OVA-Induced Food Allergy Leads to Neurobehavioral Changes in Mice and the Potential Role of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites Dysbiosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
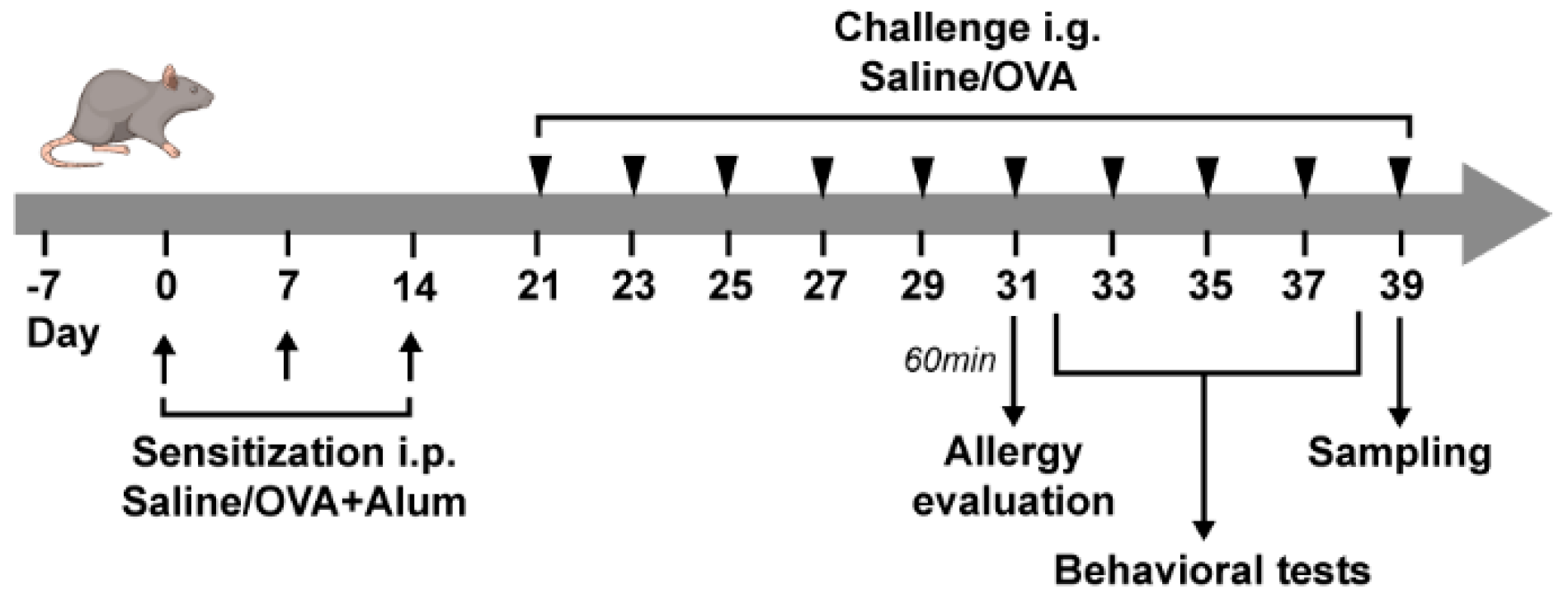
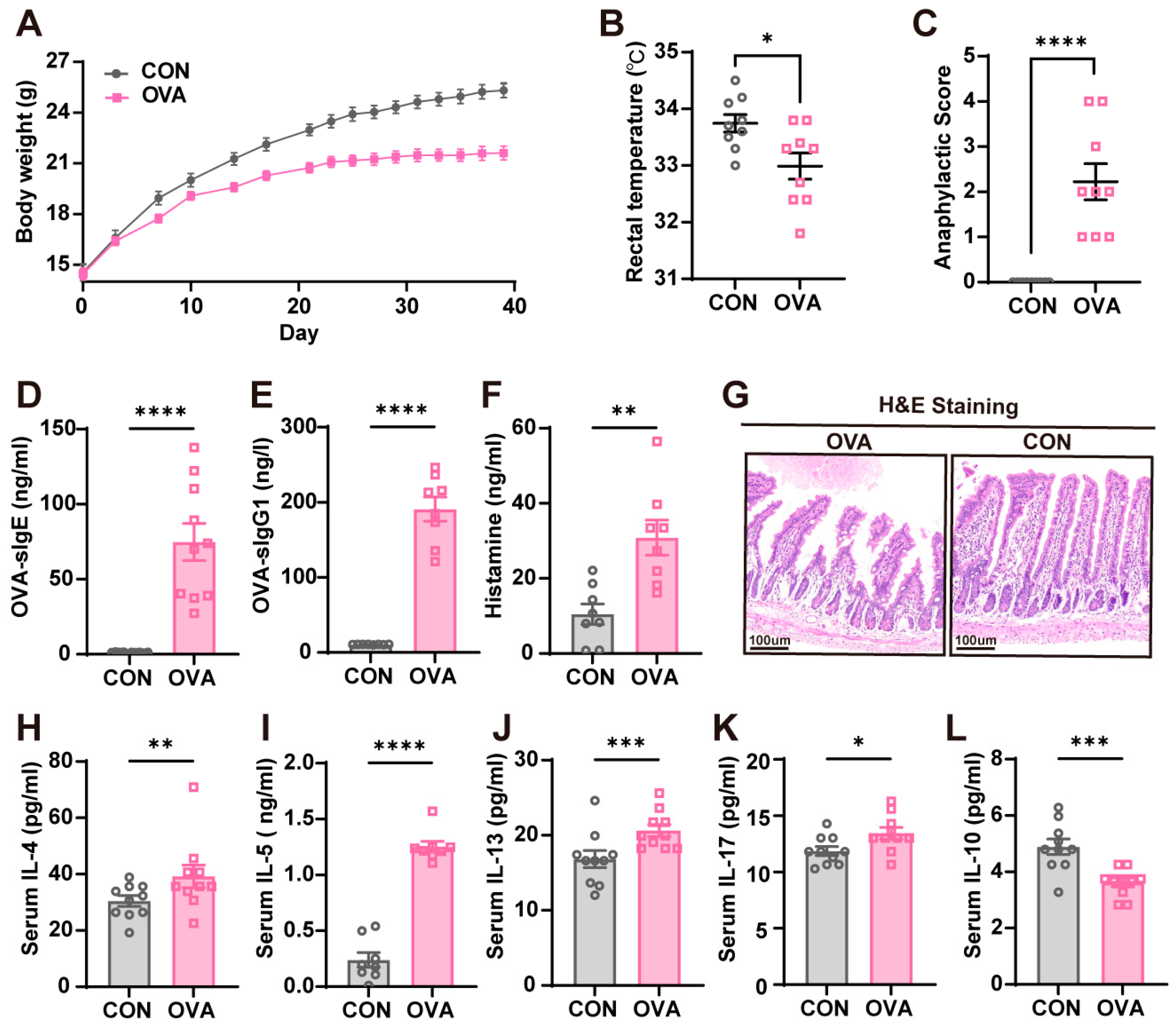
2.1. OVA-Induced Food Allergy Mouse Model
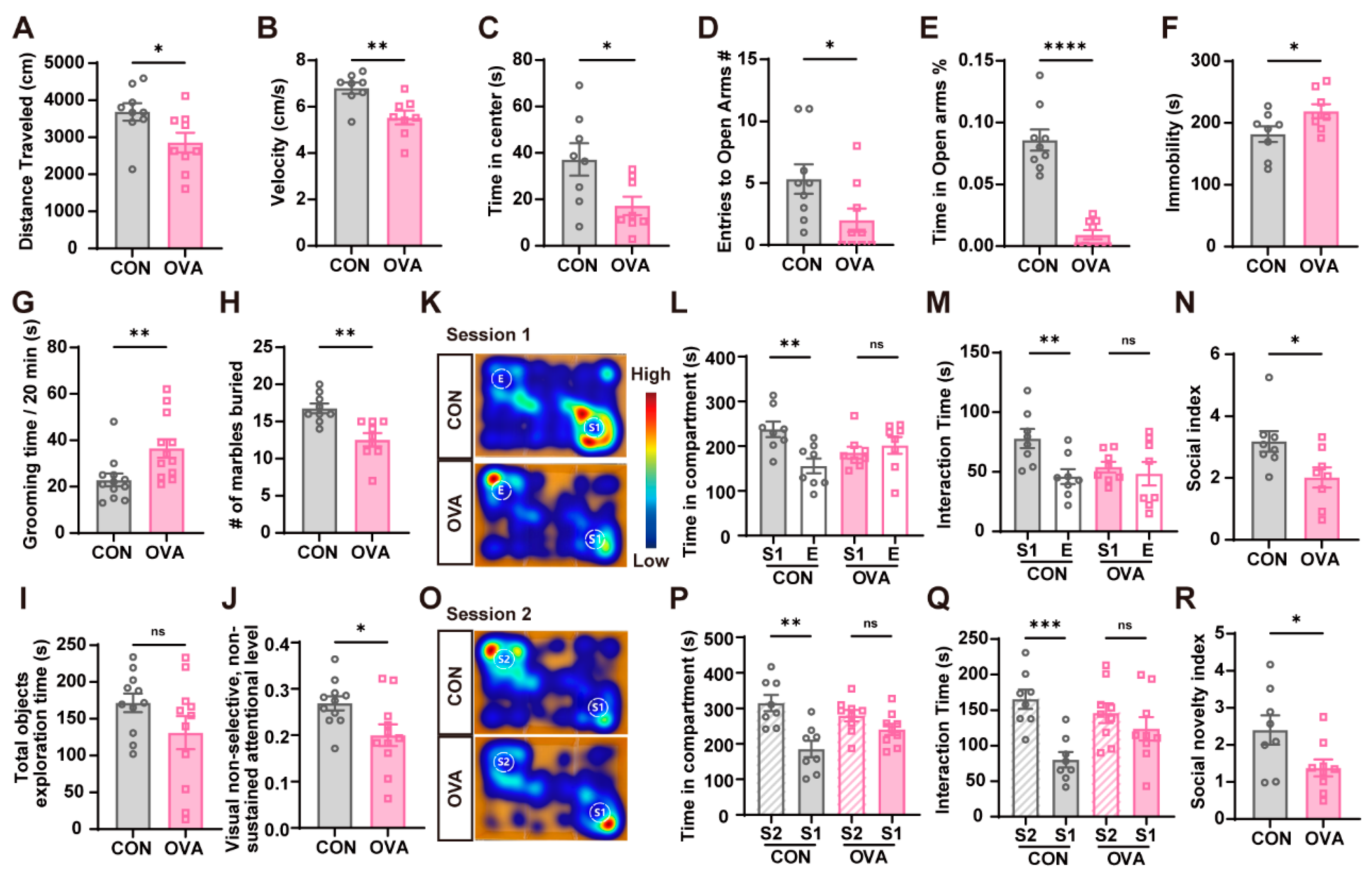
2.2. OVA Mice Exhibited Behavioral Abnormalities
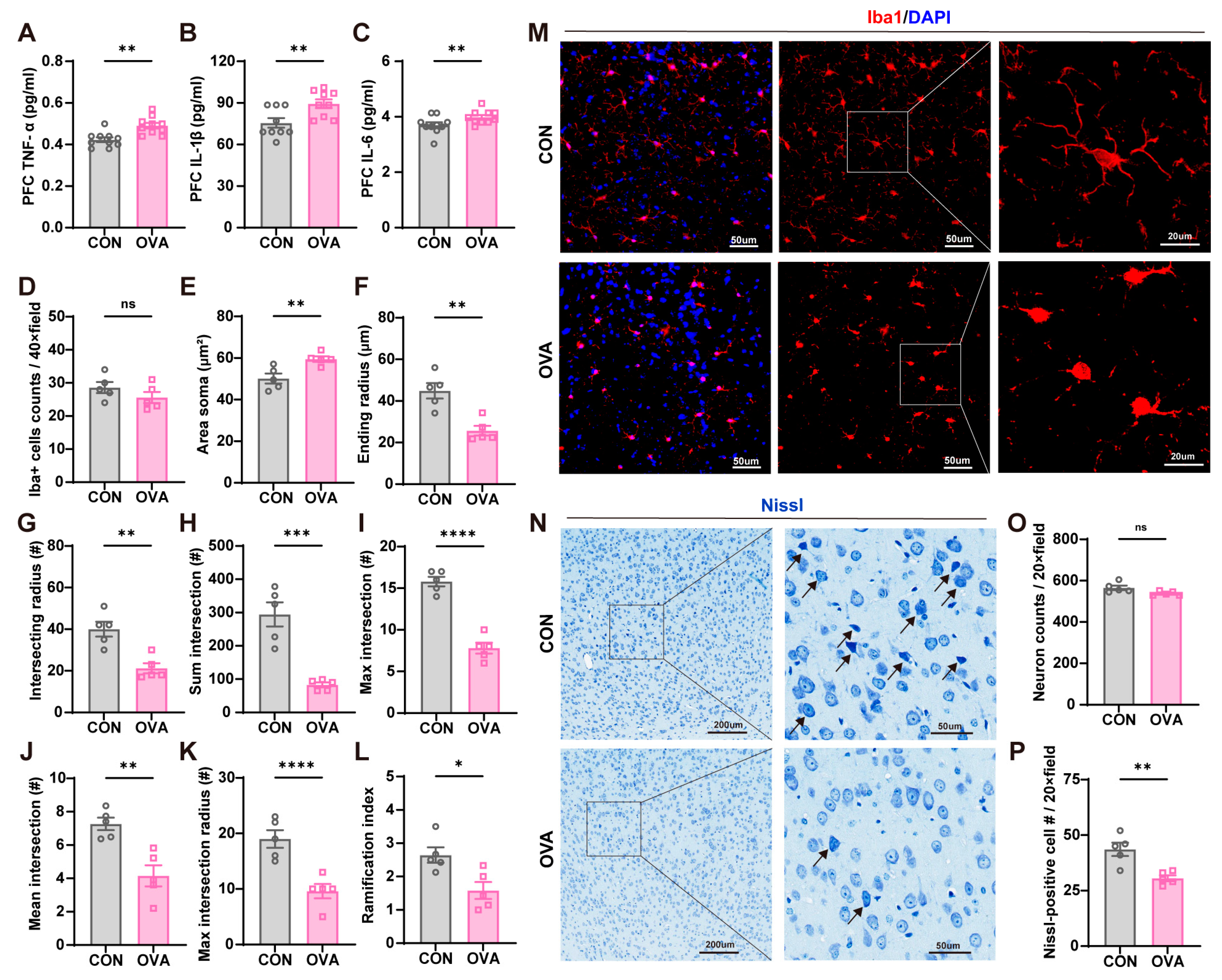
2.3. Food Allergy-Induced Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Damage
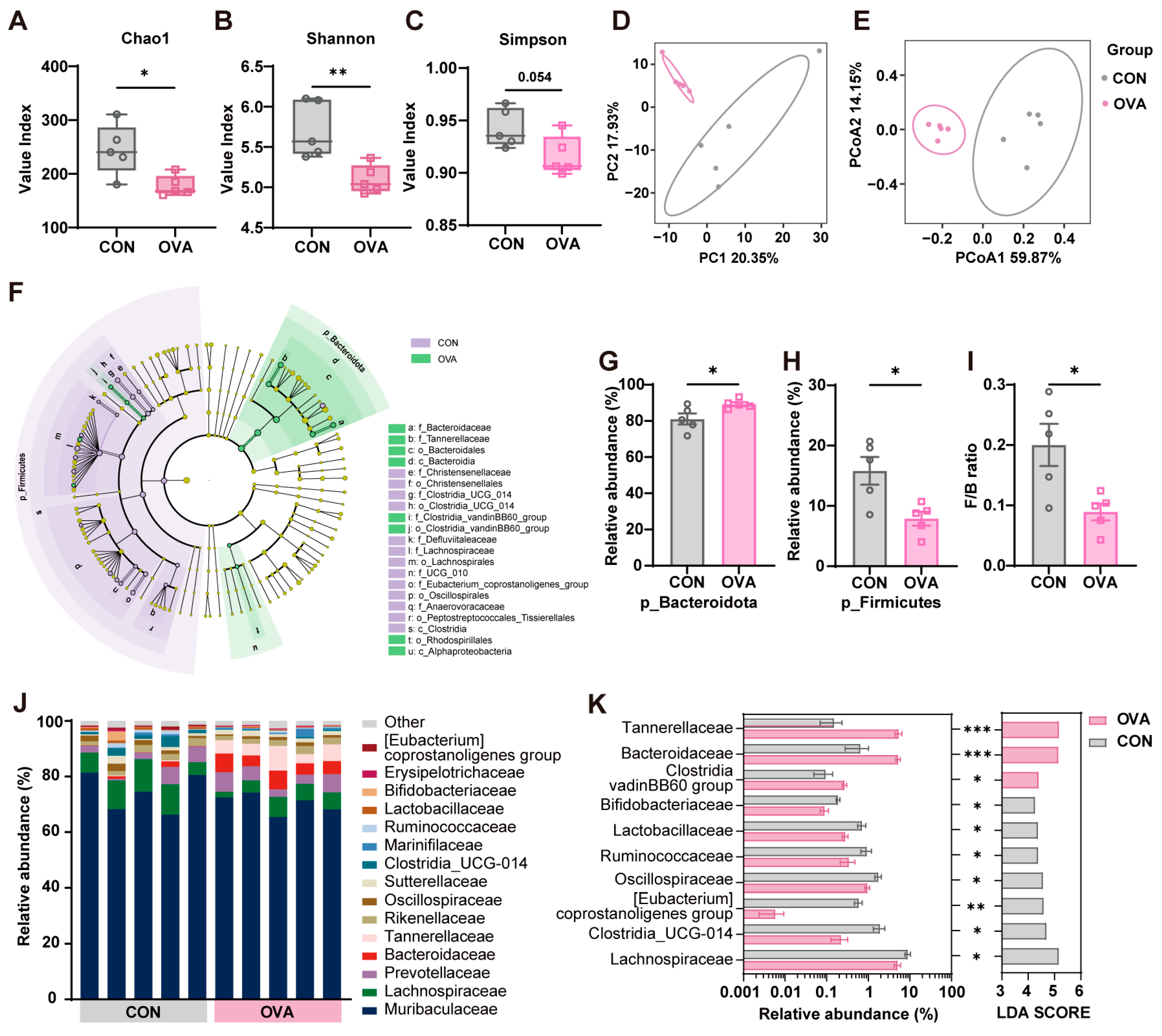
2.4. Food Allergy Induced Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis
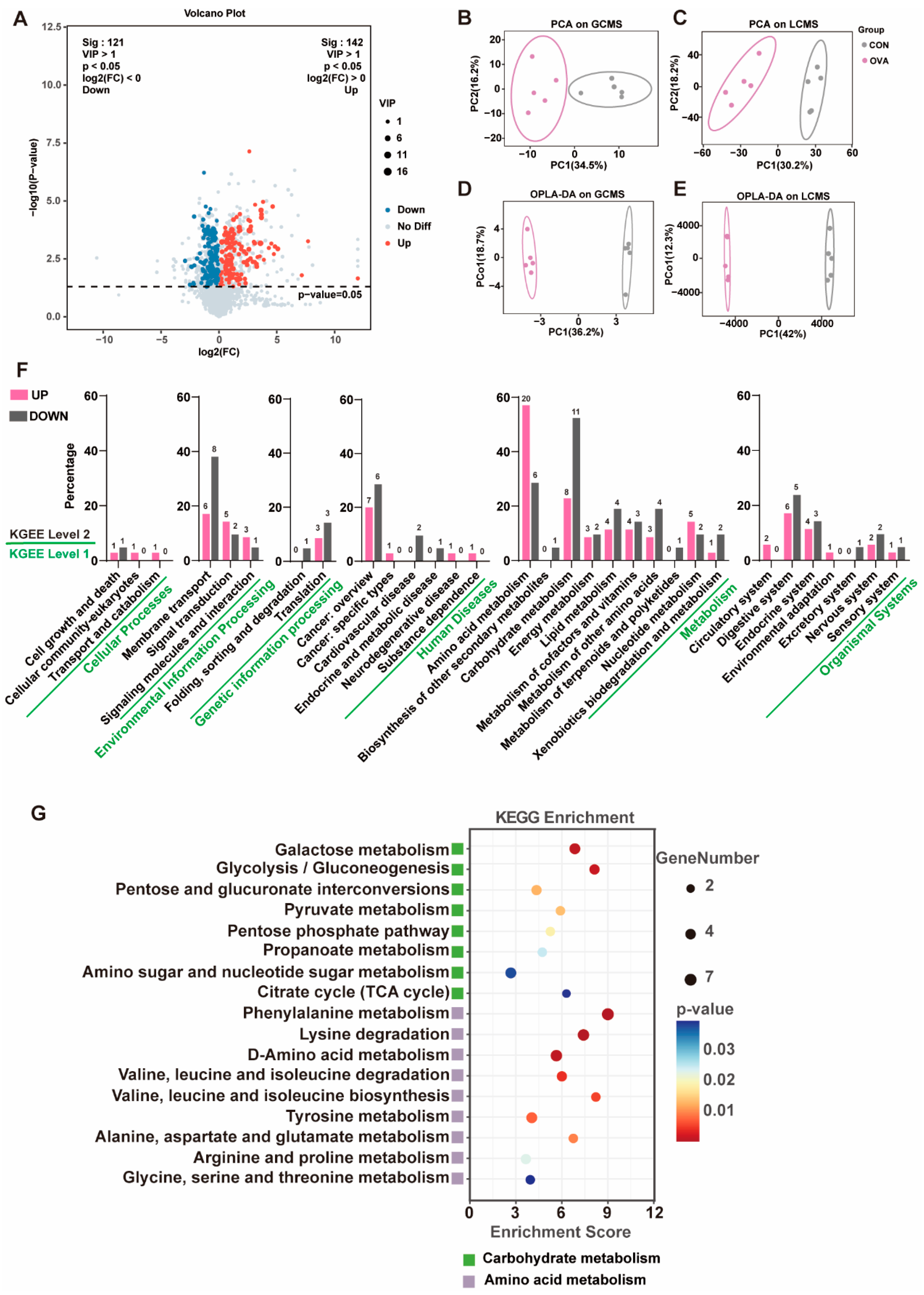
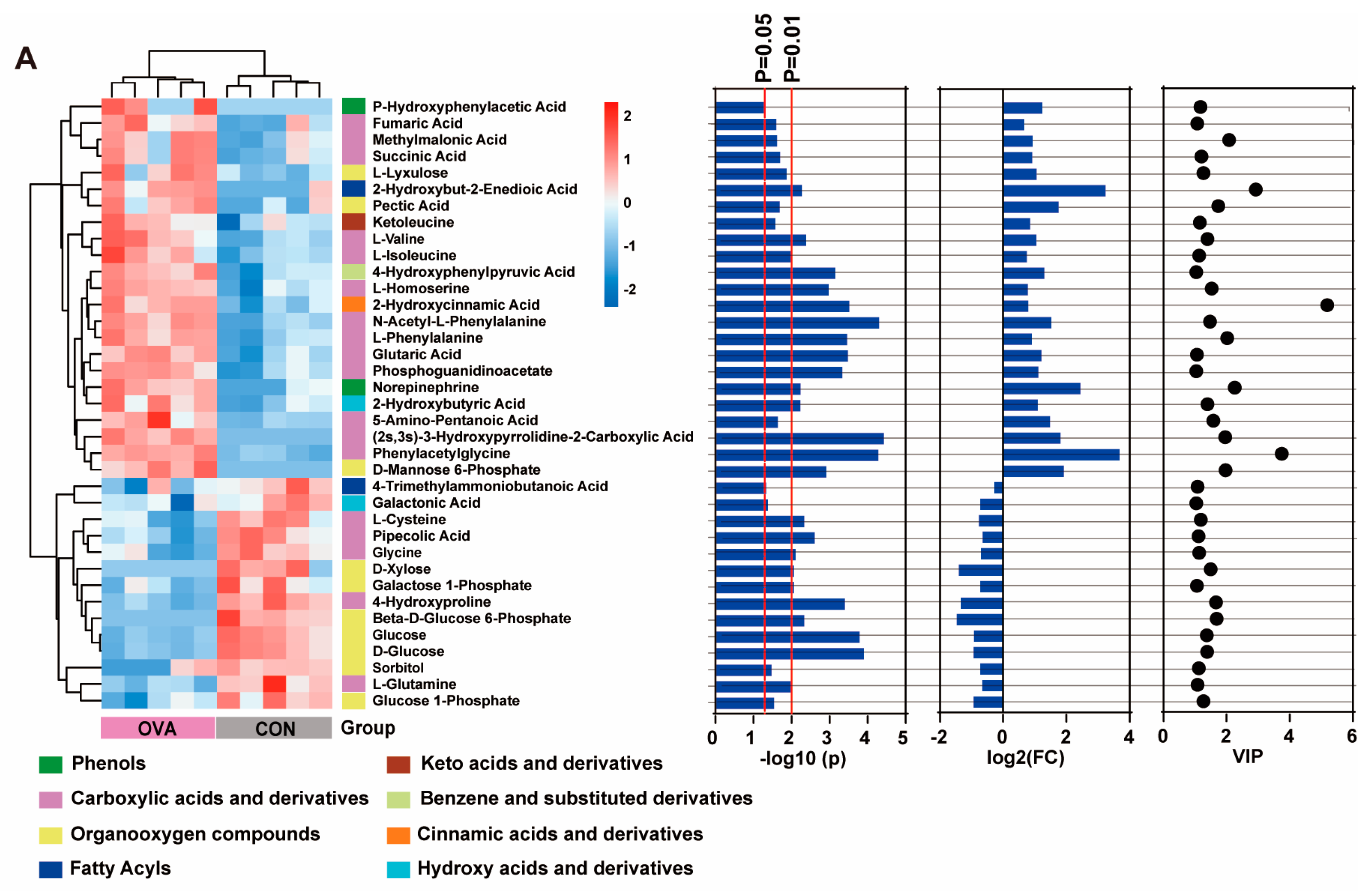
2.5. Altered Serum Metabolic Profile in OVA Mice
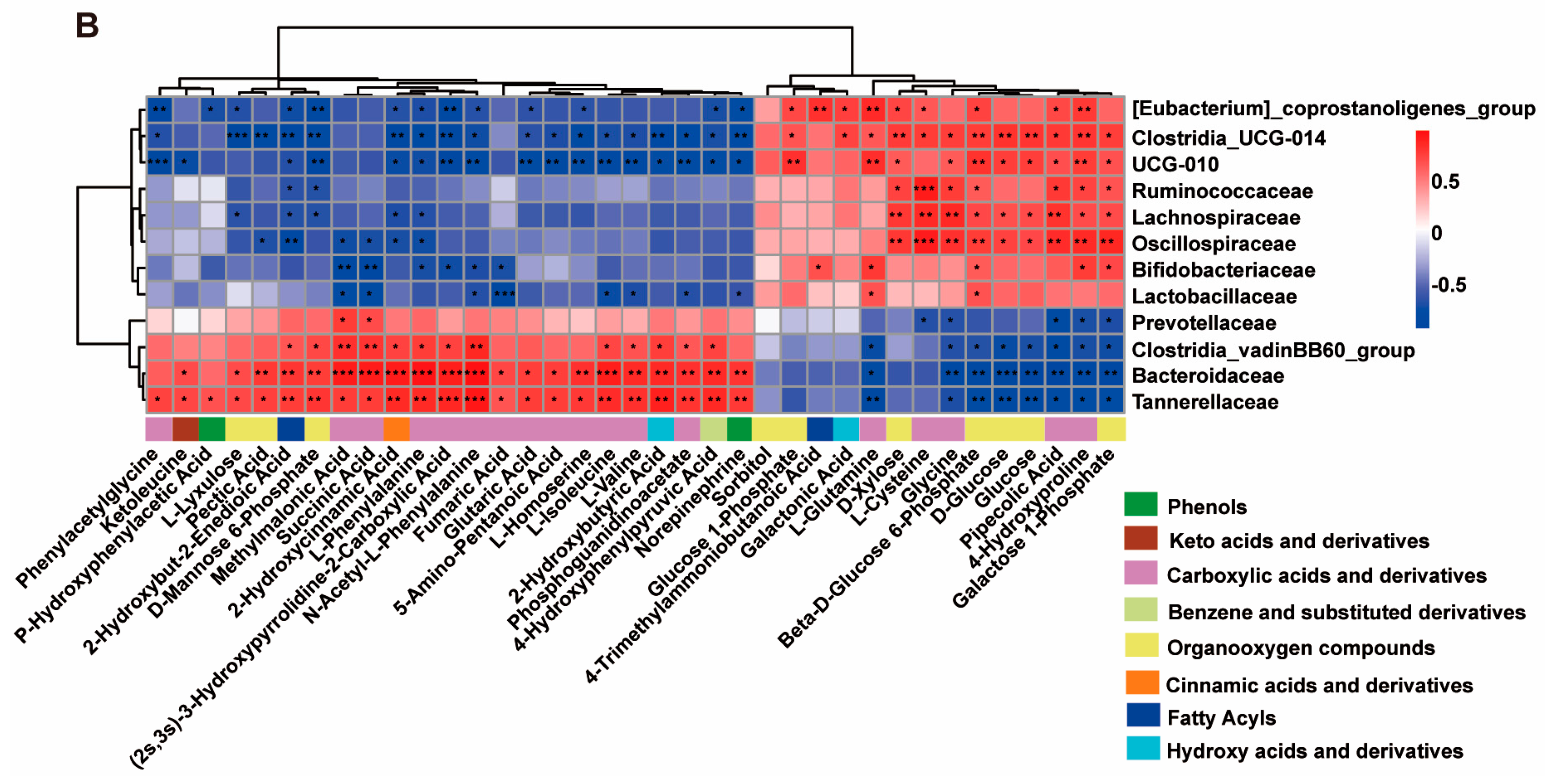
2.6. Correlation Between Altered Serum Metabolites and Gut Microbiota
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Protocol
4.3. Behavioral Experiments
4.3.1. OFT
4.3.2. EPM
4.3.3. FST
4.3.4. Self-Grooming
4.3.5. MBT
4.3.6. TST
4.3.7. NNAT
4.3.8. Barnes Maze Test
4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining and Histopathological Assessment
4.6. Fecal Microbiome Analysis
4.7. Metabolome Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FA | Food allergy |
| OVA | Ovalbumin |
| PFC | Prefrontal Cortex |
| OFT | Open-field test |
| EPM | Elevated plus test |
| FST | Forced swimming test |
| MBT | Marbles buried test |
| TST | Three-chamber social test |
| NNAT | Non-selective, non-sustained visual attention test |
References
- Boyce, J.A.; Assa’ad, A.; Burks, A.W.; Jones, S.M.; Sampson, H.A.; Wood, R.A.; Plaut, M.; Cooper, S.F.; Fenton, M.J.; Arshad, S.H.; et al. Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food Allergy in the United States: Summary of the NIAID-Sponsored Expert Panel Report. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraro, A.; Werfel, T.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Roberts, G.; Beyer, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Cardona, V.; Dubois, A.; duToit, G.; Eigenmann, P.; et al. EAACI food allergy and anaphylaxis guidelines: Diagnosis and management of food allergy. Allergy 2014, 69, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.S.; Warren, C.M.; Smith, B.M.; Jiang, J.; Blumenstock, J.A.; Davis, M.M.; Schleimer, R.P.; Nadeau, K.C. Prevalence and Severity of Food Allergies Among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e185630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, N.J.; Koplin, J.J.; Martin, P.E.; Gurrin, L.C.; Lowe, A.J.; Matheson, M.C.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Wake, M.; Tang, M.L.; Dharmage, S.C.; et al. Prevalence of challenge-proven IgE-mediated food allergy using population-based sampling and predetermined challenge criteria in infants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 668–676.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; He, T.; Che, H. Meta-Analysis: Prevalence of Food Allergy and Food Allergens—China, 2000–2021. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolidoro, G.C.I.; Amera, Y.T.; Ali, M.M.; Nyassi, S.; Lisik, D.; Ioannidou, A.; Rovner, G.; Khaleva, E.; Venter, C.; van Ree, R.; et al. Frequency of food allergy in Europe: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2023, 78, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Holdford, D.; Bilaver, L.; Dyer, A.; Holl, J.L.; Meltzer, D. The economic impact of childhood food allergy in the United States. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Freeland, D.M.H.; Nadeau, K.C. Food allergy: Immune mechanisms, diagnosis and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, H.; Allen, K.J.; Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A.; Lack, G.; Beyer, K.; Oettgen, H.C. Food allergy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 17098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.A.; Van Lieshout, R.J.; Ohayon, J.; Scott, J.G. Emotional and behavioral problems in adolescents and young adults with food allergy. Allergy 2016, 71, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liu, B.; Yang, W.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Chen, M.; Bao, W.; Strathearn, L. Association of Food Allergy, Respiratory Allergy, and Skin Allergy with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder among Children. Nutrients 2022, 14, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Jing, J.; Liu, B.; Strathearn, L.; Bao, W. Association of Food Allergy and Other Allergic Conditions With Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e180279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xuan, J.; Xu, X.; Qiu, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Effects of allergic diseases on social-emotional development in children at 12 months of age: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 374, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.A.; Yuen, A.W.T.; Woo, E.; Chu, K.H.; Kwan, H.S.; Yang, G.X.; Yang, Y.; Leung, P.S.C. Microbiota and Food Allergy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 57, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Sanchez, M.I.; Hall, G.B.; Ghajar, K.; Nardelli, A.; Bolino, C.; Lau, J.T.; Martin, F.P.; Cominetti, O.; Welsh, C.; Rieder, A.; et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 Reduces Depression Scores and Alters Brain Activity: A Pilot Study in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 448–459.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Fang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; et al. Psychobiotic Lactobacillus plantarum JYLP-326 relieves anxiety, depression, and insomnia symptoms in test anxious college via modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1158137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, D.H. The Preventive and Curative Effects of Lactobacillus reuteri NK33 and Bifidobacterium adolescentis NK98 on Immobilization Stress-Induced Anxiety/Depression and Colitis in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, M.; Rémond-Derbez, N.; Lerond, C.; Lavalle, L.; Keddani, S.; Steinmann, M.; Rytz, A.; Dalile, B.; Verbeke, K.; Van Oudenhove, L.; et al. Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum Reduces Perceived Psychological Stress in Healthy Adults: An Exploratory Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dong, P.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Lactobacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 alleviates OVA-sensitized food allergy through modulating gut microbiota and its metabolism. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10784–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrowska, B.; Ceregra, A.; Maciorkowska, E.; Surowska, B.; Zegadło-Mylik, M.A.; Konopka, E.; Trojanowska, I.; Zakrzewska, M.; Bierła, J.B.; Zakrzewski, M.; et al. The Effectiveness of Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus casei Strains in Children with Atopic Dermatitis and Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.S.; Miranda, V.C.; Trindade, L.M.; Cardoso, V.N.; Reis, D.C.; Cassali, G.D.; Nicoli, J.R.; Cara, D.C.; Martins, F.S. Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum 5(1A) Attenuates Signs of Inflammation in a Murine Model of Food Allergy. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanski, S.M.; Knight, R.T. Insights into human behavior from lesions to the prefrontal cortex. Neuron 2014, 83, 1002–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, M.; Jung, S.; Priller, J. Microglia Biology: One Century of Evolving Concepts. Cell 2019, 179, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, J.; Min, F.; Gao, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H. Oral administration of egg ovalbumin allergen induces dysregulation of tryptophan metabolism in sensitized BALB/c mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 4375–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brishti, A.; Germundson-Hermanson, D.L.; Smith, N.A.; Kearney, A.E.; Warda, Y.; Nagamoto-Combs, K. Asymptomatic sensitization to a cow’s milk protein induces sustained neuroinflammation and behavioral changes with chronic allergen exposure. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 870628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Theije, C.G.; Wu, J.; Koelink, P.J.; Korte-Bouws, G.A.; Borre, Y.; Kas, M.J.; Lopes da Silva, S.; Korte, S.M.; Olivier, B.; Garssen, J.; et al. Autistic-like behavioural and neurochemical changes in a mouse model of food allergy. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 261, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; de Theije, C.G.; da Silva, S.L.; van der Horst, H.; Reinders, M.T.; Broersen, L.M.; Willemsen, L.E.; Kas, M.J.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D. mTOR plays an important role in cow’s milk allergy-associated behavioral and immunological deficits. Neuropharmacology 2015, 97, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; de Theije, C.G.M.; da Silva, S.L.; Abbring, S.; van der Horst, H.; Broersen, L.M.; Willemsen, L.; Kas, M.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D. Dietary interventions that reduce mTOR activity rescue autistic-like behavioral deficits in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 59, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyoshi, M.K.; Oettgen, H.C.; Chatila, T.A.; Geha, R.S.; Bryce, P.J. Food allergy: Insights into etiology, prevention, and treatment provided by murine models. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fan, M.; Xu, J.X.; Yang, L.J.; Qi, C.C.; Xia, Q.R.; Ge, J.F. Exosomes derived from bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate cognitive decline in AD-like mice by improving BDNF-related neuropathology. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferencova, N.; Visnovcova, Z.; Ondrejka, I.; Hrtanek, I.; Bujnakova, I.; Kovacova, V.; Macejova, A.; Tonhajzerova, I. Peripheral Inflammatory Markers in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder at Adolescent Age. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, H.K.; Moreno, R.J.; Ashwood, P. Innate immune dysfunction and neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 108, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyanishi, K.; Sato, A.; Kihara, N.; Utsunomiya, R.; Tanaka, J. Synaptic elimination by microglia and disturbed higher brain functions. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 142, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Merre, P.; Ährlund-Richter, S.; Carlén, M. The mouse prefrontal cortex: Unity in diversity. Neuron 2021, 109, 1925–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Li, X.; He, L.; Pan, J.; Shen, Q.; Peng, Y. CB2R activation ameliorates late adolescent chronic alcohol exposure-induced anxiety-like behaviors during withdrawal by preventing morphological changes and suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation in prefrontal cortex microglia in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 110, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, H.; Ding, L.; Xia, X.; Xiong, L.; Qi, X.R.; Zheng, J.C. Microglial glutaminase 1 deficiency mitigates neuroinflammation associated depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 99, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Fan, L.; Qin, Q.; Zheng, D.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Liang, S.; et al. Exogenous PD-L1 binds to PD-1 to alleviate and prevent autism-like behaviors in maternal immune activation-induced male offspring mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 122, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.; Habib, M.Z.; Ebeid, M.A.; Abdelraouf, S.M.; El Faramawy, Y.; Aboul-Fotouh, S.; Magdy, Y. Amisulpride alleviates chronic mild stress-induced cognitive deficits: Role of prefrontal cortex microglia and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 885, 173411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germundson, D.L.; Smith, N.A.; Vendsel, L.P.; Kelsch, A.V.; Combs, C.K.; Nagamoto-Combs, K. Oral sensitization to whey proteins induces age- and sex-dependent behavioral abnormality and neuroinflammatory responses in a mouse model of food allergy: A potential role of mast cells. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut microbes and metabolites as modulators of blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.T. Food allergy induces alteration in brain inflammatory status and cognitive impairments. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 364, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay, P.A.; Hsiao, E.Y.; Patterson, P.H.; McAllister, A.K. Maternal immune activation causes age- and region-specific changes in brain cytokines in offspring throughout development. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 31, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Leak, R.K.; Shi, Y.; Suenaga, J.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, P.; Chen, J. Microglial and macrophage polarization—New prospects for brain repair. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Korenori, Y.; Tateyama, A.; Sakamoto, N.; Kiyohara, C.; Shirakawa, T.; Sonomoto, K. Aberrant structures of fecal bacterial community in allergic infants profiled by 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Hu, R.; Gong, J.; Fang, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; He, Z.; Hou, D.X.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; et al. Protection against Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Protocatechuic Acid. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2238959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Wu, S.; Li, B.; Tan, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Liu, M.; Fu, C.; Zhang, H.; et al. Dietary ferulic acid and vanillic acid on inflammation, gut barrier function and growth performance in lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Jing, J.; Han, L.; Gao, A. Probiotics ameliorate benzene-induced systemic inflammation and hematopoietic toxicity by inhibiting Bacteroidaceae-mediated ferroptosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.W.; Tung, Y.T.; Yang, S.C.; Shirakawa, H.; Su, L.H.; Loe, P.Y.; Chiu, W.C. The Effects of Rice Bran on Neuroinflammation and Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Mice Fed a Drink with Fructose. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Kou, G.; Li, Y. The relationship between gut microbiota and inflammatory response, learning and memory in mice by sleep deprivation. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1159771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, L.D.H.; Chan, J.C.Y.; Yap, G.C.; Purbojati, R.W.; Drautz-Moses, D.I.; Koh, Y.M.; Tay, C.J.X.; Huang, C.H.; Kioh, D.Y.Q.; Woon, J.Y.; et al. A compromised developmental trajectory of the infant gut microbiome and metabolome in atopic eczema. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, S.; Liu, S.; Duan, L. Beneficial effect of butyrate-producing Lachnospiraceae on stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Burton, O.T.; Wise, P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Hobson, S.A.; Garcia Lloret, M.; Chehoud, C.; Kuczynski, J.; DeSantis, T.; Warrington, J.; et al. A microbiota signature associated with experimental food allergy promotes allergic sensitization and anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Jiang, W.; Tian, Z.; Wu, H.; Ning, H.; Yan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Dong, F.; Sun, Y.; et al. Fecal g. Streptococcus and g. Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group combined with sphingosine to modulate the serum dyslipidemia in high-fat diet mice. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4234–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Lv, C.; Zhao, K.; Niu, M.; Li, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xu, K. Assessment of oral ciprofloxacin impaired gut barrier integrity on gut bacteria in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ye, Y.; Ji, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.S.; Sun, X. Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Changes in Gut Microbiota and Mechanisms of Its Regulation of Allergy in OVA-Sensitive BALB/c Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3344–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, R.; Wang, J.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhang, B.; Fu, W.; Liu, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, S. 2′-Fucosyllactose alleviates OVA-induced food allergy in mice by ameliorating intestinal microecology and regulating the imbalance of Th2/Th1 proportion. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10924–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C. Bifidobacterium breve M-16V alters the gut microbiota to alleviate OVA-induced food allergy through IL-33/ST2 signal pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 9464–9473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Li, S.; Gao, J. Bifidobacterium breve Protects the Intestinal Epithelium and Mitigates Inflammation in Colitis via Regulating the Gut Microbiota-Cholic Acid Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 3572–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Mu, C.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Zhu, W. Amino acid utilization allows intestinal dominance of Lactobacillus amylovorus. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, M.F.; Sakanaka, M.; von Burg, N.; Mörbe, U.; Andersen, D.; Moll, J.M.; Pekmez, C.T.; Rivollier, A.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mølgaard, C.; et al. Bifidobacterium species associated with breastfeeding produce aromatic lactic acids in the infant gut. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1367–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Y.; Yang, H. Xanthan gum modified fish gelatin and binary culture modulates the metabolism of probiotics in fermented milk mainly via amino acid metabolism pathways. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumbi, C.N.; Choi, H.H.T.; Huang, H.S.; Panyod, S.; Wang, T.W.; Huang, S.J.; Tsou, H.H.; Ho, C.T.; Sheen, L.Y. Amino acid metabolites profiling in unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced depressive rats and the protective effects of Gastrodia elata Blume and gastrodin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337 Pt 3, 118906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hu, M.; Wu, W.; Lou, X.; Gao, R.; Ma, T.; Dheen, S.T.; Cheng, J.; Xiong, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Indole derivatives ameliorated the methamphetamine-induced depression and anxiety via aryl hydrocarbon receptor along “microbiota-brain” axis. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2470386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, S.; Pan, F.; Liu, D.; Ho, R.C.M.; et al. Rifaximin-mediated gut microbiota regulation modulates the function of microglia and protects against CUMS-induced depression-like behaviors in adolescent rat. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Chen, Y.C.; Lasky-Su, J.; Kelly, R.S.; Zeiger, R.S.; O’Connor, G.T.; Bacharier, L.B.; Jia, X.; Beigelman, A.; Gold, D.R.; et al. Early-life fecal metabolomics of food allergy. Allergy 2023, 78, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socała, K.; Doboszewska, U.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Włodarczyk, M.; Zielińska, A.; Poleszak, E.; Fichna, J.; Wlaź, P. The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remacle, N.; Forny, P.; Cudré-Cung, H.P.; Gonzalez-Melo, M.; do Vale-Pereira, S.; Henry, H.; Teav, T.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Braissant, O.; Baumgartner, M.; et al. New in vitro model derived from brain-specific Mut-/- mice confirms cerebral ammonium accumulation in methylmalonic aciduria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 124, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, E.C.; Turton, N.; Boan, E.J.; Bennett, E.; Philips, S.; Heaton, R.A.; Hargreaves, I.P. The Effect of Methylmalonic Acid Treatment on Human Neuronal Cell Coenzyme Q(10) Status and Mitochondrial Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Huang, J.; He, H.; Zhou, L.; He, Y.; Yan, J.; Tao, A. Succinate and mitochondrial DNA trigger atopic march from atopic dermatitis to intestinal inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1050–1066.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Shi, D.D.; Liao, B.B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Lin, L.J.; Wang, Z. Human microbiota from drug-naive patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder drives behavioral symptoms and neuroinflammation via succinic acid in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 1782–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yang, Q.; Yu, N.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, W.Y.; Ma, C. Phenylalanine Metabolism Is Dysregulated in Human Hippocampus with Alzheimer’s Disease Related Pathological Changes. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 83, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, G.; Feng, T.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, T.; Xie, Z.; Chu, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium oligomannate therapeutically remodels gut microbiota and suppresses gut bacterial amino acids-shaped neuroinflammation to inhibit Alzheimer’s disease progression. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierozan, P.; Colín-González, A.L.; Biasibetti, H.; da Silva, J.C.; Wyse, A.; Wajner, M.; Santamaria, A. Toxic Synergism Between Quinolinic Acid and Glutaric Acid in Neuronal Cells Is Mediated by Oxidative Stress: Insights to a New Toxic Model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 5362–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Cheng, M.L.; Chiang, M.H.; Wang, C.J.; Tsai, M.H.; Lin, G. Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Distinct Profiles in the Plasma and Urine Associated with IgE Reactions in Childhood Asthma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.Y.; Kim, H.M.; Jeong, H.J. Cysteine ameliorates allergic inflammatory reactions by suppressing thymic stromal lymphopoietin production in activated human mast cells. Nutr. Res. 2018, 49, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorzhak, A.; Brecht, M.; Schmitz, D. Social play behavior is driven by glycine-dependent mechanisms. Curr. Biol. 2024, 34, 3654–3664.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, P.; Catović, S. Brain glycine and aggressive behavior. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1975, 3, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markel, A.L.; Achkasov, A.F.; Alekhina, T.A.; Prokudina, O.I.; Ryazanova, M.A.; Ukolova, T.N.; Efimov, V.M.; Boldyreva, E.V.; Boldyrev, V.V. Effects of the alpha- and gamma-polymorphs of glycine on the behavior of catalepsy prone rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 98, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zuo, W.; Wu, W.; Zuo, Q.K.; Fu, R.; Wu, L.; Zhang, H.; Ndukwe, M.; Ye, J.H. Activation of glycine receptors in the lateral habenula rescues anxiety- and depression-like behaviors associated with alcohol withdrawal and reduces alcohol intake in rats. Neuropharmacology 2019, 157, 107688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhong, Z.; Shi, L.; Huang, L.; Lin, C.; He, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhang, T.; Ding, W.; Yang, Y. Gut microbiota mediate early life stress-induced social dysfunction and anxiety-like behaviors by impairing amino acid transport at the gut. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2401939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Vázquez, L.; Van Ginkel Riba, G.; Arija, V.; Canals, J. Composition of Gut Microbiota in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Cruz, N.J.; Kang, D.W.; Gandal, M.J.; Wang, B.; Kim, Y.M.; Zink, E.M.; Casey, C.P.; Taylor, B.C.; Lane, C.J.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota from Autism Spectrum Disorder Promote Behavioral Symptoms in Mice. Cell 2019, 177, 1600–1618.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B.; Gregory, A.C.; Borody, T.; Chittick, L.; Fasano, A.; Khoruts, A.; Geis, E.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; et al. Microbiota Transfer Therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: An open-label study. Microbiome 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.A.; Germundson, D.L.; Gao, P.; Hur, J.; Floden, A.M.; Nagamoto-Combs, K. Anxiety-like behavior and intestinal microbiota changes as strain-and sex-dependent sequelae of mild food allergy in mouse models of cow’s milk allergy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 95, 122–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinares-Garcia, P.; Stratikopoulos, M.; Zagato, A.; Loke, H.; Lee, J. Sex: A Significant Risk Factor for Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Song, C.; Berridge, K.C.; Graybiel, A.M.; Fentress, J.C. Neurobiology of rodent self-grooming and its value for translational neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzer, J.J.; Careaga, M.; Chang, C.; Onore, C.E.; Ashwood, P. Allergic fetal priming leads to developmental, behavioral and neurobiological changes in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiao, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Yu, X. Effects of circulating vitamin D concentrations on emotion, behavior and attention: A cross-sectional study in preschool children with follow-up behavior experiments in juvenile mice. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 275, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millecamps, M.; Etienne, M.; Jourdan, D.; Eschalier, A.; Ardid, D. Decrease in non-selective, non-sustained attention induced by a chronic visceral inflammatory state as a new pain evaluation in rats. Pain. 2004, 109, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitts, M.W. Barnes Maze Procedure for Spatial Learning and Memory in Mice. Bio Protoc. 2018, 8, e2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, X. OVA-Induced Food Allergy Leads to Neurobehavioral Changes in Mice and the Potential Role of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites Dysbiosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104760
Hu S, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Li L, Yu X. OVA-Induced Food Allergy Leads to Neurobehavioral Changes in Mice and the Potential Role of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites Dysbiosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104760
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shouxun, Chunyan Zhou, Yue Zhang, Luanluan Li, and Xiaodan Yu. 2025. "OVA-Induced Food Allergy Leads to Neurobehavioral Changes in Mice and the Potential Role of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites Dysbiosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104760
APA StyleHu, S., Zhou, C., Zhang, Y., Li, L., & Yu, X. (2025). OVA-Induced Food Allergy Leads to Neurobehavioral Changes in Mice and the Potential Role of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites Dysbiosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104760



