Gap Junctional Interaction of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPC) with Endothelial Cells Induces Angiogenic Network Formation In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
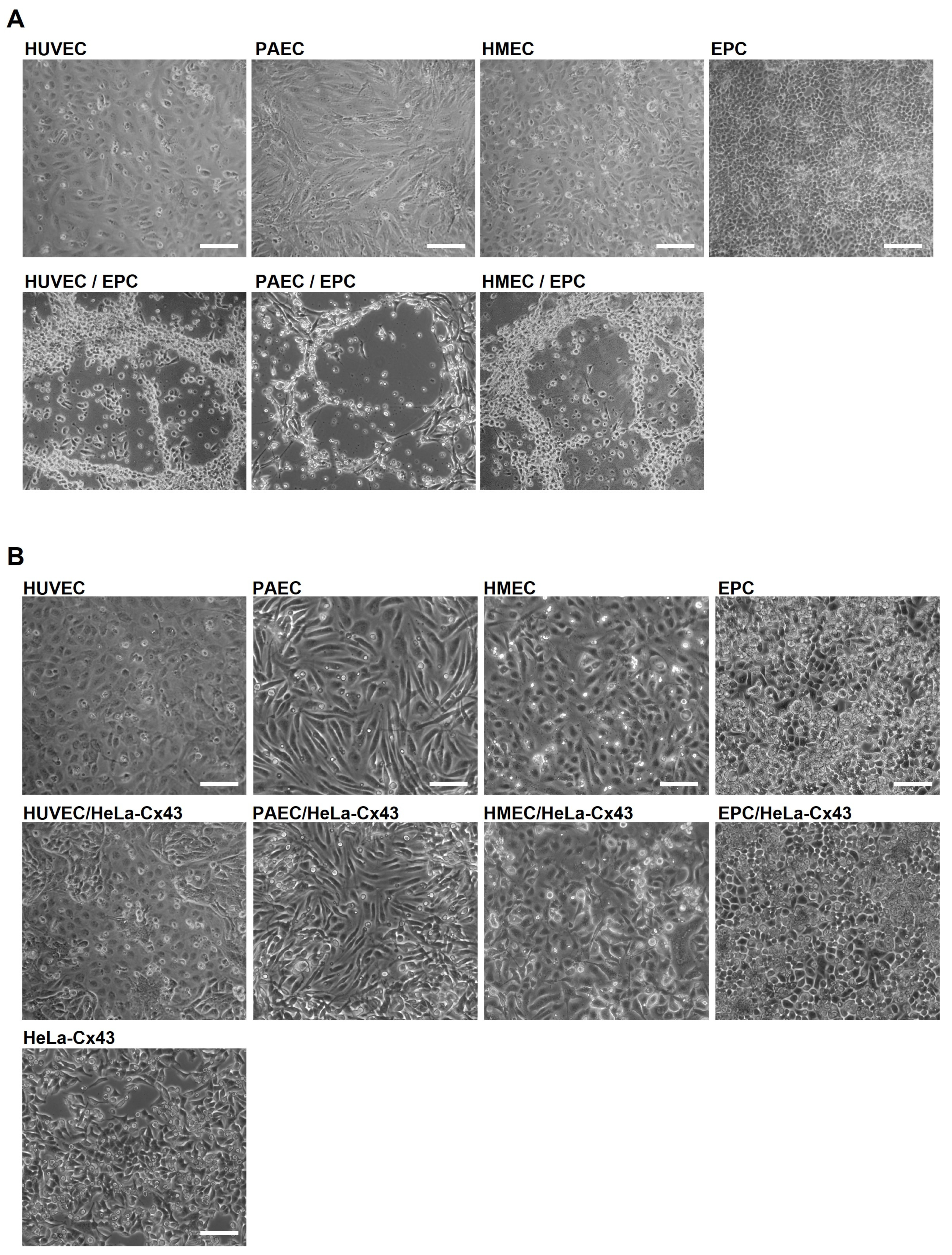
2.1. EPC Show Angiogenic Activity Only in Co-Culture with EC
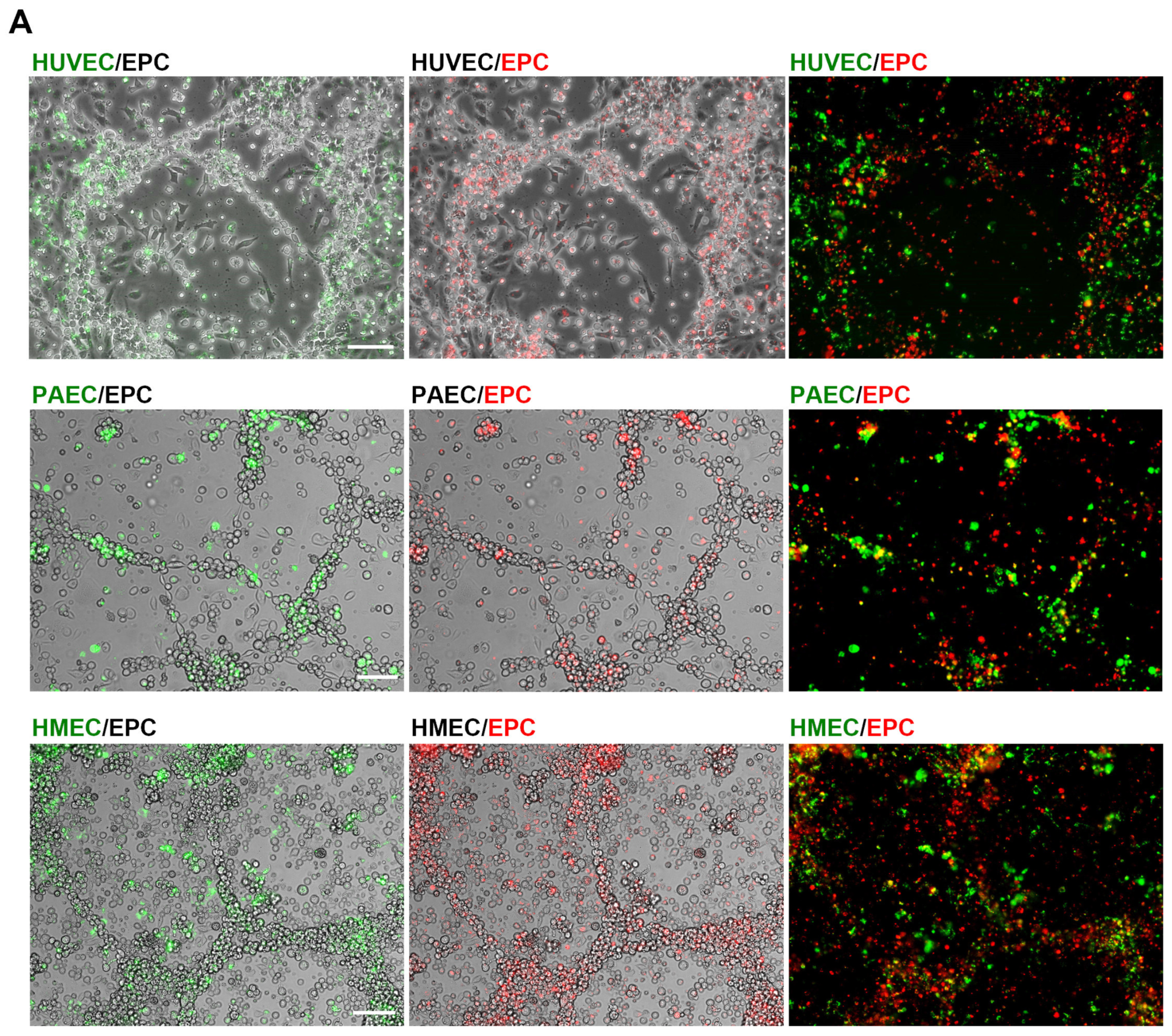
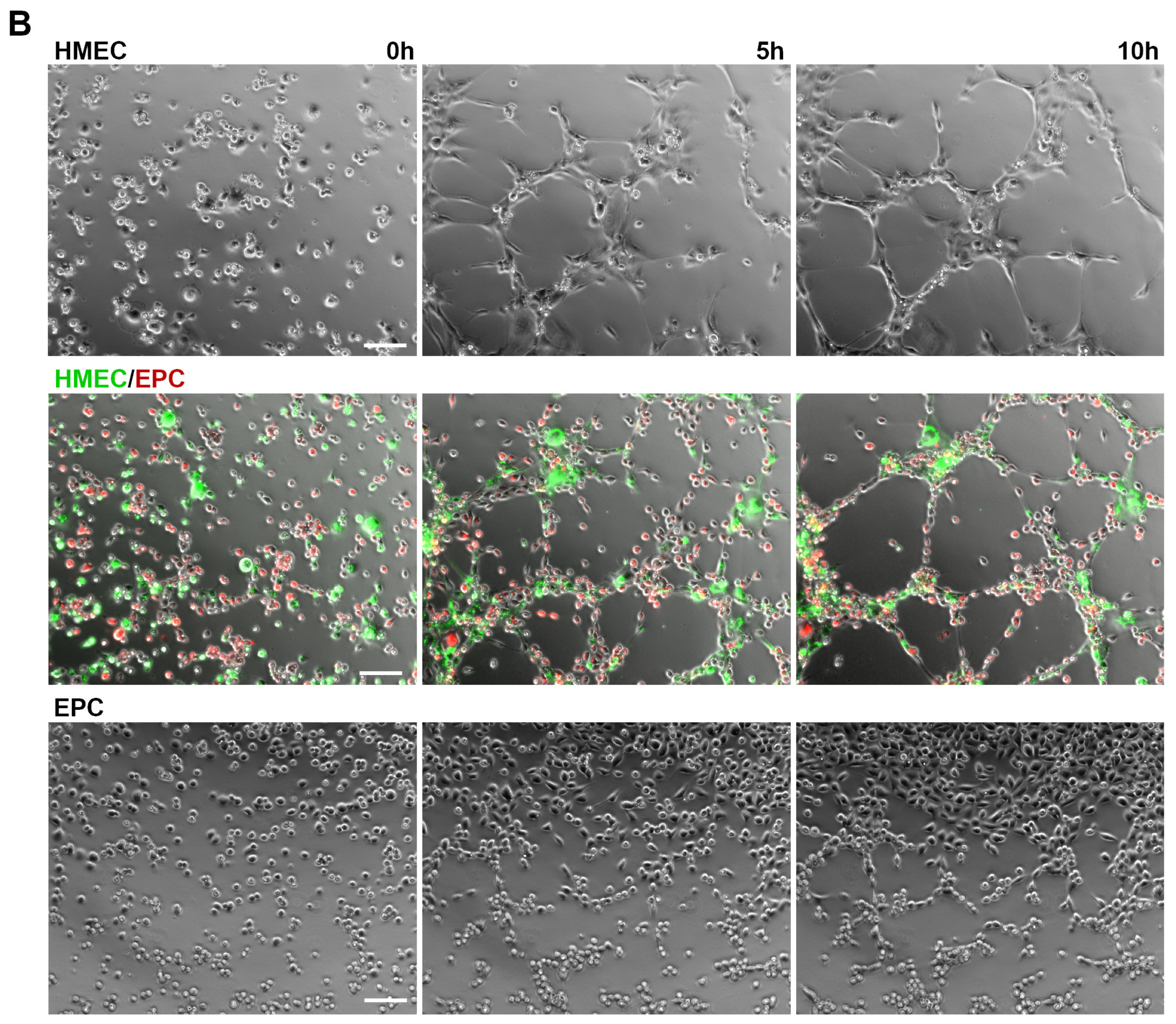
2.2. Angiogenic Networks in Co-Cultures of EC and EPC Are Formed by Both Cell Types
2.3. EPC Communicate with EC via Functional Gap Junction Channels
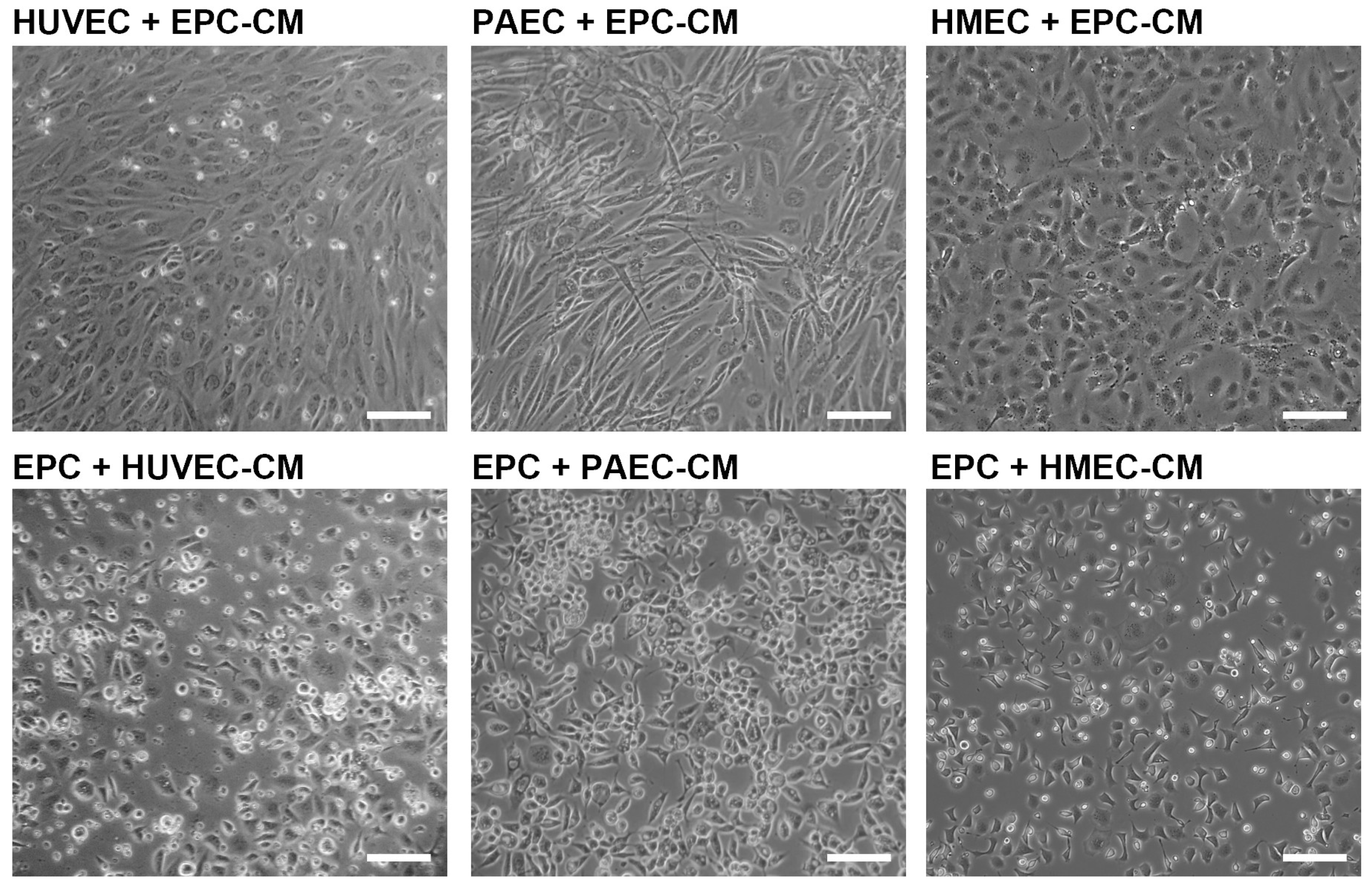
2.4. Angiogenic Network Formation Is Not Induced by Conditioned Medium
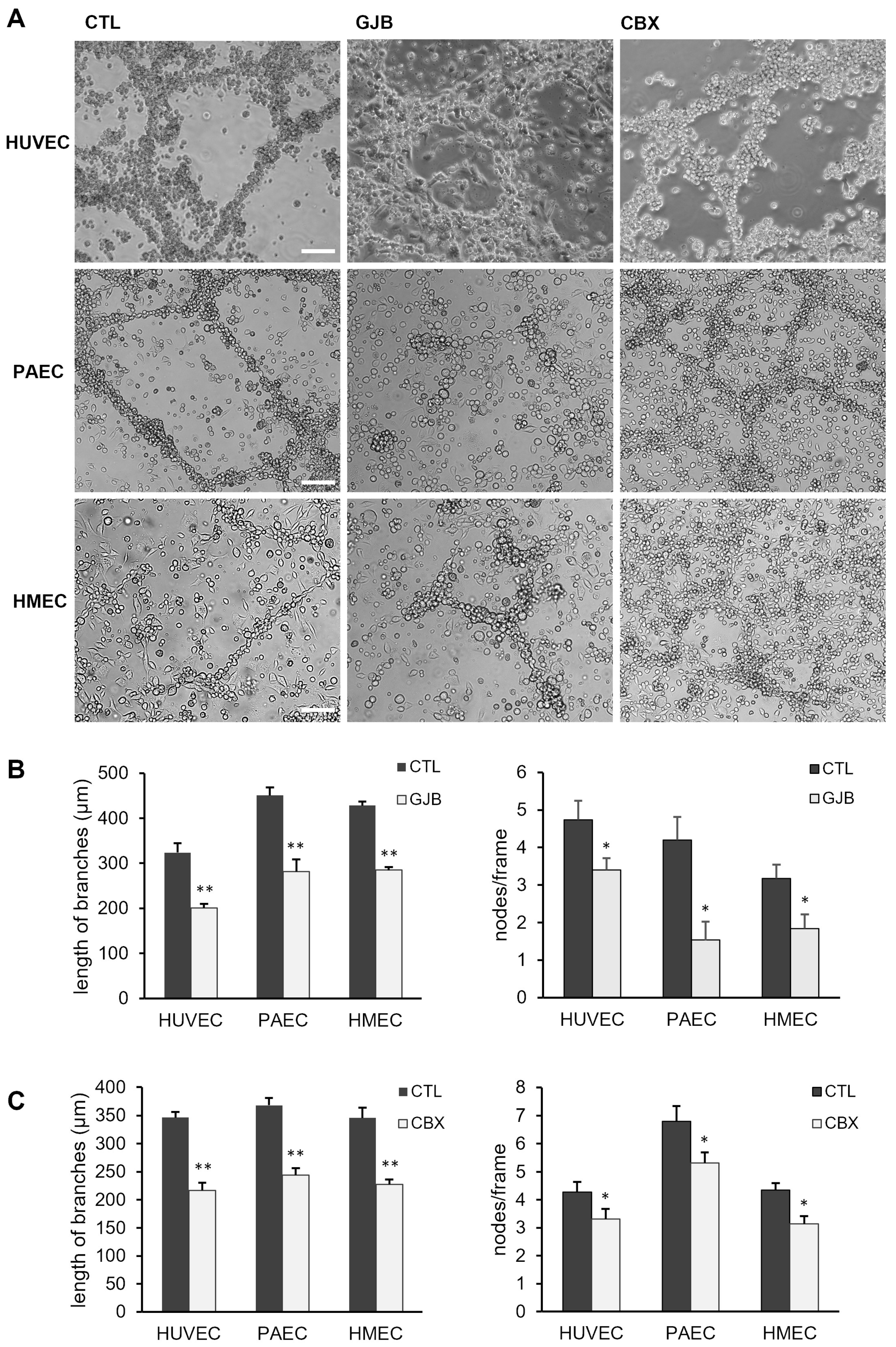
2.5. Angiogenic Network Formation Is Impaired by Inhibitors of Gap Junctions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Culture Conditions
4.2. Long-Term Co-Culture Experiments and Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Tube Formation Assay
4.4. Quantitative Evaluation of Angiogenic Networks
4.5. Fluorescence Labelling of Live Cells with PKH Linkers
4.6. Gap Junctional Dye Transfer in Co-Cultures
4.7. Analysis of Cell Coupling Using Flow Cytometry (FACS)
4.8. Scrape-Loading Dye Transfer
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Immunofluorescence Stainings
4.11. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GJB | gap junction blockers heptanol and meclofenamic acid |
| Cx | connexin/s |
| EC | endothelial cells |
| EPC | endothelial progenitor cells |
| CBX | carbenoxolone |
References
- Ratliff, B.B.; Ghaly, T.; Brudnicki, P.; Yasuda, K.; Rajdev, M.; Bank, M.; Mares, J.; Hatzopoulos, A.K.; Goligorsky, M.S. Endothelial Progenitors Encapsulated in Bioartificial Niches Are Insulated from Systemic Cytotoxicity and Are Angiogenesis Competent. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2010, 299, F178–F186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.S.; Thakore, A.; Tada, Y.; Pedroza, A.J.; Ikeda, G.; Chen, I.Y.; Chan, D.; Jaatinen, K.J.; Yajima, S.; Pfrender, E.M.; et al. Angiogenic Stem Cell Delivery Platform to Augment Post-Infarction Neovasculature and Reverse Ventricular Remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupatt, C.; Horstkotte, J.; Vlastos, G.A.; Pfosser, A.; Lebherz, C.; Semisch, M.; Thalgott, M.; Buttner, K.; Browarzyk, C.; Mages, J.; et al. Embryonic Endothelial Progenitor Cells Expressing a Broad Range of Proangiogenic and Remodeling Factors Enhance Vascularization and Tissue Recovery in Acute and Chronic Ischemia. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1576–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajkoczy, P.; Blum, S.; Lamparter, M.; Mailhammer, R.; Erber, R.; Engelhardt, B.; Vestweber, D.; Hatzopoulos, A.K. Multistep Nature of Microvascular Recruitment of Ex Vivo-Expanded Embryonic Endothelial Progenitor Cells during Tumor Angiogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, R.P.; Ushio-Fukai, M. Endothelial Progenitor Cells=Epc=Elemental Pernicious Complexity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Liu, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, W. Paracrine Mechanisms of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Vascular Repair. Acta Histochem. 2022, 124, 151833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.W. Life Cycle of Connexins in Health and Disease. Biochem. J. 2006, 394 Pt 3, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, P.D.; Laird, D.W. Recent Advances in Connexin Gap Junction Biology. Fac. Rev. 2022, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohl, G.; Willecke, K. Gap Junctions and the Connexin Protein Family. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, U. Connexins: Key Players in the Control of Vascular Plasticity and Function. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 525–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, J.L.; Lampe, P.D. Connexin43 Phosphorylation: Structural Changes and Biological Effects. Biochem. J. 2009, 419, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, J.; Kameritsch, P.; Wallner, S.; Pohl, U.; Pogoda, K. The Carboxyl Tail of Cx43 Augments P38 Mediated Cell Migration in a Gap Junction-Independent Manner. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 89, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannell, H.; Kameritsch, P.; Beck, H.; Pfeifer, A.; Pohl, U.; Pogoda, K. Cx43 Promotes Endothelial Cell Migration and Angiogenesis Via the Tyrosine Phosphatase Shp-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, C.; Ziegelhoffer, B.; Kostelka, M.; Stepan, H.; Mohr, F.W.; Dhein, S. Knock-down of Endothelial Connexins Impairs Angiogenesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepple, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huber, L.; Schulte, M.; Schmidt, K.; Gloe, T.; Kneser, U.; Schmidt, V.J.; de Wit, C. Expression of Connexin43 Stimulates Endothelial Angiogenesis Independently of Gap Junctional Communication in Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Su, C.H.; Wu, Y.J.; Li, J.Y.; Tseng, Y.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Yeh, H.I. Reduction of Connexin43 in Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells Impairs the Angiogenic Potential. Angiogenesis 2013, 16, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, H. Gap26 Inhibited Angiogenesis through the Beta-Catenin-Ve-Cadherin-Vegfr2-Erk Signaling Pathway. Life Sci. 2023, 328, 121836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzopoulos, A.K.; Folkman, J.; Vasile, E.; Eiselen, G.K.; Rosenberg, R. DIsolation and Characterization of Endothelial Progenitor Cells from Mouse Embryos. Development 1998, 125, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleiziffer, O.; Horch, R.E.; Hammon, M.; Arkudas, A.; Naschberger, E.; Rath, S.; Pryymachuk, G.; Beier, J.P.; Hatzopoulos, A.K.; Sturzl, M.; et al. T17b Murine Embryonal Endothelial Progenitor Cells Can Be Induced Towards Both Proliferation and Differentiation in a Fibrin Matrix. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidzhekov, K.; Hautmann, M.; Semisch, M.; Weber, C.; Engelmann, B.; Hatzopoulos, A.K. Rafs Constitute a Nodal Point in the Regulation of Embryonic Endothelial Progenitor Cell Growth and Differentiation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleiziffer, O.; Hammon, M.; Naschberger, E.; Lipnik, K.; Arkudas, A.; Rath, S.; Pryymachuk, G.; Beier, J.P.; Sturzl, M.; Horch, R.E.; et al. Endothelial Progenitor Cells Are Integrated in Newly Formed Capillaries and Alter Adjacent Fibrovascular Tissue after Subcutaneous Implantation in a Fibrin Matrix. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 2452–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, X.F.; Duling, B.R. Gap Junctions in the Control of Vascular Function. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjarrez-Marmolejo, J.; Franco-Perez, J. Gap Junction Blockers: An Overview of Their Effects on Induced Seizures in Animal Models. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, S.; King, A.; Crombleholme, T.M.; Keswani, S.G. The Role of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Postnatal Vasculogenesis: Implications for Therapeutic Neovascularization and Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2013, 2, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Asahara, T. Post-Natal Endothelial Progenitor Cells for Neovascularization in Tissue Regeneration. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 58, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Kalka, C.; Asahara, T. Endothelial Progenitor Cells for Regeneration. Hum. Cell 2000, 13, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Staton, C.A.; Stribbling, S.M.; Tazzyman, S.; Hughes, R.; Brown, N.J.; Lewis, C.E. Current Methods for Assaying Angiogenesis in Vitro and in Vivo. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2004, 85, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucuzian, A.A.; Greisler, H.P. In Vitro Models of Angiogenesis. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, E.T.; Bell, G.T.; Bloor, S.; Broom, I.J.; Hendry, N.F.; Wheatley, D.N. An in Vitro Model of Angiogenesis: Basic Features. Angiogenesis 1999, 3, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, G.G.Y.; Wei, N.; Sultania, S.; Lim, S.; Luo, K.Q. Bioengineered Three-Dimensional Co-Culture of Cancer Cells and Endothelial Cells: A Model System for Dual Analysis of Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckermann, C.W.; Lehle, K.; Schmid, S.A.; Wheatley, D.N.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A. Characterization and Modulation of Fibroblast/Endothelial Cell Co-Cultures for the in Vitro Preformation of Three-Dimensional Tubular Networks. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuma, S.; Zhao, S.; Gerecht, S. The Extracellular Matrix Is a Novel Attribute of Endothelial Progenitors and of Hypoxic Mature Endothelial Cells. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4925–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takens-Kwak, B.R.; Jongsma, H.J.; Rook, M.B.; Van Ginneken, A.C. Mechanism of Heptanol-Induced Uncoupling of Cardiac Gap Junctions: A Perforated Patch-Clamp Study. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 262, C1531–C1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Meng, Z.; Luo, J. Connexin 43 (Cx43) Regulates High-Glucose-Induced Retinal Endothelial Cell Angiogenesis and Retinal Neovascularization. Front Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 909207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chai, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X. Connexin 43 Overexpression Induces Lung Cancer Angiogenesis in Vitro Following Phosphorylation at Ser279 in Its C-Terminus. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Jin, H.; Sun, W.; Nan, D.; Deng, J.; Jia, J.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Y. Connexin43 Promotes Angiogenesis through Activating the Hif-1α/Vegf Signaling Pathway under Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41, 2656–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Usuda, H.; Tanaka, T.; Wada, K.; Shimaoka, M. The Functional Implications of Endothelial Gap Junctions and Cellular Mechanics in Vascular Angiogenesis. Cancers 2019, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Kung, C.I.; Tseng, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Yeh, H.I. Activation of Endothelial Cells to Pathological Status by down-Regulation of Connexin43. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Mayo, J.N.; Gourdie, R.G.; Johnstone, S.R.; Isakson, B.E.; Bearden, S.E. The Connexin 43/Zo-1 Complex Regulates Cerebral Endothelial F-Actin Architecture and Migration. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2015, 309, C600–C607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameritsch, P.; Kiemer, F.; Beck, H.; Pohl, U.; Pogoda, K. Cx43 Increases Serum Induced Filopodia Formation Via Activation of P21-Activated Protein Kinase 1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 2907–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameritsch, P.; Kiemer, F.; Mannell, H.; Beck, H.; Pohl, U.; Pogoda, K. Pka Negatively Modulates the Migration Enhancing Effect of Connexin 43. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ge, J.; Yin, Y.; Yang, R.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. Upregulated Mir-206 Aggravates Deep Vein Thrombosis by Regulating Gja1-Mediated Autophagy of Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2022, 2022, 9966306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschi, K.K.; Burt, J.M.; Hirschi, K.D.; Dai, C. Gap Junction Communication Mediates Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Activation and Endothelial-Induced Mural Cell Differentiation. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillotin, B.; Bourget, C.; Remy-Zolgadri, M.; Bareille, R.; Fernandez, P.; Conrad, V.; Amedee-Vilamitjana, J. Human Primary Endothelial Cells Stimulate Human Osteoprogenitor Cell Differentiation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 14, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, X.; Tian, S.; Yang, X.; Ning, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. The Roles of Connexins and Gap Junctions in the Progression of Cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerke, S.M.; Plaha, J.; Hager, S.; Strassburg, S.; Torio-Padron, N.; Stark, G.B.; Finkenzeller, G. Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells Induce Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Dependent Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Smooth Muscle Cells Upon Cocultivation. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2012, 18, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, F.; Brunetti, V.; Soda, T.; Berra-Romani, R.; Scarpellino, G. Cracking the Endothelial Calcium (Ca(2+)) Code: A Matter of Timing and Spacing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Tanguma, R.; O’Neil, C.; Chrones, T.; Pickering, J.G.; Sims, S.M. Essential Role for Calcium Waves in Migration of Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H315–H323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, H.; Figueroa, X.F. Opening of Cx43-Formed Hemichannels Mediates the Ca(2+) Signaling Associated with Endothelial Cell Migration. Biol. Direct 2023, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, A.; Emanueli, C. Microrna Regulation in Angiogenesis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 55, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, Y.; Sessa, W.C. Micrornas as Novel Regulators of Angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Huang, W. Regulation of Endothelial Progenitor Cell Functions in Ischemic Heart Disease: New Therapeutic Targets for Cardiac Remodeling and Repair. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 896782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamin, V.; Mani, A.M.; Singh, M.V.; Dokun, A.O. Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Macrophage Subsets Recruitment in Postischemic Mouse Hind Limbs. J. Vasc. Res. 2023, 60, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcola, M.; Rodrigues, C.E. Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Tumor Angiogenesis: Another Brick in the Wall. Stem Cells Int. 2015, 2015, 832649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pysna, A.; Bem, R.; Nemcova, A.; Fejfarova, V.; Jirkovska, A.; Hazdrova, J.; Jude, E.B.; Dubsky, M. Endothelial Progenitor Cells Biology in Diabetes Mellitus and Peripheral Arterial Disease and Their Therapeutic Potential. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2019, 15, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, Z.; Losordo, D.W. Cell Therapy of Peripheral Arterial Disease: From Experimental Findings to Clinical Trials. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1288–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianopoulos, T.; Munn, L.L.; Jain, R.K. Reengineering the Tumor Vasculature: Improving Drug Delivery and Efficacy. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogoda, K.; Fuller, M.; Pohl, U.; Kameritsch, P. No, Via Its Target Cx37, Modulates Calcium Signal Propagation Selectively at Myoendothelial Gap Junctions. Cell Commun.Signal. 2014, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ades, E.W.; Candal, F.J.; Swerlick, R.A.; George, V.G.; Summers, S.; Bosse, D.C.; Lawley, T.J. Hmec-1: Establishment of an Immortalized Human Microvascular Endothelial Cell Line. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 99, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloe, T.; Sohn, H.Y.; Meininger, G.A.; Pohl, U. Shear Stress-Induced Release of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor from Endothelial Cells Is Mediated by Matrix Interaction Via Integrin Alpha(V)Beta3. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23453–23458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begandt, D.; Bintig, W.; Oberheide, K.; Schlie, S.; Ngezahayo, A. Dipyridamole Increases Gap Junction Coupling in Bovine Gm-7373 Aortic Endothelial Cells by a Camp-Protein Kinase a Dependent Pathway. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2010, 42, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buchberger, C.; Kameritsch, P.; Mannell, H.; Beck, H.; Pohl, U.; Pogoda, K. Gap Junctional Interaction of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPC) with Endothelial Cells Induces Angiogenic Network Formation In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104827
Buchberger C, Kameritsch P, Mannell H, Beck H, Pohl U, Pogoda K. Gap Junctional Interaction of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPC) with Endothelial Cells Induces Angiogenic Network Formation In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104827
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuchberger, Christina, Petra Kameritsch, Hanna Mannell, Heike Beck, Ulrich Pohl, and Kristin Pogoda. 2025. "Gap Junctional Interaction of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPC) with Endothelial Cells Induces Angiogenic Network Formation In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104827
APA StyleBuchberger, C., Kameritsch, P., Mannell, H., Beck, H., Pohl, U., & Pogoda, K. (2025). Gap Junctional Interaction of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPC) with Endothelial Cells Induces Angiogenic Network Formation In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104827






