Disease Severity- and Hormonal Status-Dependent Alterations of EGF and MIF in the Serum of Endometriosis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Demographics and Pain Parameters of Study Participants
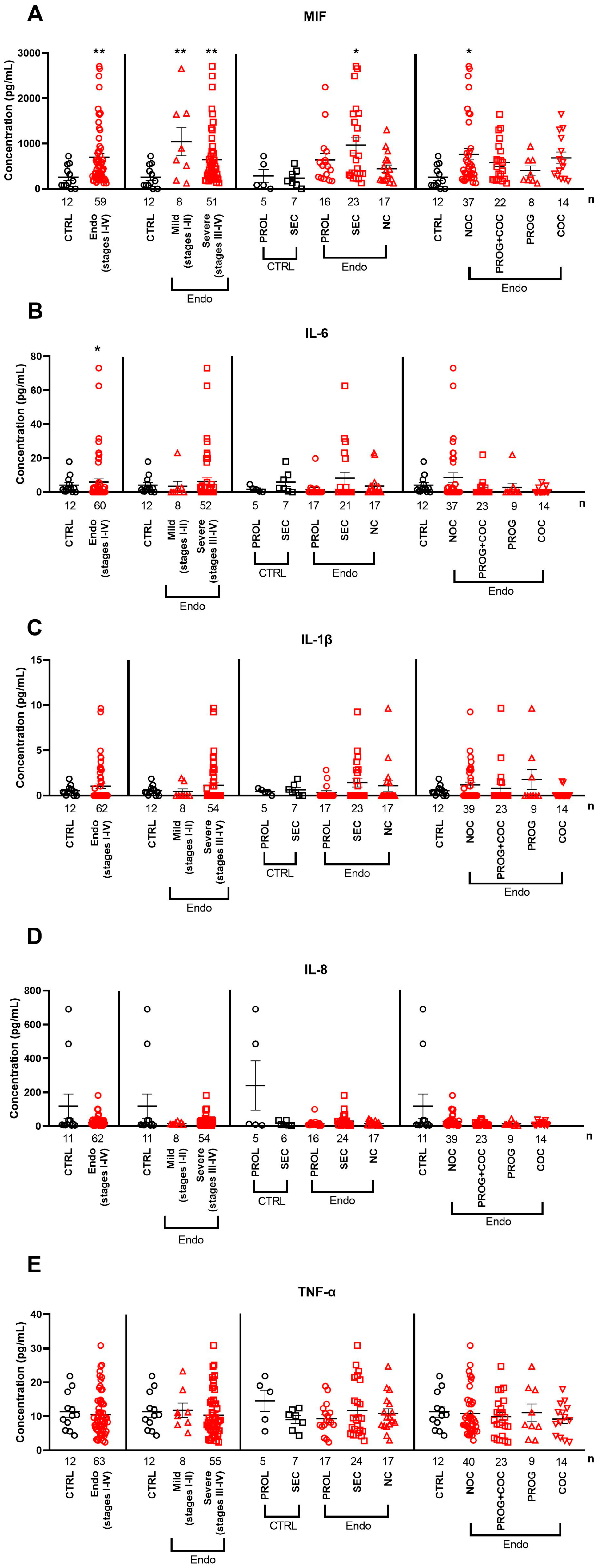
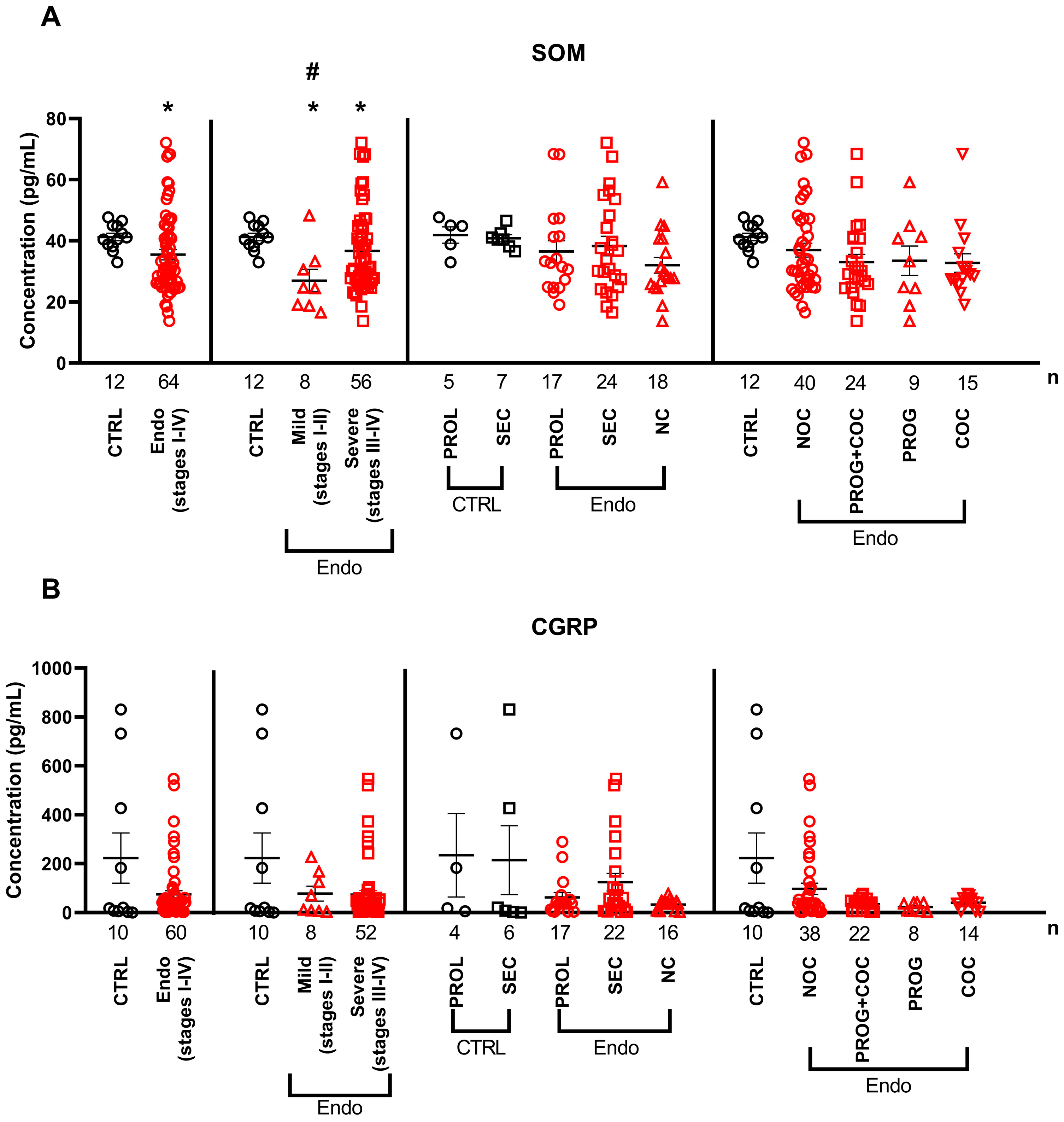
2.2. Serum Cytokine and Neuropeptide Alterations in Endometriosis
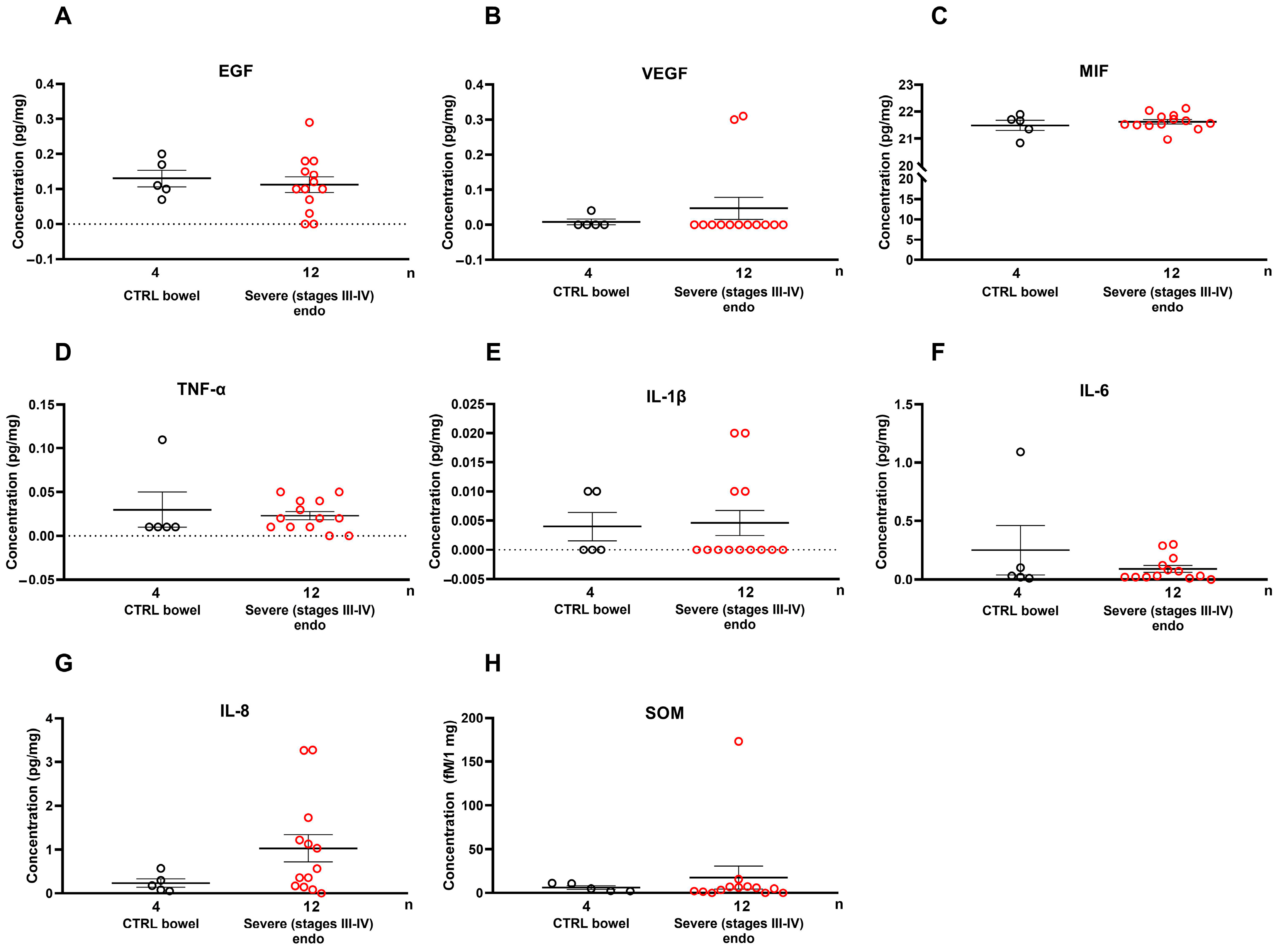
2.3. Growth Factors and Cytokines Are Not Elevated Locally in Severe Endometriosis Lesions
2.4. Serum EGF and SOM Showed Positive Correlations with Pain Parameters in Mild Endometriosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. VAS Collection
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. Measurement of Inflammatory Cytokine Concentration Using Luminex xMAP Technology
4.5. CGRP, MIF, and SOM Measurement with ELISA
4.6. Radioimmunoassay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CGRP | calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| COCs | combined oral contraceptives |
| CPP | chronic pelvic pain |
| DIER | deep-infiltrating endometriosis |
| DM | dysmenorrhea |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| IL | interleukin |
| MIF | macrophage migration inhibition factor |
| NC | no cycle |
| NOCs | no oral contraceptives |
| PROG | progesterone |
| PROL | proliferative phase |
| PVN | per vias naturales |
| rASRM | revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine |
| SC | sectio caesarea |
| SEC | secretory phase |
| SOM | somatostatin |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| VAS | visual analogue scale |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Secosan, C.; Balulescu, L.; Brasoveanu, S.; Balint, O.; Pirtea, P.; Dorin, G.; Pirtea, L. Endometriosis in Menopause—Renewed Attention on a Controversial Disease. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoens, S.; Dunselman, G.; Dirksen, C.; Hummelshoj, L.; Bokor, A.; Brandes, I.; Brodszky, V.; Canis, M.; Colombo, G.L.; Deleire, T.; et al. The burden of endometriosis: Costs and quality of life of women with endometriosis and treated in referral centres. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakhari, A.; Delpero, E.; McKeown, S.; Tomlinson, G.; Bougie, O.; Murji, A. Endometriosis recurrence following post-operative hormonal suppression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2021, 27, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krygere, L.; Jukna, P.; Jariene, K.; Drejeriene, E. Diagnostic Potential of Cytokine Biomarkers in Endometriosis: Challenges and Insights. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keckstein, J.; Saridogan, E.; Ulrich, U.A.; Sillem, M.; Oppelt, P.; Schweppe, K.W.; Krentel, H.; Janschek, E.; Exacoustos, C.; Malzoni, M.; et al. The #Enzian classification: A comprehensive non-invasive and surgical description system for endometriosis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2021, 100, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Pašalić, E.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Hromić-Jahjefendić, A. Endometriosis: Classification, pathophisiology, and treatment options. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 251, 154847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachedin, A.; Todd, N. Dysmenorrhea, Endometriosis and Chronic Pelvic Pain in Adolescents. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2020, 12, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privitera, G.; O’Brien, K.; Misajon, R.A.; Lin, C.Y. Endometriosis Symptomatology, Dyspareunia, and Sexual Distress Are Related to Avoidance of Sex and Negative Impacts on the Sex Lives of Women with Endometriosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seracchioli, R.; Mabrouk, M.; Guerrini, M.; Manuzzi, L.; Savelli, L.; Frascà, C.; Venturoli, S. Dyschezia and Posterior Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis: Analysis of 360 Cases. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2008, 15, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butrick, C.W. Patients with chronic pelvic pain: Endometriosis or interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome? JSLS 2007, 11, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Karp, B.I.; Stratton, P. Endometriosis-associated chronic pelvic pain. Med 2023, 4, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyd, M. The Graphic Rating Scale. J. Educ. Psychol. 1923, 14, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Coccia, M.E.; Lazzeri, G.; Basile, F.; Troiano, G. Variables Associated with Endometriosis-related Pain: A Pilot Study using a Visual Analogue Scale. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2019, 41, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdel, N.; Alves, J.; Pickering, G.; Ramilo, I.; Roman, H.; Canis, M. Systematic review of endometriosis pain assessment: How to choose a scale? Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 21, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morotti, M.; Vincent, K.; Becker, C.M. Mechanisms of pain in endometriosis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2017, 209, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.A.; Collins, F.; De Leo, B.; Horne, A.W.; Saunders, P.T.K. Pelvic pain correlates with peritoneal macrophage abundance not endometriosis. Reprod. Fertil. 2021, 2, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, E.N.; Mamillapalli, R.; Li, F.; Mutlu, L.; Hufnagel, D.; Krikun, G.; Taylor, H.S. Micrometastasis of endometriosis to distant organs in a murine model. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2282–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Mamillapalli, R.; Ding, S.; Chang, H.; Liu, Z.W.; Gao, X.B.; Taylor, H.S. Endometriosis alters brain electrophysiology, gene expression and increases pain sensitization, anxiety, and depression in female mice. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.S.; Kotlyar, A.M.; Flores, V.A. Endometriosis is a chronic systemic disease: Clinical challenges and novel innovations. Lancet 2021, 397, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velho, R.V.; Taube, E.; Sehouli, J.; Mechsner, S. Neurogenic Inflammation in the Context of Endometriosis—What Do We Know? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, H.; Hosseini, S.; Hajizadeh, N.; Majdi, L.; Ajdary, M.; Mofarahe, Z.S. Role of neuropeptides in patients with endometriosis: A literature review. Middle East. Fertil. Soc. J. 2024, 29, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machairiotis, N.; Vasilakaki, S.; Thomakos, N. Inflammatory mediators and pain in endometriosis: A systematic review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Expression of somatostatin and its receptor 1–5 in endometriotic tissues and cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 3777–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fu, X.; Wu, T.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.; Wu, R. Role of interleukin-6 and its receptor in endometriosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 3801–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, A. Local cytokines in endometrial tissue: The role of interleukin-8 in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 955, 101–109; discussion 118, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto-Kakiuchi, A.; Sato, I.; Nakano, K.; Ohmori, H.; Kayukawa, Y.; Tanimura, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nakamura, G.; Maeda, A.; et al. A long-acting anti–IL-8 antibody improves inflammation and fibrosis in endometriosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabq5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Alotaibi, F.T.; Sediqi, S.; Bedaiwy, M.A.; Yong, P.J. Role of interleukin-1β in nerve growth factor expression, neurogenesis and deep dyspareunia in endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 35, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergqvist, A.; Bruse, C.; Carlberg, M.; Carlström, K. Interleukin 1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in endometriotic tissue and in endometrium. Fertil. Steril. 2001, 75, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Peng, B.; Ma, J.; Lin, K.; Xu, K.; Lin, J.; Yong, P.J.; Leung, P.C.K.; Bedaiwy, M.A.; Lin, J. Epidermal growth factor promotes stromal cells migration and invasion via up-regulation of hyaluronate synthase 2 and hyaluronan in endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 114, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadisaputra, W.; Prayudhana, S. Serum biomarker profiles of interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, matrix-metalloproteinase-2, and vascular endothelial growth factor in endometriosis staging. Med. J. Indones. 2013, 22, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer, A.; Albert, C.; Mercader, A.; Bonilla-Musoles, F.; Remohí, J.; Simón, C. The follicular and endocrine environment in women with endometriosis: Local and systemic cytokine production. Fertil. Steril. 1998, 70, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaradie, S.M.Y.; Bakry, M.S.; Bosilah, A.H. Serum macrophage migration inhibition factor for diagnosing endometriosis and its severity: Case-control study. BMC Womens Health 2020, 20, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaichian, S.; Firoozabadi, Z.D.; Rokhgireh, S.; Tahermanesh, K.; Kashi, A.M.; Govahi, A.; Minaeian, S.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Ajdary, M. CGRP neuropeptide levels in patients with endometriosis-related pain treated with dienogest: A comparative study. BMC Womens. Health 2024, 24, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, K.E.; Conduit-Hulbert, S.A.; Villar, J.; Kirtley, S.; Kennedy, S.H.; Becker, C.M. Peripheral biomarkers of endometriosis: A systematic review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2010, 16, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasza, A. IL-1 and EGF regulate expression of genes important in inflammation and cancer. Cytokine 2013, 62, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, C.; Cameron, M.G.; Laird, B.; Mjåland, S. Epidermal growth factor receptor—Inhibition (EGFR-I) in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.J.; William, J.; Bulun, S. Endometriosis and ovarian cancer: A review of clinical, pathologic, and molecular aspects. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2011, 30, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, M.D.; Zhang, M.; Liu, N.; Viet, C.T.; Xie, T.; Jensen, D.D.; Amit, M.; Pan, H.; Ye, Y. Repurposing EGFR Inhibitors for Oral Cancer Pain and Opioid Tolerance. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos-González, Y.; Rodríguez-Berrocal, F.J.; Cordero, O.J.; Gómez, C.; Páez De La Cadena, M. Alteration of the serum levels of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and head and neck carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, S.; Regidor, P.A.; Schindler, A.E.; Winterhager, E. Reduced proliferation and cell adhesion in endometriosis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2000, 6, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Veeramachaneni, R.; Singh, K.; Viet, C.; Scheff, N.; Albertson, D.; Schmidt, B. (111) Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in oral cancer pain. J. Pain. 2017, 18, S4–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, C.; Cameron, M.G.; Bailey, A.G.; Fallon, M.T.; Laird, B.J.; Paterson, V.; Mitchell, R.; Fleetwood-Walker, S.M.; Daly, F.; Mjåland, S. Relief of Neuropathic Pain through Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition: A Randomized Proof-of-Concept Trial. Pain Med. (United States) 2019, 20, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mu, L. Association between macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the endometrium and estrogen in endometriosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohóczky, K.; Kun, J.; Szalontai, B.; Szöke, É.; Sághy, É.; Payrits, M.; Kajtár, B.; Kovács, K.; Környei, J.L.; Garai, J.; et al. Estrogen-dependent up-regulation of TRPA1 and TRPV1 receptor proteins in the rat endometrium. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoum, A.; Metz, C.N.; Al-Akoum, M.; Kats, R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression in the intrauterine endometrium of women with endometriosis varies with disease stage, infertility status, and pelvic pain. Fertil. Steril. 2006, 85, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillat, V.; Sengers, V.; Metz, C.N.; Roger, T.; Leboeuf, M.; Mailloux, J.; Akoum, A. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is involved in a positive feedback loop increasing aromatase expression in endometriosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, M.; Bellehumeur, C.; Therriault, M.-J.; Metz, C.; Maheux, R.; Akoum, A. Elevated levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the peripheral blood of women with endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2005, 83, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, B.; Sammel, M.D.; Fan, X.; Gerton, G.L.; Shaunik, A.; Chittams, J.; Barnhart, K.T. Panel of markers can accurately predict endometriosis in a subset of patients. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 89, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, E.E.D.R.; Hornung, D.; Salem, H.T.; Khalifa, E.A.; El-Metwally, T.H.; Al-Hendy, A. Serum cytokines as biomarkers for nonsurgical prediction of endometriosis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2008, 137, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvezzi, H.; Hernandes, C.; Piccinato, C.A.; Podgaec, S. Interleukin in endometriosis-associated infertility-pelvic pain: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Reproduction 2019, 158, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, N.Y.; Ahsan, F.; Santoso, B.; Mufid, A.F.; Sa’adi, A.; Dwiningsih, S.R.; Tunjungseto, A.; Widyanugraha, M.Y.A. IL-8 and IL-12p70 are associated with pelvic pain among infertile women with endometriosis. Pain. Med. 2023, 24, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manero, M.G.; Alcazar, J.L. Interleukin-8 serum levels do not correlate with pelvic pain in patients with ovarian endometriomas. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, J.V.; Machado, D.E.; da Silva, M.C.; de Mello, M.P.; Berardo, P.T.; Medeiros, R.; Perini, J.A. Influence of interleukin-8 polymorphism on endometriosis-related pelvic pain. Hum. Immunol. 2023, 84, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, N.; Al-Akoum, M.; Gagnon, G.; Girard, K.; Blanchet, P.; Rousseau, J.A.; Akoum, A. Decreased concentrations of soluble interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein levels in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 92, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersinger, N.A.; Günthert, A.R.; McKinnon, B.; Johann, S.; Mueller, M.D. Dose-response effect of interleukin (IL)-1β, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and interferon-γ on the in vitro production of epithelial neutrophil activating peptide-78 (ENA-78), IL-8, and IL-6 by human endometrial stromal cells. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2011, 283, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanova, L.; Giudice, L.C. Molecular evidence for differences in endometrium in severe versus mild endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 18, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütő, B.; Kun, J.; Bagoly, T.; Németh, T.; Pintér, E.; Kardos, D.; Helyes, Z. Plasma Somatostatin Levels Are Lower in Patients with Coronary Stenosis and Significantly Increase after Stent Implantation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütő, B.; Kolumbán, B.; Szabó, É.; Pásztor, S.; Németh, T.; Bagoly, T.; Botz, B.; Pintér, E.; Helyes, Z. Plasma Somatostatin Levels Increase during Scoliosis Surgery, but Not Herniated Disc Operations: Results of a Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, B.; Bagoly, T.; Borzsei, R.; Lengl, O.; Szolcsanyi, J.; Nemeth, T.; Loibl, C.; Bardonicsek, Z.; Pinter, E.; Helyes, Z. Surgery and sepsis increase somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the human plasma. Peptides 2010, 31, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, M.; Luque, R.M.; Duran-Prado, M.; Baragli, A.; Grande, C.; Volante, M.; Gahete, M.D.; Deltetto, F.; Camanni, M.; Ghigo, E.; et al. Somatostatin and somatostatin analogues reduce PDGF-induced endometrial cell proliferation and motility. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 2117–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periferakis, A.; Tsigas, G.; Periferakis, A.T.; Badarau, I.A.; Scheau, A.E.; Tampa, M.; Georgescu, S.R.; Didilescu, A.C.; Scheau, C.; Caruntu, C. Antitumoral and Anti-inflammatory Roles of Somatostatin and Its Analogs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2021, 2021, 1840069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U. Somatostatin and Somatostatin Receptors in Tumour Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florio, T.; Morini, M.; Villa, V.; Arena, S.; Corsaro, A.; Thellung, S.; Culler, M.D.; Pfeffer, U.; Noonan, D.M.; Schettini, G.; et al. Somatostatin inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth via somatostatin receptor-3-mediated regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and mitogen-activated protein kinase activities. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suto, B.; Szitter, I.; Bagoly, T.; Pinter, E.; Szolcsányi, J.; Loibl, C.; Nemeth, T.; Tanczos, K.; Molnar, T.; Leiner, T.; et al. Plasma somatostatin-like immunoreactivity increases in the plasma of septic patients and rats with systemic inflammatory reaction: Experimental evidence for its sensory origin and protective role. Peptides 2014, 54, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, T.; Tulipano, G.; Dournaud, P.; Bousquet, C.; Csaba, Z.; Kreienkamp, H.J.; Lupp, A.; Korbonits, M.; Castaño, J.P.; Wester, H.J.; et al. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. CV. somatostatin receptors: Structure, function, ligands, and new nomenclature. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 763–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somvanshi, R.K.; Kumar, U. δ-Opioid receptor and somatostatin receptor-4 heterodimerization: Possible implications in modulation of pain associated signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kántás, B.; Börzsei, R.; Szőke, É.; Bánhegyi, P.; Horváth, Á.; Hunyady, Á.; Borbély, É.; Hetényi, C.; Pintér, E.; Helyes, Z. Novel drug-like somatostatin receptor 4 agonists are potential analgesics for neuropathic pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnez, J.; Smoes, P.; Gillerot, S.; Casanas-Roux, F.; Nisolle, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 1686–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschke, M.W.; Elitzsch, A.; Vollmar, B.; Vajkoczy, P.; Menger, M.D. Combined inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor, but not inhibition of VEGF alone, effectively suppresses angiogenesis and vessel maturation in endometriotic lesions. Hum. Reprod. 2006, 21, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filindris, T.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Keramida, M.; Panteris, E.; Kalogeropoulos, S.; Georgopoulos, N.; Taniguchi, F.; Adonakis, G.; Harada, T.; Kaponis, A. The effect of GnRH-a on the angiogenesis of endometriosis. Hormones 2024, 23, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupo-Nogueira, A.; de Oliveira, R.M.; Petta, C.A.; Podgaec, S.; Dias, J.A.; Abrao, M.S. Vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations in the serum and peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2007, 99, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.I.; Lee, A.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Song, H.R.; Park, J.H.; Kang, T.B.; Lee, S.R.; Yang, S.H. The role of tumor necrosis factor alpha (Tnf-α) in autoimmune disease and current tnf-α inhibitors in therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmawati, N.Y.; Ahsan, F.; Santoso, B.; Mufid, A.F.; Sa’adi, A.; Dwiningsih, S.R.; Tunjungseto, A.; Widyanugraha, M.Y.A. Increased level of TNF-α in serum and peritoneal fluid of endometriosis women-related infertility. In Improving Health for Better Future Life: Strengthening from Basic Science to Clinical Research; CRC Press: London, UK, 2023; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Senapati, S.; Clauw, D.; As-Sanie, S. The relationship between serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) with pelvic pain symptoms in women with endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 92, S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, S.; Johnson, K.W.; Ossipov, M.H.; Aurora, S.K. CGRP and the Trigeminal System in Migraine. Headache 2019, 59, 659–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaelli, B.; Overeem, L.H.; Mecklenburg, J.; Hofacker, M.D.; Knoth, H.; Nowak, C.P.; Neeb, L.; Ebert, A.D.; Sehouli, J.; Mechsner, S.; et al. Plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in migraine and endometriosis during the menstrual cycle. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.-W. Neuropeptides Substance P and Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide Accelerate the Development and Fibrogenesis of Endometriosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frobert, Y.; Nevers, M.C.; Amadesi, S.; Volland, H.; Brune, P.; Geppetti, P.; Grassi, J.; Créminon, C. A sensitive sandwich enzyme immunoassay for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP): Characterization and application. Peptides 1999, 20, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauge-Evans, A.C.; Bowe, J.; Franklin, Z.J.; Hassan, Z.; Jones, P.M. Inhibitory effect of somatostatin on insulin secretion is not mediated via the CNS. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 225, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | CTRL (n = 12) | Endometriosis (n = 64) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild (n = 8) | Severe (n = 56) | p | ||||
| Ctrl vs. Mild | Ctrl vs. Severe | Mild vs. Severe | ||||
| Age | 25.75 ± 4.04 | 31.88 ± 4.91 | 35.36 ± 5.95 | 0.0350 | <0.0001 | 0.1327 |
| rASRM stage | ||||||
| Mild (rASRM I–II) | n.r. | 8 | - | |||
| Severe (rASRM III–IV) | n.r. | - | 56 | |||
| Menstrual phase | ||||||
| Duration of menstrual phase (days) | 29 ± 1 | 28 | 27.91 ± 0.69 | |||
| Proliferative (1–14 days) | 5 | 4 | 13 | |||
| Secretory (15–28 days) | 7 | 2 | 22 | |||
| Irregular | - | - | 1 | |||
| No cycle | - | 2 | 16 | |||
| No data available | - | - | 4 | |||
| Parity | ||||||
| SC | 0 | 4 | 15 | |||
| PVN | 0 | - | 7 | |||
| 1 child | 0 | 2 | 13 | |||
| 2 children | 0 | 1 | 4 | |||
| 3 children | 0 | - | 1 | |||
| Medication | ||||||
| No oral contraceptive | 12 | 4 | 36 | |||
| Progesterone | - | 3 | 6 | |||
| Combined oral contraceptives | - | 1 | 14 | |||
| VAS score | ||||||
| DM | n.r. | 7 ± 1.91 | 6.64 ± 3.42 | 0.7913 | ||
| Dyspareunia | n.r. | 4.14 ± 3.34 | 3.08 ± 3.44 | 0.4001 | ||
| Dysuria | n.r. | 2 ± 3.61 | 1.42 ± 2.94 | 0.7694 | ||
| Dyschezia | n.r. | 4.29 ± 4.64 | 2.34 ± 3.33 | 0.2612 | ||
| CPP | n.r. | 5.14 ± 3.53 | 2.52 ± 2.89 | 0.0503 | ||
| No data available | n.r. | 1 | 3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tóth, N.; Brubel, R.; Bokor, A.; Kemény, Á.; Farkas, N.; Pál, T.; Helyes, Z.; Pohóczky, K. Disease Severity- and Hormonal Status-Dependent Alterations of EGF and MIF in the Serum of Endometriosis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146695
Tóth N, Brubel R, Bokor A, Kemény Á, Farkas N, Pál T, Helyes Z, Pohóczky K. Disease Severity- and Hormonal Status-Dependent Alterations of EGF and MIF in the Serum of Endometriosis Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146695
Chicago/Turabian StyleTóth, Norbert, Réka Brubel, Attila Bokor, Ágnes Kemény, Nelli Farkas, Tibor Pál, Zsuzsanna Helyes, and Krisztina Pohóczky. 2025. "Disease Severity- and Hormonal Status-Dependent Alterations of EGF and MIF in the Serum of Endometriosis Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146695
APA StyleTóth, N., Brubel, R., Bokor, A., Kemény, Á., Farkas, N., Pál, T., Helyes, Z., & Pohóczky, K. (2025). Disease Severity- and Hormonal Status-Dependent Alterations of EGF and MIF in the Serum of Endometriosis Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146695






