FcRL1, a New B-Cell-Activating Co-Receptor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of FcRL1 Molecules
3. Expression Pattern of FcRL1 Molecules
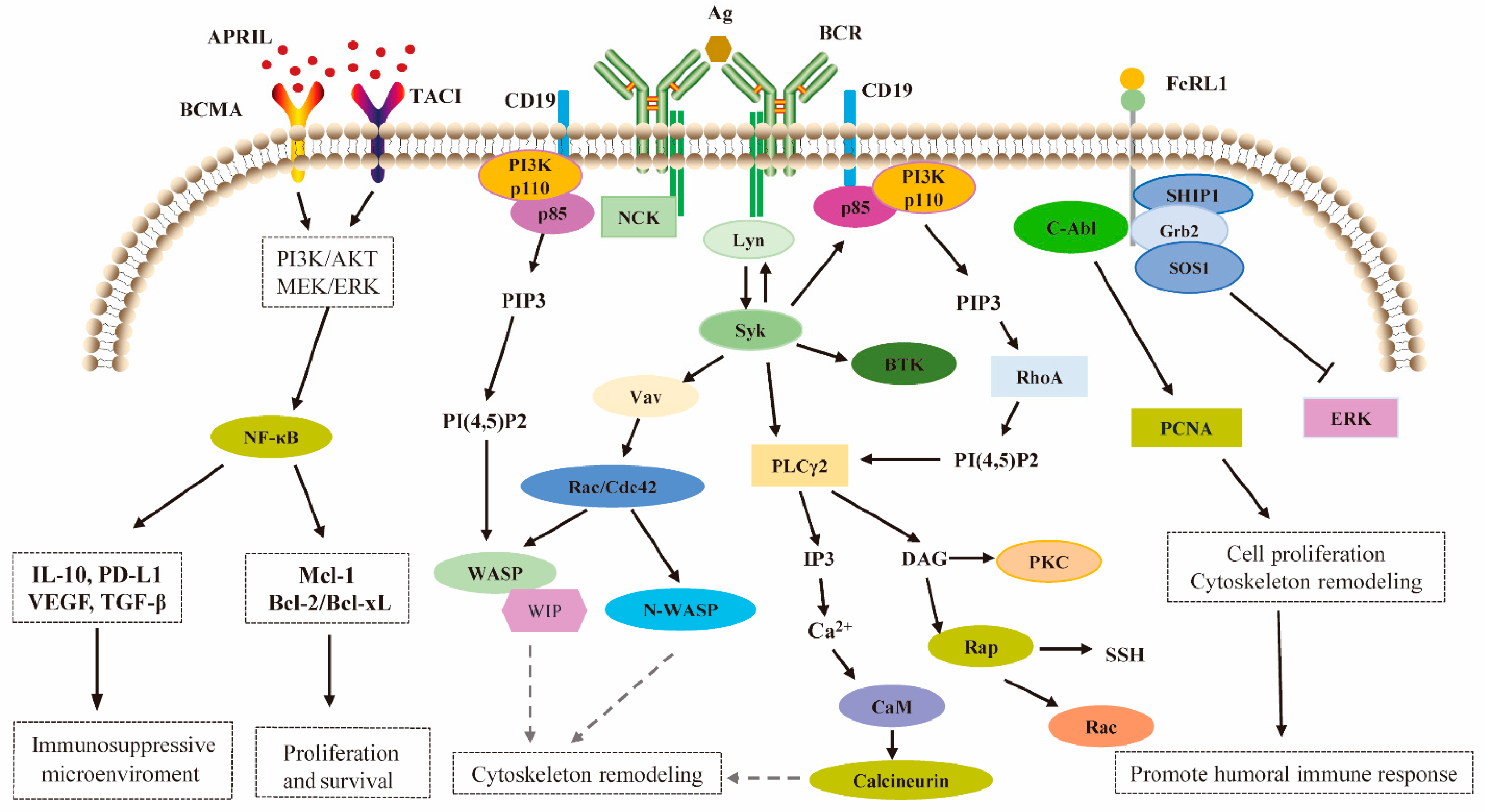
4. Molecular Mechanism of FcRL1 Regulating BCR-Mediated Immune Activation
5. FcRL1 Assumes the Regulatory Function Through Intracellular Tyrosine Motifs
6. FcRL1 Regulates the Humoral Immune Response of B-Cells
7. The Aberrant Expression of FcRL1 Observed in Patients with B-Cell Malignancy
8. Similarities and Differences Between FcRL1 and Other FcRLs in B-Cell Functional Modulation
- FcRL2
- FcRL3
- FcRL4
- FcRL5
9. The Potential of FcRL1 to Become a New Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) Target for the Treatment of B-Cell Malignancies
10. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walzik, D.; Belen, S.; Wilisch, K.; Kupjetz, M.; Kirschke, S.; Esser, T.; Joisten, N.; Schenk, A.; Proschinger, S.; Zimmer, P. Impact of Exercise on Markers of B Cell-Related Immunity: A Systematic Review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2024, 13, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, I.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Cattoretti, G.; Mendelsohn, C.; Dalla-Favera, R. IRTAs: A New Family of Immunoglobulinlike Receptors Differentially Expressed in B Cells. Blood 2002, 99, 2662–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, D.T.; Carroll, M.C. Regulation of B Lymphocyte Responses to Foreign and Self-Antigens by the CD19/CD21 Complex. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubata, T. Inhibitory B Cell Co-Receptors and Autoimmune Diseases. Immunol. Med. 2019, 42, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, A.A.M.; Nor, A.K.C.M.; Redzwan, N.M. The Immunological Understanding on Germinal Center B Cells in Psoriasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2024, 239, e31266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.S. Fc Receptor-like Molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 525–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, C.-M.; Davis, R.S.; Gartland, L.A.; Fine, W.D.; Cooper, M.D. FcRH1: An Activation Coreceptor on Human B Cells. Blood 2005, 105, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reth, M. Antigen Receptor Tail Clue. Nature 1989, 338, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xie, H.; Zhao, M.; Ahsan, A.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Yi, J.; Yang, Z.; Wu, C.; Raman, I.; et al. Fc Receptor-like 1 Intrinsically Recruits c-Abl to Enhance B Cell Activation and Function. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw0315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, V.; Liu, Y.J.; Magalski, A.; de Bouteiller, O.; Banchereau, J.; Capra, J.D. Analysis of Somatic Mutation in Five B Cell Subsets of Human Tonsil. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, A.G.; Zheng, B.; Elkins, K.; Chang, W.; Du, C.; Dowd, P.; Yen, L.; Tan, C.; Hongo, J.-A.; Koeppen, H.; et al. Expression Pattern of the Human FcRH/IRTA Receptors in Normal Tissue and in B-Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamzadeh, D.; Kazemi, T.; Amirghofran, Z.; Shabani, M. Update on Fc Receptor-like (FCRL) Family: New Immunoregulatory Players in Health and Diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidi, M.K.; Huang, J.; Honjo, K.; Li, R.; Tabengwa, E.M.; Neeli, I.; Randall, N.L.; Ponnuchetty, M.V.; Radic, M.; Leu, C.-M.; et al. FCRL1 Immunoregulation in B Cell Development and Malignancy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1251127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, N.E.; Batista, F.D. Early Events in B Cell Activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 185–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Harder, K.W.; Huntington, N.D.; Hibbs, M.L.; Tarlinton, D.M. Lyn Tyrosine Kinase: Accentuating the Positive and the Negative. Immunity 2005, 22, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monroe, J.G. ITAM-Mediated Tonic Signalling through Pre-BCR and BCR Complexes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.A.; Pleiman, C.M.; Pao, L.; Schneringer, J.; Hippen, K.; Cambier, J.C. Phosphorylated Immunoreceptor Signaling Motifs (ITAMs) Exhibit Unique Abilities to Bind and Activate Lyn and Syk Tyrosine Kinases. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 1995, 155, 4596–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Tezuka, T.; Maeda, A.; Inazu, T.; Yamanashi, Y.; Gu, H.; Kurosaki, T.; Yamamoto, T. Cbl-b Positively Regulates Btk-Mediated Activation of Phospholipase C-Gamma2 in B Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, T.; Tsukada, S. BLNK: Connecting Syk and Btk to Calcium Signals. Immunity 2000, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiai, M.; Kurosaki, M.; Pappu, R.; Okawa, K.; Ronko, I.; Fu, C.; Shibata, M.; Iwamatsu, A.; Chan, A.C.; Kurosaki, T. BLNK Required for Coupling Syk to PLC Gamma 2 and Rac1-JNK in B Cells. Immunity 1999, 10, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, T. Regulation of B-Cell Signal Transduction by Adaptor Proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, L.; Sasaki, Y.; Calado, D.P.; Zhang, B.; Paik, J.H.; DePinho, R.A.; Kutok, J.L.; Kearney, J.F.; Otipoby, K.L.; Rajewsky, K. PI3 Kinase Signals BCR-Dependent Mature B Cell Survival. Cell 2009, 139, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Shaheen, S.; Liu, S.; Zheng, W.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Growth of B Cell Receptor Microclusters Is Regulated by PIP2 and PIP3 Equilibrium and Dock2 Recruitment and Activation. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 2541–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolar, P. Cytoskeletal Control of B Cell Responses to Antigens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleire, S.J.; Goldman, J.P.; Carrasco, Y.R.; Weber, M.; Bray, D.; Batista, F.D. B Cell Ligand Discrimination through a Spreading and Contraction Response. Science 2006, 312, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Auzins, A.; Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Harnischfeger, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.-H.; Zheng, W.; Liu, W. The Synaptic Recruitment of Lipid Rafts Is Dependent on CD19-PI3K Module and Cytoskeleton Remodeling Molecules. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, J.M.; Murphy, M.K.; Wang, X.; Wilson, T.J. FCRL1 Regulates B Cell Receptor-Induced ERK Activation through GRB2. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2021, 207, 2688–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, Z.; Sharifzadeh, S.; Yar-Ahmadi, V.; Andalib, A.; Eskandari, N. Fc Receptor-Like 1 as a Promising Target for Immunotherapeutic Interventions of B-Cell-Related Disorders. Biomark. Insights 2019, 14, 1177271919882351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, G.; Wan, Z.; Liu, C.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, W. How B Cells Remember? A Sophisticated Cytoplasmic Tail of mIgG Is Pivotal for the Enhanced Transmembrane Signaling of IgG-Switched Memory B Cells. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2015, 118, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, W.; Sui, Y.; Li, H.; Shi, X.; Guo, X.; Qi, H.; Xu, C.; Liu, W. Acidic Phospholipids Govern the Enhanced Activation of IgG-B Cell Receptor. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, F.Y.; van Haaren, J.J.; Langley, D.B.; Christ, D.; Andrews, N.W.; Song, W. Surface-Associated Antigen Induces Permeabilization of Primary Mouse B-Cells and Lysosome Exocytosis Facilitating Antigen Uptake and Presentation to T-Cells. eLife 2021, 10, e66984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natkanski, E.; Lee, W.-Y.; Mistry, B.; Casal, A.; Molloy, J.E.; Tolar, P. B Cells Use Mechanical Energy to Discriminate Antigen Affinities. Science 2013, 340, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillane, K.M.; Tolar, P. Mechanics of Antigen Extraction in the B Cell Synapse. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 101, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Nagata, S.; Ise, T.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Pastan, I. FCRL1 on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Hairy Cell Leukemia, and B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma as a Target of Immunotoxins. Blood 2008, 111, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, Z.; Sharifzadeh, S.; Zare, F.; Eskandari, N. Fc Receptor-like 1 (FCRL1) Is a Novel Biomarker for Prognosis and a Possible Therapeutic Target in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, T.; Asgarian-Omran, H.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Shabani, M.; Memarian, A.; Sharifian, R.A.; Razavi, S.M.; Jeddi-Tehrani, M.; Rabbani, H.; Shokri, F. Fc Receptor-like 1-5 Molecules Are Similarly Expressed in Progressive and Indolent Clinical Subtypes of B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 2113–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, N.L.; Talpaz, M.; Nicolson, G.L. Chromatin Nucleoprotein Complexes Containing Tightly Bound C-Abl, P53 and Bcl-2 Gene Sequences: Correlation with Progression of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Gene 1996, 169, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.A.; Haga, C.L.; Ehrhardt, G.R.A.; Davis, R.S.; Cooper, M.D. FcR-like 2 Inhibition of B Cell Receptor-Mediated Activation of B Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7405–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Schreeder, D.M.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; Davis, R.S. FCRL3 Promotes TLR9-Induced B-Cell Activation and Suppresses Plasma Cell Differentiation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2980–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, M.; Robert, N.; Cren, M.; Thibaut, C.; Duperray, C.; Kassambara, A.; Cogné, M.; Tarte, K.; Klein, B.; Moreaux, J. Characterization of Human FCRL4-Positive B Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.C.; Baccarella, A.M.; Bayat, A.; Pepper, M.; Fontana, M.F. FCRL5+ Memory B Cells Exhibit Robust Recall Responses. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1446–1460.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolnay, M. Lymphocytes Sense Antibodies through Human FCRL Proteins: Emerging Roles in Mucosal Immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 111, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Kubagawa, H.; Cooper, M.D. Identification of a Family of Fc Receptor Homologs with Preferential B Cell Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9772–9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, W.-J.; Foote, J.B.; Odom, M.R.; Pan, J.; Kearney, J.F.; Davis, R.S. Fc Receptor Homolog 3 Is a Novel Immunoregulatory Marker of Marginal Zone and B1 B Cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6815–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, G.R.A.; Hsu, J.T.; Gartland, L.; Leu, C.-M.; Zhang, S.; Davis, R.S.; Cooper, M.D. Expression of the Immunoregulatory Molecule FcRH4 Defines a Distinctive Tissue-Based Population of Memory B Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Tiacci, E.; Pucciarini, A.; Bigerna, B.; Kurth, J.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Droetto, S.; Galletti, B.V.; Gambacorta, M.; Orazi, A.; et al. Expression of the IRTA1 Receptor Identifies Intraepithelial and Subepithelial Marginal Zone B Cells of the Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT). Blood 2003, 102, 3684–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, K.; Davis, R.S.; Maruyama, T.; Zhang, J.; He, T.; Cooper, M.D.; O-Wang, J.; Burrows, P.D. FcRY, an Fc Receptor Related Gene Differentially Expressed during B Lymphocyte Development and Activation. Gene 2005, 363, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masir, N.; Jones, M.; Pozzobon, M.; Marafioti, T.; Volkova, O.Y.; Mechetina, L.V.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Natkunam, Y.; Taranin, A.V.; Mason, D.Y. Expression Pattern of FCRL (FREB, FcRX) in Normal and Neoplastic Human B Cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 127, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.; Bayat, A.A.; Jeddi-Tehrani, M.; Rabbani, H.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Ulivieri, C.; Amirghofran, Z.; Baldari, C.T.; Shokri, F. Ligation of Human Fc Receptor Like-2 by Monoclonal Antibodies down-Regulates B-Cell Receptor-Mediated Signalling. Immunology 2014, 143, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Ding, S.; Pan, J.; Shakhmatov, M.A.; Kashentseva, E.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Soong, S.; Chiorazzi, N.; Davis, R.S. FCRL2 Expression Predicts IGHV Mutation Status and Clinical Progression in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2008, 112, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Du, L.; Fan, Y. The Potential of FCRL Genes as Targets for Cancer Treatment: Insights from Bioinformatics and Immunology. Aging 2023, 15, 4926–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nückel, H.; Collins, C.H.; Frey, U.H.; Sellmann, L.; Dürig, J.; Siffert, W.; Dührsen, U. FCRL2 mRNA Expression Is Inversely As-sociated with Clinical Progression in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2009, 83, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, R.; Cao, H.; Zhao, Z.J. SPAP2, an Ig Family Receptor Containing Both ITIMs and ITAMs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 293, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Liu, C.-M.; Liu, Q.-B. FCRL3 Promotes IL-10 Expression in B Cells through the SHP-1 and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.W.; Krueger, P.D.; Davis, R.S.; Pierce, S.K. FcRL4 Acts as an Adaptive to Innate Molecular Switch Dampening BCR Signaling and Enhancing TLR Signaling. Blood 2011, 118, 6332–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, G.R.A.; Hijikata, A.; Kitamura, H.; Ohara, O.; Wang, J.-Y.; Cooper, M.D. Discriminating Gene Expression Profiles of Memory B Cell Subpopulations. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, J.; Kohara, M.; Tsuruta, Y.; Nojima, S.; Tahara, S.; Ohshima, K.; Kurashige, M.; Wada, N.; Morii, E. Immunohistochemical Analysis of the Novel Marginal Zone B-Cell Marker IRTA1 in Malignant Lymphoma. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 59, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Agostinelli, C.; Bigerna, B.; Pucciarini, A.; Pacini, R.; Tabarrini, A.; Falcinelli, F.; Piccioli, M.; Paulli, M.; Gambacorta, M.; et al. IRTA1 Is Selectively Expressed in Nodal and Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Histopathology 2012, 61, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Davis, R. Fc Receptor-like 5 Has Dominant Inhibitory Function in B Cells That Is Mediated via Lyn and SHP-1 (84.5). J. Immunol. 2010, 184 (Suppl. 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.S. B-1 Cell Development and Function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1362, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, C.L.; Ehrhardt, G.R.A.; Boohaker, R.J.; Davis, R.S.; Cooper, M.D. Fc Receptor-like 5 Inhibits B Cell Activation via SHP-1 Tyrosine Phosphatase Recruitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9770–9775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ise, T.; Maeda, H.; Santora, K.; Xiang, L.; Kreitman, R.J.; Pastan, I.; Nagata, S. Immunoglobulin Superfamily Receptor Translocation Associated 2 Protein on Lymphoma Cell Lines and Hairy Cell Leukemia Cells Detected by Novel Monoclonal Antibodies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ise, T.; Nagata, S.; Kreitman, R.J.; Wilson, W.H.; Wayne, A.S.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Bishop, M.R.; Scheinberg, D.A.; Rassenti, L.; Kipps, T.J.; et al. Elevation of Soluble CD307 (IRTA2/FcRH5) Protein in the Blood and Expression on Malignant Cells of Patients with Multiple Myeloma, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, and Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Leukemia 2007, 21, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dement-Brown, J.; Newton, C.S.; Ise, T.; Damdinsuren, B.; Nagata, S.; Tolnay, M. Fc Receptor-like 5 Promotes B Cell Proliferation and Drives the Development of Cells Displaying Switched Isotypes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.; Kraus, Z.; Li, H.; Seibert, N.; Dement-Brown, J.; Tolnay, M. CD21 and FCRL5 Form a Receptor Complex with Robust B-Cell Activating Capacity. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamzadeh, D.; Dabbaghmanesh, M.H.; Shabani, M.; Hosseini, A.; Amirghofran, Z. Expression Profile of Human Fc Receptor-like 1, 2, and 4 Molecules in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Graves’ Disease. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, K.O.; Volkova, O.I.; Mechetina, L.V.; Chikaev, N.A.; Reshetnikova, E.S.; Nikulina, G.M.; Taranin, A.V.; Naiakshin, A.M. Expression of Human B-Cell Specific Receptor FCRL1 in Normal Individuals and in Patients with Autoimmune Diseases. Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadeh, A.; Habibagahi, Z.; Hosseini, A.; Amirghofran, Z. Investigation of the Human FCRL1, 2, and 4 Gene Expressions in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-X.; Liu, W.; Zhan, M.; Song, Z.-Y.; Yang, S.-Y.; Xue, L.-Q.; Pan, C.-M.; Gu, Z.-H.; Liu, B.-L.; Wang, H.-N.; et al. A Refined Study of FCRL Genes from a Genome-Wide Association Study for Graves’ Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Pei, H.; Huang, B.; Yang, R.-L.; Wu, H.-Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, L. Overexpression of Fc Receptor-like 1 Associated with B-Cell Activation during Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrier, B.; Nagata, S.; Ise, T.; Rosenzwajg, M.; Pastan, I.; Klatzmann, D.; Saadoun, D.; Cacoub, P. CD21−/Low Marginal Zone B Cells Highly Express Fc Receptor–like 5 Protein and Are Killed by Anti–Fc Receptor–like 5 Immunotoxins in Hepatitis C Virus–Associated Mixed Cryoglobulinemia Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Shi, D.; Xiao, M.; Fu, D.; Feng, S.; Kong, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Expression Profile of Fc Receptor-like Molecules in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, D.; Terrier, B.; Bannock, J.; Vazquez, T.; Massad, C.; Kang, I.; Joly, F.; Rosenzwajg, M.; Sene, D.; Benech, P.; et al. Expansion of Autoreactive Unresponsive CD21-/Low B Cells in Sjögren’s Syndrome Associated Lymphoproliferation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2013, 65, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochi, Y.; Yamada, R.; Suzuki, A.; Harley, J.B.; Shirasawa, S.; Sawada, T.; Bae, S.-C.; Tokuhiro, S.; Chang, X.; Sekine, A.; et al. A Functional Variant in FcRH3, Encoding Fc Receptor Homolog 3, Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Several Autoimmunities. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.T.; Kim, C.C.; Fontana, M.F.; Feeney, M.E.; Jagannathan, P.; Boyle, M.J.; Drakeley, C.J.; Ssewanyana, I.; Nankya, F.; Mayanja-Kizza, H.; et al. FCRL5 Delineates Functionally Impaired Memory B Cells Associated with Plasmodium Falciparum Exposure. PLOS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portugal, S.; Tipton, C.M.; Sohn, H.; Kone, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Skinner, J.; Virtaneva, K.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Porcella, S.F.; et al. Malaria-Associated Atypical Memory B Cells Exhibit Markedly Reduced B Cell Receptor Signaling and Effector Function. Elife 2015, 4, e07218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poonia, B.; Ayithan, N.; Nandi, M.; Masur, H.; Kottilil, S. HBV Induces Inhibitory FcRL Receptor on B Cells and Dysregulates B Cell-T Follicular Helper Cell Axis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Tanoue, S.; Kaplan, D.E. Peripheral CD27-CD21- B-Cells Represent an Exhausted Lymphocyte Population in Hepatitis C Cirrhosis. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 150, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal, S.; Obeng-Adjei, N.; Moir, S.; Crompton, P.D.; Pierce, S.K. Atypical Memory B Cells in Human Chronic Infectious Diseases: An Interim Report. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 321, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, M.; Bryant, J.M.; Sutkowski, N.; Haque, A. Fc Receptor-like Proteins in Pathophysiology of B-Cell Disorder. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2016, 7, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, S.A.; Cashman, K.S.; Zumaquero, E.; Marigorta, U.M.; Patel, A.V.; Wang, X.; Tomar, D.; Woodruff, M.C.; Simon, Z.; Bugrovsky, R.; et al. Distinct Effector B Cells Induced by Unregulated Toll-like Receptor 7 Contribute to Pathogenic Responses in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunity 2018, 49, 725–739.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulemzin, S.V.; Zamoshnikova, A.Y.; Yurchenko, M.Y.; Vitak, N.Y.; Najakshin, A.M.; Fayngerts, S.A.; Chikaev, N.A.; Reshetnikova, E.S.; Kashirina, N.M.; Peclo, M.M.; et al. FCRL6 Receptor: Expression and Associated Proteins. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 134, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreeder, D.M.; Pan, J.; Li, F.J.; Vivier, E.; Davis, R.S. FCRL6 Distinguishes Mature Cytotoxic Lymphocytes and Is Upregulated in Patients with B Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.S. Roles for the FCRL6 Immunoreceptor in Tumor Immunology. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.J.; Presti, R.M.; Tassi, I.; Overton, E.T.; Cella, M.; Colonna, M. FcRL6, a New ITIM-Bearing Receptor on Cytolytic Cells, Is Broadly Expressed by Lymphocytes Following HIV-1 Infection. Blood 2007, 109, 3786–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavilio, D.; Lombardo, G.; Kinter, A.; Fogli, M.; La Sala, A.; Ortolano, S.; Farschi, A.; Follmann, D.; Gregg, R.; Kovacs, C.; et al. Characterization of the Defective Interaction between a Subset of Natural Killer Cells and Dendritic Cells in HIV-1 Infection. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, S.; Wang, H.; Su, H.; Su, K.; Li, L. Identification of Pathogenic Genes Related to Rheumatoid Arthritis through Integrated Analysis of DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Profiling. Gene 2017, 634, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Tian, C.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Huang, B.; Lin, H. Fc Receptor-like a Promotes Malignant Behavior in Renal Cell Carcinoma and Correlates with Tumor Immune Infiltration. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e70072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lin, R.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Lin, Z.; Chen, S.; Ye, Z.; Chen, L. High Expression of FCRLB Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 882307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, N. Identification of Cancer-Specific Cell Surface Targets for CAR-T Cell Therapy. Inflamm. Regen. 2024, 44, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappell, K.M.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Long-Term Outcomes Following CAR T Cell Therapy: What We Know so Far. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Qiu, S.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, B.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Chen, M.; et al. Tuning Charge Density of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Optimizes Tonic Signaling and CAR-T Cell Fitness. Cell Res. 2023, 33, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Mace, E.M.; Carisey, A.F.; Ahmed, N.; Orange, J.S. Quantitative Imaging Approaches to Study the CAR Immunological Synapse. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2017, 25, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledbetter, J.A.; Rabinovitch, P.S.; June, C.H.; Song, C.W.; Clark, E.A.; Uckun, F.M. Antigen-Independent Regulation of Cytoplasmic Calcium in B Cells with a 12-kDa B-Cell Growth Factor and Anti-CD19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 1897–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krop, I.; Shaffer, A.L.; Fearon, D.T.; Schlissel, M.S. The Signaling Activity of Murine CD19 Is Regulated during Cell Development. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 1996, 157, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampaolo, S.; Wójcik, G.; Klein-Hessling, S.; Serfling, E.; Patra, A.K. B Cell Development Is Critically Dependent on NFATc1 Activity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doody, G.M.; Billadeau, D.D.; Clayton, E.; Hutchings, A.; Berland, R.; McAdam, S.; Leibson, P.J.; Turner, M. Vav-2 Controls NFAT-Dependent Transcription in B- but Not T-Lymphocytes. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6173–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, P.; Erdmann, T.; Grondona, P.; Xu, W.; Schmitt, A.; Schürch, C.; Zapukhlyak, M.; Schönfeld, C.; Serfling, E.; Kramer, D.; et al. Targeting Chronic NFAT Activation with Calcineurin Inhibitors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 135, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.R.; Migliorini, D.; Perkey, E.; Yost, K.E.; Bhaduri, A.; Bagga, P.; Haris, M.; Wilson, N.E.; Liu, F.; Gabunia, K.; et al. Single-Cell Analyses Identify Brain Mural Cells Expressing CD19 as Potential Off-Tumor Targets for CAR-T Immunotherapies. Cell 2020, 183, 126–142.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotillo, E.; Barrett, D.M.; Black, K.L.; Bagashev, A.; Oldridge, D.; Wu, G.; Sussman, R.; Lanauze, C.; Ruella, M.; Gazzara, M.R.; et al. Convergence of Acquired Mutations and Alternative Splicing of CD19 Enables Resistance to CART-19 Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, E.J.; Han, X.; Tribouley, C.; Wood, P.A.; Leary, R.J.; Riester, M.; Levine, J.E.; Qayed, M.; Grupp, S.A.; Boyer, M.; et al. Genetic Mechanisms of Target Antigen Loss in CAR19 Therapy of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnani, M.; Hayer, K.E.; Naqvi, A.S.; Zheng, S.; Yang, S.Y.; Oldridge, D.; Ibrahim, F.; Maragkakis, M.; Gazzara, M.R.; Black, K.L.; et al. Retention of CD19 Intron 2 Contributes to CART-19 Resistance in Leukemias with Subclonal Frameshift Mutations in CD19. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledererova, A.; Dostalova, L.; Kozlova, V.; Peschelova, H.; Ladungova, A.; Culen, M.; Loja, T.; Verner, J.; Pospisilova, S.; Smida, M.; et al. Hypermethylation of CD19 Promoter Enables Antigen-Negative Escape to CART-19 in Vivo and in Vitro. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.N.; Quesada, A.E.; von Keudell, G.; Raj, S.; Lewis, N.E.; Dogan, A.; Salles, G.; Palomba, M.L. CD19 Epitope Masking by Tafasitamab Leads to Delays in Subsequent Use of CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Two Patients with Aggressive Mature B-Cell Lymphomas. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Kohler, M.E.; Fry, T.; Ernst, P. Does Lineage Plasticity Enable Escape from CAR-T Cell Therapy? Lessons from MLL-r Leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2021, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, E.; Nguyen, S.M.; Fountaine, T.J.; Welp, K.; Gryder, B.; Qin, H.; Yang, Y.; Chien, C.D.; Seif, A.E.; Lei, H.; et al. CD19 CAR Immune Pressure Induces B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Lineage Switch Exposing Inherent Leukaemic Plasticity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.; Wu, D.; Cherian, S.; Fang, M.; Hanafi, L.-A.; Finney, O.; Smithers, H.; Jensen, M.C.; Riddell, S.R.; Maloney, D.G.; et al. Acquisition of a CD19-Negative Myeloid Phenotype Allows Immune Escape of MLL-Rearranged B-ALL from CD19 CAR-T-Cell Therapy. Blood 2016, 127, 2406–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-Z.; Sun, Q.; Fang, Y.; Yang, L.-J.; Xu, Z.-Y.; Hu, J.-H.; Cao, L.; Huang, J.-Y.; Hong, M.; Li, J.-Y.; et al. A Report on Lineage Switch at Relapse of CD19 CAR-T Therapy for Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 2001–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kanapuru, B.; George, B.; Lin, X.; Xu, Z.; Bryan, W.W.; Pazdur, R.; Theoret, M.R. FDA Approval Summary: Idecabtagene Vicleucel for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-F.; Lin, L.; Xing, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Anderson, K.C.; Tai, Y.-T. BCMA-Targeting Therapy: Driving a New Era of Immunotherapy in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.; Gillespie, A.; Tang, G.; Ferros, M.; Harutyunyan, N.M.; Vardanyan, S.; Gottlieb, J.; Li, M.; Wang, C.S.; Chen, H.; et al. Soluble B-Cell Maturation Antigen Mediates Tumor-Induced Immune Deficiency in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3383–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.; Li, M.; Kitto, A.; Li, J.; Wang, C.S.; Kirk, D.T.; Yellin, O.; Nichols, C.M.; Dreyer, M.P.; Ahles, C.P.; et al. Serum B-Cell Maturation Antigen Is Elevated in Multiple Myeloma and Correlates with Disease Status and Survival. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, R.O.; Evbuomwan, M.O.; Pittaluga, S.; Rose, J.J.; Raffeld, M.; Yang, S.; Gress, R.E.; Hakim, F.T.; Kochenderfer, J.N. B-Cell Maturation Antigen Is a Promising Target for Adoptive T-Cell Therapy of Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2048–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seipel, K.; Porret, N.; Wiedemann, G.; Jeker, B.; Bacher, V.U.; Pabst, T. sBCMA Plasma Level Dynamics and Anti-BCMA CAR-T-Cell Treatment in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
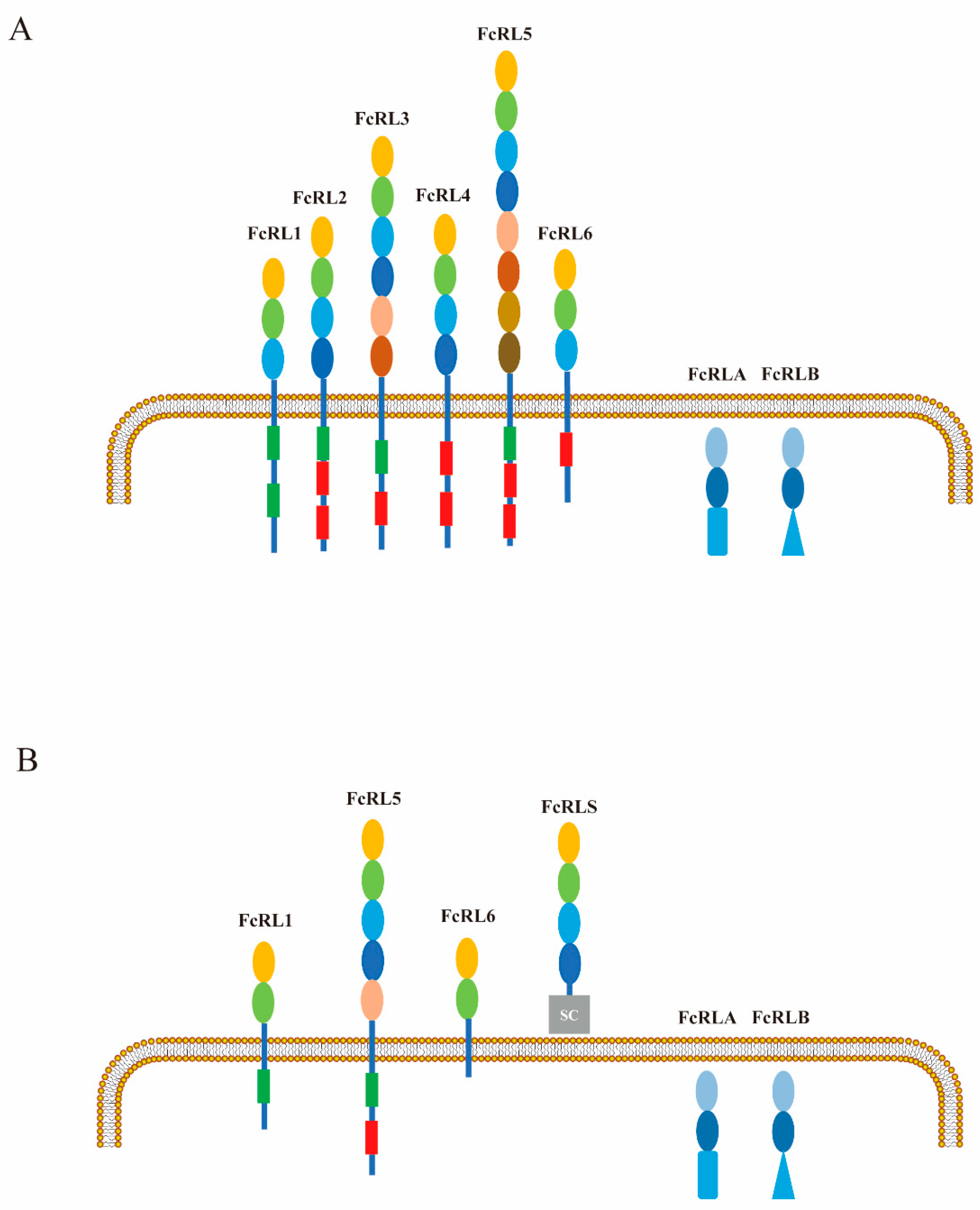


| Receptor | Designated CD | Identified Ligands | Soluble Isoforms | Protein Expression | mRNA Expression | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FcRL1 | CD307a | Not identified | Transmembrane | BM: pro-B-cells; pre-B-cells; nBC; MBC | Tonsil: nBC; pre-GC; MBC; GC; PC | [7,11,13,43] |
| Blood: nBC; MBC | ||||||
| Tonsil: nBC (follicular mantle); GC; MBC; pre-GC; PC (low level) | ||||||
| Spleen: CD38− B-cells; nBC; MBC; MZ; FO B-cells | ||||||
| LN | ||||||
| FcRL2 | CD307b | Not identified | Transmembrane | Blood: CD20+CD27+ MBC | 1. Tonsil: GC light zone, intraepithelial and interfollicular regions 2. Mantle zones and slightly outside the mantle zone from tonsil: nBC-rich and MBC-poor | [2,11,12] |
| Tonsil: CD138+CD38++ Pc (low level); CD20+IgD−CD38− MBC | ||||||
| Spleen: CD20+IgD−CD38− MBC | ||||||
| FcRL3 | CD307c | Secretory IgA | Transmembrane | BM: MBC (low level) | Tonsil: Light zone of the GC; Follicular mantle zones | [2,11,44] |
| Blood: B-cells; CD27+ MBC; Circulating innate-like MZ | ||||||
| Tonsil: nBC (low level); MBC; GC | ||||||
| Spleen: nBC; MBC; CD21highCD23low MZ | ||||||
| Peritoneal: B220+CD5+ B1a and B220+CD5− B1b cells | ||||||
| FcRL4 | CD307d | Heat-aggregated IgA | Transmembrane | BM; Blood: Very low frequency | Tonsil: MBC; nBC | [45,46] |
| Tonsil: IgD−/CD38− MBC; B-cells (underneath and within the tonsil epithelium) | ||||||
| Spleen: Low frequency in MZ | ||||||
| Dome epithelium of Peyer patches; Monocytoid B-cells in reactive LNs; MLN (very low frequency) | ||||||
| FcRL5 | CD307e | All heat-aggregated IgG subtypes | Secretory; GPI-anchored; Transmembrane | BM: PC | Tonsil: Interfollicular and intraepithelial regions (rich in MBC); Centrocyte-rich light zones of GC; Follicular mantle zones (low level) | [2,11,12] |
| Blood: nBC; MBC | ||||||
| Tonsil: nBC; MBC; PC | ||||||
| Spleen: nBC; MBC; CD38++/CD138+ PC | ||||||
| FcRLA | - | IgM; IgG; IgA | Soluble | BM: pre-B-cells | 1. Tonsil: pre-GC; GC 2. Spleen 3. LN | [6,47,48] |
| Blood: B-cells | ||||||
| Tonsil: B-cells; PC (low level); Large CD20+ GC centroblast-like B-cells | ||||||
| Spleen: GC; MZ | ||||||
| FcRLB | - | Not identified | Soluble | BM; Spleen; Tonsil: GC | Spleen; Tonsil | [6,47,48] |
| Receptor | Diseases | Overexpression | Down-Regulation | Expression Regulated by | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FcRL1 | Autoimmune | MS; Takayasu’s arteritis; Lupus anticoagulants; Von Willebrand | SLE; HT; GD | HBV infection | [66,67,68,69,70] |
| Malignancies | NHL (FL; HCL; BL; DLBCL); Pediatric retinoblastoma; Pediatric neuroblastoma; Pediatric kidney tumor; Pediatric diffuse astrocytic and oligodendro tumor | ALL; CLL; MCL | [11,12,34,35,36,66] | ||
| Infectious | AHB; HBV | HCV-MC vasculitis (CD21−/lowIgM+CD27+ MZ) | [68,70,71] | ||
| FcRL2 | Autoimmune | HT; GD | IgAN | IGHV mutation status | [68,69,72] |
| Malignancies | NHL (CLL; MCL; BL); MM | - | [11,50,51] | ||
| Infectious | HCV-MC vasculitis (CD21−/lowIgM+CD27+ MZ); Malaria; HIV | - | [11,71] | ||
| FcRL3 | Autoimmune | RA; SLE; AITD; pSS; GD | IgAN; MS | 1. TLR9 stimulation 2. 169 C/T single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) 3. CHB infection | [69,72,73,74] |
| Malignancies | CLL; FL; SKCM; BRCA | - | [11,12,50,51] | ||
| Infectious | Malaria individuals (AtMs); Malaria (hyposensitive atypical MBCs); HCV-MC vasculitis (CD21−/lowIgM+CD27+ MZ); CHB | - | [71,75,76,77] | ||
| FcRL4 | Autoimmune | GD; pSS | RA | 1. BCR and TLR9 co-stimulation 2. HIV gp120 protein 3. TGF-β1 4. CHB infection | [51,66,68,69,73] |
| Malignancies | MZL; CLL; FL | - | [46,51,58] | ||
| Infectious | Malaria individuals (AtMs); HCV (CD27−CD21− B-cells); HIV; CHB | - | [76,77,78,79,80,81] | ||
| FcRL5 | Autoimmune | SLE; RA | - | 1. Sustained BCR stimulation 2. EBV infection 3. HBV infection | [42,77] |
| Malignancies | MM; CLL; MCL; BL; HCL | - | [11,12,62,63] | ||
| Infectious | Malaria individuals (atypical MBCs); HCV-MC vasculitis (CD21−/lowIgM+CD27+ MZ); HBV | - | [71,75,77,79] | ||
| FcRL6 | Autoimmune | - | RA; SLE; ITP | 1. PD-1 directed immunotherapy 2. HIV-1 infection | [82] |
| Malignancies | CLL; LUAD; SKCM; BRCA | AML; CML | [51,82,83,84,85] | ||
| Infectious | HIV-1+ patients; Malaria | - | [85,86] | ||
| FcRLA | Autoimmune | RA | - | CHB infection | [87] |
| Malignancies | NHL (FL; MCL; MZL; CLL; BL); RCC | MM | [51,88] | ||
| Infectious | CHB | - | [77] | ||
| FcRLB | Malignancies | Colorectal cancer | - | CHB infection | [89] |
| Infectious | Malaria; CHB | - | [76,77] |
| Target | Cause | Tumor Type | Refs. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD19 | Loss of CD19 | Missense and frameshift mutations in exon 2 of CD19 | B-ALL | [100] |
| Alternative splice variants lacking exon 2 or exons 5–6 of CD19 | B-ALL | [101] | ||
| Presence of intron 2 in mature CD19 mRNA | Lymphoma; B-ALL | [102] | ||
| Hypermethylation of the CD19 promoter and decreased CD19 expression | CLL;BL | [103] | ||
| Mask of CD19 | CD19-targeted therapy with tafasitimab | r/r DLBCL | [104] | |
| Lineage switch | CD19 loss and CD34, CD33, or CD64 markers expression | Mixed lineage leukemia (MLL)-rearranged B-ALL; Philadelphia chromosome-positive B-ALL | [105,106,107,108] | |
| BCMA | Induction of immunosuppressive microenvironment | APRIL/BCMA signaling cascade induces the expression of anti-apoptotic genes (Bcl-2/Bcl-xL, Mcl-1) and immune regulatory genes (IL-10, PD-L1, VEGF, TGF-β) | MM | [109,110] |
| sBCMA | sBCMA compete to combine anti-BCMA CAR-T | MM | [111,112,113,114] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Miao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; et al. FcRL1, a New B-Cell-Activating Co-Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136306
Chen Z, Miao C, Zhang Y, Huang J, Sun Y, Chen J, Sun J, Shi W, Wang X, Wang R, et al. FcRL1, a New B-Cell-Activating Co-Receptor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136306
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhitao, Chenxi Miao, Yan Zhang, Jiaqi Huang, Yanan Sun, Juan Chen, Jiazeng Sun, Wenbiao Shi, Xifan Wang, Ran Wang, and et al. 2025. "FcRL1, a New B-Cell-Activating Co-Receptor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136306
APA StyleChen, Z., Miao, C., Zhang, Y., Huang, J., Sun, Y., Chen, J., Sun, J., Shi, W., Wang, X., Wang, R., Li, Y., & Zhao, X. (2025). FcRL1, a New B-Cell-Activating Co-Receptor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136306







