Inhibition of MCP1 (CCL2) Enhances Antitumor Activity of NK Cells Against HCC Cells Under Hypoxia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Increased Production of MCP1 by HCC Cells Under Hypoxia
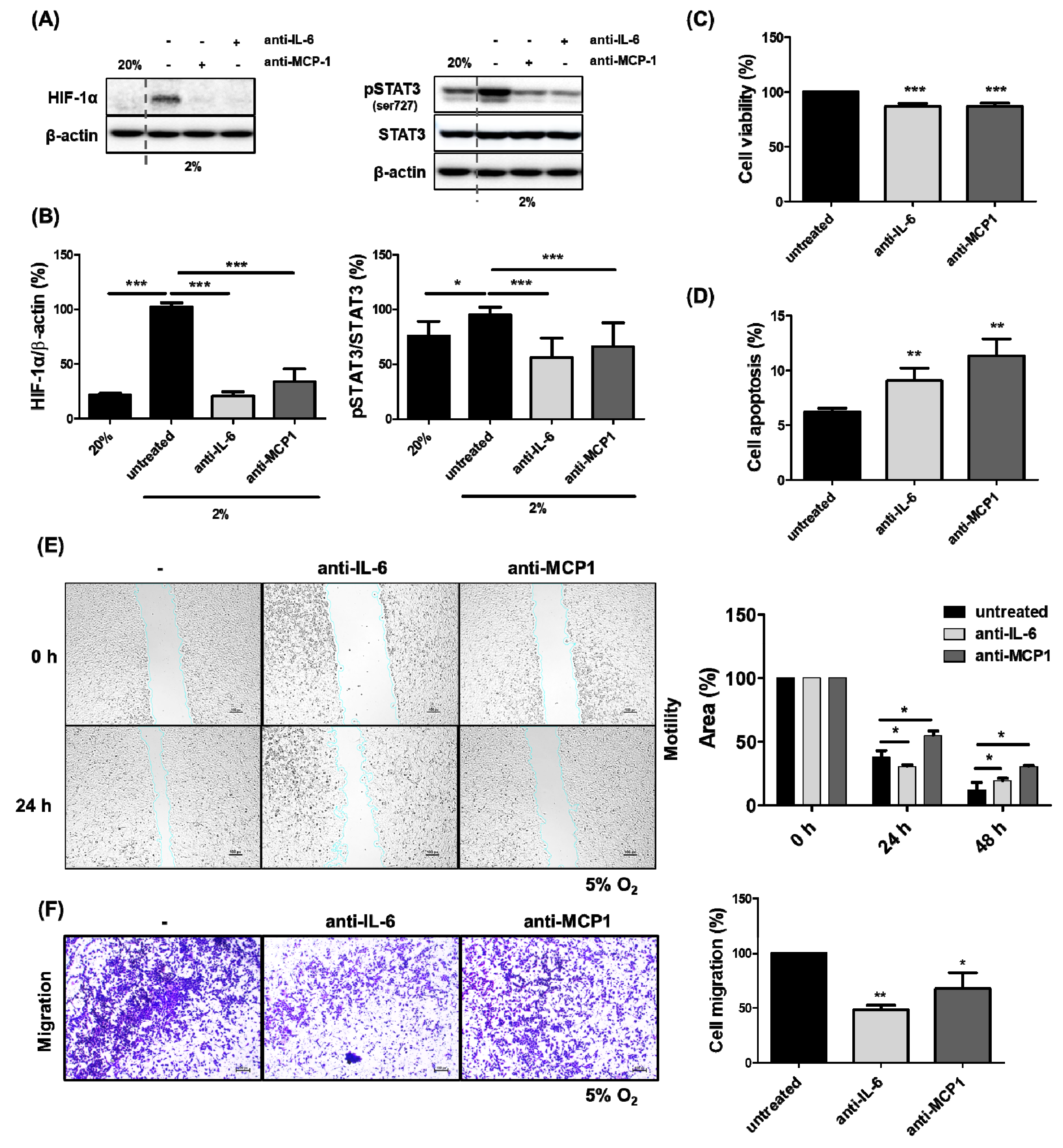
2.2. The Inhibition of HCC Cell Growth by the Reduced Expression of HIF-1α Through the Blockade of MCP1 in the Presence of Hypoxia
2.3. Inhibition of HCC Cell Migration by Blockade of MCP1 Under Hypoxia
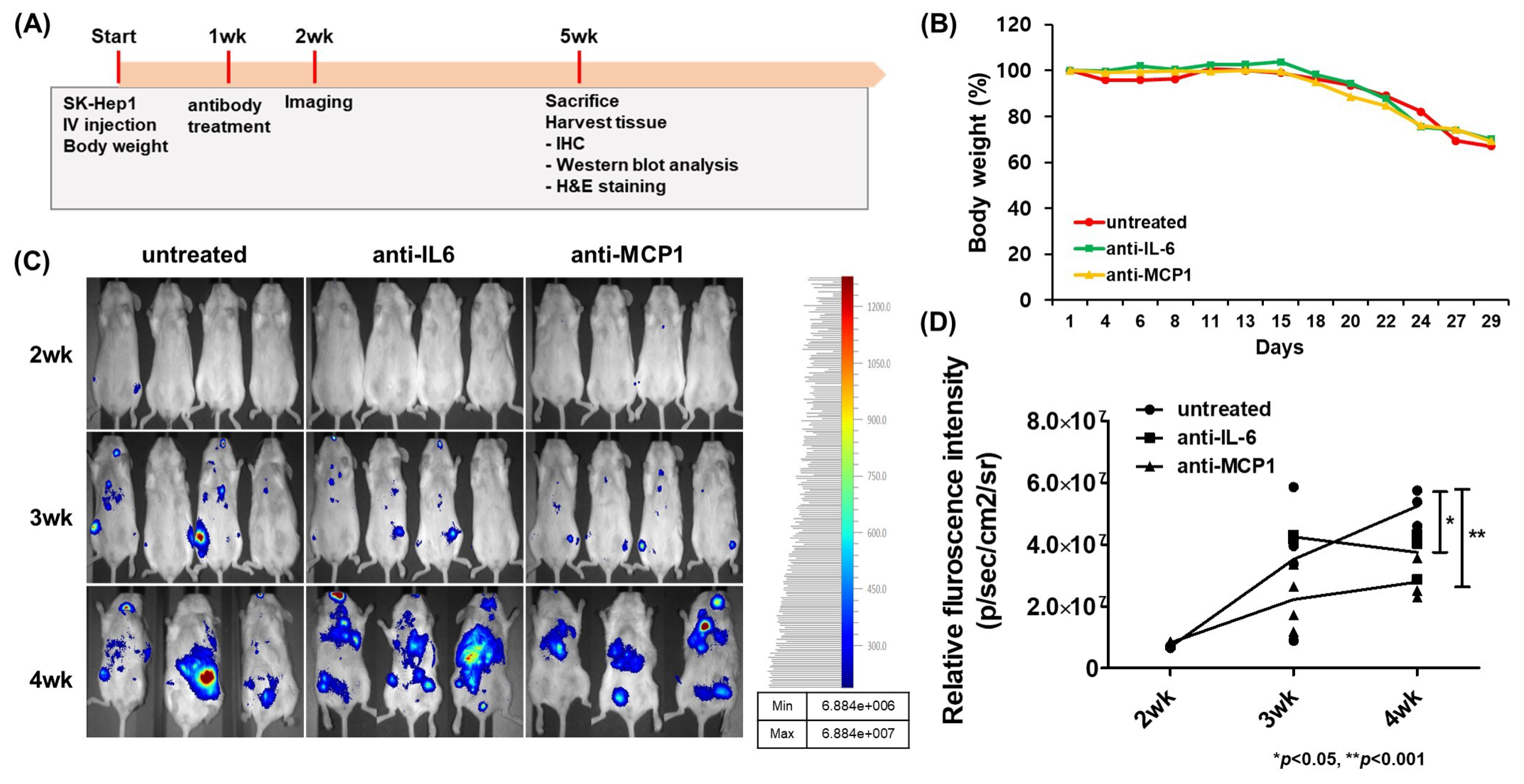
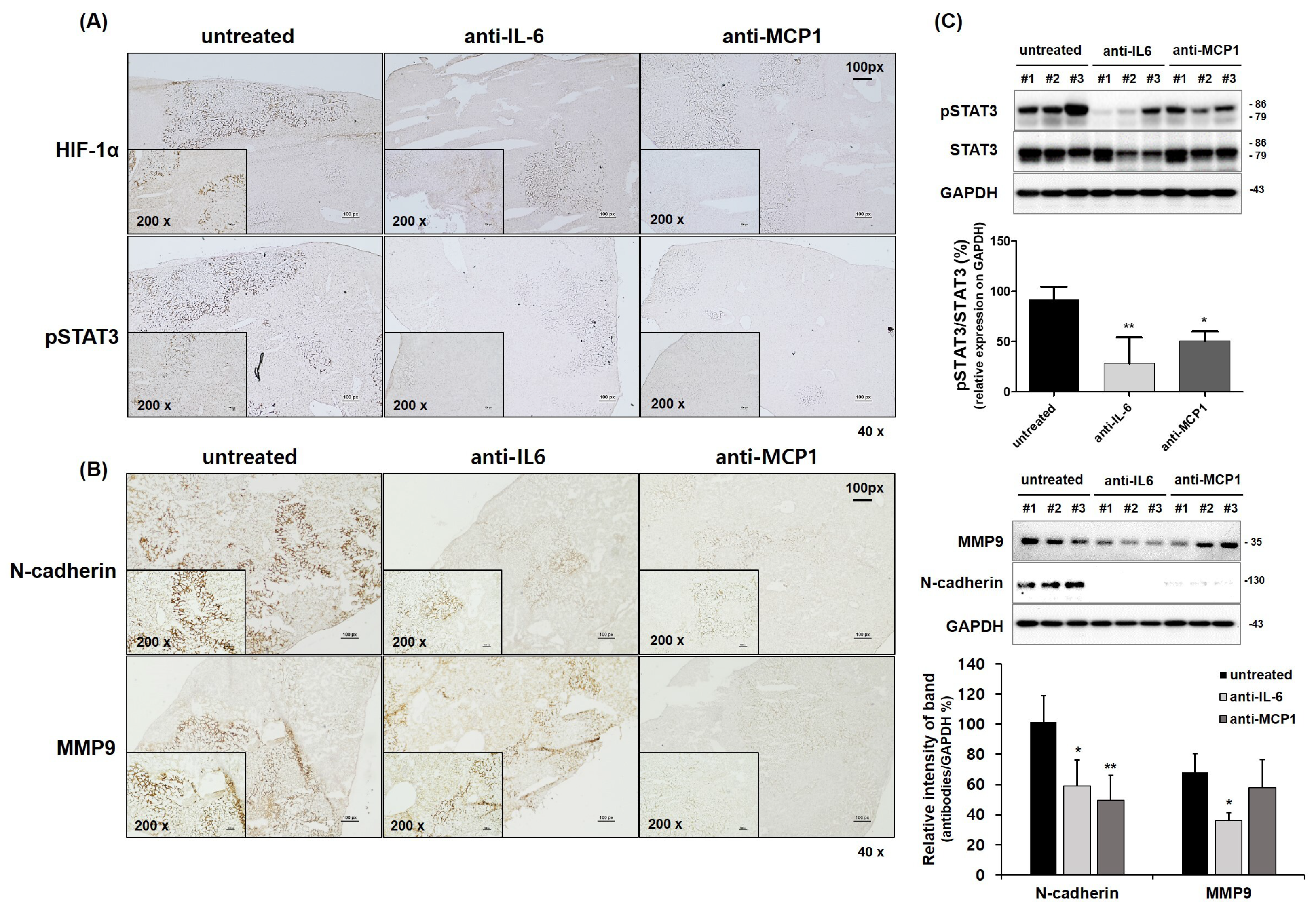
2.4. Suppression of HCC Tumorigenesis by Anti-CCL2 (MCP1) Treatment in Mice
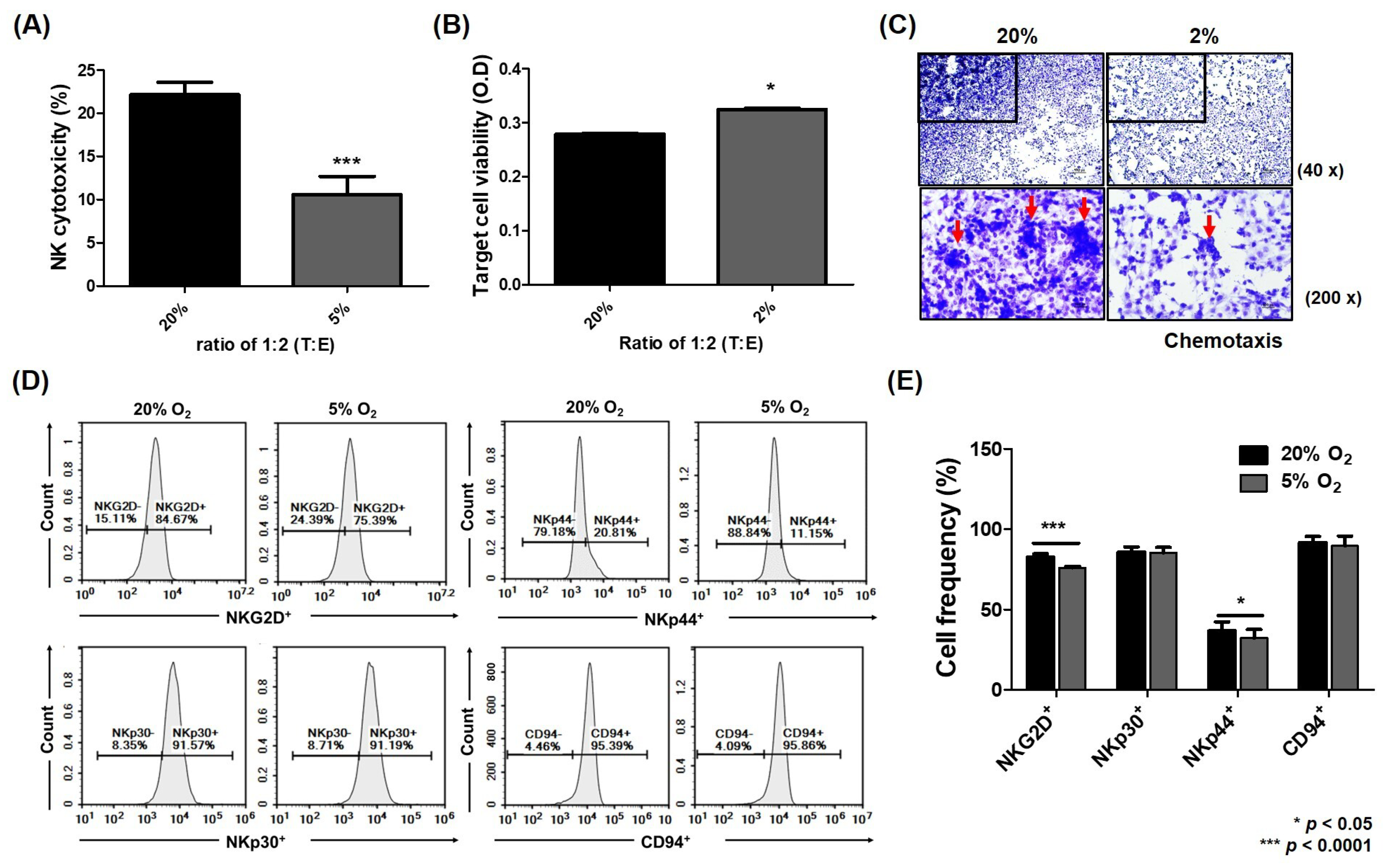
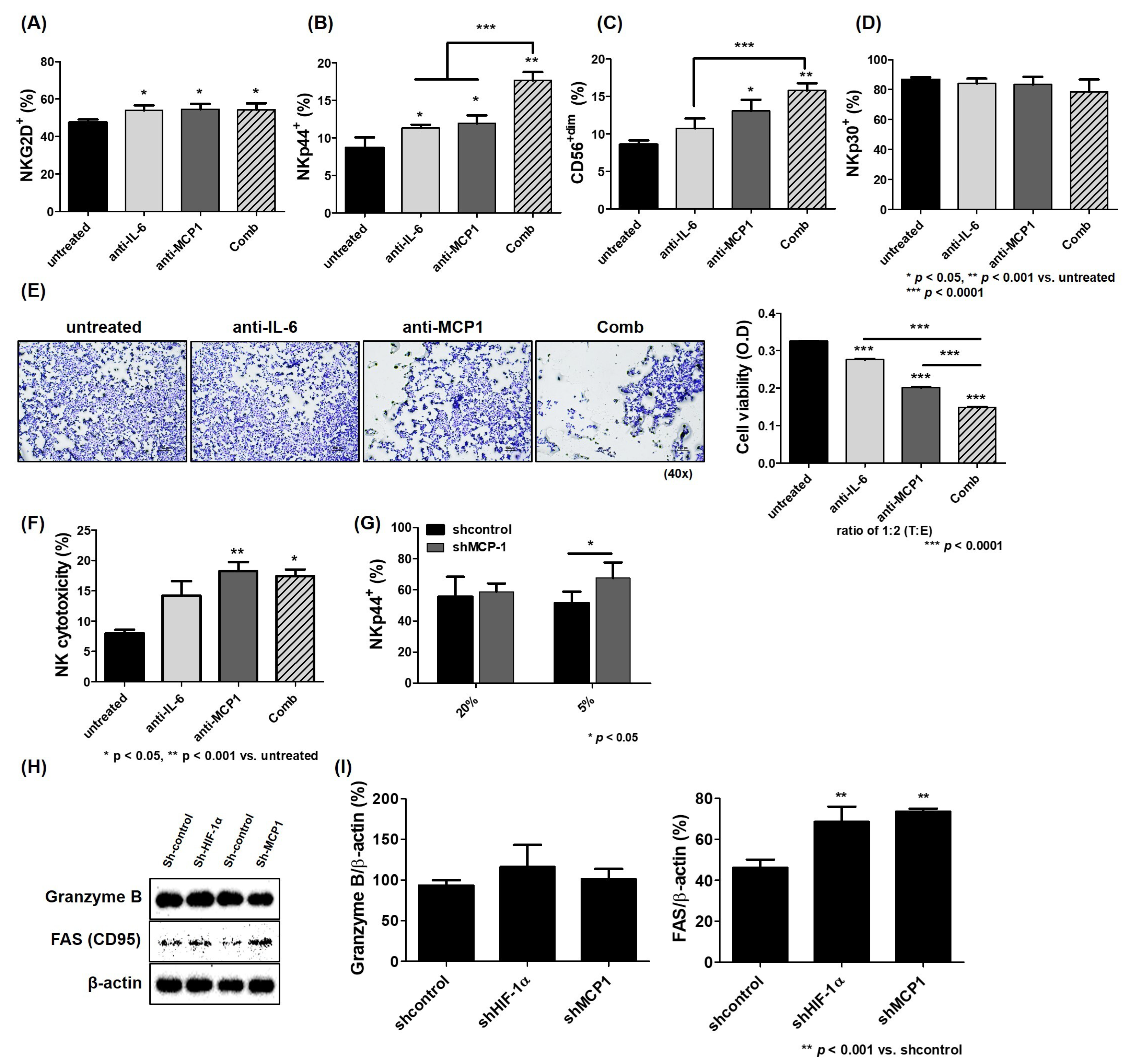
2.5. Improvement of NK Activity Against HCC ceLLs by Blockade of MCP1 Under Hypoxia
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Maintenance
4.2. Gene Knockdown Using shRNA Plasmid Transfection
4.3. Cytokine Array
4.4. Cell Apoptosis Using Annexin V Staining
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Cell Migration Assay
4.7. In Vivo Study Using Xenograft Model NRG Mice
4.8. Tissue IHC Staining Analysis
4.9. NK Cytotoxicity Using LDH-Release Assay
4.10. Chemotaxis Assay
4.11. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Y.-C.; Sun, C.-K.; Chen, Q.-M. Role of the tumor microenvironment in tumor progression and the clinical applications (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2499–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Liu, K.; He, Q.; Gu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J. Hypoxia signaling in cancer: Implications for therapeutic interventions. MedComm 2023, 4, e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavda, V.P.; Feehan, J.; Apostolopoulos, V. Inflammation: The Cause of All Diseases. Cells 2024, 13, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, M.; Mishra, A.P.; Deb, V.K.; Dimri, D.B.; Tiwari, V.; Bungau, S.G.; Bungau, A.F.; Radu, A.-F. Evaluation of the association of chronic inflammation and cancer: Insights and implications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Song, J.; Gao, D.; Huang, S.; Pang, A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Interleukin-6 and Hypoxia Synergistically Promote EMT-Mediated Invasion in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer via the IL-6/STAT3/HIF-1α Feedback Loop. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2023, 2023, 8334881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Deng, L.; Wang, D.; Li, N.; Chen, X.; Cheng, X.; Yuan, J.; Gao, X.; Liao, M.; Wang, M.; et al. Mechanism of TNF-α autocrine effects in hypoxic cardiomyocytes: Initiated by hypoxia inducible factor 1α, presented by exosomes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Wang, Y.N. Hypoxia/IL-1α axis promotes gastric cancer progression and drug resistance. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 18, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Jung, J.; Moon, A.; Kang, H.; Cho, H. Antitumor and Anti-Invasive Effect of Apigenin on Human Breast Carcinoma through Suppression of IL-6 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Choi, H.; Kim, E.S.; Lee, H.H.; Cho, H.; Moon, A. Natural killer cells inhibit breast cancer cell invasion through downregulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.; Kang, H.; Cho, H. Role of Interleukin(IL)-6 in NK Activity to Hypoxic-Induced Highly Invasive Hepatocellular Carcinoma(HCC) Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.; Delfanti, F.; Bernasconi, S.; Mengozzi, M.; Cota, M.; Polentarutti, N.; Mantovani, A.; Lazzarin, A.; Sozzani, S.; Poli, G. Interleukin-6 induces monocyte chemotactic protein-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and in the U937 cell line. Blood 1998, 91, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Sarkissyan, M.; Paico, K.; Wu, Y.; Vadgama, J.V. MCP-1 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancers and drives cancer invasiveness and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, P.F.; Sivapurapu, N.; Jovanovic, B.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A. Monocyte-Induced Prostate Cancer Cell Invasion is Mediated by Chemokine ligand 2 and Nuclear Factor-κB Activity. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2015, 6, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, P.; Leone, B.E.; Marchesi, F.; Balzano, G.; Zerbi, A.; Scaltrini, F.; Pasquali, C.; Calori, G.; Pessi, F.; Sperti, C.; et al. The CC chemokine MCP-1/CCL2 in pancreatic cancer progression: Regulation of expression and potential mechanisms of antimalignant activity. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7451–7461. [Google Scholar]
- Denko, N.C. Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose metabolism in the solid tumour. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.A.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5510–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Bhat, G.R.; Besina, S.; Thakur, N.; Zahoor, S.; Rather, R.A.; Mushtaq, I.; Dar, S.; Rah, B.; Bhat, A.A.; et al. Expression of HIF-1α and markers of angiogenesis and metabolic adaptation in molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Transl. Med. Commun. 2023, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiezzi, D.G.; Clagnan, W.S.; Mandarano, L.R.; de Sousa, C.B.; Marana, H.R.; Tiezzi, M.G.; de Andrade, J.M. Expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is associated with expression of hypoxia-inducible factors 1 and 2 alpha and predicts prognosis in locally advanced breast cancer. Clinics 2013, 68, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Kamura, T.; Minato, N.; Conaway, R.C.; Conaway, J.W.; Klausner, R.D.; Pause, A. Identification of the von Hippel-lindau tumor-suppressor protein as part of an active E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12436–12441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.H.; Jiang, G.; Zheng, J.Z.; Lu, Z.; Hunter, T.; Vogt, P.K. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling controls levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell Growth Differ. 2001, 12, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, N.; Stiehl, D.P.; Bohensky, J.; Leshchinsky, I.; Srinivas, V.; Caro, J. MAPK signaling up-regulates the activity of hypoxia-inducible factors by its effects on p300. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14013–14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Grötsch, B.; Luo, Y.; Knaup, K.X.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chen, X.-X.; Jantsch, J.; Fillatreau, S.; Schett, G.; Bozec, A. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a critical transcription factor for IL-10-producing B cells in autoimmune disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, M.M.; Lindkvist, M.; Fälker, K.; Kumawat, A.K.; Paramel, G.; Grenegård, M.; Sirsjö, A.; Ljungberg, L.U. Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways are crucial for IL-6 trans-signaling-mediated pro-inflammatory response in human vascular endothelial cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaiu, O.; Lucarini, V.; Cifaldi, L.; Fruci, D. Influence of the Tumor Microenvironment on NK Cell Function in Solid Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Sun, H.-Y.; Xiao, W.-H.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.-G. Natural killer cell dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma and NK cell-based immunotherapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Matosevic, S. Chemokine networks modulating natural killer cell trafficking to solid tumors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 59, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Su, L.; Weng, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, D.; Feng, J. Tumor-associated neutrophils suppress antitumor immunity of NK cells through the PD-L1/PD-1 axis. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ye, Y.L.; Li, M.X.; Ye, S.B.; Huang, W.R.; Cai, T.T.; He, J.; Peng, J.Y.; Duan, T.H.; Cui, J.; et al. CXCL2/MIF-CXCR2 signaling promotes the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and is correlated with prognosis in bladder cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Qi, F.; Zhao, F.; Li, G.; Shao, S.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, L.; Feng, Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance tumor-associated macrophages enrichment and suppress NK cells function in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, K.Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Hsu, S.H.; He, S.; Wani, N.A.; Barajas, J.M.; Snyder, L.A.; Frankel, W.L.; Caligiuri, M.A.; et al. Blocking the CCL2-CCR2 Axis Using CCL2-Neutralizing Antibody Is an Effective Therapy for Hepatocellular Cancer in a Mouse Model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koong, A.C.; Mehta, V.K.; Le, Q.T.; Fisher, G.A.; Terris, D.J.; Brown, J.M.; Bastidas, A.J.; Vierra, M. Pancreatic tumors show high levels of hypoxia. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigau, E.; Le Ridant, A.M.; Lambin, P.; Weeger, P.; Martin, L.; Sigal, R.; Lusinchi, A.; Luboinski, B.; Eschwege, F.; Guichard, M. Oxygenation of head and neck tumors. Cancer 1993, 71, 2319–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.E.; Rockwell, S. Hypoxic fractions of solid tumors: Experimental techniques, methods of analysis, and a survey of existing data. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1984, 10, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapani, J.A.; Sutton, V.R. Granzyme B: Pro-apoptotic, antiviral and antitumor functions. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Karin, M. Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.T.; Chen, H.R.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, C.C. Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) modulates pro-survival signaling to promote progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsis, A.; Tzikas, S.; Kassimis, G. Dysregulation of IL-6/MCP-1/STAT3 Axis: A Promising Therapeutic Postinfarction Inflammation Strategy? JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2024, 9, 605–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Carmeliet, P. Hypoxia and inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Welden, S.; Selfridge, A.C.; Hindryckx, P. Intestinal hypoxia and hypoxia-induced signalling as therapeutic targets for IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xing, C.; Deng, Y.; Ye, C.; Peng, H. HIF-1α signaling: Essential roles in tumorigenesis and implications in targeted therapies. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Tu, J.; Cai, W.; Xu, Q. HSP90 inhibits apoptosis and promotes growth by regulating HIF-1α abundance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 825–835, Corrigendum in Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 50, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L. Hypoxia inducible factor 1α in hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis: Association with prognosis. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Xi, Q.; Meng, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wu, G. Interleukin-6 promotes tumor progression in colitis-associated colorectal cancer through HIF-1α regulation. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4665–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, S.Y.; Wu, V.W.C.; Law, H.K.W. Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancers: HIF-1α and Beyond. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozik, K.M.; Blaschuk, O.W.; Cheong, C.M.; Zannettino, A.C.W.; Vandyke, K. N-cadherin in cancer metastasis, its emerging role in haematological malignancies and potential as a therapeutic target in cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersesian, S.; Schwartz, S.L.; Grantham, S.R.; MacLean, L.K.; Lee, S.N.; Pugh-Toole, M.; Boudreau, J.E. NK cell infiltration is associated with improved overall survival in solid cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpekris, F.; Voutouri, C.; Baish, J.W.; Duda, D.G.; Munn, L.L.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Jain, R.K. Combining microenvironment normalization strategies to improve cancer immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3728–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuillefroy de Silly, R.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Walker, P.R. Hypoxia and antitumor CD8(+) T cells: An incompatible alliance? Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1232236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, R.; Wang, Y.; Lv, N.; Zhang, D.; Williamson, R.A.; Lei, L.; Chen, P.; Lei, L.; Wang, B.; Fu, J.; et al. Hypoxia Impairs NK Cell Cytotoxicity through SHP-1-Mediated Attenuation of STAT3 and ERK Signaling Pathways. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 4598476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequeux, A.; Noman, M.Z.; Xiao, M.; Van Moer, K.; Hasmim, M.; Benoit, A.; Bosseler, M.; Viry, E.; Arakelian, T.; Berchem, G.; et al. Targeting HIF-1 alpha transcriptional activity drives cytotoxic immune effector cells into melanoma and improves combination immunotherapy. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4725–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Niu, G.; Kortylewski, M.; Burdelya, L.; Shain, K.; Zhang, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Gabrilovich, D.; Heller, R.; Coppola, D.; et al. Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witalisz-Siepracka, A.; Klein, K.; Zdársky, B.; Stoiber, D. The Multifaceted Role of STAT3 in NK-Cell Tumor Surveillance. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 947568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddawi-Konefka, R.; O’Sullivan, T.; Gross, E.T.; Washington, A., Jr.; Bui, J.D. Tumor-expressed IL-17D recruits NK cells to reject tumors. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e954853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Deng, B.; Wang, H.; Dong, Z.; Qu, X.; Kong, B. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Secreted by Decidual Stromal Cells Inhibits NK Cells Cytotoxicity by Up-Regulating Expression of SOCS3. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Shen, M.; Yang, D.R.; Fang, L.; Weng, G.; Tsai, Y.; Keng, P.C.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.O. Inhibition of IL-6-JAK/Stat3 signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells enhances the NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity via alteration of PD-L1/NKG2D ligand levels. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, F.-X.; Wang, C.; Qin, M.; Han, F.; Xu, T.; Hu, Z.; Long, Y.; He, X.-M.; Deng, X.; et al. IL-6 and IL-8 secreted by tumour cells impair the function of NK cells via the STAT3 pathway in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Gu, X.; Sun, X.; Hu, D. Effects of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α on the proliferation and apoptosis of human synovial mesenchymal stem cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4315–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.H.; Kim, J.; Park, E.; Kang, H.; Cho, H. Inhibition of MCP1 (CCL2) Enhances Antitumor Activity of NK Cells Against HCC Cells Under Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104900
Lee HH, Kim J, Park E, Kang H, Cho H. Inhibition of MCP1 (CCL2) Enhances Antitumor Activity of NK Cells Against HCC Cells Under Hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104900
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hwan Hee, Juhui Kim, Eunbi Park, Hyojeung Kang, and Hyosun Cho. 2025. "Inhibition of MCP1 (CCL2) Enhances Antitumor Activity of NK Cells Against HCC Cells Under Hypoxia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104900
APA StyleLee, H. H., Kim, J., Park, E., Kang, H., & Cho, H. (2025). Inhibition of MCP1 (CCL2) Enhances Antitumor Activity of NK Cells Against HCC Cells Under Hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104900





