Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-II Is Associated with Poor Poststroke Outcomes in Males: A Secondary Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Insulin-like Growth System
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics
2.2. S-IGF-II and Sex Difference
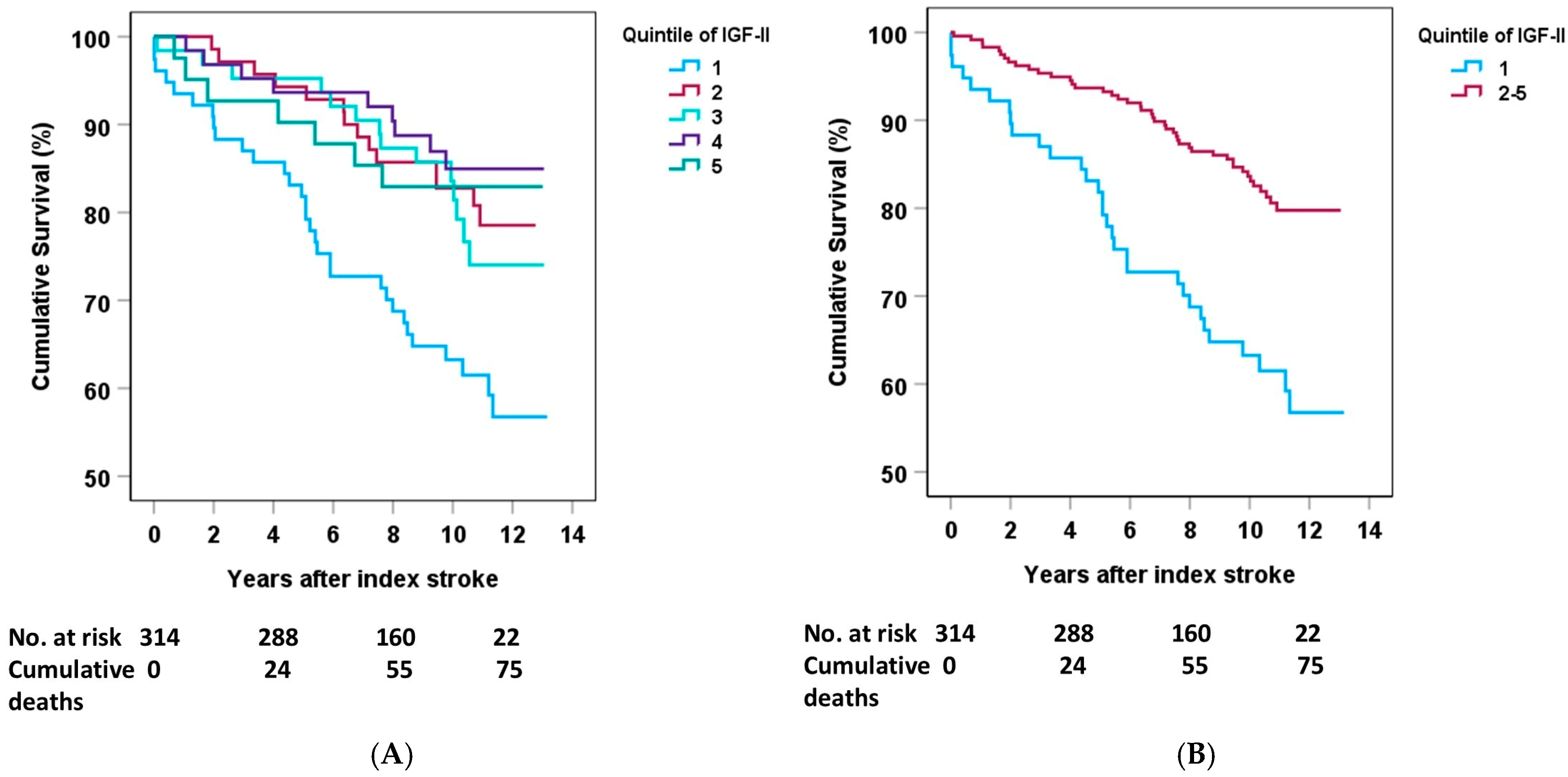
2.3. Sex Differences in IGF-II and Mortality
2.4. Sex Differences in IGF-II and Functional Outcomes
3. Discussion
3.1. Summary
3.2. Sex-Specific Neurological Outcomes of IGF-II
3.3. Other Sex-Specific Effects in Stroke
3.4. Potential Biological Pathways of IGF-II Action
3.5. Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Data Collection
4.3. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| IGF-II | Insulin-Like Growth Factor II |
| IS | Ischemic Stroke |
| mRS | Modified Rankin Scale |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| SSS | Scandinavian Stroke Scale |
References
- Ohlsson, C.; Mohan, S.; Sjogren, K.; Tivesten, A.; Isgaard, J.; Isaksson, O.; Jansson, J.O.; Svensson, J. The role of liver-derived insulin-like growth factor-I. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 494–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.C.; Gluckman, P.D.; Feldman, E.L.; Werther, G.A. The insulin-like growth factor system and its pleiotropic functions in brain. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 916–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roith, D. Seminars in medicine of the beth israel deaconess medical center. Insulin-like growth factors. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dynkevich, Y.; Rother, K.I.; Whitford, I.; Qureshi, S.; Galiveeti, S.; Szulc, A.L.; Danoff, A.; Breen, T.L.; Kaviani, N.; Shanik, M.H.; et al. Tumors, igf-2, and hypoglycemia: Insights from the clinic, the laboratory, and the historical archive. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 798–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beletskiy, A.; Chesnokova, E.; Bal, N. Insulin-like growth factor 2 as a possible neuroprotective agent and memory enhancer-its comparative expression, processing and signaling in mammalian cns. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Torres-Aleman, I. The many faces of insulin-like peptide signalling in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Miao, C.Y. Angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S.P.; Hundborg, H.H.; Sorensen, H.T.; Orskov, H.; Tjonneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Jorgensen, J.O. Insulin-like growth factor (igf) i, -ii, and igf binding protein-3 and risk of ischemic stroke. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 5937–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Clemens, J.A.; Bondy, C.A. Insulin-like growth factors in the response to cerebral ischemia. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 1992, 3, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beilharz, E.J.; Bassett, N.S.; Sirimanne, E.S.; Williams, C.E.; Gluckman, P.D. Insulin-like growth factor ii is induced during wound repair following hypoxic-ischemic injury in the developing rat brain. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1995, 29, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, M.J.; Bushnell, C.D.; Howard, G.; Gargano, J.W.; Duncan, P.W.; Lynch, G.; Khatiwoda, A.; Lisabeth, L. Sex differences in stroke: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, medical care, and outcomes. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, P.; Azcoitia, I.; Garcia-Segura, L.M. Interdependence of oestrogen and insulin-like growth factor-I in the brain: Potential for analysing neuroprotective mechanisms. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 185, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Gonzalez, C. Neuroprotective role of estrogens: Relationship with insulin/igf-1 signaling. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed) 2012, 4, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberg, D.; Aberg, N.D.; Jood, K.; Redfors, P.; Blomstrand, C.; Isgaard, J.; Jern, C.; Svensson, J. Insulin-like growth factor-ii and ischemic stroke-a prospective observational study. Life 2021, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jood, K.; Ladenvall, C.; Rosengren, A.; Blomstrand, C.; Jern, C. Family history in ischemic stroke before 70 years of age: The sahlgrenska academy study on ischemic stroke. Stroke 2005, 36, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denti, L.; Annoni, V.; Cattadori, E.; Salvagnini, M.A.; Visioli, S.; Merli, M.F.; Corradi, F.; Ceresini, G.; Valenti, G.; Hoffman, A.R.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 as a predictor of ischemic stroke outcome in the elderly. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, K.H.; Oh, M.S.; Lee, B.C. Association between serum insulin-like growth factor-1 and neurological severity in acute ischemic stroke. J. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 17, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Aguila, N.P.; Carrera, C.; Muino, E.; Cullell, N.; Carcel-Marquez, J.; Gallego-Fabrega, C.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, J.; Bustamante, A.; Delgado, P.; Ibanez, L.; et al. Clinical variables and genetic risk factors associated with the acute outcome of ischemic stroke: A systematic review. J. Stroke 2019, 21, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, C.; Buchwald, F.; Ullberg, T.; Pihlsgard, M.; Norrving, B.; Petersson, J. Epidemiology of first and recurrent ischemic stroke in sweden 2010–2019: A riksstroke study. Neuroepidemiology 2022, 56, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelros, P.; Stegmayr, B.; Terent, A. Sex differences in stroke epidemiology: A systematic review. Stroke 2009, 40, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvholm, B.; Hedman, L.; Landstrom, M.; Liv, P.; Burdorf, A.; Toren, K. Changing smoking habits and the occurrence of lung cancer in sweden-a population analysis. Eur. J. Public. Health 2024, 34, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmegard, H.N.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Jensen, G.B.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Benn, M. Sex hormones and ischemic stroke: A prospective cohort study and meta-analyses. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeilschifter, J.; Scheidt-Nave, C.; Leidig-Bruckner, G.; Woitge, H.W.; Blum, W.F.; Wuster, C.; Haack, D.; Ziegler, R. Relationship between circulating insulin-like growth factor components and sex hormones in a population-based sample of 50- to 80-year-old men and women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberg, N.D.; Brywe, K.G.; Isgaard, J. Aspects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I related to neuroprotection, regeneration, and functional plasticity in the adult brain. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.A.; Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Ashpole, N.M. Preclinical and clinical evidence of igf-1 as a prognostic marker and acute intervention with ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2021, 41, 2475–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.N.; Schneider, J.S.; Qin, M.; Tyler, W.A.; Pintar, J.E.; Fraidenraich, D.; Wood, T.L.; Levison, S.W. Igf-ii promotes stemness of neural restricted precursors. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.; Xu, M.; Liu, Z.; Xie, H.; Yu, Y.; Chu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Fang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Yao, Y.; et al. Molecular epidemiological study of exosomes circznf609, circpum1, igf2 with ischemic stroke. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2025, 25, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, N.; Elting, J.W.; Chesik, D.; Kema, I.P.; De Keyser, J. Intravenous tissue plasminogen activator in patients with stroke increases the bioavailability of insulin-like growth factor-1. Stroke 2006, 37, 2368–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, G.M. Recombinant igf-i: Past, present and future. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2016, 28, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yan, J.; Bregere, C.; Zelmer, A.; Goerne, T.; Kapfhammer, J.P.; Guzman, R.; Wellmann, S. RBM3 promotes neurogenesis in a niche-dependent manner via imp2-igf2 signaling pathway after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduzzi, P.; Concato, J.; Kemper, E.; Holford, T.R.; Feinstein, A.R. A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, C. Igf2 and cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R321–R339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, J.M.; Shun, C.T.; Liang, J.T.; Chiu, H.M.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, H.P.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, J.T. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 levels as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aked, J.; Delavaran, H.; Lindgren, A.G. Survival, causes of death and recurrence up to 3 years after stroke: A population-based study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 4060–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, L.J.; Ali, M.; Lyden, P.D.; Bath, P.M.; Virtual International Stroke Trials Archive Collaboration. Interconversion of the national institutes of health stroke scale and scandinavian stroke scale in acute stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 18, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, M.S.; Gibson, J.M.; Heald, A.H.; Dunger, D.B.; Wareham, N.J. Low circulating igf-ii concentrations predict weight gain and obesity in humans. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondanelli, M.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Zatelli, M.C.; Basaglia, N.; Degli Uberti, E.C. Prevalence of hypopituitarism in patients with cerebrovascular diseases. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2008, 31, 16–20. [Google Scholar]

| A. Healthy Controls and Patients | ||
| Controls (n = 514) | All IS Cases (n = 492) | |
| Age (years) | 57.2 ± 0.44 | 57.0 ± 0.44 |
| Hypertension (%) | 39 | 62 *** |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 6 | 19 *** |
| Current smoker (%) | 17 | 39 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.5 ± 0.18 | 26.7 ± 0.20 |
| Imputed LDL (ng/nL) | 3.33 ± 0.0 | 3.35 ± 0.04 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.13 ± 0.12 | 4.80 ± 0.25 |
| NIHSS score baseline | NA | 5.31 ± 0.25 |
| mRS score 3 months | NA | 2.34 ± 0.11 |
| mRS score 2 years | NA | 1.91 ± 0.08 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 3.06 ± 0.26 | 10.81 ± 1.00 *** |
| s-IGF-II acute (ng/mL) | 712.1 (±5.58) | 734.7 ±7.08 * |
| s-IGF-II 3 months (ng/mL) | NA | 736.8 ± 6.91 * |
| B. IS Cases, Males and Females | ||
| Males (n = 315) | Females (n = 177) | |
| Age (years) | 57.7 ± 0.52 | 56.3 ± 0.78 |
| Hypertension (%) | 64 | 57 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 21 | 16 |
| Current smoker (%) | 36 | 45 a |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.9 ± 0.21 | 26.4 ± 0.42 |
| Imputed LDL (ng/nL) | 3.29 ± 0.52 | 3.44 ± 0.07 |
| HOMA-IR | 5.10 ± 0.34 | 4.28 ± 0.31 |
| NIHSS score baseline | 5.12 ± 0.31 | 5.65 ± 0.44 |
| mRS score 3 months | 2.23 ± 0.14 | 2.53 ± 0.21 |
| mRS score 2 years | 1.96 ± 0.12 | 1.81 ± 0.11 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 11.5 ± 1.4 | 9.5 ± 1.3 |
| s-IGF-II acute (ng/mL) | 707 ± 8.9 | 783 ± 10.8 *** |
| s-IGF-II 3 months (ng/mL) | 708 ± 8.7 | 790 ± 10.2 *** |
| Stroke (Males) | Quintile 1 | Quintile 2–5 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deaths (n) | 31 | 44 | |
| Crude | 2.52 (1.59–3.99) | 1.0 referent | <0.01 |
| Model A | 2.10 (1.32–3.26) | 1.0 referent | 0.002 |
| Model B | 1.92 (1.18–3.17) | 1.0 referent | 0.009 |
| Model C | 1.83 (1.09–3.06) | 1.0 referent | 0.022 |
| Stroke (Males) | Quintile 1 | Quintiles 2–5 | p-Value | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-month mRS 3–6 | ||||
| Crude | 2.72 (1.51–4.92) | 1.0 referent | 0.002 | 298 |
| Model A | 2.54 (1.38–4.68) | 1.0 referent | 0.003 | 298 |
| Model B | 2.22 (1.17–4.20) | 1.0 referent | 0.014 | 293 |
| Model C | 1.18 (0.51–2.74) | 1.0 referent | 0.701 | 292 |
| 2-year mRS 3–6 | ||||
| Crude | 2.59 (1.44–4.66) | 1.0 referent | 0.001 | 308 |
| Model A | 2.26 (1.23–4.13) | 1.0 referent | 0.008 | 308 |
| Model B | 2.00 (1.06–3.79) | 1.0 referent | 0.033 | 300 |
| Model C | 1.34 (0.65–2.78) | 1.0 referent | 0.432 | 299 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glamheden, C.; Åberg, N.D.; Gadd, G.; Åberg, D. Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-II Is Associated with Poor Poststroke Outcomes in Males: A Secondary Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125525
Glamheden C, Åberg ND, Gadd G, Åberg D. Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-II Is Associated with Poor Poststroke Outcomes in Males: A Secondary Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125525
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlamheden, Christian, N. David Åberg, Gustaf Gadd, and Daniel Åberg. 2025. "Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-II Is Associated with Poor Poststroke Outcomes in Males: A Secondary Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125525
APA StyleGlamheden, C., Åberg, N. D., Gadd, G., & Åberg, D. (2025). Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-II Is Associated with Poor Poststroke Outcomes in Males: A Secondary Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125525






