The Double Life of microRNAs in Bone Sarcomas: Oncogenic Drivers and Tumor Suppressors
Abstract
1. Introduction
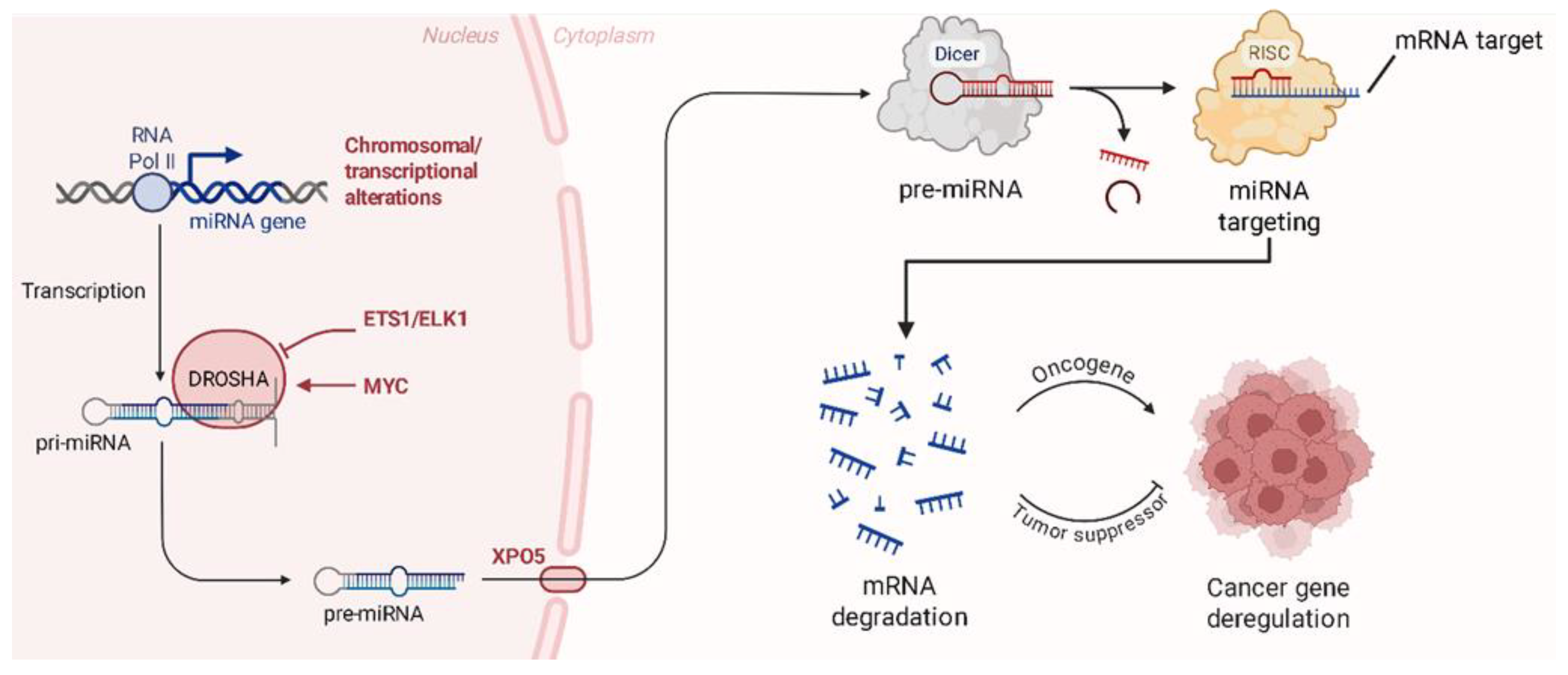
2. miRNAs Dysregulation in Bone Sarcomas
2.1. miRNAs in Osteosarcoma
2.2. Oncogenic miRNAs in Osteosarcoma
2.3. Tumor Suppressor miRNAs in Osteosarcoma
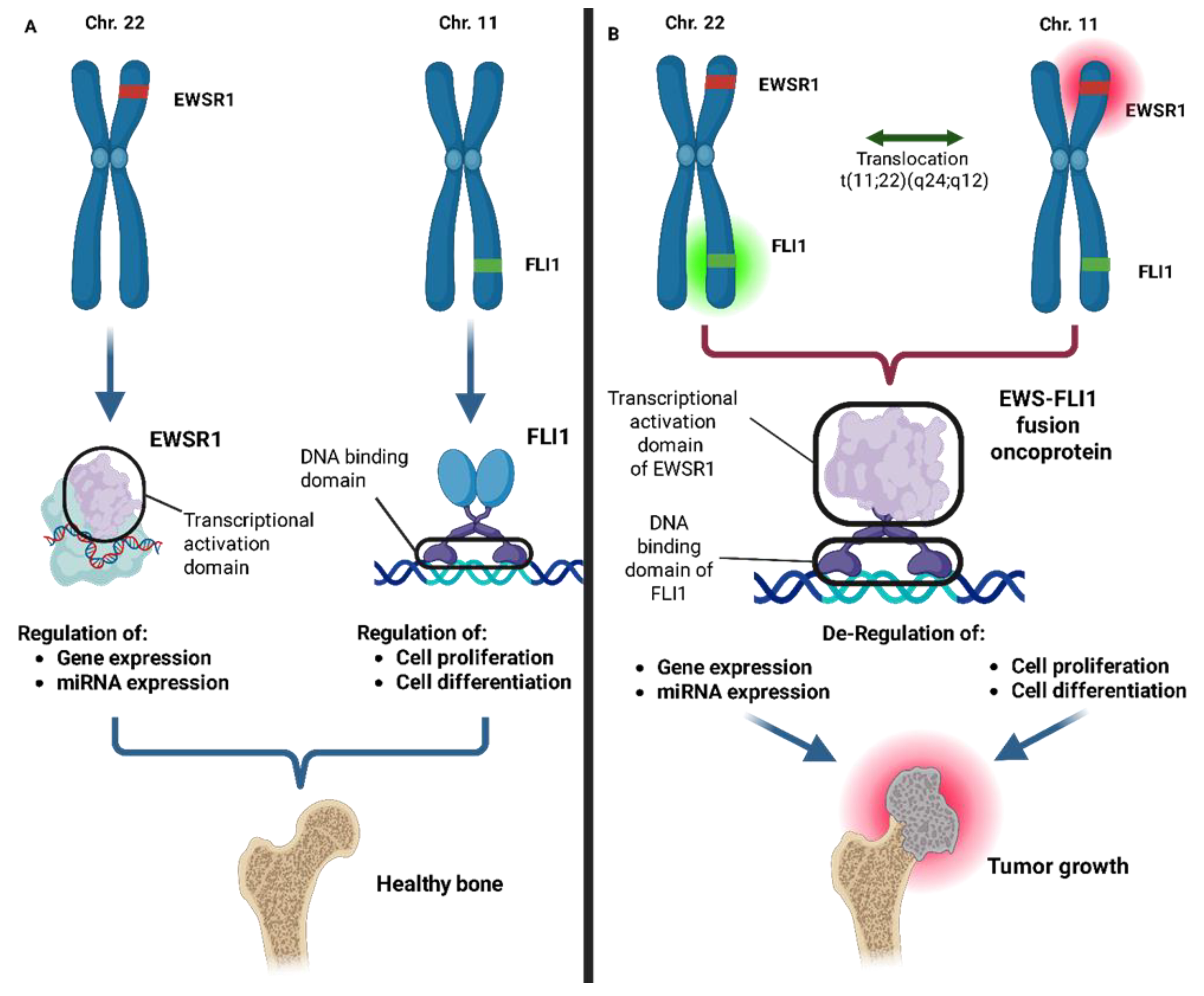
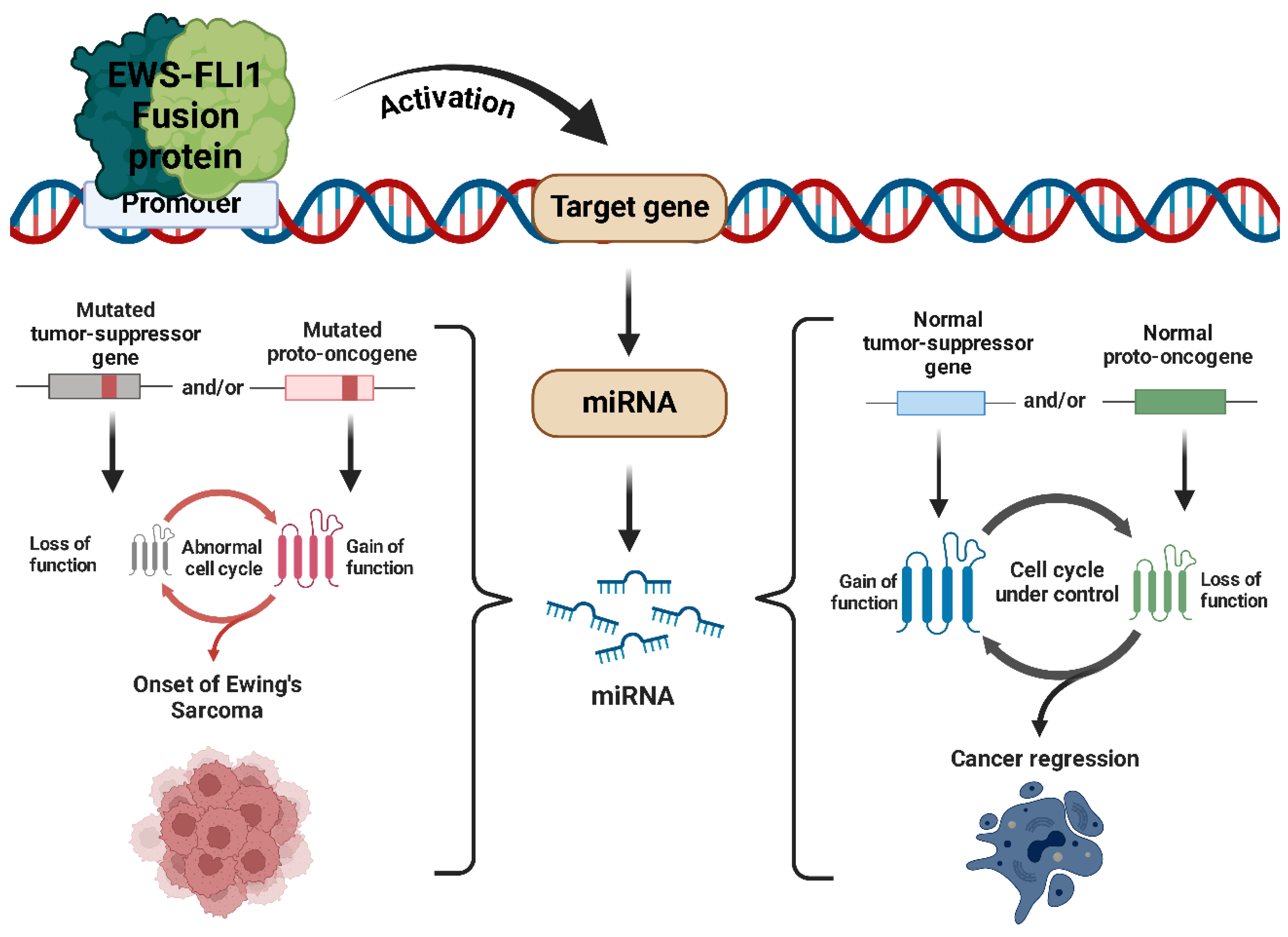
2.4. miRNAs in Ewing’s Sarcoma
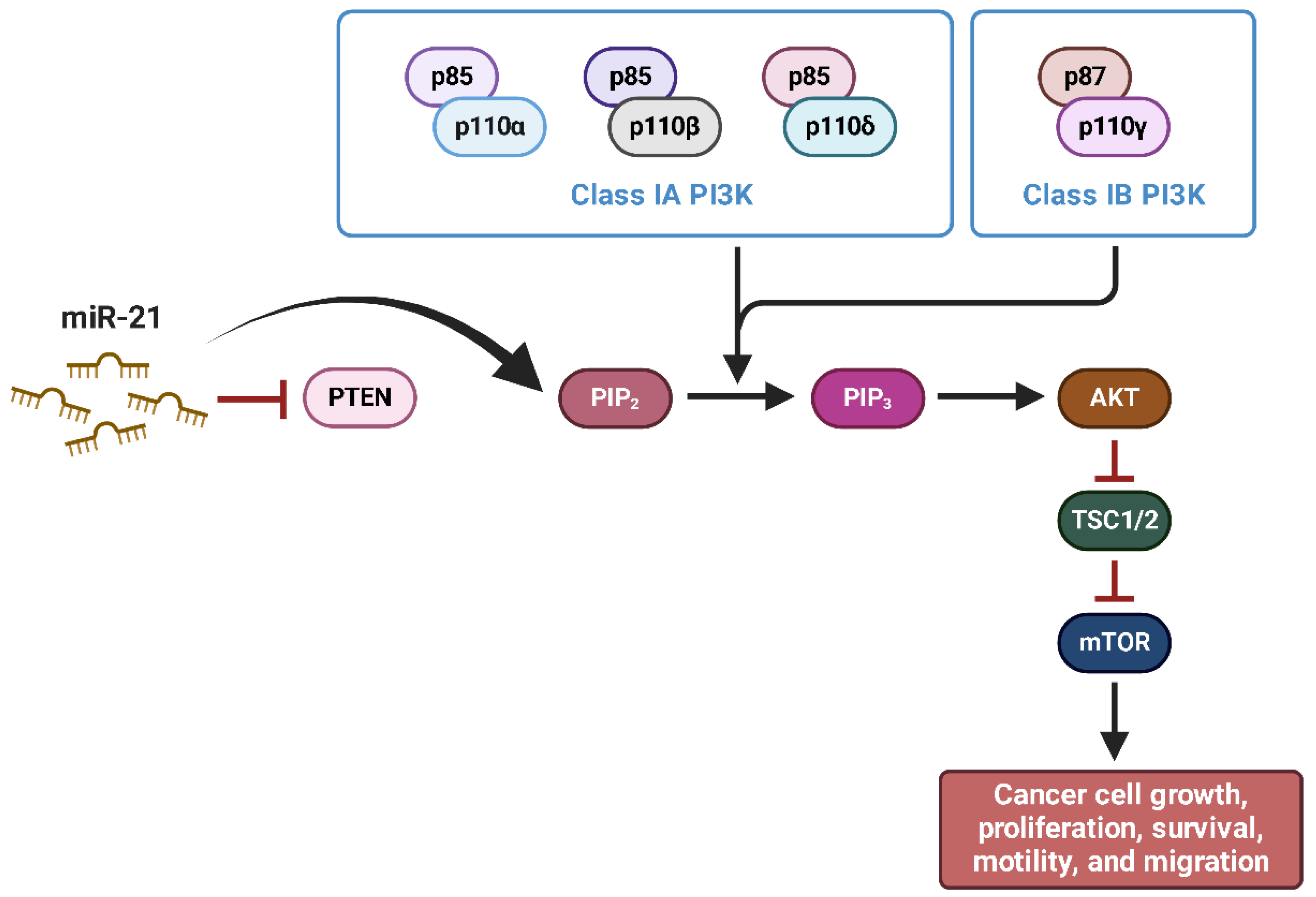
2.5. Oncogenic miRNAs in Ewing’s Sarcoma
2.6. Tumor Suppressor miRNAs in Ewing’s Sarcoma
2.7. miRNAs in Chondrosarcoma
2.8. Oncogenic miRNAs in Chondrosarcoma
2.9. Tumor Suppressor miRNAs in Chondrosarcoma
3. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, D.M.; Whelan, J. Bone Sarcomas in the Adolescent and Young Adult Population. In Cancer in Adolescents and Young Adults; Pediatric Oncology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.E.; Graves, L.A.; Rubin, E.M.; Reed, D.R.; Riedel, R.F.; Strauss, S.J. Bad to the Bone: Emerging Approaches to Aggressive Bone Sarcomas. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2023, 43, e390306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evola, F.R.; Costarella, L.; Pavone, V.; Caff, G.; Cannavò, L.; Sessa, A.; Avondo, S.; Sessa, G. Biomarkers of Osteosarcoma, Chondrosarcoma, and Ewing Sarcoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 239591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, A.J.; El-Ali, A.M.; Davis, J.C.; Gillman, J.A.M.; Khanna, G. Bone Neoplasms: Osteosarcoma and Ewing Sarcoma. In Evidence-Based Imaging in Pediatrics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrand, C.; Athanasou, N.; Brennan, B.; Grimer, R.; Judson, I.; Morland, B.; Peake, D.; Seddon, B.; Whelan, J. UK Guidelines for the Management of Bone Sarcomas. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Min, L.; Seebacher, N.A.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hornicek, F.J.; Wei, Y.; Tu, C.; Duan, Z. Targeting Mutant TP53 as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for the Treatment of Osteosarcoma. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Ali, A.M.; Deng, J.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Y.; He, M. MiR-197-3p Promotes Osteosarcoma Stemness and Chemoresistance by Inhibiting SPOPL. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Li, E.; Wu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Li, C.; Liao, B.; Ma, Q. Quantitative Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals Chemoresistance-Related Proteins and Signaling Pathways Induced by RhIL-6 in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, S.; Marchesi, I.; Bagella, L. PRC2: An Epigenetic Multiprotein Complex with a Key Role in the Development of Rhabdomyosarcoma Carcinogenesis. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, E.; Mitanoska, A.; O’Brien, Q.; Porter, K.; Molina, M.; Ahsan, H.; Jung, U.; Mills, L.; Kyba, M.; Bosnakovski, D. Pharmacological Targeting of P300/CBP Reveals EWS::FLI1-Mediated Senescence Evasion in Ewing Sarcoma. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, M.; Lamoureux, F.; Mullard, M.; Postec, A.; Regnier, L.; Baud’huin, M.; Georges, S.; Brounais-Le Royer, B.; Ory, B.; Rédini, F.; et al. Ewing Sarcoma from Molecular Biology to the Clinic. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1248753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, I.; Fais, M.; Fiorentino, F.P.; Bordoni, V.; Sanna, L.; Zoroddu, S.; Bagella, L. Bromodomain Inhibitor JQ1 Provides Novel Insights and Perspectives in Rhabdomyosarcoma Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limijadi, E.K.S.; Novriansyah, R.; Respati, D.R.P.; Tjandra, K.C. MiRNA Encoded PTEN’s Impact on Clinical-Pathological Features and Prognosis in Osteosarcoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braaten, M.; Braaten, J.; Chaddha, J.; Hu, R.; Lanoue, C.; Silberstein, P.; Tauseef, A.; Asghar, N.; Mirza, M. Survival and Treatment in Older Patients with Ewing Sarcoma: An Analysis of the National Cancer Database. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Harris, M.A.; Newton, L.M.; Harris, T.J.; Fairlie, W.D.; Lee, E.F.; Hawkins, C.J. Osteosarcoma Cells Depend on MCL-1 for Survival, and Osteosarcoma Metastases Respond to MCL-1 Antagonism plus Regorafenib In Vivo. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, A.; Tudor, M.; Montanari, J.; Commenchail, K.; Savu, D.I.; Lesueur, P.; Chevalier, F. Chondrosarcoma Resistance to Radiation Therapy: Origins and Potential Therapeutic Solutions. Cancers 2023, 15, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazendam, A.; Popovic, S.; Parasu, N.; Ghert, M. Chondrosarcoma: A Clinical Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayestarán, A.; Palma, J.; Calvo, F.A. Radiation Therapy in Chondrosarcoma. In Radiation Oncology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locquet, M.A.; Brahmi, M.; Blay, J.Y.; Dutour, A. Radiotherapy in Bone Sarcoma: The Quest for Better Treatment Option. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Han, M.; Gao, Z.; Wang, M.; Hu, G.; Xie, X.; Du, H.; et al. Identification of Key Serum Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Metastatic Prediction of Osteosarcoma by Analysis of Immune Cell Infiltration. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipar, P.; Dey, M.; Piątkowski, J.; Sulejczak, D.; Rutkowski, P.; Czarnecka, A.M. MicroRNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Chondrosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, S.; Lucariello, A.; De Luca, A.; Bagella, L. Dysregulation of MiRNAs in Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Cells 2024, 13, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Shrestha, S.; LaChaud, G.; Scott, M.A.; James, A.W. Review of MicroRNA in Osteosarcoma and Chondrosarcoma. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, S.; Sanna, L.; Bordoni, V.; Lyu, W.; Murineddu, G.; Pinna, G.A.; Forcales, S.V.; Sala, A.; Kelvin, D.J.; Bagella, L. RNAseq Analysis of Novel 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Chalcogen Analogues Reveals Anti-Tubulin Properties on Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, S.; Corona, P.; Sanna, L.; Borghi, F.; Bordoni, V.; Asproni, B.; Pinna, G.A.; Bagella, L.; Murineddu, G. Novel 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Chalcogen Analogues: Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoroddu, S.; Sanna, L.; Bordoni, V.; Weidong, L.; Gadau, S.D.; Carta, A.; Kelvin, D.J.; Bagella, L. Identification of 3-Aryl-1-Benzotriazole-1-Yl-Acrylonitrile as a Microtubule-Targeting Agent (MTA) in Solid Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, M.; Skipar, P.; Bartnik, E.; Piątkowski, J.; Sulejczak, D.; Czarnecka, A.M. MicroRNA Signatures in Osteosarcoma: Diagnostic Insights and Therapeutic Prospects. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2024, 4, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Song, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Key Link Modulates the Multidrug Resistance of Cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M. MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin, NF-KB, PI3K/AKT, STAT3, P53, and Hedgehog Pathway. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2023, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, Z.; Malekzadeh, M.; Sharifi, M.; Hashemibeni, B. The Role of MiR-16 and MiR-34a Family in the Regulation of Cancers: A Review. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Lim, J.; Jin, H.Y.; Park, M.; Park, H.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, H.G.; Won, Y.J. Osteosarcoma in Adolescents and Young Adults. Cells 2021, 10, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Davis, L.E.; Albert, C.M.; Samuels, B.; Roberts, J.L.; Wagner, M.J. Osteosarcoma in Pediatric and Adult Populations: Are Adults Just Big Kids? Cancers 2023, 15, 5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yao, X. Advances on Immunotherapy for Osteosarcoma. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.H.; Yang, Y.L.; Han, S.M.; Wu, Z.H. MicroRNA-9 Expression Is a Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Osteosarcoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wei, T.; Huang, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H. Inhibition of MiR-9 Decreases Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation. Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, S.; Luo, J. MiR-9 Depletion Suppresses the Proliferation of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting P16. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
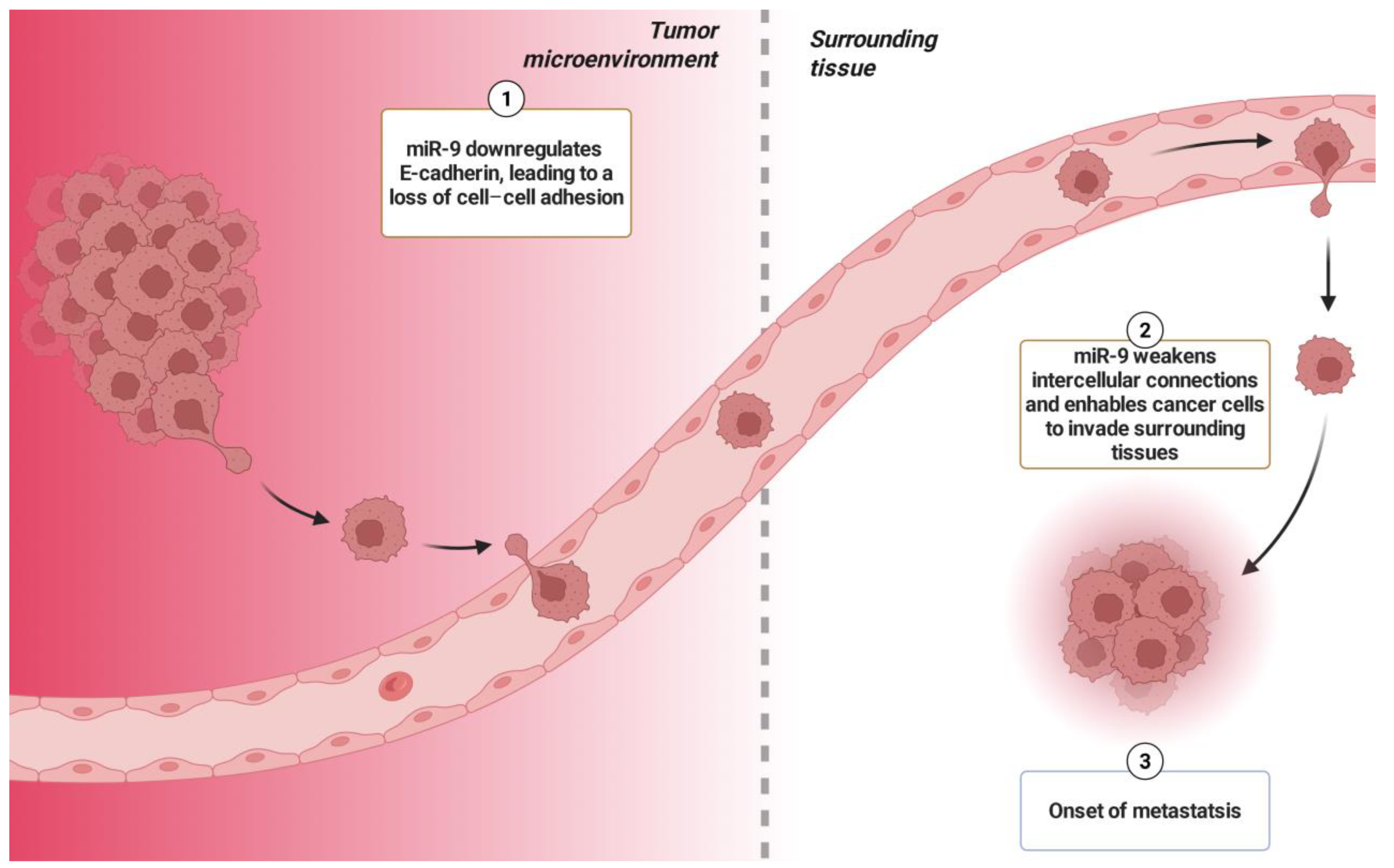
- Ma, L.; Young, J.; Prabhala, H.; Pan, E.; Mestdagh, P.; Muth, D.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Reinhardt, F.; Onder, T.T.; Valastyan, S.; et al. MiR-9, a MYC/MYCN-Activated MicroRNA, Regulates E-Cadherin and Cancer Metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abba, M.; Patil, N.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNAs in the Regulation of MMPs and Metastasis. Cancers 2014, 6, 625–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Q.; He, F.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Jin, M.; Xu, J.; Efird, J.T. The Impact of MiR-9 in Osteosarcoma: A Study Based on Meta-Analysis, TCGA Data, and Bioinformatics Analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e21902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L.; Fiori, M.E.; Albini, S.; Cifaldi, L.; Giovinazzi, S.; Forloni, M.; Boldrini, R.; Donfrancesco, A.; Federici, V.; Giacomini, P.; et al. Antagomir-17-5p Abolishes the Growth of Therapy-Resistant Neuroblastoma through P21 and BIM. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Q.; Niu, D.; Liu, B. Serum MiR-95-3p Is a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker for Osteosarcoma. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Jia, Y.; Xia, G.; Li, H.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, R. MiR-95 Promotes Osteosarcoma Growth by Targeting SCNN1A. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
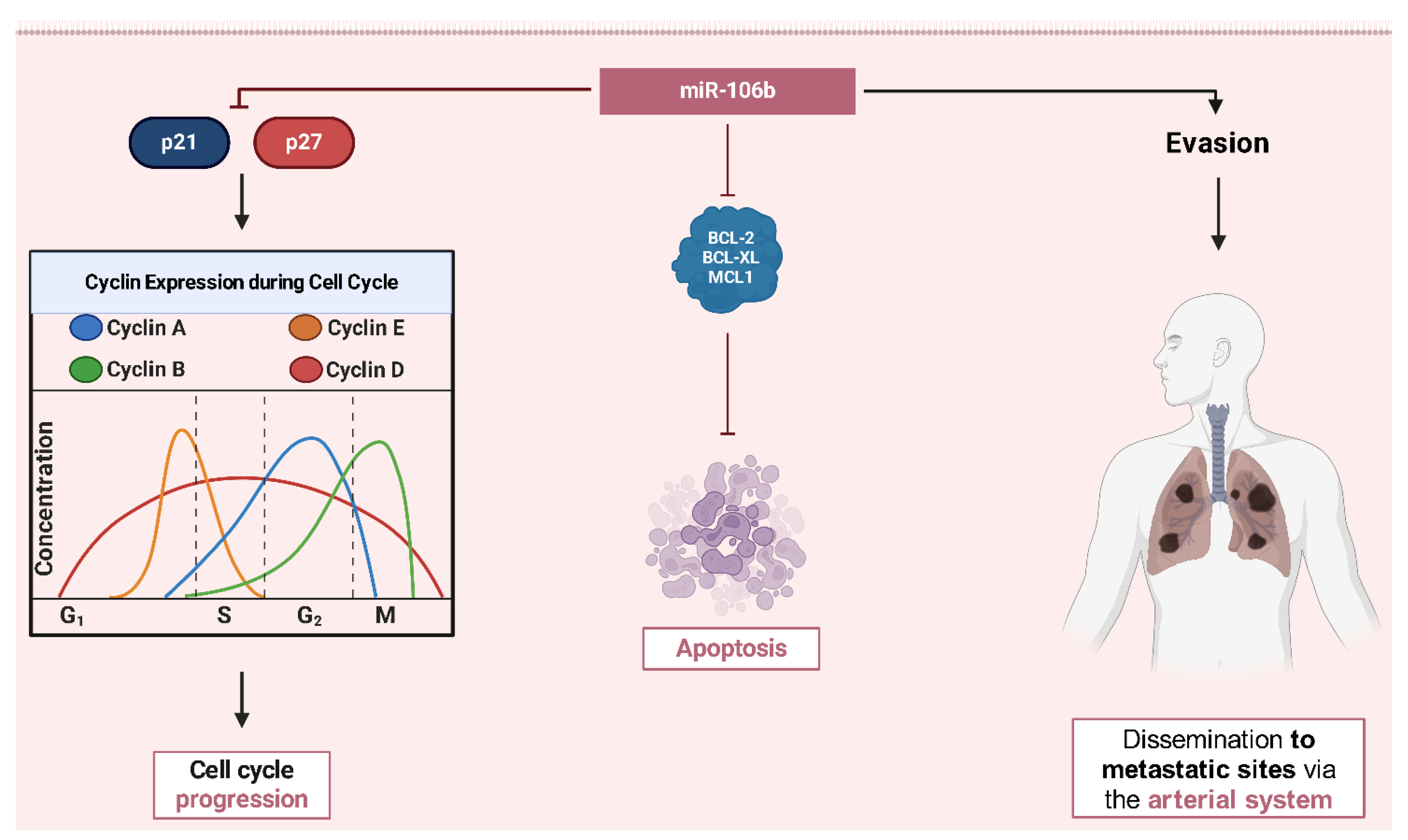
- Xu, K.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B. MicroRNA-106b Serves as a Prognostic Biomarker and Is Associated with Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3342–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Qin, Q.; Pang, Q. MiR-106b-5p Promotes Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression by Directly Targeting CDKN1A in Osteosarcoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3203–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xiao, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Si, X.; Bai, J.; et al. The MiR-106b-25 Cluster Mediates Drug Resistance in Myeloid Leukaemias by Inactivating Multiple Apoptotic Genes. Int. J. Hematol. 2023, 117, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaloni, D.; Diepstraten, S.T.; Strasser, A.; Kelly, G.L. BCL-2 Protein Family: Attractive Targets for Cancer Therapy. Apoptosis 2022, 28, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
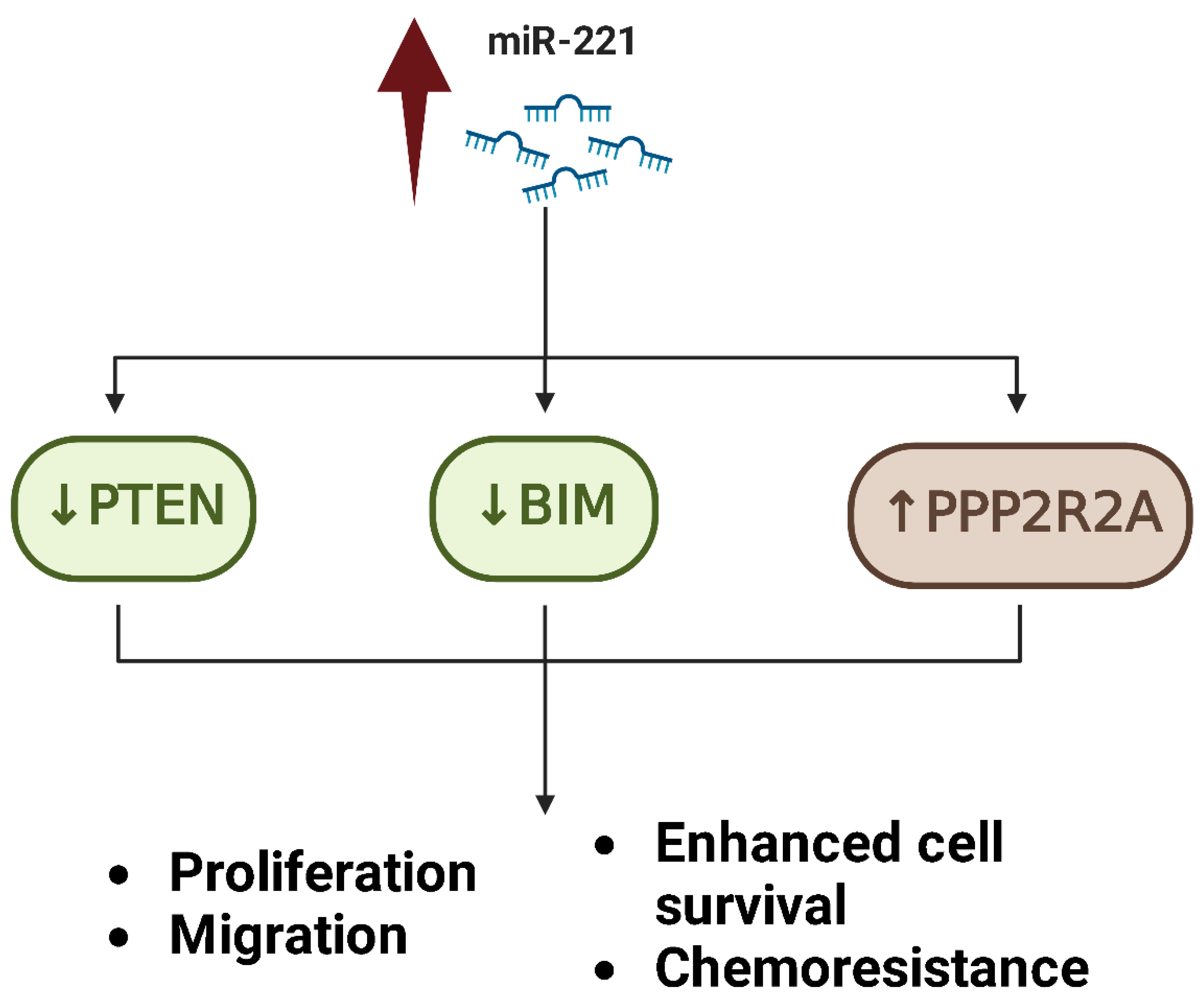
- Zhu, J.; Liu, F.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X. MiR-221 Increases Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Migration Partly through the Downregulation of PTEN. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Cai, C.; Yang, T.; Qiu, X.; Liao, B.; Li, W.; Ji, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, H.; Guo, M.; et al. MicroRNA-221 Induces Cell Survival and Cisplatin Resistance through PI3K/Akt Pathway in Human Osteosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yao, W. MicroRNA-221-3p Is Related to Survival and Promotes Tumour Progression in Pancreatic Cancer: A Comprehensive Study on Functions and Clinicopathological Value. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Hao, J.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Yu, S.; You, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, J.; et al. High Level of MiR-221/222 Confers Increased Cell Invasion and Poor Prognosis in Glioma. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Li, L.B.; She, C.; Xie, Y.; Ge, D.W.; Dong, Q.R. MiR-299-5p Targets Cell Cycle to Promote Cell Proliferation and Progression of Osteosarcoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.P.; Huang, B.; Duan, J.H.; Yi, K.J.; Zhuang, Z.L. MiR-4295 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Osteosarcoma through Targeting Interferon Regulatory Factor 1. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevalova, A.M.; Gulyaeva, L.F.; Pustylnyak, V.O. Roles of Interferon Regulatory Factor 1 in Tumor Progression and Regression: Two Sides of a Coin. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2024, 25, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianwei, Z.; Fan, L.; Xiancheng, L.; Enzhong, B.; Shuai, L.; Can, L. MicroRNA 181a Improves Proliferation and Invasion, Suppresses Apoptosis of Osteosarcoma Cell. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 3331–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Guo, J.; Yu, Z.H.; Qian, W.; Ai, F.; Xiao, L.; Guo, X. MicroRNA-181a-5p Promotes Osteosarcoma Progression via PTEN/AKT Pathway. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2022, 2022, 3421600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. MicroRNA-34 Family: A Potential Tumor Suppressor and Therapeutic Candidate in Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, X.; He, J.; Cao, Q.; Du, D.; Zhan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Yuan, S.; Sun, L. The Comprehensive Landscape of MiR-34a in Cancer Research. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 925–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Gao, J.; Yang, T.; Ma, Q.; Qiu, X.; Fan, Q.; Ma, B. MicroRNA-34a Inhibits the Proliferation and Metastasis of Osteosarcoma Cells Both In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Zhao, Y.K.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.F. MicroRNA-34a Inhibits Tumor Invasion and Metastasis in Osteosarcoma Partly by Effecting C-IAP2 and Bcl-2. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.C.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Wu, J. MiR-34a Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cells In Vitro through up-Regulation of c-Myc and Bim Signal. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 21, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhong, D.; Gao, Q.; Zhai, W.; Ding, Z.; Wu, J. MicroRNA-34a Inhibits Human Osteosarcoma Proliferation by Downregulating Ether à Go-Go 1 Expression. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, M.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, W. Long Non-Coding RNA TUG1 Promotes Migration and Invasion by Acting as a CeRNA of MiR-335-5p in Osteosarcoma Cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, G.; Gao, T.; Guo, W. miR-335 Negatively Regulates Osteosarcoma Stem Cell-like Properties by Targeting POU5F1. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Fu, Q. MiR-335 Suppresses Migration and Invasion by Targeting ROCK1 in Osteosarcoma Cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2013, 384, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Zeng, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, H.; Zhao, W. MicroRNA-335 and Its Target Rock1 Synergistically Influence Tumor Progression and Prognosis in Osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3057–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Qi, H.; Zhu, H. Hsa-MiR-199b-3p Suppresses Osteosarcoma Progression by Targeting CCDC88A, Inhibiting Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition, and Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Choy, E.; Harmon, D.; Liu, X.; Susa, M.; Mankin, H.; Hornicek, F. MicroRNA-199a-3p Is Downregulated in Human Osteosarcoma and Regulates Cell Proliferation and Migration. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, H.; Gu, G.; Hou, D.; You, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiao, G. Exosomal MiR-199a-5p Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Angiogenesis by Targeting VEGFA in Osteosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 884559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Yan, C.; Ya, J.; Yong, D.; Yujun, B.; Kai, L. MiR-199a-3p Affects the Multi-Chemoresistance of Osteosarcoma through Targeting AK4. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Shi, L.; Yuan, W.D. Tissue MicroRNA-126 Expression Level Predicts Outcome in Human Osteosarcoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tao, C.; He, A.; He, X. Overexpression of MiR-126 Sensitizes Osteosarcoma Cells to Apoptosis Induced by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; He, A.; He, X.; Tao, C. MicroRNA-126 Enhances the Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cells to Cisplatin and Methotrexate. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3769–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Qiu, X.; Zhuang, M.; Zhu, C.; Zou, H.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, D.; Qiu, X.; Zhuang, M.; Zhu, C.; et al. MicroRNAs with Prognostic Significance in Osteosarcoma: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81062–81074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; He, A.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, C. MiR-126 Inhibits Cell Growth, Invasion, and Migration of Osteosarcoma Cells by Downregulating ADAM-9. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 12645–12654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, G.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Shi, Z.W.; He, W. MicroRNA-126 Overexpression Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion in Osteosarcoma Cells. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, NP49–NP59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, R.; Osaka, E.; Sato, K.; Tokuhashi, Y. MiR-1 Suppresses Proliferation of Osteosarcoma Cells by Up-Regulating P21 via PAX3. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2019, 16, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Q.; Niu, D.; Liu, B. MiR-1 Inhibits Cell Growth, Migration, and Invasion by Targeting VEGFA in Osteosarcoma Cells. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 7068986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, C.; Pazzaglia, L.; Cingolani, C.; Conti, A.; Quattrini, I.; Manara, M.C.; Tognon, M.; Picci, P.; Benassi, M.S. MiRNA Expression Profile in Human Osteosarcoma: Role of MiR-1 and MiR-133b in Proliferation and Cell Cycle Control. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, M.; Ou, L.; Hou, M.; Feng, T.; Huang, Y.E.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, G. Biological Analysis of Cancer Specific MicroRNAs on Function Modeling in Osteosarcoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
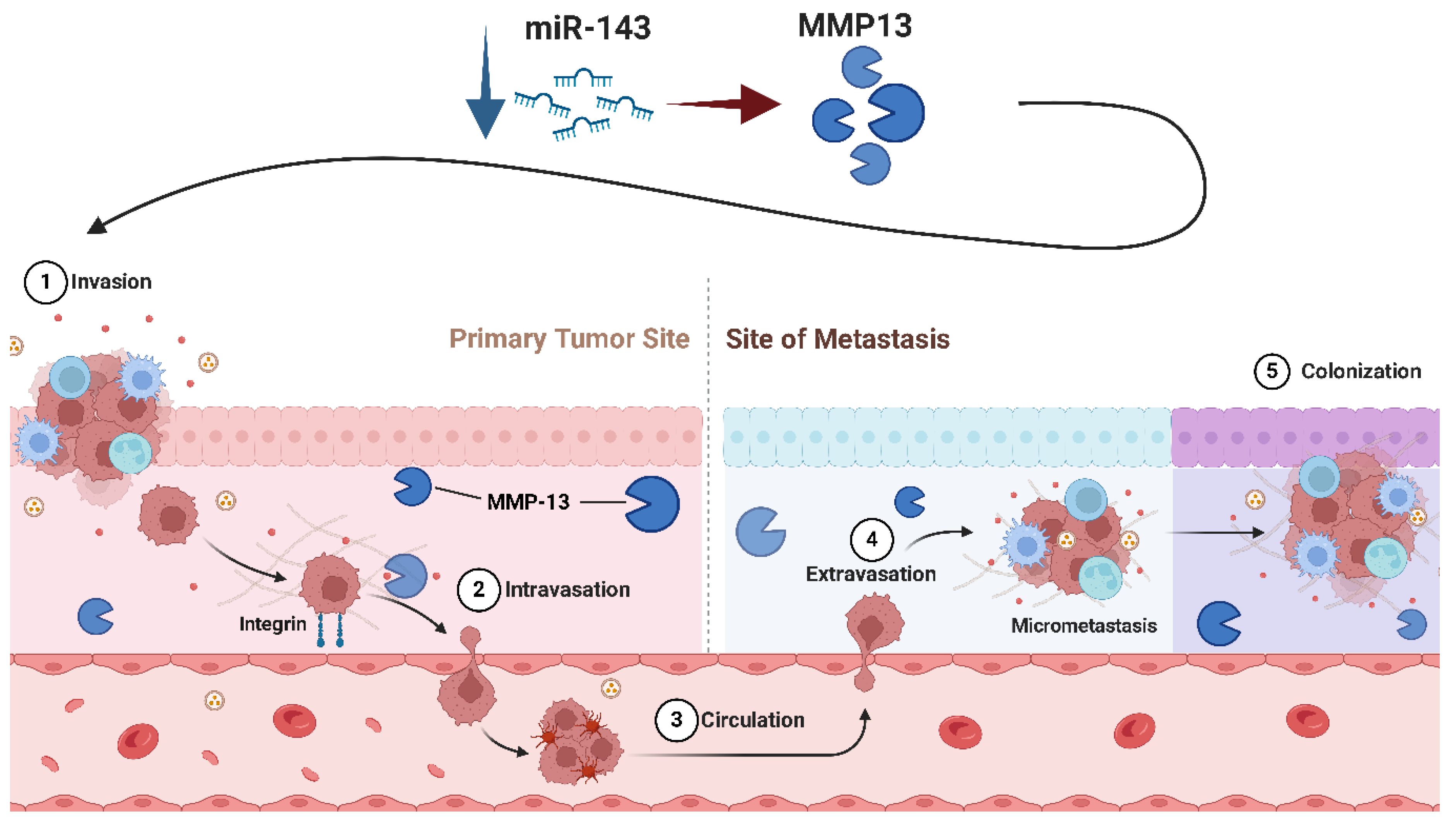
- Osaki, M.; Takeshita, F.; Sugimoto, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kobayashi, E.; Yamada, T.; Kawai, A.; Inoue, T.; et al. MicroRNA-143 Regulates Human Osteosarcoma Metastasis by Regulating Matrix Metalloprotease-13 Expression. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
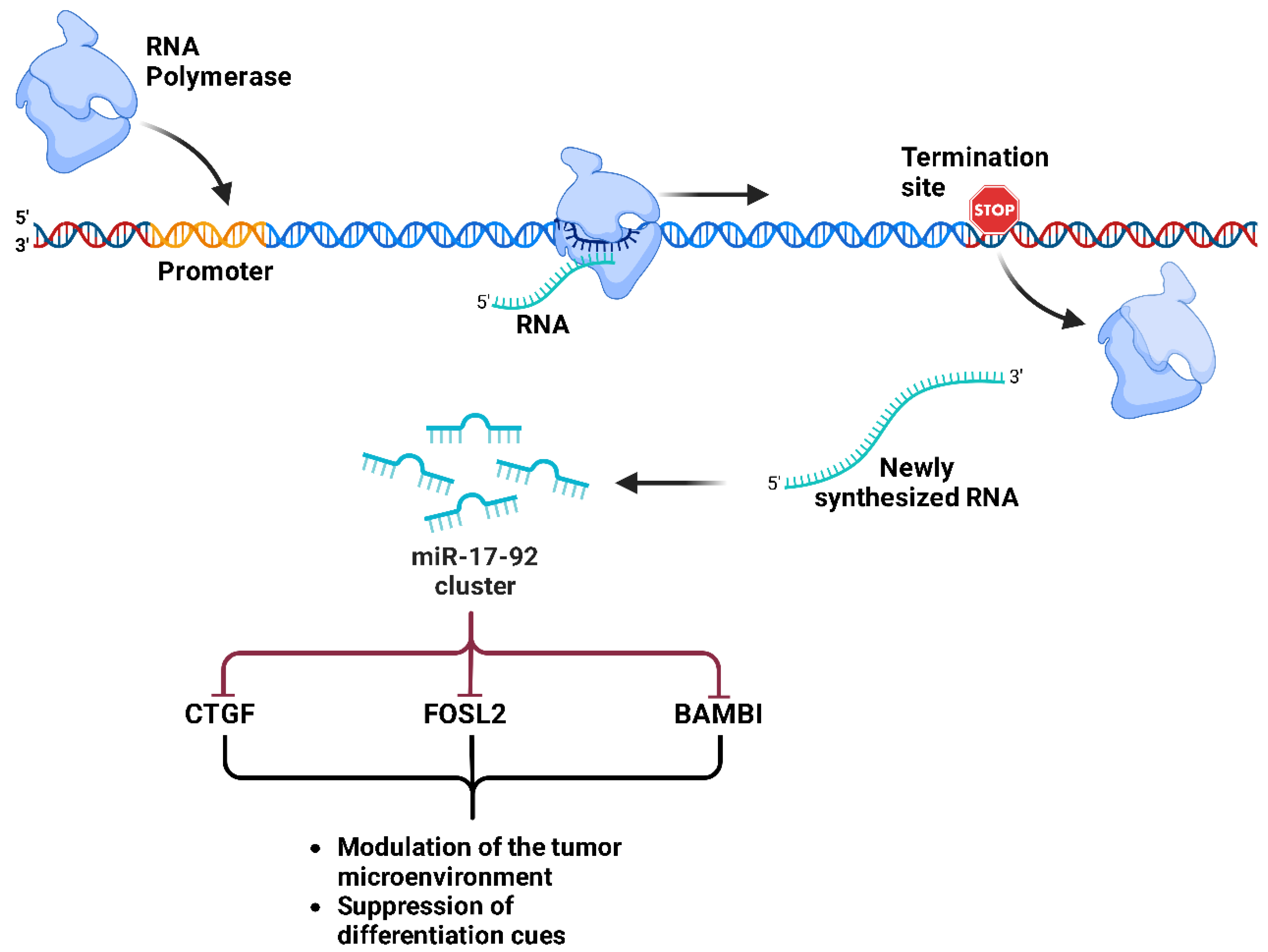
- Sun, X.; Dai, G.; Yu, L.; Hu, Q.; Chen, J.; Guo, W. MiR-143-3p Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Osteosarcoma by Targeting FOSL2. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Effect of MiR-143 on the Apoptosis of Osteosarcoma Cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Quan, H.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y. MicroRNA-143 Expression Inhibits the Growth and the Invasion of Osteosarcoma. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cai, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, C.; Zhao, J. MiR-143 Inhibits EGFR-Signaling-Dependent Osteosarcoma Invasion. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 12743–12748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Tong, D.; Ji, F. MicroRNA-143, down-Regulated in Osteosarcoma, Promotes Apoptosis and Suppresses Tumorigenicity by Targeting Bcl-2. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. MicroRNA-143 Is Associated with the Survival of ALDH1+CD133+ Osteosarcoma Cells and the Chemoresistance of Osteosarcoma. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yan, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Liang, W. Clinical Significance of Tumor MiR-21, MiR-221, MiR-143, and MiR-106a as Biomarkers in Patients with Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2019, 34, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Zhong, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, J. Non-Coding RNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Osteosarcoma. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1028477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Lin, L.; Cai, H.; Tang, J.; Zhou, Z. MicroRNA-145 Downregulation Associates with Advanced Tumor Progression and Poor Prognosis in Patients Suffering Osteosarcoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2013, 6, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, P.; Liang, J.; Yu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J.; Li, K. MiR-145 Promotes Osteosarcoma Growth by Reducing Expression of the Transcription Factor Friend Leukemia Virus Integration 1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42241–42251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zeng, M.; Yang, L.; Tan, J.; Yang, J.; Guan, H.; Kuang, M.; Li, J. Hsa_circ_0008934 Promotes the Proliferation and Migration of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting MiR-145-5p to Enhance E2F3 Expression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 127, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Pan, R.; Lu, Q.; Ren, C.; Sun, J.; Wu, H.; Wen, J.; Chen, H. MicroRNA-145-5p Inhibits Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation by Targeting E2F Transcription Factor 3. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. MicroRNA-145 Suppresses Osteosarcoma Metastasis via Targeting MMP16. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, C.; Gao, S. MicroRNA-524-5p Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Cell Cycle Arrest of Osteosarcoma Cells via Targeting CDK6. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 530, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
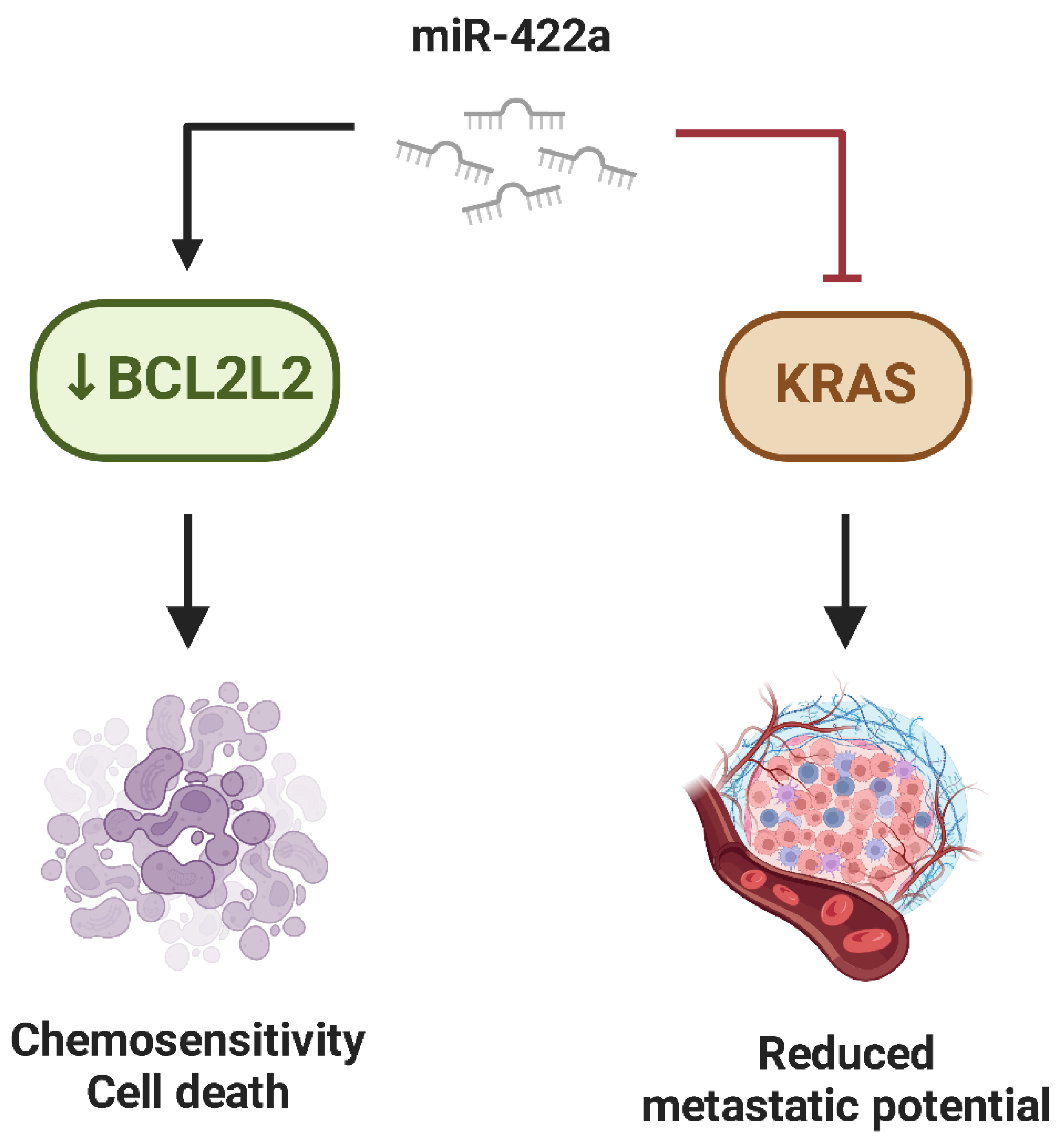
- Liu, M.; Xiusheng, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Y. Overexpression of MiR-422a Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Invasion, and Enhances Chemosensitivity in Osteosarcoma Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 3371–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Q.Y.; Wang, G.C.; Tong, D.K.; Wang, R.K.; Ding, W.B.; Li, C.; Wei, Q.; Ding, C.; Liu, P.Z.; et al. MiR-422a Inhibits Osteosarcoma Proliferation by Targeting BCL2L2 and KRAS. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F. DNA Methylation Mediated Downregulation of MiR-449c Controls Osteosarcoma Cell Cycle Progression by Directly Targeting Oncogene c-Myc. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhao, T. MiR-125b Functions as a Tumor Suppressor and Enhances Chemosensitivity to Cisplatin in Osteosarcoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, NP105–NP112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.M.; Catchpoole, D.; Hutvagner, G. Non-Coding RNAs in Pediatric Solid Tumors. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Xiong, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, L.H. MiR-125b Suppresses the Carcinogenesis of Osteosarcoma Cells via the MAPK-STAT3 Pathway. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 2616–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y. Association of Circulating MiR-125b and Survival in Patients with Osteosarcoma–A Single Center Experience. J. Bone Oncol. 2016, 5, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobat, L.; Gourbault, O. Role of MicroRNAs in Human Osteosarcoma: Future Perspectives. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
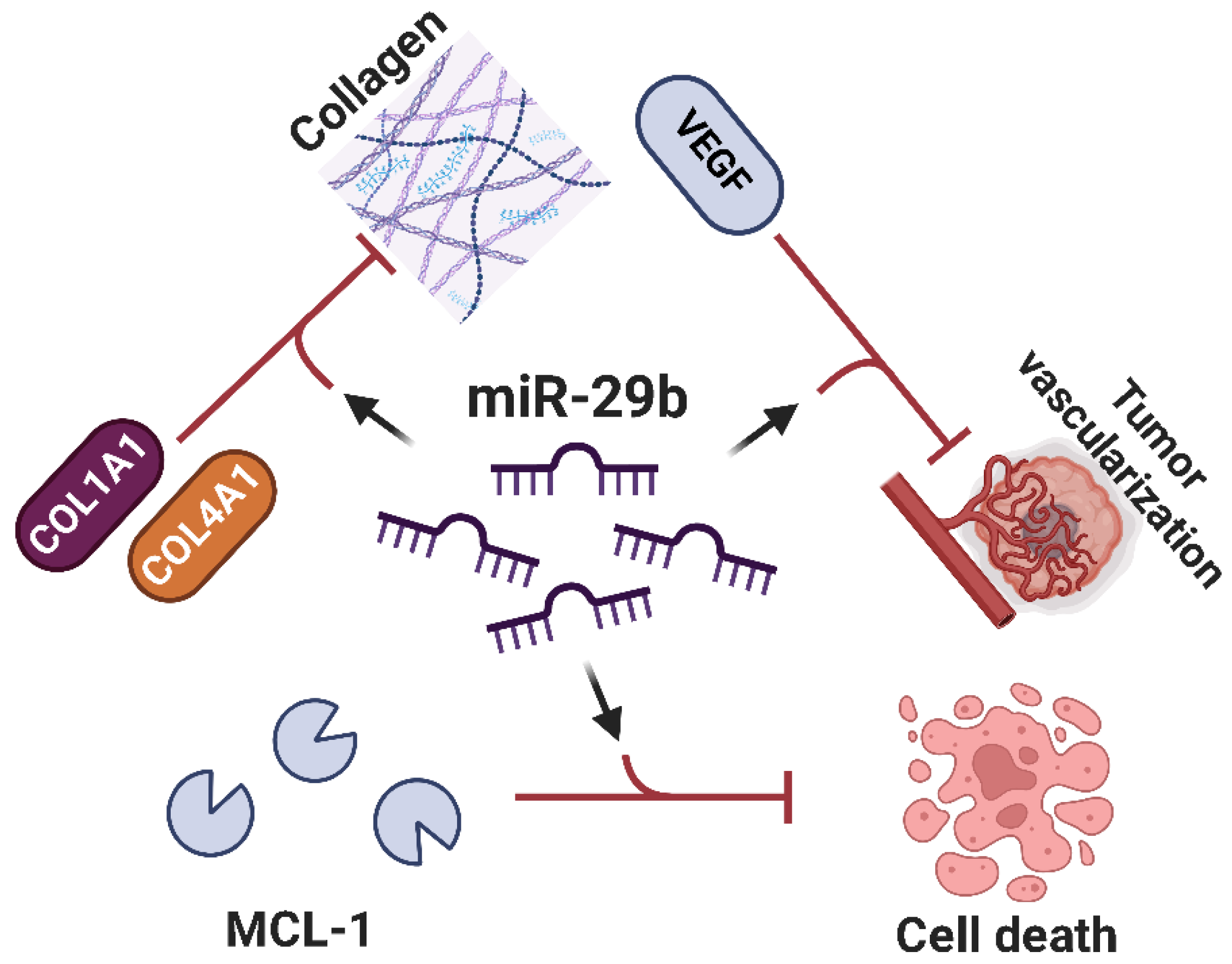
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J. A Key Role of MicroRNA-29b in Suppression of Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation and Migration via Modulation of VEGF. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5701. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.J.; Li, L.J.; Huo, H.F.; Liu, X.Q.; Cui, H.W.; Jiang, D.M. MicroRNA-29b Sensitizes Osteosarcoma Cells to Doxorubicin by Targeting Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) in Osteosarcoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Vares, G.; Ohno, T.; Takahashi, A.; Uzawa, A.; Seo, S.-J.; Sai, S. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Enhancement of Carbon Ion Beam Radiosensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cells by MiR-29b. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4357–4371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Fan, G.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, G. MiR-29b Suppresses the Proliferation and Migration of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting CDK6. Protein Cell 2016, 7, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, F.E.; Dosta, P.; Shanley, L.C.; Ramirez Tamez, N.; Riojas Javelly, C.J.; Mahon, O.R.; Kelly, D.J.; Artzi, N. Localized Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of MiR-29b Normalizes the Dysregulation of Bone Homeostasis Caused by Osteosarcoma Whilst Simultaneously Inhibiting Tumor Growth. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2207877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Xu, R.; Xu, Y. MiR-29 Family Inhibits Resistance to Methotrexate and Promotes Cell Apoptosis by Targeting COL3A1 and MCL1 in Osteosarcoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 8812–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, D.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, D. LncRNA FGD5-AS1 Potentiates Autophagy-Associated Doxorubicin Resistance by Regulating the MiR-154-5p/WNT5A Axis in Osteosarcoma. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhou, L.; Dai, Z.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Upregulation of MiRNA-154-5p Prevents the Tumorigenesis of Osteosarcoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sias, F.; Zoroddu, S.; Migheli, R.; Bagella, L. Untangling the Role of MYC in Sarcomas and Its Potential as a Promising Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey, E.L.; Parrish, J.K.; Irwin, A.E.; Niemeyer, B.F.; Kern, H.B.; Birks, D.K.; Jedlicka, P. A Novel Oncogenic Mechanism in Ewing Sarcoma Involving IGF Pathway Targeting by EWS/Fli1-Regulated MicroRNAs. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4910–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, T.P.; Smith, A.; McKinsey, E.; Reaves, L.; Jedlicka, P.; Ford, H.L. EWS/FLI1 Regulates EYA3 in Ewing Sarcoma via Modulation of MiRNA-708, Resulting in Increased Cell Survival and Chemoresistance. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vito, C.; Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.L.; Janiszewska, M.; Horlbeck, J.; Baumer, K.; Provero, P.; Stamenkovic, I. Let-7a Is a Direct EWS-FLI-1 Target Implicated in Ewing’s Sarcoma Development. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yu, X.; Shen, J.; Wu, W.K.K.; Chan, M.T.V. MicroRNA Expression and Its Clinical Implications in Ewing’s Sarcoma. Cell Prolif. 2015, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Sims, M.; Yue, J.; Wang, Y.; Linga, V.G.; Paulus, E.; Davidoff, A.M.; Pfeffer, L.M. The Oncogenic MicroRNA-21 Inhibits the Tumor Suppressive Activity of FBXO11 to Promote Tumorigenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6037–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Shahzadi, S.; Malik, A.; Din, S.U.; Yasir, M.; Chun, W.; Kloczkowski, A. Oncomeric Profiles of MicroRNAs as New Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Ewing’s Sarcoma: A Composite Review. Genes 2023, 14, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parafioriti, A.; Bason, C.; Armiraglio, E.; Calciano, L.; Daolio, P.A.; Berardocco, M.; di Bernardo, A.; Colosimo, A.; Luksch, R.; Berardi, A.C. Ewing’s Sarcoma: An Analysis of MiRNA Expression Profiles and Target Genes in Paraffin-Embedded Primary Tumor Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwentner, R.; Herrero-Martin, D.; Kauer, M.O.; Mutz, C.N.; Katschnig, A.M.; Sienski, G.; Alonso, J.; Aryee, D.N.T.; Kovar, H. The Role of MiR-17-92 in the MiRegulatory Landscape of Ewing Sarcoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10980–10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; You, T.; Jing, J. MiR-125b Inhibits Cell Biological Progression of Ewing’s Sarcoma by Suppressing the PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway. Cell Prolif. 2014, 47, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.L.; Ren, W.H.; Ma, Y.; Xi, J.S.; Han, B. Circulating MiR-125b as a Biomarker of Ewing’s Sarcoma in Chinese Children. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 19049–19056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, K.; Fukushi, J.I.; Matsumoto, Y.; Oda, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Fujiwara-Okada, Y.; Hatano, M.; Nabashima, A.; Kamura, S.; et al. MiR-125b Develops Chemoresistance in Ewing Sarcoma/Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, J.K.; Sechler, M.; Winn, R.A.; Jedlicka, P. The Histone Demethylase KDM3A Is a MicroRNA-22-Regulated Tumor Promoter in Ewing Sarcoma. Oncogene 2013, 34, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Wu, L.; Ding, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zen, K. MicroRNA-30a Sensitizes Tumor Cells to Cis-Platinum via Suppressing Beclin 1-Mediated Autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4148–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, G.A.; Laud-Duval, K.; Bellanger, D.; Stern, M.H.; Sastre-Garau, X.; Delattre, O. MiR-30a-5p Connects EWS-FLI1 and CD99, Two Major Therapeutic Targets in Ewing Tumor. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3915–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viera, G.M.; Salomao, K.B.; de Sousa, G.R.; Baroni, M.; Delsin, L.E.A.; Pezuk, J.A.; Brassesco, M.S. MiRNA Signatures in Childhood Sarcomas and Their Clinical Implications. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 21, 1583–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
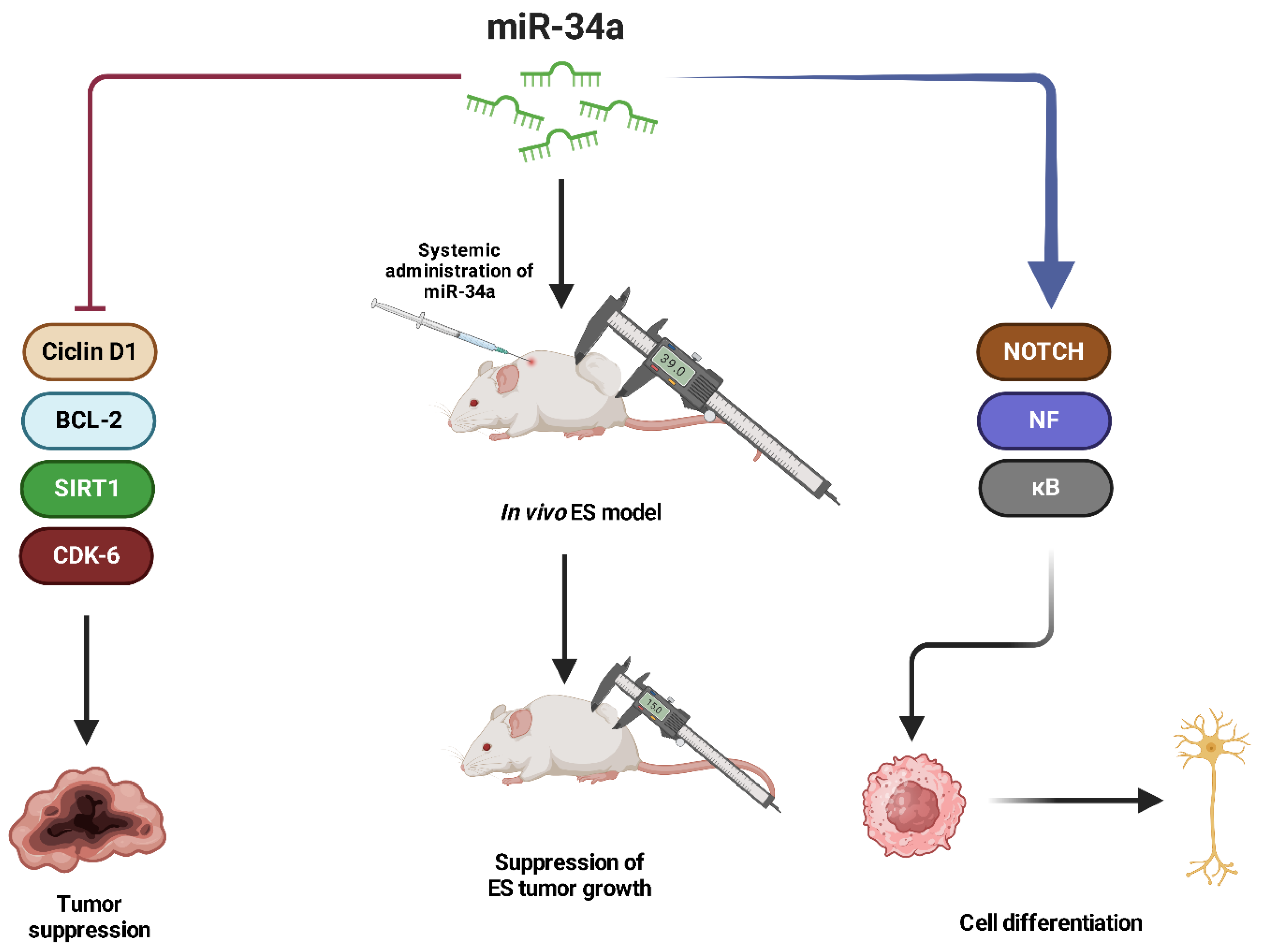
- Sciandra, M.; De Feo, A.; Parra, A.; Landuzzi, L.; Lollini, P.L.; Manara, M.C.; Mattia, G.; Pontecorvi, G.; Baricordi, C.; Guerzoni, C.; et al. Circulating MiR34a Levels as a Potential Biomarker in the Follow-up of Ewing Sarcoma. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2020, 14, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.F.; Yuan, Y.; Tu, M.J.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.Z.; Yi, W.R.; Li, P.C.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, A.M.; et al. The Optimal Outcome of Suppressing Ewing Sarcoma Growth In Vivo with Biocompatible Bioengineered MiR-34a-5p Prodrug. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.; Aryee, D.N.T.; Felicetti, F.; De Feo, A.; Mancarella, C.; Manara, M.C.; Picci, P.; Colombo, M.P.; Kovar, H.; Care, A.; et al. CD99 Regulates Neural Differentiation of Ewing Sarcoma Cells through MiR-34a-Notch-Mediated Control of NF-ΚB Signaling. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3944–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.T.; Grilli, A.; Baricordi, C.; Manara, M.C.; Ventura, S.; Pinca, R.S.; Bellenghi, M.; Calvaruso, M.; Mattia, G.; Donati, D.; et al. Prognostic Significance of MiR-34a in Ewing Sarcoma Is Associated with Cyclin D1 and Ki-67 Expression. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2080–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, F.; Ferracin, M.; Manara, M.C.; Ventura, S.; Del Monaco, V.; Ferrari, S.; Alberghini, M.; Grilli, A.; Knuutila, S.; Schaefer, K.L.; et al. MiR-34a Predicts Survival of Ewing’s Sarcoma Patients and Directly Influences Cell Chemo-Sensitivity and Malignancy. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, F.; Ren, T.; Tang, X. METTL3-Modified LncRNA-MALAT1 Regulates the Molecular Axis of MiR-124-3p/CDK4 Involved in Ewing’s Sarcoma. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-Le-Grand) 2023, 69, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, G.M.; Delsin, L.E.A.; Vieira, G.M.; Silva, M.O.; Hakime, R.G.; Gava, N.F.; Engel, E.E.; Scrideli, C.A.; Tone, L.G.; Brassesco, M.S. ROCK1-PredictedmicroRNAs Dysregulation Contributes to Tumor Progression in Ewing Sarcoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shao, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, B.; He, C.; Zhang, Z. MiR-124 Represses the Mesenchymal Features and Suppresses Metastasis in Ewing Sarcoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10274–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanoglu, E.G.; Ozturk, S. MiR-145 Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Targeting Stem Cells in Ewing Sarcoma Cells. Bratisl. Med. J. 2021, 122, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Martin, D.; Fourtouna, A.; Niedan, S.; Riedmann, L.T.; Schwentner, R.; Aryee, D.N.T. Factors Affecting EWS-FLI1 Activity in Ewing’s Sarcoma. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 352580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, J.; Jug, G.; Mestdagh, P.; Schwentner, R.; Kauer, M.; Aryee, D.N.T.; Schaefer, K.L.; Nakatani, F.; Scotlandi, K.; Reiter, M.; et al. Hsa-Mir-145 Is the Top EWS-FLI1-Repressed MicroRNA Involved in a Positive Feedback Loop in Ewing’s Sarcoma. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.; Parrish, J.K.; Jedlicka, P. MiR-193b, Downregulated in Ewing Sarcoma, Targets the ErbB4 Oncogene to Inhibit Anchorage-Independent Growth. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Jiao, G.J.; Wang, H.L.; Yan, T. Bin MiR-185 Suppresses Progression of Ewing’s Sarcoma via Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathways. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 7967–7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameiri-Grossman, M.; Porat-Klein, A.; Yaniv, I.; Ash, S.; Cohen, I.J.; Kodman, Y.; Haklai, R.; Elad-Sfadia, G.; Kloog, Y.; Chepurko, E.; et al. The Association between Let-7, RAS and HIF-1α in Ewing Sarcoma Tumor Growth. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33834–33848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Kawano, M.; Itonaga, I.; Iwasaki, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Ikeda, S.; Tsumura, H. Tumor Suppressive MicroRNA-138 Inhibits Metastatic Potential via the Targeting of Focal Adhesion Kinase in Ewing’s Sarcoma Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, T.; Shao, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. MiR-107 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Tube Formation of Ewing Sarcoma Cells Partly by Targeting HIF-1β. Hum. Cell 2018, 31, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, G.M.; Vieira, G.M.; Delsin, L.E.A.; Silva, M.d.O.; Hakime, R.G.; Engel, E.E.; Scrideli, C.A.; Tone, L.G.; Brassesco, M.S. MiR-708-5p Is Inversely Associated with EWS/FLI1 Ewing Sarcoma but Does Not Represent a Prognostic Predictor. Cancer Genet. 2019, 230, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, F.; Liu, X.Q.; Liu, H.C.; Dai, M.; Zeng, J. LncRNA TUG1 Promotes Ewing’s Sarcoma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion via the MiR-199a-3p-MSI2 Signaling Pathway. Neoplasma 2021, 68, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Feo, A.; Sciandra, M.; Ferracin, M.; Felicetti, F.; Astolfi, A.; Pignochino, Y.; Picci, P.; Carè, A.; Scotlandi, K. Exosomes from CD99-Deprived Ewing Sarcoma Cells Reverse Tumor Malignancy by Inhibiting Cell Migration and Promoting Neural Differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, J.L.; Turner, S.P. Bone Cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment Principles. Am. Fam. Physician 2018, 98, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, F.Y.; Onishi, A.C.; Hincker, A.M. Surmounting Chemotherapy and Radioresistance in Chondrosarcoma: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 381564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, S.; Mutlu, H.; Kirkbes, S.; Eroglu, S.; Kabukcuoglu, Y.S.; Kabukcuoglu, F.; Duymus, T.M.; Isik, M.; Ulasli, M. The Expression of MiR-181a-5p and MiR-371b-5p in Chondrosarcoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015; 19, 2384–2388. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Charbonneau, C.; Wei, L.; Chen, Q.; Terek, R.M. MiR-181a Targets RGS16 to Promote Chondrosarcoma Growth, Angiogenesis, and Metastasis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.H.; Yang, D.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, T.M.; Tang, C.H.; Huang, Y.L. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Suppresses Chondrosarcoma Metastasis by Upregulation of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase 3 through Suppressing MiR-101 Expression. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1380–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
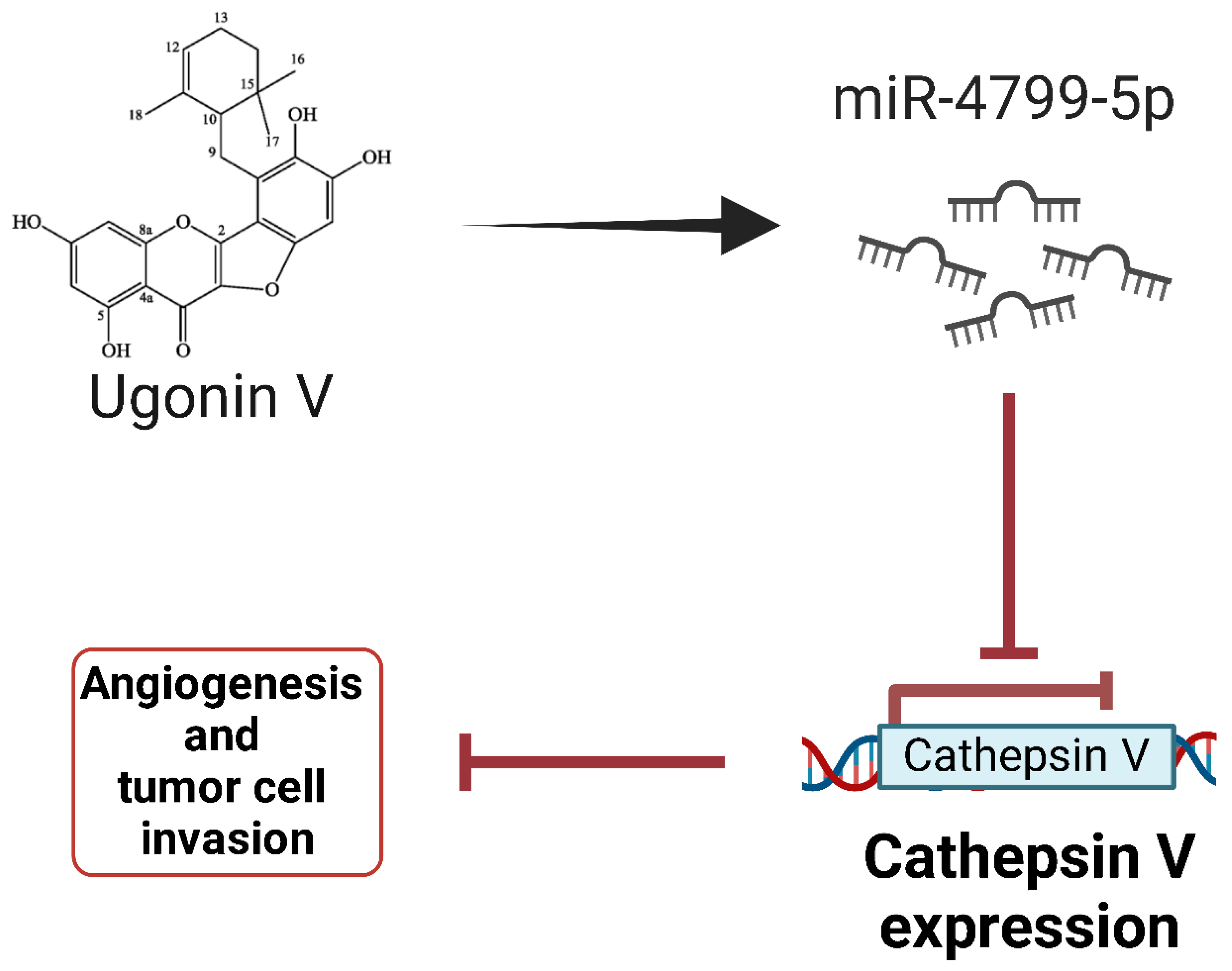
- Tran, N.B.; Chang, T.K.; Chi, N.D.P.; Lai, K.Y.; Chen, H.T.; Fong, Y.C.; Liaw, C.C.; Tang, C.H. Ugonin Inhibits Chondrosarcoma Metastasis through Suppressing Cathepsin V via Promoting MiR-4799-5p Expression. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2025, 21, 1144–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Ren, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Zheng, B.; Guo, W. Induction of the Mesenchymal to Epithelial Transition by Demethylation-Activated MicroRNA-125b Is Involved in the Anti-Migration/Invasion Effects of Arsenic Trioxide on Human Chondrosarcoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Zheng, W.; Ding, M.; Guo, K.J.; Yuan, F.; Feng, H.; Deng, B.; Sun, W.; Hou, Y.; Gao, L. MiR-125b Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Chondrosarcoma Cells by the Sensitization to Doxorubicin through Direct Targeting the ErbB2-Regulated Glucose Metabolism. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2016, 10, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.S.; Tang, Y.J.; Pan, F. Inhibition of Src by MicroRNA-23b Increases the Cisplatin Sensitivity of Chondrosarcoma Cells. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 18, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zheng, X.; Shan, W.; Shan, Y. The Overexpression of MiR-30a Affects Cell Proliferation of Chondrosarcoma via Targeting Runx2. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 5933–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Lin, T.; Wang, L.; Qi, M.; Liu, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. Association of SOX4 Regulated by Tumor Suppressor MiR-30a with Poor Prognosis in Low-Grade Chondrosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 3843–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdinez, J.; Boro, A.; Mazumdar, A.; Arlt, M.J.E.; Muff, R.; Botter, S.M.; Bode-Lesniewska, B.; Fuchs, B.; Snedeker, J.G.; Gvozdenovic, A. The MiR-143/145 Cluster, a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker in Chondrosarcoma, Acts as a Tumor Suppressor and Directly Inhibits Fascin-1. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, I.W.Y.; Singh, S.; Turcotte, R.; Ghert, M. The Epigenetic Regulation of SOX9 by MiR-145 in Human Chondrosarcoma. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.T.; Huang, Y.L.; Tzeng, H.E.; Tsai, C.H.; Wang, S.W.; Tang, C.H. CCL5 Promotes Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Induces Angiogenesis by Down-Regulating MiR-199a in Human Chondrosarcoma Cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hsu, P.; Zhong, B.; Guo, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, C. MiR-34a Enhances Chondrocyte Apoptosis, Senescence and Facilitates Development of Osteoarthritis by Targeting DLL1 and Regulating PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.W.; Chou, Y.E.; Yang, W.H.; Hsu, C.J.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. Naringin Suppress Chondrosarcoma Migration through Inhibition Vascular Adhesion Molecule-1 Expression by Modulating MiR-126. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Naseri, B.; Khorramdelazad, H.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Ghorbaninezhad, F.; Asgari, Z.; Masoumi, J.; Nemati, M. Reciprocal Interactions Between Apelin and Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Progression. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Shih, H.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Guo, J.H.; Huang, C.; Huang, H.C.; Chong, Z.Y.; Tang, C.H. MicroRNA-631 Resensitizes Doxorubicin-Resistant Chondrosarcoma Cells by Targeting Apelin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veys, C.; Jammes, M.; Rédini, F.; Poulain, L.; Denoyelle, C.; Legendre, F.; Galera, P. Tumor Suppressive Role of MiR-342-5p and MiR-491-5p in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veys, C.; Benmoussa, A.; Contentin, R.; Duchemin, A.; Brotin, E.; Lafont, J.E.; Saintigny, Y.; Poulain, L.; Denoyelle, C.; Demoor, M.; et al. Tumor Suppressive Role of MiR-342-5p in Human Chondrosarcoma Cells and 3D Organoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
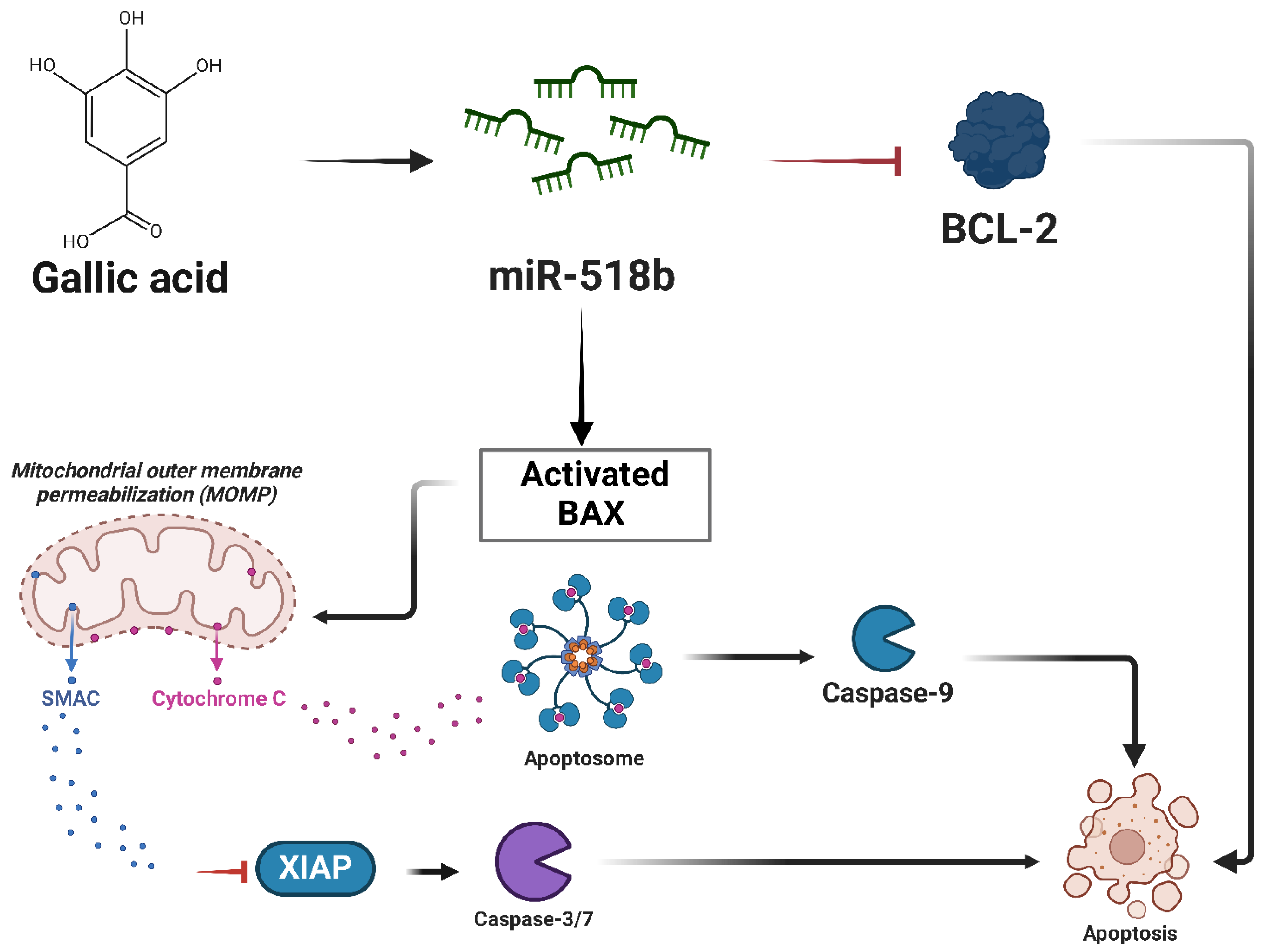
- Liang, W.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, B.; Gan, H.; Li, S.; Shen, J.; Kang, J.; Ding, S.; et al. Gallic Acid Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cell Migration by Upregulating MiR-518b in SW1353 Human Chondrosarcoma Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Ruan, G.; Ni, H.; Qin, H.; Chen, S.; Gu, X.; Shang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tao, X.; Zheng, L. Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Its Related MiRNAs in Tumor Progression. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 624725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrapin, S.; Moonmuang, S.; Udomruk, S.; Yongpitakwattana, P.; Pruksakorn, D.; Chaiyawat, P. Unlocking the Tumor-Immune Microenvironment in Osteosarcoma: Insights into the Immune Landscape and Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1394284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabeti Touchaei, A.; Vahidi, S. MicroRNAs as Regulators of Immune Checkpoints in Cancer Immunotherapy: Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 Pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


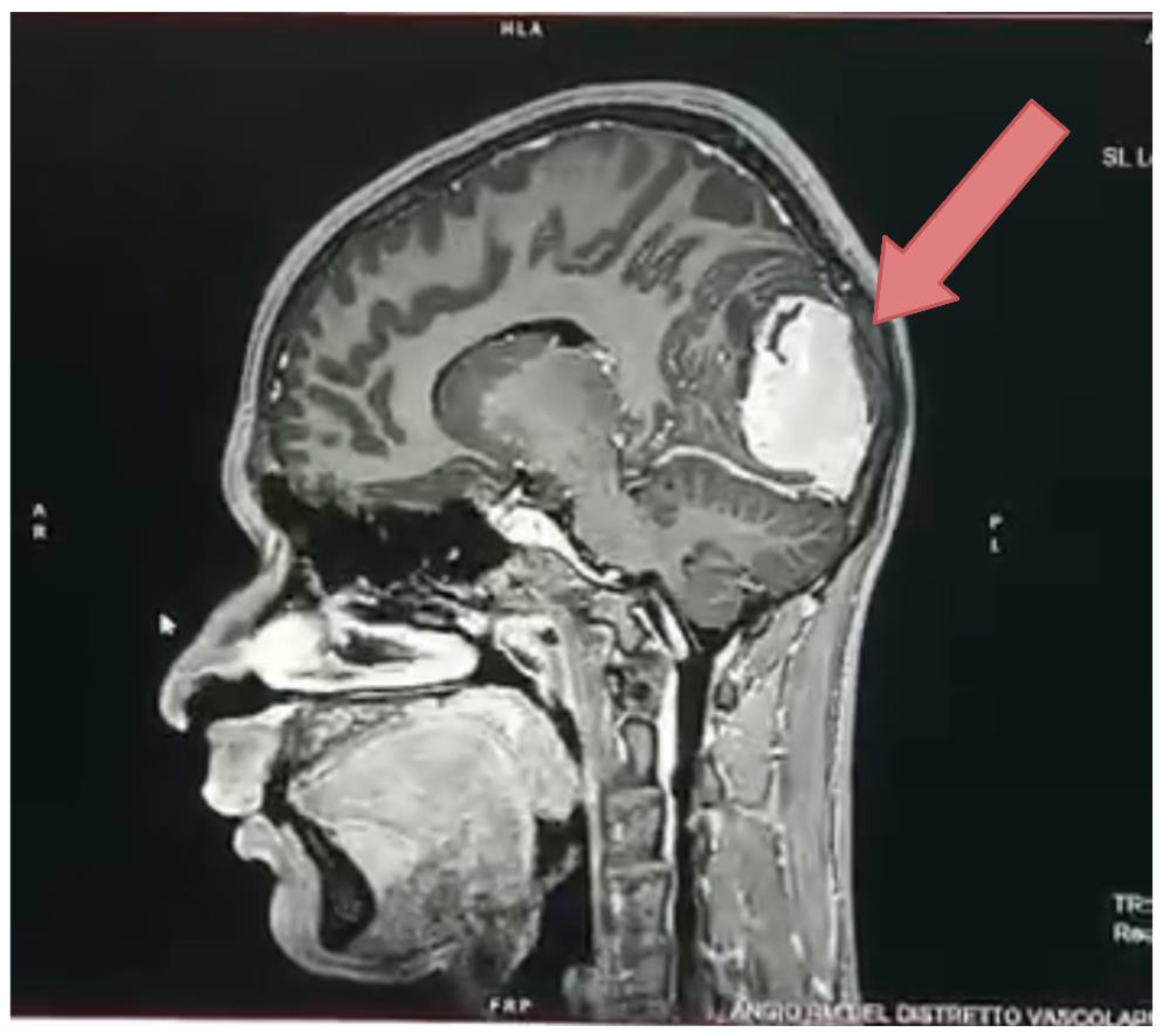
| Type of Bone Sarcoma | Incidence Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| Osteosarcoma | ~35–50% |
| Chondrosarcoma | ~20–25% |
| Ewing sarcoma | ~10–15% |
| Chordoma | ~3–5% |
| Fibrosarcoma of Bone | ~2–5% |
| Adamantinoma | <1% |
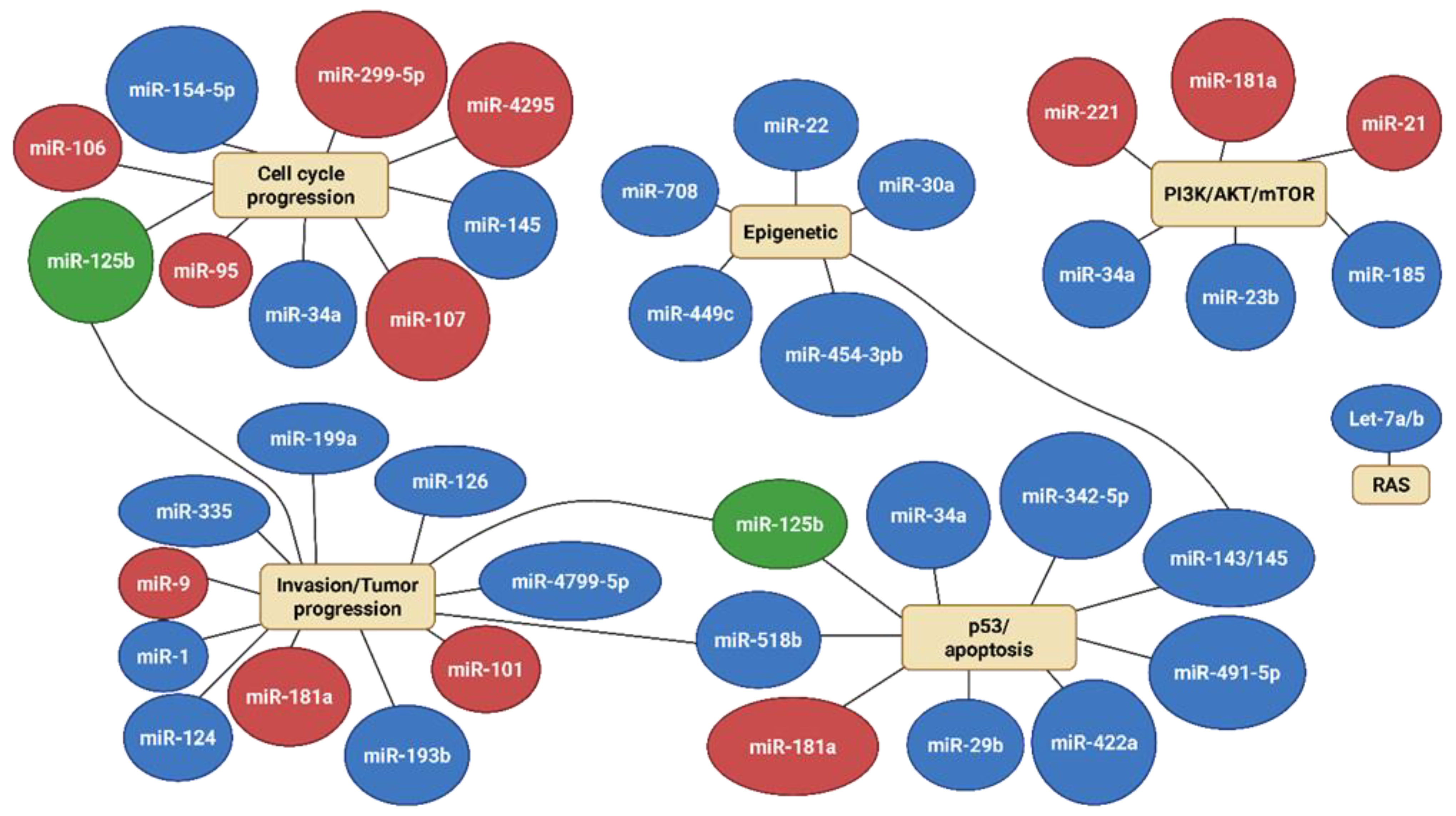
| miRNA | Role | Tumor |
|---|---|---|
| miR-9 | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-95 | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-106b | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-221 | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-299-5p | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-4295 | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-17-92 | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-30a-5p | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-181a | Oncogene | Osteosarcoma |
| Ewing’s sarcoma | ||
| Chondrosarcoma | ||
| miR-21 | Oncogene | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-30a | Oncogene | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma | |
| miR-17-92 | Oncogene | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-125b | Oncogene | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma | |
| Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma | |
| miR-101 | Oncogene | Chondrosarcoma |
| miR-34a | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| Ewing’s sarcoma | ||
| Chondrosarcoma | ||
| miR-335 | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-199a | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| Chondrosarcoma | ||
| miR-126 | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| Chondrosarcoma | ||
| miR-1 | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-143 | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| Chondrosarcoma | ||
| miR-145 | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| Ewing’s sarcoma | ||
| Chondrosarcoma | ||
| miR-422a | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-449c | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| Chondrosarcoma | ||
| miR-29b | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-154-5p | Tumor suppressor | Osteosarcoma |
| miR-22 | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-145 | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-193b | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-185 | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-138 | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| Let-7a/7b | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-107 | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-708 | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-199-3p | Tumor suppressor | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| miR-4799-5p | Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma |
| miR-23b | Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma |
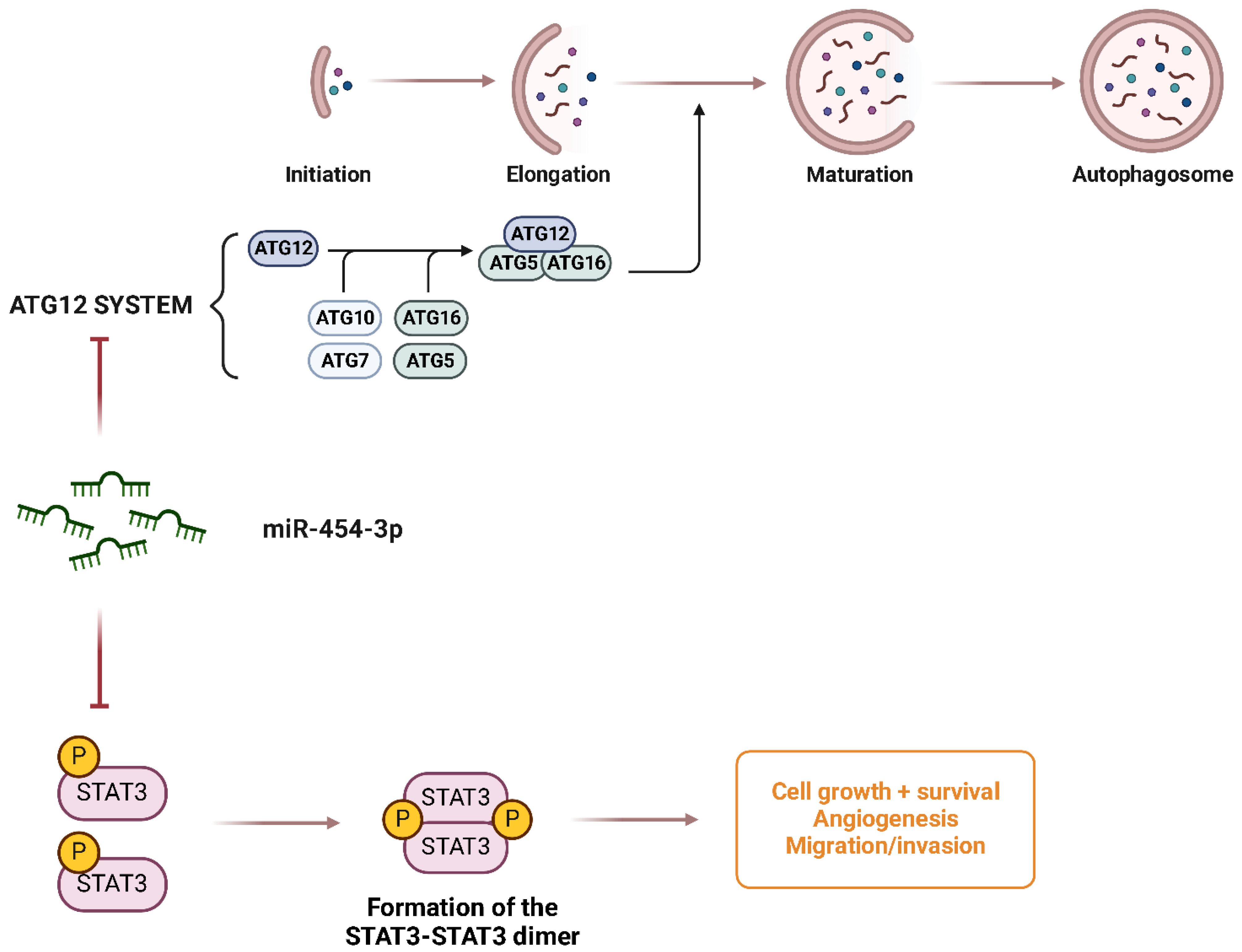
| miR-454-3b | Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma |
| miR-342-5p | Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma |
| miR-491-5p | Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma |
| miR-518b | Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma |
| miR-631 | Tumor suppressor | Chondrosarcoma |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zoroddu, S.; Sias, F.; Bagella, L. The Double Life of microRNAs in Bone Sarcomas: Oncogenic Drivers and Tumor Suppressors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104814
Zoroddu S, Sias F, Bagella L. The Double Life of microRNAs in Bone Sarcomas: Oncogenic Drivers and Tumor Suppressors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104814
Chicago/Turabian StyleZoroddu, Stefano, Fabio Sias, and Luigi Bagella. 2025. "The Double Life of microRNAs in Bone Sarcomas: Oncogenic Drivers and Tumor Suppressors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104814
APA StyleZoroddu, S., Sias, F., & Bagella, L. (2025). The Double Life of microRNAs in Bone Sarcomas: Oncogenic Drivers and Tumor Suppressors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104814







