From Detection to Prediction: Advances in m6A Methylation Analysis Through Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Implications in Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discovery of m6A Methylation
3. Regulatory Mechanisms of m6A
4. Detection Techniques for m6A
4.1. MeRIP-Seq and m6A-Seq
4.2. m6A-CLIP and miCLIP
4.3. SCARLET
4.4. scDART-Seq
4.5. Third-Generation Sequencing Technologies
4.6. Comparison of m6A Detection Techniques
5. Prediction Methods for m6A
5.1. Sequence-Based Methods
5.2. Traditional Machine Learning-Based Methods
5.3. Deep Learning-Based Methods
5.4. Other Prediction Methods
5.5. Interpretability and Variable Selection in m6A Prediction
5.6. Performance Comparison and Evaluation of Existing Tools
6. Applications of m6A in Cancer and Other Diseases
6.1. Potential of m6A for Use as a Biomarker
6.2. m6A-Targeted Therapeutic Strategies
6.3. Correlation Between m6A and Cancer Patient Prognosis
6.4. Applications in Brain-Related Topics and Neurological Disorders
7. Future Directions and Conclusions
7.1. Improving m6A Prediction Accuracy Using Multiple Methods
7.2. Development of and Demand for Customized Tools for Different Bioinformatics Applications
7.3. Data Sharing and Standardization
7.4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desrosiers, R.; Friderici, K.; Rottman, F. Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3971–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.D.; Saletore, Y.; Zumbo, P.; Elemento, O.; Mason, C.E.; Jaffrey, S.R. Comprehensive Analysis of mRNA Methylation Reveals Enrichment in 3′ UTRs and near Stop Codons. Cell 2012, 149, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, B.; Grozhik, A.V.; Olarerin-George, A.O.; Meydan, C.; Mason, C.E.; Jaffrey, S.R. Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dou, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Xu, M.M.; Zhao, S.; Shen, B.; Gao, Y.; Han, D.; et al. N6-methyladenosine of chromosome-associated regulatory RNA regulates chromatin state and transcription. Science 2020, 367, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wei, J.; Cui, Y.-H.; Park, G.; Shah, P.; Deng, Y.; Aplin, A.E.; Lu, Z.; Hwang, S.; He, C.; et al. m6A mRNA demethylase FTO regulates melanoma tumorigenicity and response to anti-PD-1 blockade. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.C.; He, C. m6A RNA methylation: From mechanisms to therapeutic potential. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Nie, Z.; Duan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. The role of m6A modification in the biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Lin, J.; Cui, Y.; Chen, Q.; Jin, C.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum reduces METTL3-mediated m6A modification and contributes to colorectal cancer metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, D.A.; Casero, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Kim, J.; Wu, X.; Vergnes, L.; Mirza, A.H.; Leon-Mimila, P.; Williams, K.J.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of N6-methyladenosine orchestrates sex-dimorphic metabolic traits. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 940–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankova, E.; Blackaby, W.; Albertella, M.; Rak, J.; De Braekeleer, E.; Tsagkogeorga, G.; Pilka, E.S.; Aspris, D.; Leggate, D.; Hendrick, A.G.; et al. Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2021, 593, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Weng, H.; Su, R.; Weng, X.; Zuo, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Nachtergaele, S.; Dong, L.; Hu, C.; et al. FTO Plays an Oncogenic Role in Acute Myeloid Leukemia as a N6-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, P.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Q. SRAMP: Prediction of mammalian N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites based on sequence-derived features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hamada, M. DeepM6ASeq: Prediction and characterization of m6A-containing sequences using deep learning. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Jin, J.; Yu, H.; Wei, L. Towards Retraining-free RNA Modification Prediction with Incremental Learning. Inf. Sci. 2024, 660, 120105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Tiwari, P.; Xu, J.; Lu, W.; Muhammad, K.; de Albuquerquee, V.H.C.; Guo, F. A deep multiple kernel learning-based higher-order fuzzy inference system for identifying DNA N4-methylcytosine sites. Inf. Sci. 2023, 630, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Pang, Y.; Liu, B. BioSeq-BLM: A platform for analyzing DNA, RNA, and protein sequences based on biological language models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, F.; Ren, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, S. A Selective Review of Multi-Level Omics Data Integration Using Variable Selection. High-Throughput 2019, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Su, R.; Feng, X.; Wei, M.; Chen, J. Role of N6-methyladenosine modification in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, H.; Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Yang, H.; Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. Low Rank Matrix Factorization Algorithm Based on Multi-Graph Regularization for Detecting Drug-Disease Association. IEEE/Acm Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2023, 20, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yan, K.; Li, X.; Liu, B. Protein Language Pragmatic Analysis and Progressive Transfer Learning for Profiling Peptide–Protein Interactions. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. Modified nucleosides and bizarre 5′-termini in mouse myeloma mRNA. Nature 1975, 255, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Wang, X.; Xie, N.; Li, Y. N6-methyladenosine in RNA and DNA: An epitranscriptomic and epigenetic player implicated in determination of stem cell fate. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 3256524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Schwartz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Ungar, L.; Osenberg, S.; Cesarkas, K.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Kupiec, M.; et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 2012, 485, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schibler, U.; Kelley, D.E.; Perry, R.P. Comparison of methylated sequences in messenger RNA and heterogeneous nuclear RNA from mouse L cells. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 115, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.-M.; Moss, B. Nucleotide sequences at the N6-methyladenosine sites of HeLa cell messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 1977, 16, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zeng, X.; Pang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Dai, Y.; Su, R.; Zou, Q. iDNA-ABF: Multi-scale deep biological language learning model for the interpretable prediction of DNA methylations. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, K.; Jiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Huang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Pan, Q.; Wan, R. RNA demethylase ALKBH5 prevents pancreatic cancer progression by posttranscriptional activation of PER1 in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Wang, R.; Qiao, J.; Shi, H.; Duan, H.; Jiang, X.; Teng, S.; Wei, L. NanoCon: Contrastive learning-based deep hybrid network for nanopore methylation detection. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccara, S.; Jaffrey, S.R. A unified model for the function of YTHDF proteins in regulating m6A-modified mRNA. Cell 2020, 181, 1582–1595.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccara, S.; Ries, R.J.; Jaffrey, S.R. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chokkalla, A.K.; Mehta, S.L.; Vemuganti, R. Epitranscriptomic regulation by m6A RNA methylation in brain development and diseases. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2020, 40, 2331–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; He, C.; Pan, T. Probing N6-methyladenosine RNA modification status at single nucleotide resolution in mRNA and long noncoding RNA. RNA 2013, 19, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegowski, M.; Flamand, M.N.; Meyer, K.D. scDART-seq reveals distinct m6A signatures and mRNA methylation heterogeneity in single cells. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 868–878.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.D. DART-seq: An antibody-free method for global m6A detection. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Guo, X.; Qin, J.; Gao, L.; Ju, F.; Zhao, C.; Yu, L. Accurate RNA velocity estimation based on multibatch network reveals complex lineage in batch scRNA-seq data. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y. Automatically detecting anchor cells and clustering for scRNA-seq data using scTSNN. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 28, 7015–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Wang, G. scESI: Evolutionary sparse imputation for single-cell transcriptomes from nearest neighbor cells. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Wang, G. MTGDC: A multi-scale tensor graph diffusion clustering for single-cell RNA sequencing data. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2023, 20, 3056–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, B.; Müller, M.; Carell, T.; Kellett, A. Third-Generation Sequencing of Epigenetic DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flusberg, B.A.; Webster, D.R.; Lee, J.H.; Travers, K.J.; Olivares, E.C.; Clark, T.A.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S.W. Direct detection of DNA methylation during single-molecule, real-time sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.; Wu, H.-C.; Jayasinghe, L.; Patel, A.; Reid, S.; Bayley, H. Continuous base identification for single-molecule nanopore DNA sequencing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, P.J. The RNA modification N6-methyladenosine and its implications in human disease. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.; Song, J.; Cheng, Q.; Tang, Y.; Ma, C. PEA: An integrated R toolkit for plant epitranscriptome analysis. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3747–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, X.; Huang, T.; Zhao, X.; Chen, W.; Gu, N.; Zhang, R. Dynamic landscape and evolution of m6A methylation in human. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 6251–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Ren, L.; Cai, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Deng, K.; Yu, X.; Lin, H.; Huang, C. Accurately identifying hemagglutinin using sequence information and machine learning methods. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1281880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yuan, S.-S.; Li, J.; Huang, C.-B.; Lin, H.; Liao, B. A First Computational Frame for Recognizing Heparin-Binding Protein. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ding, H.; Zhou, X.; Lin, H.; Chou, K.-C. iRNA (m6A)-PseDNC: Identifying N6-methyladenosine sites using pseudo dinucleotide composition. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 561, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Liang, Z.Y.; Tang, H.; Chen, W. Identifying Sigma70 Promoters with Novel Pseudo Nucleotide Composition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2019, 16, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, S.; Guo, F.; Zou, Q. HSM6AP: A high-precision predictor for the Homo sapiens N6-methyladenosine (m6A) based on multiple weights and feature stitching. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Q.; Arif, M.; Thafar, M.A.; Albaradei, S.; Cai, P.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Lin, H. PMPred-AE: A computational model for the detection and interpretation of pathological myopia based on artificial intelligence. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1529335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, M.; Sahu, C.; Mohapatra, S. Trends of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Use in Drug Targets, Discovery and Development: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Curr. Drug Targets 2025, 26, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, G.A.; Kim, J.D. Advances in Protein-Ligand Binding Affinity Prediction via Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Study of Datasets, Data Preprocessing Techniques, and Model Architectures. Curr. Drug Targets 2024, 25, 1041–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Xing, P.; Wei, L.; Liu, B. Gene2vec: Gene subsequence embedding for prediction of mammalian N6-methyladenosine sites from mRNA. RNA 2019, 25, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Ding, H.; Wang, L.; Zou, Q. A convolutional neural network using dinucleotide one-hot encoder for identifying DNA N6-methyladenine sites in the rice genome. Neurocomputing 2021, 422, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.-Y.; Wong, W.-K.; Woo, W.-C. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O. Recurrent Neural Network Regularization. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.2329. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. A Multichannel Deep Neural Network for Retina Vessel Segmentation via a Fusion Mechanism. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 697915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zou, Q.; Li, J. DeepM6ASeq-EL: Prediction of human N6-methyladenosine (m6a) sites with LSTM and ensemble learning. Front. Comput. Sci. 2022, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, X.; Song, C.; Liu, T. M6A-BERT-Stacking: A tissue-specific predictor for identifying RNA N6-methyladenosine sites based on BERT and stacking strategy. Symmetry 2023, 15, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Liu, R.; Liang, Y. Gr-m6a: Prediction of n6-methyladenosine sites in mammals with molecular graph and residual network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 163, 107202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reel, P.S.; Reel, S.; Pearson, E.; Trucco, E.; Jefferson, E. Using machine learning approaches for multi-omics data analysis: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 49, 107739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Su, R.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Zou, Q.; Gao, X. Integration of deep feature representations and handcrafted features to improve the prediction of N6-methyladenosine sites. Neurocomputing 2019, 324, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Peng, J.; Shang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. cfMethylPre: Deep transfer learning enhances cancer detection based on circulating cell-free DNA methylation profiling. Brief. Bioinform. 2025, 26, bbaf303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zou, Q. SBSM-Pro: Support bio-sequence machine for proteins. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2024, 67, 212106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Liu, P.Y.; Haase, J.; Bell, J.L.; Hüttelmaier, S.; Liu, T. The critical role of RNA m6A methylation in cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wu, R.; Ming, L. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Sheng, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y. Shining a spotlight on m6A and the vital role of RNA modification in endometrial cancer: A review. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1247309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, S.; Deng, Y.; Yi, P.; Yu, J. Targeting the RNA m6A modification for cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Gao, Z.; Lin, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Q. Prognostic signature analysis and survival prediction of esophageal cancer based on N6-methyladenosine associated lncRNAs. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2024, 23, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.-L.; Xu, X.-Q.; Liu, X.-L.; Guo, Q.-Q.; Fan, Y.-N.; He, B.-X.; Zhang, W.-Z. Emerging role of m6A methylation modification in ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zang, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Shen, H.; Shu, L.; Liang, F.; Feng, C.; Chen, D.; Tao, H.; et al. Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) protein regulates adult neurogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2398–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.J.; Ringeling, F.R.; Vissers, C.; Jacob, F.; Pokrass, M.; Jimenez-Cyrus, D.; Su, Y.; Kim, N.S.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, L.; et al. Temporal Control of Mammalian Cortical Neurogenesis by m(6)A Methylation. Cell 2017, 171, 877–889.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, C.; Chen, R.; Cao, D.; Zeng, X. Geometric Deep Learning for Drug Discovery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 240, 122498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gao, L.; Yu, L. Multiscale graph equivariant diffusion model for 3D molecule design. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadv0778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Cao, D. MPCD: A Multitask Graph Transformer for Molecular Property Prediction by Integrating Common and Domain Knowledge. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 21303–21316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hao, H.; Yu, L. Identification of microbe–disease signed associations via multi-scale variational graph autoencoder based on signed message propagation. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
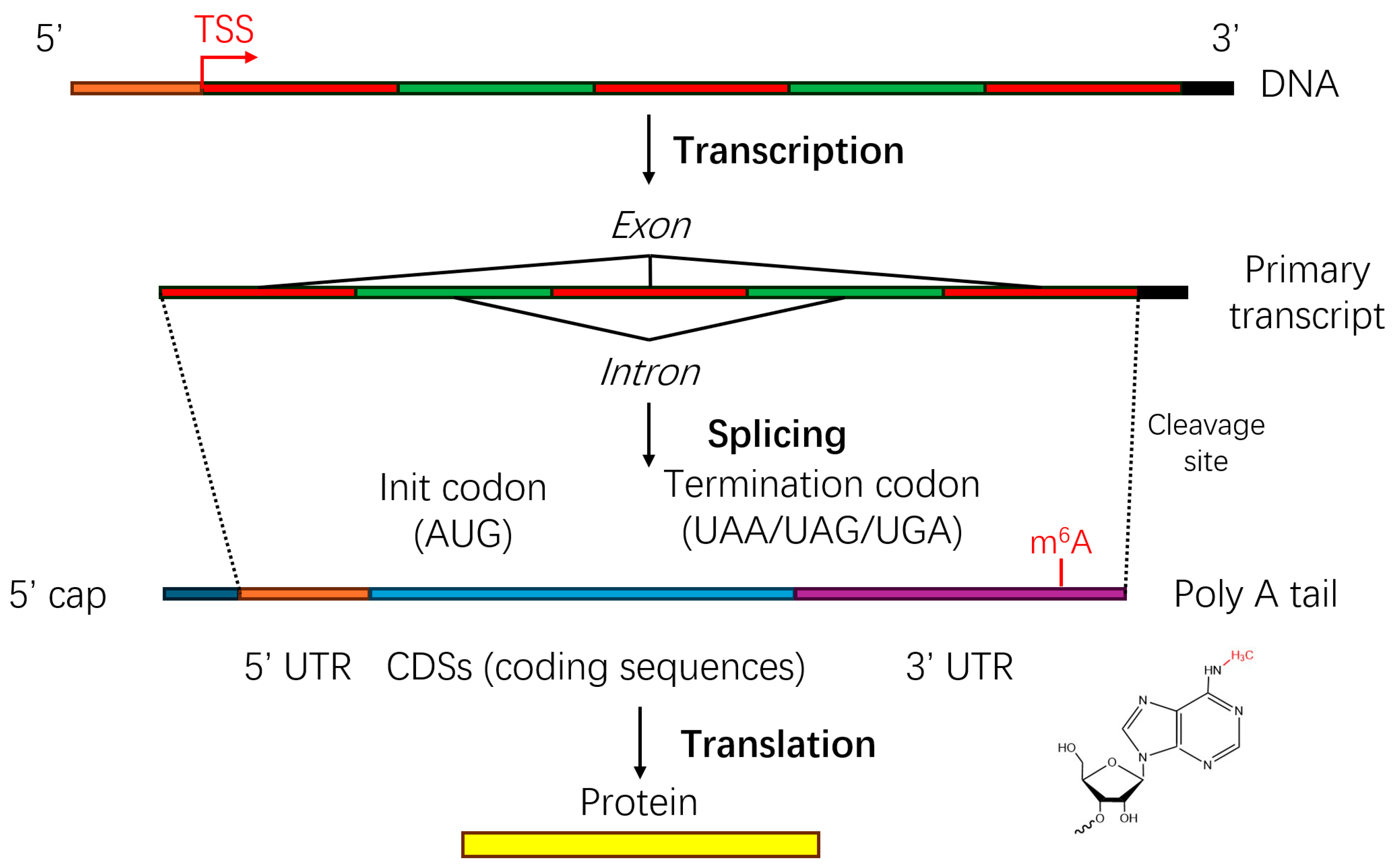
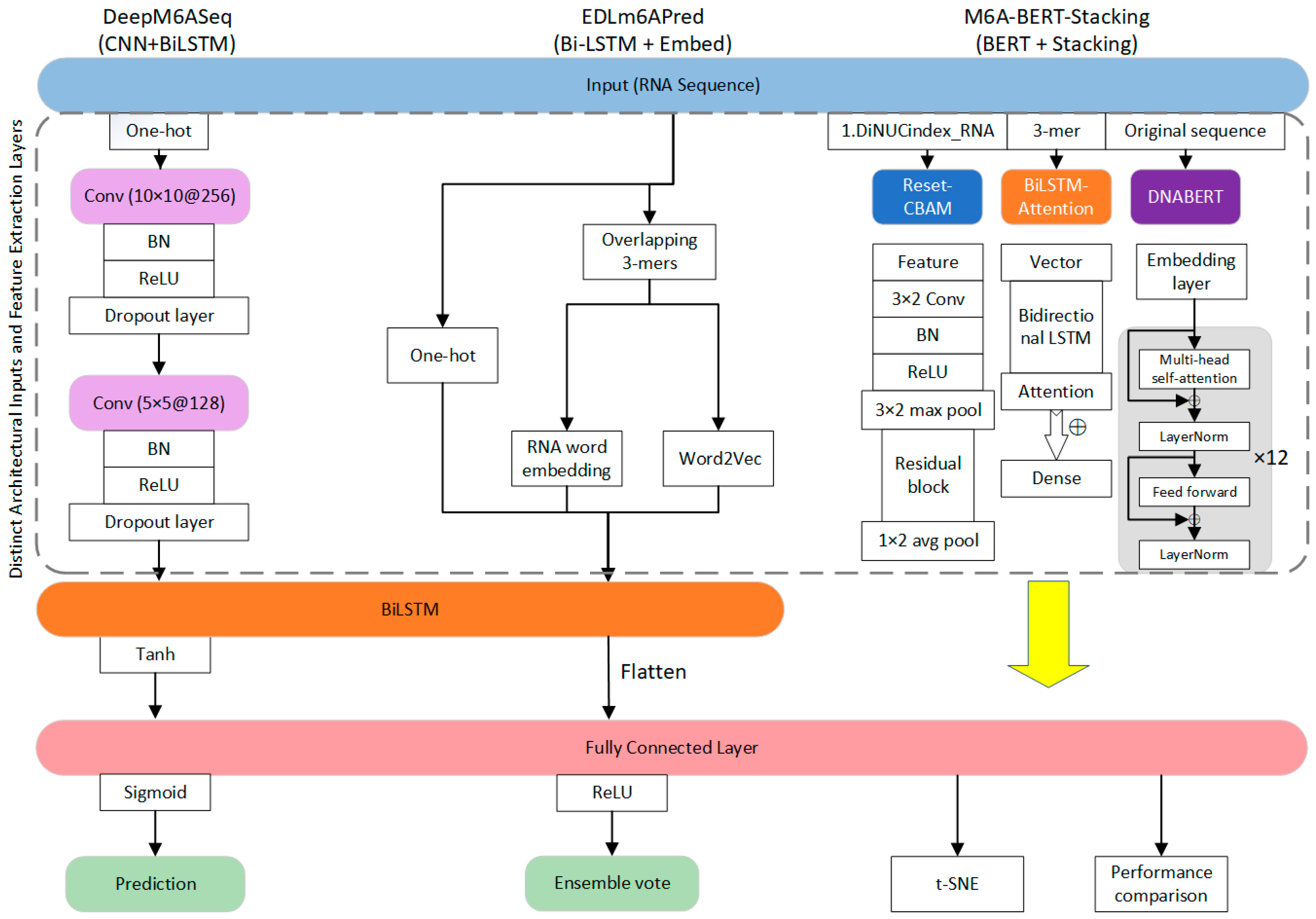
| Technique | Resolution | Throughput | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeRIP-seq | Medium (100–200 nt) | High | Low cost, suitable for whole-transcriptome analysis | Low resolution, difficult to precisely locate single nucleotides |
| m6A-CLIP | High (single-nucleotide) | Medium | High resolution, suitable for studying RNA–protein interactions | Complex experimental procedures, long operation cycles |
| miCLIP | High (single-nucleotide) | Medium | High resolution, precise mapping of m6A modification sites | Complex experimental procedures, high sample quality requirements |
| SCARLET | High (single-nucleotide) | Low | High resolution and specificity | Complex experimental procedures, involves radioisotopes |
| scDART-seq | High (single-nucleotide) | High | Single-cell resolution, revealing intercellular heterogeneity | Complex experimental procedures, high quality and condition requirements |
| SMRT Sequencing | High (single-nucleotide) | Medium | Direct detection of native RNA; long reads allow for isoform-specific m6A profiling and full-length transcript analysis; high accuracy | Lower throughput compared to short-read methods for comprehensive transcriptome-wide profiling; relatively higher cost per base |
| Oxford Nanopore Sequencing | High (single-nucleotide) | High | Direct detection of native RNA; ultra-long reads; real-time data acquisition; simultaneous detection of multiple RNA modifications | Higher raw error rates; challenges regarding development of bioinformatics pipelines for accurate m6A calling and quantification; complex signal processing needed |
| Tool/Software Name | Main Functionality | Programming Language/Platform | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| m6A-TCPred | m6A site prediction | R language/website platform based on Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML), Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP), as well as the MySQL tables for metadata storage. | Based on SVM; supports cross-validation and independent testing. |
| iRNA-m6A | m6A site prediction | Python/web server based on HTML | Utilizes SVM and integrates sequence motifs with bioinformatics attributes, employing pseudo dinucleotide composition. |
| DeepM6ASeq | m6A site prediction | Python | CNN-BiLSTM architecture for automatic extraction of local features; high predictive accuracy suitable for use with large-scale data. |
| HSM6AP | High-precision m6A site prediction | Python/web server based on HTML | XGBoost-based ensemble framework integrating sample weighting strategies and multi-dimensional feature fusion; designed for human RNA. |
| M6APred-EL | m6A site prediction | Python 2.7/web server based on HTML | SVM-based prediction model. |
| EDLm6APred | m6A site prediction | Python/web server based on HTML | Employs bidirectional LSTMs combined with word embedding algorithms to capture contextual information and long-term dependencies. |
| M6A-BERT-Stacking | Tissue-specific m6A prediction | Python 3.8.3 | Integrates BERT and stacking strategies (ResNet + BiLSTM + BERT) to capture contextual information and enhance overall prediction performance. |
| SRAMP | m6A site prediction | R language 2.15, Perl 5.8/web server based on HTML | Leverages Random Forest algorithm, based on sequence-derived features; demonstrated high predictive accuracy. |
| Gene2vec | m6A site prediction | Python 3.6 | Combines subsequence embeddings with deep learning using Word2vec-inspired NLP technique to discern contextual patterns. |
| iRicem6A-CNN | DNA N6-methyladenine prediction | Python/web server | CNN model using dinucleotide one-hot encoding; accounts for nucleotide context to enhance performance in rice DNA. |
| DeepM6ASeq-EL | m6A site prediction | Python 3 | Ensemble learning model combining five LSTM-CNN subnetworks using a hard voting strategy; utilizes diverse sequence context features for human mRNA. |
| CLSM6A | High-resolution m6A prediction | Python 3/web server based on HTML | Employs multi-layer neural networks to automatically extract single-nucleotide-resolution features. |
| DLm6Am | m6Am modification recognition | Python 3.7.12/web server | Uses multi-layer neural networks to automatically extract sequence and chemical features; high generalization ability. |
| DeepM6APred | m6A site prediction | Python 3/web server | Integrates deep feature representations (from deep belief networks) with traditional handcrafted features for enhanced accuracy. |
| Model | Testing Method | Availability of Data | Method | Performance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | Sn | Sp | MCC | AUC | ||||
| m6A-TCPred | Cross-validation and independent testing | http://www.rnamd.org/m6ATCPred/ (accessed on 8 July 2025) | SVM | 0.801 | 0.806 | 0.796 | 0.603 | 0.879 |
| iRNA-m6A | 10-fold cross-validation test | http://lin-group.cn/server/iRNA-m6A/index.html (accessed on 8 July 2025) | SVM | 0.912 | 0.868 | 0.956 | 0.83 | 0.93 |
| DeepM6ASeq | Five-fold cross-validation | https://github.com/rreybeyb/DeepM6ASeq (accessed on 8 July 2025) | CNN | 0.763 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.499 | 0.850 |
| HSM6AP | Five-fold cross-validation test | http://lab.malab.cn/~lijing/HSM6AP.html (accessed on 8 July 2025) | XGBoost | 0.953 | 0.916 | 0.943 | 0.651 | 0.981 |
| M6APred-EL | 10-fold cross-validation | https://github.com/chr2117216003/M6APred-EL (accessed on 8 July 2025) | SVM | 0.808 | 0.807 | 0.810 | 0.620 | 0.90 |
| EDLm6APred | Five-fold cross-validation | http://labiip.net/index.php (accessed on 8 July 2025) | RNN | 0.786 | 0.713 | - | 0.579 | 0.861 |
| M6A-BERT-Stacking | Five-fold CV and independent test | https://github.com/liqianyue/zeitgeist/tree/master/m6A_BERT_Stacking (accessed on 8 July 2025) | Resnet + BiLSTM + BERT | 0.790 | 0.816 | 0.764 | 0.582 | 0.871 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, R.; Zou, Q.; Luo, X. From Detection to Prediction: Advances in m6A Methylation Analysis Through Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Implications in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146701
Jin R, Zou Q, Luo X. From Detection to Prediction: Advances in m6A Methylation Analysis Through Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Implications in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146701
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Ruoting, Quan Zou, and Ximei Luo. 2025. "From Detection to Prediction: Advances in m6A Methylation Analysis Through Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Implications in Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146701
APA StyleJin, R., Zou, Q., & Luo, X. (2025). From Detection to Prediction: Advances in m6A Methylation Analysis Through Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Implications in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146701







