FR-BINN: Biologically Informed Neural Networks for Enhanced Biomarker Discovery and Pathway Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We established a formal definition of whether chronic inflammatory diseases are susceptible to carcinogenesis and compile transcriptomic datasets from chronic inflammation diseases to provide a foundation for predictive modeling.
- Based on the biological domain knowledge of the FR, we constructed the hierarchical knowledge neural network. The interpretable approaches were utilized to explore the important genes and the potential patterns of FR. Leveraging chain-of-thought reasoning, the large language model offers auxiliary semantic analysis and explanations.
- Extensive experiments and downstream analyses demonstrate the ability of FR-BINN, providing novel insights into the mechanisms of inflammation-driven carcinogenesis and offering potential targets for prevention and therapy.
2. Results
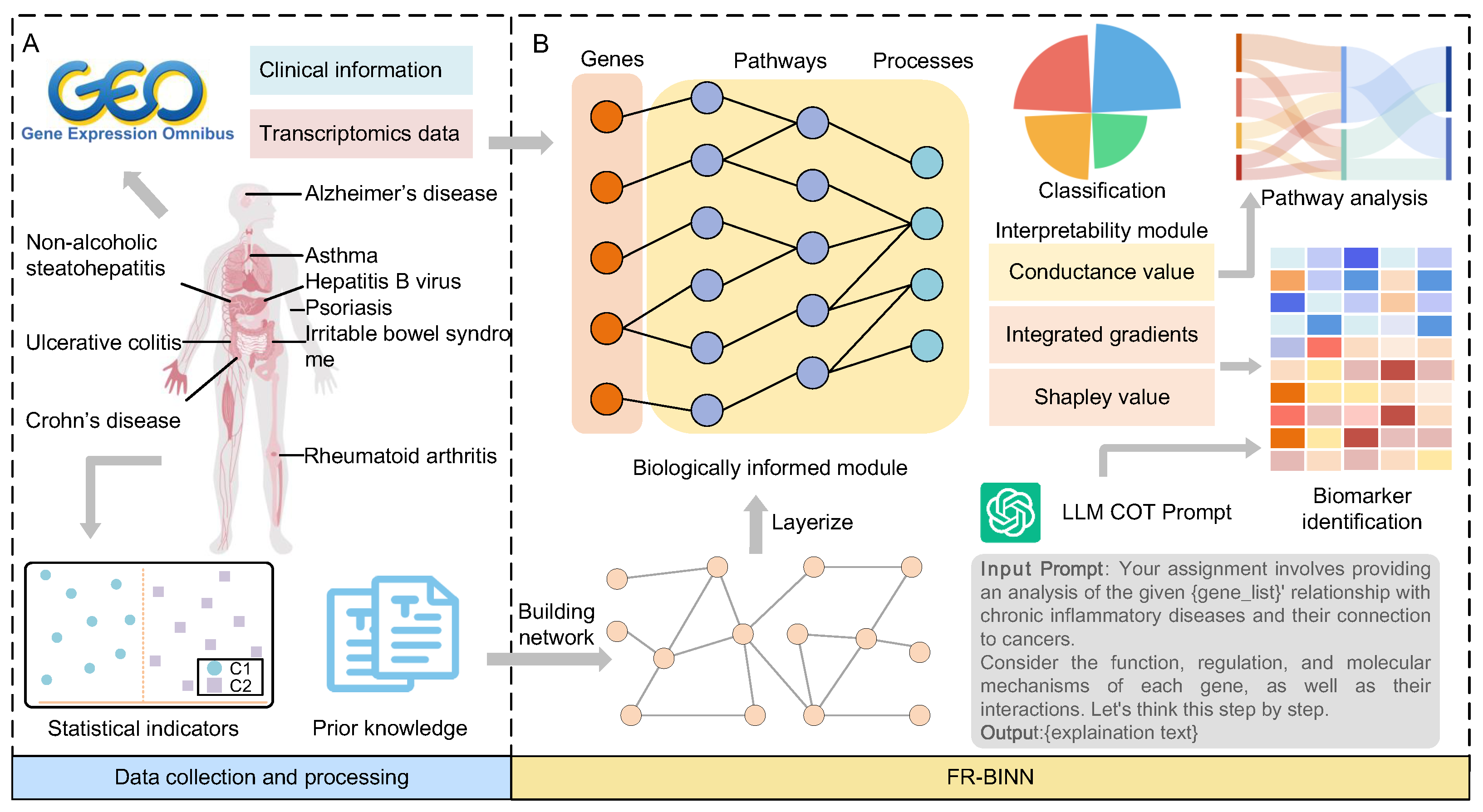
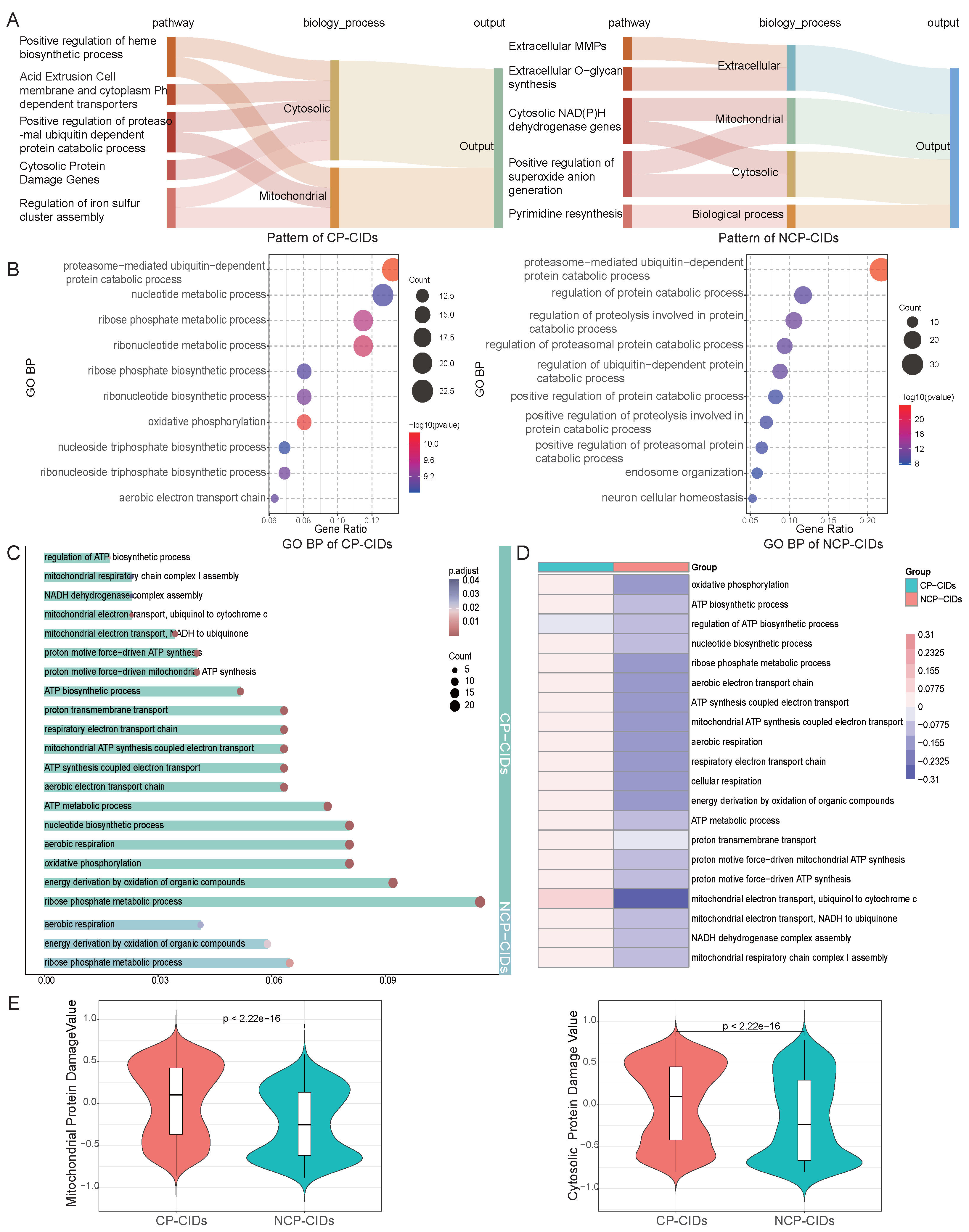
2.1. Overview of FR-BINN Framework
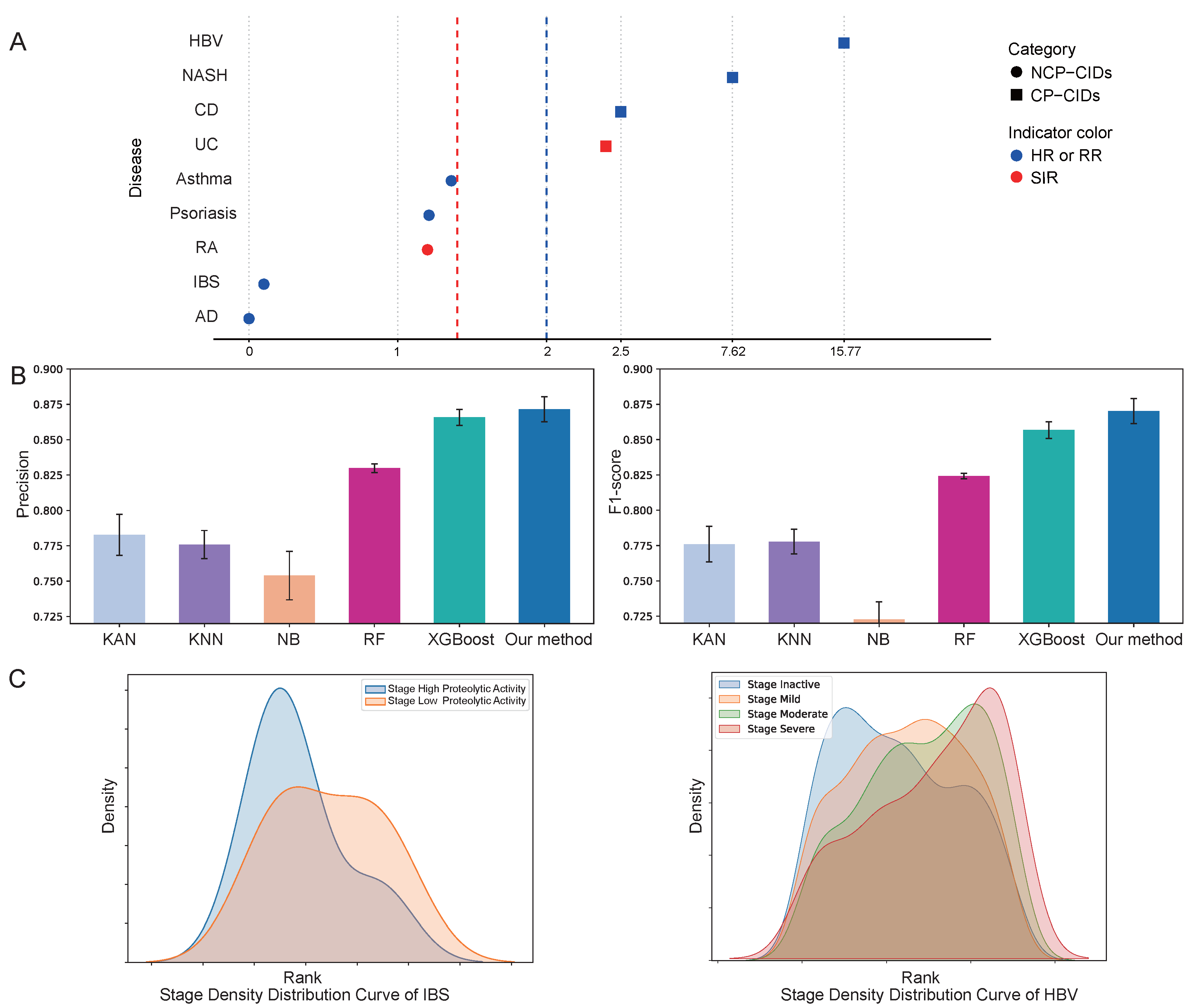
2.2. Performance Evaluation
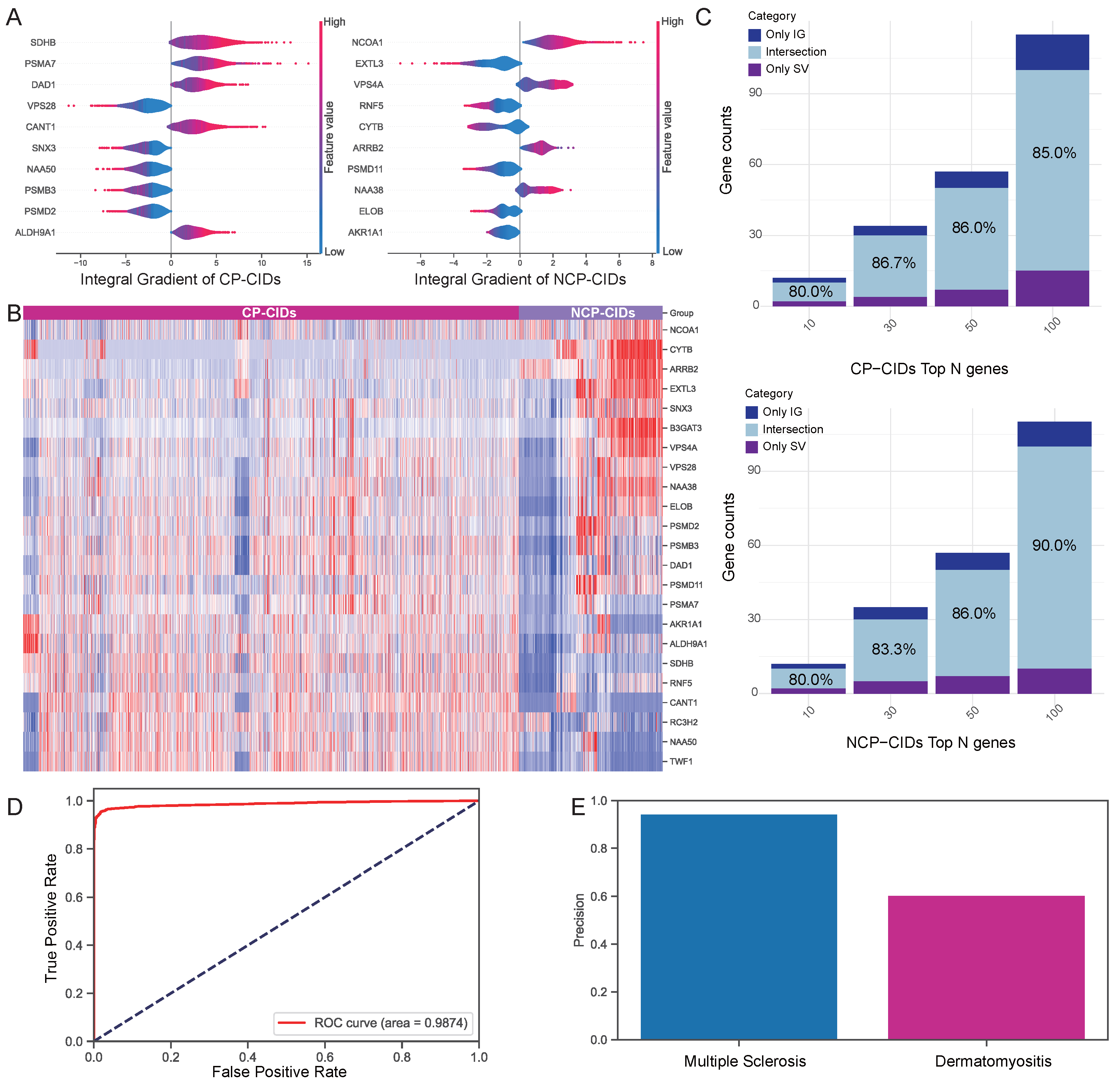
2.3. Validation of Attribution Methods
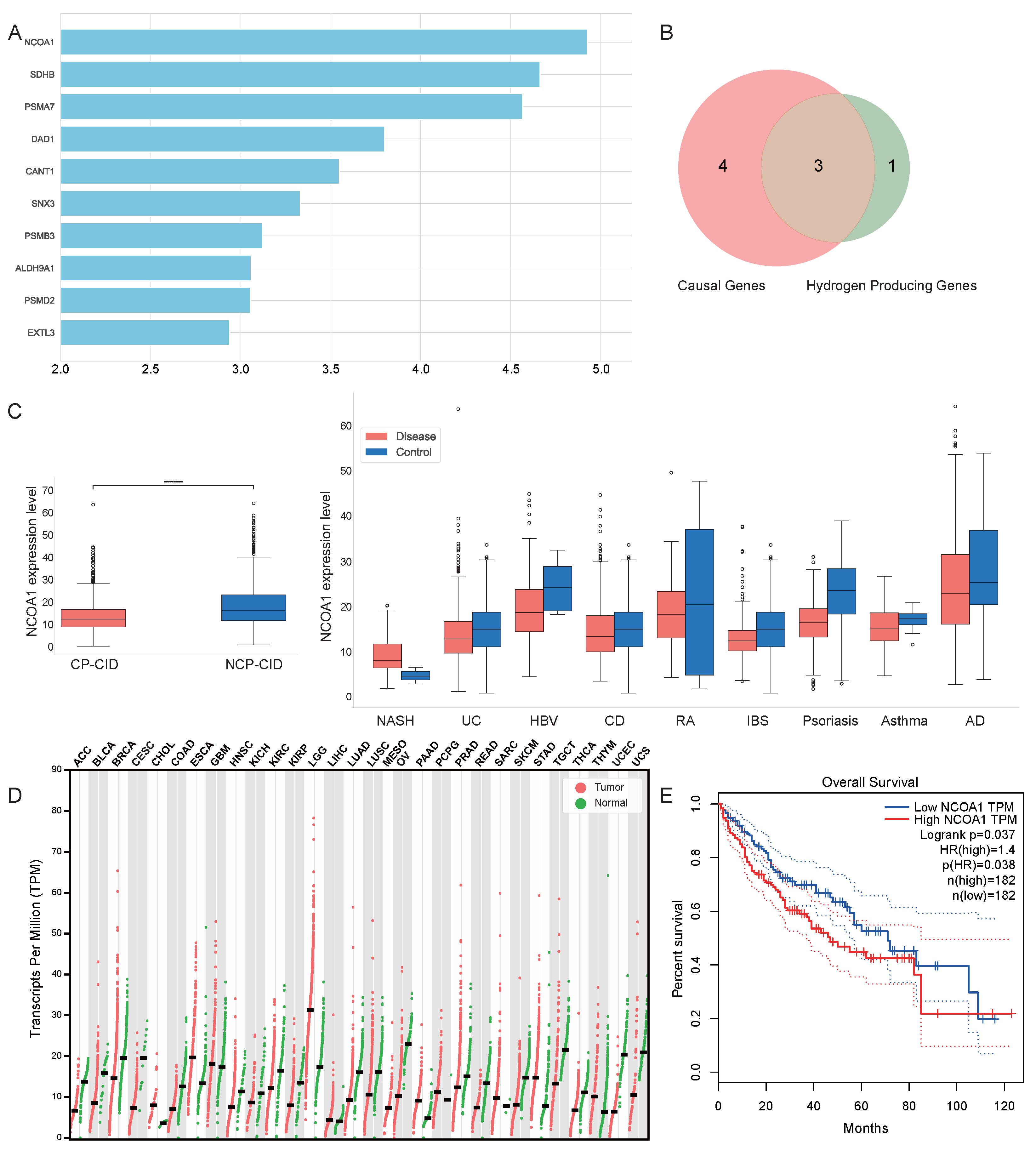
2.4. Analysis of Attribution Results
2.5. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Datasets and Data Processing
4.2. The Definition of NCP-CIDs and CP-CIDs
4.3. Construction of Prior Networks
4.4. Construction of Model
4.5. Evaluation Metrics
4.6. Implementation
5. Conclusions
- FR-BINN effectively classifies samples into four categories by integrating a hierarchical structure based on FR-related pathways. This biologically informed design enhances model performance and ensures the interpretability of its predictions.
- Through a multi-method interpretability analysis, we identified and validated key biomarkers that are critical in distinguishing CP-CIDs from NCP-CIDs. These identified key genes are promising candidate biomarkers for early diagnosis and therapeutic targets.
- Our analysis revealed clear differences in energy metabolism, oxidative stress, and pH regulation between CP-CIDs and NCP-CIDs. This understanding suggests that therapies could be developed to modulate these metabolic pathways or mitigate oxidative stress specifically in CP-CIDs, potentially preventing cancer progression.
- While FR-BINN effectively leverages the strengths of biologically informed neural networks for gene and complex pattern recognition, future research could benefit from incorporating more classical mathematical modeling approaches [91,92,93]. Although these methods typically require substantial mathematical expertise and a firm grasp of the underlying physical or biological mechanisms, they offer complementary perspectives and have the potential to enhance predictive power. This is particularly valuable for long-term predictions or when establishing precise causal links is paramount.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowski, I.; Kulcenty, K.; Suchorska, W. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca, W.A.; Petersen, R.C.; Knopman, D.S.; Hebert, L.E.; Evans, D.A.; Hall, K.S.; Gao, S.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Langa, K.M.; Larson, E.B.; et al. Trends in the incidence and prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and cognitive impairment in the United States. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Baby, D.; Rajguru, J.P.; Patil, P.B.; Thakkannavar, S.S.; Pujari, V.B. Inflammation and cancer. Ann. Afr. Med. 2019, 18, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agnese, A.; Zheng, M.M.; Moreno, S.; Platt, J.M.; Hoang, A.T.; Kannan, D.; Dall’Agnese, G.; Overholt, K.J.; Sagi, I.; Hannett, N.M.; et al. Proteolethargy is a pathogenic mechanism in chronic disease. Cell 2025, 188, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agnese, A.; Platt, J.M.; Zheng, M.M.; Friesen, M.; Dall’Agnese, G.; Blaise, A.M.; Spinelli, J.B.; Henninger, J.E.; Tevonian, E.N.; Hannett, N.M.; et al. The dynamic clustering of insulin receptor underlies its signaling and is disrupted in insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xu, H.; Cai, M.; Gao, J.; Wang, H. Mechanism of INSR clustering with insulin activation and resistance revealed by super-resolution imaging. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 7747–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.J.; Yang, L.; Meluzzi, D.; Oh, S.; Yang, F.; Friedman, M.J.; Wang, S.; Suter, T.; Alshareedah, I.; Gamliel, A.; et al. Phase separation of ligand-activated enhancers licenses cooperative chromosomal enhancer assembly. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Iron homeostasis and ferroptosis in human diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Wang, Q.; Joost, S.; Ferrena, A.; Humphreys, D.T.; Li, Z.; Blum, M.; Krause, K.; Ding, S.; Landais, Y.; et al. Ageing limits stemness and tumorigenesis by reprogramming iron homeostasis. Nature 2024, 637, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Niu, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qian, L.; Liu, P.; et al. Ferroptosis: A cell death connecting oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Zhou, Y.; An, Z.; Xu, Y. Cancer is a survival process under persistent microenvironmental and cellular stresses. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2023, 21, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoris, C.V.; Xiao, L.; Chopra, A.; Chaffin, M.D.; Al Sayed, Z.R.; Hill, M.C.; Mantineo, H.; Brydon, E.M.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, X.S.; et al. Transfer learning enables predictions in network biology. Nature 2023, 618, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, C.; Maan, H.; Pang, K.; Luo, F.; Duan, N.; Wang, B. scGPT: Toward building a foundation model for single-cell multi-omics using generative AI. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Sheng, N.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Mu, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, X. X-lda: An interpretable and knowledge-informed heterogeneous graph learning framework for lncrna-disease association prediction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 167, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. MORGAT: A Model Based Knowledge-Informed Multi-omics Integration and Robust Graph Attention Network for Molecular Subtyping of Cancer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 14–16 December 2023; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 192–206. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, P.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Kong, R.; Zhang, Z. Dual convolutional neural networks with attention mechanisms based method for predicting disease-related lncRNA genes. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Gong, J.; Zeng, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, L. Large-scale foundation model on single-cell transcriptomics. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Fang, A.; Huang, Y.; Giunchiglia, V.; Noori, A.; Schwarz, J.R.; Ektefaie, Y.; Kondic, J.; Zitnik, M. Empowering biomedical discovery with ai agents. Cell 2024, 187, 6125–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Segal, E.; Xing, E. Toward AI-Driven Digital Organism: Multiscale Foundation Models for Predicting, Simulating and Programming Biology at All Levels. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.06993. [Google Scholar]
- Elmarakeby, H.A.; Hwang, J.; Arafeh, R.; Crowdis, J.; Gang, S.; Liu, D.; AlDubayan, S.H.; Salari, K.; Kregel, S.; Richter, C.; et al. Biologically informed deep neural network for prostate cancer discovery. Nature 2021, 598, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.; Liao, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, L.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.P.P. DeepKEGG: A multi-omics data integration framework with biological insights for cancer recurrence prediction and biomarker discovery. Briefings Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Immadi, M.S.; Wang, D.; Zeng, S.; Chan, Y.O.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Joshi, T. IRnet: Immunotherapy response prediction using pathway knowledge-informed graph neural network. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 72, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, E.; Scott, A.M.; Karlsson, C.; Mohanty, T.; Vaara, S.T.; Linder, A.; Malmström, L.; Malmström, J. Interpreting biologically informed neural networks for enhanced proteomic biomarker discovery and pathway analysis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Vaidya, S.; Ruehle, F.; Halverson, J.; Soljačić, M.; Hou, T.Y.; Tegmark, M. Kan: Kolmogorov-arnold networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.19756. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.; Yang, M.; Cui, W.; Kim, J.S.; Talwalkar, A.; Ma, J. Applying interpretable machine learning in computational biology—pitfalls, recommendations and opportunities for new developments. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wu, Y.L.; Toneff, M.J.; Li, D.; Liao, L.; Gao, X.; Bane, F.T.; Tien, J.C.Y.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Z.; et al. NCOA1 directly targets M-CSF1 expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3477–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, G.; Liao, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; et al. NCOA1 promotes angiogenesis in breast tumors by simultaneously enhancing both HIF1α-and AP-1-mediated VEGFa transcription. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Wang, W.; Chen, Q.; Jin, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, C.; Mo, P.; Zhang, L.; et al. Steroid receptor coactivator 1 promotes human hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness through enhancing MMP-9. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Guo, P.; Hong, Y.; Mo, P.; Yu, C. The multifaceted therapeutic value of targeting steroid receptor coactivator-1 in tumorigenesis. Cell Biosci. 2024, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavón, M.A.; Parreño, M.; Téllez-Gabriel, M.; León, X.; Arroyo-Solera, I.; López, M.; Céspedes, M.V.; Casanova, I.; Gallardo, A.; López-Pousa, A.; et al. CKMT1 and NCOA1 expression as a predictor of clinical outcome in patients with advanced-stage head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2016, 38, E1392–E1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Guo, H.; Huang, C.; Kong, X.; Mo, P.; Xiao, N.; et al. Targeting Nuclear Receptor Coactivator SRC-1 Prevents Colorectal Cancer Immune Escape by Reducing Transcription and Protein Stability of PD-L1. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2310037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, D.; Yang, K.; Xu, N.; Peng, J.; Zhu, Z. Research progress on the pathogenesis of the SDHB mutation and related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.B.; Hong, H.S.; Michmerhuizen, B.C.; Lawrence, A.L.E.; Zhang, L.; Knight, J.S.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Abuaita, B.H.; O’Riordan, M.X. Cardiolipin coordinates inflammatory metabolic reprogramming through regulation of Complex II disassembly and degradation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golozar, M.; Motlagh, A.V.; Mahdevar, M.; Peymani, M.; InanlooRahatloo, K.; Ghaedi, K. TBX15 and SDHB expression changes in colorectal cancer serve as potential prognostic biomarkers. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2024, 136, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, K.M.; Lu, M.; Yang, P.; Wu, S.; Cai, C.; Zhong, W.d.; Olumi, A.; Young, R.H.; Wu, C.L. Succinate dehydrogenase B: A new prognostic biomarker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, A.; Pattison, A.D.; Balachander, S.; Boehm, E.; Bowen, B.; Dwight, T.; Rossello, F.J.; Hofmann, O.; Martelotto, L.; Zethoven, M.; et al. Multi-omic analysis of SDHB-deficient pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas identifies metastasis and treatment-related molecular profiles. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Mao, S.; Zhen, N.; Zhu, G.; Bian, Z.; Xie, Y.; Tang, X.; Ding, M.; Wu, H.; Ma, J.; et al. SNORA14A inhibits hepatoblastoma cell proliferation by regulating SDHB-mediated succinate metabolism. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, C.; Tissot, H.; Faron, M.; Baudin, E.; Lamartina, L.; Pradon, C.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Leboulleux, S.; Perfettini, J.L.; Paci, A.; et al. Succinate: A serum biomarker of SDHB-mutated paragangliomas and pheochromocytomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2801–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijano, C.; Trujillo, M.; Castro, L.; Trostchansky, A. Interplay between oxidant species and energy metabolism. Redox Biol. 2016, 8, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Lian, G. ROS and diseases: Role in metabolism and energy supply. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 467, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, M.C. Hepatic iron overload and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2009, 286, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Wati, M.R.; Fatima-Shad, K. Oxidative stress gated by Fenton and Haber Weiss reactions and its association with Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Neurosci. 2015, 2, e60038. [Google Scholar]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.A.; Chimenti, M.; Jacobson, M.P.; Barber, D.L. Dysregulated pH: A perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltai, T. The Ph paradigm in cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xu, Y. Elucidation of functional roles of sialic acids in cancer migration. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, S.E. Evolving evidence for relationships between periodontitis and systemic diseases: Position paper from the Canadian Dental Hygienists Association. Can. J. Dent. Hyg. 2022, 56, 155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nurminen, M.; Karjalainen, A. Epidemiologic estimate of the proportion of fatalities related to occupational factors in Finland. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2001, 27, 161–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, C.J. An effect size primer: A guide for clinicians and researchers. In Methodological Issues and Strategies in Clinical Research, 4th ed.; American Psychological Association: Worcester, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, E.D.; Hurd, S.S.; Barnes, P.J.; Bousquet, J.; Drazen, J.M.; FitzGerald, M.; Gibson, P.; Ohta, K.; O’Byrne, P.; Pedersen, S.E.; et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 31, 143–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salameh, L.; Mahboub, B.; Khamis, A.; Alsharhan, M.; Tirmazy, S.H.; Dairi, Y.; Hamid, Q.; Hamoudi, R.; Al Heialy, S. Asthma severity as a contributing factor to cancer incidence: A cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Bian, J.; Chen, Z.; Fishe, J.N.; Zhang, D.; Braithwaite, D.; George, T.J.; Shenkman, E.A.; Licht, J.D. Cancer incidence after asthma diagnosis: Evidence from a large clinical research network in the United States. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 11871–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDade, E.M. Alzheimer disease. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2022, 28, 648–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Romero, M.; Glymour, M.M.; Hayes-Larson, E.; Mayeda, E.R.; Graff, R.E.; Brenowitz, W.D.; Ackley, S.F.; Witte, J.S.; Kobayashi, L.C. Association between Alzheimer disease and cancer with evaluation of study biases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2025515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Noh, H.M.; Choi, H.G.; Min, K.W.; Kim, N.Y.; Kwon, M.J. Alzheimer’s Disease and Different Types of Cancer Likelihood: Unveiling Disparities and Potential Protective Effects in a Korean Cohort Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolen, S.C.; Evans, M.A.; Fischer, A.; Corrada, M.M.; Kawas, C.H.; Bota, D.A. Cancer—incidence, prevalence and mortality in the oldest-old. A comprehensive review. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 164, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaengebjerg, S.; Skov, L.; Egeberg, A.; Loft, N.D. Prevalence, incidence, and risk of cancer in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Kurlander, J.; Eswaran, S. Irritable bowel syndrome: A clinical review. Jama 2015, 313, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yuan, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Sun, F.; Zhan, S.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S. Irritable bowel syndrome and long-term risk of cancer: A prospective cohort study among 0.5 million adults in UK biobank. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2022, 117, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, B.; Basyal, B.; Sarao, M.S.; Nookala, V.; Thein, Y. Prevalence of cancer in rheumatoid arthritis: Epidemiological study based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Cureus 2020, 12, e7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydon, M.; Pinto, S.; De Rycke, Y.; Fautrel, B.; Mariette, X.; Seror, R.; Tubach, F. Risk of cancer for patients with rheumatoid arthritis versus general population: A national claims database cohort study. Lancet Reg.-Health -Eur. 2023, 35, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajendran, M.; Loganathan, P.; Jimenez, G.; Catinella, A.P.; Ng, N.; Umapathy, C.; Ziade, N.; Hashash, J.G. A comprehensive review and update on ulcerative colitis. Disease-A-Month 2019, 65, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jess, T.; Rungoe, C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavan, C.; Abrams, K.; Mayberry, J. Meta-analysis: Colorectal and small bowel cancer risk in patients with Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.S.; Rinella, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Mapakshi, S.; Natarajan, Y.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Richardson, P.A.; Li, L.; Desiderio, R.; Thrift, A.P.; Asch, S.M.; et al. Risk of hepatocellular cancer in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.G.; Ge, Z.; Zhu, J.; Dai, J.; Du, L.B.; Yu, C.; Guo, Y.; et al. Associations between hepatitis B virus infection and risk of all cancer types. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e195718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olazagasti, J.M.; Baez, P.J.; Wetter, D.A.; Ernste, F.C. Cancer risk in dermatomyositis: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, J.K.; Kim, W.B.; Baibergenova, A.; Alhusayen, R. Risk of malignancy in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2017, 21, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierret, C.; Mulliez, A.; Le Bihan-Benjamin, C.; Moisset, X.; Bousquet, P.J.; Leray, E. Cancer Risk Among Patients With Multiple Sclerosis: A 10-Year Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study. Neurology 2024, 103, e209885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco-Lévy, P.; Foch, C.; Grelaud, A.; Sabidó, M.; Lacueille, C.; Jové, J.; Boutmy, E.; Blin, P. Incidence and risk of cancer among multiple sclerosis patients: A matched population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, C.; Cao, S.; Sheng, T.; Dong, N.; Xu, Y. Fenton reactions drive nucleotide and ATP syntheses in cancer. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 10, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Skaro, M.F.; Wu, Y.; Qu, Z.; Mao, F.; Zhao, S.; Xu, Y. Metabolic reprogramming in cancer is induced to increase proton production. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Mu, X.; An, Z.; Xu, Y. Elucidating the Functional Roles of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Rao, Y. Comprehensive single-cell RNA-seq analysis using deep interpretable generative modeling guided by biological hierarchy knowledge. Briefings Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, M.; Taly, A.; Yan, Q. Axiomatic attribution for deep networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 3319–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Dhamdhere, K.; Sundararajan, M.; Yan, Q. How Important is a Neuron. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shrikumar, A.; Su, J.; Kundaje, A. Computationally efficient measures of internal neuron importance. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.09946. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Tang, J.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; et al. A survey on large language model based autonomous agents. Front. Comput. Sci. 2024, 18, 186345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Peng, Z.; Du, X.; Zheng, T.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, W.; et al. A Comparative Study on Reasoning Patterns of OpenAI’s o1 Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.13639. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Yu, W.; He, T.; Wang, H.; Peng, W.; Liu, M.; Qin, B.; Liu, T. Navigate through enigmatic labyrinth a survey of chain of thought reasoning: Advances, frontiers and future. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.15402. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, S.; Ou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chen, X.; Yao, Y.; Deng, S.; Tan, C.; Huang, F.; Chen, H. Reasoning with language model prompting: A survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2212.09597. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Tian, Z.; Che, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Ge, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Ma, Q.; Pan, J. DMRdb: A disease-centric Mendelian randomization database for systematically assessing causal relationships of diseases with genes, proteins, CpG sites, metabolites and other diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1363–D1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkowski, P.J. Mathematical Structures of Ergodicity and Chaos in Population Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 312. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak-Czochra, A.; Karch, G.; Suzuki, K. Instability of Turing patterns in reaction-diffusion-ODE systems. J. Math. Biol. 2017, 74, 583–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasota, A.; Mackey, M.C.; Ważewska-Czyżewska, M. Minimizing therapeutically induced anemia. J. Math. Biol. 1981, 13, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y. FR-BINN: Biologically Informed Neural Networks for Enhanced Biomarker Discovery and Pathway Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146670
Cao Y, Yin C, Zhou X, Zhao Y. FR-BINN: Biologically Informed Neural Networks for Enhanced Biomarker Discovery and Pathway Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146670
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yangkun, Chaoyi Yin, Xinsen Zhou, and Yonghe Zhao. 2025. "FR-BINN: Biologically Informed Neural Networks for Enhanced Biomarker Discovery and Pathway Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146670
APA StyleCao, Y., Yin, C., Zhou, X., & Zhao, Y. (2025). FR-BINN: Biologically Informed Neural Networks for Enhanced Biomarker Discovery and Pathway Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146670





