Urine Proteomics for Detection of Potential Biomarkers for End-Stage Renal Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of the Participants
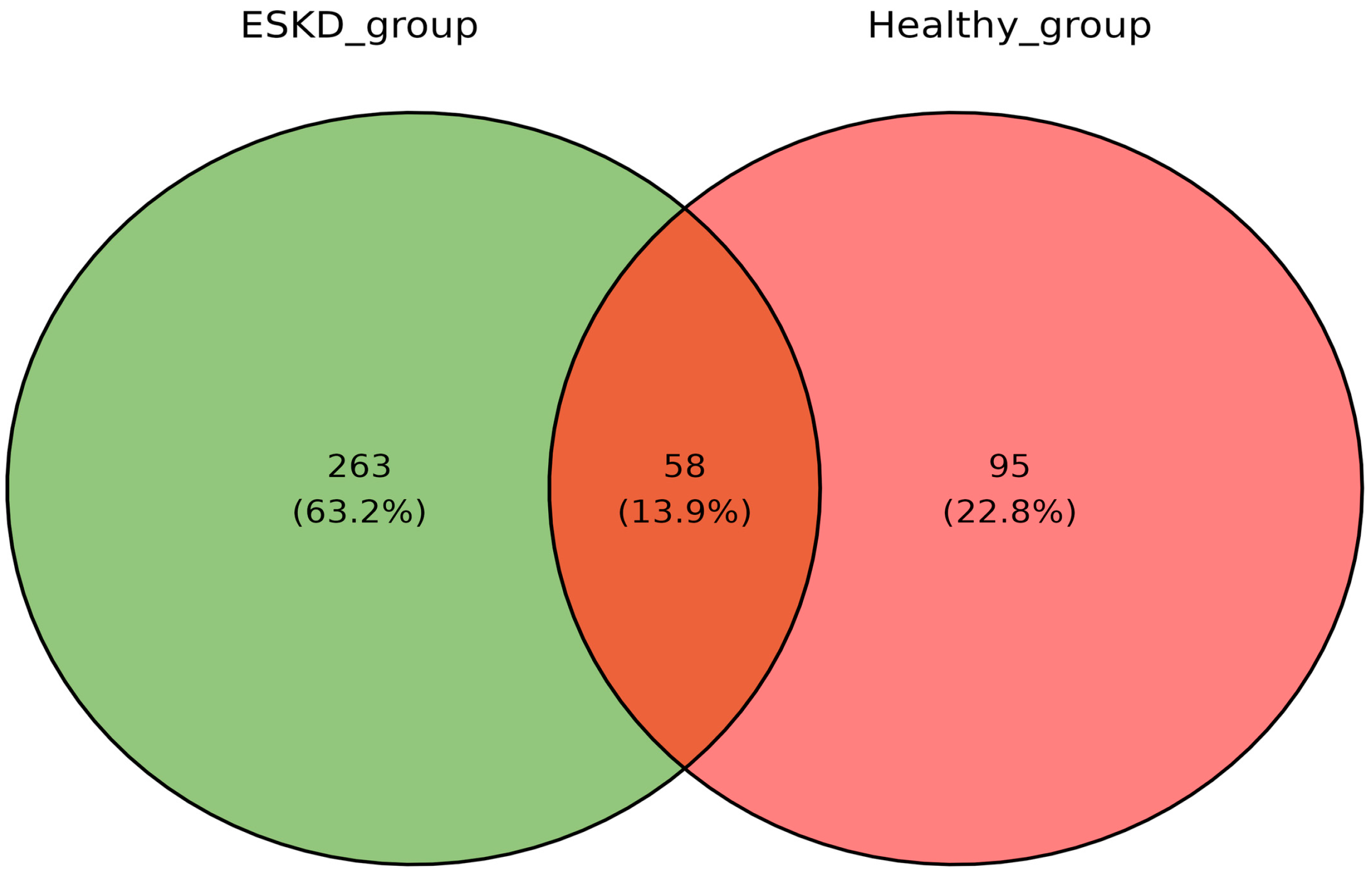
2.2. Urinary Proteomic Profile
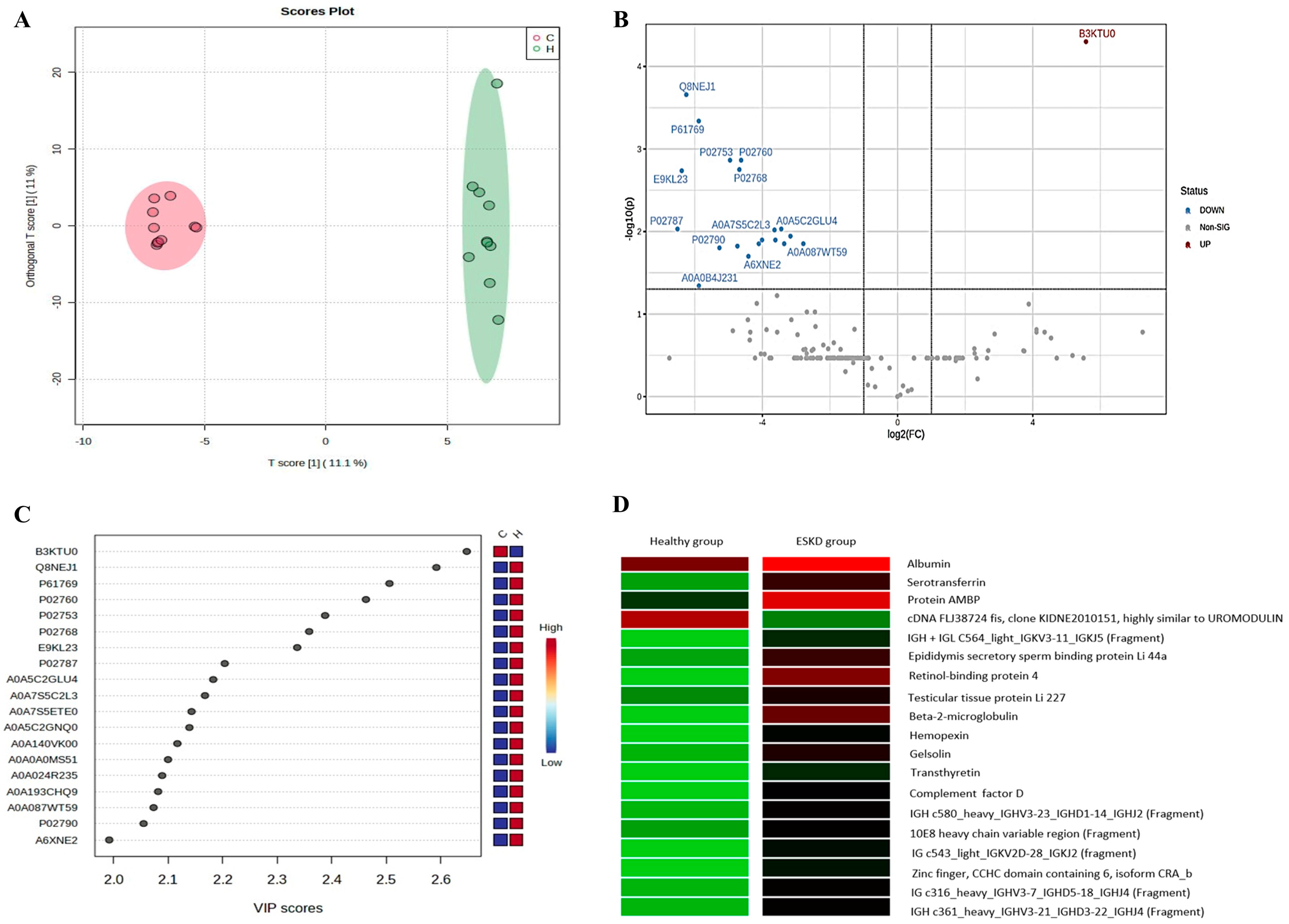
2.3. Characterization of Significant Proteins
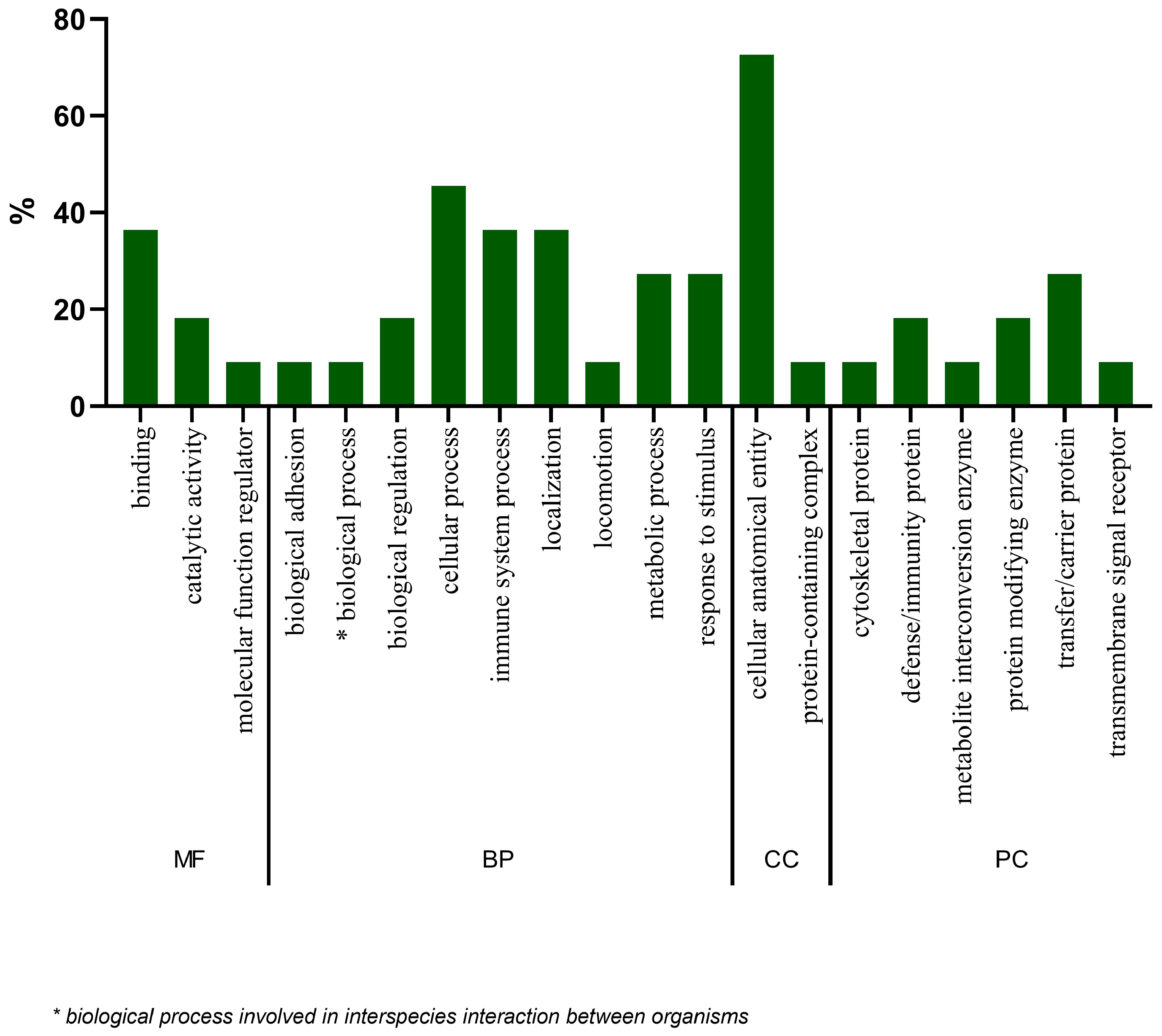
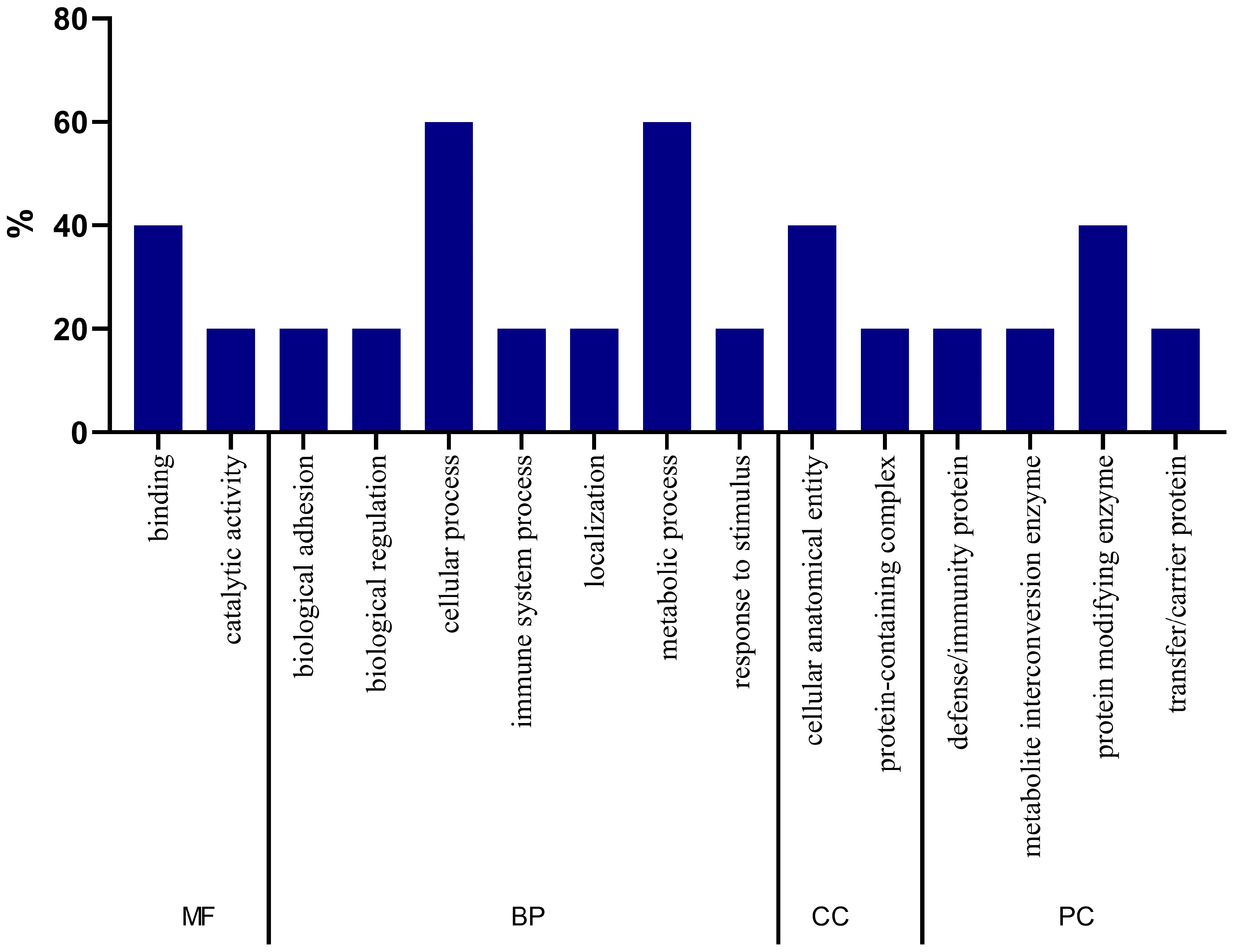
2.4. Gene Ontology Analysis of Proteins
2.5. Protein Interaction Analysis
2.6. Biomarker Candidate Proteins
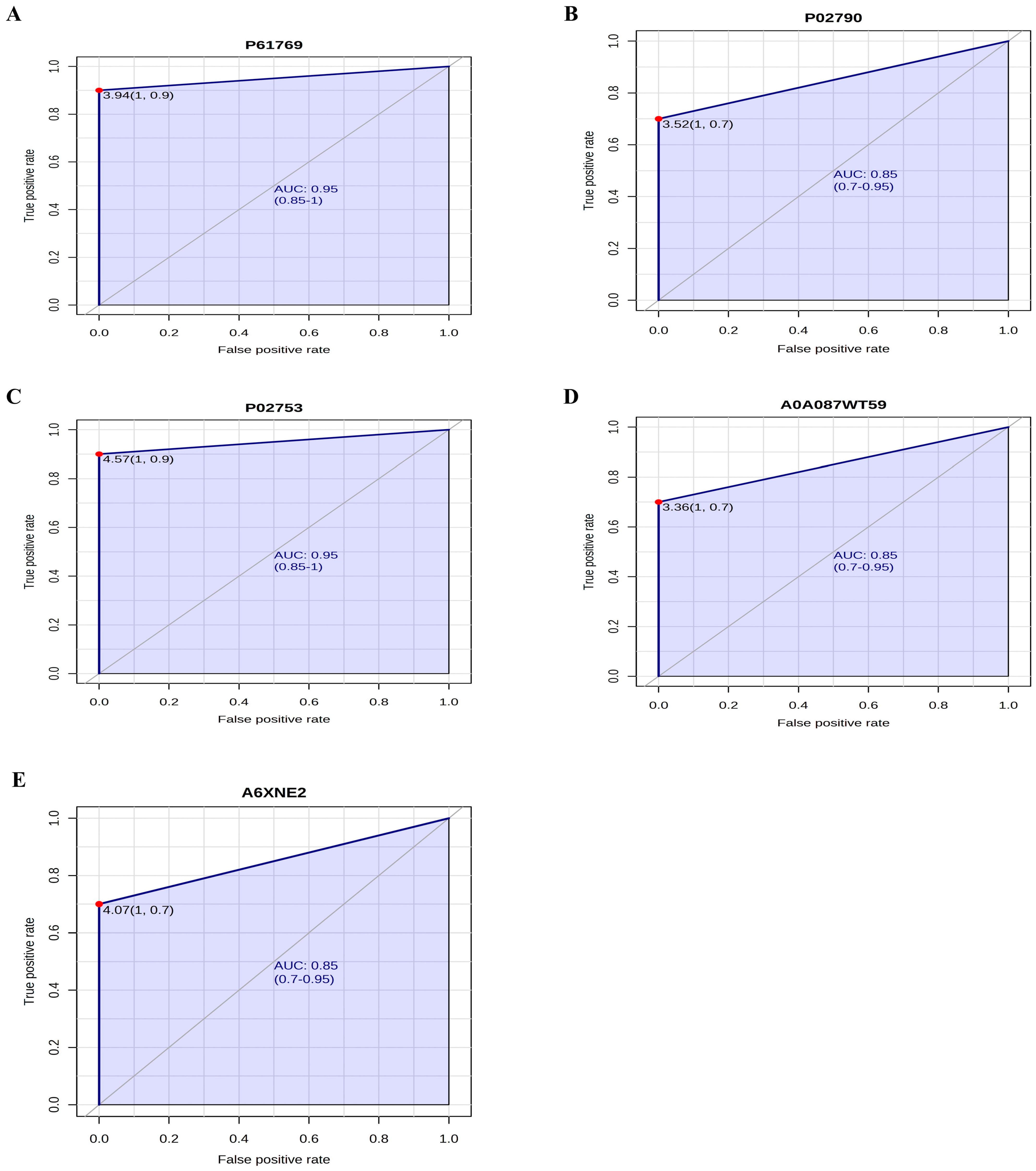
2.7. Accuracy Analysis of Biomarker Candidate Proteins
2.8. Gene Ontology Analysis of Biomarker Candidate Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Design and Selection
4.2. Data Collection
4.3. Ethical Aspects
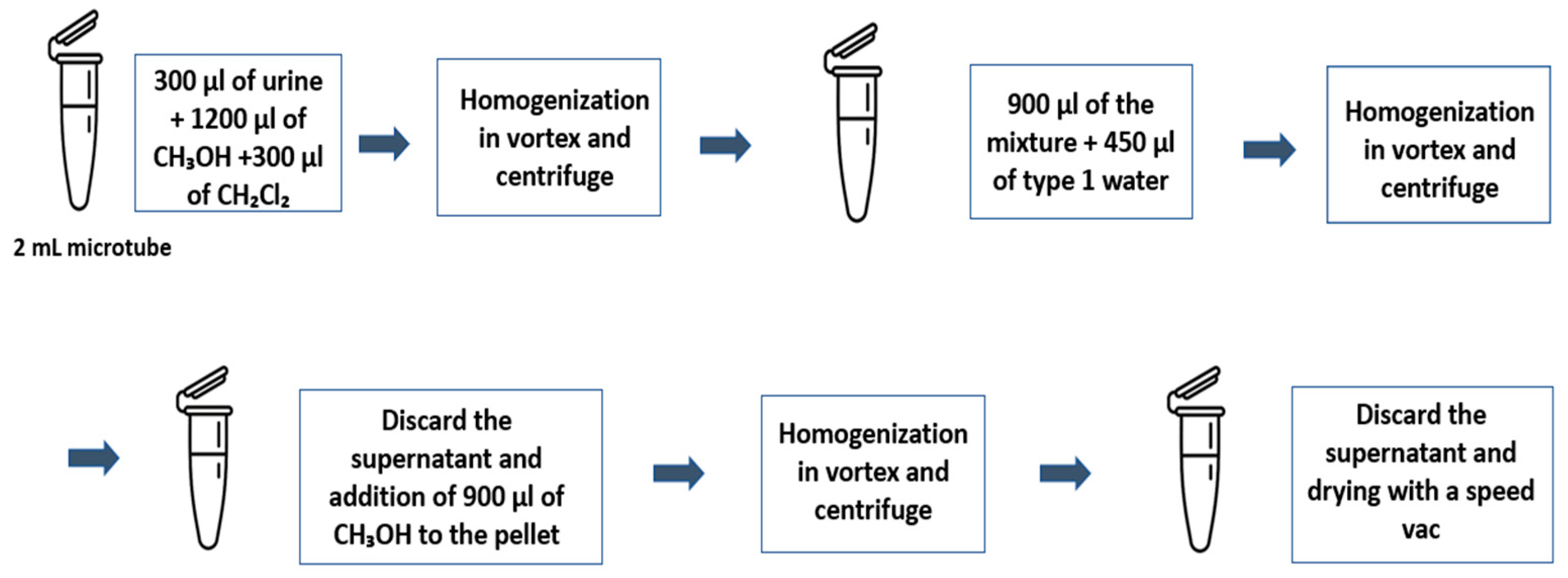
4.4. Proteomic Analysis
4.5. Enrichment Analysis
4.6. Criteria Used for the Definition of Biomarker Candidate Proteins
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aguiar, L.K.; Prado, R.R.; Gazzinelli, A.; Malta, D.C. Factors associated with chronic kidney disease: Epidemiological survey of the National Health Survey. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2020, 23, e200044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: An update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, A.; Harhay, M.N.; Ong, A.C.M.; Tummalapalli, S.L.; Ortiz, A.; Fogo, A.B.; Fliser, D.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Fontana, M.; Nangaku, M.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: An international consensus. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.; Lewis, R.D.; Morgan, A.R.; Whyte, M.B.; Hanif, W.; Bain, S.C.; Davies, S.; Dashora, U.; Yousef, Z.; Patel, D.C.; et al. A Narrative Review of Chronic Kidney Disease in Clinical Practice: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.K.; Okpechi, I.G.; Levin, A.; Ye, F.; Saad, S.; Zaidi, D. ISN–Global Kidney Health Atlas: A Report by the International Society of Nephrology: An Assessment of Global Kidney Health Care Status Focussing on Capacity, Availability, Accessibility, Affordability and Outcomes of Kidney Disease; International Society of Nephrology: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, L.S.; Manata, I.C.; Oliveira, V.A.C.D.; Acioli, M.L.B.; Pina, G.C.; Real, L.L.C.; Macedo, R.G. Chronic kidney disease: Underdiagnosed disease? Epidemiological analysis in a dialysis center. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jang, H.B.; Yoo, M.G.; Park, S.I.; Lee, H.J. Amino acid metabolites associated with chronic kidney disease: An eight-year follow-up Korean epidemiology study. Biomedicine 2020, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, D.C.; Machado, I.E.; Pereira, C.A.; Figueiredo, A.W.; Aguiar, L.K.; Almeida, W.S.; Souza, M.D.; Rosenfeld, L.G.; Szwarcwald, C.L. Evaluation of renal function in the Brazilian adult population, according to laboratory criteria from the National Health Survey. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2019, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.X.; Sun, L.; Nicholas, S.B.; Lu, Y.; Sinha, K.S.; Hua, R. Comparison of bias and accuracy using cystatin C and creatinine in CKD- EPI equations for GFR estimation. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 80, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocher, B.; Adamski, J. Metabolomics for clinical use and research in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govender, M.A.; Brandenburg, J.T.; Fabian, J.; Ramsay, M. The use of ‘Omics for diagnosing and predicting progression of chronic kidney disease: A scoping review. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 682929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, T.; Krochmal, M.; Cisek, K.; Fernandes, M.; Husi, H.; Stevens, R.; Bascands, J.L.; Schanstra, J.P.; Klein, J. Omics Databases on Kidney Disease: Where They Can Be Found and How to Benefit from Them. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, D.M.; Zürbig, P.; Argilés, A.; Bauer, H.W.; Behrens, G.; Coon, J.J.; Dakna, M.; Decramer, S.; Delles, C.; Dominiczak, A.F.; et al. Naturally occurring human urinary peptides for use in diagnosis of chronic kidney disease. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2010, 9, 2424–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Gong, T.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; et al. Urine proteomics identifies biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease at different stages. Clin. Proteom. 2021, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Duan, N.; Li, H. Urine proteomics of primary membranous nephropathy using nanoscale liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Clin. Proteom. 2018, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, F.; Siwy, J.; Biesen, W.V.; Mischak, H.; Pletinck, A.; Schepers, E.; Neirynck, N.; Magalhães, P.; Pejchinovski, M.; Pontillo, C.; et al. The urinary proteomics classifier chronic kidney disease 273 predicts cardiovascular outcome in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanese, L.; Siwy, J.; Mischak, H.; Wendt, R.; Beige, J.; Rupprecht, H. Recent advances in urinary peptide and proteomic biomarkers in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvi-Behr, S.; Ivgi, H.; Frishberg, Y.; Shalom, E.B. First-week urine beta-2 microglobulin levels in healthy neonates. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosano, E.; Fagoonee, S.; Morello, N.; Vinchi, F.; Fiorito, V. Heme scavenging and the other facets of hemopexin. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2010, 12, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Cortez, Y.A.; Barragán-Bonilla, M.I.; Mendoza-Bello, J.M.; González-Calixto, C.; Flores-Alfaro, E.; Espinoza-Rojo, M. Interplay of retinol binding protein 4 with obesity and associated chronic alterations (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczyc, K.; Konieczny, A.; Czekaj, A.; Piotrów, P.; Fiutowski, M.; Krakowska, K.; Kowal, P.; Witkiewicz, W.; Marek-Bukowiec, K. The clinical significance of urinary retinol-binding protein 4: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.D.; Othee, H.; Chan, K.A.; Man, D.C.; Belliveau, P.P.; Towle, J. Transthyretin Amiloid Cardiomyopathy—Current and future therapies. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Weitz, I. Complement factor D as a strategic target for regulating the alternative complement pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 712572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tótoli, C.; Carvalho, A.B.; Ammirati, A.L.; Draibe, S.A.; Canziani, M.E.F. Associated factors related to chronic kidney disease progression in elderly patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Pesquisa Nacional de Saúde: 2019: Percepção do Estado de Saúde, Estilos de Vida, Doenças Crônicas e Saúde Bucal: Brasil e Grandes Regiões. IBGE, Coordenação de Trabalho e Rendimento; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020; 113p. Available online: https://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/visualizacao/livros/liv101764.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Xia, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; He, L.; Su, X. Cigarette smoking and chronic kidney disease in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Clarke, A.L.; Nixon, D.G.D.; Hull, K.L.; Song, Y.; Burton, J.O.; Yates, T.; Smith, A.C. Prevalence and correlates of physical activity across kidney disease stages: An observational multicentre study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, A.; Gallaguer, H. Chronic kidney disease in adults: Assessment and management. Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Maiti, A.; Sinha, A.; Baidya, A.; Basu, A.K.; Sarkar, D.; Biswas, D.; Maisnam, I.; Pandit, K.; Raychaudhuri, M. Kidney disease in type 2 Diabetes mellitus and benefits of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: A consensus statement. Diabetes Ther. 2020, 11, 2791–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurts, C.; Panzer, U.; Anders, H.J.; Rees, A.J. The immune system and kidney disease: Basic concepts and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmito, F.T.S.; Macedo, A.G.M.; da Silva, A.P.P.; da Cavalcanti, A.R.S.L.; Serafim, E.C.G.; da Silva, I.F.; Santos, J.L.L.; Almeida, M.L.; de Oliveira, M.I.; Almeida, M.L. Biomarkers of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: Advances and challenges. Rev. Contemp. 2023, 3, 11199–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlacher, E.; Wollenhaupt, J.; Baaten, C.C.F.M.J.; Noels, H. Impact of uremic toxins on endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarakpi, T.; Mesic, A.; Speer, T. Leukocyte-endothelial interaction in CKD. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1845–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zager, R.A.; Johnson, A.C.M.; Becker, K. Renal cortical hemopexin accumulation in response to acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 303, F1460–F1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.M. Pathogenesis of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: A review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. Child. Kidney Dis. 2019, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhou, D.; Chen, X.; Zhou, L. Association of urinary biomarkers of renal tubular injury with cognitive dysfunction in older patients with chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional observational study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Zu, Y.; Wang, S. Prognostic value of beta-2 microglobulin on mortality of chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2021, 26, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, L.; Li, H.; Wang, S. High serum β2-microglobulin is a significant predictor of mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Semin. Dial. 2022, 36, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying uremic toxin-related systemic disorders in chronic kidney disease: Focused on β2-microglobulin-related amyloidosis and indoxyl sulfate-induced atherosclerosis—Oshima Award Address 2016. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yi, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dai, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Zhang, H. Urinary NGAL and RBP are biomarkers of normoalbuminuric renal insufficiency in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 5063089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.J.; Shin, D.H.; Oh, J.; Kee, Y.K.; Park, J.Y.; Ko, K.; Lee, S. Urinary retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with renal function and rapid renal function decline in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2022, 54, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, M.A.M.; Moreira, S.R.; Gomez, L.; Goulart, A.; Lotufo, P.A.; Benseñor, I.; Titan, S. Urinary retinol-binding protein: Relationship to renal function and cardiovascular risk factors in chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Koike, H.; Slama, M.; Coelho, T. Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis: A model of medical progress for a fatal disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentellis, I.; Amarenco, G.; Gamé, X.; Jericevic, D.; EL-Akri, M.; Voiry, C.; Freton, L.; Hascoet, J.; Alimi, Q.; Kerdraon, J.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of urinary and sexual dysfunction in hereditary TTR amyloidosis. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury Medicina e Saúde. Teste Diagnostica a Principal Forma de Amiloidose Familiar e a Diferença de Outros Tipos de Doença. 2022. Available online: https://www.fleury.com.br/medico/artigos-cientificos/teste-diagnostica-a-principal-forma-de-amiloidose-familiar-e-a-diferencia-de-outros-tipos-da-doenca (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Makhammajanov, Z.; Kabayeva, A.; Auganova, D.; Tarlykov, P.; Bukasov, R.; Turebekov, D.; Kanbay, M.; Molnar, M.Z.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Abidi, S.H.; et al. Candidate protein biomarkers in chronic kidney disease: A proteomics study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsudo, S.; Araújo, T.; Matsudo, V.; Andrade, D.; Andrade, E.; Oliveira, L.C.; Braggion, G. International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ): Study of validity and reliability in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ativ. Fís Saúde 2001, 10, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lipschitz, D.A. Screening for nutritional status in the elderly. Prim. Care 1994, 21, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic: Report of a WHO Consultation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42330 (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- ThermoFisher Scientific. Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit, 2020. Catalog Numbers: 23225, 23227. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/document-connect/document-connect.html?url=https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets%2FLSG%2Fmanuals%2FMAN0011430_Pierce_BCA_Protein_Asy_UG.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Waters. RapiGest SF Surfactant—Care and Use Manual. 2015. Available online: https://www.waters.com/webassets/cms/support/docs/715000122en.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, T.C.F.; Miot, H.A. Use of ROC curves in clinical and experimental studies. J. Vasc. Bras. 2020, 19, e20200186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Control Group (n = 10) | Hemodialysis Group (n = 10) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 5 (41.7) | 7 (58.3) | 0.361 |
| Female | 5 (62.5) | 3 (37.5) | ||
| Age in years, mean ± standard deviation | 40.3 ± 12.3 | 60.4 ± 8.2 | <0.001 | |
| Schooling | No education/incomplete elementary schooling | 0 | 6 (100) | 0.038 |
| Complete high school/incomplete higher education | 4 (57.1) | 3 (42.8) | ||
| Complete higher education | 6 (85.7) | 1 (14.3) | ||
| Race/color | White | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 0.580 |
| Black | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | ||
| Brown | 5 (45.5) | 6 (54.5) | ||
| Marital status | With partner | 6 (60.0) | 4 (40.0) | 0.247 |
| Without a partner | 4 (40.0) | 6 (60.0) | ||
| Nutritional status | Eutrophic | 5 (45.5) | 6 (54.5) | 0.337 |
| Overweight | 5 (55.5) | 4 (44.5) | ||
| Tobacco use | Never smoked | 10 (66.7) | 5 (33.3) | 0.010 |
| Ex smoker | 0 | 5 (100) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | Never drinks | 7 (58.3) | 5 (41.7) | 0.607 |
| Less than once a month | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | ||
| Once or more a month | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | ||
| Physical activity | Sedentary or irregularly active | 0 | 7 (100) | 0.024 |
| Active or very active | 10 (76.9) | 3 (23.1) | ||
| Creatinine, mean ± standard deviation | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 9.6 ± 1.4 | <0.001 | |
| GFR, mean ± standard deviation | 94.9 ± 27.1 | 5.4 ± 1.1 | <0.001 | |
| Total cholesterol, mean ± standard deviation | 186.3 ± 27.0 | 172.2 ± 45.1 | 0.713 | |
| Triglycerides, mean ± standard deviation | 141.1 ± 40.2 | 233.1 ± 138.4 | 0.112 | |
| Fasting blood glucose, mean ± standard deviation | 83.5 ± 4.9 | 124.5 ± 45.9 | 0.011 | |
| Chromatographic Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Column | Agilent model AdvanceBio Peptide Mapping |
| Internal diameter | 2.1 mm |
| Length | 10 cm |
| Particle size | 2.7 μm |
| Mobile phase (A) | Water acidified with formic acid (0.1% v/v) |
| Mobile phase (B) | Acetonitrile acidified with formic acid (0.1% v/v) |
| Gradient | 2% B (0 min) |
| 2% B (10 min) | |
| 15% B (40 min) | |
| 50% B (150 min) | |
| 70% B (200 min) | |
| 98% B (220 min) | |
| 98% B (300 min) | |
| 100% of B (301 min) | |
| 100% of B (400 min) | |
| Flow rate | 400 µL/min |
| Ionization parameters | |
| Nebulizer pressure | 45 psi |
| Drying gas flow rate | 8 L/min |
| Drying gas temperature | 325 °C |
| Capillary voltage | 4 kV |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, N.R.; Picolo, B.U.; de Sousa, L.C.M.; dos Santos, M.S.; Polveiro, R.C.; Almeida-Souza, H.O.; Martins, M.M.; Goulart Filho, L.R.; da Silva, L.S. Urine Proteomics for Detection of Potential Biomarkers for End-Stage Renal Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125429
Silva NR, Picolo BU, de Sousa LCM, dos Santos MS, Polveiro RC, Almeida-Souza HO, Martins MM, Goulart Filho LR, da Silva LS. Urine Proteomics for Detection of Potential Biomarkers for End-Stage Renal Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125429
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Nathalia R., Bianca U. Picolo, Letícia C. M. de Sousa, Marta S. dos Santos, Richard C. Polveiro, Hebréia O. Almeida-Souza, Mário M. Martins, Luiz R. Goulart Filho, and Luciana S. da Silva. 2025. "Urine Proteomics for Detection of Potential Biomarkers for End-Stage Renal Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125429
APA StyleSilva, N. R., Picolo, B. U., de Sousa, L. C. M., dos Santos, M. S., Polveiro, R. C., Almeida-Souza, H. O., Martins, M. M., Goulart Filho, L. R., & da Silva, L. S. (2025). Urine Proteomics for Detection of Potential Biomarkers for End-Stage Renal Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125429








