Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase (FBA) Gene Family in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
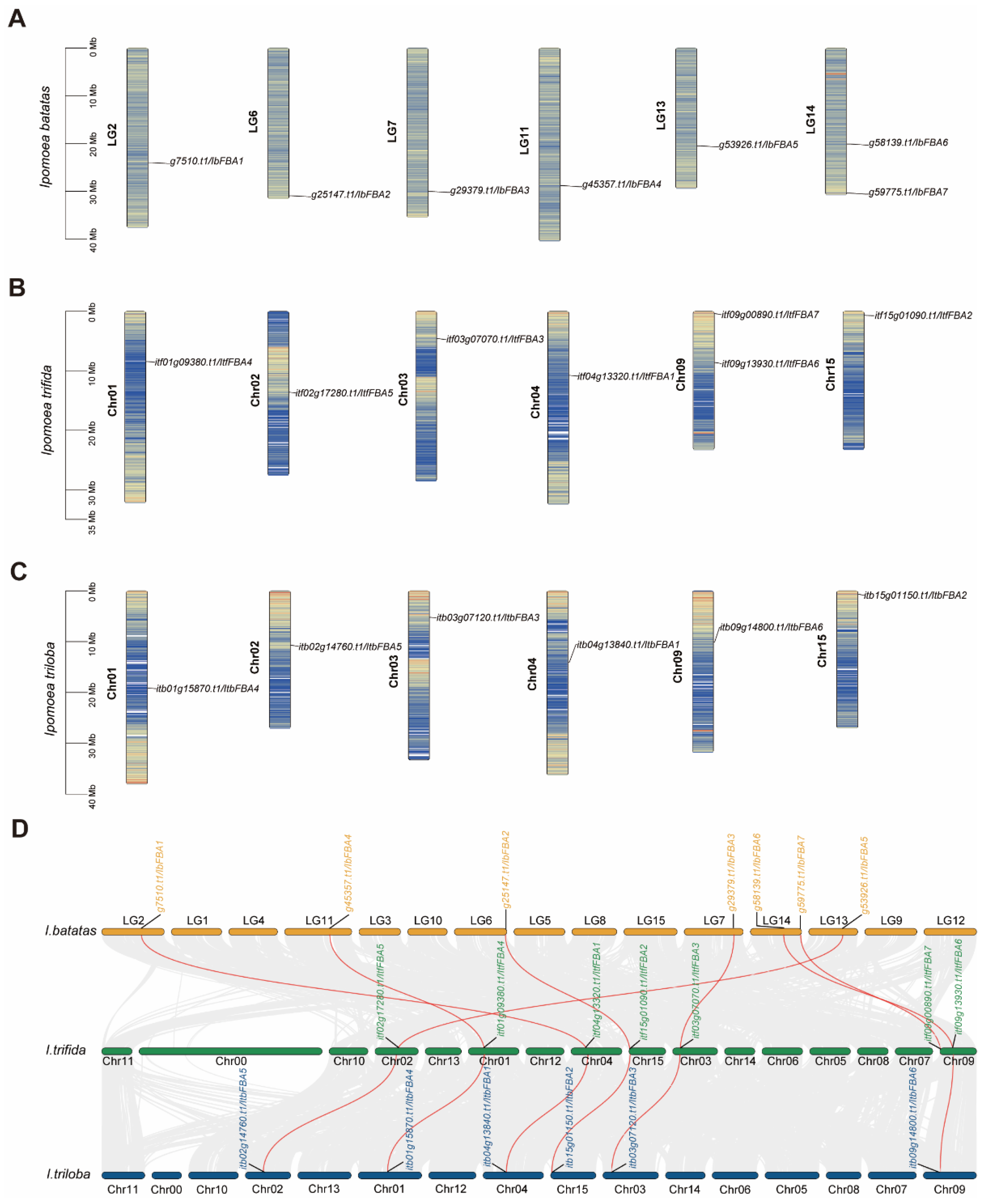
2.1. Identification of FBAs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Wild Diploid Relatives
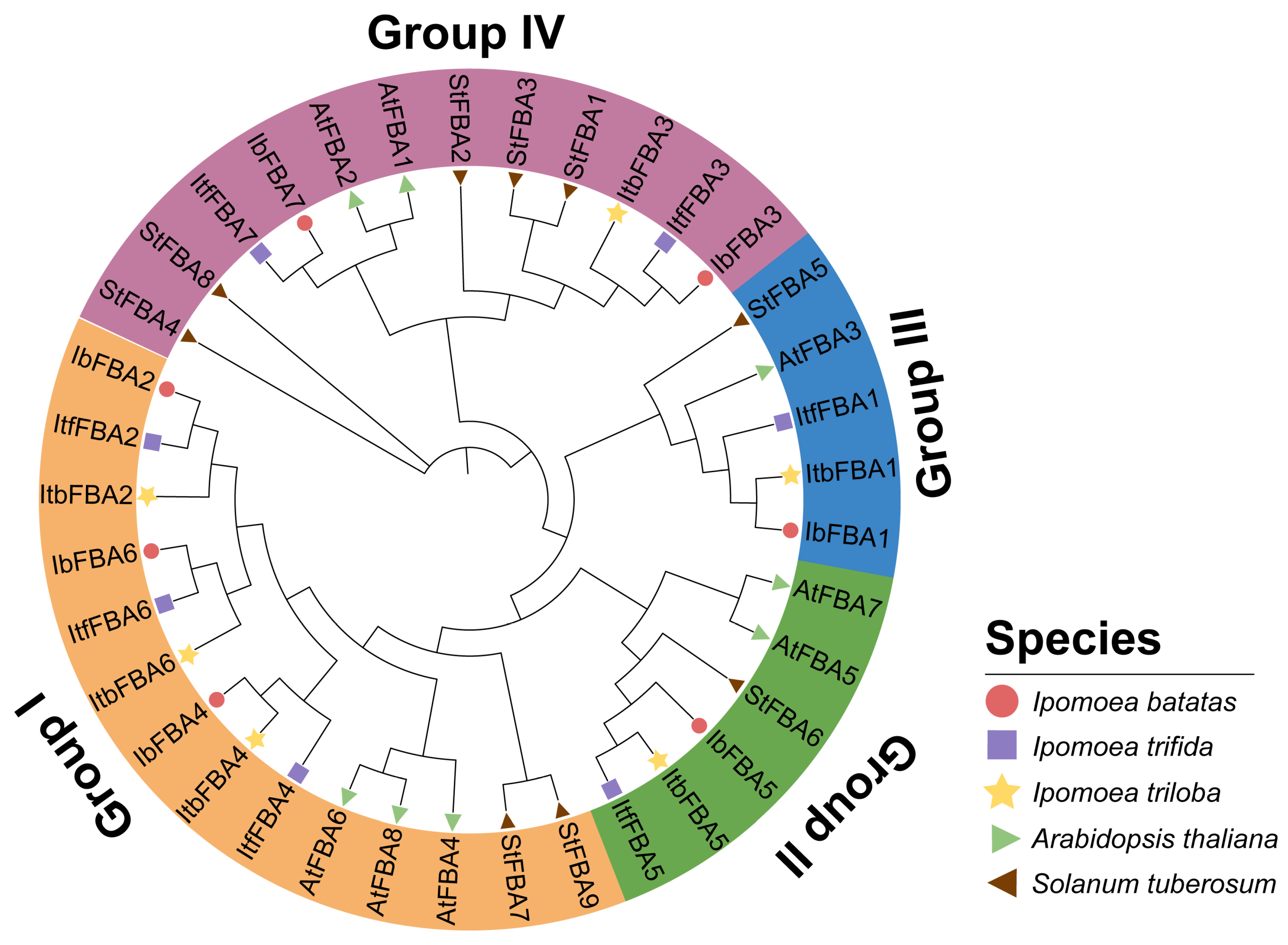
2.2. Phylogenetic Relationship Analysis of FBAs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Wild Diploid Relatives
2.3. Conserved Motif and Exon–Intron Structure Analysis of FBAs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Wild Diploid Relatives
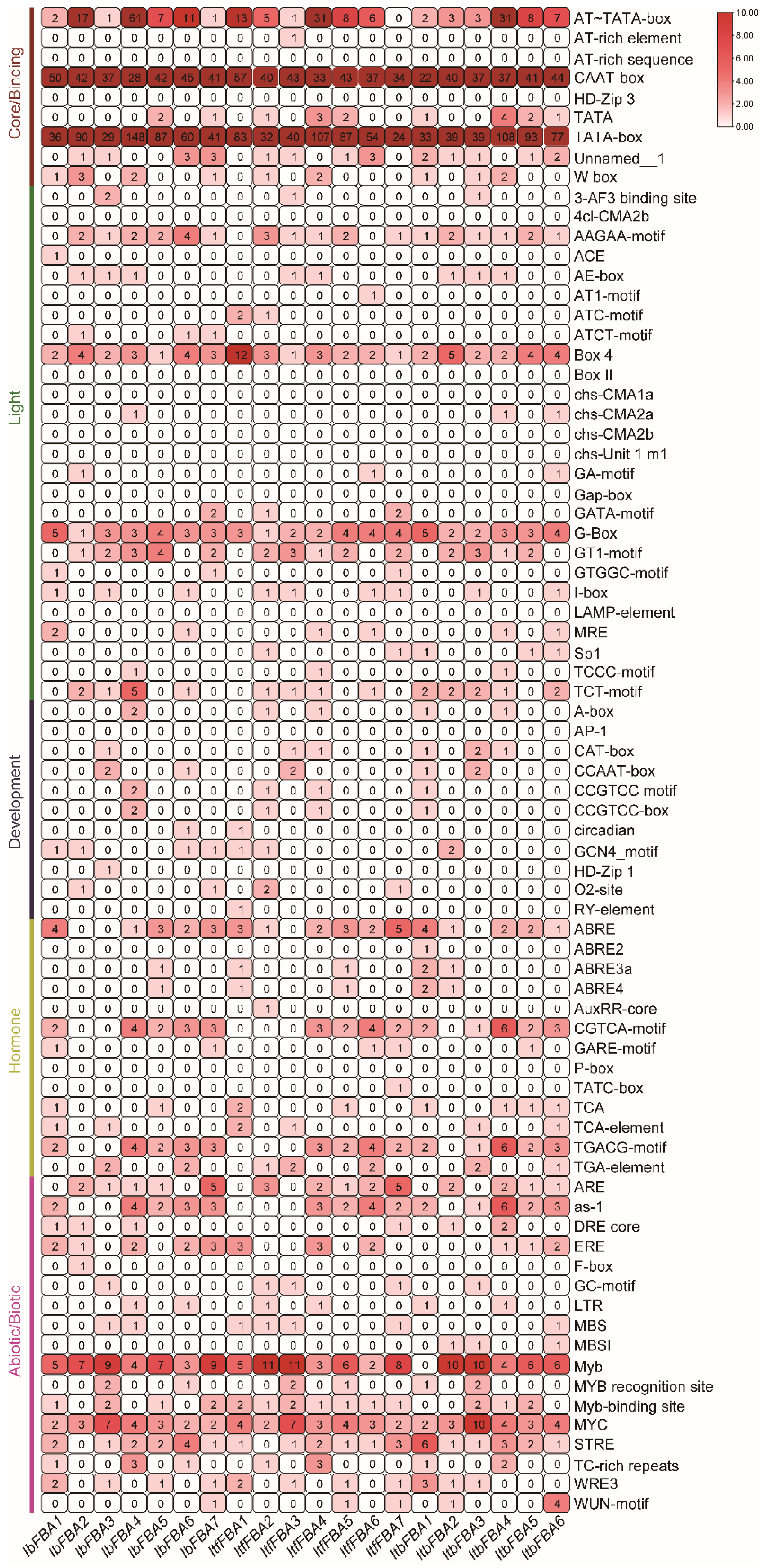
2.4. Cis-Element Analysis in the Promoters of FBAs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Wild Diploid Relatives
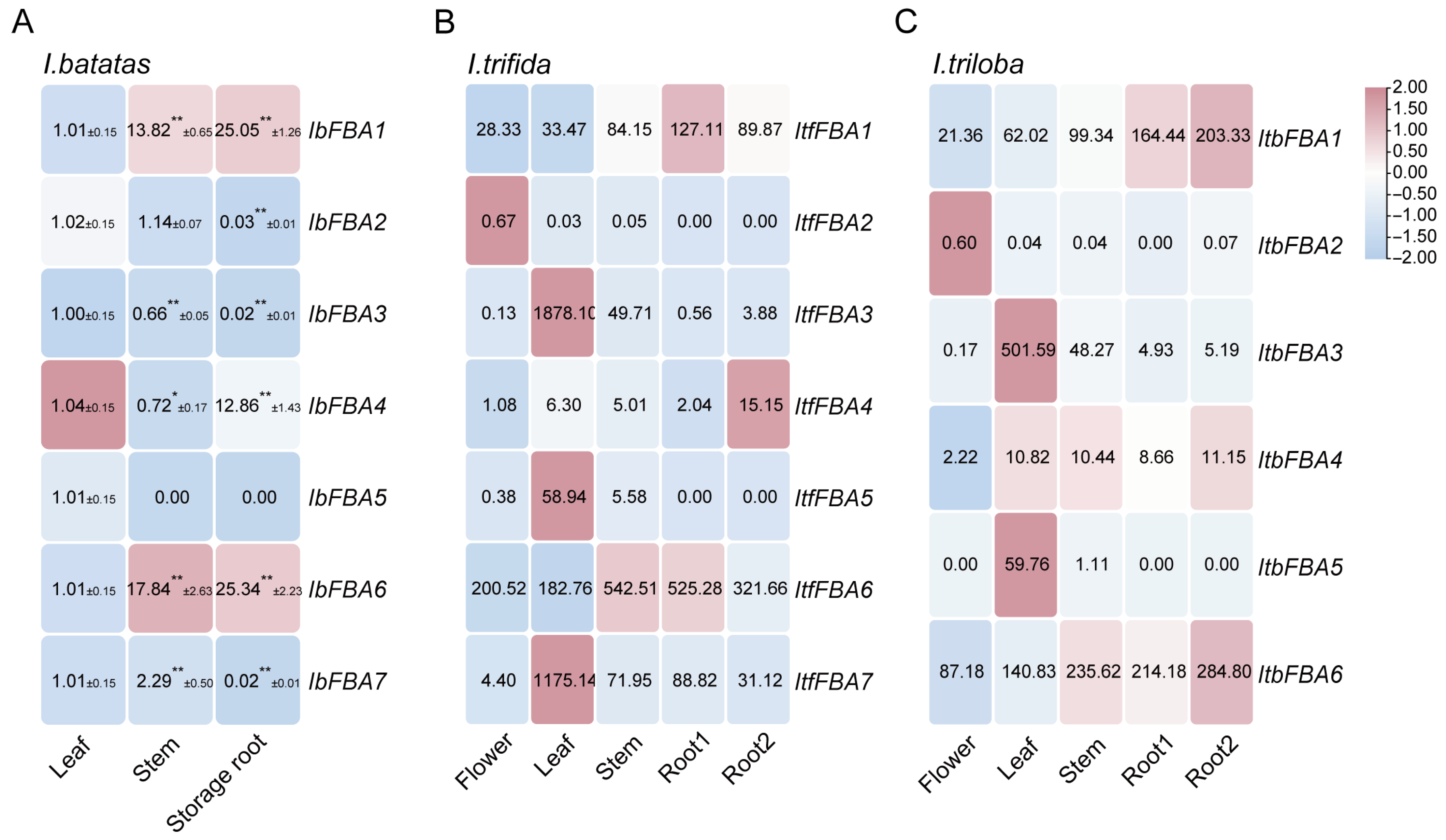
2.5. Expression Analysis of FBAs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Wild Diploid Relatives
2.5.1. Expression Analysis in Various Organs
2.5.2. Expression Analysis at Different Developmental Stages of Storage Roots in Sweet Potato
2.5.3. Expression Analysis in Sweet Potato Lines with Different Starch Contents
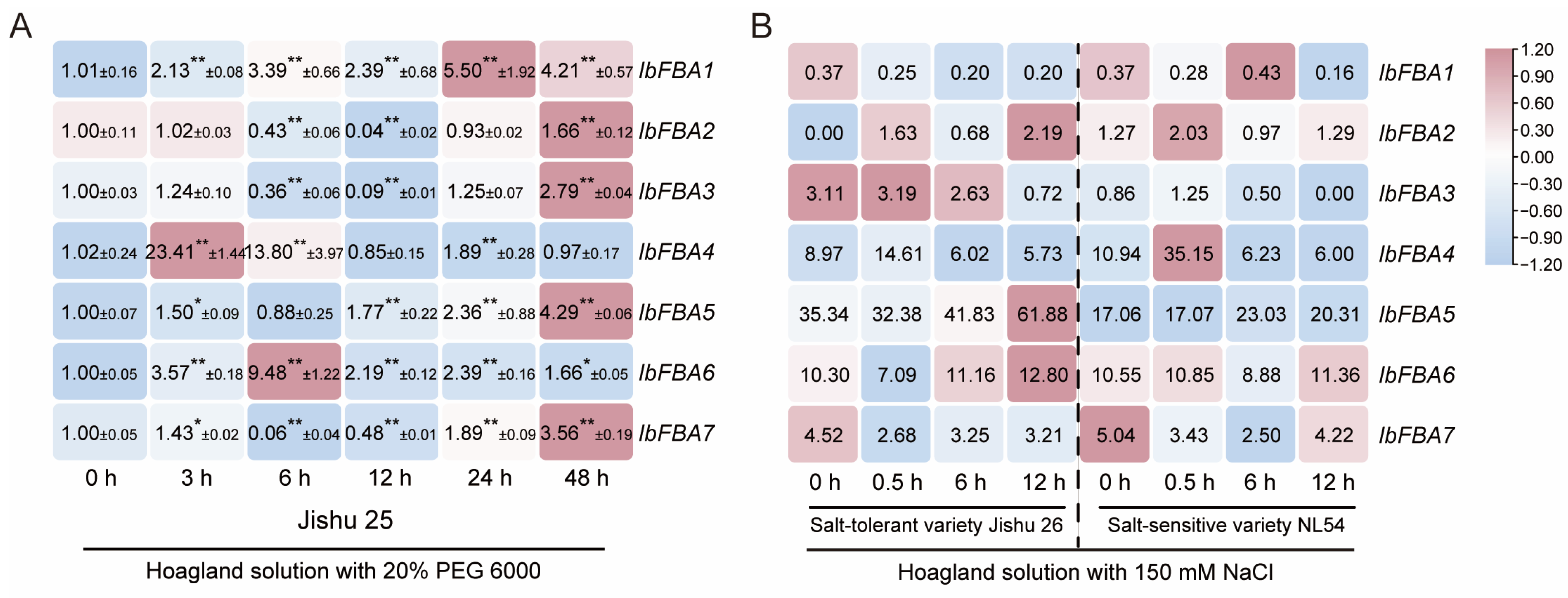
2.5.4. Expression Analysis Under Drought and Salt Stresses
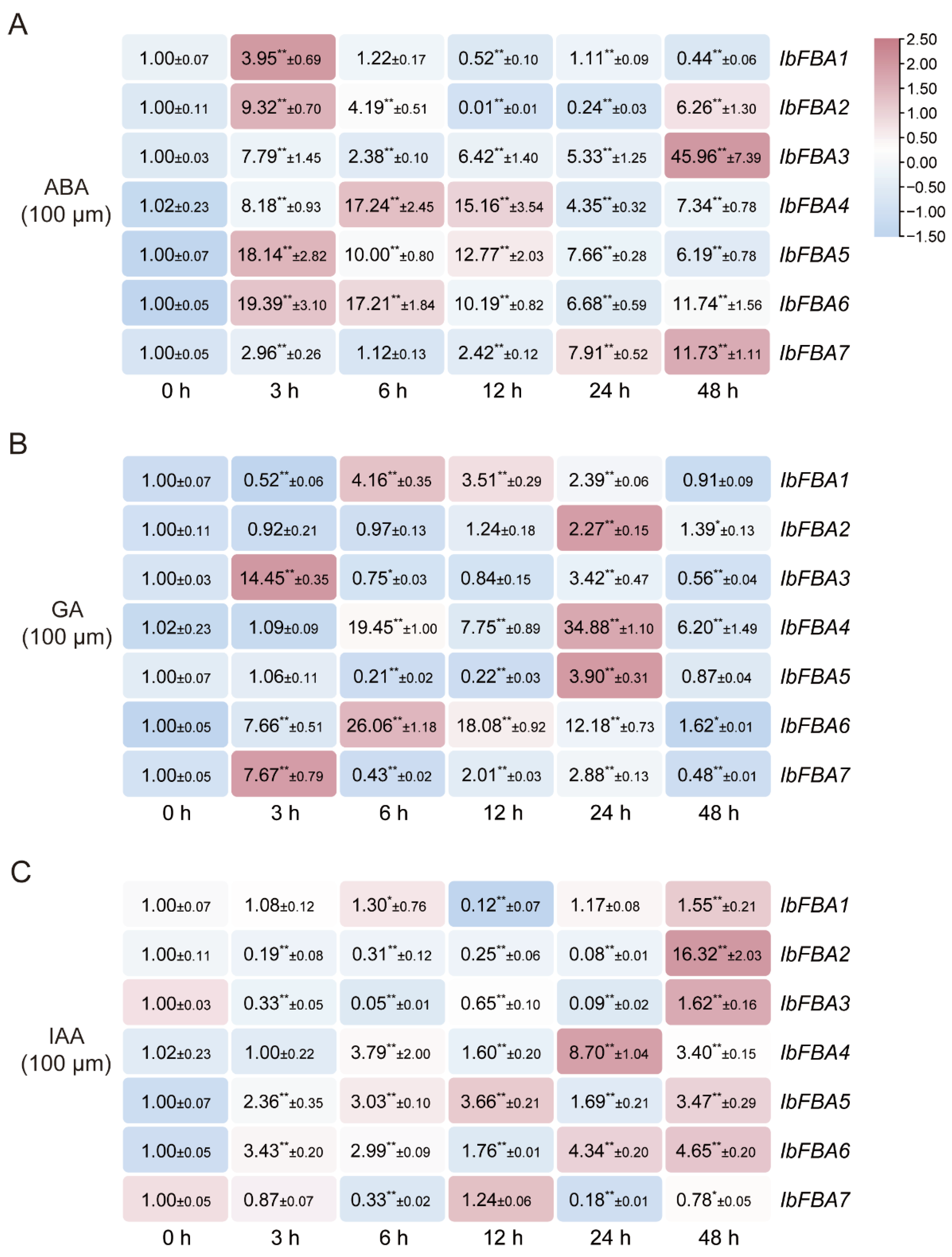
2.5.5. Expression Analysis in Response to Hormones
3. Discussion
3.1. FBAs Were Conserved During the Evolution of Sweet Potato
3.2. IbFBAs Are Involved in Storage Root Development and Starch Biosynthesis in Sweet Potato
3.3. FBAs Regulate Response to Drought and Salt Stresses in Sweet Potato and Its Two Wild Diploid Relatives
3.4. FBAs Participate in Hormone Crosstalk in Sweet Potato and Its Two Wild Diploid Relatives
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of FBAs
4.2. Chromosomal Location and Property Prediction of FBAs
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of FBAs
4.4. Gene Structures and Conserved Motifs Analysis of FBAs
4.5. Cis-Acting Elements in Promoter Regions Analysis of IbFBAs
4.6. Expression Patterns Analysis of IbFBAs
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.C. Improvement for agronomically important traits by gene engineering in sweetpotato. Breed. Sci. 2017, 67, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, H.; Gao, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Huo, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, N.; et al. IbBBX24 promotes the jasmonic acid pathway and enhances fusarium wilt resistance in sweet potato. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 1102–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.Y.; Wei, Z.H.; Zhai, H.; Xing, S.H.; Wang, Y.X.; He, S.Z.; Gao, S.P.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.C. The IbPYL8-IbbHLH66-IbbHLH118 complex mediates the abscisic acid-dependent drought response in sweet potato. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 2151–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Jin, Y.L.; Zhu, J.C.; Ma, D.F. Analysis and perspectives of sweetpotato industry contributing to national food security in China. J. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 38, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, I.A.; Kockelkorn, D.; Ramos-Vera, W.H.; Say, R.F.; Zarzycki, J.; Hügler, M.; Alber, B.E.; Fuchs, G. Autotrophic carbon fixation in archaea. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushinobu, S.; Nishimasu, H.; Hattori, D.; Song, H.J.; Wakagi, T. Structural basis for the bifunctionality of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphatase. Nature 2011, 478, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.J.; Lebherz, H.G. Fructose-bisphosphate aldolases: An evolutionary history. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1992, 17, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Miyake, C.; Yokota, A. Purification and characterization of class-I and class-II fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate aldolases from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Cell physiol. 2003, 44, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perham, R.N. The fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate aldolases: Same reaction, different enzymes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1990, 18, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, W.; Lenze, D.; Nowitzki, U.; Weiske, J.; Schnarrenberger, C. Characterization, cloning, and evolutionary history of the chloroplast and cytosolic class I aldolases of the red alga Galdieria sulphuraria. Gene 1999, 230, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebherz, H.G.; Leadbetter, M.M.; Bradshaw, R.A. Isolation and characterization of the cytosolic and chloroplast forms of spinach leaf fructose diphosphate aldolase. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, V.; Zrenner, R.; Sonnewald, U.; Stitt, M. A moderate decrease of plastid aldolase activity inhibits photosynthesis, alters the levels of sugars and starch, and inhibits growth of potato plants. Plant J. 1998, 14, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, K.; Suzuki, N.; Iwamae, T.; Inui, M.; Yukawa, H. Increased fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate aldolase in plastids enhances growth and photosynthesis of tobacco plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3001–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.B.; Li, Q.; Liu, F.J.; Bi, H.A.; Ai, X.Z. Decreasing fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase activity reduces plant growth and tolerance to chilling stress in tomato seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 163, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, D.A.; George, G.M.; Fischer-Stettler, M.; Galbier, F.; Eicke, S.; Truernit, E.; Streb, S.; Zeeman, S.C. Distinct plastid fructose bisphosphate aldolases function in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic metabolism in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 3739–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, N.; Cao, H. Identification and expression of fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate aldolase genes and their relations to oil content in developing seeds of tea oil tree (Camellia oleifera). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Komori, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Kuwata, S.; Imaseki, H.; Kubo, T. Differential expression of plastidic aldolase genes in plants under salt stress. Plant Sci. 2000, 154, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Cloning and molecular characterization of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase gene regulated by high-salinity and drought in Sesuvium portulacastrum. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.M.; Taxak, P.C.; Jain, P.K.; Saini, R.; Srinivasan, R. Glycolytic enzyme activities and gene expression in cicer arietinum exposed to water-deficit stress. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 2241–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.B.; Ning, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Q.Y.; Ai, X.Z. Effects of the chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase gene on growth and low-temperature tolerance of tomato. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tang, X.L.; Huo, Y.Q.; Xu, R.; Qi, S.D.; Huang, J.G.; Zheng, C.C.; Wu, C.A. Identification and characterization of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase genes in Arabidopsis reveal a gene family with diverse responses to abiotic stresses. Gene 2012, 503, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.B.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.C.; Yang, L.; Bi, H.G.; Ai, X.Z. Genome-wide analysis of the fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA) gene family and functional characterization of FBA7 in tomato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 108, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiao, F.; Tang, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. Genome-wide characterization, evolution, and expression profiling of FBA gene family in response to light treatments and abiotic stress in Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Signal Behav. 2021, 16, 1938442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Su, T.T.; Liu, C.G.; Han, Z.C.; Wang, A.Y.; Zhu, J.B. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis provide basis to the biological function of cotton FBA genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 696698. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Hou, X.Y.; Sun, Z.L.; Ma, B.; Wu, X.X.; Feng, T.T.; Ai, H.; Huang, X.Z.; Li, R.N. Characterization of FBA genes in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) and expression patterns in response to light spectrum and abiotic stress. Front. Plant Genet. 2024, 15, 1364944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Liu, Y.K.; Zhou, Z.P.; Yang, L.N.; Xue, Z.J.; Li, Q.Y.; Cai, B.B. Genome-wide characterization of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase genes and expression profile reveals their regulatory role in abiotic stress in cucumber. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Moeinzadeh, M.H.; Kuhl, H.; Helmuth, J.; Xiao, P.; Haas, S.; Liu, G.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Z.; Fan, W.; et al. Haplotype-resolved sweet potato genome traces back its hexaploidization history. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lau, K.H.; Cao, Q.; Hamilton, J.P.; Sun, H.; Zhou, C.; Eserman, L.; Gemenet, D.C.; Olukolu, B.A.; Wang, H.; et al. Genome sequences of two diploid wild relatives of cultivated sweetpotato reveal targets for genetic improvement. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.F.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, A.X.; Wang, Q.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Hou, F.Y.; Zhang, L.M. Genome-wide identification of the C2H2 zinc finger gene family and expression analysis under salt stress in sweetpotato. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1301848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, T.; Zhu, M.; Du, D.; Liu, R.; Yu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z. Transcriptome-and genome-wide systematic identification of expans in gene family and their expression in tuberous root development and stress responses in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas). Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1412540. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Hou, F.; Li, A.; Dong, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Transcriptome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factor and their expression profiles under salt stress in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 14, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.F.; Qin, Z.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, Q.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Hou, F.Y. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals the effect of lignin on storage roots formation in two sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) lam.) cultivars. Genes 2023, 14, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frugoli, J.A.; McPeek, M.A.; Thomas, T.L.; McClung, C.R. Intron loss and gain during evolution of the catalase gene family in angiosperms. Genetics 1998, 149, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnewald, U.; Lerchl, J.; Zrenner, R.; Frommer, W. Manipulation of sink-source relations in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Environ. 1994, 17, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.C.; Qu, L.H.; Liu, X.Q.; Luo, J. Identification of a peroxisomal-targeted aldolase involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis and sugar metabolism in rice. Plant Sci. 2016, 250, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.K.; Li, H.; Zhu, C.L.; Yang, K.B.; Lin, Z.M.; Wang, J.F.; Gao, Z.M. Unveiling the Biological Function of Phyllostachys-edulis FBA6 (PeFBA6) through the Identification of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase Gene. Plant 2024, 13, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Q.; Tie, J.Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.J.; Wang, G.Z.; Lyu, J.; Hu, L.L.; Yu, J.H. Brassinosteroid-induced S-nitrosylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase increased ATP synthesis under low temperatures in mini Chinese cabbage seedlings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorin, D.N.; Khomutova, A.E.; Eprintsev, A.T.; Igamberdiev, A.U. Involvement of miR775 in the post-transcriptional regulation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase in maize (Zea mays L.) leaves under hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.J.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, Y.; Ren, D.T. Identification of the fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA) family genes in maize and analysis of the phosphorylation regulation of ZmFBA8. Plant Sci. 2025, 350, 112311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, H.; Yamane, H.; Maeshima, M.; Komatsu, S. Characterization of fructose-bisphosphate aldolase regulated by gibberellin in roots of rice seedling. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 56, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakabe, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Seki, M.; Satou, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase1 is a key membrane bound regulator of abscisic acid early signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1105–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The Clustal_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C-T method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene ID | Gene Name | Genomic Length (bp) | CDS (bp) | Protein Size (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | Instability | GRAVY | Subcellular Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g7510.t1 | IbFBA1 | 2902 | 1182 | 393 | 42.49 | 8.61 | 38.95 | −0.238 | chloroplast |
| g25147.t1 | IbFBA2 | 1682 | 1080 | 359 | 38.97 | 7.53 | 32.85 | −0.336 | cytoplasm |
| g29379.t1 | IbFBA3 | 2345 | 1173 | 390 | 41.91 | 7.56 | 35.57 | −0.087 | chloroplast |
| g45357.t1 | IbFBA4 | 2537 | 1077 | 358 | 38.62 | 7.51 | 34.46 | −0.228 | cytoplasm |
| g53926.t1 | IbFBA5 | 2702 | 1047 | 348 | 37.14 | 6.86 | 36.14 | −0.33 | cytoplasm |
| g58139.t1 | IbFBA6 | 2418 | 1077 | 358 | 38.51 | 7.53 | 29.23 | −0.156 | cytoplasm |
| g59775.t1 | IbFBA7 | 2134 | 1170 | 389 | 41.41 | 8.17 | 36.61 | −0.13 | chloroplast |
| itf15g01090 | ItfFBA1 | 1752 | 1080 | 359 | 38.97 | 7.53 | 32.85 | −0.336 | cytoplasm |
| itf09g13930 | ItfFBA2 | 2461 | 1077 | 358 | 38.51 | 7.53 | 29.23 | −0.156 | cytoplasm |
| itf03g07070 | ItfFBA3 | 2365 | 1194 | 397 | 42.66 | 7.59 | 36.02 | −0.105 | chloroplast |
| itf04g13320 | ItfFBA4 | 3179 | 1182 | 393 | 42.49 | 8.61 | 38.95 | −0.238 | chloroplast |
| itf02g17280 | ItfFBA5 | 2273 | 1074 | 357 | 38.23 | 6.38 | 31.82 | −0.123 | cytoplasm |
| itf01g09380 | ItfFBA6 | 2527 | 1077 | 358 | 38.61 | 7.51 | 34.09 | −0.228 | cytoplasm |
| itf09g00890 | ItfFBA7 | 2611 | 1194 | 397 | 42.58 | 8.49 | 36.56 | −0.094 | chloroplast |
| itb04g138401 | ItbFBA1 | 4627 | 1182 | 393 | 42.49 | 8.61 | 38.95 | −0.238 | chloroplast |
| itb15g011501 | ItbFBA2 | 1831 | 1080 | 359 | 38.97 | 7.53 | 32.85 | −0.336 | cytoplasm |
| itb01g158701 | ItbFBA3 | 2699 | 1077 | 358 | 38.62 | 8 | 35.12 | −0.228 | cytoplasm |
| itb09g148001 | ItbFBA4 | 2864 | 1077 | 358 | 38.51 | 8.04 | 30.13 | −0.156 | cytoplasm |
| itb03g071201 | ItbFBA5 | 2316 | 1194 | 397 | 42.67 | 7.59 | 36.02 | −0.101 | chloroplast |
| itb02g147601 | ItbFBA6 | 2589 | 1191 | 396 | 42.69 | 6.97 | 38.86 | −0.101 | chloroplast |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Z.; Du, T.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hou, F. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase (FBA) Gene Family in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157348
Jiang Z, Du T, Zhou Y, Qin Z, Li A, Wang Q, Zhang L, Hou F. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase (FBA) Gene Family in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157348
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Zhicheng, Taifeng Du, Yuanyuan Zhou, Zhen Qin, Aixian Li, Qingmei Wang, Liming Zhang, and Fuyun Hou. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase (FBA) Gene Family in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157348
APA StyleJiang, Z., Du, T., Zhou, Y., Qin, Z., Li, A., Wang, Q., Zhang, L., & Hou, F. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase (FBA) Gene Family in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157348







