Increased Plasma Levels of ACE and Ang II in Prediabetes May Contribute to Adipose Tissue Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization Table of the Participants
2.1.1. Glycated Hemoglobin and Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR)
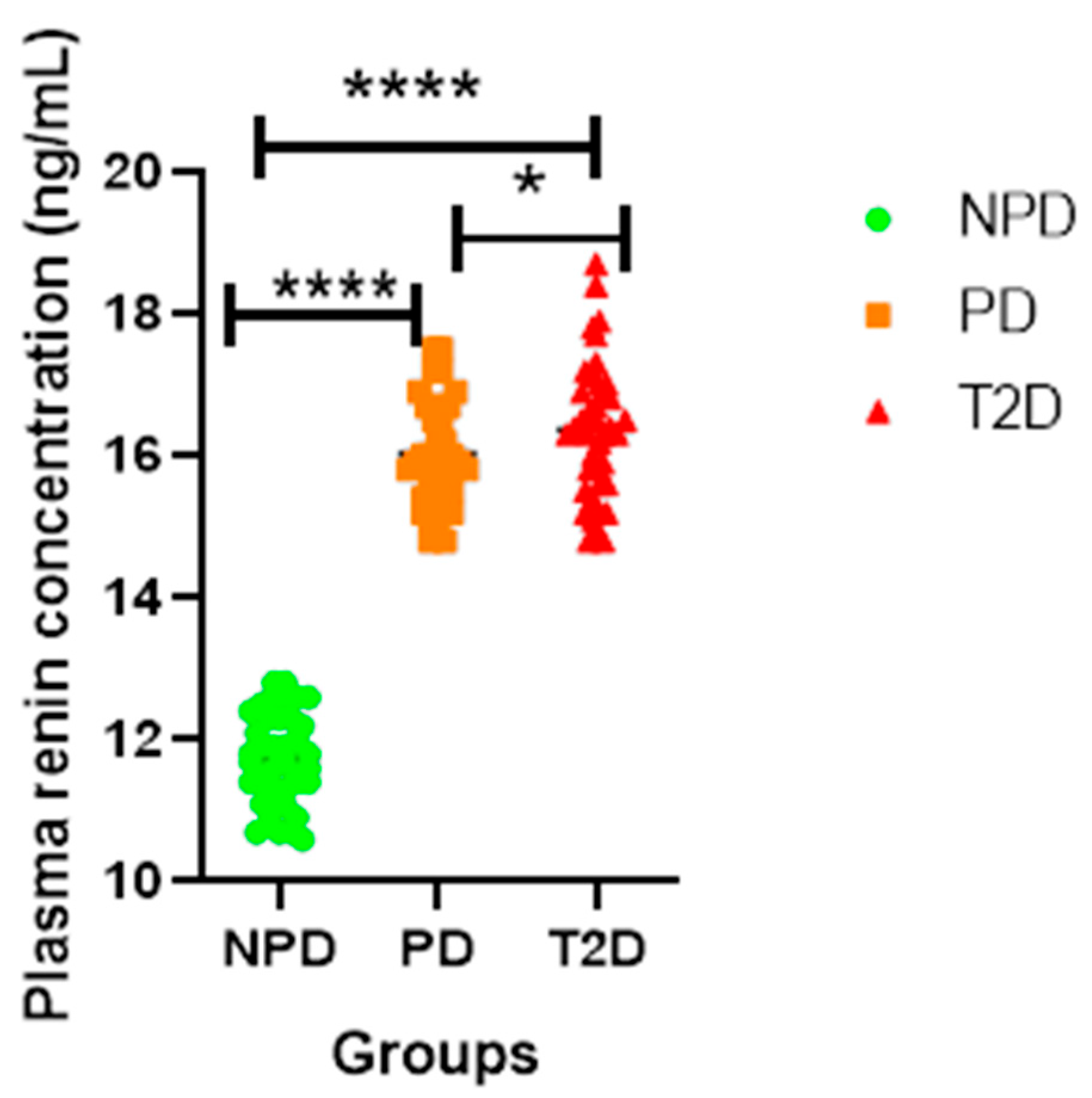
Plasma Renin Concentration
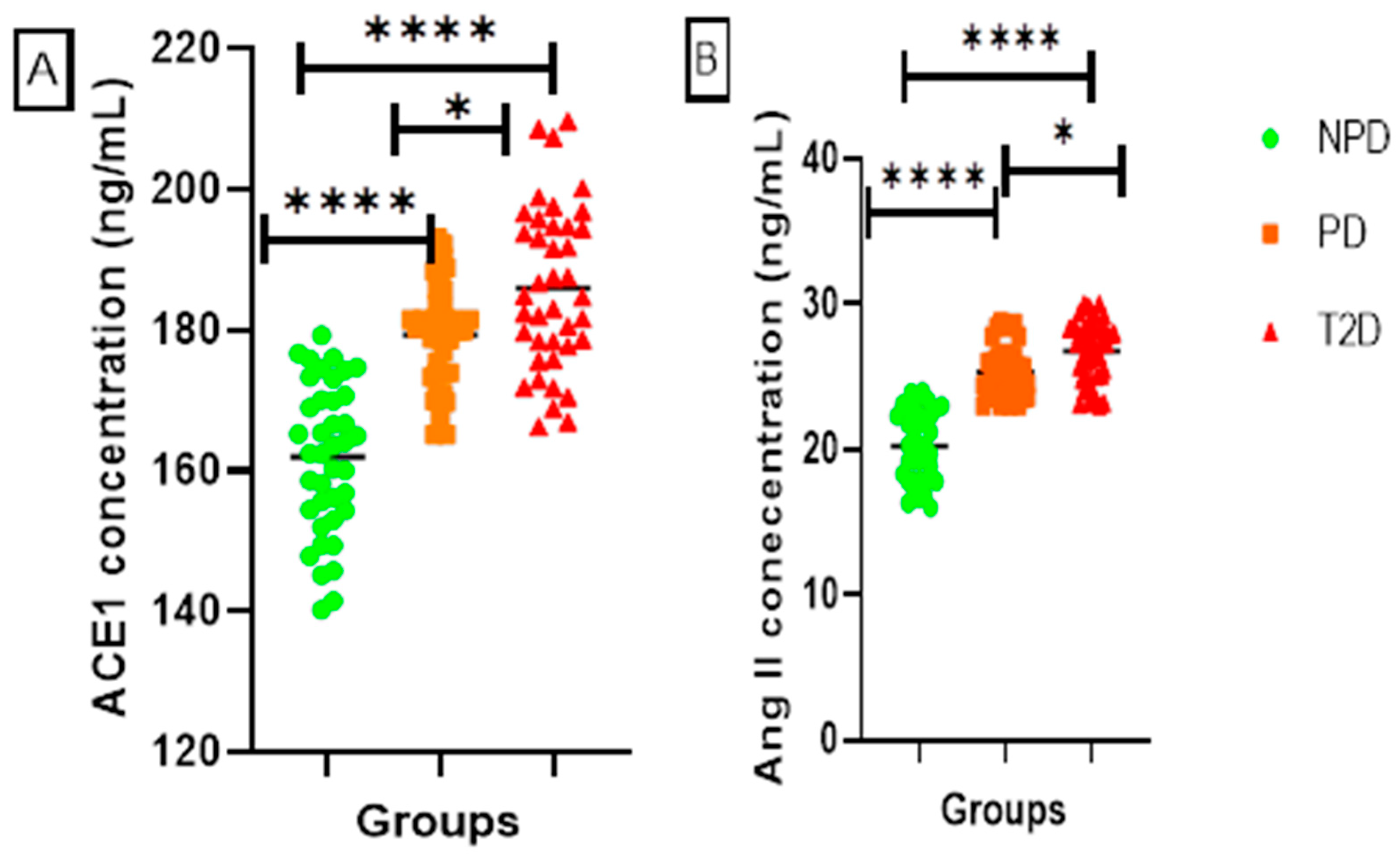
ACE1 and Ang II
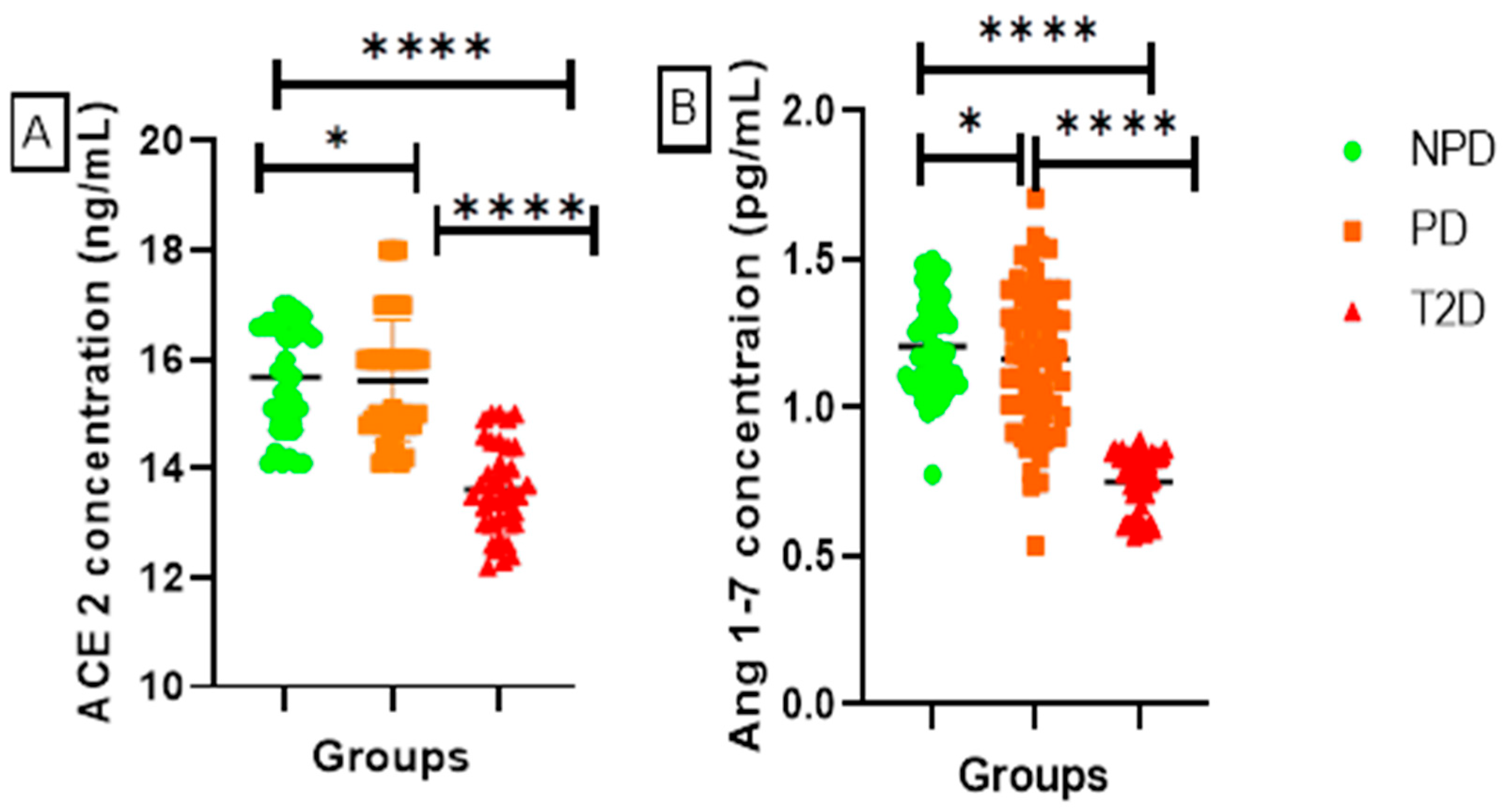
ACE2 and Ang 1-7
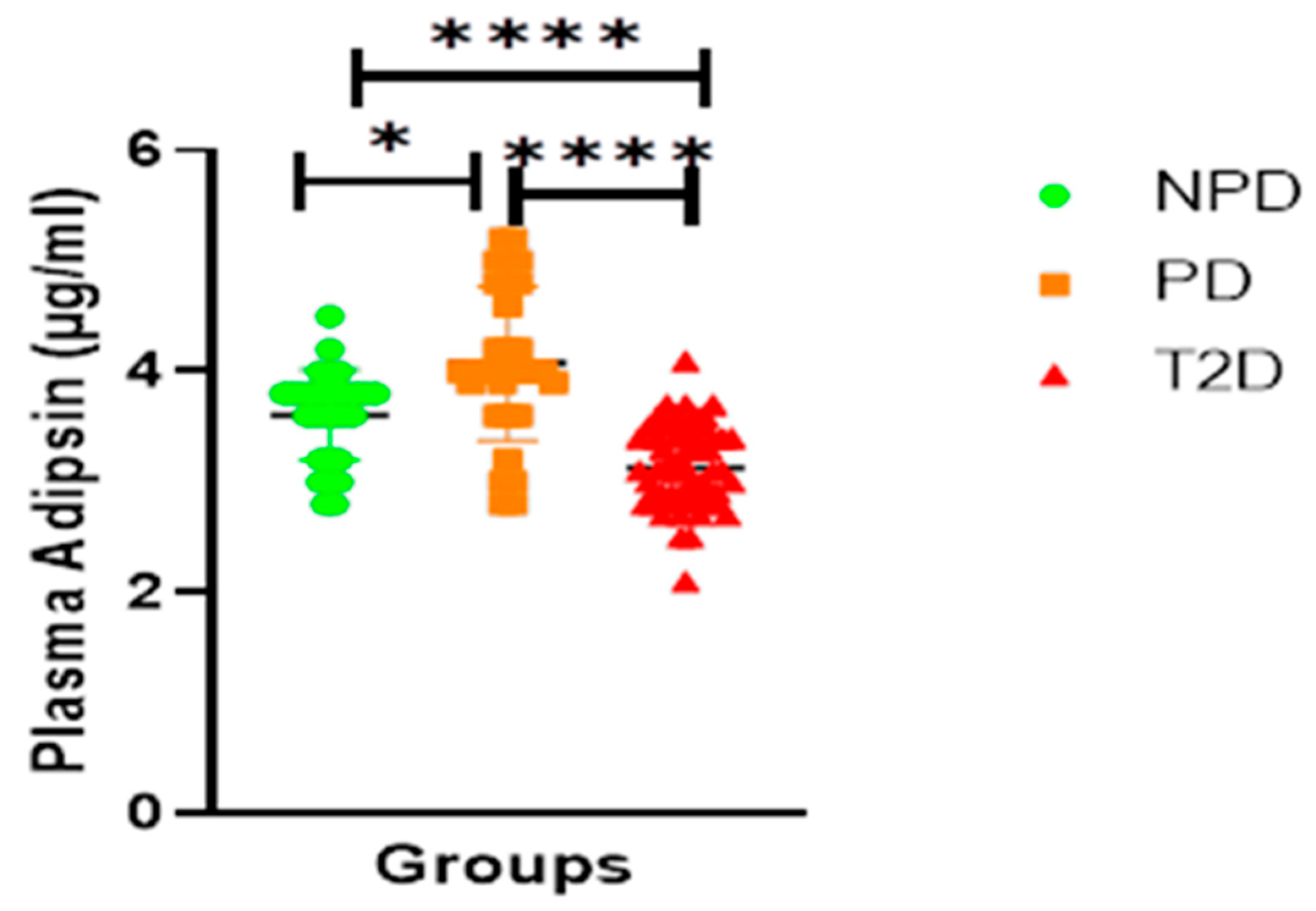
Adipsin
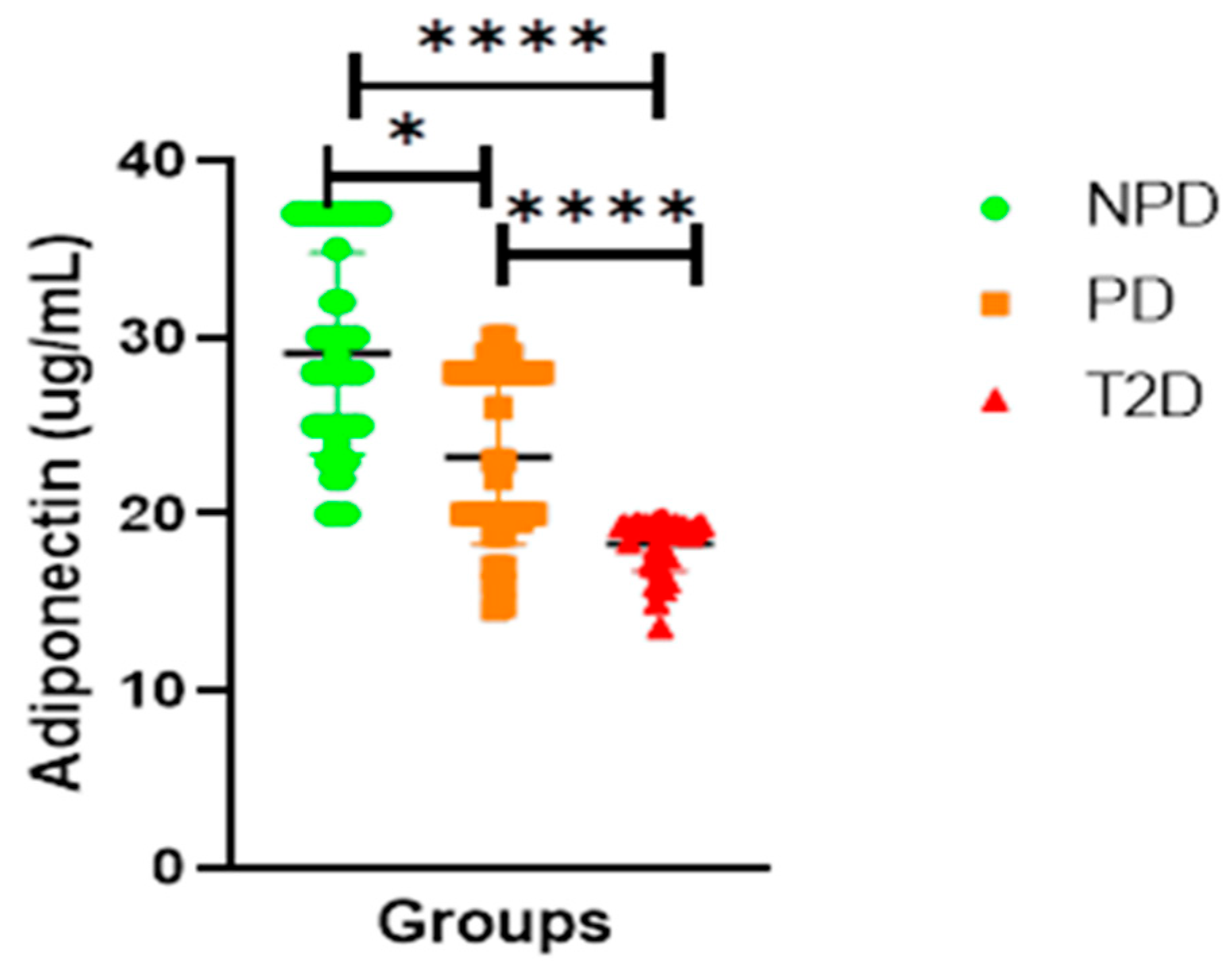
Adiponectin
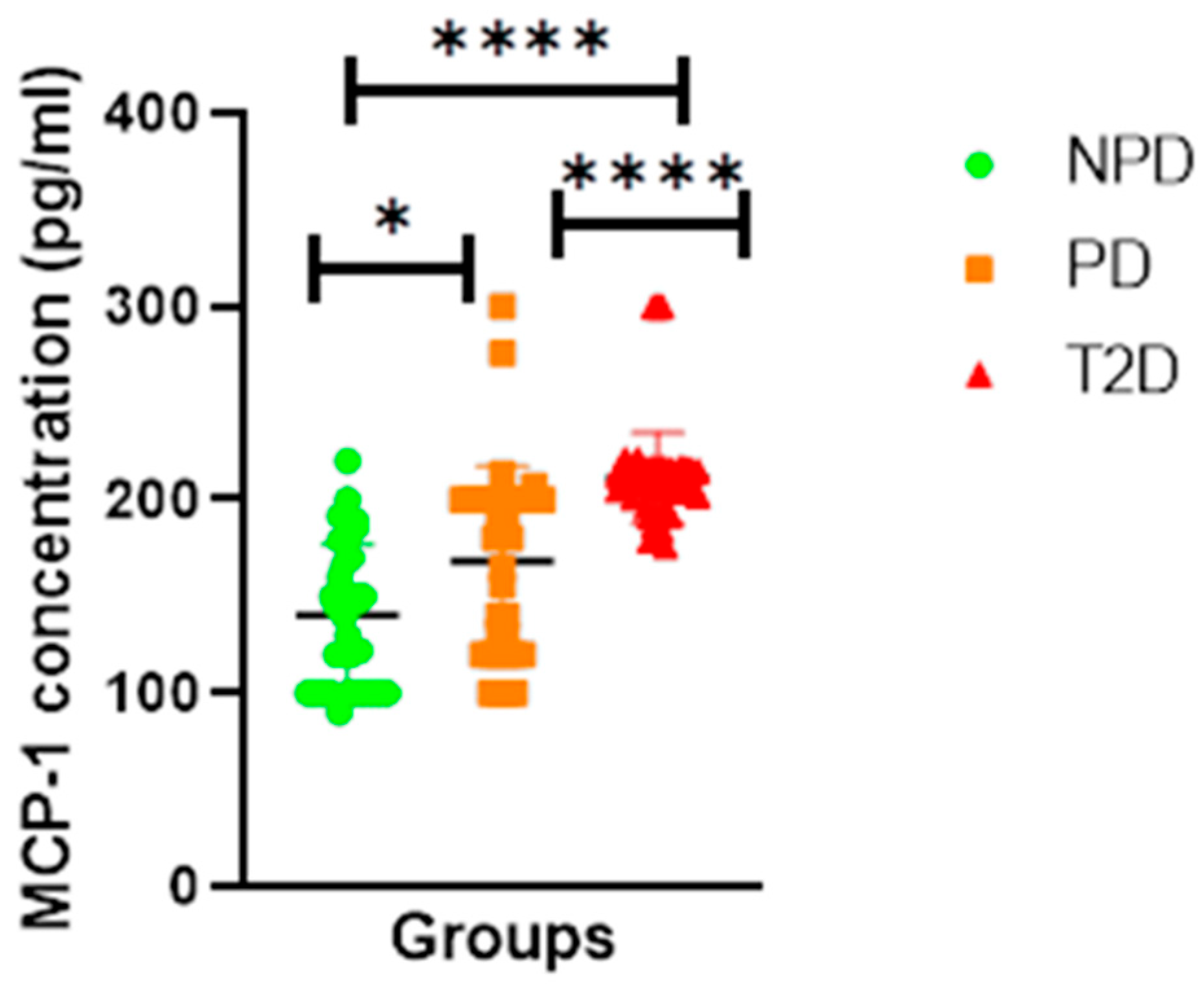
Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1)
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Study Design and Sampling
4.2. Biochemical Analysis
4.3. Plasma Lipid Profile Determination (LDL and VLDL Calculation)
- LDL and VLDL were determined using Friedewald equation
- Calculate LDL cholesterol using the Friedewald equation:LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) = total cholesterol (mg/dL) − HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) − (triglycerides (mg/dL)/5)
- Calculate VLDL cholesterol:VLDL cholesterol (mg/dL) = Triglycerides (mg/dL)/5Assay Sensitivities (minimum detectable concentrations, pg/mL)
- Link Between Lipid Profile and Insulin Resistance
- Insulin Resistance Determination (HOMA-IR Calculation)
4.3.1. Precision
4.3.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
5.1. Study Limitations
5.2. Future Studies
5.3. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gopal, S.S.; Maradgi, T.; Ponesakki, G. Antiobese properties of carotenoids: An overview of underlying molecular mechanisms. In Carotenoids: Properties, Processing and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 75–105. [Google Scholar]
- Aktaş, G.; Mustafa, Ş.; Tekçe, H. Yeni adipokinler: Leptin, adiponektin ve omentin. Abant Tıp Derg. 2013, 2, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Sun, J.; Guan, H.; Zhu, Q.; Yao, W. Angiotensin II inhibits adipogenic differentiation and promotes mature adipocyte browning through the corepressor CtBP1. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kloet, A.D.; Krause, E.G.; Woods, S.C. The renin angiotensin system and the metabolic syndrome. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 100, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunvariya, A.D.; Dave, S.A.; Modi, Z.J.; Patel, P.K.; Sagar, S.R. Exploration of multifaceted molecular mechanism of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in pathogenesis of various diseases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, D.; Soler, M.J.; Ye, M. ACE2 and diabetes: ACE of ACEs? Diabetes 2010, 59, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanová, M.; Dostálová, I.; Trachta, P.; Drápalová, J.; Kaválková, P.; Haluzíková, D.; Matoulek, M.; Lacinová, Z.; Mráz, M.; Kasalický, M. Serum concentrations and subcutaneous adipose tissue mRNA expression of omentin in morbid obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The effect of very-low-calorie diet, physical activity and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Huh, J.Y.; Sohn, J.H.; Choe, S.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lim, C.Y.; Jo, A.; Park, S.B.; Han, W.; Kim, J.B. Lipid-overloaded enlarged adipocytes provoke insulin resistance independent of inflammation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamalipour, M.; Seidi, K.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R. Implications of resistin in type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease: Impairing insulin function and inducing pro-inflammatory cytokines. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21758–21769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N. Prediabetes diagnosis and treatment: A review. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysschaert, M.; Bergman, M. Definition of prediabetes. Med. Clin. 2011, 95, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beulens, J.; Rutters, F.; Ryden, L.; Schnell, O.; Mellbin, L.; Hart, H.; Vos, R. Risk and management of pre-diabetes. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Hasan, M.; Neaz, S.; Hussain, N.; Hossain, M.; Rahman, T. Diabetes Mellitus: Insights from epidemiology, biochemistry, risk factors, diagnosis, complications and comprehensive management. Diabetology 2021, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Alsalhe, T.A.; Chalghaf, N.; Riccò, M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Wu, J. The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kebbi, I.M.; Bidikian, N.H.; Hneiny, L.; Nasrallah, M.P. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in the Middle East and North Africa: Challenges and call for action. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.H.; Myrick, J.W.; Oyageshio, O.; Uren, C.; Saayman, J.; Boolay, S.; van der Westhuizen, L.; Werely, C.; Möller, M.; Henn, B.M. Epidemiological correlates of overweight and obesity in the Northern Cape Province, South Africa. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhize, B.C.; Mosili, P.; Ngubane, P.S.; Sibiya, N.H.; Khathi, A. Diet-induced prediabetes: Effects on the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) in selected organs. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassandra Mkhize, B.; Mosili, P.; Sethu Ngubane, P.; Khathi, A. The relationship between adipose tissue RAAS activity and the risk factors of prediabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adipocyte 2023, 12, 2249763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, A.J.; White, U.; Elks, C.M.; Stephens, J.M. Adipose tissue: Physiology to metabolic dysfunction. Endotext [Internet]. 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555602/ (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Cai, Z.; Fang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, M.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, F.; Huo, H.; Pan, C. Angiotensin II Promotes White Adipose Tissue Browning and Lipolysis in Mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6022601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias Lelis, D.; de Freitas, D.F.; Machado, A.S.; Crespo, T.S.; Santos, S.H.S. Angiotensin-(1-7), adipokines and inflammation. Metabolism 2019, 95, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, A.D. Standards of care in diabetes—2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clin. Diabetes 2023, 41, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varra, F.-N.; Varras, M.; Varra, V.-K.; Theodosis-Nobelos, P. Molecular and pathophysiological relationship between obesity and chronic inflammation in the manifestation of metabolic dysfunctions and their inflammation-mediating treatment options. Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 29, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xie, S.; Xu, T.; Wu, X.; Han, M. Rasal2 deficiency reduces adipogenesis and occurrence of obesity-related disorders. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaetis, G.S.; Papakyriakou, P.; Panagiotou, T.N. State of the art paper Central obesity, type 2 diabetes and insulin: Exploring a pathway full of thorns. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, L.; Menikdiwela, K.; LeMieux, M.; Dufour, J.M.; Kaur, G.; Kalupahana, N.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. The renin angiotensin system, oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in obesity and insulin resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruze, R.; Liu, T.; Zou, X.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Yin, X.; Xu, Q. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1161521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera-Sulbarán, J.; Ryder, E.; Vargas, R.; Pedreáñez, A. Angiotensin II and human obesity. A narrative review of the pathogenesis. Investig. Clínica 2022, 63, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, S.; Yiannikouris, F.; Gupte, M.; Cassis, L. The adipose renin–angiotensin system: Role in cardiovascular disease. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y.; Shefer, G.; Stern, N. Adipose tissue renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) and progression of insulin resistance. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 378, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, R.; Dutton, H.; Sorisky, A. In vitro studies of the renin-angiotensin system in human adipose tissue/adipocytes and possible relationship to SARS-CoV-2: A scoping review. Adipocyte 2023, 12, 2194034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlavani, M.; Kalupahana, N.S.; Ramalingam, L.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Regulation and functions of the renin-angiotensin system in white and brown adipose tissue. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.-C.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system: Celebrating the 20th anniversary of the discovery of ACE2. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanugula, A.K.; Kaur, J.; Batra, J.; Ankireddypalli, A.R.; Velagapudi, R.; kumar Kanugula, A. Renin-Angiotensin System: Updated Understanding and Role in Physiological and Pathophysiological States. Cureus 2023, 15, e40725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigolet, M.E.; Torres, N.; Tovar, A.R. The renin–angiotensin system in adipose tissue and its metabolic consequences during obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 2003–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yvan-Charvet, L.; Quignard-Boulangé, A. Role of adipose tissue renin–angiotensin system in metabolic and inflammatory diseases associated with obesity. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Sun, W.; Jiang, P. Role of the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis in glucose metabolism. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Rodelo, C.; Arellano-Plancarte, A.; Hernandez-Aranda, J.; Landa-Galvan, H.V.; Parra-Mercado, G.K.; Moreno-Licona, N.J.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, K.D.; Catt, K.J.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. Angiotensin II inhibits insulin receptor signaling in adipose cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, P.; Galletti, F. Impact of the renin-angiotensin system on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2004, 13, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalupahana, N.S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. The renin-angiotensin system: A link between obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, J.P.T.; Faria, A.O.V.d.; Ribeiro, T.F.S.; Simões e Silva, A.C. The Role of Renin–Angiotensin System in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: A Narrative Review. Life 2023, 13, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorad, S.; Dou, J.-t.; Benicky, J.; Hutanu, D.; Tybitanclova, K.; Zhou, J.; Saavedra, J.M. Long-term angiotensin II AT1 receptor inhibition produces adipose tissue hypotrophy accompanied by increased expression of adiponectin and PPARγ. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 552, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.-S.; Schulman, I.H.; Zeng, Q. Link between the renin–angiotensin system and insulin resistance: Implications for cardiovascular disease. Vasc. Med. 2012, 17, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, T.; Sha, Z.; Tang, H.; Hua, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Sluijter, J.P.; Rowe, G.C. Angiotensin II-induced muscle atrophy via PPARγ suppression is mediated by miR-29b. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. New advances of adiponectin in regulating obesity and related metabolic syndromes. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, W.A.; Wyne, K. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in diabetes and hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Caruso, C.; Candore, G. The role of adipose tissue and adipokines in obesity-related inflammatory diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 802078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Luo, X.; Xu, Q.; Yu, H.; Gao, L.; Zhou, R.; Wang, T. Adipsin of the alternative complement pathway is a potential predictor for preeclampsia in early pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 702385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milek, M.; Moulla, Y.; Kern, M.; Stroh, C.; Dietrich, A.; Schön, M.R.; Gärtner, D.; Lohmann, T.; Dressler, M.; Kovacs, P. Adipsin serum concentrations and adipose tissue expression in people with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z. Adipokines in glucose and lipid metabolism. Adipocyte 2023, 12, 2202976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Banoy, N.; Guseh, J.S.; Li, G.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Chen, T.; Poirier, B.; Putzel, G.; Rosselot, C.; Pabón, M.A.; Camporez, J.P. Adipsin preserves beta cells in diabetic mice and associates with protection from type 2 diabetes in humans. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafere, G.G.; Wondafrash, D.Z.; Zewdie, K.A.; Assefa, B.T.; Ayza, M.A. Plasma adipsin as a biomarker and its implication in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.B. The complex role of adipokines in obesity, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 731–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belalcazar, L.M.; Lang, W.; Haffner, S.M.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Schwenke, D.C.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Tracy, R.P.; Kriska, A.P.; Ballantyne, C.M. Adiponectin and the mediation of HDL-cholesterol change with improved lifestyle: The Look AHEAD Study. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2726–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomono, Y.; Hiraishi, C.; Yoshida, H. Age and sex differences in serum adiponectin and its association with lipoprotein fractions. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 55, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzaki, K.; Kotani, K.; Sano, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Gazi, I.F.; Elisaf, M.; Sakane, N. The relationship between adiponectin, an adiponectin gene polymorphism, and high-density lipoprotein particle size: From the Mima study. Metabolism 2012, 61, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafiane, A.; Gasbarrino, K.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. The role of adiponectin in cholesterol efflux and HDL biogenesis and metabolism. Metabolism 2019, 100, 153953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, V.; Thakkar, H.; Aggarwal, S.; Mridha, A.R.; Ramakrishnan, L.; Singh, A. ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) expression in adipose tissue and its modulation with insulin resistance in obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Rateri, D.L.; Feldman, D.L.; Charnigo Jr, R.J.; Fukamizu, A.; Ishida, J.; Oesterling, E.G.; Cassis, L.A.; Daugherty, A. Renin inhibition reduces hypercholesterolemia-induced atherosclerosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasooriya, A.P.; Mathai, M.L.; Walker, L.L.; Begg, D.P.; Denton, D.A.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Egan, G.F.; McKinley, M.J.; Rodger, P.D.; Sinclair, A.J. Mice lacking angiotensin-converting enzyme have increased energy expenditure, with reduced fat mass and improved glucose clearance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6531–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaseda, R.; Tsuchida, Y.; Gamboa, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Dikalova, A.; Bian, A.; Davies, S.; Fogo, A. Angiotensin receptor blocker vs ACE inhibitor effects on HDL functionality in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, M.; Sorci-Thomas, M. Rediscovering SR-BI: Surprising New Roles for The HDL Receptor. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2017, 28, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Duarte, S.; Santander, N.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Wadsack, C.; Rigotti, A.; Busso, D. High density lipoprotein cholesterol and proteome in SR-B1 KO mice: Lost in precipitation. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Chait, A. Hypertriglyceridemia secondary to obesity and diabetes. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2012, 1821, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodaghi, A.B.; Ebadi, E.; Gholami, M.J.; Azizi, R.; Shariati, A. A decreased level of high-density lipoprotein is a possible risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. Pathophysiology of diabetic dyslipidemia. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.S.; Kumari, S. Fatty acids and their role in type-2 diabetes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodanisi, E.I.; Tomose, Y.; Okeleye, B.I.; Ntwampe, S.K.; Aboua, Y.G. Prevalence of dyslipidaemia among Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in the Western Cape, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dost, T.; Kafkas, S.; Gokalp, F.; Karul, A.; Birincioglu, M. Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on adiponectin levels and lipid profile in the ovariectomized-aged rats. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2014, 5, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H. Obese visceral fat tissue inflammation: From protective to detrimental? BMC Med. 2022, 20, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; Den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose tissue distribution, inflammation and its metabolic consequences, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Benigni, A.; Cassis, P.; Remuzzi, G. Angiotensin II revisited: New roles in inflammation, immunology and aging. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Hirono, Y.; Tateno, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Hirata, Y. Angiotensin II induces monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression via a nuclear factor-κB-dependent pathway in rat preadipocytes. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E771–E778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ni, W.; Kitamoto, S.; Ishibashi, M.; Usui, M.; Inoue, S.; Hiasa, K.-i.; Zhao, Q.; Nishida, K.-i.; Takeshita, A.; Egashira, K. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is an essential inflammatory mediator in angiotensin II-induced progression of established atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, K.A. Effects of Adipocyte Deficiency of Angiotensin Type 1a Receptors in Models of Obesity and Hypercholesterolemia. 2012. Available online: https://uknowledge.uky.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1006&context=nutrisci_etds (accessed on 2 March 2024).
- Jiao, B.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Q. Valsartan attenuated oxidative stress, decreased MCP-1 and TGF-β1 expression in glomerular mesangial and epithelial cells induced by high-glucose levels. Biosci. Trends 2011, 5, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.K.; Carpio, M.B.; Nicholas, S.B. Fiery Connections: Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation, the Journey from Obesity to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orliaguet, L.; Dalmas, E.; Drareni, K.; Venteclef, N.; Alzaid, F. Mechanisms of macrophage polarization in insulin signaling and sensitivity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, S.; Jeon, H.J. Association of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) 2518 A/G Polymorphism with Obesity in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 3917–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Shi, T.; Song, L.; Liu, J.; Yuan, M. Angiotensin (1–7) attenuates visceral adipose tissue expansion and lipogenesis by suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress via Mas receptor. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Lu, X. Regulation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: A Potential Target to Prevent COVID-19? Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 725967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Takeshita, H.; Rakugi, H. ACE2, angiotensin 1-7 and skeletal muscle: Review in the era of COVID-19. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 3047–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida Pinheiro, T.; Barcala-Jorge, A.S.; Andrade, J.M.O.; de Almeida Pinheiro, T.; Ferreira, E.C.N.; Crespo, T.S.; Batista-Jorge, G.C.; Vieira, C.A.; de Farias Lelis, D.; Paraíso, A.F. Obesity and malnutrition similarly alter the renin–angiotensin system and inflammation in mice and human adipose. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 48, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Than, A.; Leow, M.K.-S.; Chen, P. Control of adipogenesis by the autocrine interplays between angiotensin 1–7/Mas receptor and angiotensin II/AT1 receptor signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 15520–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Somers, K.R.; Becari, C.; Polonis, K.; Pfeifer, M.A.; Allen, A.M.; Kellogg, T.A.; Covassin, N.; Singh, P. Comparative expression of renin-angiotensin pathway proteins in visceral versus subcutaneous fat. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S. Role of Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor in Regulation of Lipid Metabolism and Adiposity. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Houston, Houston, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S17–S38. [Google Scholar]
- Strikić, D.; Vujević, A.; Perica, D.; Leskovar, D.; Paponja, K.; Pećin, I.; Merćep, I. Importance of Dyslipidaemia Treatment in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—A Narrative Review. Diabetology 2023, 4, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boachie, M.K.; Thsehla, E.; Immurana, M.; Kohli-Lynch, C.; Hofman, K.J. Estimating the healthcare cost of overweight and obesity in South Africa. Glob. Health Action 2022, 15, 2045092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mphasha, M.H.P.; Skaal, L.; Mothiba, T.M. Prevalence of overweight and obesity amongst patients with diabetes and their non-diabetic family members in Senwabarwana, Limpopo province, South Africa. S. Afr. Fam. Pract. 2022, 64, a5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosibo, A.M.; Mzimela, N.C.; Ngubane, P.S.; Khathi, A. Prevalence and correlates of pre-diabetes in adults of mixed ethnicities in the South African population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NPD (n = 40) | PD (n = 40) | T2D (n = 40) | Total (n = 120) | Overall p | NPD vs. PD | NPD vs. T2D | PD vs. T2D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 36.95 ± 6.26 | 37.28 ± 6.51 | 40.30 ± 4.96 | 120 | p = 0.03 | p = 0.77 | p = 0.02 | p = 0.04 |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Males, n (%) | 18 (45.00) | 20 (50.00) | 19 (47.50) | 57 | ||||
| Females, n (%) | 22 (55.00) | 20 (50.00) | 21 (52.50) | 63 | ||||
| FBG (mmol/L) | 5.33 ± 0.65 | 6.88 ± 0.63 | 12.47 ± 4.54 | 120 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 |
| TGs (mmol/L) | 1.56 ± 0.14 | 1.99 ± 0.25 | 2.76 ± 1.12 | 120 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.01 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.42 ± 0.39 | 5.53 ± 0.48 | 5.59 ± 0.45 | 120 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.61 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.01 ± 0.11 | 0.67 ± 0.11 | 0.50 ± 0.06 | 120 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 107.20 ± 16.75 | 145.70 ± 13.82 | 156.20 ± 22.29 | 120 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.05 |
| VLDL (mmol/L) | 0.72 ± 0.06 | 0.91 ± 0.10 | 1.23 ± 0.50 | 120 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.02 |
| Groups | NPD | PD | T2DM |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c % | 4.9 ± 0.4 | 5.9 ± 0.6 | 7.3 ± 1.1 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.1 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.8 | 5.9 ± 1.4 |
| p-values | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Analyte | MinDC (pg/mL) | MinDC + 2SD (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin | 87 | 160 |
| MCP-1 | 14 | 14 |
| Adiponectin | 11 | 21 |
| Adipsin | 4.8 | 10 |
| Analyte | Intra-Assay %CV | Inter-Assay %CV |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin | <10 | <15 |
| MCP-1 | <10 | <15 |
| Adiponectin | <10 | <15 |
| Adipsin | <10 | <10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mkhize, B.C.; Mosili, P.; Ngubane, P.S.; Sibiya, N.H.; Khathi, A. Increased Plasma Levels of ACE and Ang II in Prediabetes May Contribute to Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125517
Mkhize BC, Mosili P, Ngubane PS, Sibiya NH, Khathi A. Increased Plasma Levels of ACE and Ang II in Prediabetes May Contribute to Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125517
Chicago/Turabian StyleMkhize, Bongeka Cassandra, Palesa Mosili, Phikelelani Sethu Ngubane, Ntethelelo Hopewell Sibiya, and Andile Khathi. 2025. "Increased Plasma Levels of ACE and Ang II in Prediabetes May Contribute to Adipose Tissue Dysfunction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125517
APA StyleMkhize, B. C., Mosili, P., Ngubane, P. S., Sibiya, N. H., & Khathi, A. (2025). Increased Plasma Levels of ACE and Ang II in Prediabetes May Contribute to Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125517






