Intra-Arterial Administration of Stem Cells and Exosomes for Central Nervous System Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overall Results of IA Transplantation of Stem Cell and Exosome for CNS Disease
3. Preclinical Studies of Cell Therapy
3.1. Ischemic Stroke
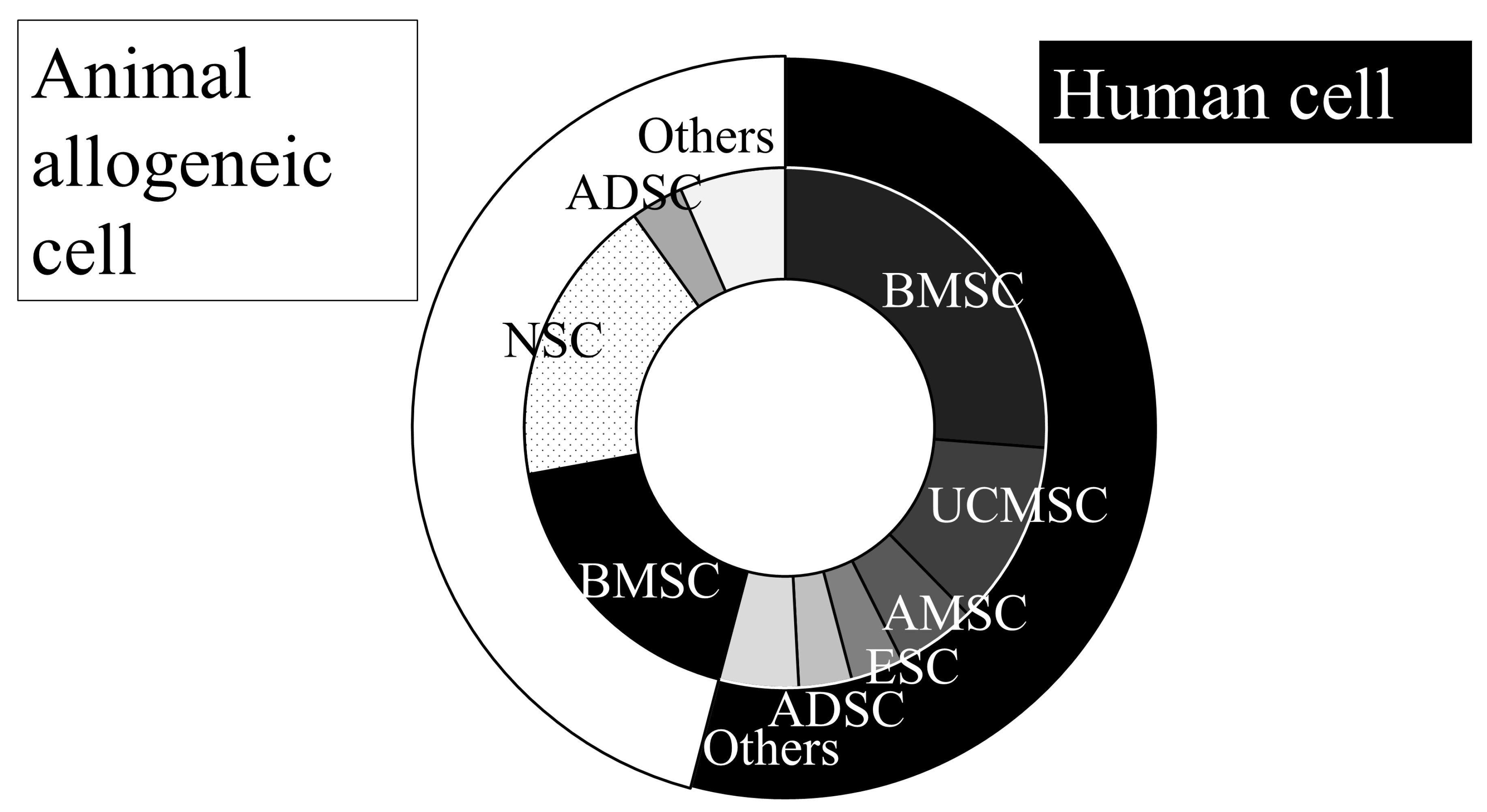
3.1.1. Cell Sources
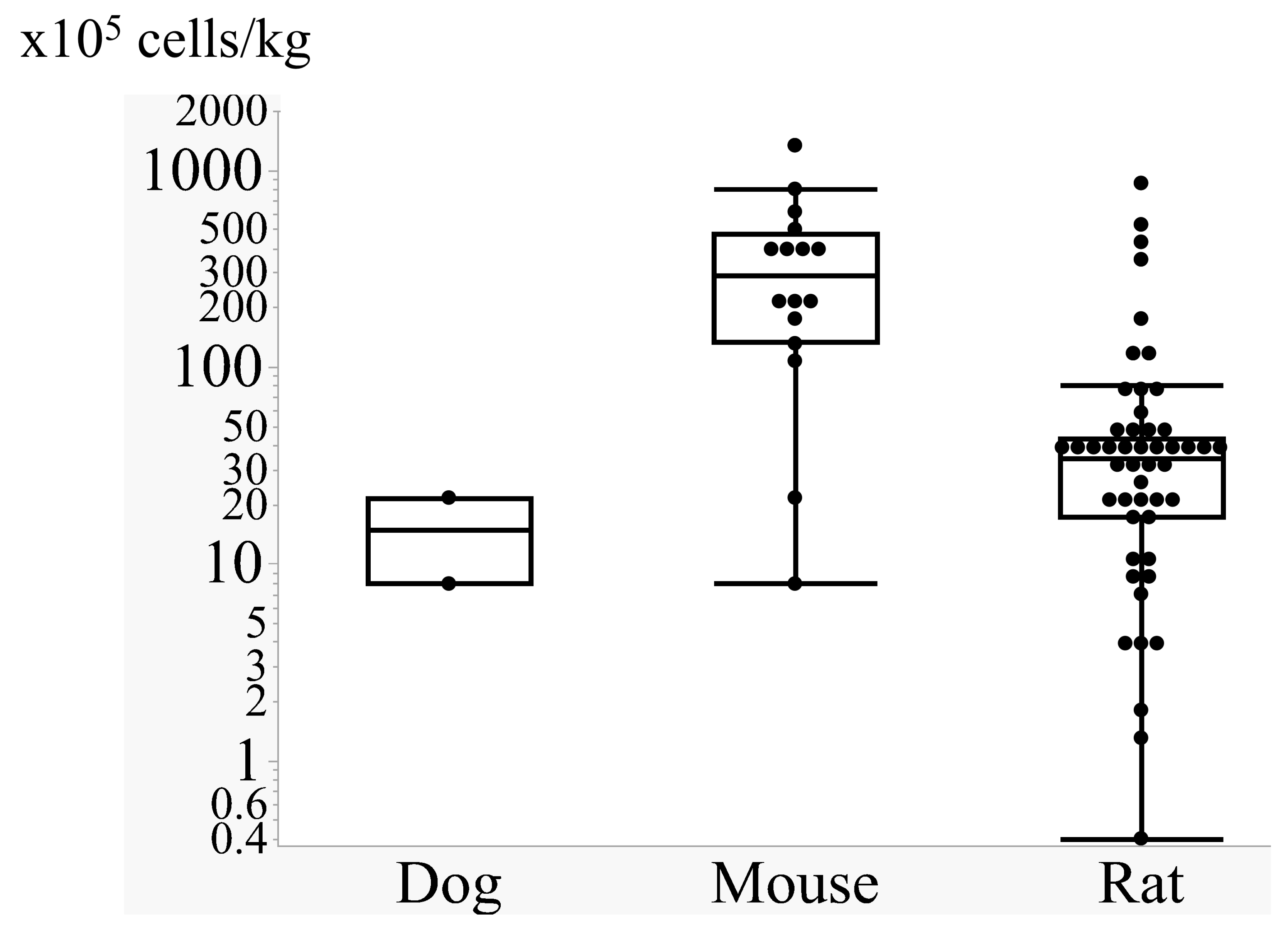
3.1.2. Cell Doses
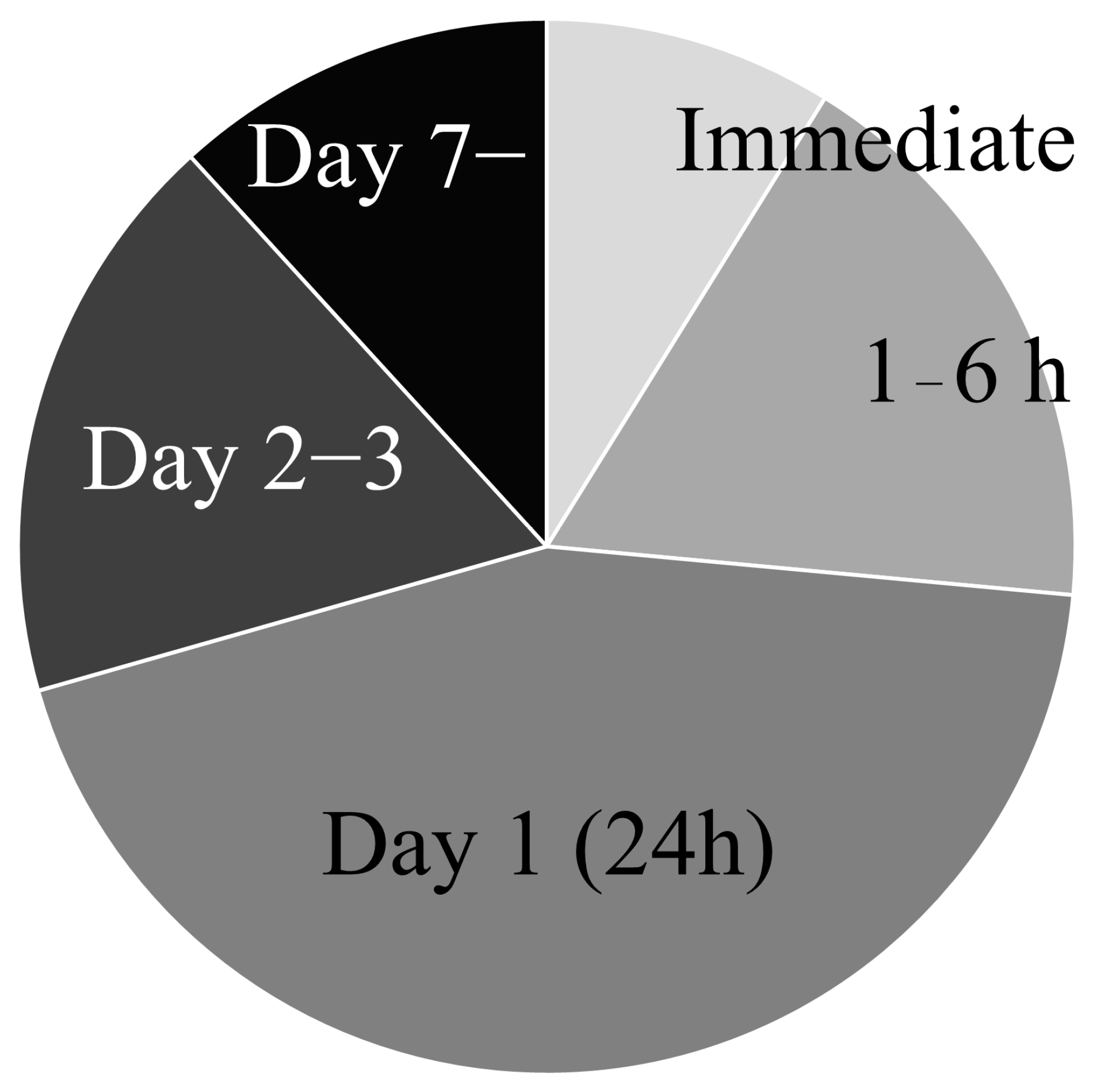
3.1.3. Transplantation Timing
3.1.4. Tracking Transplanted Cells and Visualizing Brain Condition
3.1.5. Mechanisms of Recovery
3.2. Traumatic Injury
3.3. Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH)
3.4. Glioma
3.5. Alzheimer’s Disease
3.6. Parkinson’s Disease
3.7. Safety Issues of IA Transplantation
4. Preclinical Studies of Exosome Therapy
5. Clinical Trials Using Stem Cell and Exosome via Intra-Arterial Transplantation
6. Conclusions and Future Direction
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawabori, M.; Shichinohe, H.; Kahata, K.; Miura, A.; Maeda, K.; Ito, Y.M.; Mukaino, M.; Kogawa, R.; Nakamura, K.; Gotoh, S.; et al. Phase I/II trial of intracerebral transplantation of autologous bone marrow stem cells combined with recombinant peptide scaffold for patients with chronic intracerebral haemorrhage: A study protocol. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e083959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamiya, S.; Kawabori, M.; Fujimura, M. Stem Cell Therapies for Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Cell Transplant. 2023, 32, 9636897231158153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabori, M.; Chida, D.; Nejadnik, B.; Stonehouse, A.H.; Okonkwo, D.O. Cell therapies for acute and chronic traumatic brain injury. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2022, 38, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, K.; Kawabori, M.; Seki, T.; Houkin, K. Clinical Trials of Stem Cell Treatment for Spinal Cord Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabori, M.; Shichinohe, H.; Kuroda, S.; Houkin, K. Clinical Trials of Stem Cell Therapy for Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, Y.; Kawabori, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Takamiya, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nakahara, Y.; Senjo, H.; Hashimoto, D.; Masuda, S.; Fujioka, Y.; et al. Intravenous Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Alleviates Spinal Cord Injury by Regulating Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation through Exosomal miR-125a-3p. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, S.; Kawabori, M.; Fujimura, M. Intranasal administration of stem cell-derived exosomes for central nervous system diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Kawabori, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Gotoh, S.; Nakahara, Y.; Yoshie, E.; Fujimura, M. Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Alleviates Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, S.; Kawabori, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nakahara, Y.; Yoshie, E.; Konno, K.; Mizuno, Y.; Fujioka, Y.; Ohba, Y.; Kuge, Y.; et al. Intranasal administration of stem cell-derived exosome alleviates cognitive impairment against subarachnoid hemorrhage. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 386, 115143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoker, T.B.; Andresen, K.E.R.; Barker, R.A. Hydrocephalus Complicating Intrathecal Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy for Huntington’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabori, M.; Kuroda, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Ito, M.; Shichinohe, H.; Houkin, K.; Kuge, Y.; Tamaki, N. Intracerebral, but not intravenous, transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells enhances functional recovery in rat cerebral infarct: An optical imaging study. Neuropathology 2012, 32, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbab, A.S.; Thiffault, C.; Navia, B.; Victor, S.J.; Hong, K.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Varma, N.R.; Iskander, A.; Chopp, M. Tracking of In-111-labeled human umbilical tissue-derived cells (hUTC) in a rat model of cerebral ischemia using SPECT imaging. BMC Med. Imaging 2012, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeri, A.; Mazzon, E. State of the Art and Future of Stem Cell Therapy in Ischemic Stroke: Why Don’t We Focus on Their Administration? Bioengineering 2023, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houkin, K.; Osanai, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Minematsu, K.; Taguchi, A.; Maruichi, K.; Niiya, Y.; Asaoka, K.; Kuga, Y.; Takizawa, K.; et al. Allogeneic Stem Cell Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Phase 2/3 TREASURE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niizuma, K.; Osawa, S.I.; Endo, H.; Izumi, S.I.; Ataka, K.; Hirakawa, A.; Iwano, M.; Tominaga, T. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of CL2020, an allogenic muse cell-based product, in subacute ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Sharma, A.; Garg, A.; Mohanty, S.; Bhatnagar, S.; Johri, S.; Singh, K.K.; Nair, V.; Sarkar, R.S.; Gorthi, S.P.; et al. Intravenous autologous bone marrow mononuclear stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke: A multicentric, randomized trial. Stroke 2014, 45, 3618–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.C.; Wechsler, L.R.; Clark, W.M.; Savitz, S.I.; Ford, G.A.; Chiu, D.; Yavagal, D.R.; Uchino, K.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Auchus, A.P.; et al. Safety and efficacy of multipotent adult progenitor cells in acute ischaemic stroke (MASTERS): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaillard, A.; Hommel, M.; Moisan, A.; Zeffiro, T.A.; Favre-Wiki, I.M.; Barbieux-Guillot, M.; Vadot, W.; Marcel, S.; Lamalle, L.; Grand, S.; et al. Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Motor Recovery in Subacute Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Cho, J.; D’Egidio, F.; Vignon, C.; Streefkerk, H.; de Kalbermatten, M.; Garitaonandia, I.; Borlongan, C.V. Probing Multiple Transplant Delivery Routes of CD+34 Stem Cells for Promoting Behavioral and Histological Benefits in Experimental Ischemic Stroke. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2024, 13, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.; Smith, C.J.; Allan, S.M.; Pinteaux, E. Preconditioning with interleukin-1 alpha is required for the neuroprotective properties of mesenchymal stem cells after ischemic stroke in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi-Haghighi, S.; Pandamooz, S.; Jurek, B.; Fattahi, S.; Safari, A.; Azarpira, N.; Dianatpour, M.; Hooshmandi, E.; Bayat, M.; Owjfard, M.; et al. From Hair to the Brain: The Short-Term Therapeutic Potential of Human Hair Follicle-Derived Stem Cells and Their Conditioned Medium in a Rat Model of Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 2587–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkashova, E.; Namestnikova, D.; Leonov, G.; Gubskiy, I.; Sukhinich, K.; Melnikov, P.; Chekhonin, V.; Yarygin, K.; Goldshtein, D.; Salikhova, D. Comparative study of the efficacy of intra-arterial and intravenous transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived neural progenitor cells in experimental stroke. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, D.; Datta, A.; Kaur, H.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Yavagal, D.R.; Bhattacharya, P. Sirtuin-1—Mediated NF-kappaB Pathway Modulation to Mitigate Inflammasome Signaling and Cellular Apoptosis is One of the Neuroprotective Effects of Intra-arterial Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy Following Ischemic Stroke. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Sarmah, D.; Kaur, H.; Chaudhary, A.; Mounica, K.L.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; Yavagal, D.R.; Bhattacharya, P. Post-stroke Impairment of the Blood-Brain Barrier and Perifocal Vasogenic Edema Is Alleviated by Endovascular Mesenchymal Stem Cell Administration: Modulation of the PKCdelta/MMP9/AQP4-Mediated Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 2758–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vats, K.; Sarmah, D.; Datta, A.; Saraf, J.; Kaur, H.; Pravalika, K.; Wanve, M.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; Dave, K.R.; et al. Intra-arterial Stem Cell Therapy Diminishes Inflammasome Activation After Ischemic Stroke: A Possible Role of Acid Sensing Ion Channel 1a. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Sarmah, D.; Veeresh, P.; Datta, A.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; Yavagal, D.R.; Bhattacharya, P. Endovascular Stem Cell Therapy Post Stroke Rescues Neurons from Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor/Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B Signaling. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 3745–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubskiy, I.L.; Namestnikova, D.D.; Sukhinich, K.K.; Revkova, V.A.; Melnikov, P.A.; Gubsky, L.V.; Chekhonin, V.P.; Yarygin, K.N. MRI-Based and Histologically Verified 3D Modeling of Spatial Distribution of Intra-Arterially Transplanted Cells in Rat Brain. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namestnikova, D.D.; Gubskiy, I.L.; Revkova, V.A.; Sukhinich, K.K.; Melnikov, P.A.; Gabashvili, A.N.; Cherkashova, E.A.; Vishnevskiy, D.A.; Kurilo, V.V.; Burunova, V.V.; et al. Intra-Arterial Stem Cell Transplantation in Experimental Stroke in Rats: Real-Time MR Visualization of Transplanted Cells Starting With Their First Pass Through the Brain With Regard to the Therapeutic Action. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 641970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Cao, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Duan, X.; Lu, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Peritumoral administration of IFNbeta upregulated mesenchymal stem cells inhibits tumor growth in an orthotopic, immunocompetent rat glioma model. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.S.; Pandamooz, S.; Safari, A.; Jurek, B.; Tamadon, A.; Namavar, M.R.; Dianatpour, M.; Dargahi, L.; Azarpira, N.; Fattahi, S.; et al. Epidermal neural crest stem cell transplantation as a promising therapeutic strategy for ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondori, B.J.; Asadi, M.H.; Bahadoran, H.; Yari, A.; Sarshoori, J.R. Intra-arterial transplantation of neural stem cells improve functional recovery after transient ischemic stroke in adult rats. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2020, 121, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Subash, M.; Yoon, J.S.; Jo, D.; Han, J.; Hong, J.M.; Kim, S.S.; Suh-Kim, H. Neurogenin-1 Overexpression Increases the Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Enhanced Engraftment in an Ischemic Rat Brain. Int. J. Stem Cells 2020, 13, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraf, J.; Sarmah, D.; Vats, K.; Kaur, H.; Pravalika, K.; Wanve, M.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; Dave, K.R.; Yavagal, D.R.; et al. Intra-arterial stem cell therapy modulates neuronal calcineurin and confers neuroprotection after ischemic stroke. Int. J. Neurosci. 2019, 129, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewska, A.; Nowakowski, A.; Grygorowicz, T.; Dabrowska, S.; Orzel, J.; Walczak, P.; Lukomska, B.; Janowski, M. Single-cell, high-throughput analysis of cell docking to vessel wall. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 2308–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Horie, N.; Satoh, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Mori, T.; Maeda, H.; Fukuda, Y.; Ishizaka, S.; Hiu, T.; Morofuji, Y.; et al. Age of donor of human mesenchymal stem cells affects structural and functional recovery after cell therapy following ischaemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1199–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonska, A.; Shea, D.J.; Cao, S.; Bulte, J.W.; Janowski, M.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Walczak, P. Overexpression of VLA-4 in glial-restricted precursors enhances their endothelial docking and induces diapedesis in a mouse stroke model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Cerqueira, B.; Misra, V.; Duong, T.Q. Intraarterial transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells in hyperacute stroke improves vascular function. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Xie, X.F.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Liu, S.M.; Hu, G.Z.; Cao, W.F.; Wu, X.M. Comparisons of the therapeutic effects of three different routes of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in cerebral ischemic rats. Brain Res. 2018, 1680, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lin, F.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Mei, A.; Zhu, P. Effects of intra-arterial transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells on the expression of netrin-1 and its receptor DCC in the peri-infarct cortex after experimental stroke. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudzenski, S.; Baier, S.; Ebert, A.; Pullens, P.; Lemke, A.; Bieback, K.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Schad, L.R.; Alonso, A.; Hennerici, M.G.; et al. The effect of adipose tissue-derived stem cells in a middle cerebral artery occlusion stroke model depends on their engraftment rate. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, J.S.; Joo, I.S.; Suh-Kim, H.; Kim, S.S.; Hong, J.M. Comparison of MSC-Neurogenin1 administration modality in MCAO rat model. Transl. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.X.; Li, P.C.; Qian, C.; Teng, G.J. Bioluminescence imaging of transplanted human endothelial colony-forming cells in an ischemic mouse model. Brain Res. 2016, 1642, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Chen, Z.; Kong, D.K.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, J. Novel microcatheter-based intracarotid delivery approach for MCAO/R mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 597, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doeppner, T.R.; Kaltwasser, B.; Teli, M.K.; Sanchez-Mendoza, E.H.; Kilic, E.; Bahr, M.; Hermann, D.M. Post-stroke transplantation of adult subventricular zone derived neural progenitor cells—A comprehensive analysis of cell delivery routes and their underlying mechanisms. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 273, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Chang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, C.Q.; Wang, G.; Ju, S. Synergistic Effects of Transplanted Endothelial Progenitor Cells and RWJ 67657 in Diabetic Ischemic Stroke Models. Stroke 2015, 46, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, S.; Smith, T.N.; Wang, N.; Chua, J.Y.; Westbroek, E.; Wang, K.; Guzman, R. BDNF Pretreatment of Human Embryonic-Derived Neural Stem Cells Improves Cell Survival and Functional Recovery After Transplantation in Hypoxic-Ischemic Stroke. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 2449–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khabbal, J.; Kerkela, E.; Mitkari, B.; Raki, M.; Nystedt, J.; Mikkonen, V.; Bergstrom, K.; Laitinen, S.; Korhonen, M.; Jolkkonen, J. Differential Clearance of Rat and Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells From the Brain After Intra-arterial Infusion in Rats. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.H.; Choi, C.; Chang, D.J.; Shin, D.A.; Lee, N.; Jeon, I.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, H.; Hong, K.S.; Ko, J.J.; et al. Early neuroprotective effect with lack of long-term cell replacement effect on experimental stroke after intra-arterial transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, A.; Yasuhara, T.; Kameda, M.; Morimoto, J.; Takeuchi, H.; Wang, F.; Sasaki, T.; Sasada, S.; Shinko, A.; Wakamori, T.; et al. Intra-Arterial Transplantation of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mounts Neuroprotective Effects in a Transient Ischemic Stroke Model in Rats: Analyses of Therapeutic Time Window and Its Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkari, B.; Kerkela, E.; Nystedt, J.; Korhonen, M.; Jolkkonen, J. Unexpected complication in a rat stroke model: Exacerbation of secondary pathology in the thalamus by subacute intraarterial administration of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerri, S.; Greco, R.; Levandis, G.; Ghezzi, C.; Mangione, A.S.; Fuzzati-Armentero, M.T.; Bonizzi, A.; Avanzini, M.A.; Maccario, R.; Blandini, F. Intracarotid Infusion of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease, Focusing on Cell Distribution and Neuroprotective and Behavioral Effects. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Horie, N.; Satoh, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Morofuji, Y.; Hiu, T.; Izumo, T.; Hayashi, K.; Nishida, N.; Nagata, I. Intra-arterial transplantation of low-dose stem cells provides functional recovery without adverse effects after stroke. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silachev, D.N.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Babenko, V.A.; Danilina, T.I.; Zorov, L.D.; Pevzner, I.B.; Zorov, D.B.; Sukhikh, G.T. Intra-Arterial Administration of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Promotes Functional Recovery of the Brain After Traumatic Brain Injury. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 159, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.L.; Kerkela, E.; Bakreen, A.; Nitzsche, F.; Andrzejewska, A.; Nowakowski, A.; Janowski, M.; Walczak, P.; Boltze, J.; Lukomska, B.; et al. The cerebral embolism evoked by intra-arterial delivery of allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats is related to cell dose and infusion velocity. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greggio, S.; de Paula, S.; Azevedo, P.N.; Venturin, G.T.; Dacosta, J.C. Intra-arterial transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic rats. Life Sci. 2014, 96, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavagal, D.R.; Lin, B.; Raval, A.P.; Garza, P.S.; Dong, C.; Zhao, W.; Rangel, E.B.; McNiece, I.; Rundek, T.; Sacco, R.L.; et al. Efficacy and dose-dependent safety of intra-arterial delivery of mesenchymal stem cells in a rodent stroke model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Liu, Y.; Dang, M.; Zhu, G.; Su, R.; Fan, Y.; Tan, Z.; Wang, L.X.; Fang, J. Comparison of administration routes for adipose-derived stem cells in the treatment of middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Guan, J.; Mao, G.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S.; Bao, X.; Gao, J.; Feng, M.; Li, G.; Ma, W.; et al. Intra-arterial delivery of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells is a safe and effective way to treat cerebral ischemia in rats. Cell Transplant. 2014, 23 (Suppl. 1), S73–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlupia, N.; Manley, N.C.; Prasad, K.; Schafer, R.; Steinberg, G.K. Intraarterial transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells is more efficacious and safer compared with umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells in a rodent stroke model. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkari, B.; Nitzsche, F.; Kerkela, E.; Kuptsova, K.; Huttunen, J.; Nystedt, J.; Korhonen, M.; Jolkkonen, J. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells produce efficient localization in the brain and enhanced angiogenesis after intra-arterial delivery in rats with cerebral ischemia, but this is not translated to behavioral recovery. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 259, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, T.; Zhao, R.C.; Wu, Y. The size of mesenchymal stem cells is a significant cause of vascular obstructions and stroke. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2014, 10, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ge, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.C.; Wu, Y. Three-dimensional spheroid-cultured mesenchymal stem cells devoid of embolism attenuate brain stroke injury after intra-arterial injection. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuma, Y.; Wang, F.; Toyoshima, A.; Kameda, M.; Hishikawa, T.; Tokunaga, K.; Sugiu, K.; Liu, K.; Haruma, J.; Nishibori, M.; et al. Mannitol enhances therapeutic effects of intra-arterial transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells into the brain after traumatic brain injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 554, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Tajiri, N.; Franzese, N.; Franzblau, M.; Bae, E.; Platt, S.; Kaneko, Y.; Borlongan, C.V. Stem cell-like dog placenta cells afford neuroprotection against ischemic stroke model via heat shock protein upregulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Li, S.Q.; Qiu, Y.M.; Xiong, W.H.; Yin, Y.H.; Jia, F.; Jiang, J.Y. Migration of neural stem cells to ischemic brain regions in ischemic stroke in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 552, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Migliati, E.; Parsha, K.; Schaar, K.; Xi, X.; Aronowski, J.; Savitz, S.I. Intra-arterial delivery is not superior to intravenous delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 3463–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaka, S.; Horie, N.; Satoh, K.; Fukuda, Y.; Nishida, N.; Nagata, I. Intra-arterial cell transplantation provides timing-dependent cell distribution and functional recovery after stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.S.; Liu, S.; Zu, Q.Q.; Xu, X.Q.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.B. In vivo MR imaging of intraarterially delivered magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells in a canine stroke model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, J.S.; Kwak, B.K.; Kim, J.K.; Jung, J.; Ha, B.C.; Park, S. Engraftment of human mesenchymal stem cells in a rat photothrombotic cerebral infarction model: Comparison of intra-arterial and intravenous infusion using MRI and histological analysis. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2013, 54, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, S.; Wang, N.; Smith, T.N.; Pendharkar, A.V.; Chua, J.Y.; Birk, H.; Guzman, R. Timing of intra-arterial neural stem cell transplantation after hypoxia-ischemia influences cell engraftment, survival, and differentiation. Stroke 2012, 43, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.; Sodersten, E.; Sundstrom, E.; Le Blanc, K.; Andersson, T.; Hermanson, O.; Holmin, S. Targeted intra-arterial transplantation of stem cells to the injured CNS is more effective than intravenous administration: Engraftment is dependent on cell type and adhesion molecule expression. Cell Transplant. 2012, 21, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos-dos-Santos, A.; Rosado-de-Castro, P.H.; Lopes de Souza, S.A.; da Costa Silva, J.; Ramos, A.B.; Rodriguez de Freitas, G.; Barbosa da Fonseca, L.M.; Gutfilen, B.; Mendez-Otero, R. Intravenous and intra-arterial administration of bone marrow mononuclear cells after focal cerebral ischemia: Is there a difference in biodistribution and efficacy? Stem Cell Res. 2012, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkari, B.; Kerkela, E.; Nystedt, J.; Korhonen, M.; Mikkonen, V.; Huhtala, T.; Jolkkonen, J. Intra-arterial infusion of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells results in transient localization in the brain after cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 239, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, R.H.; Choi, R.; Pendharkar, A.V.; Gaeta, X.; Wang, N.; Nathan, J.K.; Chua, J.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Palmer, T.D.; Steinberg, G.K.; et al. The CCR2/CCL2 interaction mediates the transendothelial recruitment of intravascularly delivered neural stem cells to the ischemic brain. Stroke 2011, 42, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornicka-Pawlak, E.B.; Janowski, M.; Habich, A.; Jablonska, A.; Drela, K.; Kozlowska, H.; Lukomska, B.; Sypecka, J.; Domanska-Janik, K. Systemic treatment of focal brain injury in the rat by human umbilical cord blood cells being at different level of neural commitment. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2011, 71, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, T.; Rao, G.; Yang, Y.; Gumin, J.; Shinojima, N.; Bekele, B.N.; Qiao, W.; Zhang, W.; Lang, F.F. Mesenchymal stem cells display tumor-specific tropism in an RCAS/Ntv-a glioma model. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, J.Y.; Pendharkar, A.V.; Wang, N.; Choi, R.; Andres, R.H.; Gaeta, X.; Zhang, J.; Moseley, M.E.; Guzman, R. Intra-arterial injection of neural stem cells using a microneedle technique does not cause microembolic strokes. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendharkar, A.V.; Chua, J.Y.; Andres, R.H.; Wang, N.; Gaeta, X.; Wang, H.; De, A.; Choi, R.; Chen, S.; Rutt, B.K.; et al. Biodistribution of neural stem cells after intravascular therapy for hypoxic-ischemia. Stroke 2010, 41, 2064–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.G.; Li, Q.; Panda, S.; Lu, M.; Ewing, J.R.; Chopp, M. Effects of administration route on migration and distribution of neural progenitor cells transplanted into rats with focal cerebral ischemia, an MRI study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.; Le Blanc, K.; Soderman, M.; Andersson, T.; Holmin, S. Endovascular transplantation of stem cells to the injured rat CNS. Neuroradiology 2009, 51, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakondi, B.; Shimada, I.S.; Perry, A.; Munoz, J.R.; Ylostalo, J.; Howard, A.B.; Gregory, C.A.; Spees, J.L. CD133 identifies a human bone marrow stem/progenitor cell sub-population with a repertoire of secreted factors that protect against stroke. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, R.L.; Shinojima, N.; Fueyo, J.; Gumin, J.; Vecil, G.G.; Marini, F.C.; Bogler, O.; Andreeff, M.; Lang, F.F. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for intravascular delivery of oncolytic adenovirus Delta24-RGD to human gliomas. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8932–8940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.J.; Choi, C.B.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, E.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Han, H.; Lee, J.H.; Choe, B.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Intraarterially delivered human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in canine cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 3554–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyamada, N.; Itoh, H.; Sone, M.; Yamahara, K.; Miyashita, K.; Park, K.; Taura, D.; Inuzuka, M.; Sonoyama, T.; Tsujimoto, H.; et al. Transplantation of vascular cells derived from human embryonic stem cells contributes to vascular regeneration after stroke in mice. J. Transl. Med. 2008, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, R.; De Los Angeles, A.; Cheshier, S.; Choi, R.; Hoang, S.; Liauw, J.; Schaar, B.; Steinberg, G. Intracarotid injection of fluorescence activated cell-sorted CD49d-positive neural stem cells improves targeted cell delivery and behavior after stroke in a mouse stroke model. Stroke 2008, 39, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, D.M.; Han, Y.; Yang, D.; Ding, J.; Savant-Bhonsale, S.; Shukairy, M.S.; Chopp, M. Mannitol enhances delivery of marrow stromal cells to the brain after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res. 2008, 1224, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argibay, B.; Trekker, J.; Himmelreich, U.; Beiras, A.; Topete, A.; Taboada, P.; Perez-Mato, M.; Vieites-Prado, A.; Iglesias-Rey, R.; Rivas, J.; et al. Intraarterial route increases the risk of cerebral lesions after mesenchymal cell administration in animal model of ischemia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Yang, J.; Chang, E.H.; Park, S.E.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.J.; Oh, W.; Chang, J.W.; Na, D.L. Intra-Arterially Delivered Mesenchymal Stem Cells Are Not Detected in the Brain Parenchyma in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.Y.; Ren, Y.Q.; Ni, Q.S.; Song, Z.H.; Ge, K.L.; Guo, Y.L. Transplantation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Neural Stem Cells Pretreated with Neuregulin1beta Ameliorate Cerebral Ischemic Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Lu, Q.E.; Cheung, W.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Secondary Release of Exosomes From Astrocytes Contributes to the Increase in Neural Plasticity and Improvement of Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats Treated With Exosomes Harvested From MicroRNA 133b-Overexpressing Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seras-Franzoso, J.; Diaz-Riascos, Z.V.; Corchero, J.L.; Gonzalez, P.; Garcia-Aranda, N.; Mandana, M.; Riera, R.; Boullosa, A.; Mancilla, S.; Grayston, A.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from recombinant cell factories improve the activity and efficacy of enzymes defective in lysosomal storage disorders. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, S.; Andrzejewska, A.; Strzemecki, D.; Muraca, M.; Janowski, M.; Lukomska, B. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate neuroinflammation evoked by focal brain injury in rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Zhang, C.; Mamtilahun, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zuo, C.; Cui, F.; Li, W.; et al. A simple polydopamine-based platform for engineering extracellular vesicles with brain-targeting peptide and imaging probes to improve stroke outcome. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2025, 14, e70031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.J.; Lee, T.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Baik, K.; Jung, J.H.; Yoo, H.S.; Shim, C.J.; Eom, H.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Phase I Trial of Intra-arterial Administration of Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients with Multiple System Atrophy. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 9886877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.A.; Martins, M.P.; Araujo, M.D.; Klamt, C.; Vedolin, L.; Garicochea, B.; Raupp, E.F.; Sartori El Ammar, J.; Machado, D.C.; Costa, J.C.; et al. Intra-arterial infusion of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells in patients with moderate to severe middle cerebral artery acute ischemic stroke. Cell Transplant. 2012, 21 (Suppl. 1), S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitz, S.I.; Yavagal, D.; Rappard, G.; Likosky, W.; Rutledge, N.; Graffagnino, C.; Alderazi, Y.; Elder, J.A.; Chen, P.R.; Budzik, R.F., Jr.; et al. A Phase 2 Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial of Internal Carotid Artery Infusion of Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived ALD-401 Cells in Patients With Recent Stable Ischemic Stroke (RECOVER-Stroke). Circulation 2019, 139, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniche, F.; Gonzalez, A.; Gonzalez-Marcos, J.R.; Carmona, M.; Pinero, P.; Espigado, I.; Garcia-Solis, D.; Cayuela, A.; Montaner, J.; Boada, C.; et al. Intra-arterial bone marrow mononuclear cells in ischemic stroke: A pilot clinical trial. Stroke 2012, 43, 2242–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistella, V.; de Freitas, G.R.; da Fonseca, L.M.; Mercante, D.; Gutfilen, B.; Goldenberg, R.C.; Dias, J.V.; Kasai-Brunswick, T.H.; Wajnberg, E.; Rosado-de-Castro, P.H.; et al. Safety of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation in patients with nonacute ischemic stroke. Regen. Med. 2011, 6, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Song, S.K.; Lee, H.S.; Nam, H.S.; Cheong, J.W.; Jeong, Y.; Park, H.J.; Kim, D.J.; et al. A randomized trial of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple system atrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bentley, P.; Hamady, M.; Marley, S.; Davis, J.; Shlebak, A.; Nicholls, J.; Williamson, D.A.; Jensen, S.L.; Gordon, M.; et al. Intra-Arterial Immunoselected CD34+ Stem Cells for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaCosta, J.C.; Portuguez, M.W.; Marinowic, D.R.; Schilling, L.P.; Torres, C.M.; DaCosta, D.I.; Carrion, M.J.M.; Raupp, E.F.; Machado, D.C.; Soder, R.B.; et al. Safety and seizure control in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy treated with regional superselective intra-arterial injection of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e648–e656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Gupta, V.; Khurana, D.; Sharma, R.R.; Khandelwal, N. Randomized Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of Intra-Arterial Infusion of Autologous Stem Cells in Subacute Ischemic Stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, R.; Canesi, M.; Isalberti, M.; Marfia, G.; Campanella, R.; Vincenti, D.; Cereda, V.; Ranghetti, A.; Palmisano, C.; Isaias, I.U.; et al. Safety and Effectiveness of Cell Therapy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Take-Home Messages From a Pilot Feasibility Phase I Study of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 723227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniche, F.; Cabezas-Rodriguez, J.A.; Valverde, R.; Escudero-Martinez, I.; Lebrato-Hernandez, L.; Pardo-Galiana, B.; Ainz, L.; Medina-Rodriguez, M.; de la Torre, J.; Escamilla-Gomez, V.; et al. Safety and efficacy of intra-arterial bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation in patients with acute ischaemic stroke in Spain (IBIS trial): A phase 2, randomised, open-label, standard-of-care controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammadi, A.M.A.; Alhimyari, F. Intra-Arterial Injection of Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Mononuclear Cells in Ischemic Stroke Patients. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 17 (Suppl. 1), 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 973–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, N.; Fisher, M. Extending the Time Window for Endovascular and Pharmacological Reperfusion. Transl. Stroke Res. 2016, 7, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, R.; McKinney, A.M.; Swenson, B.; Janardhan, V. Blood-brain barrier, reperfusion injury, and hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 2012, 79 (Suppl. 1), S52–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warach, S.; Latour, L.L. Evidence of reperfusion injury, exacerbated by thrombolytic therapy, in human focal brain ischemia using a novel imaging marker of early blood-brain barrier disruption. Stroke 2004, 35 (Suppl. 1), 2659–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabori, M.; Weintraub, A.H.; Imai, H.; Zinkevych, L.; McAllister, P.; Steinberg, G.K.; Frishberg, B.M.; Yasuhara, T.; Chen, J.W.; Cramer, S.C.; et al. Cell Therapy for Chronic TBI: Interim Analysis of the Randomized Controlled STEMTRA Trial. Neurology 2021, 96, e1202–e1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabori, M.; Karasawa, Y.; Suenaga, J.; Nakamura, H.; Imai, H.; Yasuhara, T.; Tani, N.; Sasaki, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Totsuka, K.; et al. Relationship Between Location of Cell Transplantation and Recovery for Intracerebral Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Traumatic Brain Injury: Post-hoc Analysis of STEMTRA Trial. Neurotrauma Rep. 2025, 6, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.; Yusubalieva, G.M.; Baklaushev, V.P.; Chumakov, P.M.; Lipatova, A.V. Recent Developments in Glioblastoma Therapy: Oncolytic Viruses and Emerging Future Strategies. Viruses 2023, 15, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Gumin, J.; Gao, F.; Hossain, A.; Shpall, E.J.; Kondo, A.; Parker Kerrigan, B.C.; Yang, J.; Ledbetter, D.; Fueyo, J.; et al. Characterization of patient-derived bone marrow human mesenchymal stem cells as oncolytic virus carriers for the treatment of glioblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 136, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamoto, S.; Furukawa, T.; Kawabori, M.; Akino, M.; Kato, S.; Fuse, H.; Ohtsuki, S.; Torimoto, Y.; Fujimura, M.; Kino, S. Human platelet lysate produced from leukoreduction filter contents enables sufficient MSC growth. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2025, 16, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlongan, C.V.; Lee, J.Y.; D’Egidio, F.; de Kalbermatten, M.; Garitaonandia, I.; Guzman, R. Nose-to-brain delivery of stem cells in stroke: The role of extracellular vesicles. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2024, 13, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Methods | Modification Detail | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Pretreatment | IL-1a | Anti-inflammatory effect |
| neuregulin1 | Neural differentiation | |
| MAPK inhibitor | Cell survival | |
| BDNF | Neural differentiation | |
| Gene induction | Neural cell differentiation | Neural differentiation |
| Integrin alpha 4 | Cell adhesion | |
| The integrin Very Late Antigen-4 (VLA-4) | Cell adhesion | |
| Neurogenin | Neural differentiation | |
| CCL2 | Cell migration to damaged area | |
| Cell purification | CD34 | Neurogenesis, angiogenesis |
| CD133 | Growth factor release |
| Mode of Action | Detail of Action | Evaluated Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Regeneration | Neurogenesis | DCX, NeuN, MAP2, NGF, Nestin, SOX10, B-III tubulin, GFAP, Musashi1, Ki-67, Bur-U, Nogo-A, SYN, NF-200, NSE, Netrin-1, DCC |
| Synaptogenesis | PSD95, Synaptophysin, GAP-43 | |
| Angiogenesis | VEGF, HIF1a, Angiogenin, vWF, RECA, CD31 | |
| Damage reduction | Anti-inflammatory effect | IL-1b, IL-6, TNF-a, NLRP, IL-10, ED-1, MCP-1, Iba-1, CD45, IL-12, CD68, iNOS |
| Anti-oxidative stress | GSH, MDA, Nitrite, catalase, Mitochondrial damage, ASIC1a, TBARS, | |
| Anti-apoptosis | caspase 3, caspase 12, TUNEL, FluoroJade C, bFGF, SDF-1a, Bcl-2 | |
| Anti-ferroptosis | DMT1, TFR1, p53, SLC7A11, GPX4 | |
| Neuro-protective function | SIRT-1, BDNF, NF-kb, neurotrophin-3, GDNF, HSP-27 | |
| Endoplasmic reticulum-protective | GRP87, TrkB, p-eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP | |
| BBB-protective function | AQP4, PKC-d, MMP-9, VEGF | |
| Exosome release | CD63 |
| Author | PMID | Year | Phase | Disease | Number of Participants | Transplantation Route | Cell Source | Main Inclusion Criteria | Transplantation Timing | Endpoint Timing | IA Cell Doses, (×105/kg *) | Cell Tracking | Main Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | Control | Total Cell Numbers | Cell Dose (×105/kg) | ||||||||||||
| Battistella et al. [102] | 21175286 | 2011 | I | ischemic stroke | 6 | - | IA | Autologous BMMNC | NIHSS; 4–17 | 2–3 months | 6 months | 1–5 × 108 | 16–83 × 105/kg | 99m-Tc | Feasible and safe, cells soon distributed in the liver |
| Friedrich et al. [99] | 22507676 | 2012 | I/II | ischemic stroke | 20 | - | IA | Autologous BMMNC | NIHSS > 8 | 3–7 days | 6 months | 5–60 × 107 | 8–100 × 105/kg | - | Feasible and safe, satisfactory clinical improvement occurred in 30% of patients |
| Moniche et al. [101] | 22764211 | 2012 | I/II | ischemic stroke | 10 | 10 | IA | Autologous BMMNC | NIHSS 15.6 (mean) | 5–9 days | 6 months | 1.6 × 108 (mean) | 26 × 105/kg | - | Safe, but no difference regarding the functional recovery was seen compared with control group |
| Lee et al. [103] | 22829267 | 2012 | II | multiple-system atrophy | 11 | 16 | IA and IV | Autologous BMSC | UMSRS 30–50 | - | 12 months | 4 × 107 | 7 × 105/kg | - | Functional recovery and MRI findings were significantly better in treatment group |
| Banerjee et al. [104] | 25107583 | 2014 | I | ischemic stroke | 5 | - | IA | Autologous BMMNC (CD34+) | NIHSS > 8 | 7 days | 6 months | 1.2–2.7 × 106 | 2–5 × 105/kg | - | Feasible and safe |
| DaCosta et al. [105] | 27688159 | 2018 | I/II | temporal lobe epilepsy | 20 | - | IA | Autologous BMMNC | Medically refractory epilepsy | - | 6 months | 1–10 × 108 | 16–160 × 105/kg | - | Feasible and safe, 40% of the patients became seizure-free after transplantation |
| Bhatia et al. [106] | 29545253 | 2018 | II | ischemic stroke | 10 | 10 | IA | Autologous BMMNC | NIHSS > 7 | 8–15 days | 6 months | 5 × 108 | 83 × 105/kg | - | Feasible and safe, better trend of recovery for treatment group (p = 0.07) |
| Savitz et al. [100] | 30586746 | 2019 | II | ischemic stroke | 29 | 17 | IA | Autologous BMMNC (ALDH+) | mRS > 3 | 9–15 days | 3 months | 1.6–7.5 × 107 | 3–13 × 105/kg | - | No statistical differences were seen between treatment and control groups |
| Hammadi et al. [109] | 30777565 | 2019 | I | ischemic stroke | 37 | 0 | IA | Autologous BMMNC | MCA territory | 3 months–5 years | 6 months | 5.0–6.0 × 108 | 83–100 × 105/kg | - | 67% of patients showed functional recovery |
| Chung et al. [98] | 34712335 | 2021 | I | multiple-system atrophy | 9 | 0 | IA | Autologous BMSC | UMSRS 30–50, Disease duration < 5 years | - | 3 months | - | 3, 6, 9 × 105/kg | - | Feasible and safe, medium and high dose groups showed a slower increase in UMSARS score than low group |
| Giordano et al. [107] | 34712113 | 2021 | I | progressive supranuclear palsy | 7 | 0 | IA | Autologous BMSC | PSP diagnosis criteria | - | 12 months | 77–156 × 106 | 10–20 × 105/kg | - | Asymptomatic abnormal signs were found in the MRI, no significant functional recovery |
| Moniche et al. [108] | 36681446 | 2023 | II | ischemic stroke | 37 | 36 | IA | Autologous BMMNC | NIHSS 6–20 | 1–7 days | 6 months | - | 0, 20, 50 × 105/kg | - | No statistical differences were seen between treatment and control groups |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Honda, T.; Kawabori, M.; Fujimura, M. Intra-Arterial Administration of Stem Cells and Exosomes for Central Nervous System Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157405
Honda T, Kawabori M, Fujimura M. Intra-Arterial Administration of Stem Cells and Exosomes for Central Nervous System Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157405
Chicago/Turabian StyleHonda, Taishi, Masahito Kawabori, and Miki Fujimura. 2025. "Intra-Arterial Administration of Stem Cells and Exosomes for Central Nervous System Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157405
APA StyleHonda, T., Kawabori, M., & Fujimura, M. (2025). Intra-Arterial Administration of Stem Cells and Exosomes for Central Nervous System Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157405







