Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Applications: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
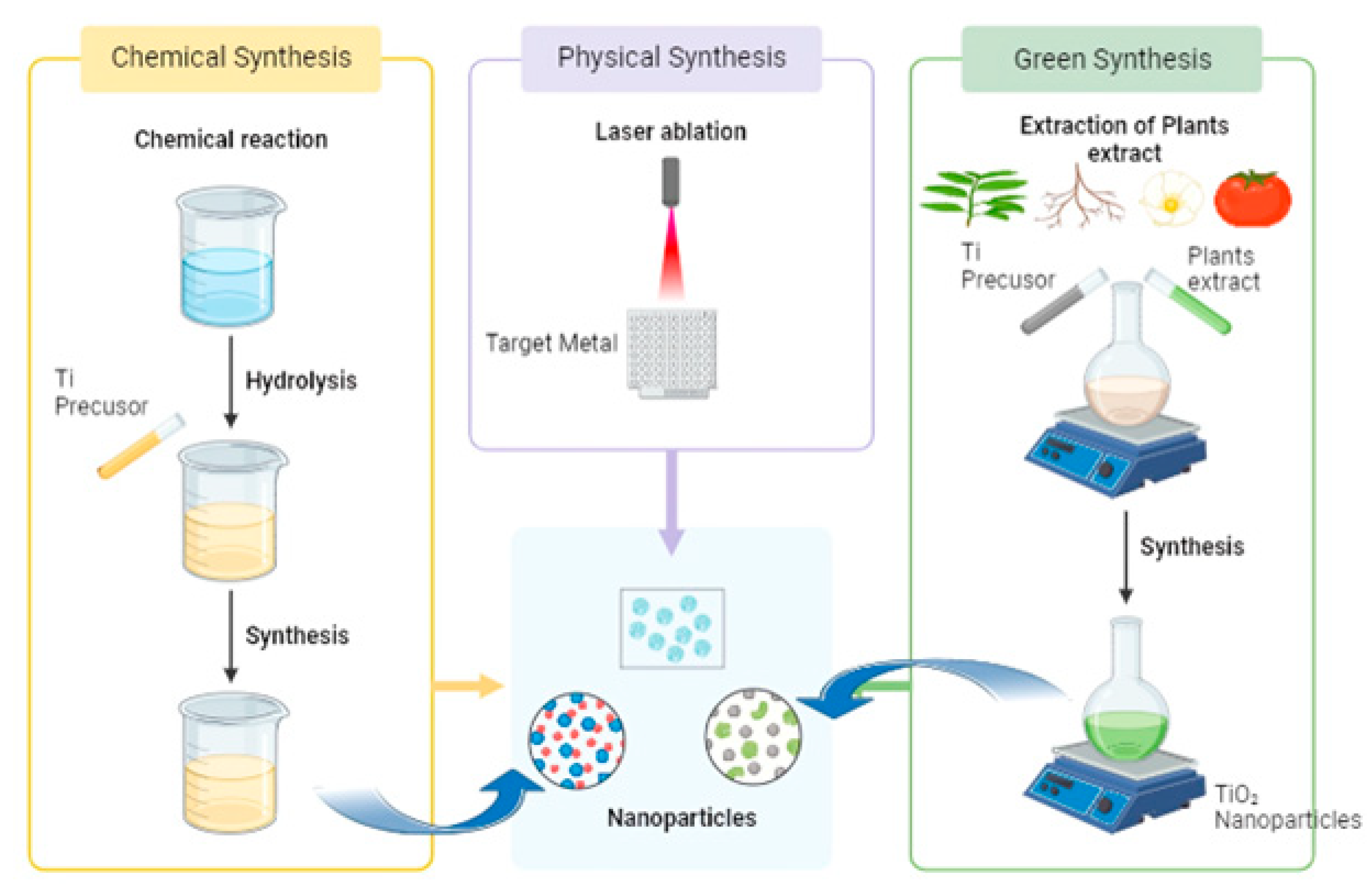
2. Synthesis of TiO2 NPs from Green Plant Extracts
3. The Mechanism of Synthesis of TiO2 NPs Prepared with the Use of Green Methods
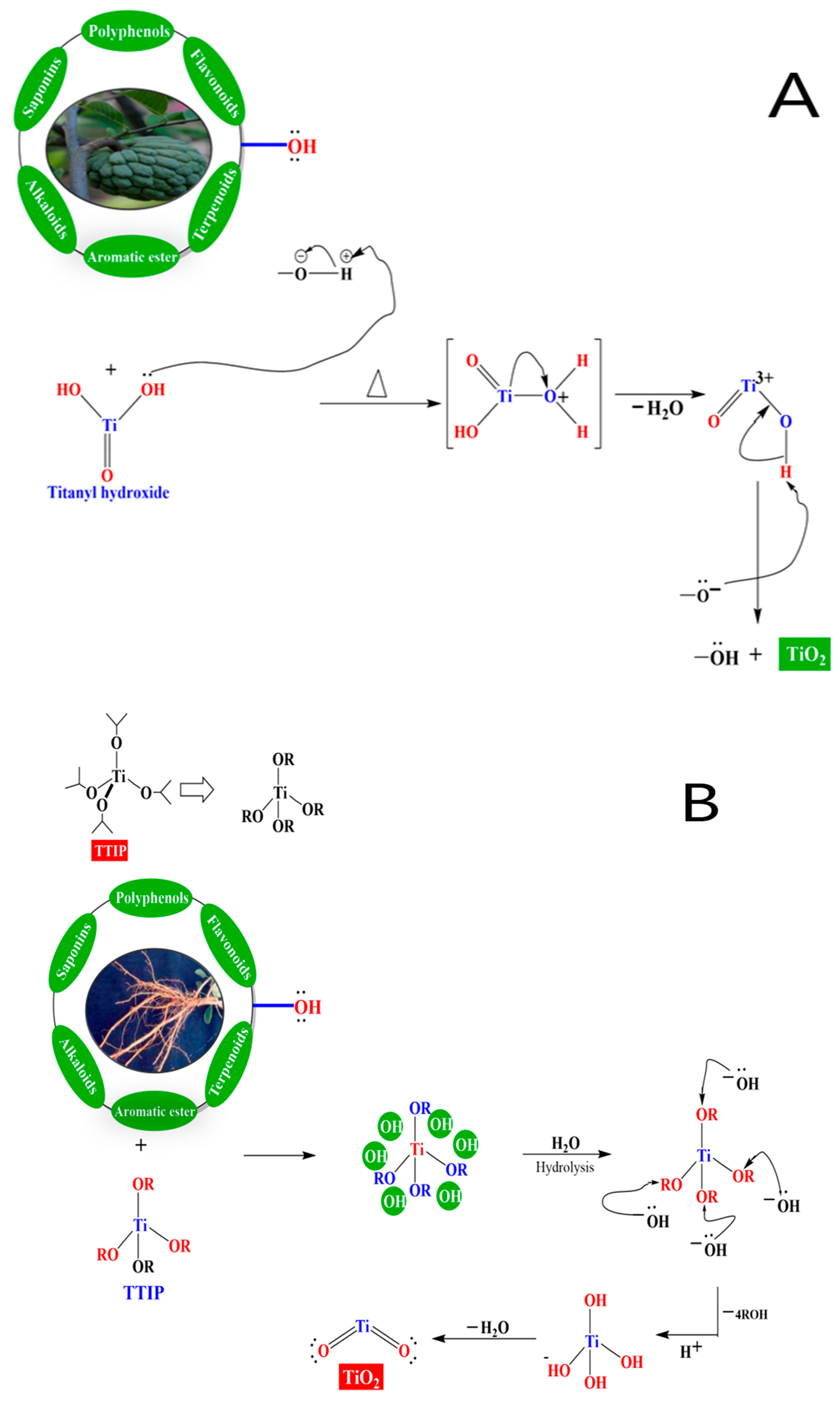
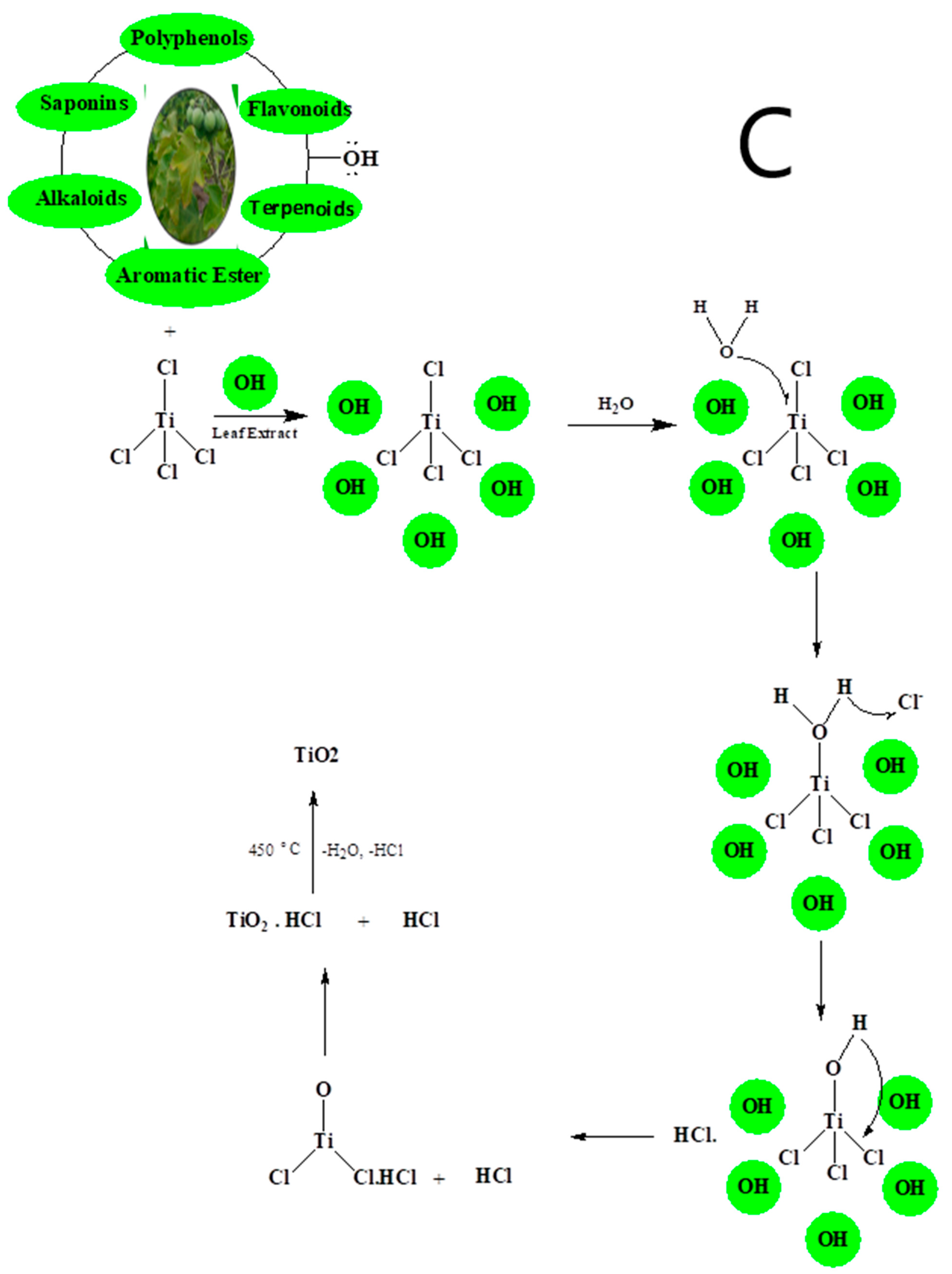
4. Limitations of Green Method for NPs Synthesis
- Green synthesis is hindered by the inability to precisely manipulate nanoparticle (NP) size and form depending on reaction duration, temperature, pH, and reactant concentration [70].
- Green synthesis also faces nanoparticle stability and surface chemistry issues. Nanoparticle surface chemistry greatly affects their interactions with biological systems and other materials. The use of natural extracts or microorganisms as reducing agents can make nanoparticle surface chemistry difficult to manage. Natural extracts used as reducing agents can also absorb contaminants onto nanoparticle surfaces, changing their characteristics [73].
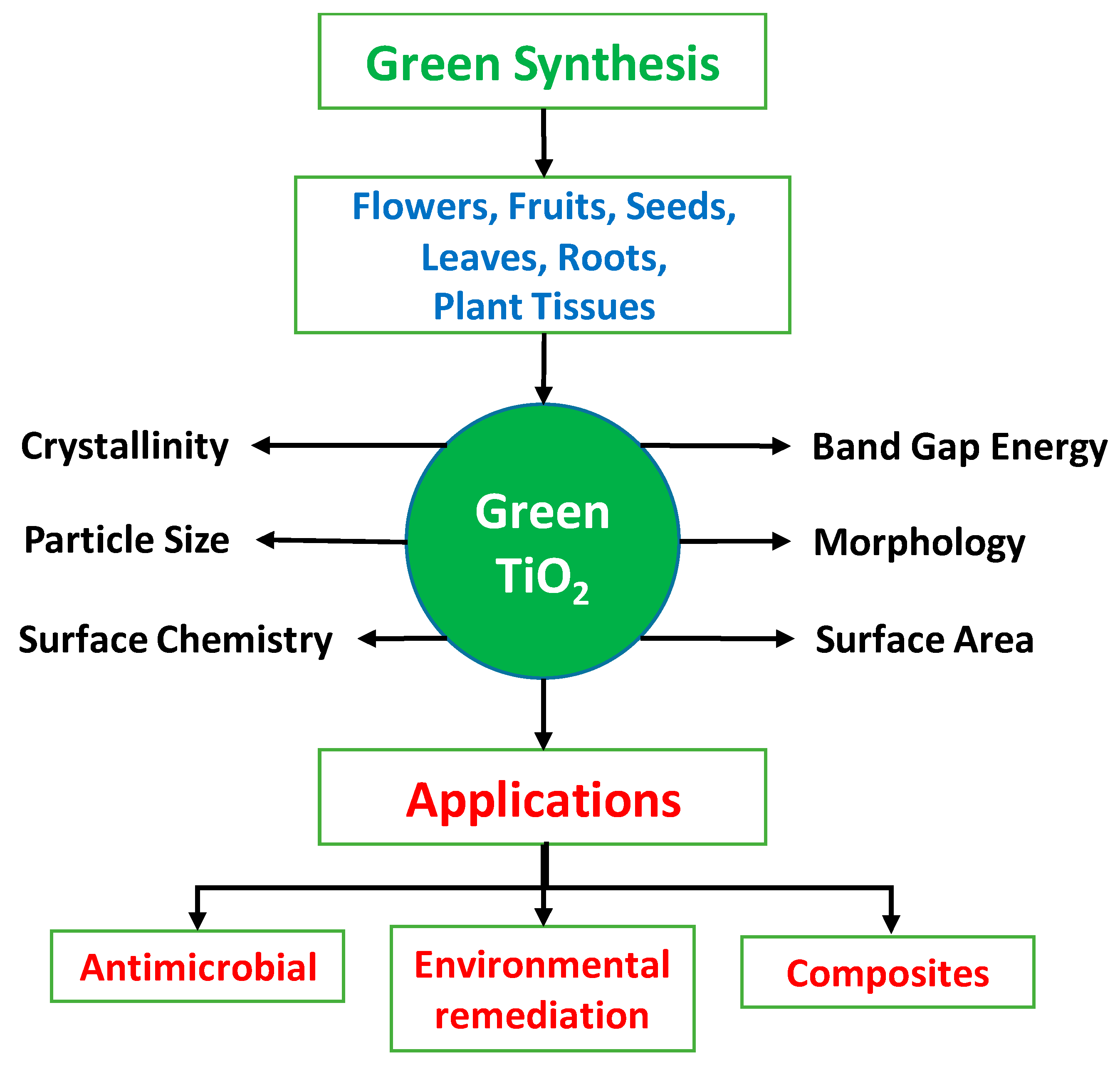
5. Characterization of TiO2 NPs
6. Optical Properties of TiO2 NPs
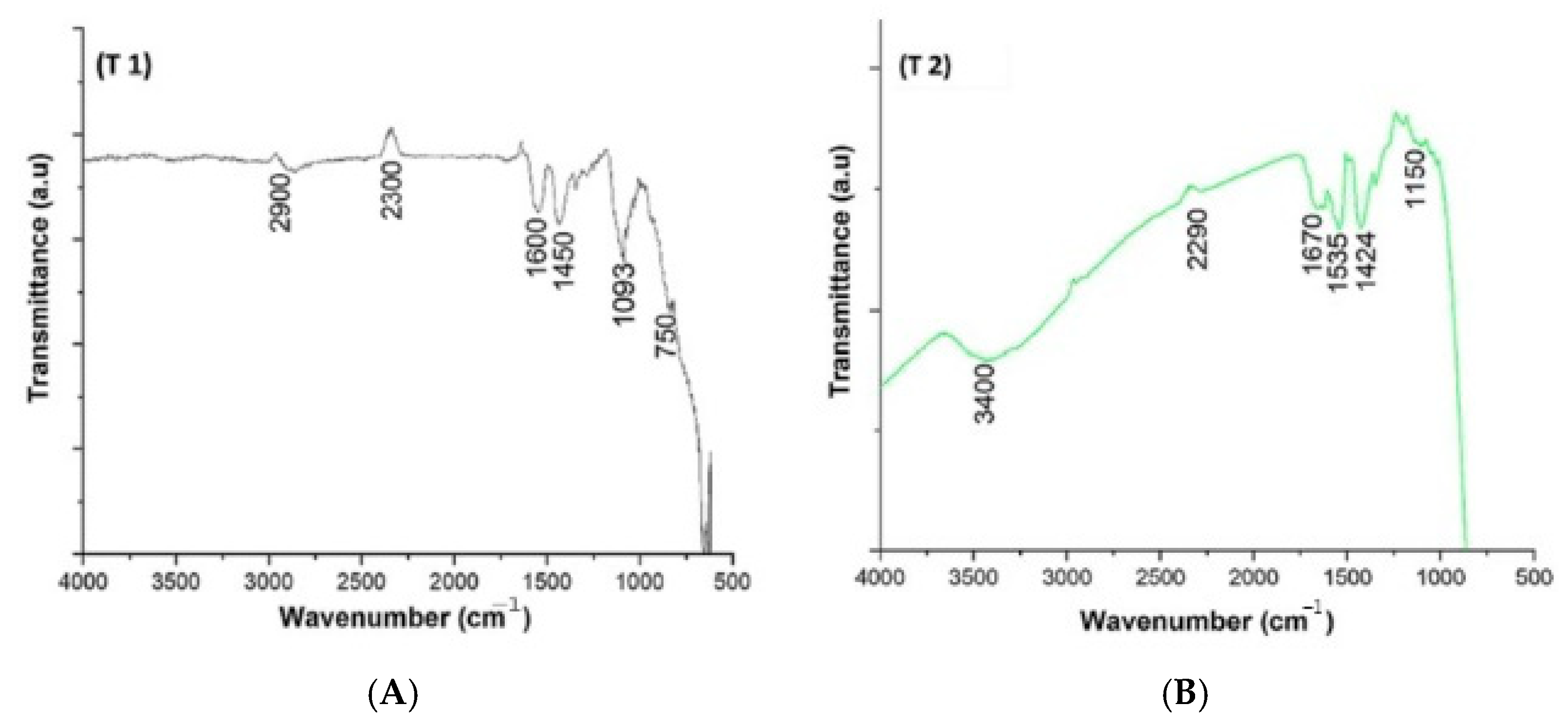
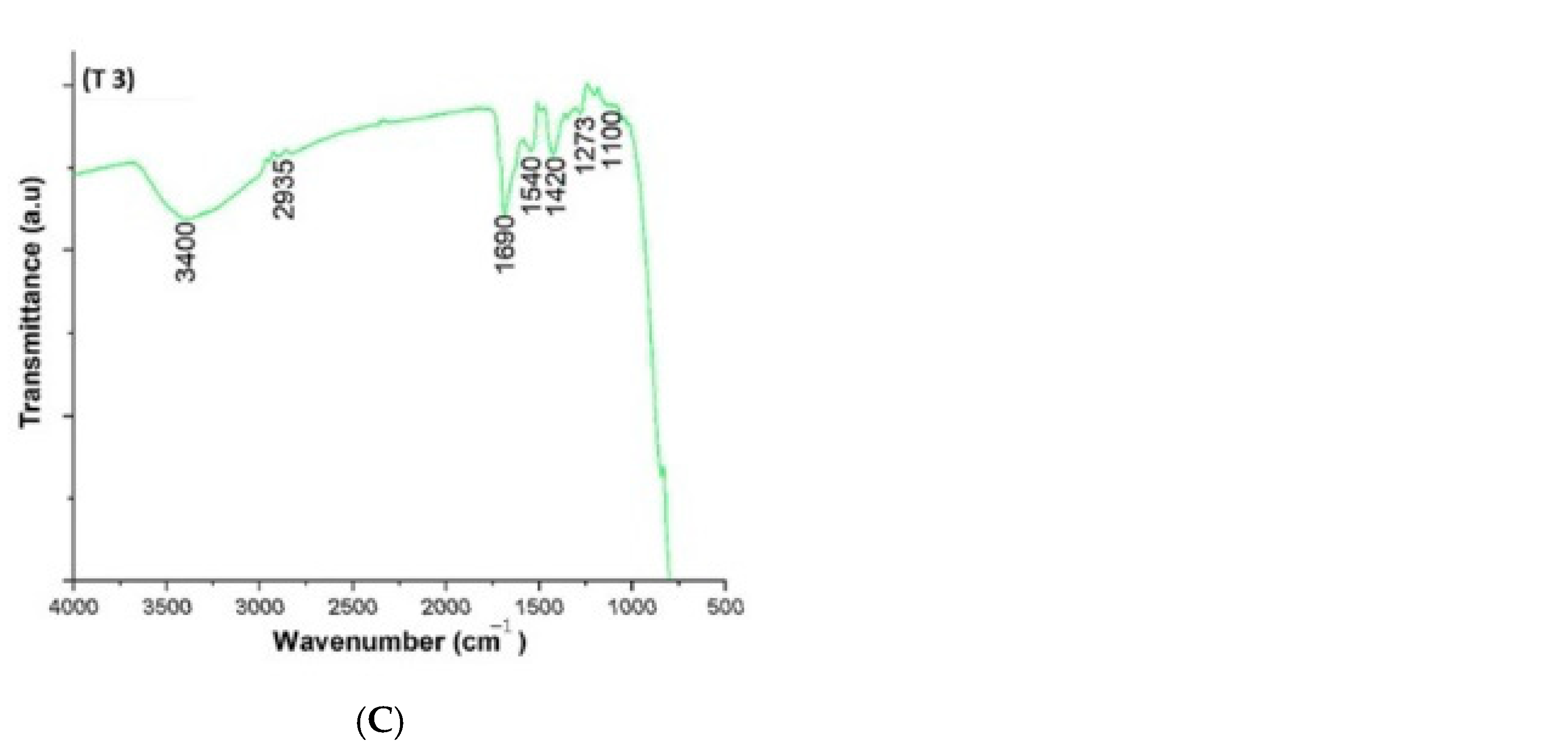
7. Functional Group Characterization of TiO2 NPs Prepared Using Green Method
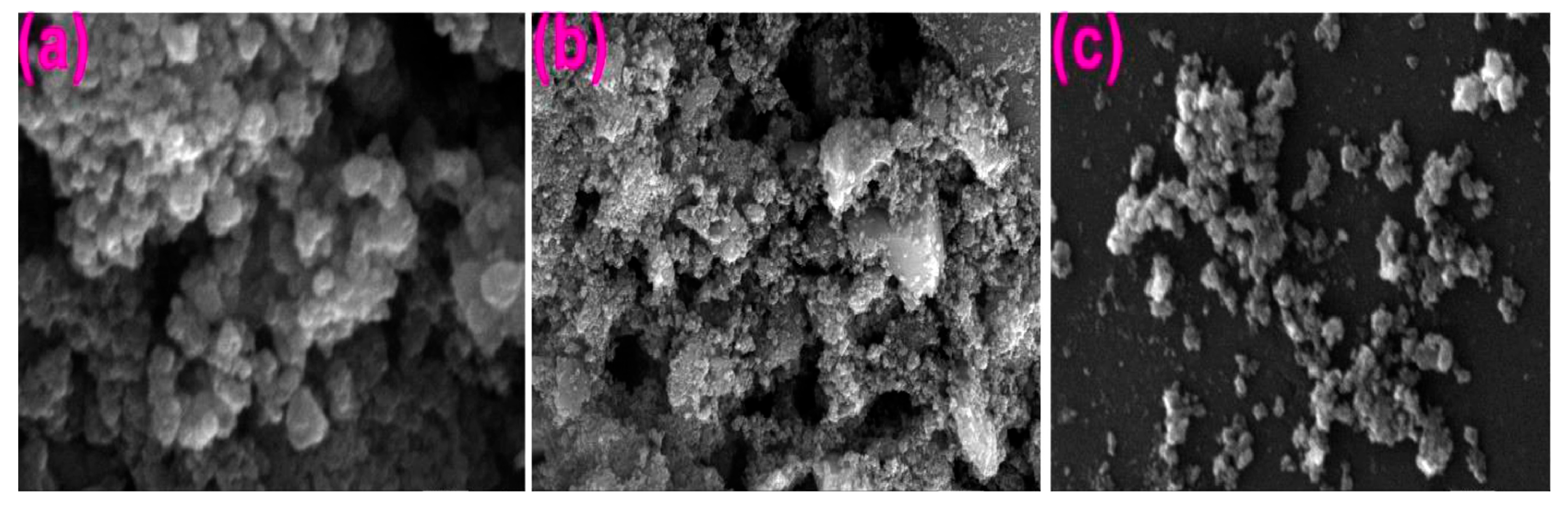
8. Morphology of TiO2 NPs
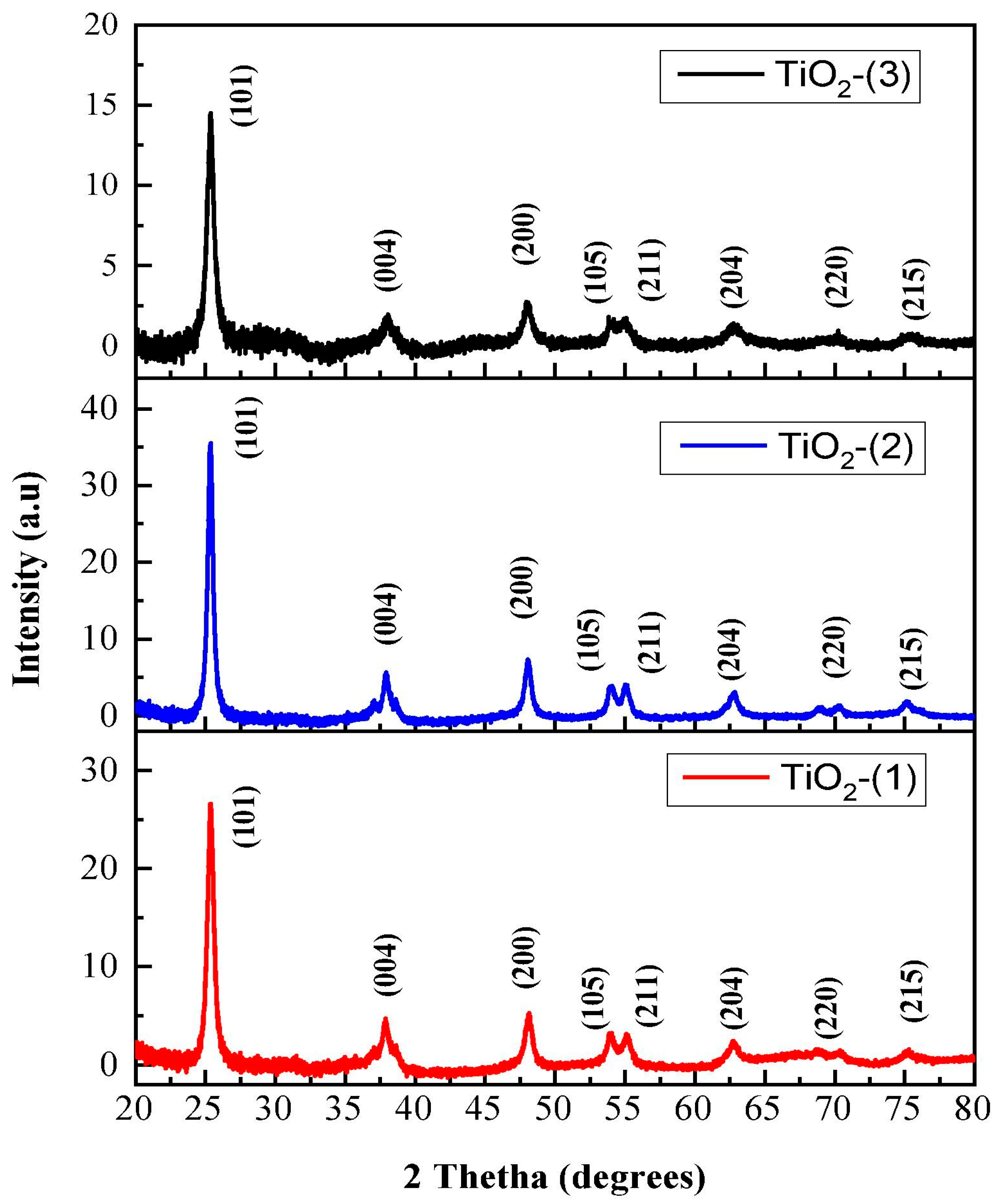
9. Analysis of Crystallographic and Phase Structure of TiO2 NPs
10. Applications for Green TiO2 NPs
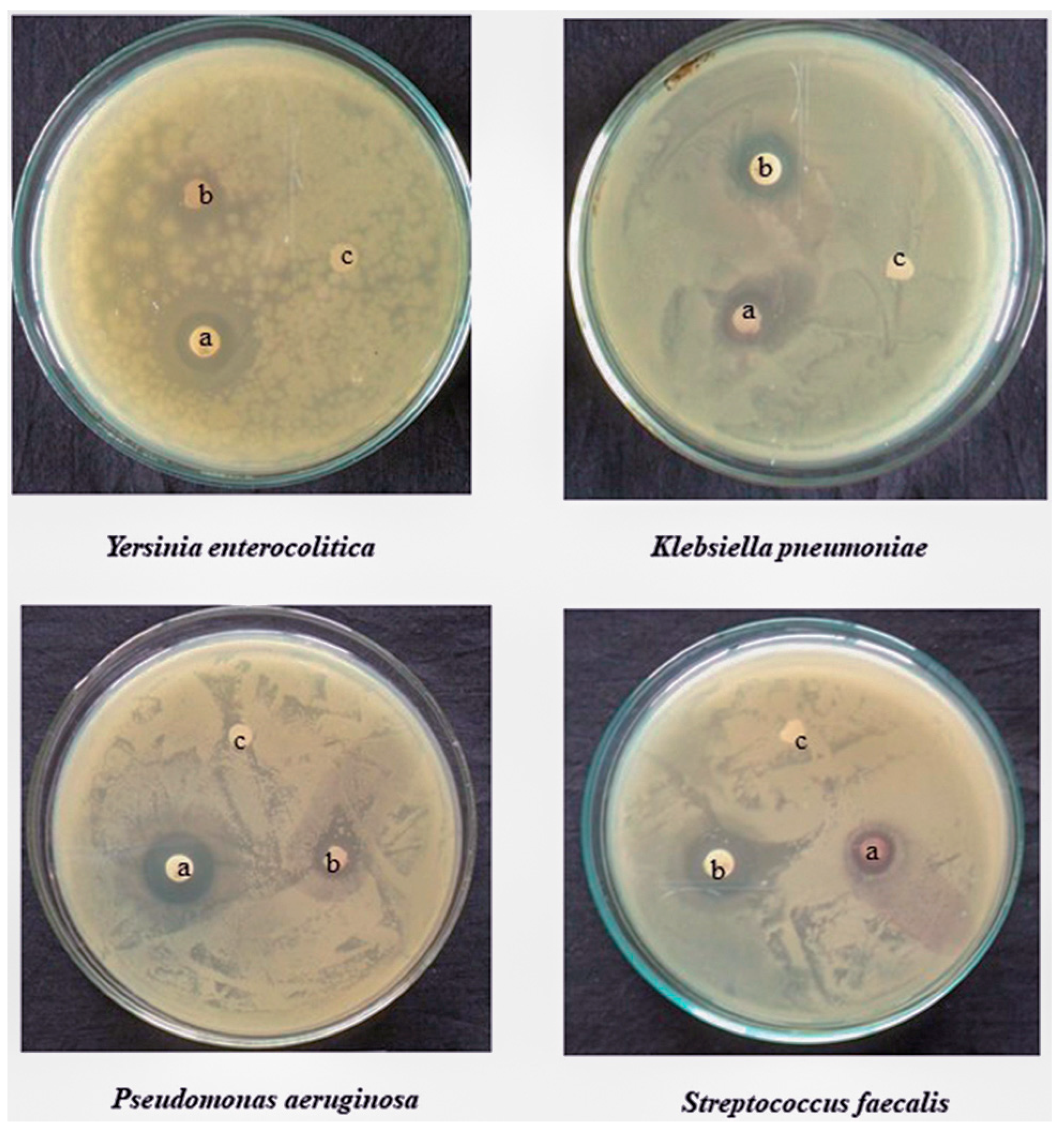
11. Antimicrobial Activity of Green Synthesis TiO2 NPs
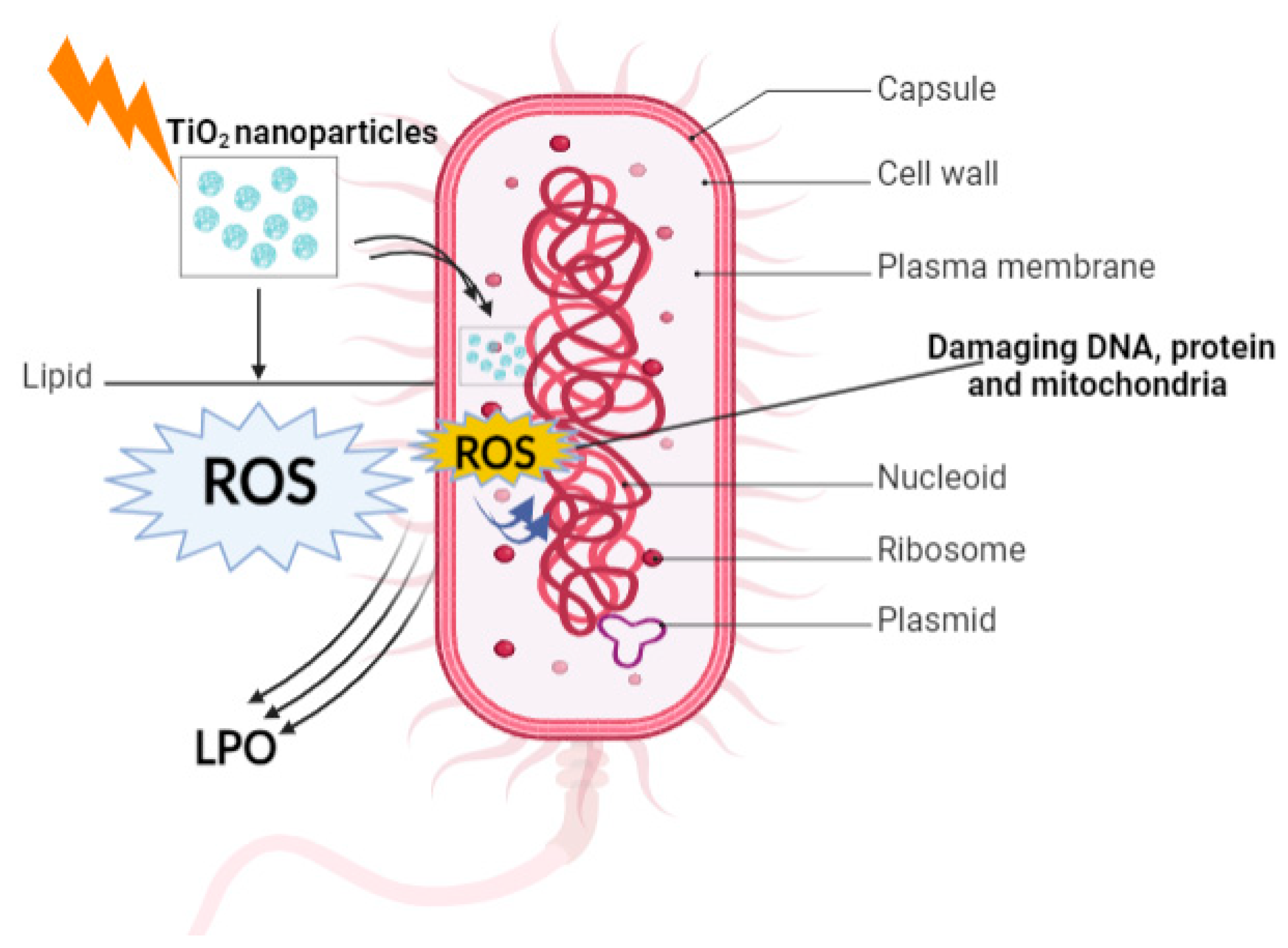
12. Mechanism of Antimicrobial Activity
13. Green TiO2 as a Photocatalyst for the Degradation of Dyes
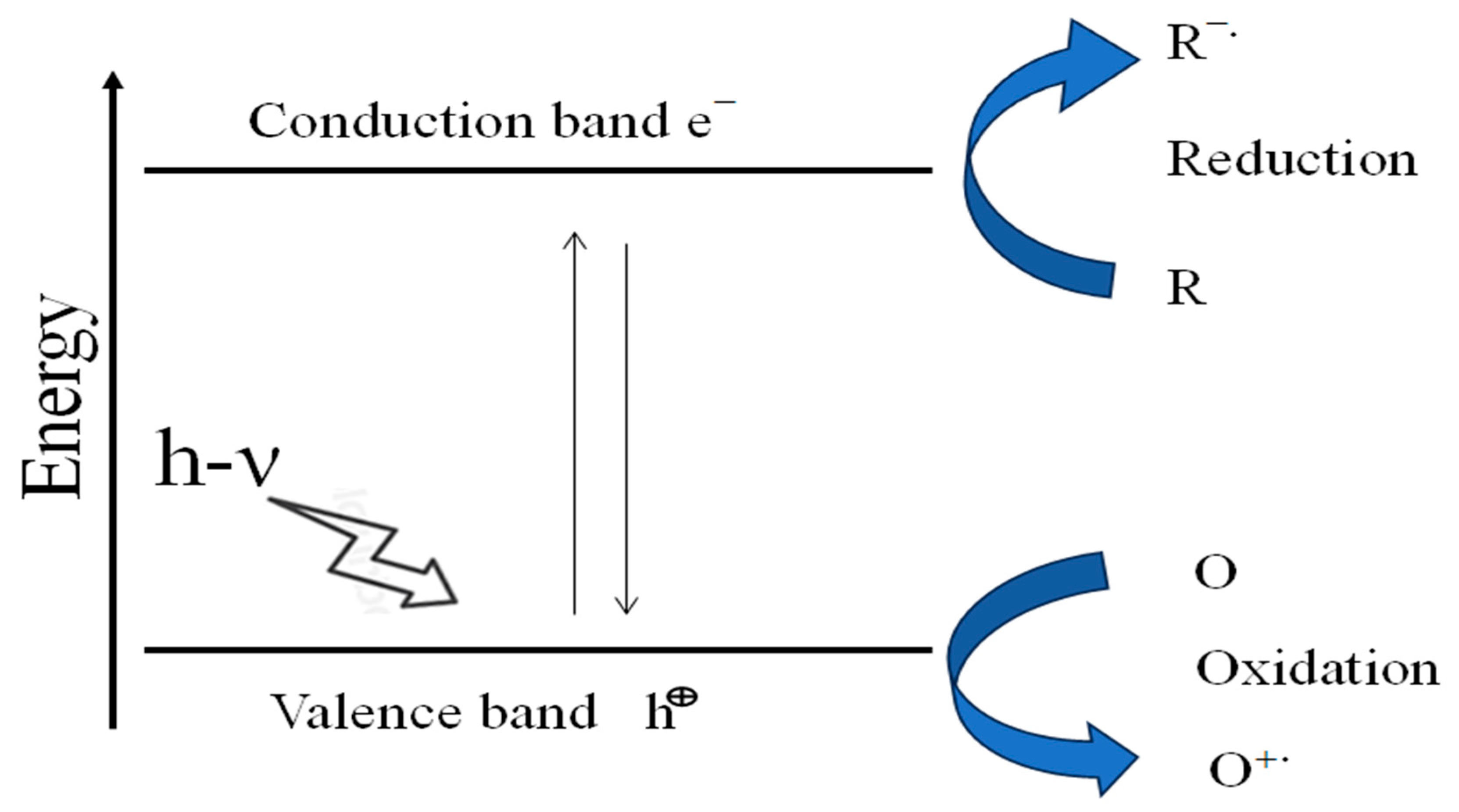
14. Mechanism of Photocatalysis

15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, W.; Huang, L.; Tang, J. Recent advances in synthetic methods and applications of Ag2S-based heterostructure photocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 3988–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharsini, P.; Sundar, R.P.; Grace, P.K.; Naveen, S.; Sanjay, K.S.; Gnanaprakash, D.; Arun, J.; Pugazhendhi, A. Nanohybrid photocatalysts in dye (Colorants) wastewater treatment: Recent trends in simultaneous dye degradation, hydrogen production, storage and transport feasibility. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, T.; Nowotny, J.; Rekas, M.; Sorrell, C.C. Photo-electrochemical hydrogen generation from water using solar energy. Materials-related aspects. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2002, 27, 991–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaveni, K.; Sivalingam, G.; Hedge, M.S.; Madras, G. Solar photocatalytic degradation of dyes: High activity of combustion synthesized nano TiO2. Appl. Catal. B 2004, 48, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Anpo, M.; He, D. Preparation, photocatalytic activity, and mechanism of nano-TiO2 co-doped with nitrogen and iron (III). J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10618–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, D.P.; Dave, P.N.; Chaturvedi, S. A review on nano-TiO2 sol–gel type syntheses and its applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3669–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Semiconductor heterojunction photocatalysts: Design, construction, and photocatalytic performances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5234–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.G.; Devi, L.G. Review on modified TiO2 photocatalysis under UV/visible light: Selected results and related mechanisms on interfacial charge carrier transfer dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. 2011, 115, 13211–13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, H.; Chandra, A.; Ingole, P.P.; Garg, S. Recent advancements in enhancement of photocatalytic activity using bismuth-based metal oxides Bi2MO6 (M = W, Mo, Cr) for environmental remediation and clean energy production. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 95, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, N.; Kumar, U. Noble metal modified TiO2: Selective photoreduction of CO2 to hydrocarbons. Mol. Catal. 2017, 439, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Akiyoshi, M.; Umebayashi, T.; Asai, K.; Mitsui, T.; Matsumura, M. Preparation of S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts and their photocatalytic activities under visible light. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 265, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Haneda, H.; Hishita, S.; Ohashi, N. Visible-light-driven N−F−codoped TiO2 photocatalysts. 1. Synthesis by spray pyrolysis and surface characterization. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bttcher, C.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Dohrmann, J.K. A comparative study of nanometer sized Fe(III)-doped TiO2 photocatalysts: Synthesis, characterization and activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2003, 5, 11143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, M. Applications of TiO2 nanotube arrays in environmental and energy fields: A review. Microporous Mater. 2015, 202, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Lai, Q.; Fan, M. Review of the progress in preparing nano TiO2: An important environmental engineering material. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 2139–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, Y.; Kim, W.; Choi, W. Surface modification of TiO2 photocatalyst for environmental applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2013, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattalung, S.; Harding, D.J.; Pattanasattayavong, P.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Hwang, D.W.; Chung, T.D.; Yu, J. Band gap narrowing of TiO2 nanoparticles: A passivated Co-doping approach for enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2022, 162, 110503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Liang, Y. First principles study on band gap modulation of TiO2 (112) surface for enhancing optical properties. Phys. B 2024, 674, 415579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, A.; Fouda, A.; Kishk, R.M.; El Kazzaz, W.M. Unlocking the potential of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: An insight into green synthesis, optimizations, characterizations, and multifunctional applications. MCFs 2024, 23, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, G.; Mohammadi, A.; Akbari, A.; Panahirad, S.; Dadpour, M.R.; Fotopoulos, V.; Kimura, S. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) promote growth and ameliorate salinity stress effects on essential oil profile and biochemical attributes of Dracocephalum moldavica. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liza, T.Z.; Tusher, M.M.; Anwar, F.; Monika, M.F.; Amin, K.F.; Asrafuzzaman, F.N. Effect of Ag-doping on morphology, structure, band gap and photocatalytic activity of bio-mediated TiO2 nanoparticles. Res. Mater. 2024, 22, 100559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Kao, L.-C.; Huang, Y.; Bañares, M.A.; Liou, S.Y.-H. Uniform deposition of coupled CdS and CdSe quantum dots on ZnO nanorod arrays as electrodes for photoelectrochemical solar water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravallika, P.L.; Mohan, G.K.; Rao, K.V.; Shanker, K. Biosynthesis, characterization and acute oral toxicity studies of synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using ethanolic extract of Centella asiatica plant. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.H.; Le, A.T. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, toxicology, applications and perspectives. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 14, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Kumar, P. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Tinospora cordifolia plant extract & its potential application for photocatalysis and antibacterial activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 156, 111221. [Google Scholar]
- Yitagesu, G.B.; Leku, D.T.; Workneh, G.A. Green synthesis of TiO2 using Impatiens rothii hook. f. leaf extract for efficient removal of methylene blue dye. ACS Omega 2023, 46, 43999–44012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Al-Dossari, M.; Singh, J.; Rawat, M.; Kordy, M.G.; Shaban, M. A review on green synthesis of TiO2 NPs: Photocatalysis and antimicrobial applications. Polymers 2022, 7, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.S.; Daneshjou, S. Optimizing the green synthesis of antibacterial TiO2-anatase phase nanoparticles derived from spinach leaf extract. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huo, K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Chu, P.K. Influence of structure parameters and crystalline phase on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanotube arrays. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 12, 11200–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, S.; Pandian, M.S.; Ramasamy, G.; Karchiyappan, T. Green synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles using plant extracts: A sustainable approach to combat antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2025, 23, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Khan, S.U.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, I. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Rhizophora apiculata leaves extract and their photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 392, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, S.; Sahu, M.; Rath, R.N. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum extract and their catalytic and antibacterial applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 3, 103284. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, T.; Mondal, S.; Jana, N.R. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using seed extract of Butea monosperma and their photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 186, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Plant-mediated green synthesis of nanostructures: Mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 12, 7468–7533. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, D.; Gao, S.; Zhang, M.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. A novel Xanthan gum-based conductive hydrogel with excellent mechanical, biocompatible, and self-healing performances. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, H.; Yaqoob, S.; Awan, K.A.; Imtiaz, A.; Naveed, H.; Ahmad, N.; Naeem, M.; Sultan, W.; Ma, Y. Unveiling the chemistry of citrus peel: Insights into nutraceutical potential and therapeutic applications. Foods 2024, 13, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, N.R.; Brumaghim, J.L. A Review of the Antioxidant Mechanisms of Polyphenol Compounds Related to Iron Binding. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 53, 75–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications—An updated report. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebold, U. The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2003, 48, 53–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Burda, C. The electronic origin of the visible-light absorption properties of C-, N- and S-doped TiO2 nanomaterials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5018–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis: Present situation and future approaches. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2006, 9, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.; Xu, X.; Shang, Y. Pilot-scale and large-scale Fenton-like applications with nano-metal catalysts: From catalytic modules to scale-up applications. Water Res. 2024, 266, 122425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, P.; Jeice, A.R.; Jayakumar, K. Review of green synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles for diverse applications. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 39, 102912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Boora, A.; Thakur, A.; Gupta, T.K. Green and sustainable synthesis of nanomaterials: Recent advancements and limitations. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, N.J.; Rendy, B.; Fei, Y.; Kumar, R.E.; He, T.; Milsted, D.; McDermott, M.J.; Gallant, M.; Cubuk, E.D.; Merchant, A.; et al. An autonomous laboratory for the accelerated synthesis of novel materials. Nature 2023, 624, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Thompson, L. Energy consumption in TiO2 synthesis: A comparative study of various methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, M.; Fernandez, R. Green synthesis approaches for TiO2 nanoparticles: Challenges and prospects. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 35, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Gatou, M.A.; Syrrakou, A.; Lagopati, N.; Pavlatou, E.A. Photocatalytic TiO2-based nanostructures as a promising material for diverse environmental applications: A review. Reactions 2024, 1, 135–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, V.H.; Jeice, A.R. Green fabrication of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and their applications in photocatalytic dye degradation and microbial activities. Chem. Phys. 2023, 6, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, S.; Villa, S.; Singh, G.; Seland, F.; Martinelli, A.; Ferretti, M.; Canepa, F.; Caratto, V. Systematic Study on TiO2 Crystallization via Hydrothermal Synthesis in the Presence of Different Ferrite Nanoparticles as Nucleation Seeds. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 8, 4994–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, S.; Alok, A.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Rawat, M.; Tsang, D.C. The potential of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nutrient source for plant growth. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H.; Hashmi, S.S.; Ahmad, W. The current trends in the green syntheses of titanium oxide nanoparticles and their applications. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2018, 11, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhapriya, S.; Gomathipriya, P. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by Trigonella foenum-graecum extract and its antimicrobial properties. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopape, D.A.; Tetana, Z.N.; Mabuba, N.; Motaung, D.E.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Biosynthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Commelina benghanlensis for the photodegradation of methylene blue dye and antibiotics: Effect of plant concentration. Res. Chem. 2023, 5, 100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbenga, Y.; Adeyemi, J.; Mthiyane, D.M.N.; Singh, M.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Green synthesis, antioxidant and anticancer activities of TiO2 nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Tulbhagia violacea. Results. Chem. 2023, 6, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimi, A.K.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Islam, M.A.; Rane, K.P.; Jeevan, T.S. Photocatalytic Activity of Green Construction TiO2 Nanoparticles from Phyllanthus niruri Leaf Extract. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 7011539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Kaur, S.; Kumar, S. Eco-friendly approach: Synthesis of novel green TiO2 nanoparticles for degradation of reactive green 19 dye and replacement of chemical synthesized TiO2. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 32, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, M.; Amalanathan, M.; Mary, M. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by chemical and green synthesis methods and their multifaceted properties. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, N.K.; Arif, Z.; Mishra, P.K.; Kumar, P. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles from Syzygium cumini extract for photo-catalytic removal of lead (Pb) in explosive industrial wastewater. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, N.; Kianvas, A.; Hajalilou, A.; Abouzarati-Lotf, E.; Abbasi-Chianeh, V.A. A facile and green synthetic approach toward fabrication of Alcea-and Thyme-stabilized TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.K.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, A.S. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dalo, M.; Jaradat, A.; Albiss, B.A.; Al-Rawashdeh, N.A. Green synthesis of TiO2 NPs/pristine pomegranate peel extract nanocomposite and its antimicrobial activity for water disinfection. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, S.; Tahir, A.; Chen, Y. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their environmental applications and implications. Nanomaterials 2016, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M. Synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Euphorbia heteradena Jaub root extract and evaluation of their stability. Ceram. Int. 2015, 10, 14435–14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumari, J.; Magdalane, C.M.; Siddhardha, B.; Madhavan, J.; Ramalingam, G.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V.; Ghilan, A.K.; Duraipandiayan, V.; Kaviyarasu, K. Synthesis of titanium oxide nanoparticles using Aloe barbadensis mill and evaluation of its antibiofilm potential against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2019, 201, 111667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutam, S.P.; Saxena, G.; Singh, V.; Yadav, A.K.; Bharagava, R.N.; Thapa, K.B. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using leaf extract of Jatropha curcas L. for photocatalytic degradation of tannery wastewater. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 336, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Shin, H.S.; Jacob, J.M.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Bhaisare, M.; Kumar, G. New insights on the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant and waste biomaterials: Current knowledge, their agricultural and environmental applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10164–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, B.; Zaker, Y.; Bigioni, T.P. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles: Challenges and opportunities. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain Chem. 2018, 12, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Ying, S.; Ofoegbu, P.C.; Clubb, P.; Rico, C.; He, F.; Hong, J. Green synthesis of nanoparticles: Current developments and limitations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102336. [Google Scholar]
- Parveen, K.; Banse, V.; Ledwani, L. Green synthesis of nanoparticles: Their advantages and disadvantages. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1, 020048. [Google Scholar]
- Woźniak, A.; Malankowska, A.; Nowaczyk, G.; Grześkowiak, B.F.; Tuśnio, K.; Słomski, R.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Jurga, S. Size and shape-dependent cytotoxicity profile of gold nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudot, C.; Tan, C.M.; Kong, J.C. FTIR spectroscopy as a tool for nano-material characterization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2010, 6, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.A.; Nawaz, R.; Rehman, M.Z.; Imran, M.; Ahmad, M.J.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, S. Synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles by chemical and green methods and their antifungal activities against wheat rust. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, R. Nanofertilizer and nanotechnology: A quick look. Better Crops 2018, 3, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, T. Stress and defense responses in plant secondary metabolites production. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Farooq, M.; Wakeel, A.; Nawaz, A.; Cheema, S.A.; Rehman, H.; Ashraf, I.; Sanaullah, M. Nanotechnology in agriculture: Current status, challenges and future opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 15, 137721–137778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandoliya, R.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, V.; Joshi, R.; Sivanesan, I. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis, Applications and Toxicity. Plants 2024, 21, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Burkitt, S.; Dong, N.; Zavaleta, C. Nanoparticle characterization techniques. In Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 129–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shimpi, N.G.; Mishra, S.; Shirole, S.D. Efficient green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Murraya koenigii leaf extract. J. Nanosci. Nanoeng. Appl. 2016, 1, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Solano, R.A.; Herrera, A.P.; Maestre, D.; Cremades, A. Fe-TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by green chemistry for potential application in wastewater photocatalytic treatment. J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 2019, 4571848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Kaur, S.; Singh, J.; Rawat, M.; Kumar, S. Expanding horizon: Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Carica papaya leaves for photocatalysis application. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 9, 095034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, R.N.; Khaghani, S.; Azizi, A.; Mortazaeinezhad, F.; Gomarian, M. Facile and eco-friendly synthesis of TiO2 NPs using extracts of Verbascum thapsus plant: An efficient photocatalyst for reduction of Cr (VI) ions in the aqueous solution. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 17, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhoshkumar, T.; Rahuman, A.A.; Jayaseelan, C.; Rajakumar, G.; Marimuthu, S.; Kirthi, A.V.; Velayutham, K.; Thomas, J.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Psidium guajava extract and its antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 12, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Soni, S. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by using Mentha arvensis leaves extract and its antimicrobial properties. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2020, 50, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, S.; Amr, A.; El-Shafei, A.; Asker, M.S.; Ibrahim, H.M. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles via bacterial cellulose (BC) produced from agricultural wastes. Cellulose 2021, 28, 7619–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanulla, A.M.; Sundaram, R.J. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using orange peel extract for antibacterial, cytotoxicity and humidity sensor applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 8, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, E.T.; Gonfa, B.A.; Zelekew, O.A.; Belay, H.H.; Sabir, F.K. Synthesis of titanium oxide nanoparticles using root extract of Kniphofia foliosa as a template, characterization, and its application on drug resistance bacteria. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 2817037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, D.; Thangamuniyandi, P.; Selvakumar, P.; Devan, U.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Vasantharaja, R.; Nehru, L.C. Green approach synthesis of Pd@TiO2 nanoparticles: Characterization, visible light active picric acid degradation and anticancer activity. Process Biochem. 2019, 87, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swathi, N.; Sandhiya, D.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Lakshmi, T. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Cassia fistula and its antibacterial activity. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 10, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, F. Chemical basis of reactive oxygen species reactivity and involvement in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Bactericidal and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regmi, C.; Joshi, B.; Ray, S.K.; Gyawali, G.; Pandey, R.P. Understanding the mechanism of photocatalytic microbial decontamination of environmental wastewater. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.; Tomoda, R.; Nakajima, T.; Wake, H. Photoelectrochemical sterilization of microbial cells by semiconductor powders. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1985, 29, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.W.; Chang, H.H. Bactericidal effects and mechanisms of visible light-responsive titanium dioxide photocatalysts on pathogenic bacteria. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2012, 60, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Srivastava, S.; Ghosh, S.; Khare, S.K. Phytochemical delivery through nanocarriers: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BinSabt, M.; Sagar, V.; Singh, J.; Rawat, M.; Shaban, M. Green synthesis of CS-TiO2 NPs for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Polymers 2022, 13, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunthakudee, N.; Puangpetch, T.; Ramakul, P.; Serivalsatit, K.; Ponchio, C.; Hunsom, M. Ultra-fast green synthesis of a defective TiO2 photocatalyst towards hydrogen production. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 24213–24225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, S.; MAL, A.R.; Prabha, C.; Vidya, C. Tamarindus indica mediated biosynthesis of nano TiO2 and its application in photocatalytic degradation of Titan yellow. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7338–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, S.; Bessy, T.C.; Bindhu, M.R.; Venkatesan, R.; Parimaladevi, R.; Alam, M.M.; Mayandi, J.; Umadevi, M. Photocatalytic and photovoltaic applications of green synthesized titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by Calotropis gigantea extract. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Siddiqui, V.U.; Rehman, W.U.; Akram, M.K.; Siddiqi, W.A.; Alosaimi, A.M.; Hussein, M.A.; Rafatullah, M. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Acorus calamus leaf extract and evaluating its photocatalytic and in vitro antimicrobial activity. Catalysts 2022, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoepe, N.M.; Mathipa, M.M.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Biosynthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles for the photodegradation of dyes and removal of bacteria. Optik 2020, 224, 65728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carp, O.; Huisman, C.L.; Reller, A. Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2004, 32, 33–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Beibei, Y.; Wei, C.; Junjiao, Y. Preparation and photocatalytic activities of TiO2-based composite catalysts. Catalysts 2022, 10, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, B.; Goutham, R.; Badri Narayan, R.; Ramprasath, A.; Gopinath, K.P.; Sankaranarayanan, A.R. Recent advancements in supporting materials for immobilised photocatalytic applications in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 200, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ma, Z.; Yang, X. Fundamentals of TiO2 photocatalysis: Concepts, mechanisms, and challenges. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, I.; Chawla, H.; Chandra, A.; Sagadevan, S.; Garg, S. Advances in the strategies for enhancing the photocatalytic activity of TiO2: Conversion from UV-light active to visible-light active photocatalyst. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 1, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Features | Traditional Chemical Synthesis | Green-Synthesized TiO2 NPs |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost Reduction | Baseline | 30–50% lower |
| Photocatalytic Efficiency | Low | 25% higher |
| Antimicrobial Activity | Low | 30% improved |
| Reusability | Typically, single use | Up to 10 cycles |
| Waste Utilization | Significant hazardous waste | Reduces plants waste by 90% |
| Scalability | Easily scalable but less sustainable | Potential for 1 ton/month |
| Economic Value from Waste | No value recovery from waste | USD 1000 per ton of plants by-products |
| Property | TiO2 NPs | Silver NPs | Zinc Oxide NPs | Gold NPs | Iron Oxide NPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Extracts | Aloe vera, neem, green tea | Cinnamon, neem, green tea | Hibiscus, aloe vera, turmeric | Mangosteen, green tea, | Green tea, eucalyptus, moringa |
| Photocatalytic Activity | High (under UV/visible light) | Moderate | High (UV light) | Low | Moderate (good under visible light) |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Moderate | High | Moderate | High | High |
| Cost of Synthesis | Low | Moderate | Low | High | Low |
| Effectiveness in Wastewater Treatment | High (removes dyes, heavy metals, organic pollutants) | High (antimicrobial, removes organic pollutants) | High (removes dyes, heavy metals, and pathogens) | Moderate (mainly used for sensing contaminants) | High (effective in removing dyes and heavy metals) |
| Sr. No. | Plants | Morphology | Size [nm] | Characterization | Application | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kniphofia foliosa |  | Spherical | ---- | UV–VIS, XRD, SEM TEM, TGA and DTA | Antibacterial against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Streptococcus pyogenes | [90] |
| 2 | Syzygium cumini |  | Irregular structure | 18 | UV–vis, HRTEM, TEM and XRD | Picric Acid Degradation and Anticancer activity | [91] |
| 3 | Cassia fistula |  | Spherical | UV–VIS, XRD, SEM, TEM and TGA | Antibacterial against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus | [92] | |
| 4 | Averrhoa bilimbi fruit |  | Spherical | 1–8 | EDX, FTIR, SEM, and TGA | Antibacterial against S. aureus P. aeruginosa, and Candida albicans fungi Degradation of methylene blue (MB) | [88] |
| 5 | Carica papaya |  | Spherical and cages like | 15.6 | UV–VIS, XRD, SEM and TEM | Degradation of dye | [84] |
| 6 | Trianthema portulacastrum |  | Porous crystallites with small round particles | 10–12 | XRD, FTIR, SEM and EDX | Antifungal against U. tritici | [76] |
| 7 | Jatropha curcas L. |  | Spherical, tetragonal | 13.0 | UV–Visible, FESEM, EDS, FT-IR, XRD, DLS, BET and BJH | removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and chromium (Cr) from secondary treated TWW | [69] |
| 8 | Azadirachta indica |  | Spherical | 124 | XRD, SEM, TEM and FT-IR | Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Salmonella typhi and Klebsiella pneumonia | [64] |
| 9 | Alcea and Thyme |  | Irregularly shaped and spherical | 10.1 | XRD, FTIR, FESE and EDX | Degradation of methylene blue (MB) | [63] |
| 10 | Jasmine Flowers |  | Spherical | 31–42 | XRD, UV−vis and SEM | Antibacterial against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus and Degradation of methylene blue (MB) | [61] |
| 11 | Lagenaria siceraria leaf |  | Irregular | 303 | XRD, FTIR, FESEM, EDX, HRTEM and UV−vis | photo-degradation of RG-19 dye | [60] |
| 12 | Phyllanthus niruri leaf |  | Crystalline | 23 | UV-DRS, EDX, FTIR, FESEM | Degradation of methylene blue (MB) | [59] |
| 13 | Syzygium cumini |  | Spherical round shaped | 22 | HRSEM, HRTEM, EDS, FTIR, XRD, DLS and BET | lead removal from wastewater | [58] |
| 14 | Tulbhagia violacela |  | Rectangular and Irregular shaped | 3.0–3.4 | XRD, SEM, EDX, TEM, and UV−vis | antioxidant assay and Anticancer activity | [58] |
| 15 | Commelina benghalensis |  | Spherical and agglomerated | 30–200 | XRD, SEM, EDX, BET, TGA and UV−vis | Degradation of methylene blue (MB) and SSX | [57] |
| 16 | Wrightia tinctoria leaf |  | Spherical | 22 | FTIR, UV, XRD, HR-TEM and HR-SEM | Antifungal against S. aureus, S. faecalis, E. coli, P. vulgaris, E. faecalis, P. aeruginosa, Y. enterocolitica, B. subtilis and fungus C. albicans | [56] |
| 17 | Nervilaaragona leaf, Ceaspinapulcherrima flower, Manihotesculante plant extract |  | Spherical | 15–28 | XRD, FTIR, SEM, EDX, TEM and UV−vis | Antibacterial against E. coli and S. aureus and Degradation of methylene blue (MB) | [52] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shakeel, N.; Piwoński, I.; Iqbal, P.; Kisielewska, A. Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Applications: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125454
Shakeel N, Piwoński I, Iqbal P, Kisielewska A. Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Applications: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125454
Chicago/Turabian StyleShakeel, Nasir, Ireneusz Piwoński, Parvaz Iqbal, and Aneta Kisielewska. 2025. "Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Applications: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125454
APA StyleShakeel, N., Piwoński, I., Iqbal, P., & Kisielewska, A. (2025). Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Applications: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125454








