Attenuation of Ventilation-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Associated with Lung Injury Through Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Gamma in a Murine Endotoxemia Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
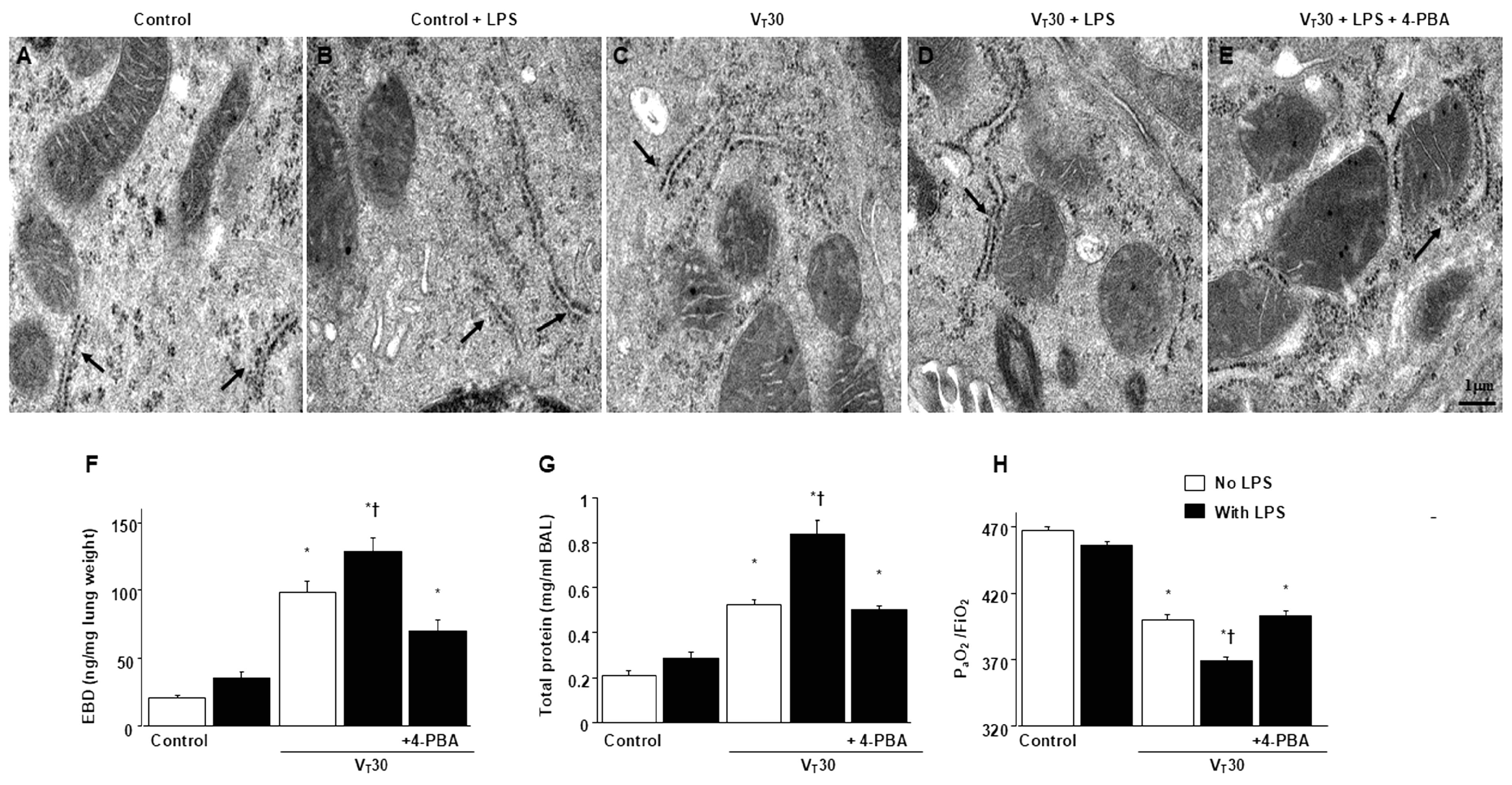
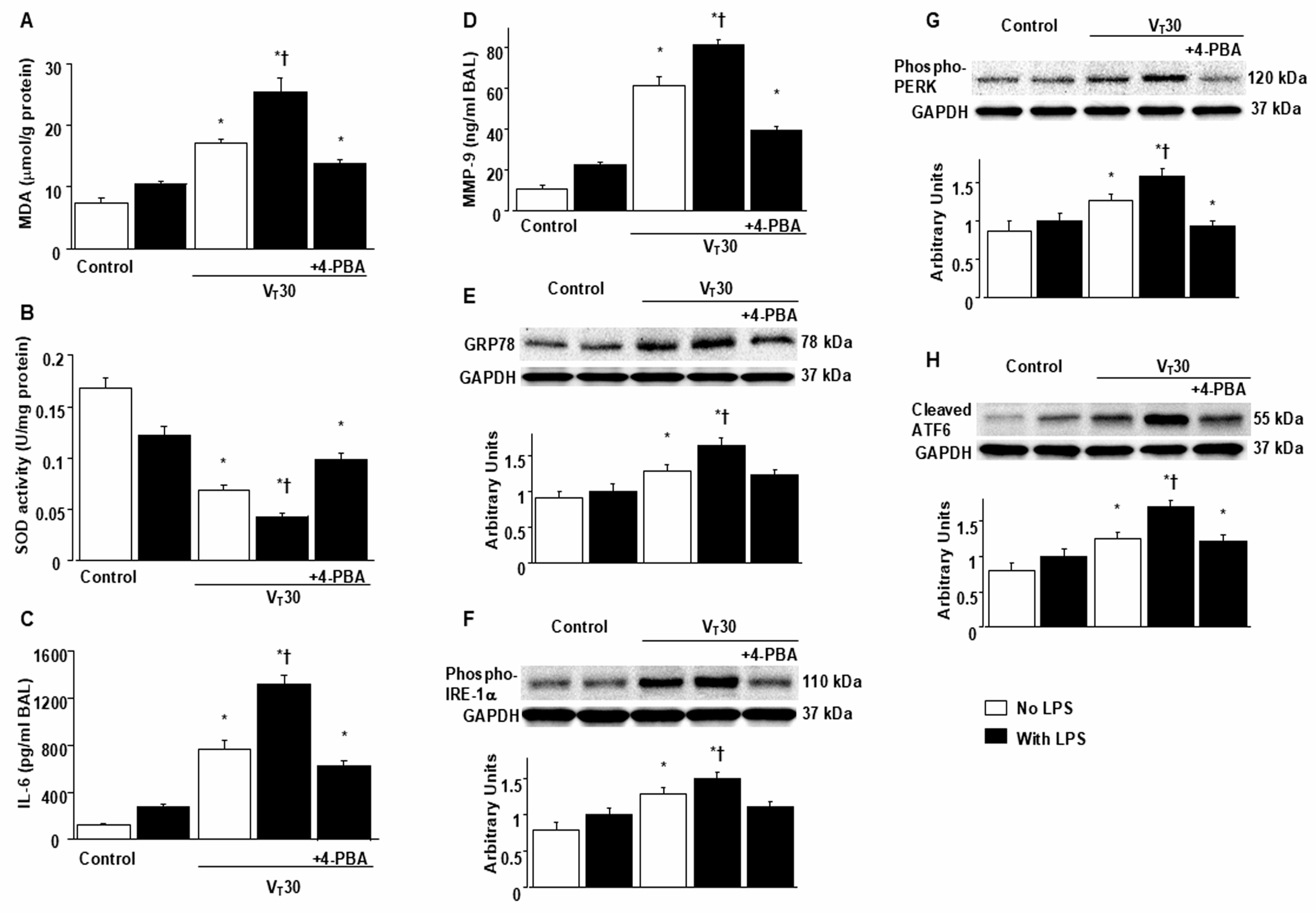
2.1. Suppression of Endotoxin-Enhanced MV-Induced Microvascular Leak, Lung Edema, Hypoxemia, ER Accumulation, Oxidative Stress, IL-6, and MMP-9 Production, and ER Stress Protein Expression Through 4-PBA
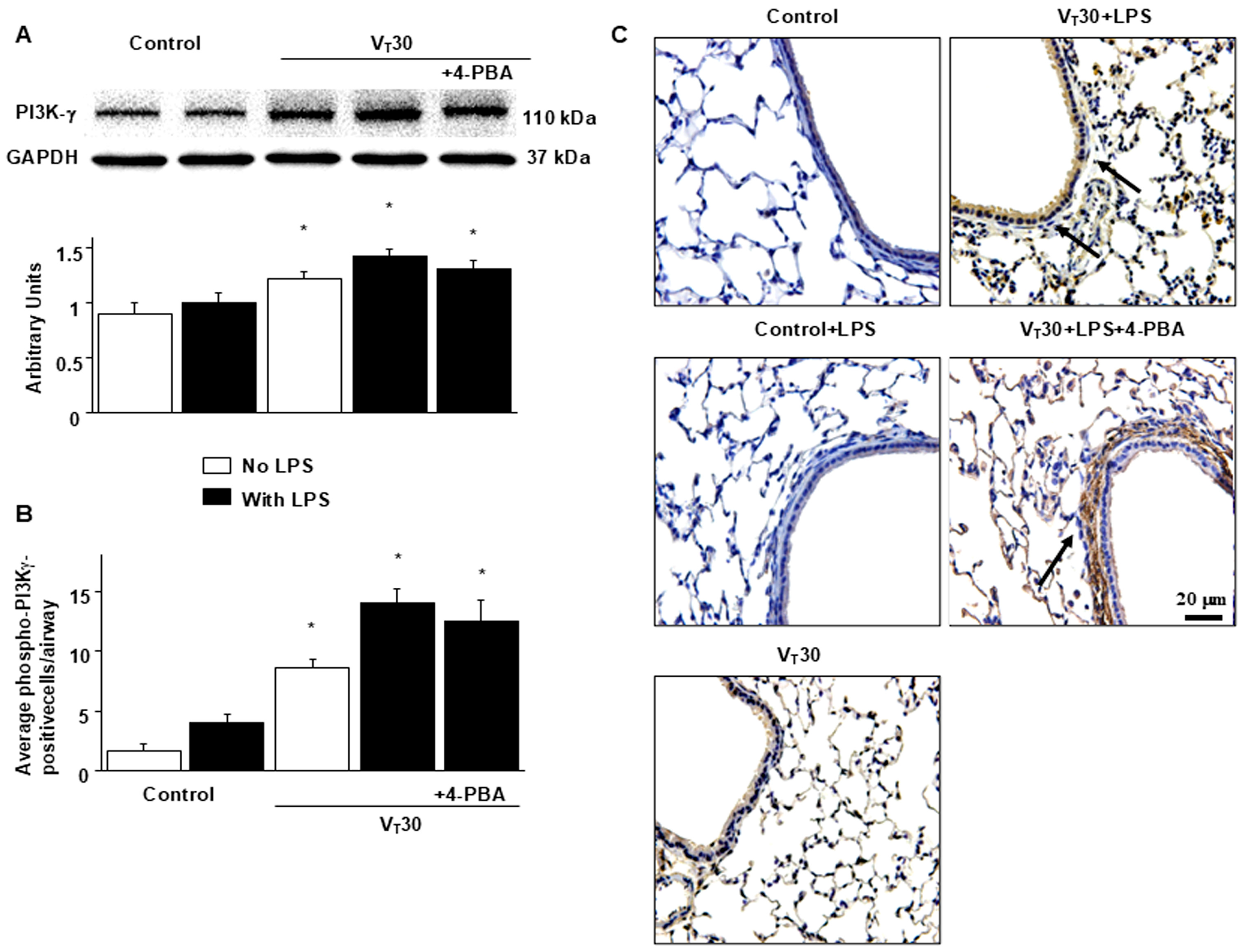
2.2. Endotoxin-Augmented MV-Induced PI3K-γ Protein Expression
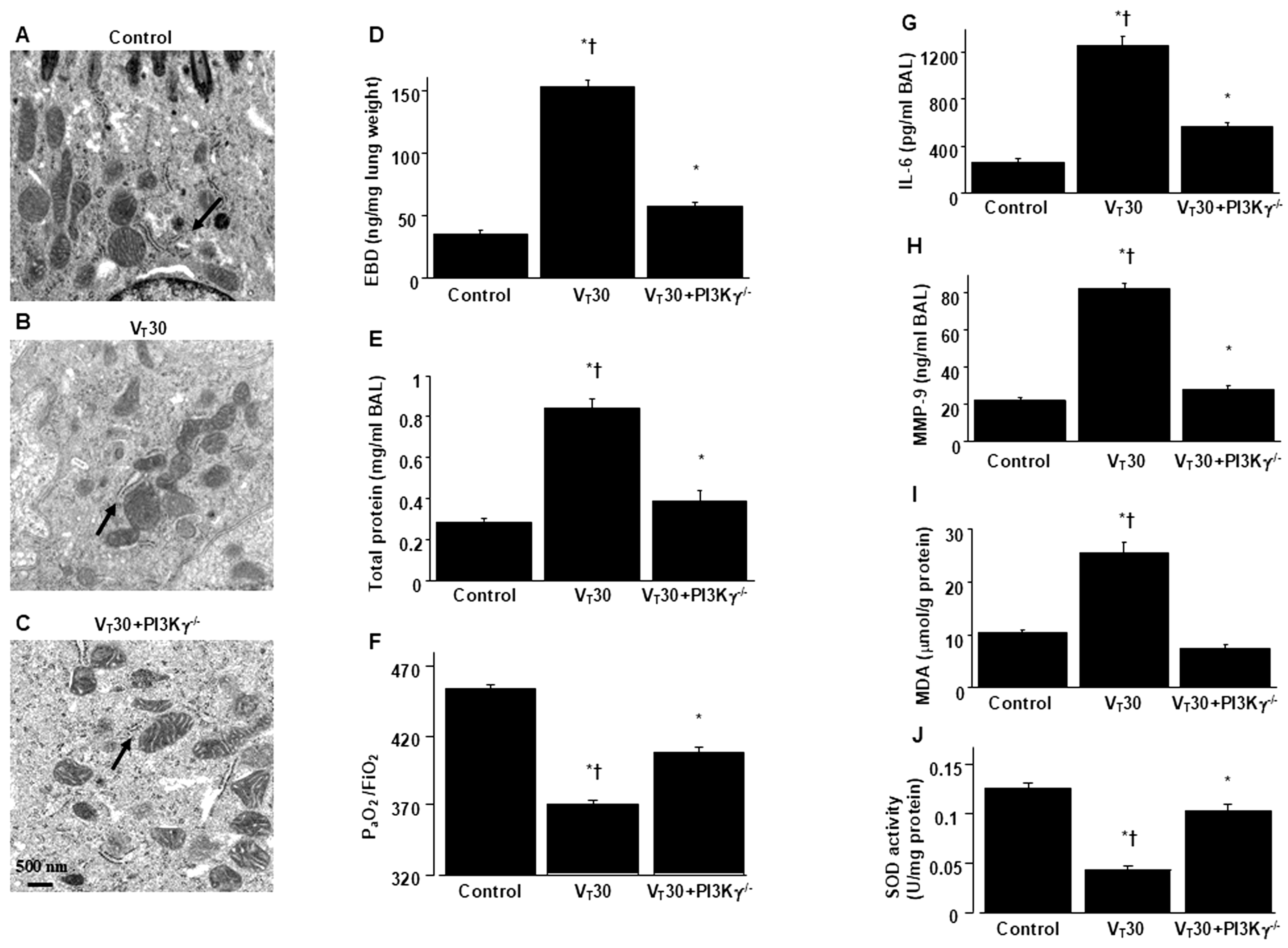
2.3. Reduction In Endotoxin-Augmented MV-Induced Lung Inflammation and ER Stress in PI3K-γ-Deficient Mice
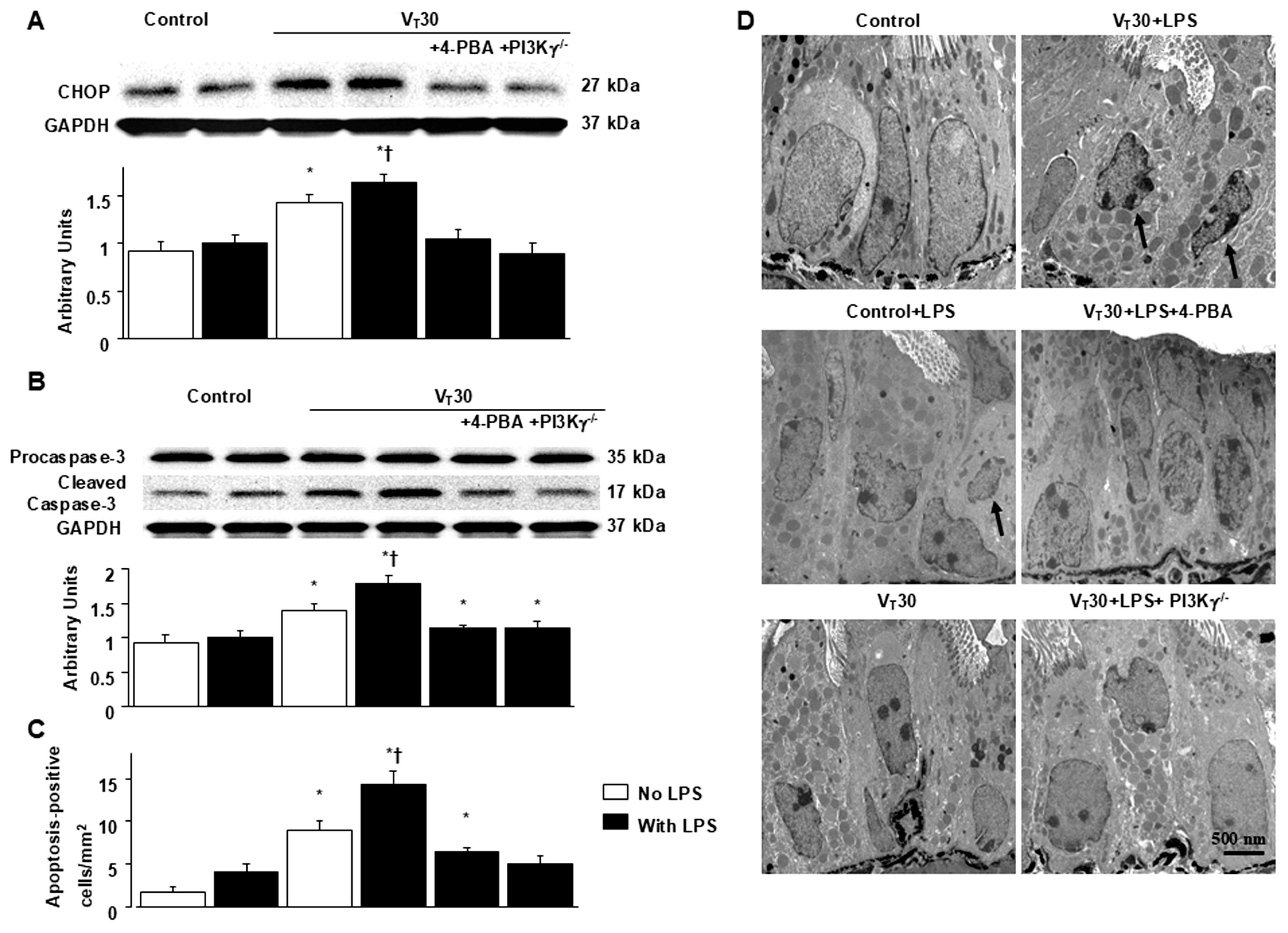
2.4. Inhibition of MV-Induced Effects on Endotoxin-Enhanced CHOP Expression, Caspase-3, and Epithelial Apoptosis in PI3K-γ-Deficient Mice
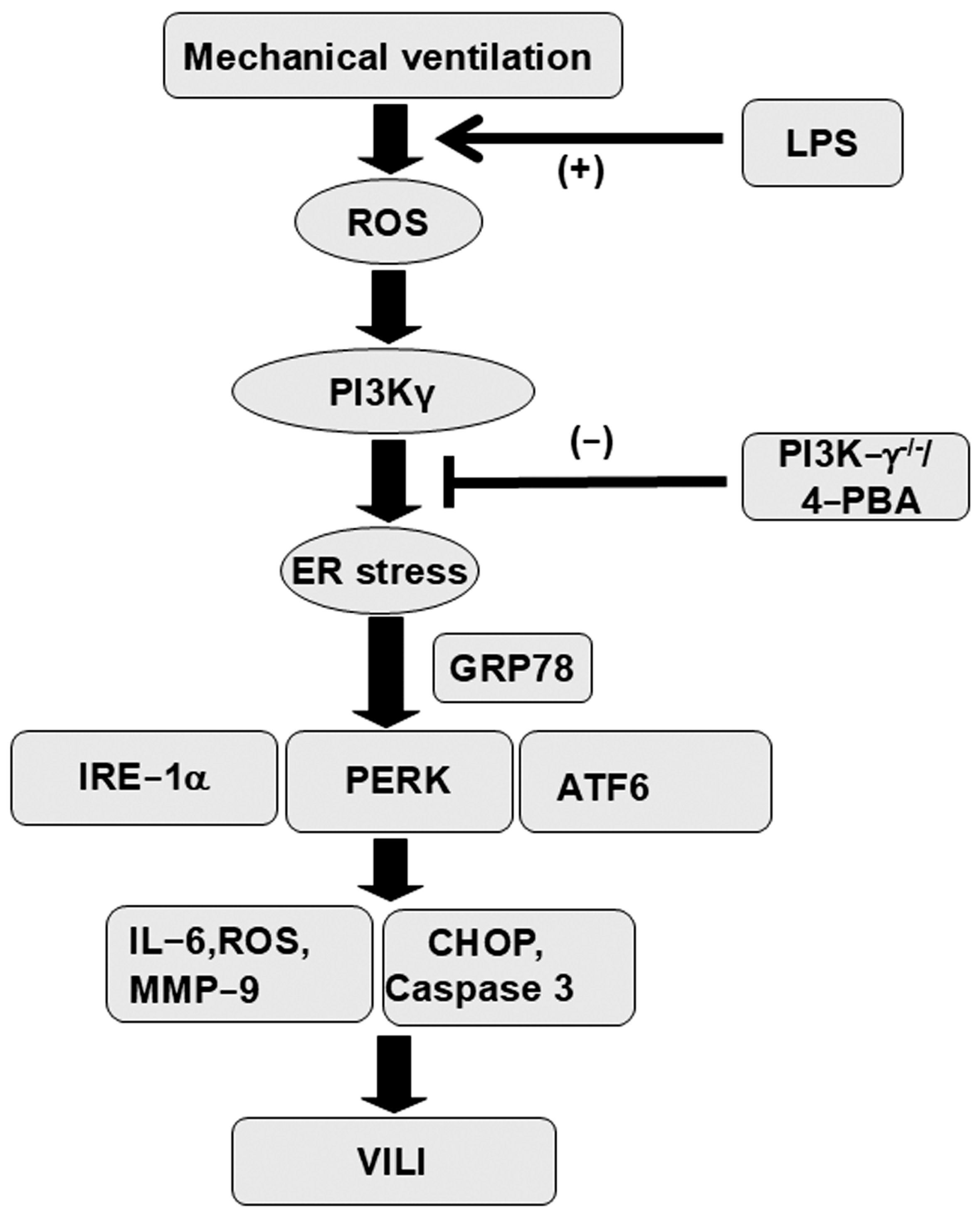
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Pharmacological Inhibitors
4.3. Measurement of Inflammatory Cytokines
4.4. Immunoblot Analysis of ER Stress and PI3K-γ
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALI | Acute lung injury |
| MV | Mechanical ventilation |
| VILI | Ventilator-induced lung injury |
| ER stress | Endoplasmic reticulum stress |
| GRP78 | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein |
| PERK | Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase |
| IRE1a | Inositol-requiring enzyme 1a |
| ATF6 | Activating transcription factor 6 |
| PI3K-g | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-g |
| LPSs | Lipopolysaccharides |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| MMP-9 | Metalloproteinase-9 |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
| XBP-1 | X-box binding protein |
| CHOP | CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| SOD | Sodium dismutase |
| EBD | Evans blue dye |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TUNEL t | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end-labeling. |
| 4-PBA | 4-phenylbutyric acid |
References
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genga, K.R.; Russell, J.A. Update of Sepsis in the Intensive Care Unit. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Hattori, K.; Suzuki, T.; Matsuda, N. Recent advances in the pathophysiology and molecular basis of sepsis-associated organ dysfunction: Novel therapeutic implications and challenges. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 177, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.F.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lin, S.W.; Chang, C.H.; Chen, N.H.; Hung, C.Y.; Lee, C.S. Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Reduces Ventilation-Induced Lung Injury through Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha in a Murine Endotoxemia Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.C.; Burr, L.; McGuckin, M.A. Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in respiratory disease. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2018, 7, e1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zheng, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. Mechanotransduction Regulates the Interplays Between Alveolar Epithelial and Vascular Endothelial Cells in Lung. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 818394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandl, J.; Meszaros, T.; Banhegyi, G.; Csala, M. Minireview: Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Control in protein, lipid, and signal homeostasis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sun, J.; Fei, A.; Gao, C.; Pan, S.; Wu, Z. Hydrogen sulfide treatment alleviated ventilator-induced lung injury through regulation of autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2872–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Wang, H.; Cui, N. mTOR pathway mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced CD4(+) T cell apoptosis in septic mice. Apoptosis 2022, 27, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zeng, Q.; Dai, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Ma, R.; Hong, X.; Zhao, C.; Pan, L. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in ventilator-induced lung injury in mice via the IRE1alpha-TRAF2-NF-kappaB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 78, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zeng, Q.; Ling, M.; Ma, R.; Chen, H.; Lin, F.; Li, Z.; Pan, L. Inhibition of IP3R/Ca2+ Dysregulation Protects Mice From Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury via Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondrial Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 729094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyadomari, S.; Mori, M. Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, W.C.; Jiang, W.P.; Huang, G.J. Attenuation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Hispolon in Mice, Through Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways, and Suppressing Oxidative Stress-Mediated ER Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, V.; Lisi, A.; Patrucco, E.; De Giuli, P.; Milazzo, M.G.; Ceci, S.; Wymann, M.; Lena, A.; Gremigni, V.; Fanelli, V.; et al. Lack of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-gamma attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, L.; Park, H.J.; Seo, E.H.; Kim, T.W.; Shin, J.K.; Kim, S.H. The effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress on the expression of exosomes in ventilator-induced lung injury. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Xu, Q.; Wan, H.; Hu, Y.; Xing, S.; Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; He, Z. PI3K-Akt-mTOR/PFKFB3 pathway mediated lung fibroblast aerobic glycolysis and collagen synthesis in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; He, W.; Meng, H.; Li, P.; Qu, J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in acute lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e70232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.; Tong, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Z. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction Due to Molecules Secreted by Macrophages in Sepsis. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Mejia, C.; Torres-Cordon, M.F.; Becerra-Bayona, S.; Paez, C.M.; Vargas, C.I.; Cardenas, M.E.; Serrano, S.E.; Baquero, I.; Martinez-Vega, R.; Schulz, R.; et al. Prognostic Value of MMP-9 -1562 C/T Gene Polymorphism in Patients With Sepsis. Biomark. Insights 2019, 14, 1177271919847951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Loeches, I.; Singer, M.; Leone, M. Sepsis: Key insights, future directions, and immediate goals. A review and expert opinion. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, F.G.; Mazza, B. Mechanical Ventilation in Sepsis: A Reappraisal. Shock 2017, 47, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altemeier, W.A.; Matute-Bello, G.; Frevert, C.W.; Kawata, Y.; Kajikawa, O.; Martin, T.R.; Glenny, R.W. Mechanical ventilation with moderate tidal volumes synergistically increases lung cytokine response to systemic endotoxin. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, L533–L542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Dedaj, R.; Zhao, H.; Mrabat, H.; Sheidlin, A.; Syrkina, O.; Huang, P.M.; Garg, H.G.; Hales, C.A.; et al. High-molecular-weight hyaluronan—A possible new treatment for sepsis-induced lung injury: A preclinical study in mechanically ventilated rats. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanza, A.; Carlesso, A.; Chintha, C.; Creedican, S.; Doultsinos, D.; Leuzzi, B.; Luis, A.; McCarthy, N.; Montibeller, L.; More, S.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling—From basic mechanisms to clinical applications. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 241–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.J.; Teng, M.; Jing, X.; Pritchard, K.A., Jr.; Day, B.W.; Naylor, S.; Teng, R.J. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Contributor or Consequence? Cells 2024, 13, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Bai, M.; Wang, T.; Chu, Y.; Qin, Y. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Caused by Damaged Mitochondria and Imbalanced Protein Homeostasis in Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cell. Adv. Biol. 2024, 9, e2400297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.M.; Yang, W.L.; Brenner, M.; Bolognese, A.C.; Wang, P. Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) causes sepsis-associated acute lung injury via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinay, T.; Himes, B.E.; Shumyatcher, M.; Lawrence, G.G.; Margulies, S.S. Integrated Stress Response Mediates Epithelial Injury in Mechanical Ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Han, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Shang, X.; Hu, W.; Xue, C. The endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis signal pathway is involved in sepsis-induced abnormal lymphocyte apoptosis. Eur. Surg. Res. 2008, 41, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Oyadomari, S.; Suga, M.; Mori, M.; Gotoh, T. The ER stress pathway involving CHOP is activated in the lungs of LPS-treated mice. J. Biochem. 2005, 138, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, S.R.; Park, S.Y.; Chae, H.J.; Lee, Y.C. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation through modulation of NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Su, Q.; Wang, C.; Shen, L.; Chen, H.; Feng, S.; Peng, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; et al. SDF4 Is a Prognostic Factor for 28-Days Mortality in Patients With Sepsis via Negatively Regulating ER Stress. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 659193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinay, T.; Aonbangkhen, C.; Zacharias, W.; Cantu, E.; Pogoriler, J.; Stablow, A.; Lawrence, G.G.; Suzuki, Y.; Chenoweth, D.M.; Morrisey, E.; et al. Protein kinase R-like endoplasmatic reticulum kinase is a mediator of stretch in ventilator-induced lung injury. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuRose, J.B.; Tam, A.B.; Niwa, M. Intrinsic capacities of molecular sensors of the unfolded protein response to sense alternate forms of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.B.; O’Donnell, A.C.; Stamateris, R.E.; Ha, B.; McCloskey, K.M.; Reynolds, P.R.; Arvan, P.; Alonso, L.C. Insulin demand regulates beta cell number via the unfolded protein response. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3831–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, V.; Della Sala, A.; Ghigo, A.; Hirsch, E. Roles of phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase gamma (PI3Kgamma) in respiratory diseases. Cell Stress 2021, 5, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Yu, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Wu, H.P.; Chu, C.M.; Liu, P.C.; Liu, Y.Y. Attenuation of Ventilation-Enhanced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-gamma in a Murine Bleomycin-Induced Acute Lung Injury Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.S.; Liu, C.C.; Lin, J.H.; Hsu, T.W.; Hsu, J.W.; Su, K.; Hung, S.C. Involvement of ER stress, PI3K/AKT activation, and lung fibroblast proliferation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaria, J.P.; Moretta, L.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Hirsch, E. PI3K Signaling in Mechanisms and Treatments of Pulmonary Fibrosis Following Sepsis and Acute Lung Injury. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, A.T.; Babic, P.; Hoffmann, B.; Muller, T.; Foo, W.; Hauswald, W.; Benecke, J.; Beretta, M.; Cseresnyes, Z.; Hoeppener, S.; et al. Targeted delivery of a phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma inhibitor to restore organ function in sepsis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e14436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, V.; Puntorieri, V.; Assenzio, B.; Martin, E.L.; Elia, V.; Bosco, M.; Delsedime, L.; Del Sorbo, L.; Ferrari, A.; Italiano, S.; et al. Pulmonary-derived phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma (PI3Kgamma) contributes to ventilator-induced lung injury and edema. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.L.; Souza, D.G.; Fagundes, C.T.; Amaral, F.A.; Assenzio, B.; Puntorieri, V.; Del Sorbo, L.; Fanelli, V.; Bosco, M.; Delsedime, L.; et al. Phosphoinositide-3 kinase gamma activity contributes to sepsis and organ damage by altering neutrophil recruitment. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Jin, R.; Xiao, A.Y.; Chen, R.; Li, J.; Zhong, W.; Feng, X.; Li, G. Induction of Neuronal PI3Kgamma Contributes to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Long-Term Functional Impairment in a Murine Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragagnin, A.M.G.; Sundaramoorthy, V.; Farzana, F.; Gautam, S.; Saravanabavan, S.; Takalloo, Z.; Mehta, P.; Do-Ha, D.; Parakh, S.; Shadfar, S.; et al. ALS/FTD-associated mutation in cyclin F inhibits ER-Golgi trafficking, inducing ER stress, ERAD and Golgi fragmentation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Jia, L.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, M.; Jin, J.; Zhu, J. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory effects of PI3Kδ/γ inhibitors for treating acute lung injury. Immunobiology. 2023, 228, 152753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Yu, C.C.; Wu, H.P.; Chu, C.M.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, P.C.; Liu, Y.Y. Reduction in Ventilation-Induced Diaphragmatic Mitochondrial Injury through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1alpha in a Murine Endotoxemia Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.-F.; Yu, C.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Wu, H.-P.; Chu, C.-M.; Liu, P.-C.; Liu, Y.-Y. Attenuation of Ventilation-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Associated with Lung Injury Through Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Gamma in a Murine Endotoxemia Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125761
Li L-F, Yu C-C, Huang C-Y, Wu H-P, Chu C-M, Liu P-C, Liu Y-Y. Attenuation of Ventilation-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Associated with Lung Injury Through Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Gamma in a Murine Endotoxemia Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125761
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Li-Fu, Chung-Chieh Yu, Chih-Yu Huang, Huang-Pin Wu, Chien-Ming Chu, Ping-Chi Liu, and Yung-Yang Liu. 2025. "Attenuation of Ventilation-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Associated with Lung Injury Through Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Gamma in a Murine Endotoxemia Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125761
APA StyleLi, L.-F., Yu, C.-C., Huang, C.-Y., Wu, H.-P., Chu, C.-M., Liu, P.-C., & Liu, Y.-Y. (2025). Attenuation of Ventilation-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Associated with Lung Injury Through Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Gamma in a Murine Endotoxemia Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125761







