Fenofibrate Treatment Inhibits Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Transport Vesicle Formation by Reducing Sar1b Protein Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
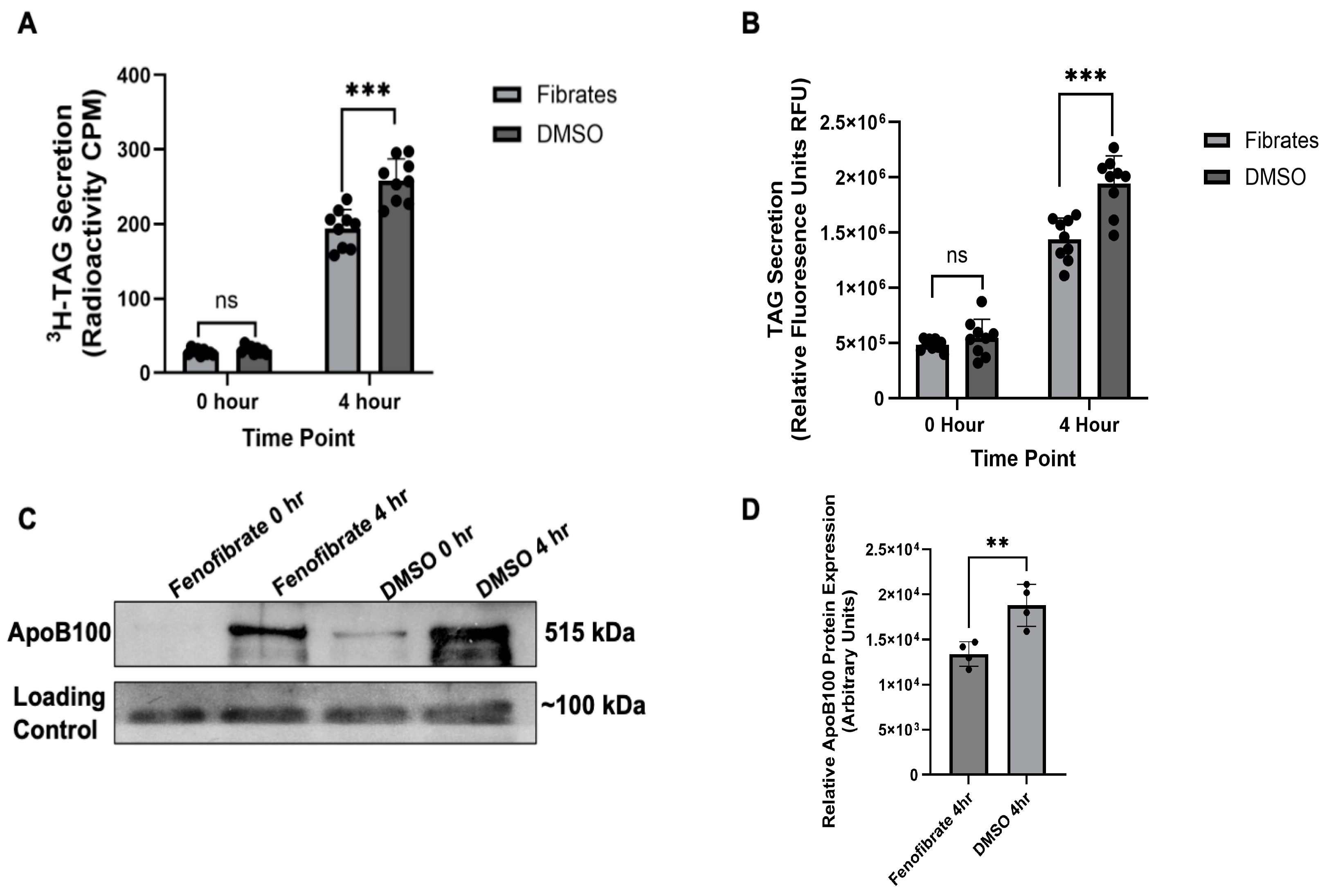
2.1. Validating Fenofibrates Effect on VLDL Secretion
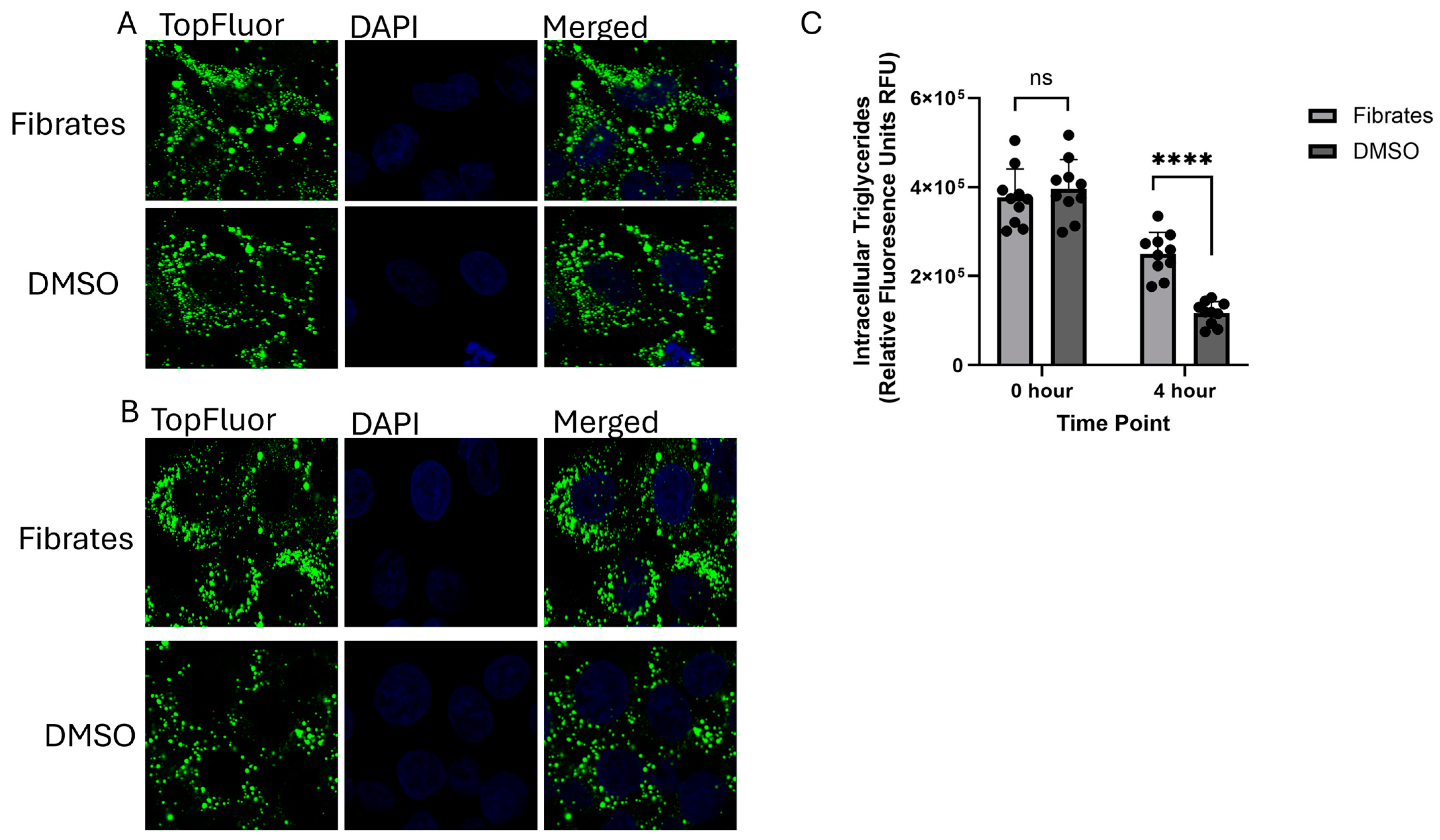
2.2. Monitoring the Effects of Fenofibrate on Intracellular VLDL Trafficking
2.3. Determining the Cause of the Intracellular VLDL Trafficking Defect
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Fenofibrate Preparation and Treatment
4.3. 3H-TAG Secretion Assay
4.4. TopFluor-Tagged Oleic Acid Assay
4.5. Immunostaining and Confocal Microscopy
4.6. Immunoblotting
4.6.1. ApoB100
4.6.2. Sar1B, β-Actin, LFABP, and SVIP
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Setorki, M.; Doudi, M.; Baradaran, A.; Nasri, H. Atherosclerosis: Process, indicators, risk factors and new hopes. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 927–946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pahwa, R.; Jialal, I. Atherosclerosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507799/ (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Linton, M.F.; Yancey, P.G.; Davies, S.S.; Jerome, W.G.; Linton, E.F.; Song, W.L.; Doran, A.C.; Vickers, K.C. The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000; Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26844337/ (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Ginsberg, H.N.; Packard, C.J.; Chapman, M.J.; Boren, J.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Averna, M.; Ference, B.A.; Gaudet, D.; Hegele, R.A.; Kersten, S.; et al. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants: Metabolic insights, role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and emerging therapeutic strategies-a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4791–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonjans, K.; Staels, B.; Auwerx, J. The peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARS) and their effects on lipid metabolism and adipocyte differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1302, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonjans, K.; Staels, B.; Auwerx, J. Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in mediating the effects of fibrates and fatty acids on gene expression. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors and lipoprotein metabolism. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 132960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, G.M.; Croom, K.F. Fenofibrate: A review of its use in primary dyslipidaemia, the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2007, 67, 121–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiukka, A.; Leinonen, E.; Jauhiainen, M.; Sundvall, J.; Ehnholm, C.; Keech, A.C.; Taskinen, M.R. Long-term effects of fenofibrate on VLDL and HDL subspecies in participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Zhao, S.P.; Ye, H.J. Efficacy and safety of coenzyme A versus fenofibrate in patients with hyperlipidemia: A multicenter, double-blind, double-mimic, randomized clinical trial. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 36, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.J. Fibrates in 2003: Therapeutic action in atherogenic dyslipidaemia and future perspectives. Atherosclerosis 2003, 171, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balfour, J.A.; McTavish, D.; Heel, R.C. Fenofibrate. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use in dyslipidaemia. Drugs 1990, 40, 260–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijland, S.; Pieterman, E.J.; Maas, A.C.; van der Hoorn, J.W.; van Erk, M.J.; van Klinken, J.B.; Havekes, L.M.; van Dijk, K.W.; Princen, H.M.; Rensen, P.C. Fenofibrate increases very low density lipoprotein triglyceride production despite reducing plasma triglyceride levels in APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 25168–25175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staels, B.; Vu-Dac, N.; Kosykh, V.A.; Saladin, R.; Fruchart, J.C.; Dallongeville, J.; Auwerx, J. Fibrates downregulate apolipoprotein C-III expression independent of induction of peroxisomal acyl coenzyme A oxidase. A potential mechanism for the hypolipidemic action of fibrates. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeage, K.; Keating, G.M. Fenofibrate: A review of its use in dyslipidaemia. Drugs 2011, 71, 1917–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Shen, W.; Lu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y. Upregulation of hepatic VLDLR via PPARalpha is required for the triglyceride-lowering effect of fenofibrate. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnich, A.; Tian, N.; Byan, L.; Bilder, G. A potent PPARalpha agonist stimulates mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation in liver and skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E270–E279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, E.; Farrell, G.C.; Robertson, G.; Hall, P.; Kirsch, R.; Leclercq, I. Central role of PPARalpha-dependent hepatic lipid turnover in dietary steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2003, 38, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harano, Y.; Yasui, K.; Toyama, T.; Nakajima, T.; Mitsuyoshi, H.; Mimani, M.; Hirasawa, T.; Itoh, Y.; Okanoue, T. Fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonist, reduces hepatic steatosis and lipid peroxidation in fatty liver Shionogi mice with hereditary fatty liver. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staels, B.; Dallongeville, J.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Leitersdorf, E.; Fruchart, J.C. Mechanism of action of fibrates on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Circulation 1998, 98, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S.; Siddiqi, S.A. Intracellular trafficking and secretion of VLDL. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.; Thorne-Tjomsland, G.; DeLong, C.J.; Cui, Z.; Shan, J.; Burton, L.; Jamieson, J.C.; Yao, Z. Intracellular assembly of very low-density lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B100 in rat hepatoma McA-RH7777 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 31187–31200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, S.A. VLDL exits from the endoplasmic reticulum in a specialized vesicle the VLDL transport Vesicle, in rat primary hepatocytes. Biochem. J. 2008, 413, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuge, O.; Dascher, C.; Orci, L.; Rowe, T.; Amherdt, M.; Plutner, H.; Ravazzola, M.; Tanigawa, G.; Rothman, J.E.; Balch, W.E. Sar1B promotes vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum but not Golgi compartments. J. Cell Biol. 1984, 125, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aridor, M.; Fish, K.N.; Bannykn, S.; Weissman, J.; Roberts, T.H.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Balch, W.E. The Saar1GTPase Coordinates biosynthetic cargo selection with endoplasmic reticulum export site assembly. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlowe, C.; Schekman, R. SEC12 encodes a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor essential for transport vesicle budding from the ER. Nature 1993, 365, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenson, D.; Schekman, R. COPII- mediated vesicle formation at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, M.J.; Herrmann, J.M.; Schekman, R. COPII_ cargo interactions direct protein sorting into ER- derived transport vesicles. Nature 1998, 391, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Siddiqi, S.; Zhelyabovska, O.; Siddiqi, S.A. Silencing of Small Valosin-containing Protein-interacting Protein (SVIP) Reduces Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) Secretion from Rat Hepatocytes by Disrupting Its Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi Trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12514–12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Siddiqi, S.; Siddiqi, S.A. CideB protein is required for the biogenesis of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) transport vesicle. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 5157–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, S.; Zhelyabovska, O.; Siddiqi, S.A. Reticulon 3 regulates very low-density lipoprotein secretion by controlling very low-density lipoprotein transport vesicle biogenesis. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, L.L. Role of the Golgi apparatus in the phosphorylation of apolipoprotein B. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31491–31495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukmirica, J.; Nishimaki-Mogami, T.; Tran, K.; Shan, J.; McLeod, R.S.; Yuan, J.; Yao, Z. The N-linked oligosaccharides at the amino terminus of human apoB are important for the assembly and secretion of VLDL. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C.A.; Hamilton, R.L.; Havel, R.J. Subcellular localization of B apoprotein of plasma lipoproteins in rat liver. J. Cell Biol. 1976, 69, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamberger, M.J.; Lane, M.D. Possible role of the Golgi apparatus in the assembly of very low-density lipoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 2390–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusarova, V.; Brodsky, J.L.; Fisher, E.A. Apolipoprotein B100 exit from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is COPII-dependent, and its lipidation to very low-density lipoprotein occurs post-ER. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48051–48058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinol, A.; Verkade, H.; Vance, J.E. Assembly of rat hepatic very low-density lipoproteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 3555–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, T.; Riad, A.; Siddiqi, S.; Parthasarathy, S.; Siddiqi, S.A. Mature VLDL triggers the biogenesis of a distinct vesicle from the trans-Golgi network for its export to the plasma membrane. Biochem. J. 2014, 459, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, S.A. In Vitro Analysis of the Very-Low Density Lipoprotein Export from the Trans-Golgi Network. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2015, 67, 11. 21. 1–11. 21. 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, G.; Tripp, J. Fenofibrate. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025; Updated 13 March 2023; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559219/ (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Winterfeldt, K.; Rejanur Tasin, F.; Siddiqi, S.A. Establishing the Role of Liver Fatty Acid-Binding Protein in Post-Golgi Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Using a Novel Fluoresence Based Assay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arving, A.; Osganian, S.A.; Cohen, D.E.; Corey, K.E. Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism in Liver Disease. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, D.E.; Fisher, E.A. Lipoprotein metabolism, dyslipidemia, and nonalcohlic fatty liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2013, 33, 380–388. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, M.; Cardoso Toniasso, S.C.; Riedel, P.G.; Baldin, C.P.; Dos Reis, F.L.; Pereira, R.M.; Brum, M.C.B.; Joveleviths, D.; Alvares-da-Silva, M.R. Metabolic disease and the liver: A review. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, A.H.; Van Horn, L. Very low-fat diets. Circulation 1987, 83, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulas-Ray, A.C.; Wilson, P.W.; Harris, W.S.; Brinton, E.A.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Richter, C.K.; Jacobson, T.A.; Engler, M.B.; Miller, M.; Robinson, J.G.; et al. Omega-3 fatty acids for the management of hypertriglyceridemia: A Science Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeli, I.; Siddiqi, S.A.; Siddiqi, S.; Mahan, J.; Lagakos, W.S.; Binas, B.; Gheyi, T.; Storch, J.; Mansbach, C.M. Liver fatty acid-binding protein initiates budding of pre-chylomicron transport vesicles from intestinal endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17974–17984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Winterfeldt, K.; Tasin, F.R.; Sekhar, V.; Siddiqi, S.A. Fenofibrate Treatment Inhibits Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Transport Vesicle Formation by Reducing Sar1b Protein Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104720
Winterfeldt K, Tasin FR, Sekhar V, Siddiqi SA. Fenofibrate Treatment Inhibits Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Transport Vesicle Formation by Reducing Sar1b Protein Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104720
Chicago/Turabian StyleWinterfeldt, Kayli, Fahim Rejanur Tasin, Vandana Sekhar, and Shadab A. Siddiqi. 2025. "Fenofibrate Treatment Inhibits Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Transport Vesicle Formation by Reducing Sar1b Protein Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104720
APA StyleWinterfeldt, K., Tasin, F. R., Sekhar, V., & Siddiqi, S. A. (2025). Fenofibrate Treatment Inhibits Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Transport Vesicle Formation by Reducing Sar1b Protein Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104720






