The Potential Contribution of the IL-37/IL-18/IL-18BP/IL-18R Axis in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics of Patients
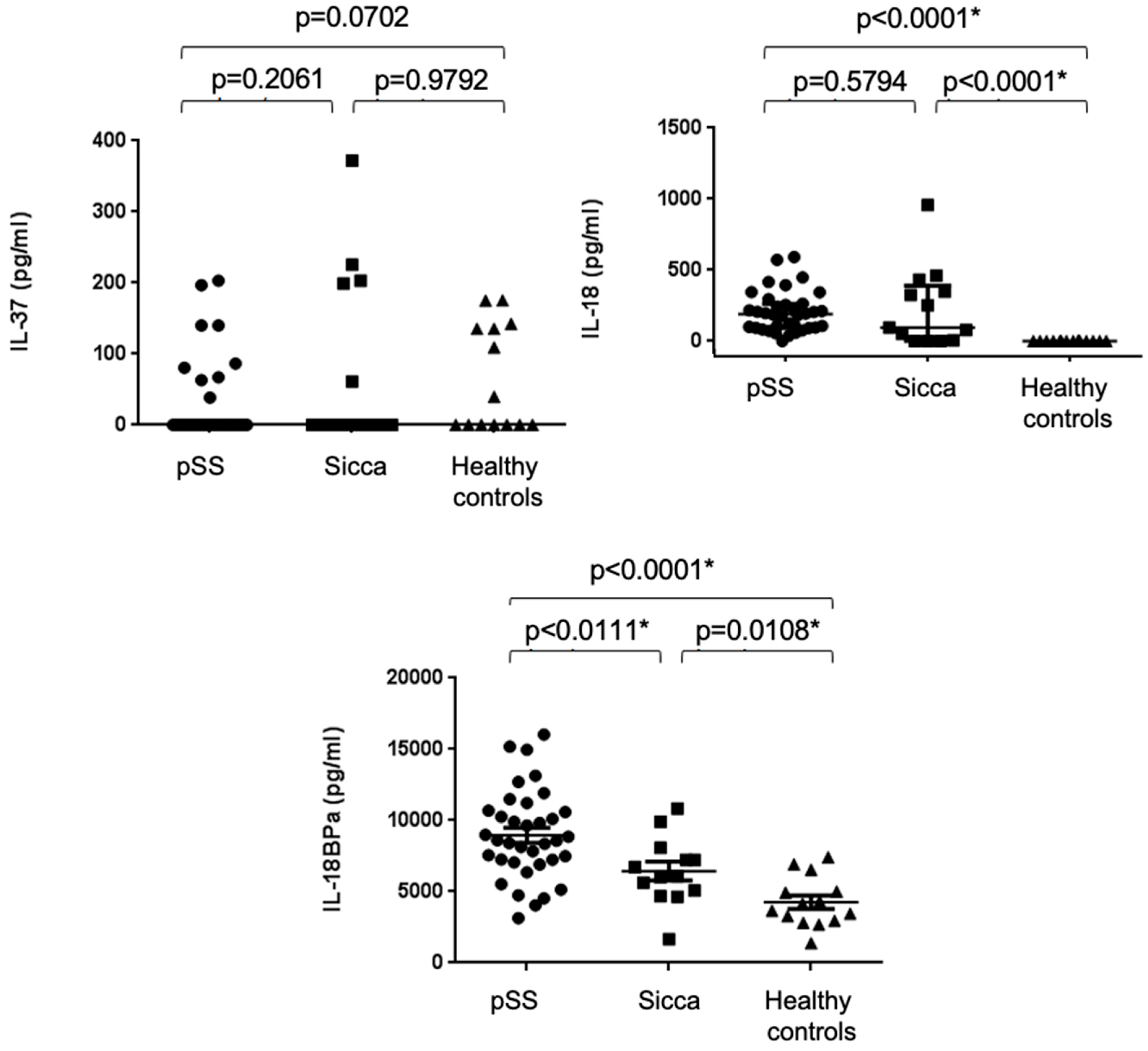
2.2. Increased Serum Concentrations of IL-18 and IL-18BPa, but Not IL-37, in pSS Patients
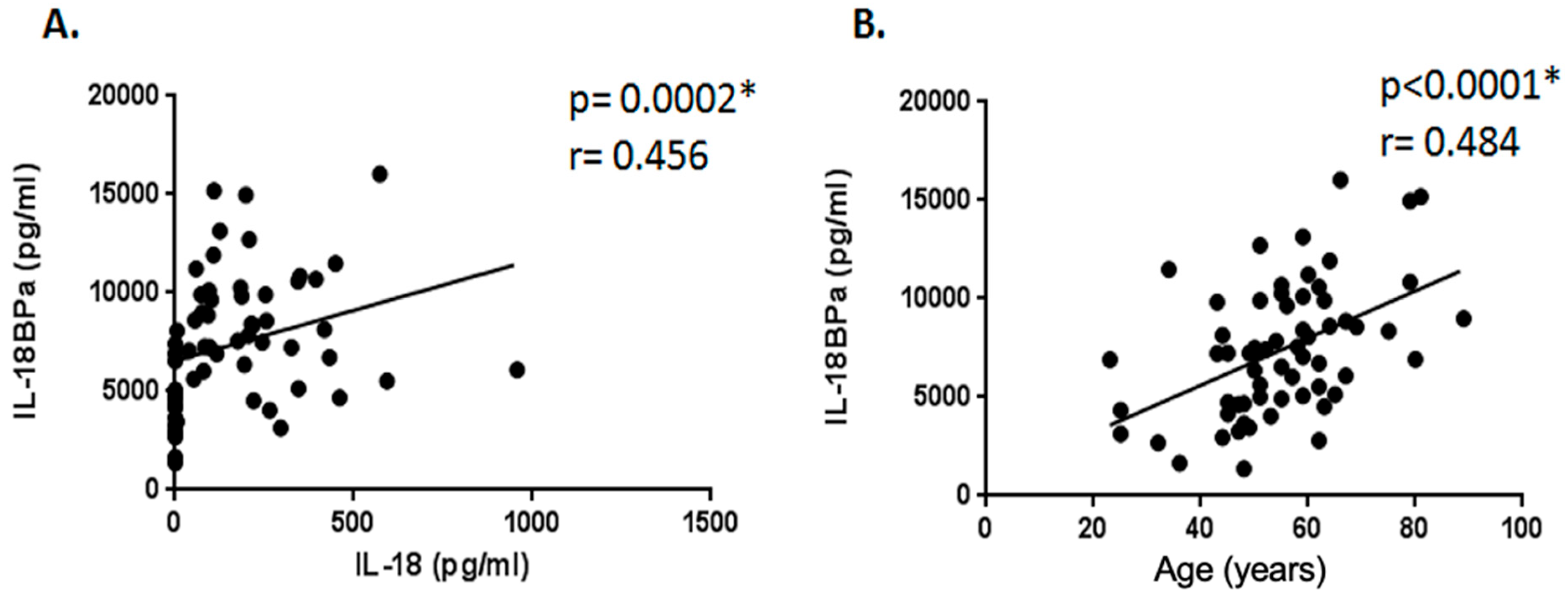
2.3. Correlation Study Between Serum Levels of IL-18, IL-37, and IL-18BPa and Demographic, Clinical, and Laboratory Parameters
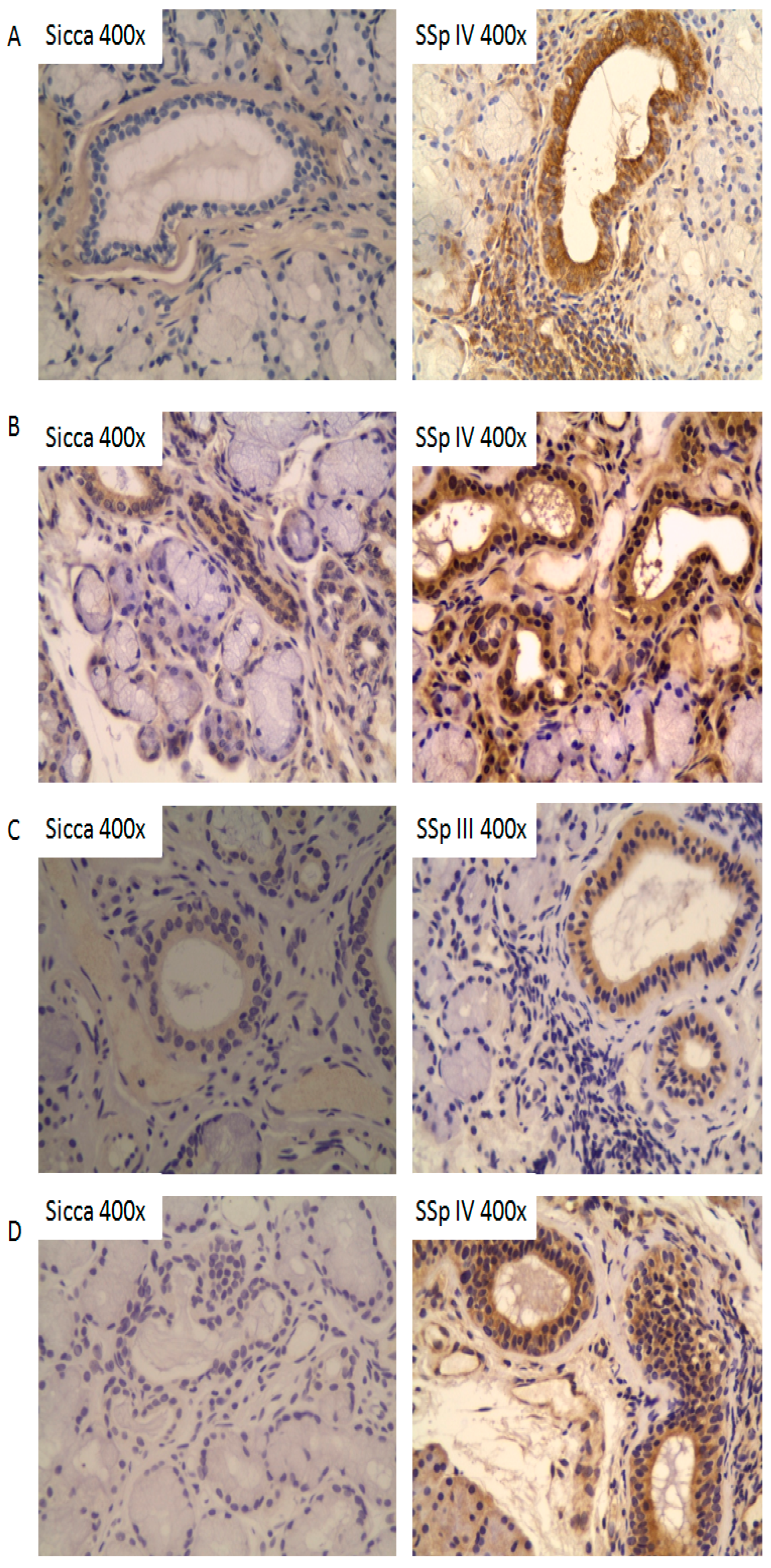
2.4. Tissue Expression Profiles of IL-37, IL-18, IL-18Rα, and IL-18BPa in Salivary Glands of pSS Patients
3. Discussion
4. Patients and Methods
4.1. Cytokine Determination by ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAFF | B-cell Activating Factor |
| CD | cluster differentiation |
| DAB | diaminobenzidine |
| DAMPs | damage-associated molecular pattern molecules |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ESSDAI | European Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index |
| Fas | First apoptosis signal receptor |
| FASL | Fas ligand |
| HLA | Human Leukocyte Antigen |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL-18R | Interleukin-18 Receptor |
| IL-18BP | Interleukin-18 Binding Protein |
| IFN | interferon |
| NK | natural killer |
| PDX | 1,3-diethyl-8-phenylxanthine |
| pSS | primary Sjögren’s syndrome |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| SG | salivary gland |
| SIGIRR | single immunoglobulin IL-1R-related receptor |
| SMAD3 | Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 3 |
| SS | Sjögren’s syndrome |
| TBS | Tris-Buffered Saline |
| TGF- | Transforming Growth Factor |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
References
- Parisis, D.; Chivasso, C.; Perret, J.; Soyfoo, M.S.; Delporte, C. Current State of Knowledge on Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome, an Autoimmune Exocrinopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, R.I. Sjogren’s syndrome. Lancet 2005, 366, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutsopoulos, H.M. Sjogren’s syndrome: Autoimmune epithelitis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 72, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrand, J.; Baglione, L.; Parisis, D.; Soyfoo, M. The Involvement of Alarmins in the Pathogenesis of Sjogren’s Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvaux, E.; Pers, J.O. Autoimmune epithelitis in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Jt. Bone Spine 2023, 90, 105479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold, M.F.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Zepp, J.A.; Palmer, B.E.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C.A. IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Tao, X. Current Understanding of IL-37 in Human Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Nold, M.F.; Bufler, P.; Norris, D.; Dinarello, C.A.; Fujita, M. Suppression of antigen-specific adaptive immunity by IL-37 via induction of tolerogenic dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15178–15183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, E.N.; Masterson, J.C.; Jedlicka, P.; McManus, M.; Grenz, A.; Collins, C.B.; Nold, M.F.; Nold-Petry, C.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; et al. Interleukin 37 expression protects mice from colitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16711–16716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza Lahimchi, M.; Eslami, M.; Yousefi, B. Interleukin-35 and Interleukin-37 anti-inflammatory effect on inflammatory bowel disease: Application of non-coding RNAs in IBD therapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 117, 109932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yin, D. Pathophysiological Effects of Various Interleukins on Primary Cell Types in Common Heart Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Long, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, L.; Dou, Q.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, C.; Jia, R. Neutrophil-derived nanovesicles deliver IL-37 to mitigate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via endothelial cell targeting. J. Control. Release 2024, 370, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boraschi, D.; Lucchesi, D.; Hainzl, S.; Leitner, M.; Maier, E.; Mangelberger, D.; Oostingh, G.J.; Pfaller, T.; Pixner, C.; Posselt, G.; et al. IL-37: A new anti-inflammatory cytokine of the IL-1 family. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2011, 22, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulau, A.M.; Nold, M.F.; Li, S.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Fink, M.; Mansell, A.; Schwerd, T.; Hong, J.; Rubartelli, A.; Dinarello, C.A.; et al. Role of caspase-1 in nuclear translocation of IL-37, release of the cytokine, and IL-37 inhibition of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2650–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, J.M. Early events in Sjogren’s Syndrome pathogenesis: The importance of innate immunity in disease initiation. Cytokine 2014, 67, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold-Petry, C.A.; Lo, C.Y.; Rudloff, I.; Elgass, K.D.; Li, S.; Gantier, M.P.; Lotz-Havla, A.S.; Gersting, S.W.; Cho, S.X.; Lao, J.C.; et al. IL-37 requires the receptors IL-18Ralpha and IL-1R8 (SIGIRR) to carry out its multifaceted anti-inflammatory program upon innate signal transduction. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, P.; Sun, X.; Che, Y.; Jiang, Y. Elevated levels of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma interleukin-37 in patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 639712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imaeda, H.; Takahashi, K.; Fujimoto, T.; Kasumi, E.; Ban, H.; Bamba, S.; Sonoda, H.; Shimizu, T.; Fujiyama, Y.; Andoh, A. Epithelial expression of interleukin-37b in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 172, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Huang, Z. Increased expression of IL-37 in patients with Graves’ disease and its contribution to suppression of proinflammatory cytokines production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Hu, Z.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Guan, T.; Liu, N.; Liu, X.; Ye, N.; Deng, G.; Luo, C.; et al. IL-37 ameliorates the inflammatory process in psoriasis by suppressing proinflammatory cytokine production. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.W.; Jiang, W.G.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Shan, Y.X.; Jiang, Y.F. Plasma levels of IL-37 and correlation with TNF-alpha, IL-17A, and disease activity during DMARD treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Ji, L.; Wen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, D.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; et al. IL-37 inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Its correlation with disease activity. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, K.; Ye, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; et al. Interleukin-37 is increased in ankylosing spondylitis patients and associated with disease activity. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, P.; Andersson, C.; Ekerfelt, C.; Ernerudh, J.; Skogh, T. Sjogren’s syndrome with myalgia is associated with subnormal secretion of cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 729–735. [Google Scholar]
- Bombardieri, M.; Barone, F.; Pittoni, V.; Alessandri, C.; Conigliaro, P.; Blades, M.C.; Priori, R.; McInnes, I.B.; Valesini, G.; Pitzalis, C. Increased circulating levels and salivary gland expression of interleukin-18 in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome: Relationship with autoantibody production and lymphoid organization of the periductal inflammatory infiltrate. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, R447–R456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, F.; Zheng, J.; Yin, J.; Huang, R.; Liu, W.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.; Gao, X.; Yu, X.; et al. High circulating level of interleukin-18 in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome is associated with disease activity. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, A.; Sugawara, Y.; Kuroishi, T.; Sasano, T.; Sugawara, S. Identification of IL-18 and Th17 cells in salivary glands of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome, and amplification of IL-17-mediated secretion of inflammatory cytokines from salivary gland cells by IL-18. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2898–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoussakis, M.N.; Boiu, S.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Kavantzas, N.; Ziakas, P.; Patsouris, E.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Rates of infiltration by macrophages and dendritic cells and expression of interleukin-18 and interleukin-12 in the chronic inflammatory lesions of Sjogren’s syndrome: Correlation with certain features of immune hyperactivity and factors associated with high risk of lymphoma development. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3977–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Lei, M.; Luo, Y.; Gu, W.; Cai, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, N. Expression of interleukin-18 in primary Sjogren syndrome and its potential mechanisms with disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2025, 104, e41919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkowski, E.C.; Reth, P.; Pelusa, F.; Bosch, J.; Pujol-Borrell, R.; Coll, J.; Jaraquemada, D. Th1 predominance and perforin expression in minor salivary glands from patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 1999, 13, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, A.; Nicaise, C.; Ena, S.; Schandene, L.; Rasschaert, J.; Popescu, I.; Gangji, V.; Soyfoo, M.S. Potential involvement of the IL-33-ST2 axis in the pathogenesis of primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Ming, B.; Gao, R.; Mo, Q.; Wu, X.; Zheng, F.; Zhong, J.; Dong, L. The IL-33/ST2 Axis Promotes Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome by Enhancing Salivary Epithelial Cell Activation and Type 1 Immune Response. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 2652–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, S.; Fang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; He, J.; Wang, X.; He, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, D.; et al. IL-37 Isoform A Prevents Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice by Modulating the Th17/Treg Balance via IL1R8 Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Qiu, F.; Fan, Y.; Ding, F.; Liu, H.; Shu, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, X. Glucocorticoid regulates interleukin-37 in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moneim, N.H.A.; Hosny, M.M.; Omar, H.H.; Abdelnaby, M.M.; Fouad, M.M.; Abd El-Waheed, W.O.; Elmedany, S.H.; Zaki, H.M. Relative CTLA-4, PTPN-22, and interleukin 37 mRNA expressions in patients with lupus nephritis. Reumatol. Clin. 2023, 19, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, A.S.; Ad’hiah, A.H. A novel signature of interleukins 36alpha, 37, 38, 39 and 40 in ankylosing spondylitis. Cytokine 2023, 162, 156117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, C.; Bombardieri, S.; Jonsson, R.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Alexander, E.L.; Carsons, S.E.; Daniels, T.E.; Fox, P.C.; Fox, R.I.; Kassan, S.S.; et al. Classification criteria for Sjogren’s syndrome: A revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SS (N = 36) | Sicca (N = 13) | Healthy Controls (N = 14) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data | |||||
| Age (years) | Mean ± SEM | 57.2 ± 2.3 | 54.2 ± 3.2 | 49.50 ± 3.416 | 0.1765 |
| Sex ratio | n (F:M) | 32 (8:1) | 12 (12:1) | 13 (13:1) | 0.8834 |
| Diagnosis criteria | |||||
| Chisholm ≥ 3 | n (%) | 24/33 (72.7%) | 0 | ||
| Focus score | Mean ± SEM | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 0 | ||
| SSA and/or SSB | n (%) | 19/34 (55.9%) | 0 | ||
| Ocular signs | n (%) | 25/32 (78.1%) | 6/8 (75%) | 1 | |
| Oral signs | n (%) | 12/22 (54.5%) | 3/7 (42.9%) | 1 | |
| Ocular symptoms | n (%) | 36 (100%) | 12 (92.3%) | 0.2653 | |
| Oral symptoms | n (%) | 34 (94.4%) | 11 (84.6%) | 0.2839 | |
| ESSDAI | Med [range] | 1.424 [0–21] | |||
| Clinical | |||||
| Raynaud | n (%) | 4 (11.1%) | 2 (15.4%) | 0.6495 | |
| Arthralgia | n (%) | 25 (69.4%) | 7 (53.8%) | 0.3309 | |
| Myalgia | n (%) | 10 (27.8%) | 5 (38.5%) | 0.5001 | |
| Paresthesia | n (%) | 8 (22.2%) | 3 (23.1%) | 1 | |
| Biologic | |||||
| ANA + | n (%) | 26/35 (74.3%) | 0 (0%) | <0.0001 * | |
| Inflammatory syndrome | n (%) | 9/35 (25.7%) | 1/12 (8.3%) | 0.2479 | |
| RF | n (%) | 9/34 (26.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0.0468 * | |
| Hyperγ | n (%) | 8/34 (23.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0.0855 | |
| Cryoglobulinemia | n (%) | 3 (8.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0.5555 | |
| IL-37/IL-18/IL-18BP axis | |||||
| IL-37 (pg/mL) | Med [range] | 0 [0–203.2] | 0 [0–372.1] | 0 [0–175.6] | 0.1695 |
| IL-18 (pg/mL) | Med [range] | 190.3 [0–593.2] | 96.09 [0–957.3] | 0 [0–5] | <0.0001 * |
| IL-18 BP (pg/mL) | Mean ± SEM | 8958 ± 517.3 | 6447 ± 657.5 | 4251 ± 467.7 | <0.0001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parisis, D.; Sarrand, J.; Soyfoo, M. The Potential Contribution of the IL-37/IL-18/IL-18BP/IL-18R Axis in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104877
Parisis D, Sarrand J, Soyfoo M. The Potential Contribution of the IL-37/IL-18/IL-18BP/IL-18R Axis in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104877
Chicago/Turabian StyleParisis, Dorian, Julie Sarrand, and Muhammad Soyfoo. 2025. "The Potential Contribution of the IL-37/IL-18/IL-18BP/IL-18R Axis in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104877
APA StyleParisis, D., Sarrand, J., & Soyfoo, M. (2025). The Potential Contribution of the IL-37/IL-18/IL-18BP/IL-18R Axis in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104877






