A Dual-Targeting Peptide Inhibitor Simultaneously Blocking Viral Attachment and Membrane Fusion for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
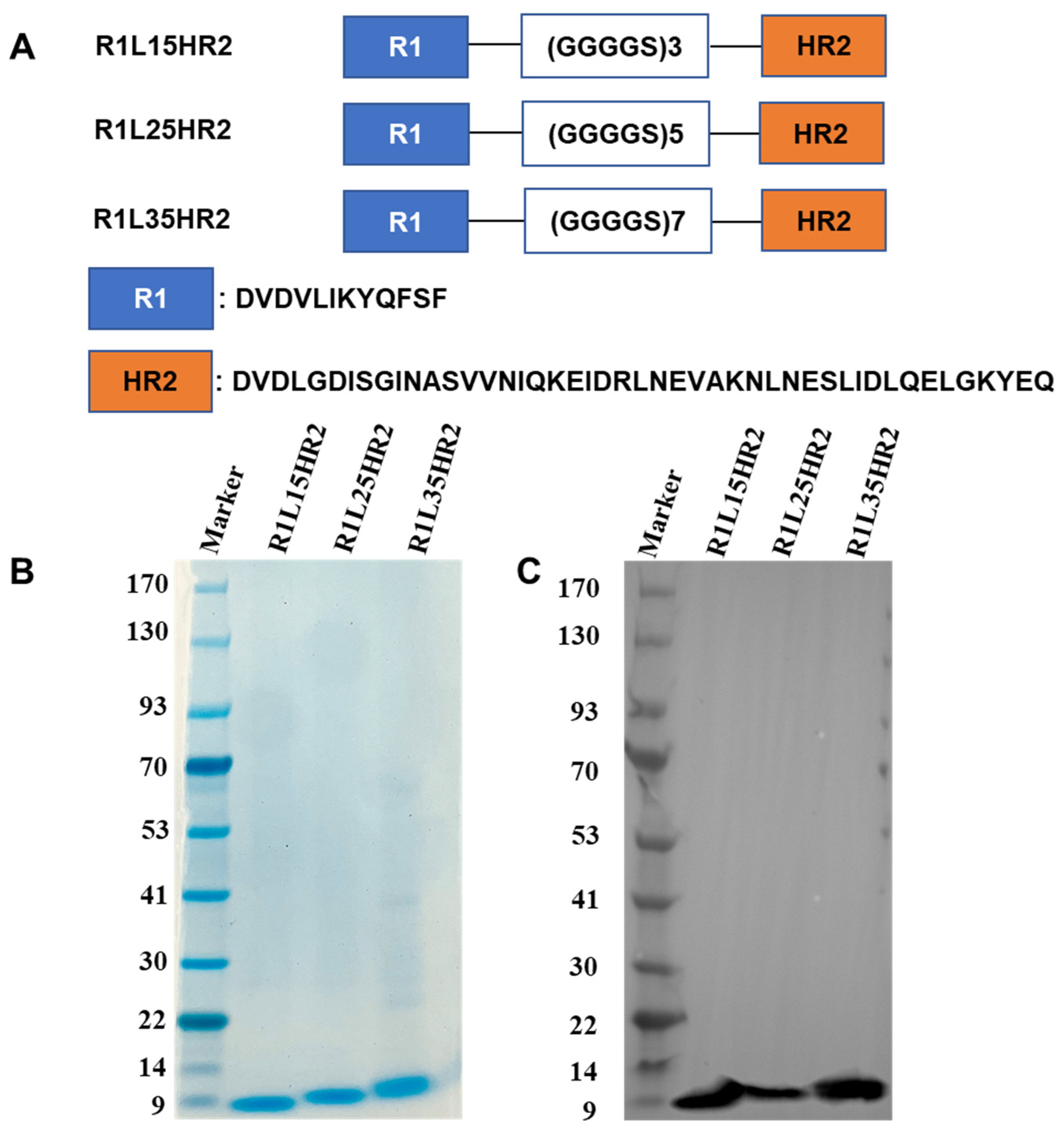
2.1. Design and Identification of the Bispecific Peptide Inhibitors
2.2. Conjugating RBD- and HR1-Targeting Peptides Could Synergistically Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infection
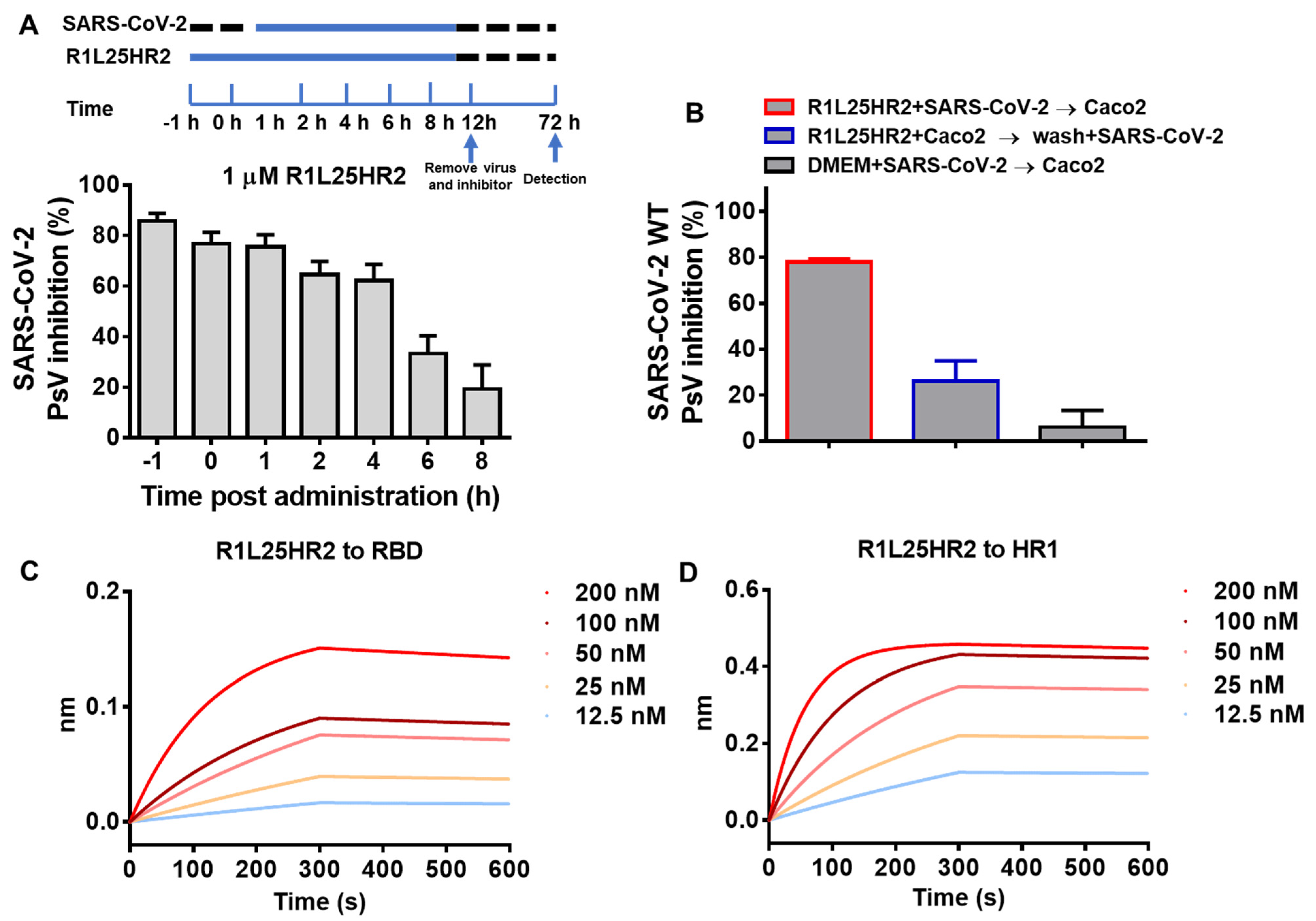
2.3. R1L25HR2 Inhibited SARS-CoV-2 Entry at the Early Stage and Exhibited a High Affinity to RBD and HR1
2.4. R1L25HR2 Inhibited SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Preventing Cell Surface Attachment and Blocking S Protein-Mediated Membrane Fusion
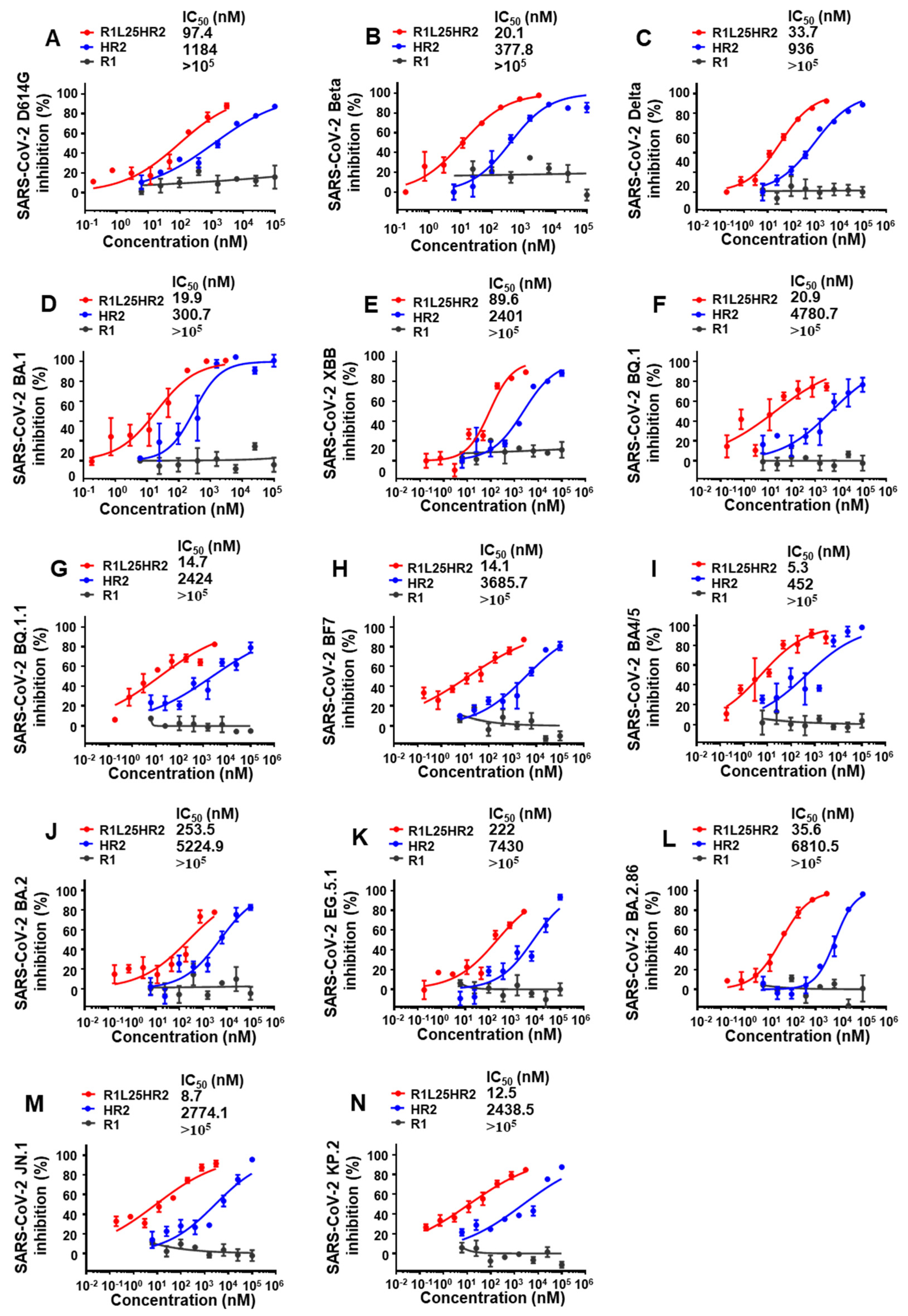
2.5. R1L25HR2 Exhibited Broad and Potent Inhibitory Activity Against Different SARS-CoV-2 Variants
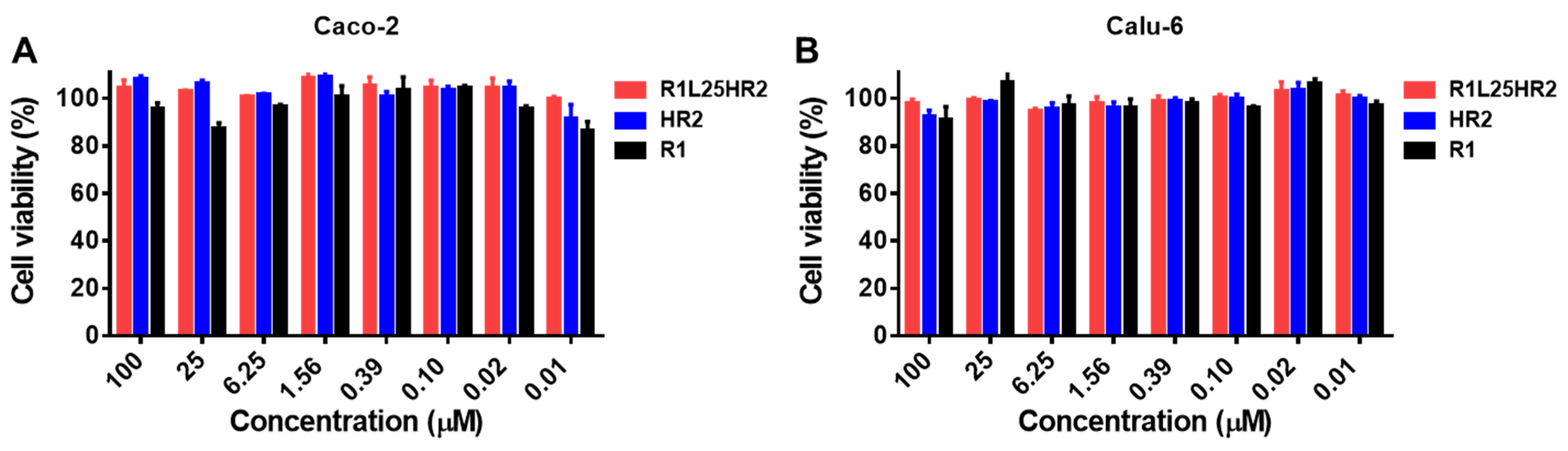
2.6. R1L25HR2 Showed No Cytotoxicity to Target Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmids and Cells
4.2. Construction, Expression and Purification of Bispecific Peptides
4.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Inhibition of Pseudotyped Virus Infection
4.5. Binding Affinity Determination Using Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI)
4.6. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 D614G S-Mediated Cell–Cell Fusion
4.7. Cell Viability Assay
4.8. Time-of-Addition Assay
4.9. Washout Assay
4.10. Attachment Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossler, A.; Riepler, L.; Bante, D.; von Laer, D.; Kimpel, J. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Neutralization in Serum from Vaccinated and Convalescent Persons. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, P.V.; Katzourakis, A.; Stilianakis, N. Antigenic evolution will lead to new SARS-CoV-2 variants with unpredictable severity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.F.; Han, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.J.; Yu, W.E.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, J.W.; Zhang, S.Y.; Kong, Y.D.; Guo, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: Epidemiological Features, Biological Characteristics, and Clinical Significance. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 877101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yisimayi, A.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Xiao, T.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature 2022, 608, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.N.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, M.; Lan, Q.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Ying, T.; Liu, S.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, S.; et al. Fusion mechanism of 2019-nCoV and fusion inhibitors targeting HR1 domain in spike protein. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.W.; Yu, J.F.; Shan, S.S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.L.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.L.; Wang, Q.S.; Zhang, L.Q.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wu, L.L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lu, G.W.; Qiao, C.P.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Bidon, M.; Jaimes, J.A.; Whittaker, G.R.; Daniel, S. Coronavirus membrane fusion mechanism offers a potential target for antiviral development. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.X.; Goreshnik, I.; Coventry, B.; Case, J.B.; Miller, L.; Kozodoy, L.; Chen, R.E.; Carter, L.; Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; et al. De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors. Science 2020, 370, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomplun, S.; Jbara, M.; Quartararo, A.J.; Zhang, G.W.; Brown, J.S.; Lee, Y.C.; Ye, X.Y.; Hanna, S.; Pentelute, B.L. Discovery of High-Affinity Peptide Binders for the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Acs Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, R.; Wen, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, C. Peptide Binder with High-Affinity for the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 28527–28536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yu, D.; Yan, H.; Chong, H.; He, Y. Design of Potent Membrane Fusion Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2, an Emerging Coronavirus with High Fusogenic Activity. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00635-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.L.; Wang, C.C.; Kreutzberger, A.J.B.; Ojha, R.; Kuivanen, S.; Couoh-Cardel, S.; Muratcioglu, S.; Eisen, T.J.; White, K.I.; Held, R.G.; et al. Nanomolar inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection by an unmodified peptide targeting the prehairpin intermediate of the spike protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2210990119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanmardi, K.; Chou, C.W.; Terrace, C.; Annapareddy, A.; Kaoud, T.S.; Guo, Q.Q.; Lutgens, J.; Zorkic, H.; Horton, A.P.; Gardner, E.C.; et al. Rapid characterization of spike variants via mammalian cell surface display. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 5099–5111.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, N.; Hu, Y.; Chong, H.; He, Y. Resistance profile and mechanism of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 variants to LCB1 inhibitor targeting the spike receptor-binding motif. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1022006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.W.; Chen, G.L.; Dang, B.B. Novel Engineered SARS-CoV-2 HR1 Trimer Exhibits Improved Potency and Broad-Spectrum Activity against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e00681-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Tang, K.; Chen, G.; Xie, Y.; Polizzi, N.F.; DeGrado, W.F.; Yuan, S.; Dang, B. An enhanced broad-spectrum peptide inhibits Omicron variants in vivo. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Lan, Q.; Feng, S.; Qi, F.; Bao, L.; Du, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.M.; Yang, W.L.; Yang, F.Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.J.; Hou, W.; Fan, C.F.; Jin, R.H.; Feng, Y.M.; Wang, Y.C.; et al. Cathepsin L plays a key role in SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and humanized mice and is a promising target for new drug development. Signal Transduct. Tar. 2021, 6, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorici, M.A.; Veesler, D. Structural insights into coronavirus entry. Adv. Virus Res. 2019, 105, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcink, T.C.; Kicmal, T.; Armbruster, E.; Zhang, Z.N.; Zipursky, G.; Golub, K.L.; Idris, M.; Khao, J.; Drew-Bear, J.; McGill, G.; et al. Intermediates in SARS-CoV-2 spike-mediated cell entry. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunst, M.W.; Qin, Z.; Dodero-Rojas, E.; Ding, S.L.; Prévost, J.; Chen, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.P.; Pazgier, M.; Wu, S.P.; Xie, X.P.; et al. Structure and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 spike refolding in membranes. Science 2024, 385, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.J.; Boyer, J.L.; Korn, E.D. Comparative Biochemistry of Non-Muscle Actins. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 8300–8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.C.; Xu, Z.L.; Shao, M.L.; Li, D.X.; Duan, Y.K.; Tang, J.L.; Yu, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; et al. Structure-based discovery of dual pathway inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 entry. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.X.; Xu, W.; Tang, J.Y.; Cao, N.J.; Lan, Q.S.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S.B. A bivalent protein targeting glycans and HR1 domain in spike protein potently inhibited infection of SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.X.; Liu, Z.M.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Xu, W.; Mao, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Hao, A.H.; Xia, S.; Liu, Z.Z.; et al. Early fusion intermediate of ACE2-using coronavirus spike acting as an antiviral target. Cell 2025, 188, 1297–1314.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepkowitz, K.A. Effect of HAART on natural history of AIDS-related opportunistic disorders. Lancet 1998, 351, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, Z.Q.; Xie, X.P.; Lin, J.Q.; Gao, P.; Wu, B.; El Sahili, A.; Su, H.; Liu, Y.; Ye, X.H.; Tan, E.Y.; et al. Engineering SARS-CoV-2 specific cocktail antibodies into a bispecific format improves neutralizing potency and breadth. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.P.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhan, W.Q.; Zheng, Q.W.; Zhang, M.; Ji, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.Y.; et al. Combating the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (BA.1) and BA.2 with potent bispecific antibodies engineered from non-Omicron neutralizing antibodies. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Qian, Q.; Jiang, Y.S.; Liang, Z.X.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Y.; Shen, C.G. Design and Characterization of Bispecific and Trispecific Antibodies Targeting SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2025, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, W.W.; Xu, W.; Cheng, L.; Xue, J.; Wang, Q.; Yu, F.; Xia, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.M.; Qin, C.; et al. IgG Fc-binding motif-conjugated HIV-1 fusion inhibitor exhibits improved potency and in vivo half-life: Potential application in combination with broad neutralizing antibodies. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.J.; To, K.K.W.; Lam, H.; Zhou, X.X.; Chan, J.F.W.; Peng, Z.; Lee, A.C.Y.; Cai, J.P.; Chan, W.M.; Ip, J.D.; et al. Cross-linking peptide and repurposed drugs inhibit both entry pathways of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Yan, L.; Xu, W.; Agrawal, A.S.; Algaissi, A.; Tseng, C.T.K.; Wang, Q.; Du, L.Y.; Tan, W.J.; Wilson, I.A.; et al. A pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting the HR1 domain of human coronavirus spike. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Protein | KD (M) | kon (1/Ms) | koff (1/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RBD | 5.02 × 10−9 | 3.81 × 104 | 1.92 × 10−4 |
| HR1 | 8.52 × 10−10 | 8.88 × 104 | 7.57 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, W.; Zhu, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. A Dual-Targeting Peptide Inhibitor Simultaneously Blocking Viral Attachment and Membrane Fusion for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125729
Bi W, Zhu T, Xu Y, Li J. A Dual-Targeting Peptide Inhibitor Simultaneously Blocking Viral Attachment and Membrane Fusion for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125729
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Wenwen, Tao Zhu, Yawen Xu, and Jianmin Li. 2025. "A Dual-Targeting Peptide Inhibitor Simultaneously Blocking Viral Attachment and Membrane Fusion for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125729
APA StyleBi, W., Zhu, T., Xu, Y., & Li, J. (2025). A Dual-Targeting Peptide Inhibitor Simultaneously Blocking Viral Attachment and Membrane Fusion for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125729





