Administration of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Lowers the Initial Levels of IL6 and TNF-Alpha in the Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
1.2. Cytokines in Necrotizing Enterocolitis
1.3. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
2. Results
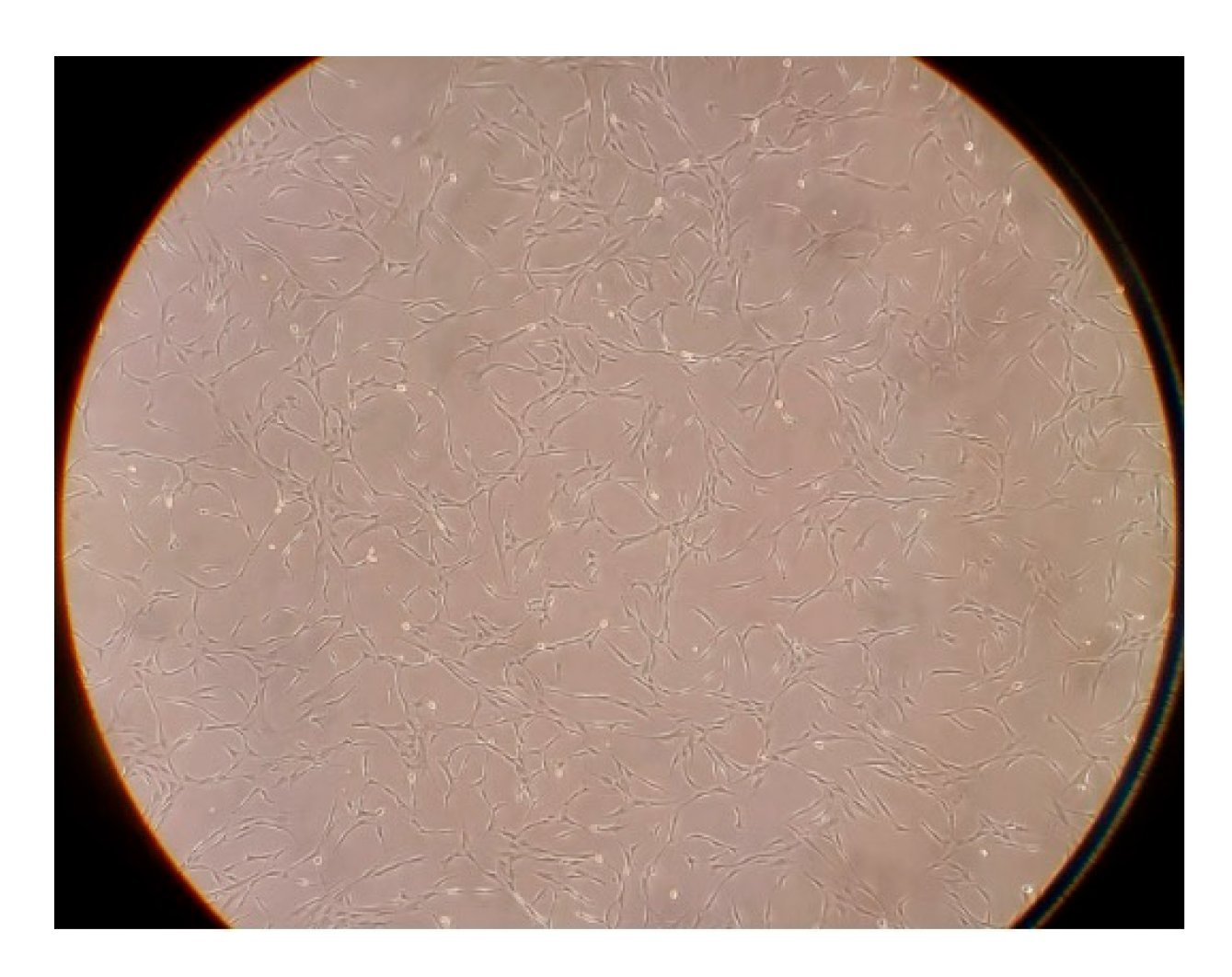
2.1. Engraftment
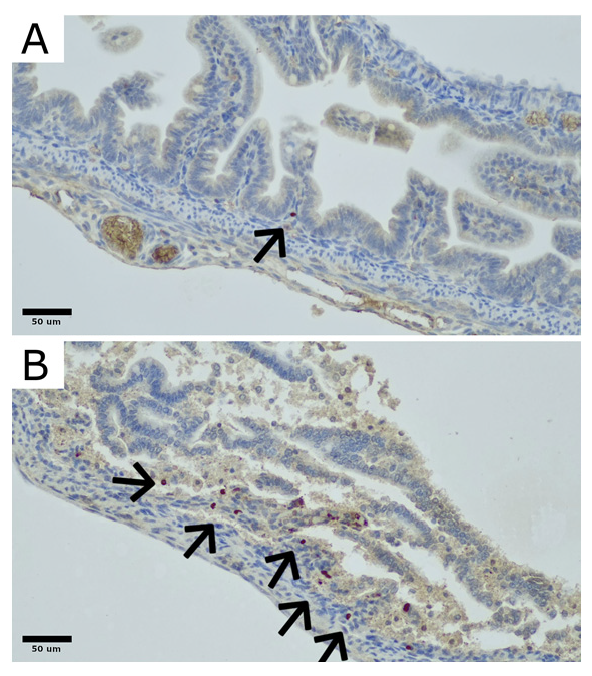
2.2. Histopathology
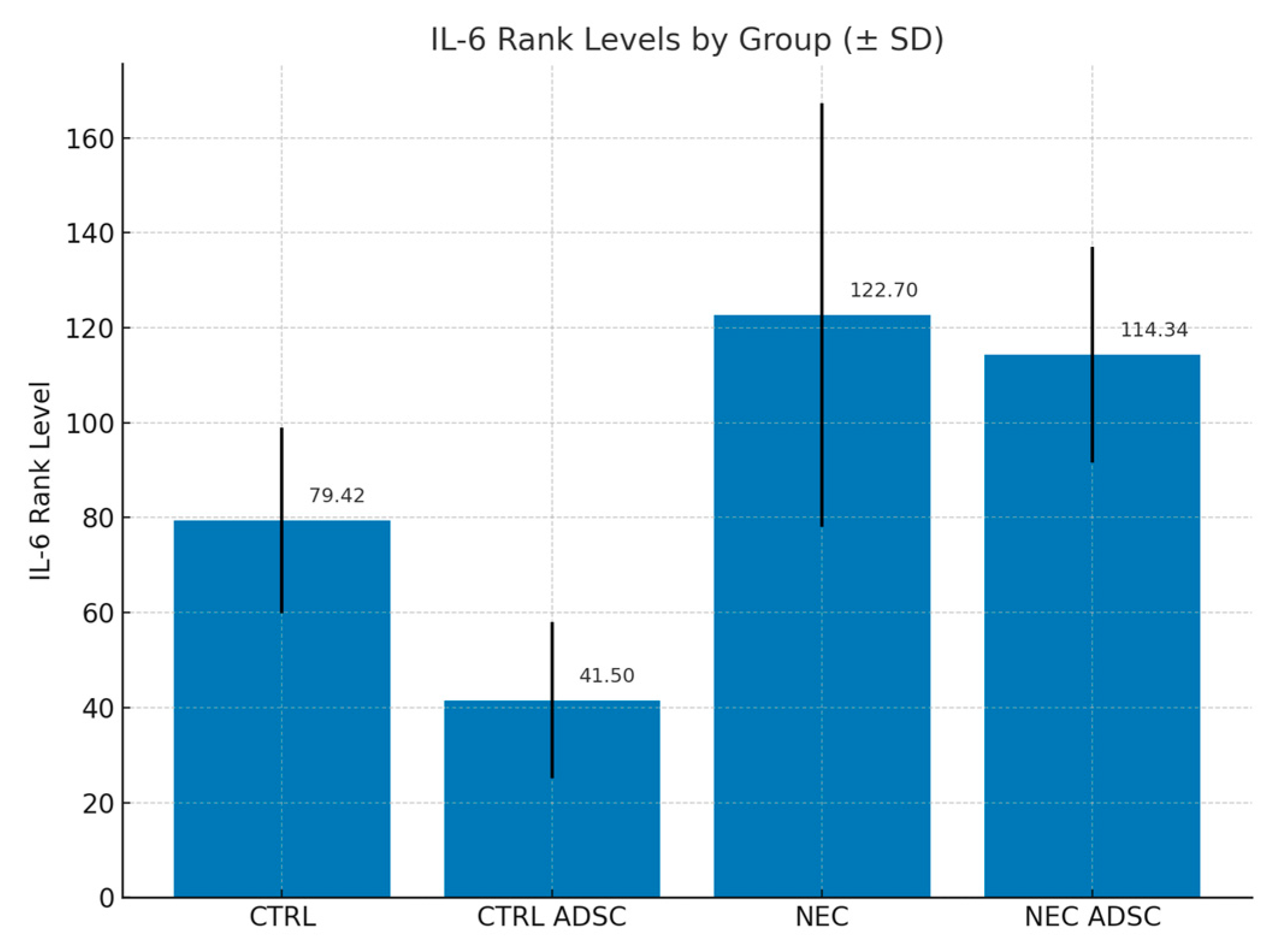
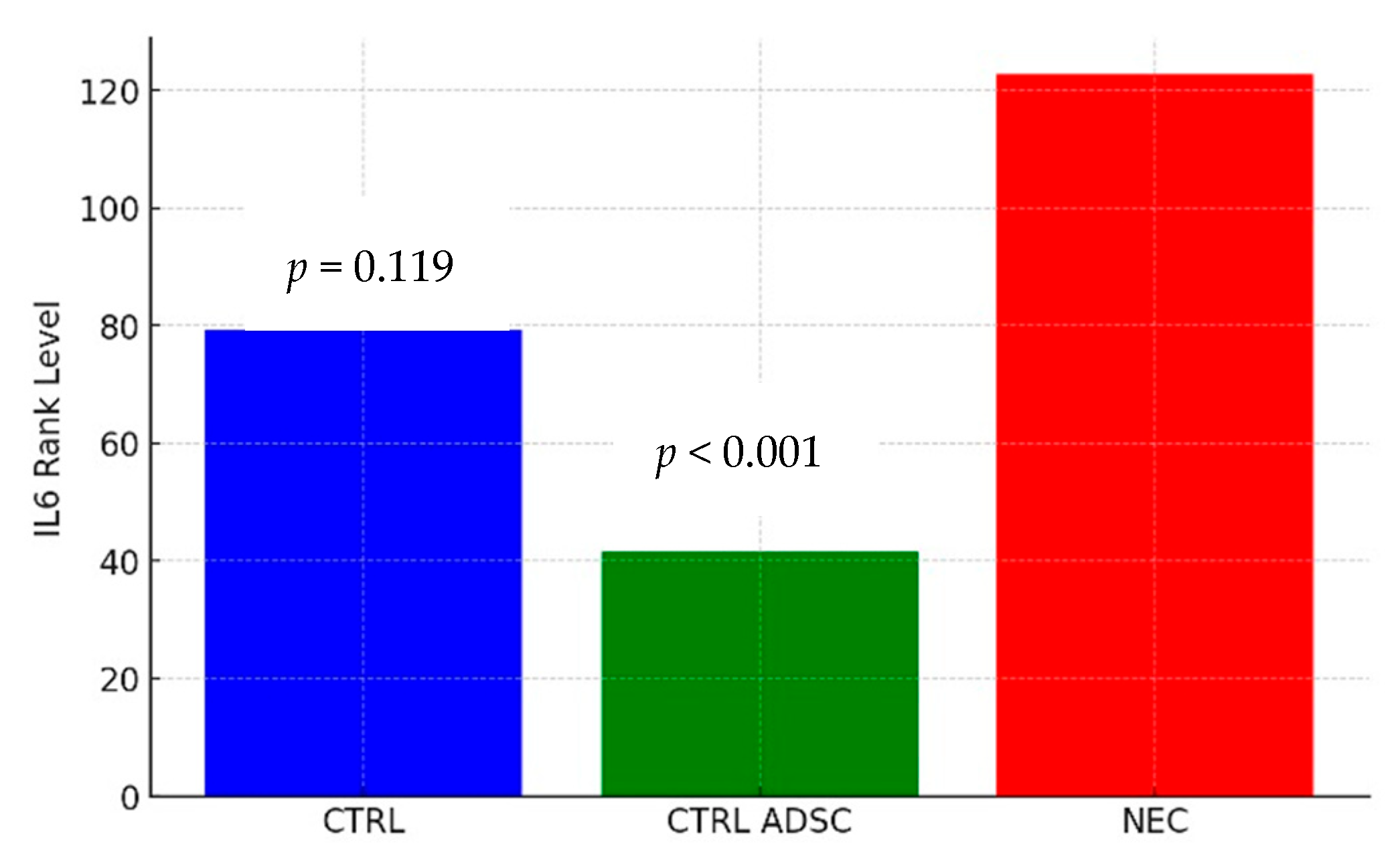
2.3. Cytokine Concentrations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. NEC Protocol
4.2. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
4.3. Engraftment Analysis
4.4. Cytokine Concentrations—ELISA Analysis
4.5. Histopathology
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neu, J. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Future. Neonatology 2020, 117, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alganabi, M.; Lee, C.; Bindi, E.; Li, B.; Pierro, A. Recent advances in understanding necrotizing enterocolitis. F1000Research 2019, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, S.; Rees, C.M.; Hall, N.J. Current Research on the Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Management of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Neonatology 2017, 111, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginglen, J.G.; Butki, N. Necrotizing Enterocolitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wolski, M. Modification of Experimental Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) in Rat Pups by Single Exposure to Hypothermia and Hypoxia and Impact of Mother’s Milk on Incidence of Disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e943443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.M.; Sampah, M.E.S.; Duess, J.W.; Ishiyama, A.; Ahmad, R.; Sodhi, C.P.; Hackam, D.J. Models of necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Perinatol. 2023, 47, 151695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, C.; Richardson, W.; Gribar, S.; Hackam, D.J. The development of animal models for the study of necrotizing enterocolitis. Dis. Model. Mech. 2008, 1, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markel, T.A.; Crisostomo, P.R.; Wairiuko, G.M.; Pitcher, J.; Tsai, B.M.; Meldrum, D.R. Cytokines in necrotizing enterocolitis. Shock 2006, 25, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, M.A.; Good, M.; Weitkamp, J.H. Innate and adaptive immunity in necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MohanKumar, K.; Namachivayam, K.; Ho, T.T.; Torres, B.A.; Ohls, R.K.; Maheshwari, A. Cytokines and growth factors in the developing intestine and during necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Perinatol. 2017, 41, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, M.D.; Richardson, W.M.; Sodhi, C.P.; Russo, A.; Hackam, D.J. Intestinal stem cells and their roles during mucosal injury and repair. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 167, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, V.; Karin, M. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracey, K.J.; Fong, Y.; Hesse, D.G.; Manogue, K.R.; Lee, A.T.; Kuo, G.C.; Lowry, S.F.; Cerami, A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature 1987, 330, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebach, D.R.; Riehl, T.E.; Stenson, W.F. Opposing effects of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and 2 in sepsis due to cecal ligation and puncture. Shock 2005, 23, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pender, S.L.; Fell, J.M.; Chamow, S.M.; Ashkenazi, A.; MacDonald, T.T. A p55 TNF receptor immunoadhesin prevents T cell-mediated intestinal injury by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase production. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 4098–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pender, S.L.; Braegger, C.; Gunther, U.; Monteleone, G.; Meuli, M.; Schuppan, D.; Macdonald, T.T. Matrix metalloproteinases in necrotising enterocolitis. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 54, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghadban, S.; Bunnell, B.A. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Immunomodulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential. Physiology 2020, 35, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Schubiger, G.; Harder, F.; Müller, A.M. Stem cell plasticity in mammals and transdetermination in Drosophila: Common themes? Stem Cells 2000, 18, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banas, A.; Teratani, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tokuhara, M.; Takeshita, F.; Quinn, G.; Okochi, H.; Ochiya, T. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a source of human hepatocytes. Hepatology 2007, 46, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strioga, M.; Viswanathan, S.; Darinskas, A.; Slaby, O.; Michalek, J. Same or not the same? Comparison of adipose tissue-derived versus bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem and stromal cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 2724–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Song, K.; Fan, X.; Ma, X.; Cui, Z. Adipose-derived stem cell: A better stem cell than BMSC. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2008, 26, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhou, X.; Wen, J.; Jin, M.; Cang, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, D.; Ma, Y. Isolation, expansion, and differentiation of goat adipose-derived stem cells. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.N.; Rosenkrantz, W.S.; Hong, J.H.; Griffin, C.E.; Mendelsohn, C.M. Evaluation of the potential use of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in the treatment of canine atopic dermatitis: A pilot study. Vet. Ther. 2010, 11, E1–E14. [Google Scholar]
- Efimenko, A.; Starostina, E.; Kalinina, N.; Stolzing, A. Angiogenic properties of aged adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells after hypoxic conditioning. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloh, C.J.; Olson, J.K.; Wang, Y.; Vu, J.; Gartner, S.; Besner, G.E. Evaluating the efficacy of different types of stem cells in preserving gut barrier function in necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 214, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloh, C.J.; Olson, J.K.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Besner, G.E. Stem cells and necrotizing enterocolitis: A direct comparison of the efficacy of multiple types of stem cells. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayman, C.; Uckan, D.; Kilic, E.; Ulus, A.T.; Tonbul, A.; Murat Hirfanoglu, I.; Helvacioglu, F.; Haltas, H.; Koseoglu, B.; Tatli, M.M. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in necrotizing enterocolitis: A rat study. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolski, M.; Ciesielski, T.; Buczma, K.; Fus, Ł.; Girstun, A.; Trzcińska-Danielewicz, J.; Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska, A. Administration of Adipose Tissue Derived Stem Cells Before the Onset of the Disease Lowers the Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines IL-1 and IL-6 in the Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolski, M.; Ciesielski, T.; Buczma, K.; Fus, Ł.; Girstun, A.; Trzcińska-Danielewicz, J.; Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska, A. Administration of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells After the Onset of the Disease Does Not Lower the Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines IL1 and IL6 in a Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yuan, Q.; Xie, L. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Immunomodulation: Properties and Clinical Application. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 3057624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, K.B.; Calkins, C.L.; Golubkova, A.; Leiva, T.; Schlegel, C.; Hunter, C.J. Despite Recovery from Necrotizing Enterocolitis Infants Retain a Hyperinflammatory Response to Injury. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkoe, T.; Baumann, S.; Weninger, M.; Pones, M.; Reck, C.; Rebhandl, W.; Oehler, R. Comprehensive evaluation of 11 cytokines in premature infants with surgical necrotizing enterocolitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.X.; Fan, H.; Tang, Q.; Shou, Z.X.; Zuo, D.M.; Zou, Z.; Xu, M.; Chen, Q.Y.; Peng, Y.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect against Experimental Colitis via Attenuating Colon Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, K.; Hou, J.; Shao, C.; Wang, Y. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zani, A.; Cananzi, M.; Fascetti-Leon, F.; Lauriti, G.; Smith, V.V.; Bollini, S.; Ghionzoli, M.; D’Arrigo, A.; Pozzobon, M.; Piccoli, M.; et al. Amniotic fluid stem cells improve survival and enhance repair of damaged intestine in necrotising enterocolitis via a COX-2 dependent mechanism. Gut 2014, 63, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolocinska, A.; Siennicka, K.; Debski, T.; Gut, G.; Mazur, S.; Gajewska, M.; Kaminski, A.; Pojda, Z. Comparison of mouse, rat and rabbit models for adipose—Derived stem cells (ASC) research. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2020, 68, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimatsu, H.; Onoda, A.; Kazama, T.; Nishijima, K.; Shimoyama, Y.; Go, S.; Ueda, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Hayakawa, M.; et al. Dedifferentiated fat cells administration ameliorates abnormal expressions of fatty acids metabolism-related protein expressions and intestinal tissue damage in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Fatheree, N.Y.; Liu, X.; Pacheco, S.E.; Tatevian, N.; Rhoads, J.M. Changes in intestinal Toll-like receptors and cytokines precede histological injury in a rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G442–G450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pisano, C.; Besner, G.E. Potential role of stem cells in disease prevention based on a murine model of experimental necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xia, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Hua, Z. Clinical characteristics of neonatal fulminant necrotizing enterocolitis in a tertiary Children’s hospital in the last 10 years. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.M.; O’Connor, A.; Ansari, M.A.Y.; Vu, B.; Hobart, H.; Paschal, J.L.; Multani, H.; Josephson, C.D.; Okhomina, V. Hematological predictors of mortality in neonates with fulminant necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akduman, H.; Dilli, D.; Ergün, E.; Çakmakçı, E.; Çelebi, S.K.; Çitli, R.; Zenciroğlu, A. Successful Mesenchymal Stem Cell Application in Supraventricular Tachycardia-Related Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A Case Report. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2021, 40, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
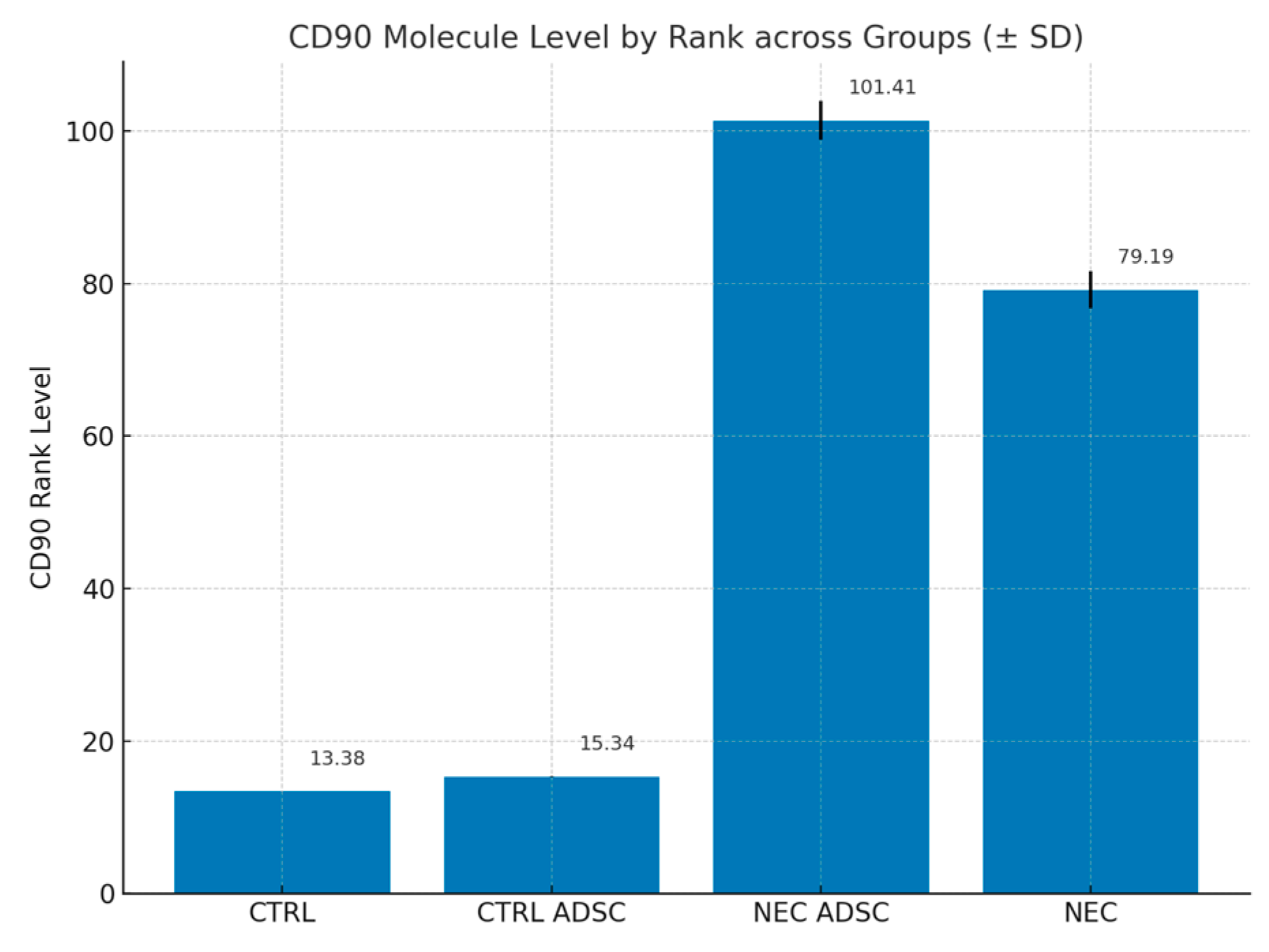
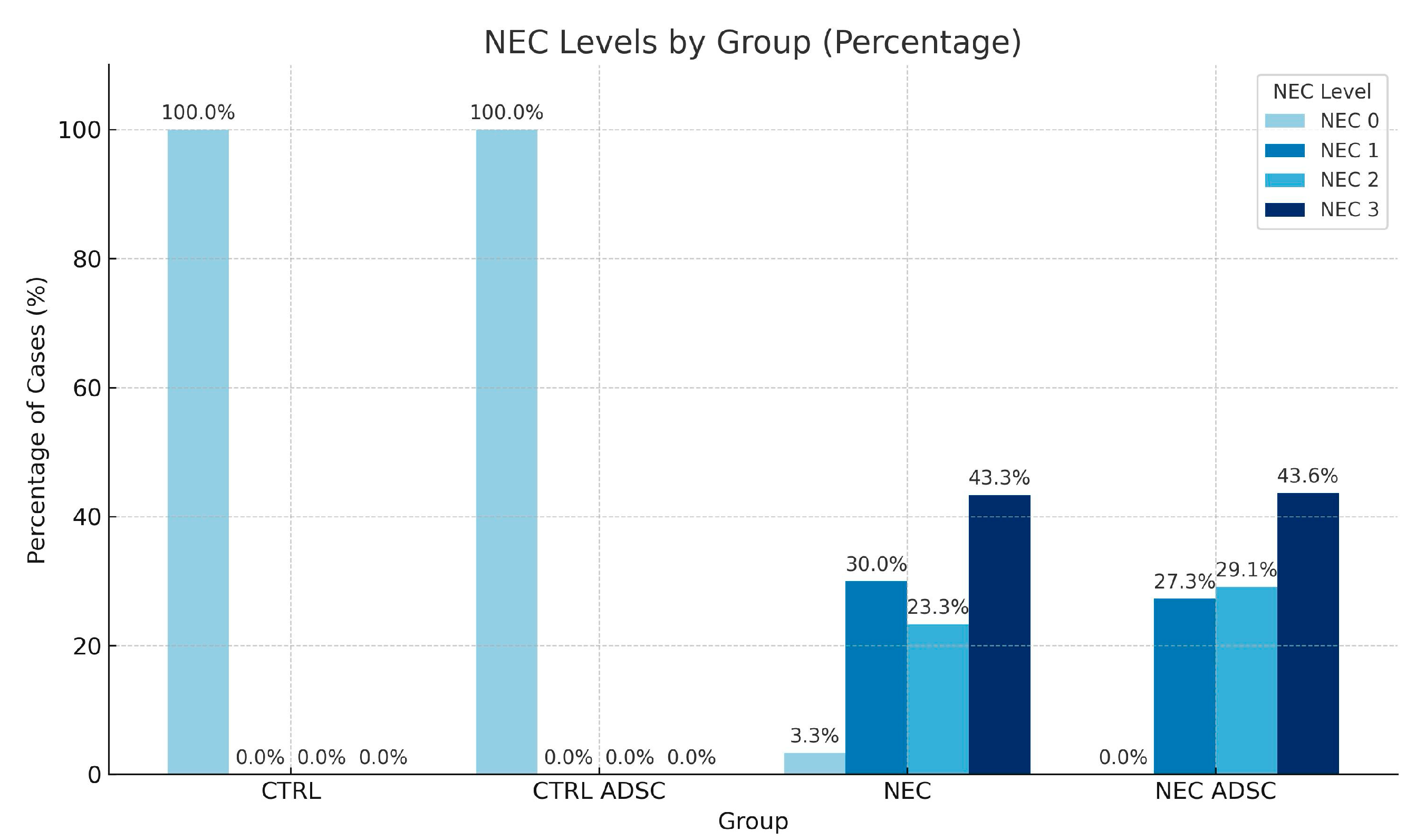
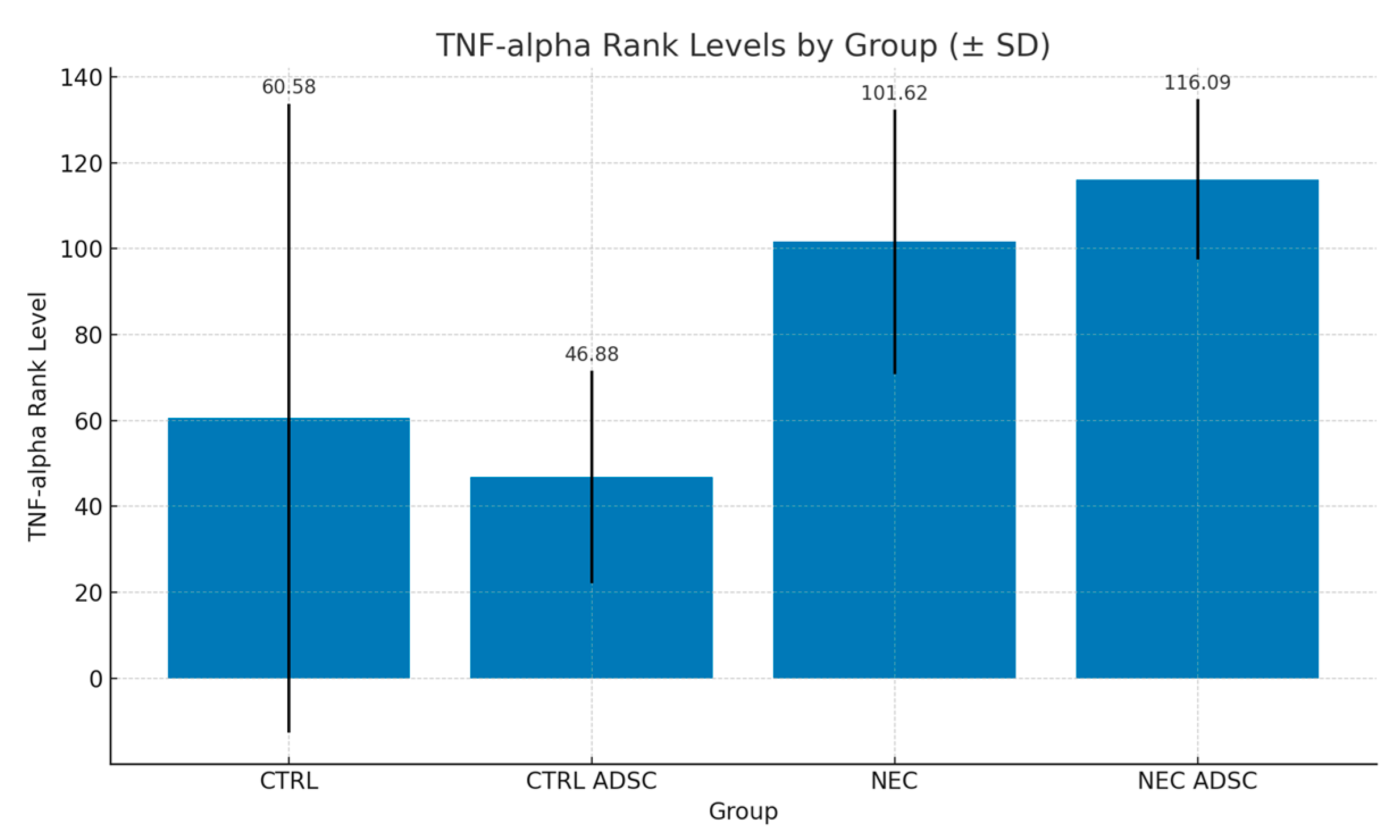
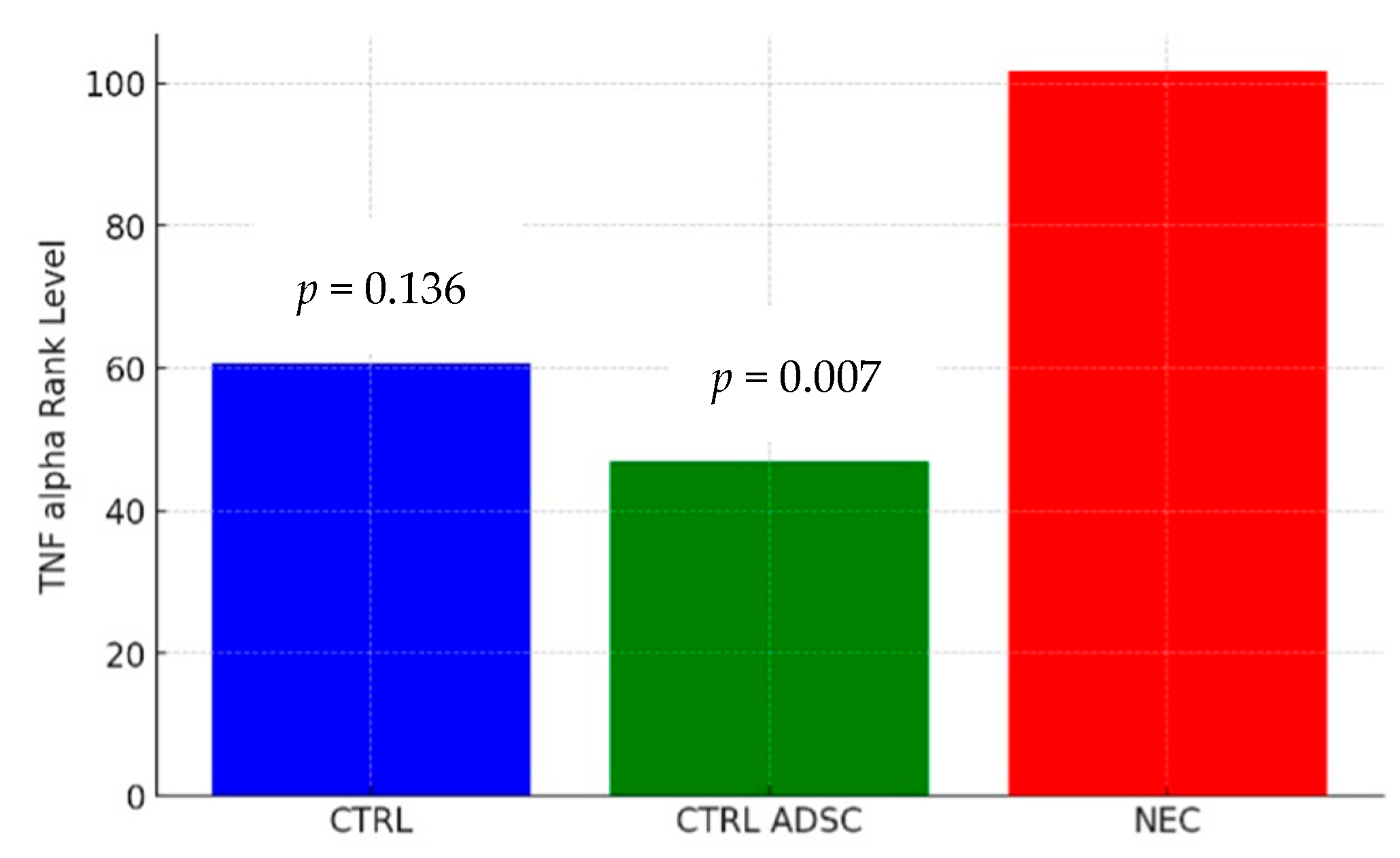

| Group | n | Min | Max | M | SD | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 12 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 13.38 |
| CTRL ADSC | 16 | 0 | 10 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 15.34 |
| NEC ADSC | 55 | 0 | 10 | 3.1 | 2.58 | 101.41 |
| NEC | 60 | 0 | 10 | 2.17 | 2.4 | 79.19 |
| Group | CTRL | CTRL ADSC | NEC | NEC ADSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEC | ||||
| 0 | 12 (100%) | 16 (100%) | 2 (3.33%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| 1 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 18 (30.00%) | 15 (27.27%) |
| 2 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 14 (23.33%) | 16 (29.09%) |
| 3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 26 (43.33%) | 24 (43.64%) |
| Total | 12 (100%) | 16 (100%) | 60 (100.00%) | 55 (100%) |
| Group | n | Min | Max | M | SD | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 12 | 35.33 | 300.4 | 71.14 | 73.16 | 60.58 |
| CTRL ADSC | 16 | 6.45 | 100.3 | 46.26 | 24.73 | 46.88 |
| NEC | 60 | 23.15 | 212.4 | 71.22 | 30.78 | 101.62 |
| NEC ADSC | 55 | 28.5 | 109.4 | 75.78 | 18.68 | 116.09 |
| Group | n | Min | Max | M | SD | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 12 | 35.33 | 100.36 | 67.75 | 19.60 | 79.42 |
| CTRL ADSC | 16 | 25.44 | 85.46 | 51.54 | 16.45 | 41.50 |
| NEC | 60 | 25.30 | 220.47 | 94.55 | 44.64 | 122.70 |
| NEC ADSC | 55 | 29.46 | 150.38 | 81.12 | 22.7 | 114.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wolski, M.; Ciesielski, T.; Buczma, K.; Fus, Ł.; Girstun, A.; Trzcińska-Danielewicz, J.; Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska, A. Administration of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Lowers the Initial Levels of IL6 and TNF-Alpha in the Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146555
Wolski M, Ciesielski T, Buczma K, Fus Ł, Girstun A, Trzcińska-Danielewicz J, Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska A. Administration of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Lowers the Initial Levels of IL6 and TNF-Alpha in the Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146555
Chicago/Turabian StyleWolski, Marek, Tomasz Ciesielski, Kasper Buczma, Łukasz Fus, Agnieszka Girstun, Joanna Trzcińska-Danielewicz, and Agnieszka Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska. 2025. "Administration of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Lowers the Initial Levels of IL6 and TNF-Alpha in the Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146555
APA StyleWolski, M., Ciesielski, T., Buczma, K., Fus, Ł., Girstun, A., Trzcińska-Danielewicz, J., & Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska, A. (2025). Administration of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Lowers the Initial Levels of IL6 and TNF-Alpha in the Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146555







