Biomarkers as Beacons: Illuminating Sepsis-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sepsis Phenotypes and Endotypes
3. The Liver and Kidney in Sepsis
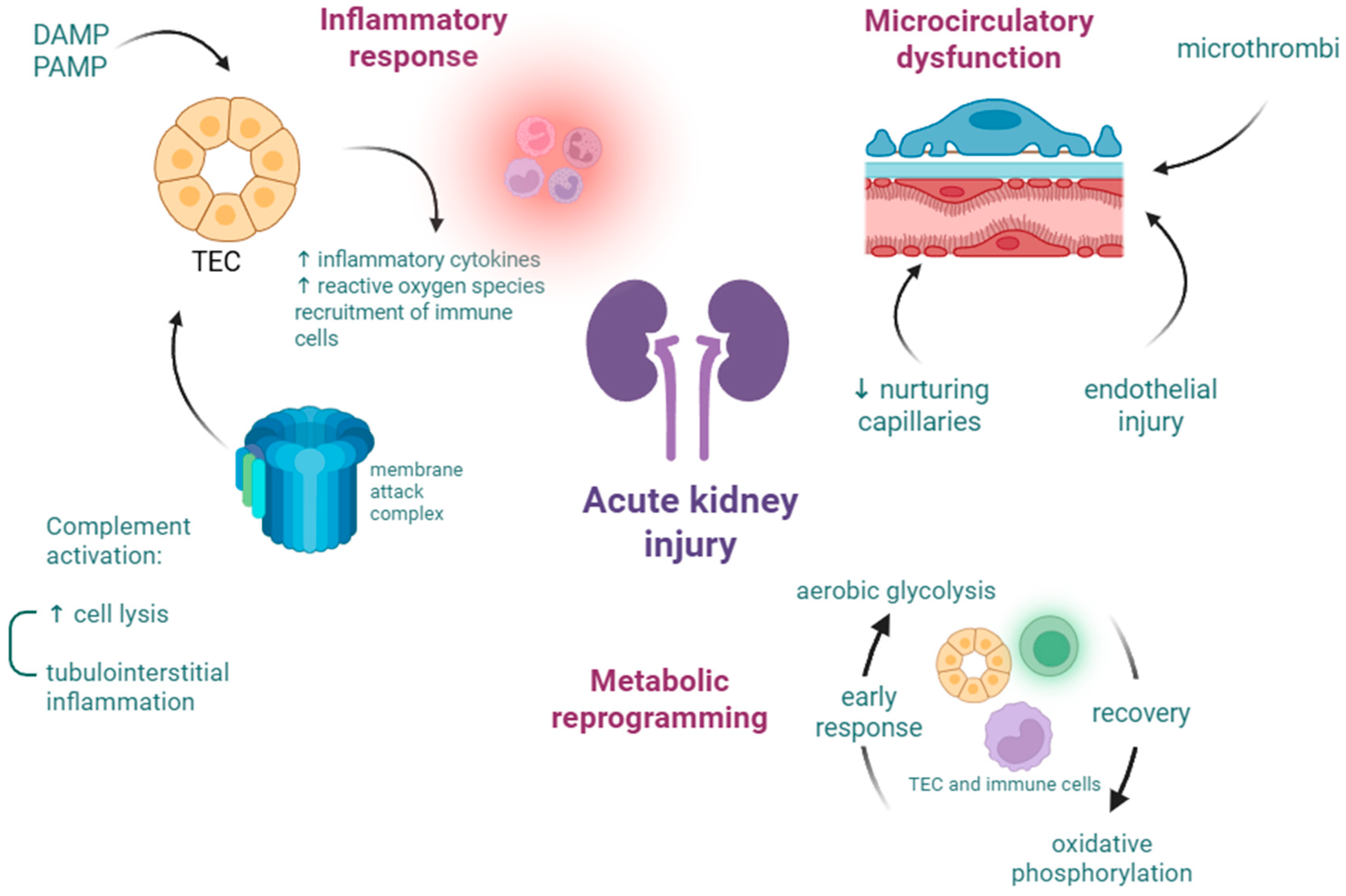
3.1. Acute Kidney Injury
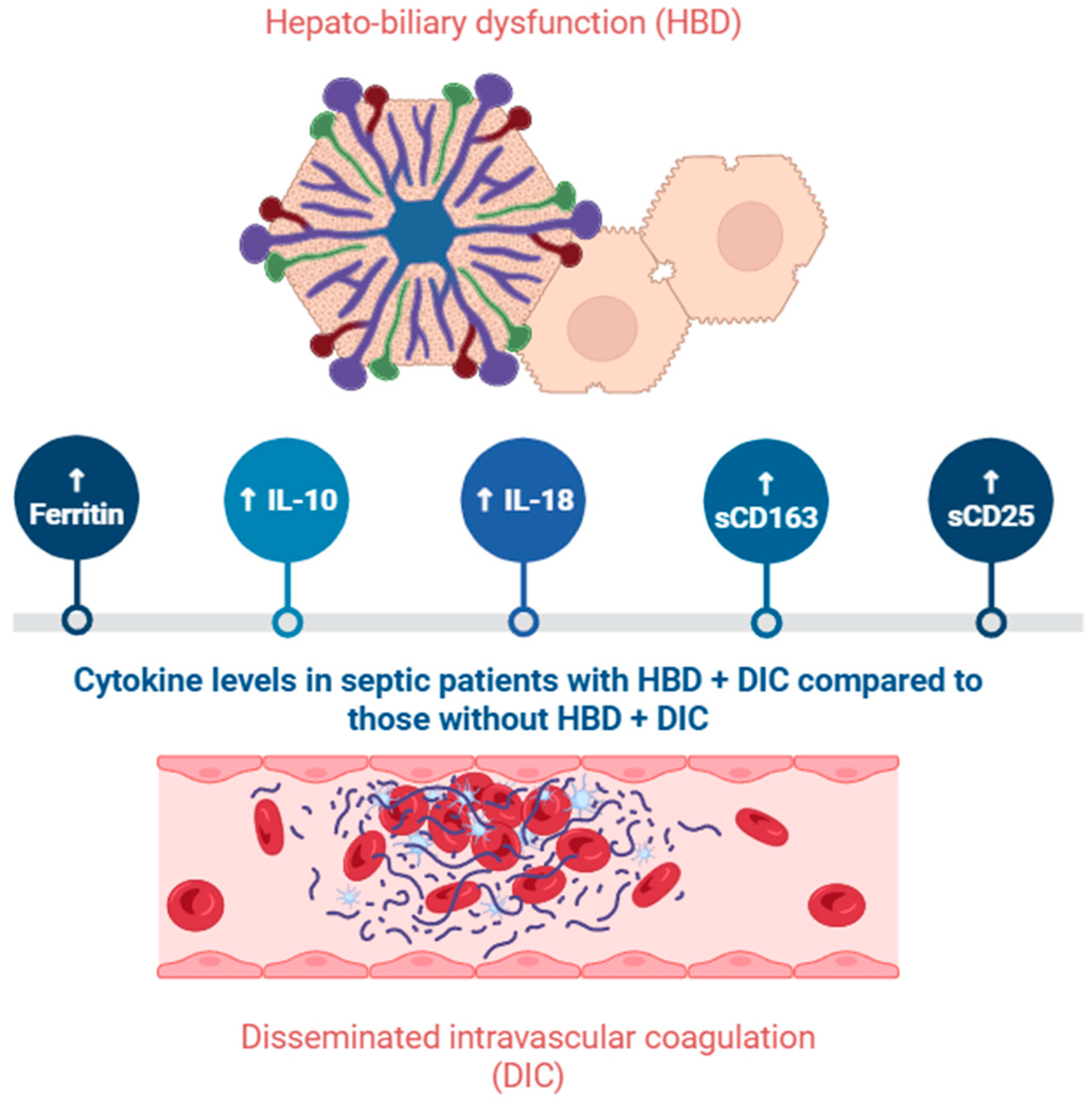
3.2. Acute Liver Failure and Liver Dysfunction
4. Biomarkers That Pertain to AKI or ALF
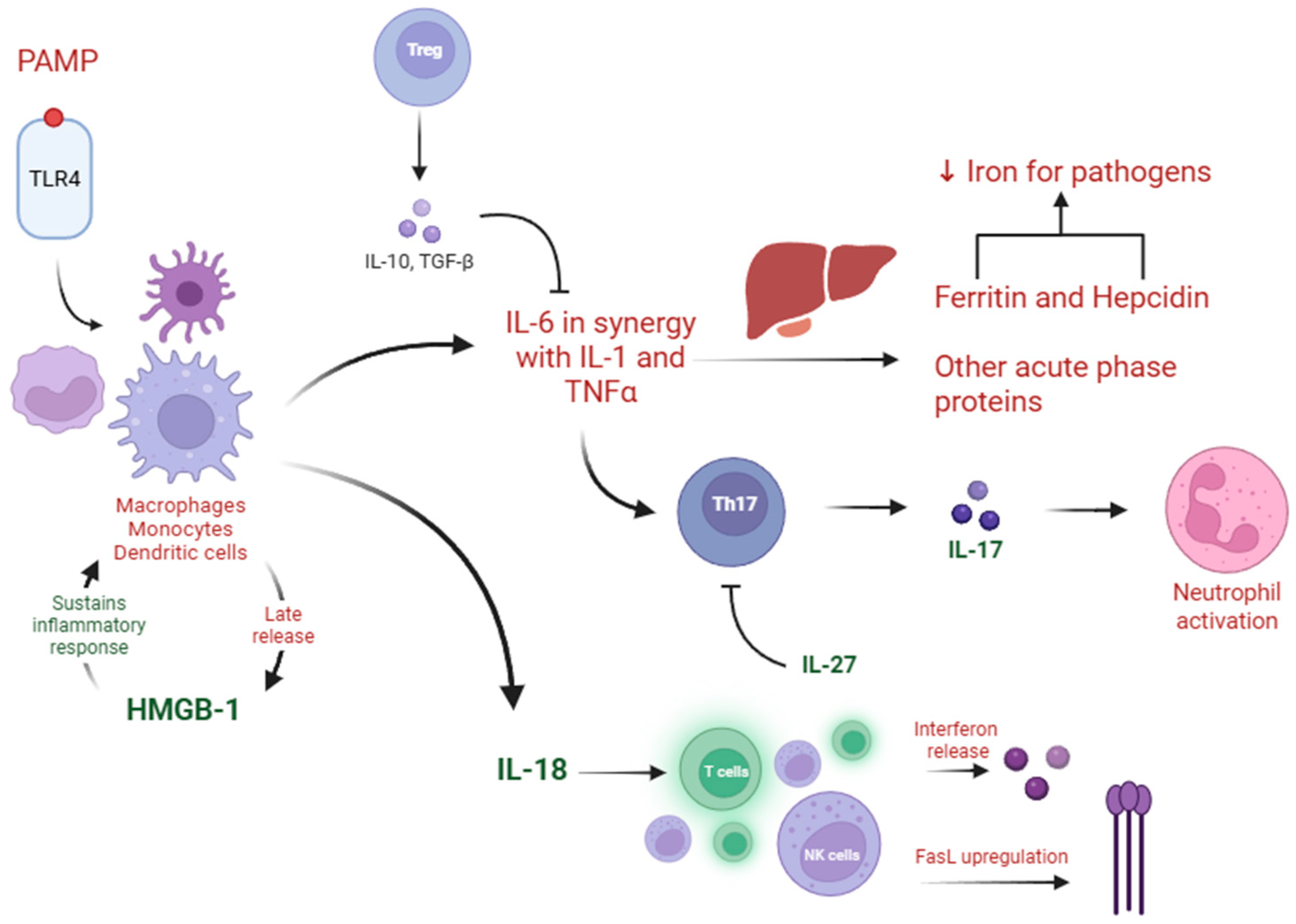
4.1. IL-18
4.2. Hepcidin
4.3. Ferritin
4.4. IL-27
4.5. IL-17A
4.6. IL-10
4.7. IL-33 and ST2
4.8. HMGB1
4.9. Proenkephalin
4.10. C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 9
4.11. Soluble CD163
4.12. Soluble CD25
5. Future Directions and Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambden, S.; Laterre, P.F.; Levy, M.M.; Francois, B. The SOFA score—Development, utility and challenges of accurate assessment in clinical trials. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, K.E.; Kissoon, N.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Bory, S.; Mutahunga, B.; Seymour, C.W.; Angus, D.C.; West, T.E. The global burden of sepsis: Barriers and potential solutions. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miftode, R.-S.; Costache, I.-I.; Constantinescu, D.; Mitu, O.; Timpau, A.-S.; Hancianu, M.; Leca, D.-A.; Miftode, I.-L.; Jigoranu, R.-A.; Oancea, A.-F.; et al. Syndecan-1: From a Promising Novel Cardiac Biomarker to a Surrogate Early Predictor of Kidney and Liver Injury in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. Life 2023, 13, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Via, L.; Sangiorgio, G.; Stefani, S.; Marino, A.; Nunnari, G.; Cocuzza, S.; La Mantia, I.; Cacopardo, B.; Stracquadanio, S.; Spampinato, S.; et al. The Global Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Epidemiologia 2024, 5, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakike, E.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Kyprianou, M.; Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Pletz, M.W.; Netea, M.G.; Reinhart, K.; Kyriazopoulou, E. Coronavirus Disease 2019 as Cause of Viral Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis*. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 2042–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarczak, D.; Kluge, S.; Nierhaus, A. Sepsis—Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Concepts. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 628302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strnad, P.; Tacke, F.; Koch, A.; Trautwein, C. Liver—guardian, modifier and target of sepsis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C.; Wald, R.; Martensson, J.; Maiden, M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Glassford, N.J.; Lankadeva, Y.; Vaara, S.T.; et al. Acute kidney injury in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotts, J.E.; Matthay, M.A. Sepsis: Pathophysiology and clinical management. BMJ 2016, 353, i1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poston, J.T.; Koyner, J.L. Sepsis associated acute kidney injury. BMJ 2019, 364, k4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesseler, N.; Launey, Y.; Aninat, C.; Morel, F.; Mallédant, Y.; Seguin, P. Clinical review: The liver in sepsis. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, J.; Das, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, L.; Kaushik, S.; Kumar Srivastava, V.; Jamal Siddiqui, A.; Jyoti, A. Biomarkers in sepsis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 562, 119891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavani, S.V.; Wolfe, K.S.; Hrusch, C.L.; Greenberg, J.A.; Krishack, P.A.; Lin, J.; Lecompte-Osorio, P.; Carey, K.A.; Kress, J.P.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. Temperature Trajectory Subphenotypes Correlate With Immune Responses in Patients With Sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijte, G.P.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. Fever in Sepsis: Still a Hot Topic. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanakos, G.; Andrianopoulos, I.; Xenikakis, M.; Papathanasiou, A.; Koulenti, D.; Blot, S.; Koulouras, V. Clinical Sepsis Phenotypes in Critically Ill Patients. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, C.W.; Kennedy, J.N.; Wang, S.; Chang, C.-C.H.; Elliott, C.F.; Xu, Z.; Berry, S.; Clermont, G.; Cooper, G.; Gomez, H.; et al. Derivation, Validation, and Potential Treatment Implications of Novel Clinical Phenotypes for Sepsis. JAMA 2019, 321, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghela, A.; Pena, O.M.; Lee, A.H.; Baquir, B.; Falsafi, R.; An, A.; Farmer, S.W.; Hurlburt, A.; Mondragon-Cardona, A.; Rivera, J.D.; et al. Predicting sepsis severity at first clinical presentation: The role of endotypes and mechanistic signatures. eBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventogiannis, K.; Kyriazopoulou, E.; Antonakos, N.; Kotsaki, A.; Tsangaris, I.; Markopoulou, D.; Grondman, I.; Rovina, N.; Theodorou, V.; Antoniadou, E.; et al. Toward personalized immunotherapy in sepsis: The PROVIDE randomized clinical trial. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazopoulou, E.; Leventogiannis, K.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; Pantazi, A.; Orfanos, S.E.; Rovina, N.; Tsangaris, I.; Gkavogianni, T.; Botsa, E.; et al. Macrophage activation-like syndrome: An immunological entity associated with rapid progression to death in sepsis. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbro, I.; Gentile, G.; Tinti, F.; Muiesan, P.; Mitterhofer, A.P. Recent advances in pathophysiology and biomarkers of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. J. Infect. 2016, 72, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gómez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Del Rio-Pertuz, G.; Gomez, H. Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, F.; Zetoune, F.S.; Ward, P.A. Complement as a Major Inducer of Harmful Events in Infectious Sepsis. Shock 2020, 54, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, L.; Jordan, B.; Druml, W.; Bauer, P.; Metnitz, P.G.H. Incidence and prognosis of early hepatic dysfunction in critically ill patients—A prospective multicenter study. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 1099-e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, D.; Yin, Y. Advances in sepsis-associated liver dysfunction. Burn. Trauma 2014, 2, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsantes, A.G.; Parastatidou, S.; Tsantes, E.A.; Bonova, E.; Tsante, K.A.; Mantzios, P.G.; Vaiopoulos, A.G.; Tsalas, S.; Konstantinidi, A.; Houhoula, D.; et al. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines. Life 2023, 13, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Tsutsui, H. Interleukin-18 in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M.; Kuranaga, N.; Matsumoto, A.; Ono, S.; Shinomiya, N.; Hiraide, H.; Seki, S. Multiple interleukin-18 injections promote both mouse Th1 and Th2 responses after sublethal Escherichia coli infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 143, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M.; Shinomiya, N.; Ono, S.; Tsujimoto, H.; Kawabata, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Hiraide, H.; Seki, S. Restoration of Natural IgM Production from Liver B Cells by Exogenous IL-18 Improves the Survival of Burn-Injured Mice Infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4627–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priori, R.; Colafrancesco, S.; Alessandri, C.; Minniti, A.; Perricone, C.; Iaiani, G.; Palazzo, D.; Valesini, G. Interleukin 18: A Biomarker for Differential Diagnosis Between Adult-onset Still’s Disease and Sepsis. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzchala-Pasierb, M.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Lesnik, P.; Adamik, B.; Placzkowska, S.; Serek, P.; Gamian, A.; Lipinska-Gediga, M. Interleukin-18 serum levels in sepsis: Correlation with disease severity and inflammatory markers. Cytokine 2019, 120, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidt, M.V.; Nunes, F.B.; Pedrazza, L.; Caeran, G.; Pellegrin, G.; Melo, D.A.S.; Possuelo, L.; Jost, R.T.; Dias, H.B.; Donadio, M.V.F.; et al. Biochemical and inflammatory aspects in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: The predictive role of IL-18 in mortality. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 453, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisula, S.; Yang, R.; Poukkanen, M.; Vaara, S.T.; Kaukonen, K.M.; Tallgren, M.; Haapio, M.; Tenhunen, J.; Korhonen, A.M.; Pettilä, V.; et al. Predictive value of urine interleukin-18 in the evolution and outcome of acute kidney injury in critically ill adult patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthumana, J.; Ariza, X.; Belcher, J.M.; Graupera, I.; Ginès, P.; Parikh, C.R. Urine Interleukin 18 and Lipocalin 2 Are Biomarkers of Acute Tubular Necrosis in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1003–1013.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarbock, A.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury revisited: Pathophysiology, prevention and future therapies. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, A.M.; Mohamed, M.F.; Thabet, K.K.; Ramzy, T.; Abdelhamid, Y.M. Serum Interleukin-18, Kidney Injury Molecule-1, and the Renal Resistive Index for Predicating Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2023, 34, S153–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttone, G.; Geraci, G.; La Via, L.; Sorbello, M.; Pappalardo, F.; Carollo, C. Exploring the Utility of Renal Resistive Index in Critical Care: Insights into ARDS and Cardiac Failure. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.-Q.; Snyder, J.; Connolly, J.; Glessner, J.; Kao, C.; Sleiman, P.; Hakonarson, H. Circulating LIGHT (TNFSF14) and Interleukin-18 Levels in Sepsis-Induced Multi-Organ Injuries. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Guo, S.; Cui, Z.; Kang, H.; Ma, Z.; Wang, H. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Interleukin-18 in the Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury in Sepsis Patients. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 6335–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, B.; Huang, H. Upregulation of Peripheral Blood NLRP3 and IL-18 in Patients With Acute Kidney Injury in Sepsis and Its Clinical Significance. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e70113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, R.; Hossain, N.; Butt, S.; Bhellar, Z.; Fatima, E.; Imtiaz, S.; Ghulam Moosa, P.; Abbas, K.; Jafri, S.B.; Khan, S. Efficacy of multiple Biomarkers: NGAL, KIM1, Cystatin C and IL18 in predicting pregnancy related acute kidney injury. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 39, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Xu, G.; Liang, X.; Wei, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, G.-N.; Yan, X.-D.; Zhong, M.; Lv, X. Inhibition of hepatic cells pyroptosis attenuates CLP-induced acute liver injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5685. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.; Trehanpati, N.; Maiwall, R.; Sehgal, R.; Singh, R.; Islam, M.; Jagdish, R.K.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Maheshwari, D.; Bhat, S.; et al. Soluble factors and suppressive monocytes can predict early development of sepsis in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderko, R.R.; Gómez, H.; Canna, S.W.; Shakoory, B.; Angus, D.C.; Yealy, D.M.; Huang, D.T.; Kellum, J.A.; Carcillo, J.A. Sepsis with liver dysfunction and coagulopathy predicts an inflammatory pattern of macrophage activation. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2022, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, A.; Charles, M.V.; Seetharam, R.S. Hepcidin—A novel biomarker with changing trends. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2015, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olinder, J.; Ehinger, D.; Liljenborg, E.; Herwald, H.; Rydén, C. Plasma Levels of Hepcidin and Reticulocyte Haemoglobin during Septic Shock. J. Innate Immun. 2020, 12, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olinder, J.; Börjesson, A.; Norrman, J.; West, T.; Carlström, J.; Gustafsson, A.; Annborn, M.; Herwald, H.; Rydén, C. Hepcidin discriminates sepsis from other critical illness at admission to intensive care. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suastika, N.K.W.; Suega, K. The Role of Hepcidin Level as a Predictor for Mortality in Cancer Patients with Sepsis. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 10, 2599–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortová-Kohoutková, M.; Skotáková, M.; Onyango, I.G.; Slezáková, M.; Panovský, R.; Opatřil, L.; Slanina, P.; De Zuani, M.; Mrkva, O.; Andrejčinová, I.; et al. Hepcidin and ferritin levels as markers of immune cell activation during septic shock, severe COVID-19 and sterile inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1110540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Q.; Song, S.; Fang, X. Hepatic Hepcidin Protects against Polymicrobial Sepsis in Mice by Regulating Host Iron Status. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scindia, Y.; Wlazlo, E.; Leeds, J.; Loi, V.; Ledesma, J.; Cechova, S.; Ghias, E.; Swaminathan, S. Protective Role of Hepcidin in Polymicrobial Sepsis and Acute Kidney Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaf, D.E.; Rajapurkar, M.; Lele, S.S.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Boerger, E.A.S.; Mc Causland, F.R.; Eisenga, M.F.; Singh, K.; Babitt, J.L.; Kellum, J.A.; et al. Iron, Hepcidin, and Death in Human AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.-L.; Yan, B.-Q.; Xu, D.-W.; Zhao, R.; Shen, K.; Lu, S.-Q. Mortality and serum hepcidin are associated with persistent and transient acute kidney injury in septic patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2021, 95, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.-L.; Yan, B.-Q.; Zhao, R.; Xu, D.-W.; Shen, K.; Deng, X.; Lu, S.-Q. Combination of hepcidin with neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for prediction of the development of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 523, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olinder, J.; Stjernqvist, M.J.; Lindén, A.; Salomonsson, E.T.; Annborn, M.; Herwald, H.; Rydén, C. Hepcidin, in contrast to heparin binding protein, does not portend acute kidney injury in patients with community acquired septic shock. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Knovich, M.A.; Coffman, L.G.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Serum ferritin: Past, present and future. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2010, 1800, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.C.R.; Longhi, F.; Branco, R.G.; Piva, J.P.; Lacks, D.; Tasker, R.C. Ferritin levels in children with severe sepsis and septic shock. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 96, 1829–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonial, C.T.; Costa, C.A.D.; Andrades, G.R.H.; Crestani, F.; Einloft, P.R.; Bruno, F.; Miranda, A.P.; Fiori, H.H.; Garcia, P.C.R. Prediction of Poor Outcomes for Septic Children According to Ferritin Levels in a Middle-Income Setting*. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 21, e259–e266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.; Roychowdhury, S.; Uz Zaman, M.; Raut, S.; Bhakta, S.; Nandy, M. Can serum ferritin be employed as prognostic marker of pediatric septic shock and severe sepsis? J. Pediatr. Crit. Care 2021, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Guo, C.; Su, Y.; Ding, N. The relationship between serum ferritin level and clinical outcomes in sepsis based on a large public database. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarjou, A.; Black, L.M.; McCullough, K.R.; Hull, T.D.; Esman, S.K.; Boddu, R.; Varambally, S.; Chandrashekar, D.S.; Feng, W.; Arosio, P.; et al. Ferritin Light Chain Confers Protection Against Sepsis-Induced Inflammation and Organ Injury. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odum, J.D.; Akhter, J.; Verma, V.; Vollmer, G.; Davidson, A.; Hyndman, K.A.; Bolisetty, S. Myeloid-specific ferritin light chain deletion does not exacerbate sepsis-associated AKI. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2024, 327, F171–F183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijevic, Z.M.; Salinger-Martinovic, S.S.; Jankovic, R.J.; Mitic, B.P. Elevated Serum Ferritin Levels Are Predictive of Renal Function Recovery among Patients with Acute Kidney Injury. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2019, 248, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.-P.; Zhang, H.-J.; Guo, Z.; Ren, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Effect of Serum Ferritin on the Prognosis of Patients with Sepsis: Data from the MIMIC-IV Database. Emerg. Med. Int. 2022, 2022, 2104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, T.; Luo, Y.; Lu, M.; Xie, Y. Association Between Serum Ferritin and In-hospital Mortality in Critical Ills with Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Mod. Health Sci. 2025, 8, p58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, S.; Carlos, A.R.; Moita, M.R.; Singh, S.; Blankenhaus, B.; Cardoso, S.; Larsen, R.; Rebelo, S.; Schäuble, S.; Del Barrio, L.; et al. Metabolic Adaptation Establishes Disease Tolerance to Sepsis. Cell 2017, 169, 1263–1275.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-W.; Zhou, L.-L.; Yuan, J.; Zhou, W.-X.; Wang, H.-R.; Yu, T.-T.; Zhai, J.-C.; Tang, C.-B.; Jiang, W.; Yu, J.-Q.; et al. Study of the relationship between iron metabolism disorders and sepsis-associated liver injury: A prospective observational study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 31, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpau, A.-S.; Miftode, R.-S.; Petris, A.O.; Costache, I.-I.; Miftode, I.-L.; Rosu, F.M.; Anton-Paduraru, D.-T.; Leca, D.; Miftode, E.G. Mortality Predictors in Severe COVID-19 Patients from an East European Tertiary Center: A Never-Ending Challenge for a No Happy Ending Pandemic. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Wu, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Elevated serum ferritin level effectively discriminates severity illness and liver injury of coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia. Biomarkers 2021, 26, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpau, A.-S.; Miftode, R.-S.; Costache, I.-I.; Petris, A.O.; Miftode, I.-L.; Gheorghe, L.; Timpau, R.; Miftode, I.D.; Prepeliuc, C.S.; Coman, I.; et al. An Overview of the Impact of Bacterial Infections and the Associated Mortality Predictors in Patients with COVID-19 Admitted to a Tertiary Center from Eastern Europe. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Hunter, C.A. The Immunobiology of Interleukin-27. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 417–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, S.; Tubbe, I.; Galle, P.R.; Schild, H.J.; Birkenbach, M.; Blumberg, R.S.; Neurath, M.F. Protection from lethal septic peritonitis by neutralizing the biological function of interleukin 27. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xu, F.; Lin, S.; Song, Z.; Zhang, L.; Luo, P.; Xu, H.; Li, D.; Zheng, K.; Ren, G.; et al. IL-27 controls sepsis-induced impairment of lung antibacterial host defence. Thorax 2014, 69, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Liu, S. Interleukin-27 as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Patients with Sepsis: A Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5516940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; He, M.; Wu, Z. IL-27 is elevated in sepsis with acute hepatic injury and promotes hepatic damage and inflammation in the CLP model. Cytokine 2020, 127, 154936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; He, M.; Wang, C.-J.; Zhang, M. Gadolinium Chloride Inhibits the Production of Liver Interleukin-27 and Mitigates Liver Injury in the CLP Mouse Model. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 2605973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Wang, L.; Kuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, Q.; He, M.; Fan, J. IL-27 aggravates acute hepatic injury by promoting macrophage M1 polarization to induce Caspase-11 mediated Pyroptosis in vitro and in vivo. Cytokine 2025, 188, 156881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Deng, B.; Wu, M.; Ding, F.; Wang, L. Interleukin-27 Ameliorates Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription 3 Signaling Pathway. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Fan, T.; Jiang, L.; Guo, R.; Liu, Q. Interleukin-27 is elevated in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction and mediates inflammation. Cytokine 2016, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shou, S.; Jin, H. The role of IL-17 in acute kidney injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 119, 110307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Luo, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Cai, G.; Fu, B.; Feng, Z.; Sun, X.; Chen, X. Knockout of interleukin-17A protects against sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maravitsa, P.; Adamopoulou, M.; Pistiki, A.; Netea, M.G.; Louis, K.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. Systemic over-release of interleukin-17 in acute kidney injury after septic shock: Clinical and experimental evidence. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 178, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yao, J.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Duan, M. Th17/Regulatory T-Cell Imbalance and Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Sepsis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, A.; Sun, K.; Lin, X.; Liu, Q.; Shou, S.; Zhang, Y. The roles of interleukin-17A in risk stratification and prognosis of patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 42, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Lin, F.; Mu, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Mi, L.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y. Study of the Expression of Inflammatory Factors IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-17 in Liver Failure Complicated by Coagulation Dysfunction and Sepsis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, R. IL-10 family of cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knolle, P.A.; Löser, E.; Protzer, U.; Duchmann, R.; Schmitt, E.; Zum Büschenfelde, K.-H.M.; Rose-John, S.; Gerken, G. Regulation of endotoxin-induced IL-6 production in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and Kupffer cells by IL-10. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 107, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, I.J.; McGonagill, P.W.; Butler, N.S.; Harty, J.T.; Griffith, T.S.; Badovinac, V.P. NK Cell–Derived IL-10 Supports Host Survival during Sepsis. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; Chen, D.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, X.; Ye, C.; Tao, H.; Sheng, W.; Wu, Y. Combination of C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, IL -6, IL -8, and IL -10 for early diagnosis of hyperinflammatory state and organ dysfunction in pediatric sepsis. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; Choi, H.-M.; Ko, Y.-S.; Lee, H.-Y.; Jo, S.-K.; Cho, W.-Y.; Kim, H.-K. Distinct pathophysiologic mechanisms of septic acute kidney injury: Role of immune suppression and renal tubular cell apoptosis in murine model of septic acute kidney injury. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, H.J.; Oh, S.W.; Jo, S.K.; Cho, W.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.Y. Soluble CD25 is increased in patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrology 2014, 19, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Turnquist, H.R.; Hoffman, R.; Billiar, T.R. Role of the IL-33-ST2 axis in sepsis. Mil. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z. Role of IL-33-ST2 pathway in regulating inflammation: Current evidence and future perspectives. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, H.S.; Magrini, L.; Marino, R.; Cardelli, P.; Somma, S.D.; Network, O.B.O.G. Soluble ST2 Has a Prognostic Role in Patients With Suspected Sepsis. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepoi, M.-R.; Duca, S.T.; Chetran, A.; Costache, A.D.; Spiridon, M.R.; Afrăsânie, I.; Leancă, S.A.; Dmour, B.-A.; Matei, I.T.; Miftode, R.S.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Ischemic Heart Disease: To What Extent Do Biomarkers Help? Life 2023, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Filho, J.C.; Sônego, F.; Souto, F.O.; Freitas, A.; Verri, W.A.; Auxiliadora-Martins, M.; Basile-Filho, A.; McKenzie, A.N.; Xu, D.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. Interleukin-33 attenuates sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Lv, R.; Lei, M. IL-33 attenuates mortality by promoting IFN-γ production in sepsis. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrsaljko, N.; Radmanic Matotek, L.; Zidovec-Lepej, S.; Vince, A.; Papic, N. The Impact of Steatotic Liver Disease on Cytokine and Chemokine Kinetics During Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcay, A.; Nguyen, Q.; He, Z.; Turkmen, K.; Won Lee, D.; Hernando, A.A.; Altmann, C.; Toker, A.; Pacic, A.; Ljubanovic, D.G.; et al. IL-33 Exacerbates Acute Kidney Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfurt, S.; Hoffmeister, M.; Oess, S.; Asmus, K.; Patschan, S.; Ritter, O.; Patschan, D. Soluble IL-33 receptor predicts survival in acute kidney injury. J. Circ. Biomark. 2022, 11, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, L. HMGB1, a potent proinflammatory cytokine in sepsis. Cytokine 2010, 51, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, K.R.; Al-Dasooqi, N.; Lousberg, E.L.; Hayball, J.D. The multifunctional alarmin HMGB1 with roles in the pathophysiology of sepsis and cancer. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2013, 91, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibot, S.; Massin, F.; Cravoisy, A.; Barraud, D.; Nace, L.; Levy, B.; Bollaert, P.-E. High-mobility group box 1 protein plasma concentrations during septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundén-Cullberg, J.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Rouhiainen, A.; Rauvala, H.; Herman, G.; Tracey, K.J.; Lee, M.L.; Andersson, J.; Tokics, L.; Treutiger, C.J. Persistent elevation of high mobility group box-1 protein (HMGB1) in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock*. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakike, E.; Adami, M.-E.; Lada, M.; Gkavogianni, T.; Koutelidakis, I.M.; Bauer, M.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Tsangaris, I. Late Peaks of HMGB1 and Sepsis Outcome: Evidence For Synergy With Chronic Inflammatory Disorders. Shock 2019, 52, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Deng, Y.; Tang, J. Synergistic effects of antibodies against high-mobility group box 1 and tumor necrosis factor-α antibodies on d -(+)-galactosamine hydrochloride/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zang, K.; Shang, F.; Guo, S.; Gao, L.; Zhang, X. HMGB1 mediates acute liver injury in sepsis through pyroptosis of liver macrophages. Int. J. Burn. Trauma 2020, 10, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, F.; Shi, C.; Pei, M.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Gong, Z. TNF-α/HMGB1 inflammation signalling pathway regulates pyroptosis during liver failure and acute kidney injury. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Shi, M.; Ding, G. HMGB1 Turns Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells into Inflammatory Promoters by Interacting with TLR4 During Sepsis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorashadi, M.; Beunders, R.; Pickkers, P.; Legrand, M. Proenkephalin: A New Biomarker for Glomerular Filtration Rate and Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2020, 144, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beunders, R.; Struck, J.; Wu, A.H.B.; Zarbock, A.; Di Somma, S.; Mehta, R.L.; Koyner, J.L.; Nadim, M.K.; Maisel, A.S.; Murray, P.T.; et al. Proenkephalin (PENK) as a Novel Biomarker for Kidney Function. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2017, 2, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, J.; Dépret, F.; Hartmann, O.; Pickkers, P.; Laterre, P.-F.; Uhle, F. AdrenOSS-1 study investigators. Clinical performance of proenkephalin A 119–159 for the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis or septic shock. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caironi, P.; Latini, R.; Struck, J.; Hartmann, O.; Bergmann, A.; Bellato, V.; Ferraris, S.; Tognoni, G.; Pesenti, A.; Gattinoni, L.; et al. Circulating Proenkephalin, Acute Kidney Injury, and Its Improvement in Patients with Severe Sepsis or Shock. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.-C.; Chuan, M.-H.; Liu, J.-H.; Liao, H.-W.; Ng, L.L.; Magnusson, M.; Jujic, A.; Pan, H.-C.; Wu, V.-C.; Forni, L.G. Proenkephalin as a biomarker correlates with acute kidney injury: A systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verras, C.; Bezati, S.; Bistola, V.; Ventoulis, I.; Matsiras, D.; Tsiodras, S.; Parissis, J.; Polyzogopoulou, E. Point-of-Care Serum Proenkephalin as an Early Predictor of Mortality in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department with Septic Shock. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hur, M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Somma, S.D.; GREAT Network. Proenkephalin Predicts Organ Failure, Renal Replacement Therapy, and Mortality in Patients With Sepsis. Ann. Lab. Med. 2020, 40, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, R.; Zhang, W.; Naseem, M.; Puccini, A.; Berger, M.D.; Soni, S.; McSkane, M.; Baba, H.; Lenz, H.-J. CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11/CXCR3 axis for immune activation—A target for novel cancer therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 63, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Antonelli, M.; Bloos, F.; Kotsamidi, I.; Psarrakis, C.; Dakou, K.; Thomas-Rüddel, D.; Montini, L.; Briegel, J.; Damoraki, G.; et al. Interferon-gamma driven elevation of CXCL9: A new sepsis endotype independently associated with mortality. eBioMedicine 2024, 109, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moledina, D.G.; Obeid, W.; Smith, R.N.; Rosales, I.; Sise, M.E.; Moeckel, G.; Kashgarian, M.; Kuperman, M.; Campbell, K.N.; Lefferts, S.; et al. Identification and validation of urinary CXCL9 as a biomarker for diagnosis of acute interstitial nephritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e168950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y. Advances in the diagnosis of early biomarkers for acute kidney injury: A literature review. BMC Nephrol. 2025, 26, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiman, Y.; Friedman, S.L. The Role of Chemokines in Acute Liver Injury. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevriti, A.; Lamprou, M.; Mourkogianni, E.; Skoulas, N.; Giannakopoulou, M.; Sajib, M.S.; Wang, Z.; Mattheolabakis, G.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Marazioti, A.; et al. The Role of Soluble CD163 (sCD163) in Human Physiology and Pathophysiology. Cells 2024, 13, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Zhou, X.; Su, L.-X.; Feng, D.; Jia, Y.-H.; Xie, L.-X. Clinical Significance of Soluble Hemoglobin Scavenger Receptor CD163 (sCD163) in Sepsis, a Prospective Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaïni, S.; Pedersen, S.S.; Koldkjær, O.G.; Pedersen, C.; Moestrup, S.K.; Møller, H.J. New immunological serum markers in bacteraemia: Anti-inflammatory soluble CD163, but not proinflammatory high mobility group-box 1 protein, is related to prognosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 151, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, R.; Wagih, A.; Elbarbary, A. The diagnostic value of serum level of soluble hemoglobin scavenger receptor CD163 for sepsis in the ICU. Tanta Med. J. 2015, 43, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzchała-Pasierb, M.; Lipińska-Gediga, M.; Lewandowski, Ł.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M. Alterations in Serum Concentration of Soluble CD163 within Five Study Days from ICU Admission Are Associated with In-Hospital Mortality of Septic Patients—A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Xiao, K.; Yan, P.; Jia, Y.; Feng, D.; Xie, L. Diagnostic value of urine sCD163 levels for sepsis and relevant acute kidney injury: A prospective study. BMC Nephrol. 2012, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.J.; Grønbæk, H.; Schiødt, F.V.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Schilsky, M.; Munoz, S.; Hassanein, T.; Lee, W.M. Soluble CD163 from activated macrophages predicts mortality in acute liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornai, T.; Vitalis, Z.; Sipeki, N.; Dinya, T.; Tornai, D.; Antal-Szalmas, P.; Karanyi, Z.; Tornai, I.; Papp, M. Macrophage activation marker, soluble CD 163, is an independent predictor of short-term mortality in patients with cirrhosis and bacterial infection. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damoiseaux, J. The IL-2—IL-2 receptor pathway in health and disease: The role of the soluble IL-2 receptor. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 218, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Obregon, S.; Azkargorta, M.; Seijas, I.; Pilar-Orive, J.; Borrego, F.; Elortza, F.; Boyano, M.D.; Astigarraga, I. Identification of a panel of serum protein markers in early stage of sepsis and its validation in a cohort of patients. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komorowski, M.; Green, A.; Tatham, K.C.; Seymour, C.; Antcliffe, D. Sepsis biomarkers and diagnostic tools with a focus on machine learning. eBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.-R.; Yue, G.-L.; Dong, M.-L.; Wang, J.-Q.; Cheng, C. Sepsis Biomarkers: Advancements and Clinical Applications—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Advantages | Limitations | |
|---|---|---|
| IL-18 |
|
|
| Hepcidin |
|
|
| Ferritin |
|
|
| Advantages | Limitations | |
|---|---|---|
| IL-27 |
|
|
| IL-17A |
|
|
| IL-10 |
|
|
| IL-33 and ST2 |
|
|
| HMGB1 |
|
|
| Proenkephalin |
|
|
| CXCL9 |
|
|
| sCD163 |
|
|
| sCD25 |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pasare, M.-A.; Prepeliuc, C.S.; Grigoriu, M.G.; Miftode, I.-L.; Miftode, E.G. Biomarkers as Beacons: Illuminating Sepsis-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104825
Pasare M-A, Prepeliuc CS, Grigoriu MG, Miftode I-L, Miftode EG. Biomarkers as Beacons: Illuminating Sepsis-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104825
Chicago/Turabian StylePasare, Maria-Antoanela, Cristian Sorin Prepeliuc, Maria Gabriela Grigoriu, Ionela-Larisa Miftode, and Egidia Gabriela Miftode. 2025. "Biomarkers as Beacons: Illuminating Sepsis-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104825
APA StylePasare, M.-A., Prepeliuc, C. S., Grigoriu, M. G., Miftode, I.-L., & Miftode, E. G. (2025). Biomarkers as Beacons: Illuminating Sepsis-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104825










