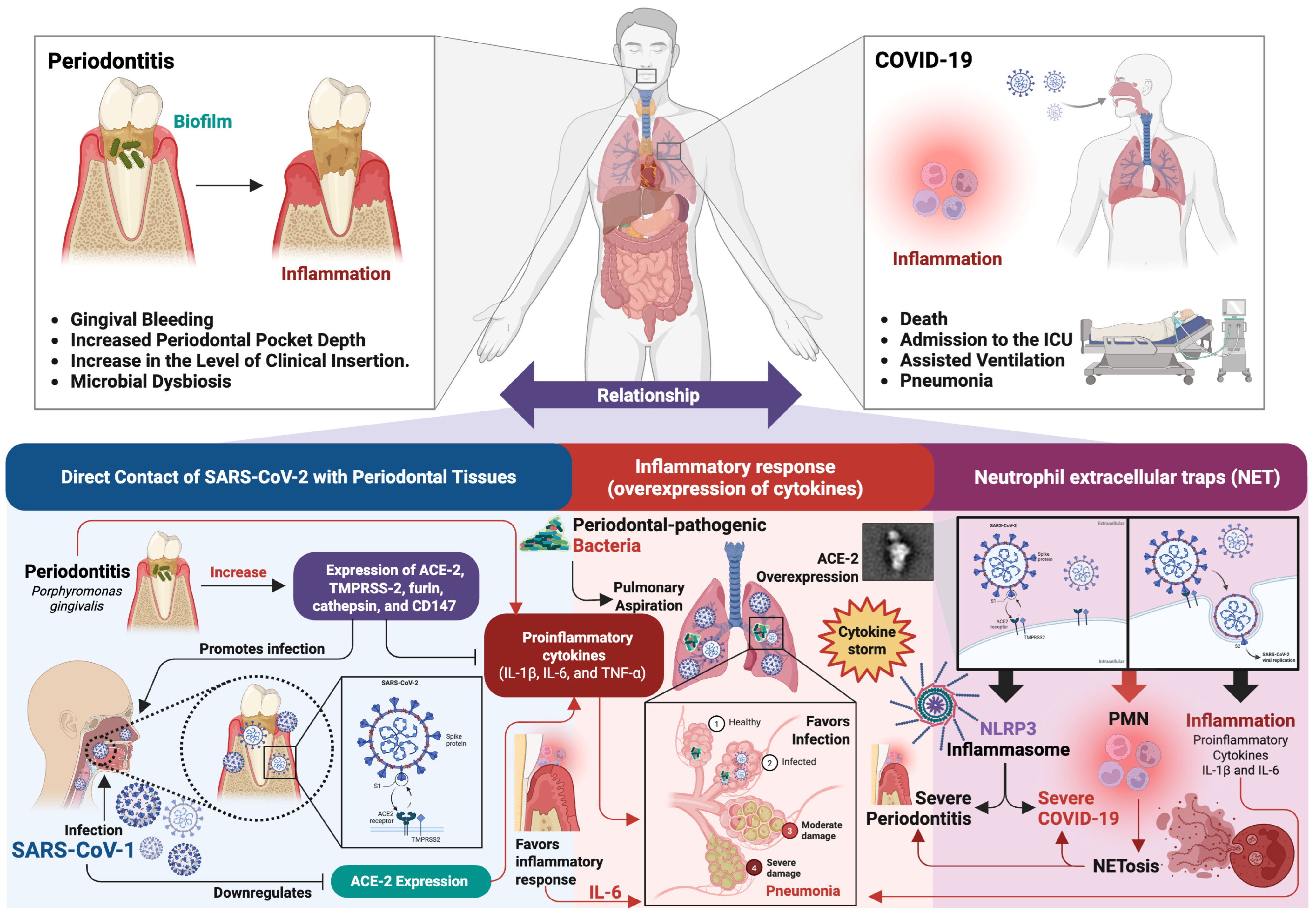
4. Periodontitis and COVID-19
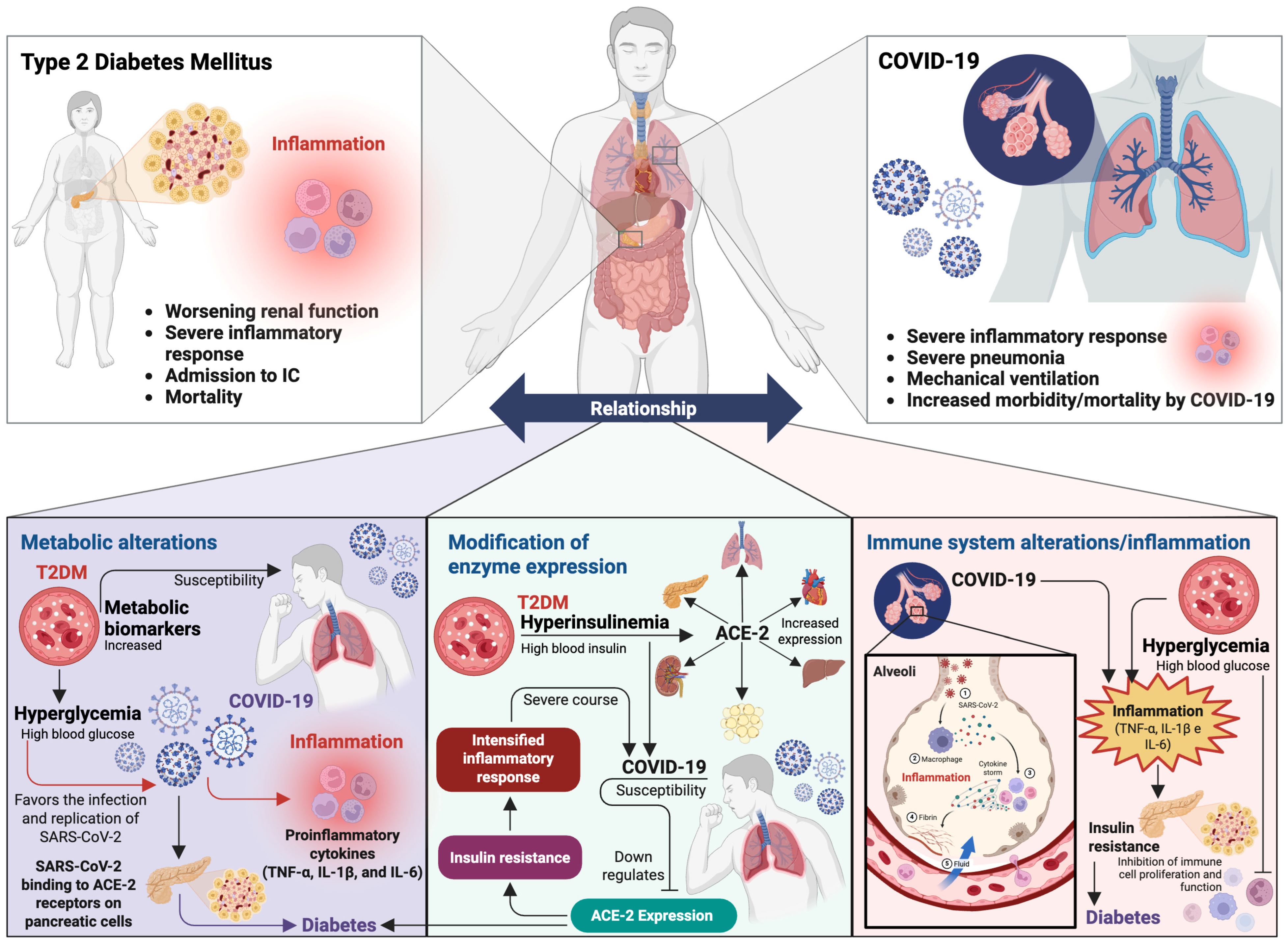
5. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
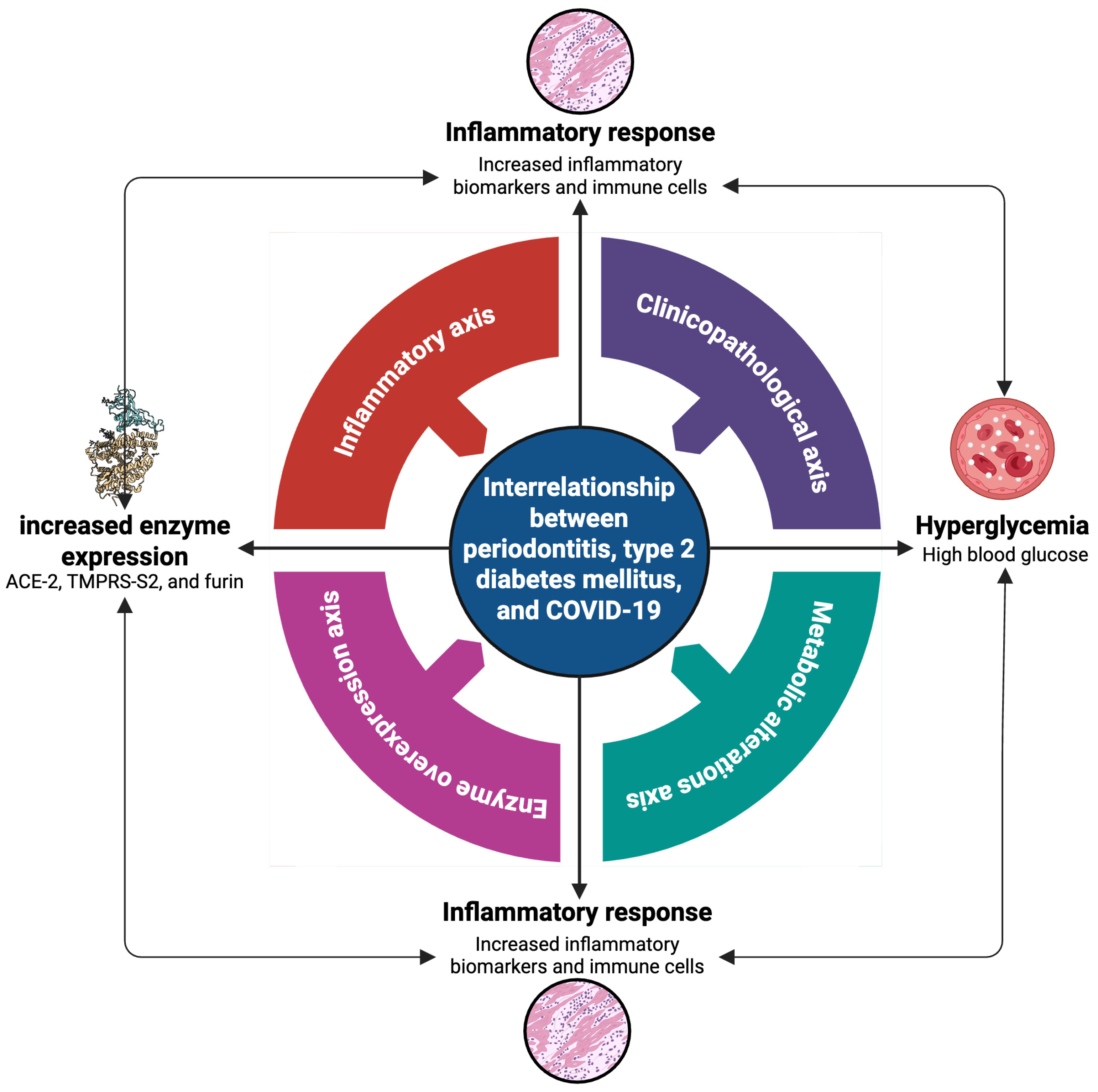
6. Discussion: Interrelationship Between Periodontitis, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and COVID-19
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE-1 | angiotensin-converting enzyme 1 |
| ACE-2 | angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| AIP | plasma atherogenic index |
| ARD | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| CD147 | cluster of differentiation 147 |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| GCF | gingival crevicular fluid |
| HbA1c | glycosylated hemoglobin |
| HGEC | human gingival epithelial cells |
| IL-6R | IL-6 receptor |
| IL | interleukin |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinases |
| NET | neutrophil extracellular traps |
| NETosis | generation of NET |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| NLR | NOD-like receptor |
| NLRP-3 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| PGE2 | prostaglandin E2 |
| PMN | polymorphonuclear cells |
| RANKL | receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand |
| SARS-CoV-2 | severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor beta |
| Th1 cells | type 1 T helper cells |
| TIMPs | tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases |
| TMPRSS-2 | transmembrane serine protease 2 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
References
- Chapple, I.L.C.; Mealey, B.L.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Bartold, P.M.; Dommisch, H.; Eickholz, P.; Geisinger, M.L.; Genco, R.J.; Glogauer, M.; Goldstein, M.; et al. Periodontal Health and Gingival Diseases and Conditions on an Intact and a Reduced Periodontium: Consensus Report of Workgroup 1 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), S74–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mira, A.; Simon-Soro, A.; Curtis, M.A. Role of Microbial Communities in the Pathogenesis of Periodontal Diseases and Caries. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44 (Suppl. S18), S23–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Carrillo, J.L.; Hernández-Reyes, V.E.; García-Huerta, O.E.; Chávez-Ruvalcaba, F.; Chávez-Ruvalcaba, M.I.; Chávez-Ruvalcaba, K.M.; Díaz-Alfaro, L. Pathogenesis of Periodontal Disease. In Diagnostic and Adjunctive Non-Surgical Considerations; Nermin, Y., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–14. ISBN 978-1-78984-461-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kedlaya, M.N.; Puzhankara, L.; Prasad, R.; Raj, A. Periodontal Disease Pathogens, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutics: The CRISPR-Cas Effect. Cris. J. 2023, 6, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno Caicedo, L.F.; Amaya Sánchez, S.; Cruz Olivo, E.A. Factores de Riesgo Modificables e Inmodificables de La Periodontitis: Revisión Narrativa. Univ. Odontol. 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, M.A.; Godfrey, K.M. Genetics: Epigenetic Mechanisms Underlying Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stančáková, A.; Laakso, M. Genetics of Type 2 Diabetes. Endocr. Dev. 2016, 31, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sircana, A.; Framarin, L.; Leone, N.; Berrutti, M.; Castellino, F.; Parente, R.; De Michieli, F.; Paschetta, E.; Musso, G. Altered Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes: Just a Coincidence? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pollin, T.I. Epigenetics Variation and Pathogenesis in Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defronzo, R.A. From the Triumvirate to the Ominous Octet: A New Paradigm for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 2009, 58, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunton, S. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes: The Evolution of Our Understanding. PubMed 2016, 65, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Javeed, N.; Matveyenko, A.V. Circadian Etiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Physiology 2018, 33, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbudi, A.; Khairani, S.; Tjahjadi, A. Interplay Between Insulin Resistance and Immune Dysregulation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications for Therapeutic Interventions. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2025, 14, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dror, E.; Dalmas, E.; Meier, D.T.; Wueest, S.; Thévenet, J.; Thienel, C.; Timper, K.; Nordmann, T.M.; Traub, S.; Schulze, F.; et al. Postprandial Macrophage-Derived IL-1β Stimulates Insulin, and Both Synergistically Promote Glucose Disposal and Inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrits, A.J.; Gitz, E.; Koekman, C.A.; Visseren, F.L.; van Haeften, T.W.; Akkerman, J.W.N. Induction of Insulin Resistance by the Adipokines Resistin, Leptin, Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Retinol Binding Protein 4 in Human Megakaryocytes. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Pérez, J.Z.; Villarreal-Martínez, J.Z.; Lavalle-González, F.J.; Torres-Sepúlveda, M.D.R.; Ruiz-Herrera, C.; Cerda-Flores, R.M.; Castillo-García, E.R.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; De Villarreal, L.E.M. Plasma and Urine Metabolic Profiles Are Reflective of Altered Beta-Oxidation in Non-Diabetic Obese Subjects and Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, H.; Yin, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, P.; Shi, Y.; Mao, F.; Yan, Y.; et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Reversing Peripheral Insulin Resistance and Relieving β-Cell Destruction. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7613–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.M.M.L.; Lira, R.; Fischer, R.G.; Santos, A.P.P.; Oliveira, B.H. Systemic Antibiotics in Periodontal Treatment of Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, C. Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontal Disease: The Profession’s Choices. Br. Dent. J. 2022, 233, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.; Hayes, C.; Taylor, G.W. Glycemic Control of Type 2 Diabetes and Severe Periodontal Disease in the US Adult Population. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2002, 30, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, S.; Karima, M.; Wang, H.-Y.; Dyke, T.E. Van Association between Interleukin-1 Genotype and Periodontal Disease in a Diabetic Population. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liccardo, D.; Cannavo, A.; Spagnuolo, G.; Ferrara, N.; Cittadini, A.; Rengo, C.; Rengo, G. Periodontal Disease: A Risk Factor for Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yazici, D.; Azkur, D.; Ogulur, I.; Azkur, A.K.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, A.Z.; et al. Recent Developments in the Immunopathology of COVID-19. Allergy 2023, 78, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Song, B. Chest CT Manifestations of New Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Pictorial Review. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4381–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Ullah, A.; Gul, A.; Mousavi, T.; Khan, M.W. Novel Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic Outbreak: A Comprehensive Review of the Current Literature. Vacunas 2021, 22, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; Sehgal, K.; Nair, N.; Mahajan, S.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Bikdeli, B.; Ahluwalia, N.; Ausiello, J.C.; Wan, E.Y.; et al. Extrapulmonary Manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniyappa, R.; Gubbi, S. COVID-19 Pandemic, Coronaviruses, and Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E736–E741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurwitz, D. Angiotensin Receptor Blockers as Tentative SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutics. Drug Dev. Res. 2020, 81, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xie, X. COVID-19 and the Cardiovascular System. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; et al. Human Kidney Is a Target for Novel Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Long, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. ACE2 Expression in Pancreas May Cause Pancreatic Damage After SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2128–2130.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Carrillo, J.L.; Guevara-López, G.W.; González-Díaz, C.; Palos-Del Toro, E.J.; De León-Madrigal, J.; Álvarez-Pinto, J.U.; Reyes-Ortiz, R.B.; Chávez-Ruvalcaba, F. Obesidad y COVID-19: Comorbilidad de Dos Pandemias. Rednutrición 2024, 15, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, A.; Jalilian, M.; Sarbarzeh, P.A.; Vlaisavljevic, Z. Diabetes and COVID-19: A Systematic Review on the Current Evidences. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 166, 108347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Vigueras, S.; Aquino-Martínez, R.; Hernández-Vigueras, S.; Aquino-Martínez, R. Potencial Rol de La Periodontitis En La Severidad de COVID-19. Revisión. Int. J. Odontostomatol. 2021, 15, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhera, J. Narrative Reviews: Flexible, Rigorous, and Practical. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2022, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, D.; Gupta, A.; Duraisamy, A.K.; Mrinalini, M. The Influence of Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Resistin Levels of Gingival Crevicular Fluid- a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2025, 15, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanto, H.; Nesse, W.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Agustina, D.; Vissink, A.; Abbas, F. Periodontitis Prevalence and Severity in Indonesians with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamala, A.; Al-Hajri, M.; Ali Al-Wesabi, M.; Shamala De-, A. Risk Factors for Periodontal Diseases among Yemeni Type II Diabetic Patients. A Case-Control Study. J. Oral Res. 2017, 6, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, M.S.; de Carli, J.P.; Ferreira, M.d.C.; Gambin, D.J.; da Silva, S.O.; Lisboa, H. Prevalence and Severity of Periodontal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Biosci. J. 2018, 34, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasqah, M.; Mokeem, S.; Alrahlah, A.; Al-Hamoudi, N.; Abduljabbar, T.; Akram, Z.; Vohra, F.; Javed, F. Periodontal Parameters in Prediabetes, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Non-Diabetic Patients. Braz. Oral Res. 2018, 32, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Z.; Yuan, Y.H.; Liu, H.H.; Li, S.S.; Zhang, B.W.; Chen, W.; An, Z.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Wu, Y.Z.; Han, B.; et al. Epidemiologic Relationship between Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monod Nuñez, M.S.; Aransibia, L.V.; Blanco Fernández, M.J.; Hernández Oropesa, T.; Linari, M.A. Frecuencia de Enfermedad Periodontal En Pacientes Adultos Con Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2 En La Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires y La Provincia de Buenos Aires. Rev. Soc. Argent. Diabetes 2022, 56, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.; Oliveira, T.; Fernandes, R. Biochemistry of Adipose Tissue: An Endocrine Organ. Arch. Med. Sci. 2013, 9, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Hu, Z.; Yang, S.; Sun, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, G. Role of Adaptive and Innate Immunity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 7457269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackey, D.E.; Olefsky, J.M. Regulation of Metabolism by the Innate Immune System. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadad, N.; Burgazliev, O.; Elgazar-Carmon, V.; Solomonov, Y.; Wueest, S.; Item, F.; Konrad, D.; Rudich, A.; Levy, R. Induction of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2á Is Required for Adipose Neutrophil Infiltration and Hepatic Insulin Resistance Early in the Course of High-Fat Feeding. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oostrom, A.J.; van Wijk, J.P.; Sijmonsma, T.P.; Rabelink, T.J.; Castro Cabezas, M. Increased Expression of Activation Markers on Monocytes and Neutrophils in Type 2 Diabetes. Neth. J. Med. 2004, 62, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gyurko, R.; Siqueira, C.C.; Caldon, N.; Gao, L.; Kantarci, A.; Van Dyke, T.E. Chronic Hyperglycemia Predisposes to Exaggerated Inflammatory Response and Leukocyte Dysfunction in Akita Mice. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7250–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatanaka, E.; Monteagudo, P.T.; Marrocos, M.S.M.; Campa, A. Neutrophils and Monocytes as Potentially Important Sources of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 146, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, K.; Ohira, T.; Uchida, Y.; Ayilavarapu, S.; Batista, E.L.; Yagi, M.; Iwata, T.; Liu, H.; Hasturk, H.; Kantarci, A.; et al. Priming of Neutrophil Oxidative Burst in Diabetes Requires Preassembly of the NADPH Oxidase. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komesu, M.C.; Tanga, M.B.; Buttros, K.R.; Nakao, C. Effects of Acute Diabetes on Rat Cutaneous Wound Healing. Pathophysiol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Pathophysiol. 2004, 11, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennenberg, S.D.; Finkenauer, R.; Dwivedi, A. Absence of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inhibition of Neutrophil Apoptosis in Patients with Diabetes. Arch. Surg. 1999, 134, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, G.; Shapira, L. How Has Neutrophil Research Improved Our Understanding of Periodontal Pathogenesis? J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38 (Suppl. S11), 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, M.R.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Matthews, J.B. Peripheral Blood Neutrophil Cytokine Hyper-Reactivity in Chronic Periodontitis. Innate Immun. 2015, 21, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, S.; Mortezagholi, B.; Movahed, E.; Ghaedi, A.; Bazrgar, A.; Abdolalizadehil, S.; Khanzadeh, S. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio with Periodontitis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.W. Bidirectional Interrelationships between Diabetes and Periodontal Diseases: An Epidemiologic Perspective. Ann. Periodontol. 2001, 6, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenschein, S.K.; Meyle, J. Local Inflammatory Reactions in Patients with Diabetes and Periodontitis. Periodontol. 2000 2015, 69, 221–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, J.M.; Sonnenschein, S.K.; Groeger, S.E.; Ewald, N.; Arneth, B.; Meyle, J. Refractory Neutrophil Activation in Type 2 Diabetics with Chronic Periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2020, 55, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhir, S.; Wangnoo, S.; Kumar, V. Impact of Glycemic Levels in Type 2 Diabetes on Periodontitis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 22, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manosudprasit, A.; Kantarci, A.; Hasturk, H.; Stephens, D.; Van Dyke, T.E. Spontaneous PMN Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetes and the Impact of Periodontitis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlan, M.T.; Sharma, K. Challenging the Dogma of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Overproduction in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhruddin, S.; Alanazi, W.; Jackson, K.E. Diabetes-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species: Mechanism of Their Generation and Role in Renal Injury. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 8379327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.C.; Ko, K.I.; Mattos, M.; Fang, M.; Zhang, C.; Feinberg, D.; Sindi, H.; Li, S.; Alblowi, J.; Kayal, R.A.; et al. TNFα Contributes to Diabetes Impaired Angiogenesis in Fracture Healing. Bone 2017, 99, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, S.; Albiero, M.L.; Vieira, G.H.A.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.Q.; Graves, D.T. Diabetes Activates Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts via NF-ΚB In Vivo. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, A.B.; Thakur, S.; Muddapur, M.V.; Kulkarni, R.D. Cytokine Ratios in Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2017, 11, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janket, S.J.; Jones, J.A.; Meurman, J.H.; Baird, A.E.; Van Dyke, T.E. Oral Infection, Hyperglycemia, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2008, 105, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurav, A.N. The Implication of Periodontitis in Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 44, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ouyang, X.; Lin, J. The Impact of Periodontitis on Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 998313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polak, D.; Shapira, L. An Update on the Evidence for Pathogenic Mechanisms That May Link Periodontitis and Diabetes. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, O.; Ghallab, N.A.; Hamdy, E.; Sayed, S. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (INOS) in Gingival Tissues of Chronic Periodontitis with and without Diabetes: Immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR Study. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, F.; Al-Askar, M.; Al-Hezaimi, K. Cytokine Profile in the Gingival Crevicular Fluid of Periodontitis Patients with and without Type 2 Diabetes: A Literature Review. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesia, R.; Gholami, F.; Huang, H.; Clare-Salzler, M.; Aukhil, I.; Wallet, S.M.; Shaddox, L.M. Systemic Inflammatory Responses in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes with Chronic Periodontitis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2016, 4, e000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, G.E.; Yalda, B.; Collins, J.G.; Jones, B.H.; Smith, F.W.; Arnold, R.R.; Offenbacher, S. Inflammatory Mediator Response as a Potential Risk Marker for Periodontal Diseases in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Patients. J. Periodontol. 1997, 68, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, G.E.; Beck, J.D.; Offenbacher, S. PGE2, IL-1 Beta, and TNF-Alpha Responses in Diabetics as Modifiers of Periodontal Disease Expression. Ann. Periodontol. 1998, 3, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingueti, C.P.; Dusse, L.M.S.A.; Carvalho, M.D.G.; De Sousa, L.P.; Gomes, K.B.; Fernandes, A.P. Diabetes Mellitus: The Linkage between Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Hypercoagulability and Vascular Complications. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, V.R.; Lima, J.A.; Gonçalves, T.E.D.; Bastos, M.F.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Shibli, J.A.; Duarte, P.M. Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Ligand/Osteoprotegerin Ratio in Sites of Chronic Periodontitis of Subjects with Poorly and Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyke, T.E. Pro-Resolving Mediators in the Regulation of Periodontal Disease. Mol. Aspects Med. 2017, 58, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, J.K.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Metabolic Messengers: Tumour Necrosis Factor. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, F.; Iwamoto, Y.; Mineshiba, J.; Shimizu, A.; Soga, Y.; Murayama, Y. Periodontal Disease and Diabetes Mellitus: The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in a 2-Way Relationship. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallasamy, P.; Kang, Z.Y.; Sun, X.; Anandh Babu, P.V.; Liu, D.; Jia, Z. Natural Compound Resveratrol Attenuates TNF-Alpha-Induced Vascular Dysfunction in Mice and Human Endothelial Cells: The Involvement of the NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Xu, L.; Yu, X.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Xiao, S.; Guo, M.; Wang, H. Protective Effect of KLF15 on Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by TNF-α. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Cai, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qiu, C.; Xie, J.; Huang, W.; Sui, Z. Protective Role of Antioxidant Huskless Barley Extracts on TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 3846029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhananjayan, R.; Koundinya, K.S.S.; Malati, T.; Kutala, V.K. Endothelial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 31, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.R.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Y. Endothelial Dysfunction in Vascular Complications of Diabetes: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms and Implications. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1359255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrazin, S.; Adam, E.; Lyon, M.; Depontieu, F.; Motte, V.; Landolfi, C.; Lortat-Jacob, H.; Bechard, D.; Lassalle, P.; Delehedde, M. Endocan or Endothelial Cell Specific Molecule-1 (ESM-1): A Potential Novel Endothelial Cell Marker and a New Target for Cancer Therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1765, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnoush, A.H.; Khalaji, A.; Bahiraie, P.; Alehossein, P.; Shobeiri, P.; Peisepar, M.; Cannavo, A. Endocan as a Marker of Endothelial Dysfunction in Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 2388–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arman, Y.; Akpinar, T.S.; Kose, M.; Emet, S.; Yuruyen, G.; Akarsu, M.; Ozcan, M.; Yegit, O.; Cakmak, R.; Altun, O.; et al. Effect of Glycemic Regulation on Endocan Levels in Patients with Diabetes: A Preliminary Study. Angiology 2016, 67, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türer, Ç.C.; Durmuş, D.; Balli, U.; Güven, B. Effect of Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatment on Gingival Crevicular Fluid and Serum Endocan, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A, and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Levels. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Ponnaiyan, D.; Parthasarathy, H.; Tadepalli, A.; Veeramani, S. Evaluation of Endocan and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α as Inflammatory Biomarkers in Type 2 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2020, 24, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Kong, Y.; Chen, H.; Xia, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y. Unraveling the Priming Phase of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Molecular Insights and Clinical Relevance. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 146, 113821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, N.S.; Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Pereira, C.A.; Zanotto, C.Z.; Prado, D.S.; Silva, J.F.; Rassi, D.M.; Foss-Freitas, M.C.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Carlos, D.; et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Mineralocorticoid Receptors Are Associated with Vascular Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cells 2019, 8, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didilescu, A.C.; Chinthamani, S.; Scannapieco, F.A.; Sharma, A. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activity and Periodontal Disease Pathogenesis—A Bidirectional Relationship. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 4069–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Hernández, A.L.; Muñoz-Saavedra, Á.E.; González-Alva, P.; Moreno-Fierros, L.; Llamosas-Hernández, F.E.; Cifuentes-Mendiola, S.E.; Rubio-Infante, N. Upregulation of Proteins of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Patients with Periodontitis and Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, G.; Polizzi, A.; Santonocito, S.; Alibrandi, A.; Williams, R.C. Periodontitis Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Serum and Saliva. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostanci, N.; Emingil, G.; Saygan, B.; Turkoglu, O.; Atilla, G.; Curtis, M.A.; Belibasakis, G.N. Expression and Regulation of the NALP3 Inflammasome Complex in Periodontal Diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 157, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Na, H.S.; Song, Y.R.; Shin, S.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Chung, J. Activation of NLRP3 and AIM2 Inflammasomes by Porphyromonas Gingivalis Infection. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Zhou, R.; Tschopp, J. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: A Sensor for Metabolic Danger? Science 2010, 327, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdan, T.; Godlewski, G.; Cinar, R.; Bertola, A.; Szanda, G.; Liu, J.; Tam, J.; Han, T.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Skarulis, M.C.; et al. Activation of the Nlrp3 Inflammasome in Infiltrating Macrophages by Endocannabinoids Mediates Beta Cell Loss in Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Ni, J.; Xie, B.; Liu, Y.; Xuan, D.; Zhang, J. Hyperglucose Contributes to Periodontitis: Involvement of the NLRP3 Pathway by Engaging the Innate Immunity of Oral Gingival Epithelium. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.M.; Hou, L.T.; Wong, M.Y.; Rossomando, E.F. Relationships between Clinical Parameters, Interleukin 1B and Histopathologic Findings of Gingival Tissue in Periodontitis Patients. Cytokine 1996, 8, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacios, S.; Andriankaja, O.; Kang, J.; Alnammary, M.; Bae, J.; De Brito Bezerra, B.; Schreiner, H.; Fine, D.H.; Graves, D.T. Bacterial Infection Increases Periodontal Bone Loss in Diabetic Rats through Enhanced Apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, H.; Luthra, S. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the Bidirectional Relationship between Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontal Disease. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2013, 17, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapna, G.; Gokul, S.; Bagri-Manjrekar, K. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Periodontal Diseases. Oral Dis. 2014, 20, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collazos, J.; Asensi, V.; Martin, G.; Montes, A.H.; Suárez-Zarracina, T.; Valle-Garay, E. The Effect of Gender and Genetic Polymorphisms on Matrix Metalloprotease (MMP) and Tissue Inhibitor (TIMP) Plasma Levels in Different Infectious and Non-Infectious Conditions. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkinen, A.M.; Kettunen, K.; Kovanen, L.; Haukka, J.; Elg, J.; Husu, H.; Tervahartiala, T.; Pussinen, P.; Meurman, J.; Sorsa, T. Inflammatory Mediator Polymorphisms Associate with Initial Periodontitis in Adolescents. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2016, 2, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, J.K.d.A.; Migliore, R.; Waisberg, J.; Ribeiro Junior, M.A.F. The Influence of Bariatric Surgery on Matrix Metalloproteinase Plasma Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Death, A.K.; Fisher, E.J.; McGrath, K.C.Y.; Yue, D.K. High Glucose Alters Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression in Two Key Vascular Cells: Potential Impact on Atherosclerosis in Diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2003, 168, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papazafiropoulou, A.; Perrea, D.; Moyssakis, I.; Kokkinos, A.; Katsilambros, N.; Tentolouris, N. Plasma Levels of MMP-2, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 Are Not Associated with Arterial Stiffness in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2010, 24, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woessner, J.F. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Connective Tissue Remodeling. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lira-Junior, R.; Öztürk, V.Ö.; Emingil, G.; Bostanci, N.; Boström, E.A. Salivary and Serum Markers Related to Innate Immunity in Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiros, D.; Nelson-Filho, P.; Paula-Silva, F.W.G.; de Oliveira, K.M.H.; Lucisano, M.P.; de Rossi, A.; Silva, L.A.B.; Küchler, E.C.; Silva, R.A.B. MMP2 and MMP9 Are Associated with Apical Periodontitis Progression and Might Be Modulated by TLR2 and MyD88. Braz. Dent. J. 2018, 29, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bătăiosu, M.; Taisescu, C.I.; Pisoschi, C.G.; Pascu, E.I.; Ţuculină, M.J.; Dăguci, L.; Dăguci, C.; Baniţă, I.M. Effects of Therapy with Two Combinations of Antibiotics on the Imbalance of MMP-2÷TIMP-2 in Chronic Periodontitis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2015, 56, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costa Fernandes, C.J.d.; Zambuzzi, W.F. Fibroblast-Secreted Trophic Factors Contribute with ECM Remodeling Stimulus and Upmodulate Osteocyte Gene Markers in Osteoblasts. Biochimie 2020, 168, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arreguin-Cano, J.A.; Ayerdi-Nájera, B.; Tacuba-Saavedra, A.; Navarro-Tito, N.; Dávalos-Martínez, A.; Emigdio-Vargas, A.; Barrera-Rodríguez, E.; Blanco-García, N.; Gutiérrez-Venegas, G.; Ventura-Molina, E.; et al. MMP-2 Salivary Activity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, A.; Dikmen, N.K.; Nibali, L. Association between Periodontal Diseases and COVID-19 Infection: A Case-Control Study with a Longitudinal Arm. Odontology 2023, 111, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Wu, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, J. Relationship between Periodontitis and COVID-19: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, X. Association between Periodontitis and COVID-19 Infection: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppolu, P.; Genady, E.; Albdeirat, L.; Sebai, F.; Alrashdi, D.; Lingam, A.; Alsada, F.R.; Al-Khalifa, F.; Abdelrahim, R. Association between Severity of COVID-19, Periodontal Health and Disease in Riyadh Subpopulation. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2023, 12, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamimi, F.; Altigani, S.; Sanz, M. Periodontitis and Coronavirus Disease 2019. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 89, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Joseph, B.; Anil, S. Does Periodontitis Influence the Risk of COVID-19? A Scoping Review. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, K.N.; Al-Momani, A.M.; Almaseeh, J.A.; Marouf, N.; Shatta, A.; Al-Abdulla, J.; Alaji, S.; Daas, H.; Tharupeedikayil, S.S.; Chinta, V.R.; et al. Association of Periodontal Therapy, with Inflammatory Biomarkers and Complications in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Control Study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 6721–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardelis, P.; Zekeridou, A.; Suh, N.; Le Terrier, C.; Stavropoulos, A.; Giannopoulou, C. A Pilot Clinical and Radiographic Study on the Association between Periodontitis and Serious COVID-19 Infection. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnomay, N.; Alolayan, L.; Aljohani, R.; Almashouf, R.; Alharbi, G. Association between Periodontitis and COVID-19 Severity in a Tertiary Hospital: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Saudi Dent. J. 2022, 34, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marouf, N.; Cai, W.; Said, K.N.; Daas, H.; Diab, H.; Chinta, V.R.; Hssain, A.A.; Nicolau, B.; Sanz, M.; Tamimi, F. Association between Periodontitis and Severity of COVID-19 Infection: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Mohindra, R.; Singla, M.; Khera, S.; Sahni, V.; Kanta, P.; Soni, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Gauba, K.; Goyal, K.; et al. The Clinical Association between Periodontitis and COVID-19. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Sandhu, H.S.; Sarwal, A.; Bhagat, S.; Dodwad, R.; Singh, G.; Gambhir, R.S. Assessment of Correlation of COVID-19 Infection and Periodontitis- A Comparative Study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsi, R.; Ahmad, Z.; Siddharth, M.; Vandana, K.; Arora, S.; Saurav, K. Correlation of COVID-19 with Severity of Periodontitis-A Clinical and Biochemical Study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2022, 33, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.S.; Jadhav, P.; Kamath, K.P.; Kumar, S.R.; Vijayalaxmi, S.; Anil, S. A Case-Control Study on the Association between Periodontitis and Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukumar, K.; Tadepalli, A. Nexus between COVID-19 and Periodontal Disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 03000605211002695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, L.; Chacun, D.; Sy, K.; Grosgogeat, B.; Gritsch, K. Periodontal Diseases and COVID-19: A Scoping Review. Eur. J. Dent. 2021, 15, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, G.; Bizzoca, M.E.; Lo Muzio, L. COVID-19 and Periodontitis: Reflecting on a Possible Association. Head Face Med. 2021, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitkov, L.; Knopf, J.; Krunić, J.; Schauer, C.; Schoen, J.; Minnich, B.; Hannig, M.; Herrmann, M. Periodontitis-Derived Dark-NETs in Severe COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slots, J.; Contreras, A. Herpesviruses: A Unifying Causative Factor in Periodontitis? Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 15, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, Z.; Gaudin, A.; Struillou, X.; Amador, G.; Soueidan, A. Periodontal Pockets: A Potential Reservoir for SARS-CoV-2? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 143, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes Matuck, B.; Dolhnikoff, M.; Maia, G.V.A.; Isaac Sendyk, D.; Zarpellon, A.; Costa Gomes, S.; Duarte-Neto, A.N.; Rebello Pinho, J.R.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Sousa, S.C.O.M.; et al. Periodontal Tissues Are Targets for SARS-CoV-2: A Post-Mortem Study. J. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 13, 1848135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Mohindra, R.; Chauhan, P.K.; Singla, V.; Goyal, K.; Sahni, V.; Gaur, R.; Verma, D.K.; Ghosh, A.; Soni, R.K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Gingival Crevicular Fluid. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascolo, L.; Zupin, L.; Melato, M.; Tricarico, P.M.; Crovella, S. TMPRSS2 and ACE2 Coexpression in SARS-CoV-2 Salivary Glands Infection. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1120–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, M.K.; Fatih, M.T.; Kurda, H.A.; Mahmood, N.K.; Shareef, F.U.; Faraidun, H.; Tassery, H.; Tardivo, D.; Lan, R.; Noori, Z.F.; et al. Role of Viruses in Periodontitis: An Extensive Review of Herpesviruses, Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Coronavirus-19, Papillomavirus and Hepatitis Viruses. World J. Virol. 2024, 13, 99070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Pérez, P.; Kato, T.; Mikami, Y.; Okuda, K.; Gilmore, R.C.; Conde, C.D.; Gasmi, B.; Stein, S.; Beach, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection of the Oral Cavity and Saliva. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdzik, A. COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Periodontology: A Narrative Review. J. Periodontal Res. 2022, 57, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandini, D.A.; Takamiya, A.S.; Thakkar, P.; Schaller, S.; Rahat, R.; Naqvi, A.R. COVID-19 and Oral Diseases: Crosstalk, Synergy or Association? Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, e2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhong, L.; Deng, J.; Peng, J.; Dan, H.; Zeng, X.; Li, T.; Chen, Q. High Expression of ACE2 Receptor of 2019-NCoV on the Epithelial Cells of Oral Mucosa. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, L.; Quinzi, V.; Mummolo, S.; Marzo, G.; Marchetti, E. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 as a Possible Correlation between COVID-19 and Periodontal Disease. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, D.; Martínez-Sanz, J.; Sainz, T.; Calvo, C.; Méndez-Echevarría, A.; Moreno, E.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Vizcarra, P.; Rodríguez, M.; Jenkins, R.; et al. Differences in Saliva ACE2 Activity among Infected and Non-Infected Adult and Pediatric Population Exposed to SARS-CoV-2. J. Infect. 2022, 85, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, W.; Kubota, N.; Shimizu, T.; Saruta, J.; Fuchida, S.; Kawata, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sugimoto, M.; Yakeishi, M.; Tsukinoki, K. Existence of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Molecules in the Oral Cavity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baima, G.; Marruganti, C.; Sanz, M.; Aimetti, M.; Romandini, M. Periodontitis and COVID-19: Biological Mechanisms and Meta-Analyses of Epidemiological Evidence. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, M.; La, V.D.; Lombardo Bedran, T.B.; Palomari Spolidorio, D.M.; Grenier, D. Porphyromonas Gingivalis-Mediated Shedding of Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer (EMMPRIN) by Oral Epithelial Cells: A Potential Role in Inflammatory Periodontal Disease. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakizaki, M.; Hashimoto, R.; Nagata, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Okura, T.; Katoh, H.; Kitai, Y.; Akahori, Y.; Shirato, K.; Ryo, A.; et al. The Respective Roles of TMPRSS2 and Cathepsins for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Respiratory Organoids. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0185324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoriadis, A.; Räisänen, I.T.; Pärnänen, P.; Tervahartiala, T.; Sorsa, T.; Sakellari, D. Is There a Link between COVID-19 and Periodontal Disease? A Narrative Review. Eur. J. Dent. 2022, 16, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Shima, K.; Noguchi, K.; Chiba, N.; Matsuguchi, T. Periodontitis Promotes the Expression of Gingival Transmembrane Serine Protease 2 (TMPRSS2), a Priming Protease for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). J. Oral Biosci. 2022, 64, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, M.; Bahammam, S.; Sima, C. The Relationships Among Periodontitis, Pneumonia and COVID-19. Front. Oral Health 2022, 2, 801815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sena, K.; Furue, K.; Setoguchi, F.; Noguchi, K. Altered Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Entry and Processing Genes by Porphyromonas Gingivalis-Derived Lipopolysaccharide, Inflammatory Cytokines and Prostaglandin E2 in Human Gingival Fibroblasts. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 129, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, A.R.; Schwartz, J.; Brandini, D.A.; Schaller, S.; Hussein, H.; Valverde, A.; Naqvi, R.A.; Shukla, D. COVID-19 and Oral Diseases: Assessing Manifestations of a New Pathogen in Oral Infections. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 41, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, M.; Saito, J.; Zhao, H.; Sakamoto, A.; Hirota, K.; Ma, D. Inflammation Triggered by SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 Augment Drives Multiple Organ Failure of Severe COVID-19: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications. Inflammation 2021, 44, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Kamio, N.; Kobayashi, R.; Iinuma, T.; Imai, K. Aspiration of Periodontopathic Bacteria Due to Poor Oral Hygiene Potentially Contributes to the Aggravation of COVID-19. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 63, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Kamio, N.; Yokoe, S.; Suzuki, R.; Sato, S.; Iinuma, T.; Imai, K. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 and Proinflammatory Cytokines Induced by the Periodontopathic Bacterium Fusobacterium Nucleatum in Human Respiratory Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Maweri, S.A.; Alhajj, M.N.; Halboub, E.; Tamimi, F.; Salleh, N.M.; Al-Ak’hali, M.S.; Kassim, S.; Abdulrab, S.; Anweigi, L.; Mohammed, M.M.A. The Impact of Periodontal Disease on the Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitones-Rubio, V.; Chávez-Cortez, E.G.; Hurtado-Camarena, A.; González-Rascón, A.; Serafín-Higuera, N. Is Periodontal Disease a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19 Illness? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona Loayza, D.A.; Lafebre, M.F. Periodontal Disease and COVID-19: Prognosis and Potential Pathways of Association in Their Pathogenesis. Can. J. Dent. Hyg. 2023, 57, 44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sampson, V.; Kamona, N.; Sampson, A. Could There Be a Link between Oral Hygiene and the Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Infections? Br. Dent. J. 2020, 228, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.M.; Marques, R.S.; de Moura, T.R.; de Paiva, S.M.; Gurgel, R.Q.; Martins-Filho, P.R. Is There a Bidirectional Interaction between Periodontitis and the Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Infection? EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mootha, A. Is There a Similarity in Serum Cytokine Profile between Patients with Periodontitis or 2019-Novel Coronavirus Infection?-A Scoping Review. Biology 2023, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, F.J.; Márquez-Arrico, C.F. COVID-19 and Periodontitis: A Dangerous Association? Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 789681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacHado, V.; Botelho, J.; Lopes, J.; Patrão, M.; Alves, R.; Chambrone, L.; Alcoforado, G.; Mendes, J.J. Periodontitis Impact in Interleukin-6 Serum Levels in Solid Organ Transplanted Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, G.; Lo Giudice, A.; Polizzi, A.; Alibrandi, A.; Murabito, P.; Indelicato, F. Identification of the Different Salivary Interleukin-6 Profiles in Patients with Periodontitis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 122, 104997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bemquerer, L.M.; Oliveira, S.R.; de Arruda, J.A.A.; Costa, F.P.D.; Miguita, L.; Bemquerer, A.L.M.; de Sena, A.C.V.P.; de Souza, A.F.; Mendes, D.F.; Schneider, A.H.; et al. Clinical, Immunological, and Microbiological Analysis of the Association between Periodontitis and COVID-19: A Case-Control Study. Odontology 2024, 112, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa Cruz, A.; Mendes-Frias, A.; Oliveira, A.I.; Dias, L.; Matos, A.R.; Carvalho, A.; Capela, C.; Pedrosa, J.; Castro, A.G.; Silvestre, R. Interleukin-6 Is a Biomarker for the Development of Fatal Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 613422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Ma, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, R.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Gao, G.; Liu, F.; et al. Profiling Serum Cytokines in COVID-19 Patients Reveals IL-6 and IL-10 Are Disease Severity Predictors. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Sun, W.; Wang, K.; Li, W.; Lin, J.; Gong, J.; Wang, L. Periodontitis and COVID-19: Immunological Characteristics, Related Pathways, and Association. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şehirli, A.Ö.; Aksoy, U.; Koca-Ünsal, R.B.; Sayıner, S. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in COVID-19 and Periodontitis: Possible Protective Effect of Melatonin. Med. Hypotheses 2021, 151, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.C.; Chiang, Y.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Tseng, S.Y.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Shieh, J.A.; Huang, Y.H.; Tsai, H.T.; Feng, S.W.; Peng, T.Y.; et al. Unraveling the Link between Periodontitis and Coronavirus Disease 2019: Exploring Pathogenic Pathways and Clinical Implications. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-ΚB Signaling in Inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Lv, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, W.; Yuan, H. NLRP3 Regulates Alveolar Bone Loss in Ligature-Induced Periodontitis by Promoting Osteoclastic Differentiation. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodin, P. Immune Determinants of COVID-19 Disease Presentation and Severity. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.R.; Kanneganti, T.D. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Cancer and Metabolic Diseases. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Y.; Song, J.H.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, M.N.; Piao, X.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, O.S.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome Reduces Age-Related Experimental Alveolar Bone Loss. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainas, G.; Nibali, L.; Ide, M.; Mahmeed, W.A.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Al-Alawi, K.; Banach, M.; Banerjee, Y.; Ceriello, A.; Cesur, M.; et al. Associations between Periodontitis, COVID-19, and Cardiometabolic Complications: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence. Metabolites 2022, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.; Aktar, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Chowdhury, M.M.H. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in COVID-19: An Interlink between Risk Factors and Disease Severity. Microbes Infect. 2022, 24, 104913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.J.A.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Gouveia, M.I.M.; Marcelino, B.d.R.; Santos, C.S.d.; Lima, K.V.B.; Lima, L.N.G.C. Hyperinflammatory Response in COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Viruses 2023, 15, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, D.F.; te Velde, A.A. Severe COVID-19: NLRP3 Inflammasome Dysregulated. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Di, B.; Xu, L. li The NLRP3 Inflammasome and COVID-19: Activation, Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 61, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldo, S.; Bussani, R.; Nuzzi, V.; Bonaventura, A.; Mauro, A.G.; Cannatà, A.; Pillappa, R.; Sinagra, G.; Nana-Sinkam, P.; Sime, P.; et al. Inflammasome Formation in the Lungs of Patients with Fatal COVID-19. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, A.; Ito, H.; Åsman, B.; Bergström, K. Hyper-Reactive Mononuclear Cells and Neutrophils in Chronic Periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2006, 33, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.B.; Wright, H.J.; Roberts, A.; Cooper, P.R.; Chapple, I.L.C. Hyperactivity and Reactivity of Peripheral Blood Neutrophils in Chronic Periodontitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masso-Silva, J.A.; Moshensky, A.; Lam, M.T.Y.; Odish, M.F.; Patel, A.; Xu, L.; Hansen, E.; Trescott, S.; Nguyen, C.; Kim, R.; et al. Increased Peripheral Blood Neutrophil Activation Phenotypes and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, P.; Saffarzadeh, M.; Weber, A.N.R.; Rieber, N.; Radsak, M.; von Bernuth, H.; Benarafa, C.; Roos, D.; Skokowa, J.; Hartl, D. Neutrophils: Between Host Defence, Immune Modulation, and Tissue Injury. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Sha, Z.; Wu, H. Mechanisms and Immune Crosstalk of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Response to Infection. MBio 2025, 16, e0018925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darestani, M.N.; Akbari, A.; Yaghobee, S.; Taheri, M.; Akbari, S. COVID-19 Pandemic and Periodontal Practice: The Immunological, Clinical, and Economic Points of View. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 3918980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keykha, E.; Khodadadifard, L.; Moosavi, M.-S.; Fathi, Y.; Hajisadeghi, S. Proposed Mechanisms for the Relationship between Periodontal Diseases and the Severity of COVID-19: Common Pathogens, Inflammatory Mediators, and Risk Factors. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2024, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magán-Fernández, A.; O’Valle, F.; Abadía-Molina, F.; Muñoz, R.; Puga-Guil, P.; Mesa, F. Characterization and Comparison of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Gingival Samples of Periodontitis and Gingivitis: A Pilot Study. J. Periodontal Res. 2019, 54, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitkov, L.; Klappacher, M.; Hannig, M.; Krautgartner, W.D. Neutrophil Fate in Gingival Crevicular Fluid. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2010, 34, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitkov, L.; Klappacher, M.; Hannig, M.; Krautgartner, W.D. Extracellular Neutrophil Traps in Periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2009, 44, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, C.; Kobayashi, T.; Ito, S.; Sugita, N.; Murasawa, A.; Nakazono, K.; Yoshie, H. Circulating Levels of Carbamylated Protein and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are Associated with Periodontitis Severity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcanjo, A.; Logullo, J.; Menezes, C.C.B.; de Souza Carvalho Giangiarulo, T.C.; dos Reis, M.C.; de Castro, G.M.M.; da Silva Fontes, Y.; Todeschini, A.R.; Freire-de-Lima, L.; Decoté-Ricardo, D.; et al. The Emerging Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (COVID-19). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veras, F.P.; Pontelli, M.C.; Silva, C.M.; Toller-Kawahisa, J.E.; de Lima, M.; Nascimento, D.C.; Schneider, A.H.; Caetité, D.; Tavares, L.A.; Paiva, I.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Triggered Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Mediate COVID-19 Pathology. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20201129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, M.; Anders, H.J.; Bilyy, R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Daniel, C.; De Lorenzo, R.; Egeblad, M.; Henneck, T.; Hidalgo, A.; Hoffmann, M.; et al. Patients with COVID-19: In the Dark-NETs of Neutrophils. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 3125–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casqueiro, J.; Casqueiro, J.; Alves, C. Infections in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Pathogenesis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16 (Suppl. 1), 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. Coronavirus Infections and Type 2 Diabetes-Shared Pathways with Therapeutic Implications. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albai, O.; Frandes, M.; Sima, A.; Timar, B.; Vlad, A.; Timar, R. Practical Applicability of the ISARIC-4C Score on Severity and Mortality Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Medicina 2022, 58, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albai, O.; Braha, A.; Timar, B.; Sima, A.; Deaconu, L.; Timar, R. Assessment of the Negative Factors for the Clinical Outcome in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes. Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Huang, S.F.; Lin, J.X.; Zhi, H.N.; Xiao, L.; Wang, X.Z.; Guo, K.H.; Zhou, L.; Long, T.; You, H.M.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Acute Complication of COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes: A Multicenter, Retrospective Study in Southern China. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1237832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk Wensveen, T.; Gašparini, D.; Rahelić, D.; Wensveen, F.M. Type 2 Diabetes and Viral Infection; Cause and Effect of Disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 172, 108637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Kaminga, A.C.; Xu, H. Comorbidities’ Potential Impacts on Severe and Non-Severe Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, E24971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Shah, G.H.; Schwind, J.S.; Richmond, H.L. Community Characteristics and COVID-19 Outcomes: A Study of 159 Counties in Georgia, United States. J. Public Health Manag. Pract. 2021, 27, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.J.; Shih, H.M.; Su, K.P.; Hsueh, P.R. Risk Factors for Poor COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients with Psychiatric Disorders. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2023, 114, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ren, H.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X.; Yu, X.; Dong, K. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Severe COVID-19 with Diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhi, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Bi, Z.; Zhao, Y. Prevalence and Impact of Cardiovascular Metabolic Diseases on COVID-19 in China. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Gupta, R.; Ghosh, A.; Misra, A. Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, Pathophysiology, Prognosis and Practical Considerations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, C.; Cipponeri, E.; Roden, M. Diabetes Mellitus, Energy Metabolism, and COVID-19. Endocr. Rev. 2024, 45, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgay Yıldırım, Ö.; Kaya, Ş. The Atherogenic Index of Plasma as a Predictor of Mortality in Patients with COVID-19. Heart Lung 2021, 50, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereda, G. COVID-19 Is Associated with High Blood Glucose Levels: Diabetic Neuropathy during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: A Case Report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2024, 86, 7318–7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Yan, Y.; Shi, X.; Dong, K.; Yu, X.; Zhang, S. Association of the Insulin Resistance Marker TyG Index with the Severity and Mortality of COVID-19. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani-Rasaf, M.; Mirjalili, K.; Vatannejad, A.; Teimouri, M. Are Lipid Ratios and Triglyceride-Glucose Index Associated with Critical Care Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients? PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, S.; AlMasoudi, A.S.; AlBuhayri, A.H.; AlAtwi, H.M.; AlHwiti, S.S.; Alaidi, H.M.; Alshehri, A.M.; Alanazi, N.A.; Aljabri, A.; Al-Gayyar, M.M. Effect of COVID-19 on Glycemic Control, Insulin Resistance, and PH in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Cureus 2023, 15, e35390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furumachi, K.; Kagatsume, T.; Higuchi, A.; Kozaru, M.; Kumagai, E.; Hosohata, K. Association Between COVID-19 and Diabetes Management Indices in Japanese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2024, 17, 3759–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabestari, M.; Azizi, R.; Ghadiri-Anari, A. Type 2 Diabetes and Susceptibility to COVID-19: A Machine Learning Analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seino, Y.; Nanjo, K.; Tajim, N.; Kadowaki, T.; Kashiwagi, A.; Araki, E.; Ito, C.; Inagaki, N.; Iwamoto, Y.; Kasuga, M.; et al. Report of the Committee on the Classification and Diagnostic Criteria of Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2010, 1, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeagu, E.I. Red Blood Cells as Biomarkers and Mediators in Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Medicine 2024, 103, e37265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Youn, H.M.; Quan, J.; Lee, L.L.S.; Mak, I.L.; Yu, E.Y.T.; Chao, D.V.K.; Ko, W.W.K.; Wong, I.C.K.; Lau, G.K.K.; et al. The Indirect Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and without COVID-19 Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prim. Care Diabetes 2023, 17, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, M.A.; Gönel, A.; Karaaslan, H.; Uyar, N.; Cindoğlu, Ç.; Sabuncu, T. Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on the Metabolic Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 67, e000621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuma, K.; Sawada, M.; Aihara, M.; Doi, S.; Sekine, R.; Usami, S.; Ohe, K.; Kubota, N.; Yamauchi, T. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Glycemic Control in People with Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2023, 14, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; He, W.; Yu, B.; Zhong, K.; Zhou, D.; Wang, D.W. Effects of Different Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Mortality of Coronavirus Disease from 2019 to 2021 in China: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Study. Mol. Biomed. 2024, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Rodriguez, D.P.; González-Cantú, A.; Garza-Silva, A.; Rivera-Cavazos, A.; Fernández-Chau, I.F.; Cepeda-Medina, A.B.; Sanz-Sánchez, M.A.; del Rio-Parra, G.F.; Torres-Fuentes, M.A.; Rodriguez-Puente, M.A.; et al. Effect of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on Metabolic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A 5-Year Cohort Follow-up Managed by a Dynamic Multidisciplinary Team in Northeastern Mexico. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabestari, M.; Salari, F.; Azizi, R.; Ghadiri-Anari, A.; Namiranian, N. Impact of COVID-19 on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. BMC Pulm. Med. 2025, 25, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.C.; Shu, H.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Q.; Li, J.J.; Huang, X.L.; Hua, F. Inflammatory Biomarkers Predict Higher Risk of Hyperglycemic Crises but Not Outcomes in Diabetic Patients with COVID-19. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Rohli, K.E.; Shen, P.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Kong, X.; Yang, S.; Jia, P. The Epidemiology, Pathophysiological Mechanisms, and Management toward COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Prim. Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelle, M.C.; Zaffina, I.; Provenzano, M.; Moirano, G.; Arturi, F. COVID-19 and Diabetes-Two Giants Colliding: From Pathophysiology to Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 974540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Meng, W. COVID-19 and Diabetes: The Contributions of Hyperglycemia. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Alblihed, M.; Guerreiro, S.G.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Batiha, G.E.S. COVID-19 in Relation to Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 644095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S.; Yang, Y.; Zou, D.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Rong, X.; Ye, D. COVID-19 and Metabolic Comorbidities: An Update on Emerging Evidences for Optimal Therapies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.T.; Lidsky, P.V.; Xiao, Y.; Lee, I.T.; Cheng, R.; Nakayama, T.; Jiang, S.; Demeter, J.; Bevacqua, R.J.; Chang, C.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infects Human Pancreatic β Cells and Elicits β Cell Impairment. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Bao, L.; Song, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, P.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; et al. Infection with SARS-CoV-2 Can Cause Pancreatic Impairment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, B.; Abdelalim, E.M. ACE2 Function in the Pancreatic Islet: Implications for Relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and Diabetes. Acta Physiol. 2021, 233, e13733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhulu, C.A.; Singla, D.K. Mechanisms of COVID-19 Pathogenesis in Diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2022, 323, H403–H420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramchandani, B.P.; Azmath, M.F.; Bendaram, S.R.; Mirza, F.S. A Sweet Paradox: Severe Insulin Resistance and Hyperglycemia in Asymptomatic COVID-19 Infection. Cureus 2023, 15, 640529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Ma, P.; Luo, H.; Wang, M.; Jin, Y. Association Between Longitudinal Change in Abnormal Fasting Blood Glucose Levels and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients Without Previous Diagnosis of Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 640529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, D.E.; Andor, M.; Buda, V.; Kundnani, N.R.; Duda-Seiman, D.M.; Craciun, L.M.; Neagu, M.N.; Carlogea, I.-S.; Dragan, S.-R. Insulin Resistance in Long COVID-19 Syndrome. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, M.J.; Yang, J.K.; Lin, S.S.; Ji, X.J.; Guo, L.M. Loss of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Leads to Impaired Glucose Homeostasis in Mice. Endocrine 2008, 34, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, C.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X. Lymphocytes Regulate Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Factor ACE2 in the Pancreas of T2DM Patients. Diabet. Med. 2023, 40, e15106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocki, J.; Ye, M.; Soler, M.J.; Gurley, S.B.; Xiao, H.D.; Bernstein, K.E.; Coffman, T.M.; Chen, S.; Batlle, D. ACE and ACE2 Activity in Diabetic Mice. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Ho, H.; Riera, M.; Palau, V.; Pascual, J.; Soler, M.J. Characterization of ACE and ACE2 Expression within Different Organs of the NOD Mouse. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Lau, A.; So, H.C. Exploring Diseases/Traits and Blood Proteins Causally Related to Expression of ACE2, the Putative Receptor of SARS-CoV-2: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis Highlights Tentative Relevance of Diabetes-Related Traits. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.K.; Awasthi, K.; Usman, K.; Banerjee, M. Role of Renin-Angiotensin System/Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 Mechanism and Enhanced COVID-19 Susceptibility in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 606–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govender, N.; Khaliq, O.P.; Moodley, J.; Naicker, T. Insulin Resistance in COVID-19 and Diabetes. Prim. Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, C.; Rysä, J.; Almgren, P.; Nilsson, J.; Engström, G.; Orho-Melander, M.; Ruskoaho, H.; Melander, O. Plasma Levels of the Proprotein Convertase Furin and Incidence of Diabetes and Mortality. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.; Mobeen, A.; Chandra, A.; Joshi, S.; Ramachandran, S. A Meta-Analysis of Comorbidities in COVID-19: Which Diseases Increase the Susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Infection? Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 130, 104219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusmartseva, I.; Wu, W.; Syed, F.; Van Der Heide, V.; Jorgensen, M.; Joseph, P.; Tang, X.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Yang, C.; Nick, H.; et al. Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Factors in the Pancreas of Normal Organ Donors and Individuals with COVID-19. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 1041–1051.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.K.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, M.Y.; Yuan, S.Y.; Fu, H.J.; Wu, B.Y.; Sun, G.Z.; Yang, G.R.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, L.; et al. Plasma Glucose Levels and Diabetes Are Independent Predictors for Mortality and Morbidity in Patients with SARS. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.K.; Lin, S.S.; Ji, X.J.; Guo, L.M. Binding of SARS Coronavirus to Its Receptor Damages Islets and Causes Acute Diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2010, 47, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.; Luan, Y.; He, H.; Jue, B.; Yang, Y.; Qin, B.; Ren, K. Glucose Metabolism Disorder: A Potential Accomplice of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, B.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Wen, Z. Effect of Hyperglycemia on the Immune Function of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Study. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Ma, G.; Sheng, L.; Feng, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Li, R. Evaluation of Inflammatory Markers in Patients with COVID-19 Combined with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2024, 17, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, L.; Xu, M.D.; Wu, J.; Luo, D.; Zhu, Y.S.; Li, B.X.; Song, X.Y.; Zhou, X. Prognostic Value of Interleukin-6, C-Reactive Protein, and Procalcitonin in Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, M.; Chen, E.W.; Toh, S.A.; Gascoigne, N.R.J. Autoimmune Responses and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuschik, L.; Riabov, V.; Schmuttermaier, C.; Sevastyanova, T.; Weiss, C.; Klüter, H.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Hyperglycemia Induces Inflammatory Response of Human Macrophages to CD163-Mediated Scavenging of Hemoglobin-Haptoglobin Complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Dinarello, C.A.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Targeting Innate Immune Mediators in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Liaqat, A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha: Role in Development of Insulin Resistance and Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrakis, V.; Panagopoulos, P.; Trypsianis, G.; Papazoglou, D.; Papanas, N. Fasting Plasma Glucose Increase and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as Risk Predictors of Clinical Outcome of COVID-19 Pneumonia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2023, 131, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, K.; Morris, J.; Bridson, T.; Govan, B.; Rush, C.; Ketheesan, N. Immunological Mechanisms Contributing to the Double Burden of Diabetes and Intracellular Bacterial Infections. Immunology 2015, 144, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuschieri, S.; Grech, S. COVID-19 and Diabetes: The Why, the What and the How. J. Diabetes Complications 2020, 34, 107637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, H.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Clinical Course and Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Single-Centered, Retrospective, Observational Study. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtiar, E.W.; Bachtiar, B.M.; Kusumaningrum, A.; Sunarto, H.; Soeroso, Y.; Sulijaya, B.; Theodorea, C.F.; Pratomo, I.P.; Yudhistira; Efendi, D.; et al. Association between Dysbiotic Perio-Pathogens and Inflammatory Initiators and Mediators in COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casillas Santana, M.A.; Arreguín Cano, J.A.; Dib Kanán, A.; Dipp Velázquez, F.A.; Munguía, P.D.C.S.; Martínez Castañón, G.A.; Castillo Silva, B.E.; Sámano Valencia, C.; Salas Orozco, M.F. Should We Be Concerned about the Association of Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontal Disease in the Risk of Infection by SARS-CoV-2? A Systematic Review and Hypothesis. Medicina 2021, 57, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Carrillo, J.L.; Gutiérrez-Coronado, O.; Villalobos-Gutiérrez, P.T.; Villacis-Valencia, M.S.; Chávez-Ruvalcaba, F.; Vázquez-Alcaraz, S.J.; Rivera-Lozada, O.; Barboza, J.J. Current Landscape of the Interrelationship Between Periodontitis, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188756
Muñoz-Carrillo JL, Gutiérrez-Coronado O, Villalobos-Gutiérrez PT, Villacis-Valencia MS, Chávez-Ruvalcaba F, Vázquez-Alcaraz SJ, Rivera-Lozada O, Barboza JJ. Current Landscape of the Interrelationship Between Periodontitis, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and COVID-19. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188756
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Carrillo, José Luis, Oscar Gutiérrez-Coronado, Paola Trinidad Villalobos-Gutiérrez, Marcelo Stalin Villacis-Valencia, Francisca Chávez-Ruvalcaba, Silverio Jafet Vázquez-Alcaraz, Oriana Rivera-Lozada, and Joshuan J. Barboza. 2025. "Current Landscape of the Interrelationship Between Periodontitis, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and COVID-19" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188756
APA StyleMuñoz-Carrillo, J. L., Gutiérrez-Coronado, O., Villalobos-Gutiérrez, P. T., Villacis-Valencia, M. S., Chávez-Ruvalcaba, F., Vázquez-Alcaraz, S. J., Rivera-Lozada, O., & Barboza, J. J. (2025). Current Landscape of the Interrelationship Between Periodontitis, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and COVID-19. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188756









