Transcriptional Dynamics of Receptor-Based Genes Reveal Immunity Hubs in Rice Response to Magnaporthe oryzae Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
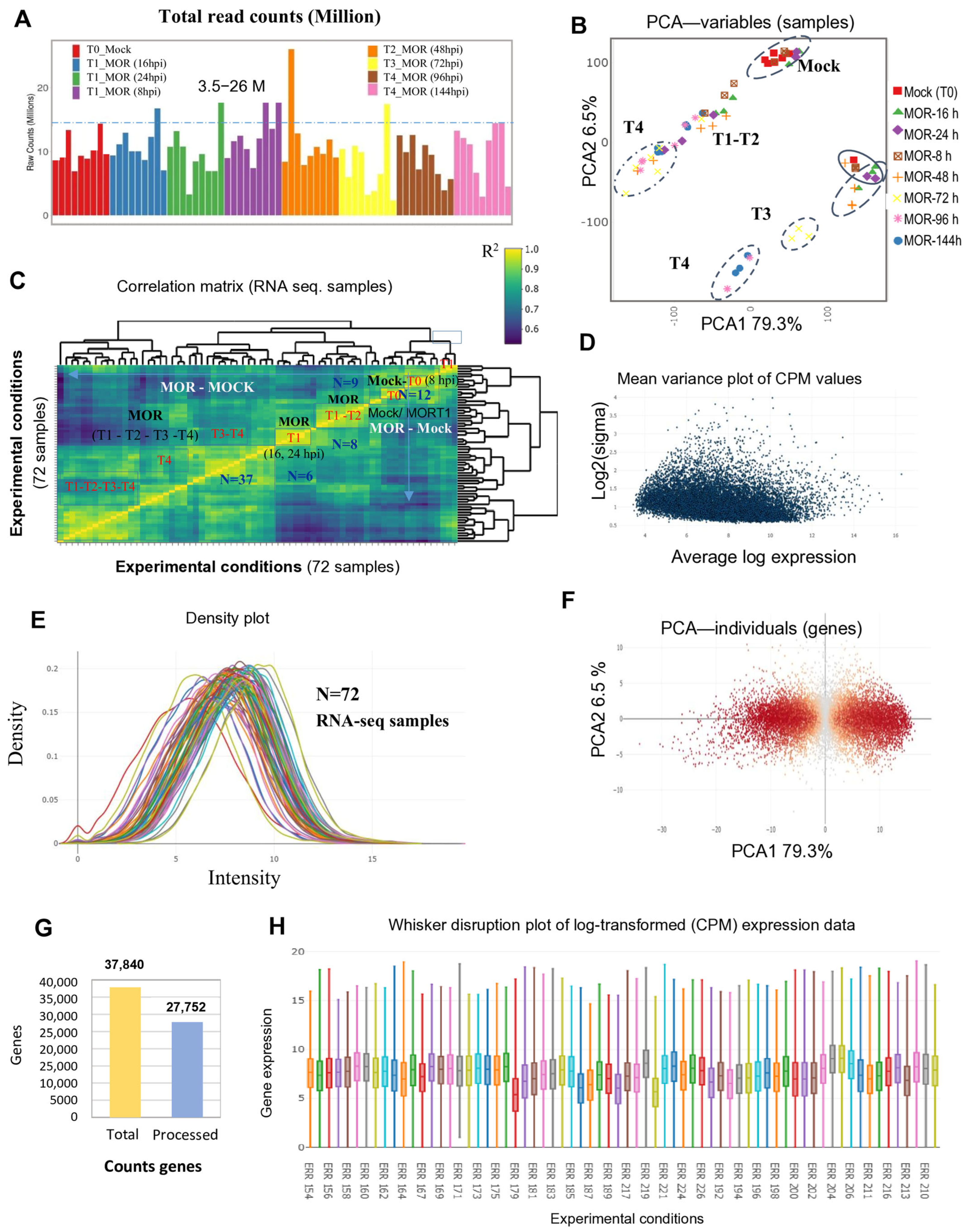
2.1. Exploratory Data Analysis and Overview of the Analyzed Rice RNA-Seq Data
2.2. Exploratory Data Analysis and Overview of the Rice Microarray Data
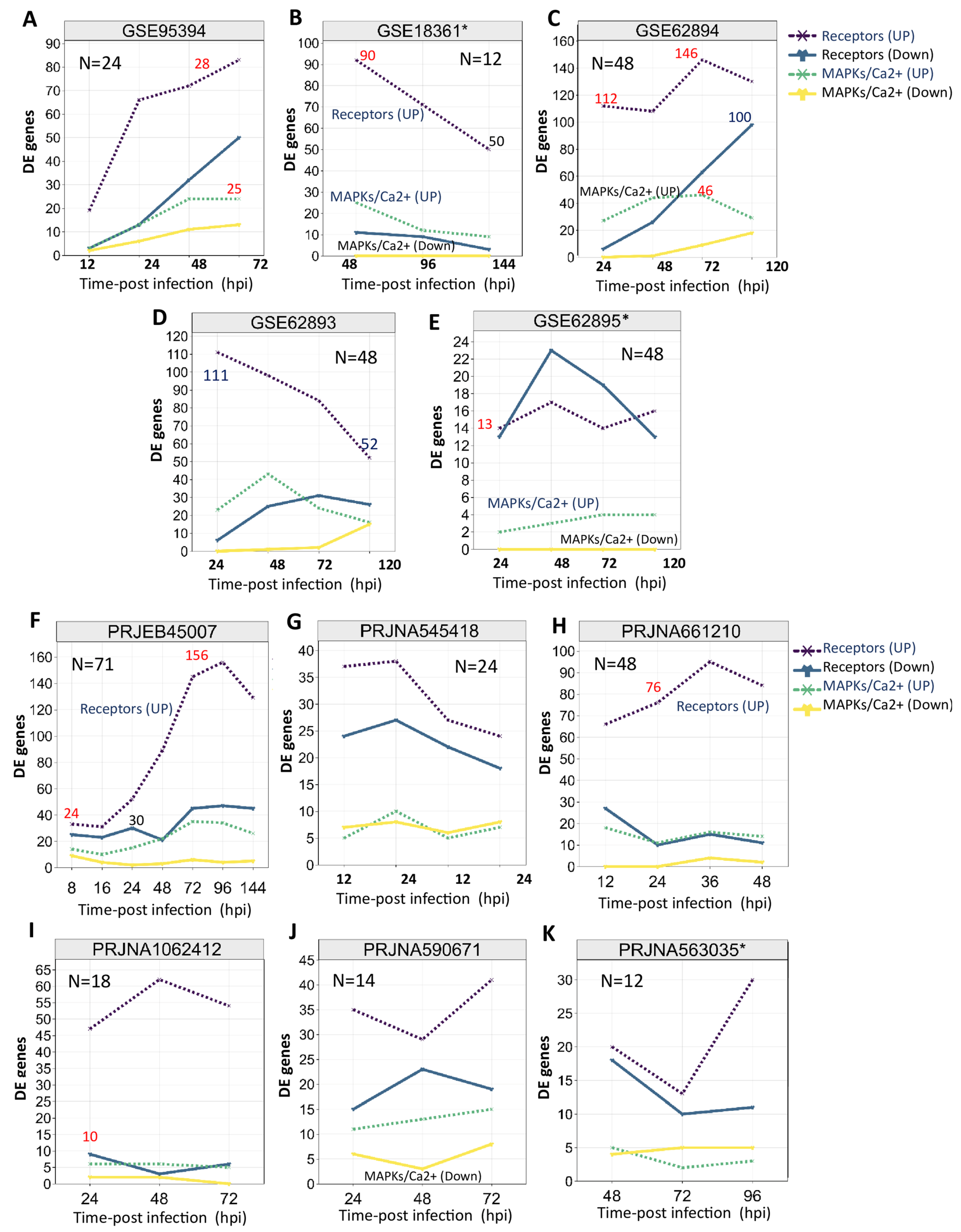
2.3. Transcriptional Landscape of Rice PTI-Related Genes upon MOR Infection
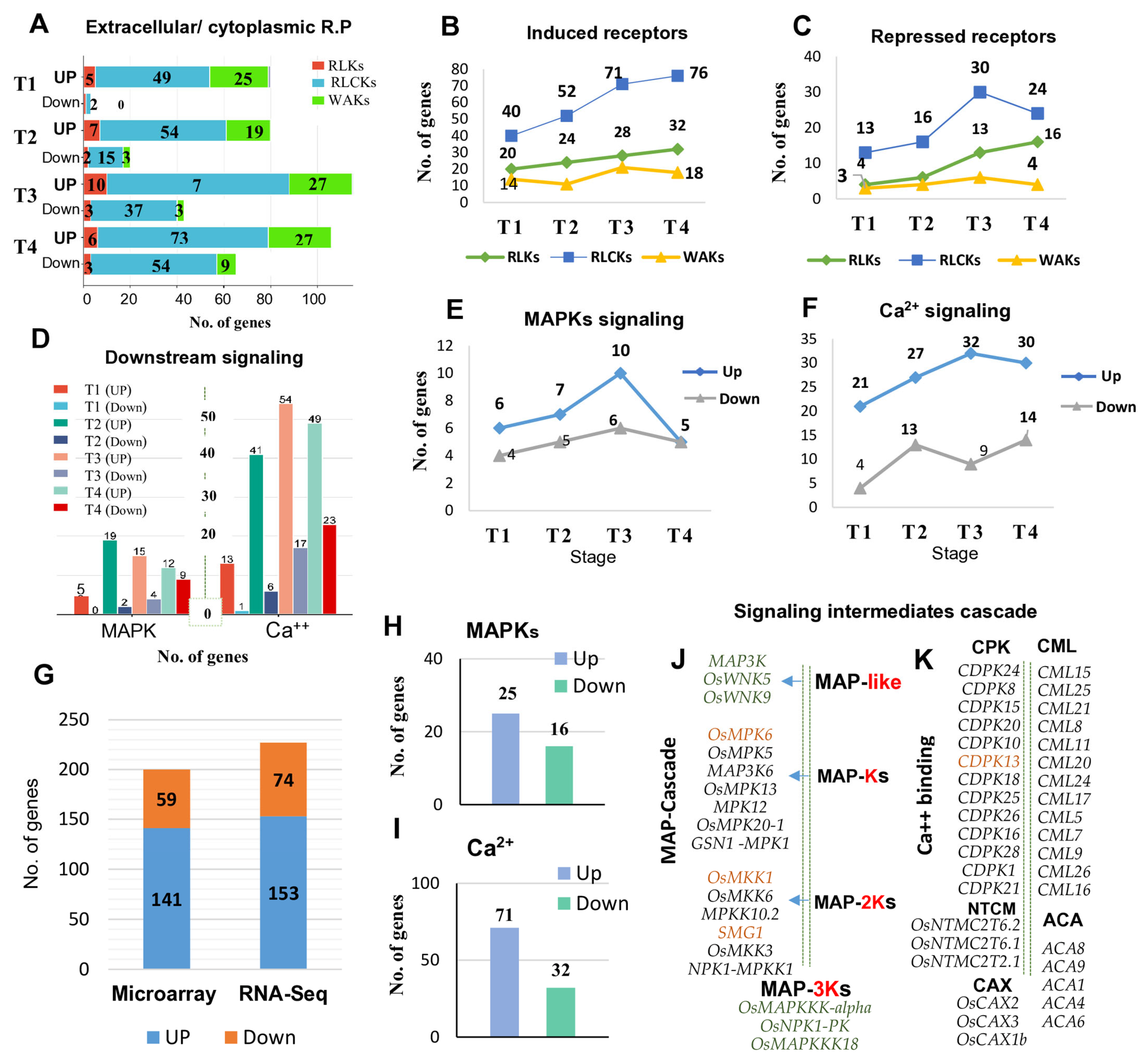
2.4. Transcript Dynamics of Robust Extracellular and Cytoplasmic Receptor-Based Genes
2.5. Top Induced Receptors in Rice Response to MOR Infection
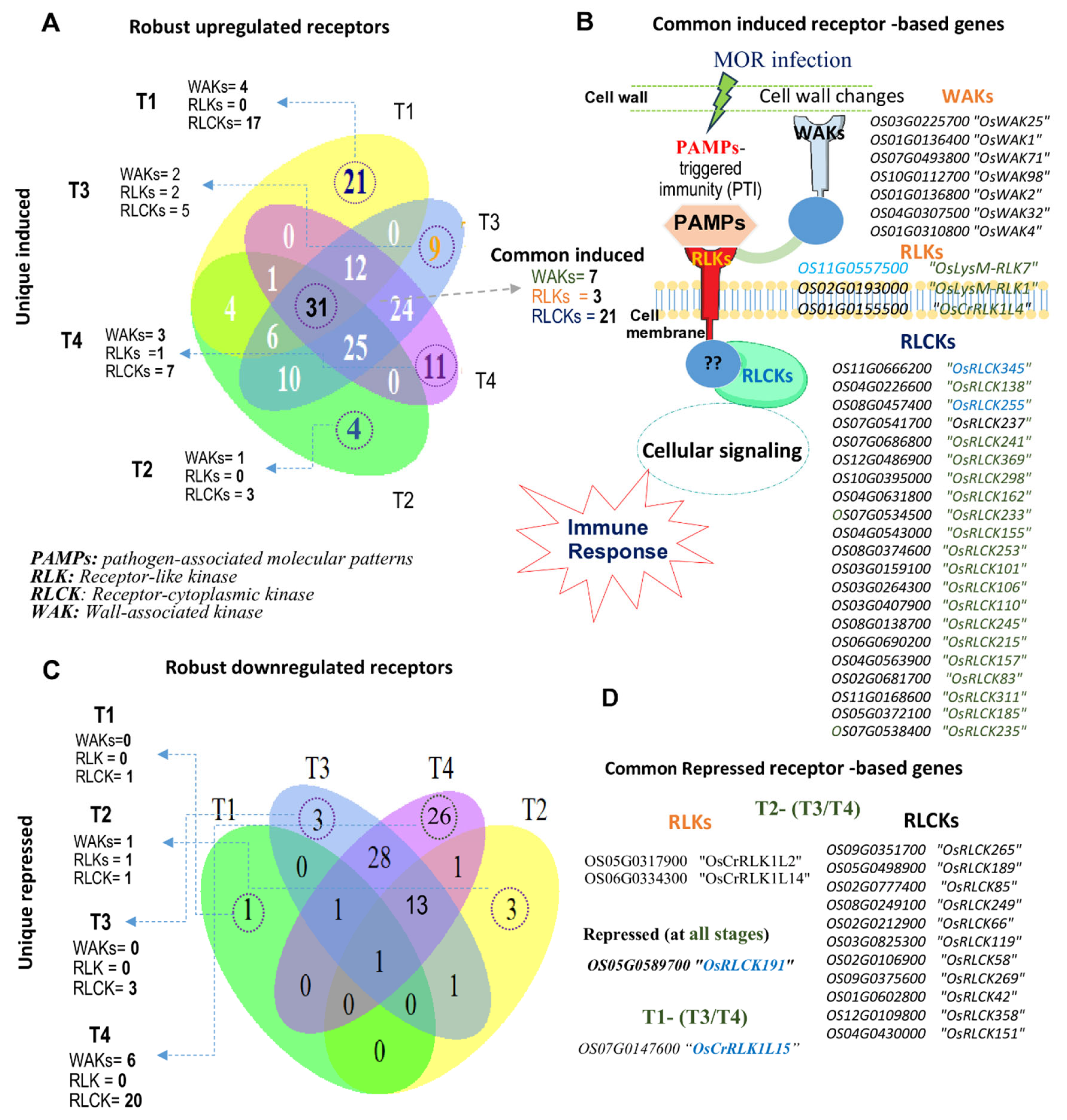
2.6. Common Robust Receptor-Based Genes in Rice Response to MOR Infection
2.7. Stage-Specific Transcription of Receptor-Based Genes in Rice Response to MOR
2.8. Transcript Dynamic and Scaffolding Profile of Robust Downstream Signaling Intermediates in Response to MOR Infection
2.9. Top-Induced Signal Intermediates in Rice Response to MOR Infection
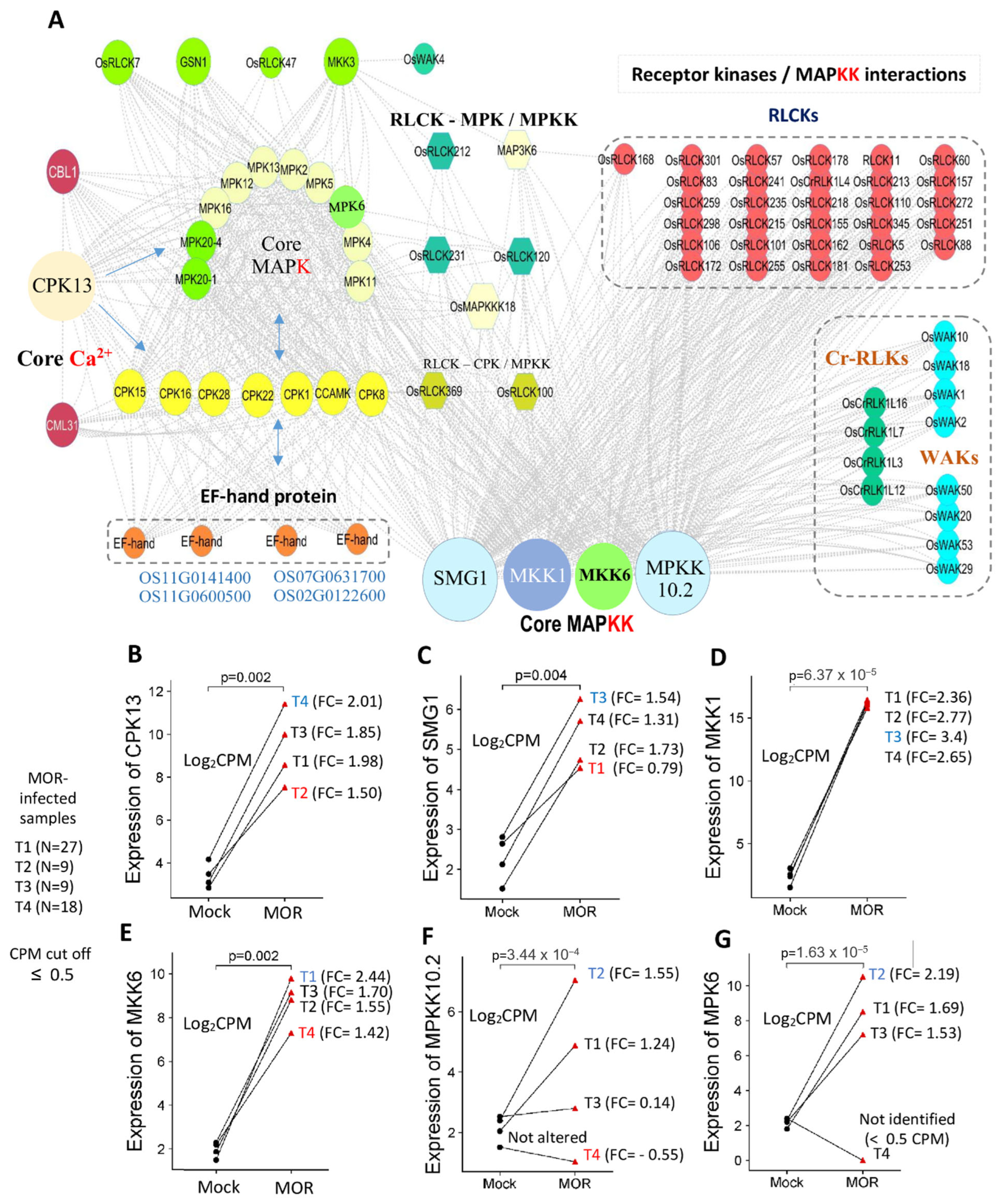
2.10. Key Interconnected Genes Among the Extracellular/Cytoplasmic Receptors and Signaling Intermediates in Rice Response to MOR Infection
3. Discussion
3.1. Overview and Exploratory Data Analysis of Rice RNA-Seq and Microarray Transcriptomic Data
3.2. Transcriptional Landscape of Receptor-Based Genes in Rice Response to MOR Infection
3.3. PTI-Related Genes Were Prominently Induced in Rice Response to MOR Infection
3.4. Interconnecting Genes of PTI and Downstream Signaling upon MOR Infection
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Retrieving and Processing of High-Throughput Sequencing Data
4.1.1. Retrieving and Processing of RNA-Seq Datasets
4.1.2. Retrieving and Processing of Microarray Datasets
4.2. Exploratory Data Analysis and Differential Gene Expression Analysis
4.3. Analysis of Receptor-Based Genes and Signaling Intermediate Genes in Rice Response to MOR Infection
4.4. PPI Network Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MOR | Magnaporthe oryzae |
| RNA-seq | RNA sequencing |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| GSE | Gene Expression Omnibus series |
| GPL | Gene expression platform |
| CPM | Counts per million |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| PPIs | Protein–protein interactions |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| DAMPs | host damage-associated molecular patterns |
| PTI | Pathogen-triggered immunity |
| WAK | Wall-associated kinase |
| RLK | Receptor-like kinases |
| RLCK | Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase |
| MAPK (MPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MAPKK (MKK) | MAPK kinases |
| MAPKKK | MAPK kinases kinase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| NLR | nucleotide binding and leucine-rich-repeat |
References
- Asibi, A.E.; Chai, Q.; Coulter, J.A. Rice blast: A disease with implications for global food security. Agronomy 2019, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, M.U.; Ahmad, I.; Qasim, M.; Ijaz, Z.; Rajput, N.; Memon, S.P.; Zaman, W.U.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, S. Progress in the management of rice blast disease: The role of avirulence and resistance genes through gene-for-gene interactions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Shi, H.; Qiu, J.; Tao, Z.; Wang, W. Effectors and environment modulating rice blast disease: From understanding to effective control. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Ngou, B.P.M.; Ding, P.; Xin, X.F. PTI-ETI crosstalk: An integrative view of plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 62, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngou, B.P.M.; Ahn, H.K.; Ding, P.; Jones, J.D.G. Mutual potentiation of plant immunity by cell-surface and intracellular receptors. Nature 2021, 592, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Jiang, Z.; Bi, G.; Nomura, K.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Cai, B.; Zhou, J.M.; He, S.Y.; Xin, X.F. Pattern-recognition receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immunity. Nature 2021, 592, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y. Plant mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in environmental stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhar, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Roy, A. The captivating role of calcium in plant-microbe interaction. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1138252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edel, K.H.; Marchadier, E.; Brownlee, C.; Kudla, J.; Hetherington, A.M. The Evolution of Calcium-Based Signalling in Plants. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R667–R679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, G.-L. Plant innate immunity in rice: A defense against pathogen infection. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngou, B.P.M.; Jones, J.D.G.; Ding, P. Plant immune networks. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Luan, S. Calcium homeostasis and signaling in plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2024, 77, 102485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Meng, X.; Shan, L.; He, P. Transcriptional Regulation of Pattern-Triggered Immunity in Plants. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.W.; Klessig, D.F. DAMPs, MAMPs, and NAMPs in plant innate immunity. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.N.; Li, Y.T.; Wu, Y.Z.; Li, T.; Geng, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Tan, X.L. Plant disease resistance-related signaling pathways: Recent progress and future prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shan, L.; Meng, X. Plant cell surface receptor-mediated signaling—A common theme amid diversity. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs209353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngou, B.P.M.; Wyler, M.; Schmid, M.W.; Kadota, Y.; Shirasu, K. Evolutionary trajectory of pattern recognition receptors in plants. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Dong, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. Characterization of wall-associated kinase/wall-associated kinase-like (WAK/WAKL) family in rose (Rosa chinensis) reveals the role of RcWAK4 in Botrytis resistance. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Shimamoto, K. Early signaling network in rice PRR-mediated and R-mediated immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, A.; Bagheri, A.; Chalvon, V.; Meusnier, I.; Kroj, T.; Kakhki, A.M. The RLCK subfamily VII-4 controls pattern-triggered immunity and basal resistance to bacterial and fungal pathogens in rice. Plant J. 2023, 115, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutus, A.; Sicilia, F.; Macone, A.; Cervone, F.; De Lorenzo, G. A domain swap approach reveals a role of the plant wall-associated kinase 1 (WAK1) as a receptor of oligogalacturonides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9452–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohorn, B.D.; Kohorn, S.L.; Saba, N.J.; Martinez, V.M. Requirement for pectin methyl esterase and preference for fragmented over native pectins for wall-associated kinase-activated, EDS1/PAD4-dependent stress response in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18978–18986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. MAPK kinase 10.2 promotes disease resistance and drought tolerance by activating different MAPKs in rice. Plant J. 2017, 92, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Yuan, M. Update on the roles of rice MAPK cascades. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Coaker, G.; Zhou, J.M.; Dong, X. Plant immune mechanisms: From reductionistic to holistic points of View. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1358–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, T.D.; Basak, J. Plant-pathogen interactions: What microarray tells about it? Mol. Biotechnol. 2012, 50, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanna, B.N.; Jain, P.; Solanke, A.U.; Das, A.; Thakur, S.; Singh, P.K.; Kumari, M.; Dubey, H.; Jaswal, R.; Pawar, D.; et al. Understanding the dynamics of blast resistance in rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interactions. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.R.; Rai, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Vijayan, J.; Devanna, B.N.; Ray, S. Rice Blast Management Through Host-Plant Resistance: Retrospect and Prospects. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xu, X.; Kong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.-W.; Liu, A.; Zou, L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of rice NLR genes responsive to the infections of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and Magnaporthe oryzae. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 111, 101488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.W.; Alhamdoosh, M.; Su, S.; Smyth, G.K.; Ritchie, M.E. RNA-seq analysis is easy as 1-2-3 with limma, Glimma and edgeR. F1000Research 2016, 5, ISCB Comm J-1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Ou, B.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, D.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gu, H.; Li, C.; Qin, G.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of rice early response to Magnaporthe oryzae identified OsWRKYs as important regulators in rice blast resistance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kwon, S.J.; Wu, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Agrawal, G.K.; Tamogami, S.; Rakwal, R.; Park, S.R.; Kim, B.G.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Early Responsive Genes in Rice during Magnaporthe oryzae Infection. Plant Pathol. J. 2014, 30, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, G.; Giraldo, M.C.; Khang, C.H.; Coughlan, S.; Valent, B. Interaction transcriptome analysis identifies Magnaporthe oryzae BAS1-4 as Biotrophy-associated secreted proteins in rice blast disease. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Sharma, V.; Katara, P. Comparative transcriptomics of rice and exploitation of target genes for blast infection. Agri Gene 2016, 1, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yao, S.; Kosami, K.I.; Guo, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fukao, Y.; Kaneko-Kawano, T.; Zhang, H.; She, Y.M.; et al. Identification of endogenous small peptides involved in rice immunity through transcriptomics- and proteomics-based screening. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbruscato, P.; Nepusz, T.; Mizzi, L.; Del Corvo, M.; Morandini, P.; Fumasoni, I.; Michel, C.; Paccanaro, A.; Guiderdoni, E.; Schaffrath, U.; et al. OsWRKY22, a monocot WRKY gene, plays a role in the resistance response to blast. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Singh, P.K.; Kapoor, R.; Khanna, A.; Solanke, A.U.; Krishnan, S.G.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, T.R. Understanding host-pathogen interactions with expression profiling of NILs carrying rice-blast resistance Pi9 gene. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Jain, P.; Venkadesan, S.; Karkute, S.G.; Bhati, J.; Abdin, M.Z.; Sevanthi, A.M.; Mishra, D.C.; Chaturvedi, K.K.; Rai, A.; et al. Understanding Rice-Magnaporthe Oryzae Interaction in Resistant and Susceptible Cultivars of Rice under Panicle Blast Infection Using a Time-Course Transcriptome Analysis. Genes 2021, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Veerappapillai, S.; Karuppasamy, R. Deciphering early responsive signature genes in rice blast disease: An integrated temporal transcriptomic study. J. Appl. Genet. 2024, 65, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Ding, L.; Xia, X. Identification and characterization of genes frequently responsive to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and Magnaporthe oryzae infections in rice. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Shi, S.; Nasir, F.; Chang, C.; Li, W.; Tran, L.P.; Tian, C. Comparative analysis of the root transcriptomes of cultivated and wild rice varieties in response to Magnaporthe oryzae infection revealed both common and species-specific pathogen responses. Rice 2018, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang; Dewei; Li, S.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Tang, D.; Cui, H. Transcriptome analysis of rice response to blast fungus identified core genes involved in immunity. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 3103–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Wang, A.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Yi, X.; Li, S.; Deng, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study and transcriptome analysis discover new genes for bacterial leaf blight resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakade, R.; Ingole, K.D.; Deshpande, S.; Pal, G.; Patil, S.S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Prasannakumar, M.K.; Ramu, V.S. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Rice Resistant and Susceptible Genotypes to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Identifies Novel Genes to Control Bacterial Leaf Blight. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, T.R.; Fischer, S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Katrekar, A.; Jung, K.H.; Ronald, P.C.; Fiehn, O. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of the rice response to the bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, S.; Xia, K.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, X. Integrative genomic and transcriptomic analysis of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae pathotype IV, V, and IX in China reveals rice defense-responsive genes. Phytopathol. Res. 2024, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Yu, H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Mao, X.; Zhang, J.; Lv, S.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Rice Near-Isogenic Lines Inoculated with Two Strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, AH28 and PXO99(A). Plants 2024, 13, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, O.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Wen, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative transcriptome and genome analysis between susceptible Zhefang rice variety Diantun 502 and its resistance variety Diantun 506 upon Magnaporthe oryzae infection. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liang, D.; Qi, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; Song, T.; Yu, M.; Cao, H.; Pan, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Transcriptome and differential expression analysis revealed the pathogenic-related genes in Magnaporthe oryzae during leaf and panicle infection. Phytopathol. Res. 2024, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, R.; Guo, W.; Khaskhali, S.; Fan, R.; Zhao, R.; Li, C.; He, C.; Niu, X.; Chen, Y. The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase OsRLCK118 regulates plant development and basal immunity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Trop. Plants 2022, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, A.; Ren, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, G.; Xu, Y.; Lei, C.; Zhu, S.; Pan, T.; et al. A cyclic nucleotide-gated channel mediates cytoplasmic calcium elevation and disease resistance in rice. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Yamada, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Hayashi, N.; Uchihashi, K.; Ishihama, N.; Kishi-Kaboshi, M.; Takahashi, A.; Tsuge, S.; et al. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase targeted by a plant pathogen effector is directly phosphorylated by the chitin receptor and mediates rice immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, T.; He, S.Y. Innate Immunity in Plants: An Arms Race Between Pattern Recognition Receptors in Plants and Effectors in Microbial Pathogens. Science 2009, 324, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, T.; Felix, G. A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delteil, A.; Gobbato, E.; Cayrol, B.; Estevan, J.; Michel-Romiti, C.; Dievart, A.; Kroj, T.; Morel, J.B. Several wall-associated kinases participate positively and negatively in basal defense against rice blast fungus. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.; Dinneny, J.R. A wall with integrity: Surveillance and maintenance of the plant cell wall under stress. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Pombo, M.A.; Rosli, H.G.; Martin, G.B. Tomato wall-associated kinase SlWak1 depends on Fls2/Fls3 to promote apoplastic immune responses to Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 1869–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmochowska-Boguta, M.; Kloc, Y.; Zielezinski, A.; Werecki, P.; Nadolska-Orczyk, A.; Karlowski, W.M.; Orczyk, W. TaWAK6 encoding wall-associated kinase is involved in wheat resistance to leaf rust similar to adult plant resistance. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saintenac, C.; Lee, W.S.; Cambon, F.; Rudd, J.J.; King, R.C.; Marande, W.; Powers, S.J.; Berges, H.; Phillips, A.L.; Uauy, C.; et al. Wheat receptor-kinase-like protein Stb6 controls gene-for-gene resistance to fungal pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Marcel, T.C.; Hartmann, F.E.; Ma, X.; Plissonneau, C.; Zala, M.; Ducasse, A.; Confais, J.; Compain, J.; Lapalu, N.; et al. A small secreted protein in Zymoseptoria tritici is responsible for avirulence on wheat cultivars carrying the Stb6 resistance gene. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Zhou, S.; Da, X.; Yan, P.; Wang, K.; Xu, J.; Mo, X. OsMKK6 Regulates Disease Resistance in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, P.; Xue, Y.; Yin, P.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. Pathogen-inducible OsMPKK10.2-OsMPK6 cascade phosphorylates the Raf-like kinase OsEDR1 and inhibits its scaffold function to promote rice disease resistance. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Kishi-Kaboshi, M.; Matsushita, A.; Jiang, C.J.; Goto, S.; Takahashi, A.; Hirochika, H.; Takatsuji, H. Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi-Kaboshi, M.; Okada, K.; Kurimoto, L.; Murakami, S.; Umezawa, T.; Shibuya, N.; Yamane, H.; Miyao, A.; Takatsuji, H.; Takahashi, A.; et al. A rice fungal MAMP-responsive MAPK cascade regulates metabolic flow to antimicrobial metabolite synthesis. Plant J. 2010, 63, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Roux, B.; Feng, F.; Guy, E.; Li, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.; Lautier, M.; Jardinaud, M.F.; Chabannes, M.; et al. The Decoy Substrate of a Pathogen Effector and a Pseudokinase Specify Pathogen-Induced Modified-Self Recognition and Immunity in Plants. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shirakawa, T.; Nakagami, H.; Mine, A.; Ishikawa, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Narusaka, M.; Narusaka, Y.; Ichimura, K.; et al. The Arabidopsis CERK1-associated kinase PBL27 connects chitin perception to MAPK activation. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 2468–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; de la Bastide, M.; Hamilton, J.P.; Kanamori, H.; McCombie, W.R.; Ouyang, S.; Schwartz, D.C.; Tanaka, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, S.; et al. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.; Meltzer, P.S. GEOquery: A bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1846–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Kruger, P.; Nagel, A.; Hannemann, J.; Giorgi, F.M.; Childs, L.; Osorio, S.; Walther, D.; Selbig, J.; et al. Robin: An intuitive wizard application for R-based expression microarray quality assessment and analysis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.P.; Grassi, L.; Henkin, R.; Smeraldi, F.; Spargo, T.P.; Kabiljo, R.; Koks, S.; Ibrahim, Z.; Dobson, R.J.B.; Al-Chalabi, A.; et al. GEOexplorer: A webserver for gene expression analysis and visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W367–W374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, G.K. Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biology. 2004, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R.; Laur, S.; Adler, P.; Vilo, J. Robust rank aggregation for gene list integration and meta-analysis. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Szklarczyk, D.; Frankild, S.; Kuhn, M.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Lin, J.; Minguez, P.; Bork, P.; von Mering, C.; et al. STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D808–D815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoot, M.E.; Ono, K.; Ruscheinski, J.; Wang, P.L.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Pathogen Infection Time Course (HPI) | Total DEGs | Extracellular Receptor Genes | Signaling-MAPK/Ca2+ Signaling Genes | N—Samples | Expression Profile (GEO-Code) | Data Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | ||||
| 12 h (T1) | 785 | 386 | 19 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 paired | GSE95394 | arrays |
| 24 h (T1) | 2910 | 2512 | 66 | 13 | 13 | 6 | 3 paired | GSE95394 | arrays |
| 48 h (T2) | 3151 | 2059 | 72 | 32 | 24 | 11 | 3 paired | GSE95394 | arrays |
| 72 h (T3) | 4425 | 6352 | 83 | 50 | 24 | 13 | 3 paired | GSE95394 | arrays |
| 24 h (T1) | 511 | 791 | 13 | 12 | 2 | 5 | 12 MOR | GSE30941 | arrays |
| 24 h (T1) | 1933 | 975 | 67 | 1 | 11 | 3 | 9 paired | GSE41798 | arrays |
| 72 h (T3) | 2535 | 2862 | 28 | 23 | 5 | 7 | 2 paired | GSE28308 | arrays |
| 48 h (T2) | 2875 | 1913 | 92 | 11 | 25 | 0 | 2 paired | GSE18361 * | arrays |
| 96 h (T4) | 1500 | 1324 | 71 | 9 | 12 | 0 | 2 paired | GSE18361 * | arrays |
| 144 h (T4) | 1182 | 720 | 50 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 2 paired | GSE18361 * | arrays |
| 24 h (T1) | 3316 | 509 | 112 | 6 | 27 | 0 | 6 paired | GSE62894 | arrays |
| 48 h (T2) | 5905 | 1721 | 108 | 26 | 44 | 1 | 6 paired | GSE62894 | arrays |
| 72 h (T3) | 3568 | 1655 | 146 | 63 | 46 | 9 | 6 paired | GSE62894 | arrays |
| 120 h (T4) | 5427 | 7804 | 130 | 98 | 29 | 18 | 6 paired | GSE62894 | arrays |
| 24 h (T1) | 2911 | 175 | 111 | 6 | 23 | 0 | 6 paired | GSE62893 | arrays |
| 48 h (T2) | 4827 | 1962 | 98 | 25 | 43 | 1 | 6 paired | GSE62893 | arrays |
| 72 h (T3) | 3568 | 1655 | 84 | 31 | 24 | 2 | 6 paired | GSE62893 | arrays |
| 120 h (T4) | 2329 | 2372 | 52 | 26 | 16 | 15 | 6 paired | GSE62893 | arrays |
| 24 h (T1) | 1697 | 1748 | 14 | 13 | 2 | 0 | 6 paired | GSE62895 * | arrays |
| 48 h (T2) | 1247 | 1855 | 17 | 23 | 3 | 0 | 6 paired | GSE62895 * | arrays |
| 72 h (T3) | 1412 | 1680 | 14 | 19 | 4 | 0 | 6 paired | GSE62895 * | arrays |
| 120 h (T4) | 1523 | 1364 | 16 | 13 | 4 | 0 | 6 paired | GSE62895 * | arrays |
| 8 h (T1) | 1027 | 1760 | 33 | 25 | 14 | 9 | 9 MOR | PRJEB45007 | RNA-seq |
| 16 h (T1) | 1868 | 2485 | 31 | 23 | 10 | 4 | 9 MOR | PRJEB45007 | RNA-seq |
| 24 h (T1) | 2162 | 1859 | 52 | 30 | 15 | 2 | 9 MOR | PRJEB45007 | RNA-seq |
| 48 h (T2) | 2942 | 1487 | 89 | 21 | 22 | 3 | 9 MOR | PRJEB45007 | RNA-seq |
| 72 h (T3) | 4337 | 3294 | 145 | 45 | 35 | 6 | 9 MOR | PRJEB45007 | RNA-seq |
| 96 h (T4) | 4902 | 3807 | 156 | 47 | 34 | 4 | 9 MOR | PRJEB45007 | RNA-seq |
| 144 h (T4) | 4315 | 3604 | 129 | 45 | 26 | 5 | 9 MOR | PRJEB45007 | RNA-seq |
| 12 h (T1) | 2243 | 1913 | 37 | 24 | 5 | 7 | 3 paired | PRJNA545418 | RNA-seq |
| 24 h (T1) | 2375 | 1951 | 38 | 27 | 10 | 8 | 3 paired | PRJNA545418 | RNA-seq |
| 12 h (T1) | 1749 | 1965 | 27 | 22 | 5 | 6 | 3 paired | PRJNA545418 | RNA-seq |
| 24 h (T1) | 1734 | 2130 | 24 | 18 | 7 | 8 | 3 paired | PRJNA545418 | RNA-seq |
| 12 h (T1) | 3098 | 1869 | 66 | 27 | 18 | 0 | 6 paired | PRJNA661210 | RNA-seq |
| 24 h (T1) | 1871 | 1169 | 76 | 10 | 11 | 0 | 6 paired | PRJNA661210 | RNA-seq |
| 36 h (T2) | 2497 | 1921 | 95 | 15 | 16 | 4 | 6 paired | PRJNA661210 | RNA-seq |
| 48 h (T2) | 2291 | 2011 | 84 | 11 | 14 | 2 | 6 paired | PRJNA661210 | RNA-seq |
| 24 h (T1) | 719 | 668 | 47 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 3 paired | PRJNA1062412 | RNA-seq |
| 48 h (T2) | 946 | 803 | 62 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 paired | PRJNA1062412 | RNA-seq |
| 72 h (T3) | 719 | 298 | 54 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 3 paired | PRJNA1062412 | RNA-seq |
| 24 h (T1) | 1560 | 945 | 35 | 15 | 11 | 6 | 2 MOR | PRJNA590671 | RNA-seq |
| 72 h (T3) | 2181 | 1056 | 29 | 23 | 13 | 3 | 2 MOR | PRJNA590671 | RNA-seq |
| 120 (T4) | 2046 | 1358 | 41 | 19 | 15 | 8 | 2 MOR | PRJNA590671 | RNA-seq |
| 24 h (T1) | 1683 | 1412 | 48 | 11 | 8 | 3 | 2 MOR | PRJNA310071 | RNA-seq |
| 48 h (T2) | 1965 | 1684 | 35 | 13 | 14 | 3 | 2 MOR | PRJNA310071 | RNA-seq |
| 48 h (T2) | 834 | 610 | 20 | 18 | 5 | 4 | 2 paired | PRJNA563035 * | RNA-seq |
| 72 h (T3) | 1120 | 918 | 13 | 10 | 2 | 5 | 2 paired | PRJNA563035 * | RNA-seq |
| 96 h (T4) | 1023 | 457 | 30 | 11 | 3 | 5 | 2 paired | PRJNA563035 * | RNA-seq |
| 24 h (T1) | 2991 | 3014 | 37 | 40 | 10 | 17 | 6 paired | PRJNA634330 | RNA-seq |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Receptor Type | Frequency Across the Analyzed Datasets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infection Stage | No. of Samples | |||||
| Total | Arrays | RNA-Seq | ||||
| Os08G0457400 | OsRLCK255 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 190 | 72 | 118 |
| Os02G0807900 | OsWAK21 | WALL-associated kinase | T1 | 21 | 18 | 3 |
| Os02G0807200 | OsWAK18 | WALL-associated kinase | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 81 | 72 | 9 |
| Os09G0561500 | WAK90 | WALL-associated kinase | T1-T3-T4 | 90 | 54 | 36 |
| Os04G0226600 | OsRLCK138 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T1-T3-T4 | 45 | 18 | 27 |
| Os11G0666200 | OsRLCK345 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 72 | 72 | 0 |
| Os02G0632800 | OsWAK14 | WALL-associated kinase | T1-T2-T3 | 54 | 54 | 0 |
| Os07G0541700 | OsRLCK237 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 72 | 72 | 0 |
| Os02G0807800 | OsWAK20 | WALL-associated kinase | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 126 | 72 | 54 |
| Os07G0686800 | OsRLCK241 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T1–T2 | 63 | 36 | 27 |
| Os11G0557500 | OsLysM-RLK7 | Lysin-motif extracellular receptor protein | T1-T2-T3 | 54 | 54 | 0 |
| Os11G0514500 | -- | Leucine repeat with extracellular domain | T2-T4 | 36 | 36 | 0 |
| Os08G0374600 | OsRLCK253 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T2-T3-T4 | 54 | 54 | 0 |
| Os12G0486900 | OsRLCK369 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T2-T3-T4 | 63 | 54 | 9 |
| Os07G0534500 | OsRLCK233 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T2 | 27 | 18 | 9 |
| Os03G0407900 | OsRLCK110 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T2–T3 | 81 | 36 | 45 |
| Os04G0631800 | OsRLCK162 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T2–T3 | 36 | 36 | 0 |
| Os02G0193000 | OsLysM-RLK1 | Lysin-motif-extracellular receptor | T3 | 18 | 18 | 0 |
| Os02G0811200 | OsWAK24 | WALL-associated kinase | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 158 | 36 | 122 |
| Os04G0598900 | OsWAK50 | WALL-associated kinase | T3–T4 | 45 | 18 | 27 |
| Os01G0136400 | OsWAK1 | WALL-associated kinase | T1–T4 | 40 | 18 | 22 |
| Os04G0127500 | OsWAK29 | WALL-associated kinase | T2-T3-T4 | 57 | 54 | 3 |
| Os03G0264300 | OsRLCK106 | Cytoplasmic-like kinase | T4 | 44 | 26 | 18 |
| OS02G0553000 | LRR-RLK | Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase | T1-T3-T4 | 60 | 0 | 60 |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Receptor Type | Stage | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os04G0369100 | OsRLCK145 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os01G0137200 | OsRLCK20 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os11G0225000 | OsRLCK319 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os06G0541600 | OsRLCK206 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os04G0369000 | OsRLCK144 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os03G0241600 | OsRLCK105 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os03G0179400 | OsRLCK103 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os02G0186500 | OsRLCK64 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os01G0929200 | OsRLCK53 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os01G0114900 | OsRLCK9 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os11G0609500 | OsRLCK339 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os01G0545500 | OsRLCK36 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os06G0727400 | OsRLCK220 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os01G0117300 | OsRLCK17 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os01G0784500 | OsRLCK44 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os01G0117200 | OsRLCK16 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os04G0365100 | OsWAK37 | WALL-associated kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os11G0694100 | OsWAK123 | WALL-associated kinase | T1 | Up |
| Os05G0463000 | OsRLCK188 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T2 | Up |
| Os06G0663900 | OsRLCK212 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T2 | Up |
| Os03G0825800 | OsRLCK120 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T2 | Up |
| Os01G0689900 | OsWAK10 | WALL-associated kinase | T2 | Up |
| Os02G0227700 | OsRLK5 | Extracellular receptor | T3 | Up |
| Os06G0663200 | OsRLCK211 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T3 | Up |
| Os02G0787200 | OsRLCK87 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T3 | Up |
| Os01G0789200 | OsRLCK45 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T3 | Up |
| Os06G0202900 | OsRLCK203 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T3 | Up |
| Os03G0283900 | OsRLCK108 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T3 | Up |
| Os12G0615100 | OsWAK128 | WALL-associated kinase | T3 | Up |
| Os11G0549300 | OsLysM-RLK8 | Lysin-motif extracellular receptor | T4 | Up |
| Os04G0655400 | OsRLCK169 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os09G0479200 | OsRLCK275 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os01G0267800 | OsRLCK29 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os02G0639100 | OsRLCK78 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os02G0565500 | OsRLCK74 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os09G0533600 | OsRLCK278 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os07G0537200 | OsRLCK234 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os04G0517700 | OsWAK51 | WALL-associated kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os03G0841100 | OsWAK28 | WALL-associated kinase | T4 | Up |
| Os01G0137500 | OsRLCK22 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T1 | Down |
| Os01G0546000 | OsLysM-RLK3 | Lysin-motif extracellular receptor | T2 | Down |
| Os08G0506400 | OsRLCK257 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T2 | Down |
| Os04G0220300 | OsWAK30 | WALL-associated kinase | T2 | Down |
| Os10G0200000 | OsRLCK295 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T3 | Down |
| Os11G0300700 | OsRLCK325 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T3 | Down |
| Os04G0654600 | OsRLCK167 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T3 | Down |
| Os01G0929200 | OsRLCK53 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os10G0431900 | OsRLCK300 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os11G0445300 | OsRLCK327 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os01G0114600 | OsRLCK8 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os01G0117400 | OsRLCK18 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os05G0100700 | OsRLCK175 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os01G0296000 | OsRLCK30 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os01G0117000 | OsRLCK15 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os03G0844100 | OsRLCK123 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os02G0152300 | OsRLCK61 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os01G0117300 | OsRLCK17 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os04G0619600 | OsRLCK161 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os07G0134200 | OsRLCK222 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os03G0274800 | OsRLCK107 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os03G0130900 | OsRLCK96 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os06G0168800 | OsRLCK200 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os08G0200500 | OsRLCK247 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os11G0194900 | OsRLCK315 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os01G0115600 | OsRLCK11 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os01G0310500 | OsRLCK31 | Cytoplasmic-receptor-like kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os10G0180800 | WAK112 | WALL-associated kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os09G0471400 | OsWAK81 | WALL-associated kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os04G0365100 | OsWAK37 | WALL-associated kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os09G0471800 | OsWAK85 | WALL-associated kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os04G0286300 | OsWAK33 | WALL-associated kinase | T4 | Down |
| Os12G0615300 | OsWAK129 | WALL-associated kinase | T4 | Down |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Protein Domain | Frequency Across the Analyzed Datasets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infection Stage | No. of Samples | |||||
| Total | Arrays | RNA-Seq | ||||
| Os01G0955100 | OsCML31 | Calmodulin-like protein | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 176 | 54 | 122 |
| Os12G0603800 | OsCML5 | Calmodulin-like protein | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 131 | 18 | 113 |
| Os05G0577500 | OsCML14 | Calmodulin-like protein | T1–T4 | 63 | 36 | 27 |
| Os11G0105000 | OsCML25 | Calmodulin-like protein | T3–T4 | 60 | 18 | 42 |
| Os12G0104900 | OsCML26 | Calmodulin-like protein | T4 | 27 | 18 | 9 |
| Os10G0418100 | ACA8 | Ca2+ P-type ATPase | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 45 | 36 | 9 |
| Os04G0644900 | OsNTMC2T2.1 | N-terminal trans-membrane | T1 | 18 | 18 | 0 |
| Os03G0397400 | OsCAX2 | Vacuolar cation exchanger protein | T1–T3 | 54 | 21 | 33 |
| Os12G0624200 | OsCCX4 | Ca2+ exchanger | T3–T4 | 36 | 36 | 0 |
| Os04G0584600 | OsCDPK13 | Ca2+-dependent protein kinase | T1–T3 | 60 | 18 | 42 |
| Os07G0631700 | EF-hand | EF-hand type domain | T3 | 54 | 54 | 0 |
| Os07G0584100 | OsWNK5 | MAP kinase-like protein | T1-T2-T3 | 81 | 72 | 9 |
| Os12G0162100 | OsWNK9 | MAP kinase-like protein | T3 | 18 | 18 | 0 |
| Os03G0415200 | MAP3K | MAP kinase-like protein | T1-T2-T3 | 117 | 72 | 45 |
| Os01G0699500 | MAP3K6 | MAP kinase-like protein | T2-T3-T4 | 54 | 54 | 0 |
| Os06G0147800 | OsMKK1 | MAP (2) K | T1-T2-T4 | 120 | 72 | 48 |
| Os01G0510100 | OsMKK6 | MAP (2) K | T2–T3 | 36 | 36 | 0 |
| Os03G0285800 | OsMSRMK2 | MAPK | T1-T2-T3-T4 | 176 | 54 | 122 |
| Os10G0533600 | OsMPK6 | MAPK | T1-T2-T3 | 72 | 36 | 36 |
| Os02G0135200 | OsMPK13 | MAPK | T2–T4 | 63 | 36 | 27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salem, F.; ElGamal, A.; Tang, X.; Yang, J.; Kong, W. Transcriptional Dynamics of Receptor-Based Genes Reveal Immunity Hubs in Rice Response to Magnaporthe oryzae Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104618
Salem F, ElGamal A, Tang X, Yang J, Kong W. Transcriptional Dynamics of Receptor-Based Genes Reveal Immunity Hubs in Rice Response to Magnaporthe oryzae Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104618
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalem, Fatma, Ahmed ElGamal, Xiaoya Tang, Jianyuan Yang, and Weiwen Kong. 2025. "Transcriptional Dynamics of Receptor-Based Genes Reveal Immunity Hubs in Rice Response to Magnaporthe oryzae Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104618
APA StyleSalem, F., ElGamal, A., Tang, X., Yang, J., & Kong, W. (2025). Transcriptional Dynamics of Receptor-Based Genes Reveal Immunity Hubs in Rice Response to Magnaporthe oryzae Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104618






