Cellular Lyso-Gb3 Is a Biomarker for Mucolipidosis II
Abstract
1. Introduction
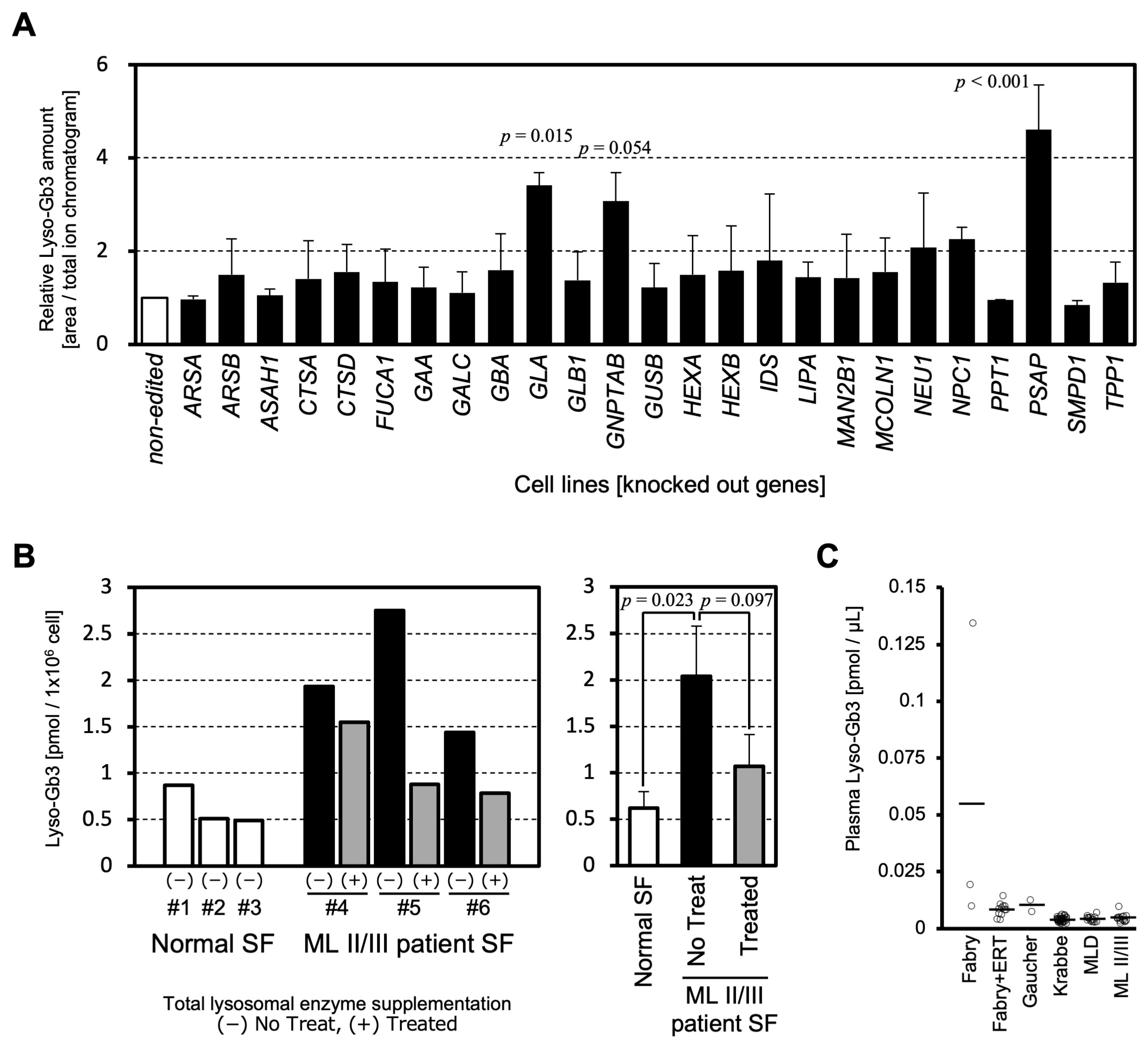
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Knockout (KO) Cell Lines
3.2. Patient Specimens
3.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis for Lyso-Gb3
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LSD | lysosomal storage disease |
| Lyso-Gb3 | globotriaosylsphingosine |
| ML II/III | mucolipidosis II/III |
| LAL-D | lysosomal acid lipase deficiency |
| M6P | mannose 6-phosphate |
| Gb3 | globotriaosylceramide |
| KO | knockout |
| SF | skin fibroblast |
| ERT | enzyme replacement therapy |
References
- Platt, F.M.; d’Azzo, A.; Davidson, B.L.; Neufeld, E.F.; Tifft, C.J. Lysosomal storage diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otomo, T.; Higaki, K.; Nanba, E.; Ozono, K.; Sakai, N. Lysosomal storage causes cellular dysfunction in mucolipidosis II skin fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35283–35290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, T.; Terawaki, S.; Otomo, T. Impaired lysosomal acidity maintenance in acid lipase-deficient cells leads to defective autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 105743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Maksimova, N.; Otomo, T.; Kato, H.; Imai, A.; Asano, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Nojima, S.; Nakaya, A.; Hamada, Y.; et al. Mutation in VPS33A affects metabolism of glycosaminoglycans: A new type of mucopolysaccharidosis with severe systemic symptoms. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 27, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyske, Z.; Gaffke, L.; Pierzynowska, K.; Węgrzyn, G. Mucopolysaccharidosis-Plus Syndrome: Is This a Type of Mucopolysaccharidosis or a Separate Kind of Metabolic Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desnick, R.J.; Ioannou, Y.A.; Eng, C.M. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, Part 16: Lysosomal Disorders, α-Galactosidase A Deficiency: Fabry Disease. Available online: https://ommbid.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=2709§ionid=225546984 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Aerts, J.M.; Groener, J.E.; Kuiper, S.; Donker-Koopman, W.E.; Strijland, A.; Ottenhoff, R.; van Roomen, C.; Mirzaian, M.; Wijburg, F.A.; Linthorst, G.E.; et al. Elevated globotriaosylsphingosine is a hallmark of Fabry disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2812–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, H.; Miyata, K.; Mikame, M.; Taguchi, A.; Guili, C.; Shimura, M.; Murayama, K.; Inoue, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sugimura, K.; et al. Effectiveness of plasma lyso-Gb3 as a biomarker for selecting high-risk patients with Fabry disease from multispecialty clinics for genetic analysis. Genet. Med. 2018, 21, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswami, U.; West, M.L.; Tylee, K.; Castillon, G.; Braun, A.; Ren, M.; Doobaree, I.U.; Howitt, H.; Nowak, A. The use and performance of lyso-Gb3 for the diagnosis and monitoring of Fabry disease: A systematic literature review. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2025, 145, 109110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Sanz, A.B.; Carrasco, S.; Saleem, M.A.; Mathieson, P.W.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. Globotriaosylsphingosine actions on human glomerular podocytes: Implications for Fabry nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, Y.; Hiraiwa, M.; O’Brien, J.S. Saposins: Structure, function, distribution, and molecular genetics. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhoff, K.; Kolter, T.; Harzer, K.; Schepers, U.; Remmel, N. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, Part 16: Lysosomal Disorders, Sphingolipid Activator Proteins. Available online: https://ommbid.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=2709§ionid=225543732 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Hulková, H.; Cervenková, M.; Ledvinová, J.; Tochácková, M.; Hrebícek, M.; Poupetová, H.; Befekadu, A.; Berná, L.; Paton, B.C.; Harzer, K.; et al. A novel mutation in the coding region of the prosaposin gene leads to a complete deficiency of prosaposin and saposins, and is associated with a complex sphingolipidosis dominated by lactosylceramide accumulation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhardt, M. Pathology and current treatment of neurodegenerative sphingolipidoses. Neuromolecular Med. 2011, 12, 362–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiede, S.; Storch, S.; Lübke, T.; Henrissat, B.; Bargal, R.; Raas-Rothschild, A.; Braulke, T. Mucolipidosis II is caused by mutations in GNPTA encoding the alpha/beta GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Tomatsu, S.C. Mucolipidoses Overview: Past, Present, and Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braulke, T.; Raas-Rothschild, A.; Kornfeld, S. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, Part 16: Lysosomal Disorders, I-Cell Disease and Pseudo-Hurler Polydystrophy: Disorders of Lysosomal Enzyme Phosphorylation and Localization. Available online: https://ommbid.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=2709§ionid=225544648 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Kornfeld, S. Trafficking of lysosomal enzymes. FASEB J. 1987, 1, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiewak, J.; Doykov, I.; Papandreou, A.; Hällqvist, J.; Mills, P.; Clayton, P.T.; Gissen, P.; Mills, K.; Heywood, W.E. New Perspectives in Dried Blood Spot Biomarkers for Lysosomal Storage Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otomo, T.; Schweizer, M.; Kollmann, K.; Schumacher, V.; Muschol, N.; Tolosa, E.; Mittrücker, H.W.; Braulke, T. Mannose 6 phosphorylation of lysosomal enzymes controls B cell functions. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, J.J.; Pyl, P.T.; Rausch, T.; Zichner, T.; Tekkedil, M.M.; Stütz, A.M.; Jauch, A.; Aiyar, R.S.; Pau, G.; Delhomme, N.; et al. The genomic and transcriptomic landscape of a HeLa cell line. G3 2014, 3, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipidomics Standards Initiative Consortium. Lipidomics needs more standardization. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | CRISPR Guide (5′ to 3′) | Clone #1 | Clone #2 | Clone #3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARSA | GGGAGTCCCCAAATGGCCCG | delC/del7bp | del13bp/insG | del16bp homo |
| ARSB | GCTGCGTGTAGTAGTTGTCC | del2/del11bp | delC/delCACC | insC/del8bp |
| ASAH1 | TCAAGATTTATGGTGTACCA | insT homo | del7bp homo | insT/delG |
| CTSA | CTTTGAGGTAGCCGGAGTAC | del11 homo | del11bp/del23bp | delTC/delCTCC |
| CTSD | GTCCATCCGCCGGACCATGT | del10bp homo | delCA/del40bp | delT homo |
| FUCA1 | GAACTTGGCTTCGTCGAACC | delT/insG | delTC/del8bp | insT homo |
| GAA | AGGGATGTAGCAACAGCCGC | delGC homo | CTGT > GCTGC homo | insG/delCTG |
| GALC | GTAATTTACTAGAAGTCGGG | insT/delC | insG homo | insGA homo |
| GBA | AGACCAATGGAGCGGTGAAT TGTGGTGAGTACTGTTGGCG * | del4bp/del5bp | insA/insCC | insC/delA |
| GLA | GCTAGCTGGCGAATCCCATG | delG homo | delG homo | delG/insGG |
| GLB1 | CCCGTGTGCCCCGCTTCTAC | del8/del19bp | insAT/del19bp | delACT/del26bp |
| GNPTAB | ACACGTAGAGCCCATACCTG | delGT/del8bp | delG homo | delAG/del12bp |
| GUSB | GTGGTACCGGCGGCCGCTGT | delGC homo | insT/insG | insC homo |
| HEXA | GTTGTCTCTGTAGTCACACC | delCC/del13bp | insC/delTCAC | delAC/del5bp |
| HEXB | GAGGGGCCCGCCGTGGAATT | delT/del8bp | delT/insT | delT homo |
| IDS | GAACGTTCTTCTCATCATCG | insA homo | delT/delC | delA/delTC |
| LIPA | TCCCATGAGGAATTCGGTTA | delC homo | del13bp homo | insC/del5bp |
| MAN2B1 | ACGTAAATGAAGCGACGGGT | delCC homo | insCG/del5 | delC homo |
| MCOLN1 | AGTATTTGAGACGACGGCGA | delC homo | delC homo | delC/delGC |
| NEU1 | CCAAGTTCATCGCCCTGCGG | del5 homo | delG/delG | delC homo |
| NPC1 | GCGCTGGACACAGTAGCAGC | del12bp homo | insT/del8bp | del7bp homo |
| PPT1 | GCAGCAAGGCTACAATGCTA | delTG/del5bp | delTG homo | del5bp/del8bp |
| PSAP | TGAAGACGGCGTCCGACTGC | insT/delAC | del7bp homo | delT/ del5bp |
| SMPD1 | GTTCTTTGGCCACACTCATG | insC/del14bp | insC homo | insT/del10bp |
| TPP1 | TGTGGAAAGACTCTCGGAGC | delG/delGG | delGG homo | delGG/delTCGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terawaki, S.; Nakanishi, H.; Shibuya, T.; Sakai, N.; Otomo, T. Cellular Lyso-Gb3 Is a Biomarker for Mucolipidosis II. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136275
Terawaki S, Nakanishi H, Shibuya T, Sakai N, Otomo T. Cellular Lyso-Gb3 Is a Biomarker for Mucolipidosis II. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136275
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerawaki, Seigo, Hiroki Nakanishi, Toko Shibuya, Norio Sakai, and Takanobu Otomo. 2025. "Cellular Lyso-Gb3 Is a Biomarker for Mucolipidosis II" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136275
APA StyleTerawaki, S., Nakanishi, H., Shibuya, T., Sakai, N., & Otomo, T. (2025). Cellular Lyso-Gb3 Is a Biomarker for Mucolipidosis II. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136275








