An Ionic Liquid-Assisted Mixed Micelle-Mediated Centrifuge-Less Cloud Point Extraction Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Molybdenum(VI)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. CPE–Spectrophotometric Optimization
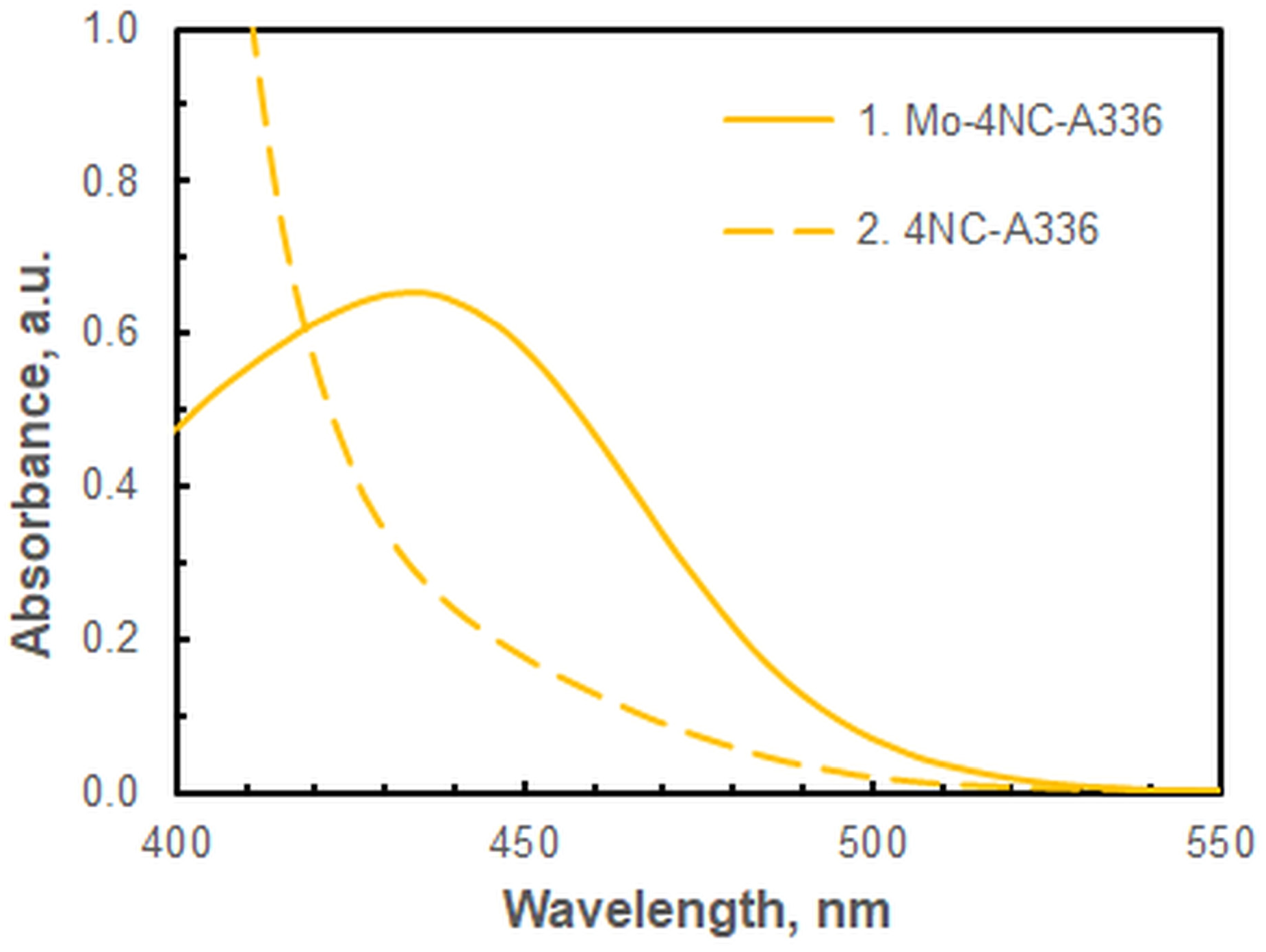
2.1.1. Absorption Spectrum
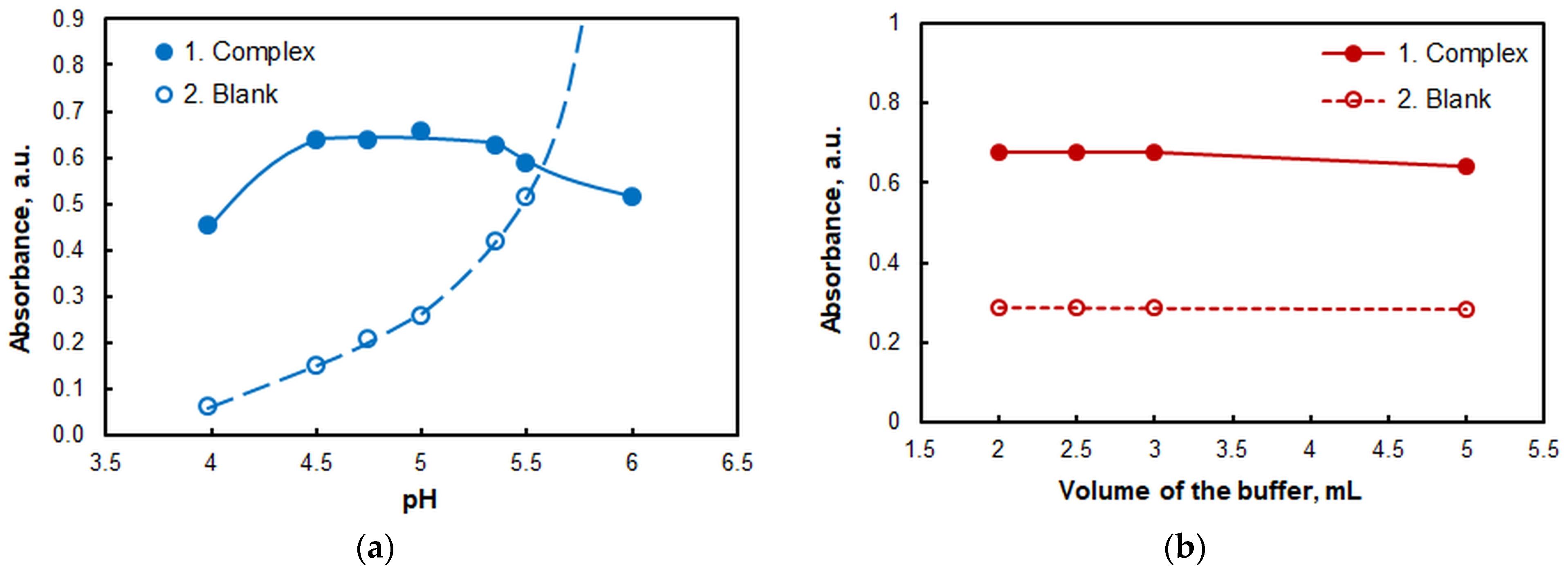
2.1.2. The Effect of pH and Volume of the Buffer
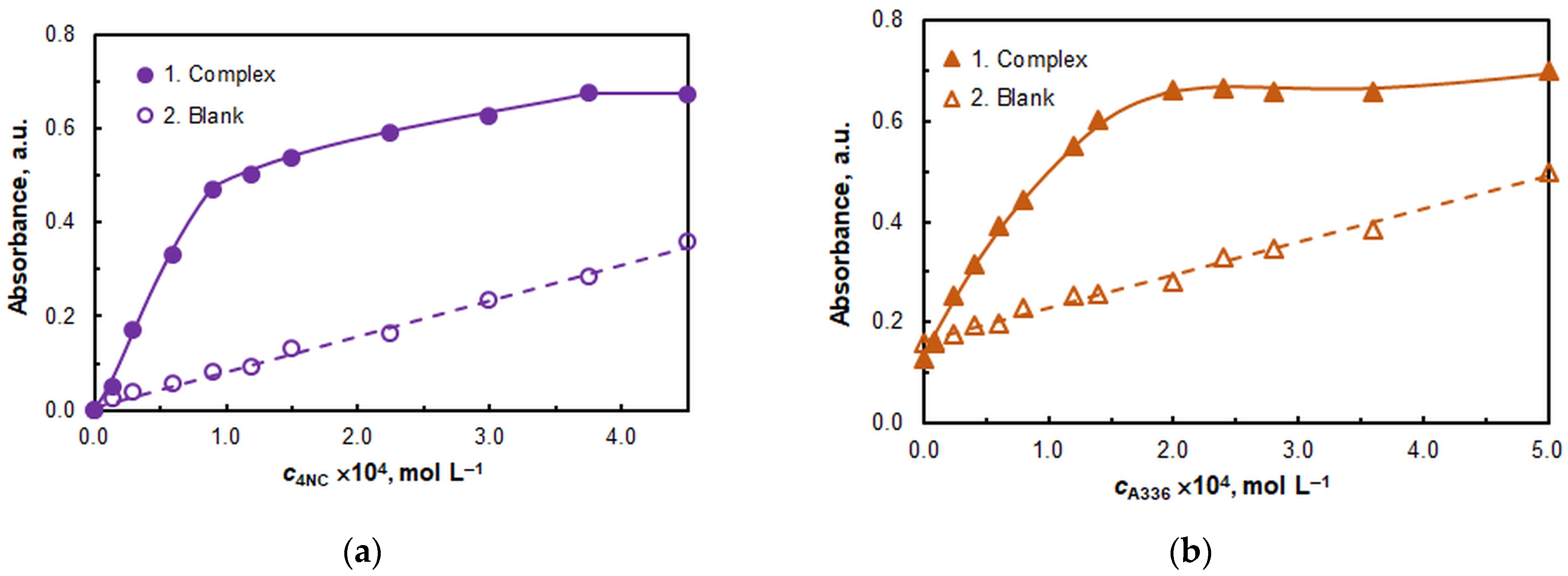
2.1.3. The Effect of Reagent Concentrations
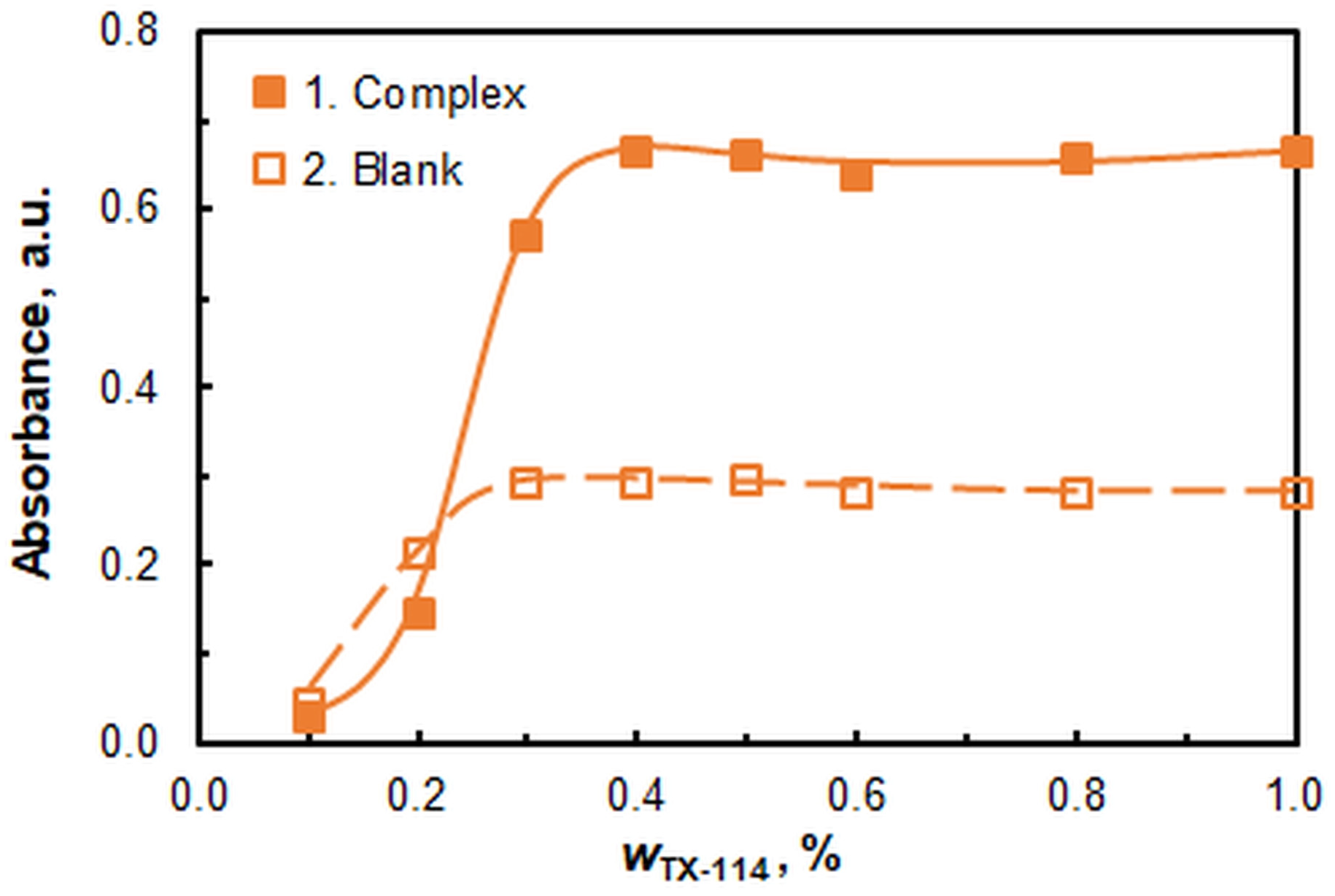
2.1.4. The Effect of TX-114 Mass Fraction
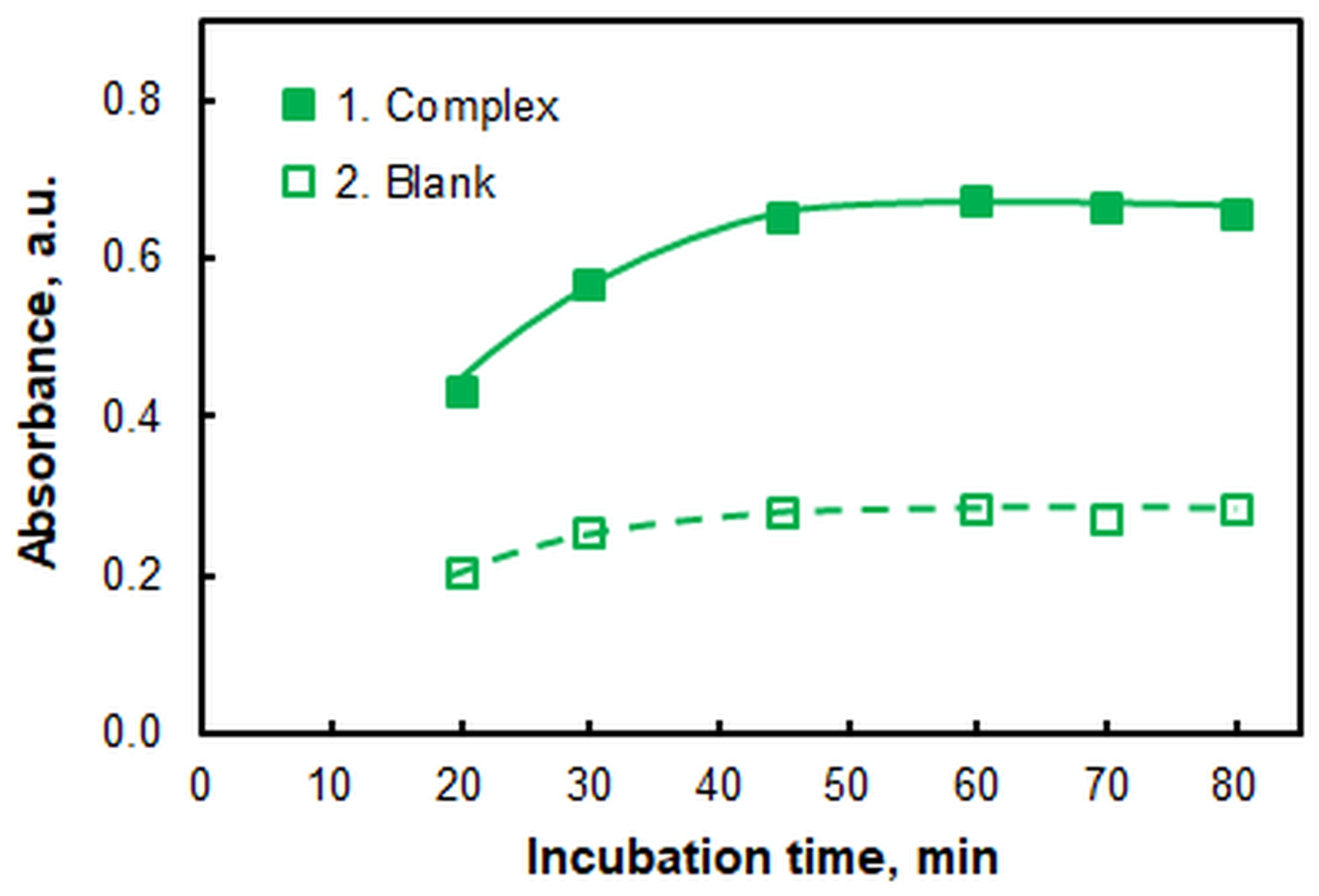
2.1.5. The Effect of Incubation Time
2.1.6. The Cooling Time Experiments
2.1.7. SRP Processing
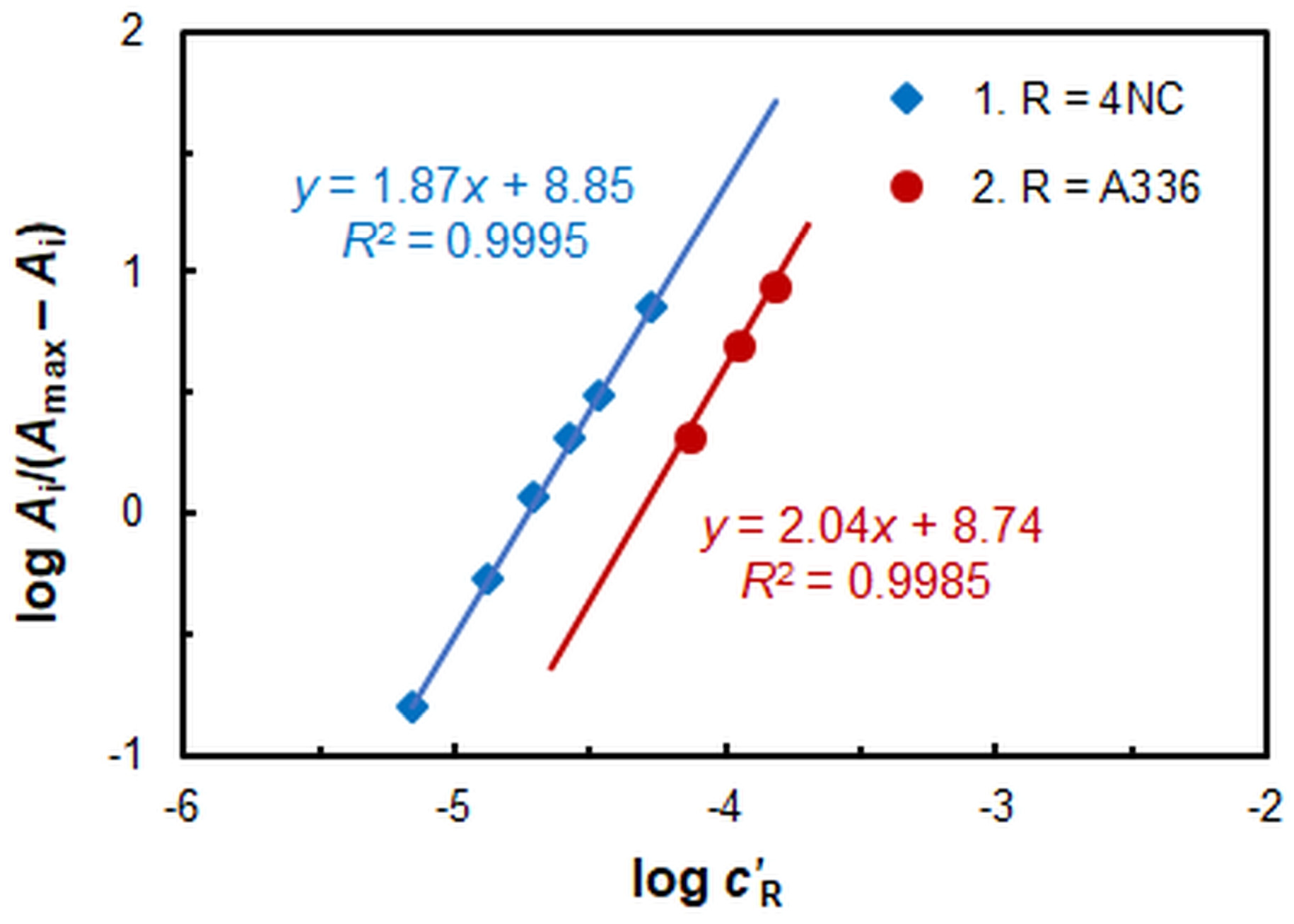
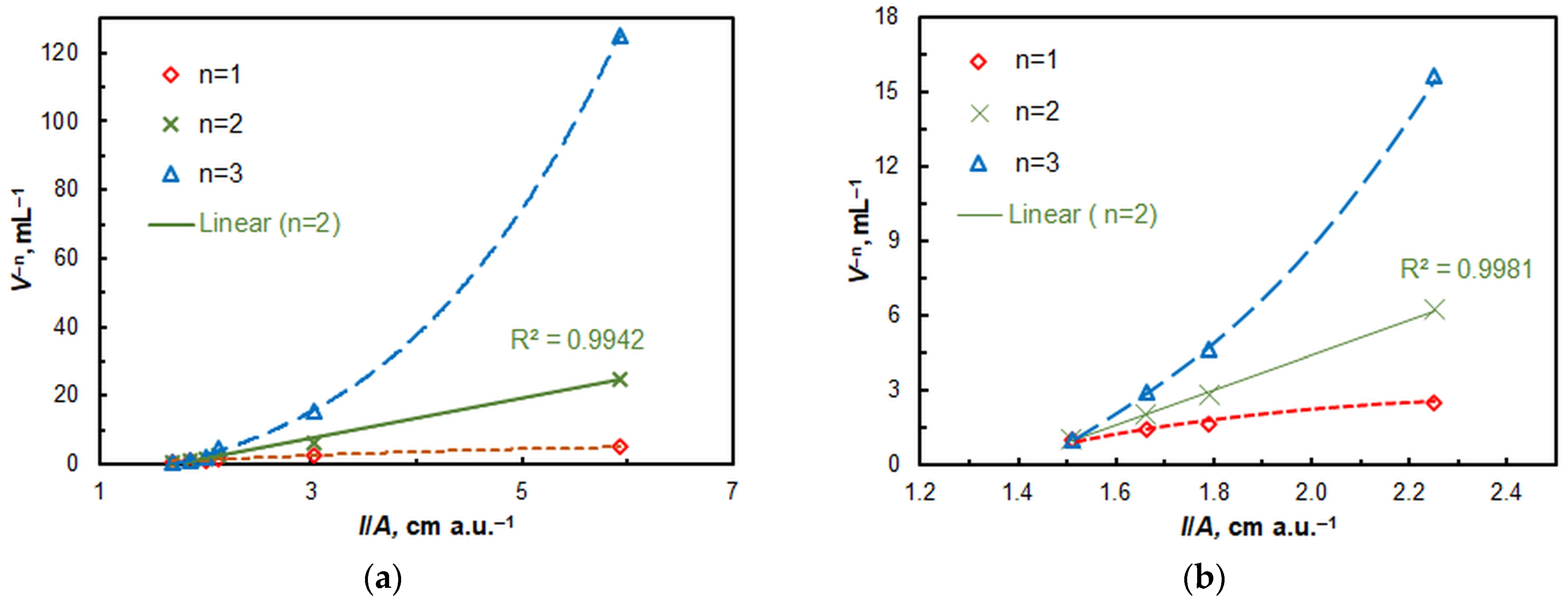
2.2. Stoichiometry, Formula of the Extracted Complex, and Equation of Complexation
2.3. The Constant of Extraction
2.4. Beer’s Law and Analytical Characteristics
2.5. The Effect of Foreign Ions
2.6. Analytical Application
2.7. Comparison with Other Extractive Methods
| Reagent (s) | Procedure | Detection | Surfactant (s) | pH | Sample | Linear Range/ ng mL−1 | LOD, ng mL−1 | λmax, nm | 10−4ε, L mol−1 cm−1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR | MM-CPE | UV–Vis | TX-114 + CTAB | 4.6 | River water and coastal waters | 1.23–37.0 | 1.24 | 608 | NR | [11] |
| DHDPhB + NaSal | RT-CPE | UV–Vis | TX-100 | 1.8 | Water and milk | 7.9–160 | 2.3 | 560 | NR | [15] |
| DHMPhB + NaSal | RT-CPE | UV–Vis | TX-100 | 2.0 | Water, rose hips, and pharmaceuticals | 160–1800 | 50 | 530 | NR | [16] |
| Nile blue A + Oxalate | UTA-CPE | FAAS | PONPE 7.5 | 4.5 | Milk, vegetables, and foodstuffs | 3–340 | 0.86 | – | – | [53] |
| VPB + KSCN | MM-CPE | FAAS | TX-114 + CPC | 2.0 | Beverages and foodstuffs | 7.5–1800 | 2.18 | 543 | – | [44] |
| 8-HQ | CPE | FAAS | TX-114 | 4.5 | Mineral water | NR | 40 | – | – | [52] |
| QA | CPE | GFAAS | TX-114 | 3.6 | Seawater and tap water | 0.03–0.6 | 0.007 | 545 | – | [56] |
| BPR + KI | CPE | UV–Vis | CTAB | 1 | Steel and water | 0.3–320 | 0.1 | 576 | NR | [14] |
| 4NC + BTC | LLE | UV–Vis | – | 1.8–4.0 | Steel and ferromolybdenum | 200–6700 | NR | 445 | 2.38 | [18] |
| 4NC + BZC | LLE | UV–Vis | – | 1.4 | Synthetic mixtures, steel, and water | 18.6–3100 | 5.6 | 439 | 5.5 | [17] |
| 4NC | IL-MM-CL-CPE | UV–Vis | TX-114 + A336 | 4.5 | Mineral water, steel, and a food supplement | 10.8–580 | 3.2 | 435 | 33.4 | This work |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Samples and Sample Preparation
3.4. Optimization Procedure
3.5. Recommended Procedure for the Determination of Mo(VI)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giovannuzzi, S. Chapter 10-Molybdenum enzymes. In Metalloenzymes; Supuran, C.T., Donald, W.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2024; pp. 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, J.A. Molybdenum Nutriture in Humans. J. Evid.-Based Integr. Med. 2011, 16, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albin, M.; Oskarsson, A. Chapter 23-Molybdenum. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals (Fifth Edition); Nordberg, G.F., Costa, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2022; Volume 2, pp. 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Proposes Adequate Intake Levels for Fluoride and Molybdenum. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/press/news/130808 (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Novotny, J.A.; Peterson, C.A. Molybdenum. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 272–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outteridge, T.; Kinsman, N.; Ronchi, G.; Mohrbacher, H. Editorial: Industrial relevance of molybdenum in China. Adv. Manuf. 2020, 8, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.K. Uses of Metals and Metallic Minerals; New Age International (P) Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2007; pp. 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Z. Molybdenum and its alloys in advanced engine applications: From material selection to surface optimization. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 560, 02016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynie, D.E. Modern extraction techniques. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3997–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, P.; Bhat, G.P.; Gandhi, S. Green extraction and separation processes. In Advances in Separation Sciences: Sustainable Processes and Technologies; Ingole, P.G., Chaudhery, M.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2025; pp. 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalakshmi, K.V.; Shyamala, P.; Khan, S.A.; Puranam, D.H. Cloud Point Extraction Method for Separation and Pre-concentration of Molybdenum and Zirconium Using Mixture of Surfactants from Natural Waters and their Determination by Spectrophotometry. Methods Objects Chem. Anal. 2024, 19, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehbaghi, M.; Shemirani, F. Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and enhanced spectrophotometric determination of molybdenum(VI) in water and plant leaves samples by FO-LADS. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelit, L.; Koçak, S.; Pelit, F.O.; Türkmen, H.; Ertaş, F.N. A spectrophotometric method for determination of molybdenum in water samples by using pyrogallol red and a water soluble ionic liquid. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 5792–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrakian, T.; Ghazizadeh, F. Cloud-point preconcentration and spectrophotometric determination of trace amounts of molybdenum(VI) in steels and water samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snigur, D.; Barbalat, D.; Chebotarev, A.; Synievyd, A.; Bevziuk, K. A rapid cloud point extraction of molybdenum(VI) with 6,7-dihydroxy-2,4-diphenylbenzopyrylium perchlorate prior to its spectrophotometric determination. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snigur, D.; Chebotarev, A.; Dubovyiy, V.; Barbalat, D.; Bevziuk, K. Salicylic acid assisted cloud point extraction at room temperature: Application for preconcentration and spectrophotometric determination of molybdenum(VI). Microchem. J. 2018, 142, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divarova, V.V.; Saravanska, A.D.; Toncheva, G.K.; Milcheva, N.; Delchev, V.B.; Gavazov, K.B. Spectrophotometric determination of molybdenum(VI) as a ternary complex with 4-nitrocatechol and benzalkonium chloride. Molecules 2022, 27, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, A.; Lekova, V.; Gavazov, K.; Boyanov, B. Ternary complex of molybdenum(VI) with 4-nitrocatechol and tetrazolium blue chloride and its application to extraction-spectrophotometric analysis of ferrous metallurgy products. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 62, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, A.; Lekova, V.; Gavazov, K.; Boyanov, B. Investigation of the extraction equilibrium of ion-association complexes of molybdenum(VI) with some polyphenols and thiazolyl blue. Extraction-spectrophotometric determination of molybdenum. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2005, 3, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, L.; Ackermann, G.; Burns, D.T.; Savvin, S.B. Present and future status of organic analytical reagents-Part I: General remarks. Pure Appl. Chem. 1990, 62, 2147–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich Safety Data Sheet: 4-Nitrocatechol. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/BG/en/sds/aldrich/n15553?userType=anonymous (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Divarova, V.V.; Stojnova, K.T.; Radkovska, I.D.; Saravanska, A.D.; Toncheva, G.K.; Delchev, V.B.; Gavazov, K.B. Extraction system for the spectrophotometric determination of tungsten(VI) with 4-nitrocatechol and benzalkonium chloride. Acta Chim. Slov. 2024, 71, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racheva, P.V.; Saravanska, A.D.; Toncheva, G.K.; Kiradzhiyska, D.D.; Milcheva, N.P.; Divarova, V.V.; Pencheva, I.P.; Stojnova, K.T.; Delchev, V.B.; Gavazov, K.B. A semi-micro extraction spectrophotometric determination of iron using 4-nitrocatechol and xylometazoline hydrochloride. Molecules 2025, 30, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojnova, K.T.; Lekova, V.D. Study on the equilibria of chelate formation and the ion-association of anionic chelate of germanium(IV) with 4-nitrocatechol and 2-(4-iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyl-2H-tetrazolium cation. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 64, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazov, K.B. Nitroderivatives of catechol: From synthesis to application. Acta Chim. Slov. 2012, 59, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Alempijević, S.B.; Vidović, K.; Vukosav, P.; Frka, S.; Kroflič, A.; Mihaljević, I.; Grgić, I.; Strmečki, S. Integrating voltammetry in ecotoxicology: Cu(II)-nitrocatechol complexes formation as a driver of Cu(II) and nitrocatechol toxicity in aquatic systems. Electrochim. Acta 2025, 522, 145938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tôei, K. Ion-association reagents. A review. Anal. Sci. 1987, 3, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamini, Y.; Ghambarian, M. 3.33-Environmental Applications of Cloud-Point Extraction. In Comprehensive Sampling and Sample Preparation; Pawliszyn, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 657–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytlakowska, K.; Kozik, V.; Dabioch, M. Complex-forming organic ligands in cloud-point extraction of metal ions: A review. Talanta 2013, 110, 202–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, A.; Namieśnik, J.; Wolska, L. Theory and recent applications of coacervate-based extraction techniques. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, W.I. Recent developments and applications of cloud point extraction: A critical review. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halko, R.; Hagarová, I.; Andruch, V. Innovative Approaches in Cloud-Point Extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1701, 464053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snigur, D.; Azooz, E.A.; Zhukovetska, O.; Guzenko, O.; Mortada, W. Recent innovations in cloud point extraction towards a more efficient and environmentally friendly procedure. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 164, 117113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semysim, F.A.; Shabaa, G.J.; Azooz, E.A.; Snigur, D. Alternative green solvents in cloud point extraction methods: Recent developments, challenges, and greenness evaluation. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2025, 45, e00250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanova, T.S.; Simitchiev, K.K.; Gavazov, K.B. Liquid–liquid extraction and cloud point extraction for spectrophotometric determination of vanadium using 4-(2-pyridylazo) resorcinol. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, J.-P.; Virtanen, P.; Sjoholm, R. Aliquat 336—A versatile and affordable cation source for an entirely new family of hydrophobic ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zari, N.; Hassan, J.; Tabar-Heydar, K.; Ahmadi, S.H. Ion-association dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of trace amount of gold in water samples and ore using Aliquat 336 prior to inductivity coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry determination. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 86, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhoum, A.A.; Mohamed, B.T.; Abdulmoteleb, S.S.; Mohamady, S.I.; Falila, N.I. Solvent extraction of titanium(IV) from orthophosphoric acid media using Aliquat-336/kerosene and stripping with nitric acid. Hydrometallurgy 2025, 231, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.E.; Amin, A.S.; El-Maghrabey, M.; El Hamd, M.A.; Mahdi, W.A.; Alshehri, S.; Batakoushy, H.A. Sustainable non-plasticized polymer inclusion membrane containing an immobilizing optode ligand for in situ ultra-sensitive colorimetric measurement and pre-concentration of beryllium ions in environmental and biological matrices. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 2024, 452, 115624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oukebdane, K.; Semmoud, R.; Didi, M.A. Cloud point extraction of Telon Orange anionic azo-dye from aqueous sulphate solutions using Aliquat 336 ionic liquid/Tween 40 as extracting system: Factorial design optimization methodology. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 247, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Krishna, D.; Noorbasha, N.M.; Jai Kumar, S. A new sequential and simultaneous speciation analysis of thallium in coal effluents by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after a novel ligandless mixed micelle cloud point extraction. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 100, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnagar, M.M.; Hashem, M.A.; Hassanien, M.M.; Ismail, M.A. pH-controlled mixed micelle cloud point extraction for selective removal of trace levels of iron from titanium concentrates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 265, 118534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet-Chouinard, G.; Larivière, D. Determination of Pb in environmental samples after cloud point extraction using crown ether. Talanta 2018, 179, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürkan, R.; Aksoy, T.; Ulusoy, H.T.; Akçay, M. Determination of low levels of molybdenum (VI) in food samples and beverages by cloud point extraction coupled with flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 32, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazov, K.B.; Racheva, P.V.; Saravanska, A.D.; Genc, F.; Delchev, V.B. Mono- and binuclear complexes in a centrifuge-less cloud-point extraction system for the spectrophotometric determination of zinc(II). Molecules 2024, 29, 4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazov, K.B.; Racheva, P.V.; Milcheva, N.P.; Divarova, V.V.; Kiradzhiyska, D.D.; Genç, F.; Saravanska, A.D. Use of a hydrophobic azo dye for the centrifuge-less cloud point extraction–spectrophotometric determination of cobalt. Molecules 2022, 27, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natansohn, S.; Krugler, J.I.; Lester, J.E.; Chagnon, M.S.; Finocchiaro, R.S. Stability constants of complexes of molybdate and tungstate ions with o-hydroxy aromatic ligands. J. Phys. Chem. 1980, 84, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiming, Z.; Dongsten, M.; Cunxiao, Y. Mobile equilibrium method for determining composition and stability constant of coordination compounds of the form MmRn. J. Rare Earths 1997, 15, 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Asmus, E. Eine neue Methode zur Ermittlung der Zusammensetzung schwacher Komplexe (A new method for the determination of composition of weak complexes). Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1960, 178, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, A.; Langmyhr, F.J. A modified and a new straight-line method for determining the composition of weak complexes of the form AmBn. Anal. Chim. Acta 1966, 36, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molybdenum Drops, Extract Pharma LTD. Available online: https://epharm.bg/molibden-koncentrat-extract-pharma.html (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- de Jesus, A.M.; Oliveira, L.F.; Canevari, N.T.; Pereira-Filho, E.R. Sequential preconcentration using cloud point extraction: Determination of vanadium and molybdenum in water and pharmaceutical samples using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Braz. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 10, 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Gürkan, R.; Korkmaz, S.; Altunay, N. Preconcentration and determination of vanadium and molybdenum in milk, vegetables and foodstuffs by ultrasonic-thermostatic-assisted cloud point extraction coupled to flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 155, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousi, N.; Wojnowski, W.; Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Samanidou, V. Blue applicability grade index (BAGI) and software: A new tool for the evaluation of method practicality. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 7598–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, F.R.; Bedair, A.; Locatelli, M. Click Analytical Chemistry Index as a novel concept and framework, supported with open source software to assess analytical methods. Adv. Sample Prep. 2025, 14, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, H.; Çengel, T.; Apak, R. Selective cloud point extraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric determination of molybdenum (VI) ion in seawater samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaneyulu, Y.; Reddy, M.P.; Kumar, P.V.S.; Kavipurapu, C.; Rao, B. Selective and sensitive extraction spectrophotometric method for the determination of vanadium (V) as a mixed ligand complex with N-phenyl benzohydroxamic acid and 4-(2-pyridylazo)resorcinol in non-aqueous media. Microchim. Acta 1990, 100, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerramilli, A.; Kavipurapu, C.S.; Manda, R.R.; Pillutla, C.M. Extractive spectrophotometric method for the determination of vanadium(V) in steels and titanium base alloy. Anal. Chem. 1986, 58, 1451–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
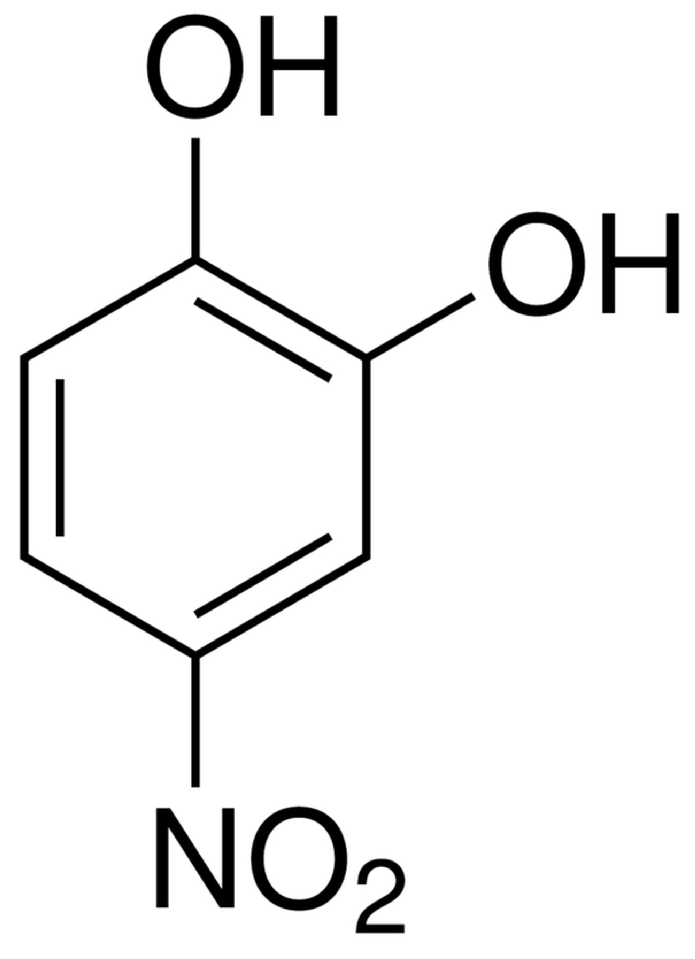
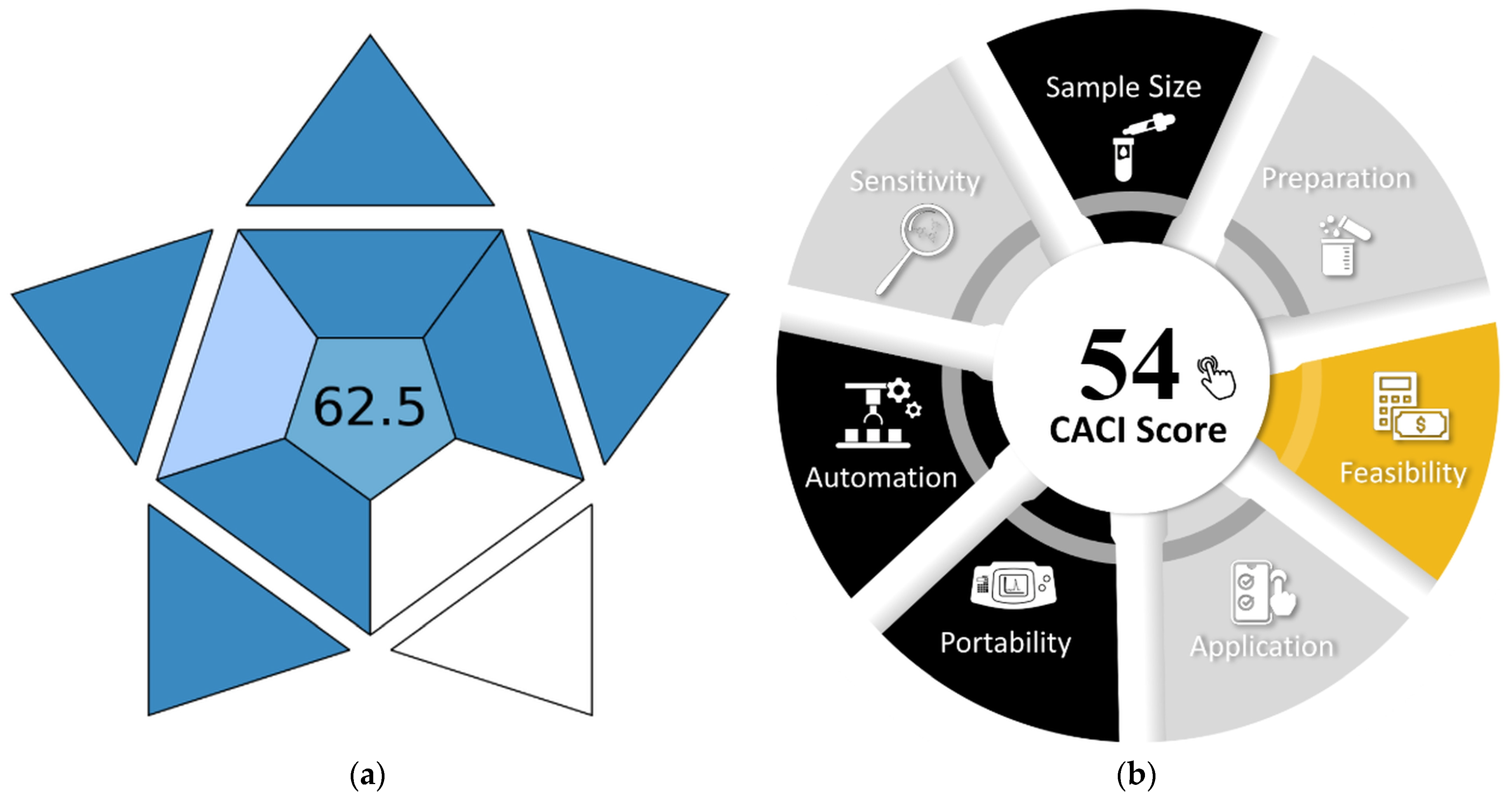
| Parameter | Optimal Value/Range | Figure |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength, nm | 435 | Figure 2 |
| pH | 4.5–5.0 | Figure 3a |
| Volume of the buffer, mL | 2–3 | Figure 3b |
| Concentration of 4NC, mol L−1 | 3.75 × 10−4 | Figure 4a |
| Concentration of A336, mol L−1 | 2.0 × 10−4 | Figure 4b |
| Mass fraction of TX-114 | 0.4–0.5 | Figure 5 |
| Incubation time at 60 °C, min | 55 | Figure 6 |
| Refrigeration time at −20 °C, min | 55 | – |
| Test tube capacity, mL | 50 | – |
| Mass * of the final solution, g | 3 | – |
| Method | Log Kex * |
|---|---|
| Holme–Langmyhr method | 8.8 ± 0.4 |
| Mobile equilibrium method | 8.6 ± 0.3 |
| Ion | Salt Formula | Ion:Mo(VI) Mass Ratio | Mo(VI) Found, μg | R, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al(III) | Al2(SO4)3·18H2O | 1 a 100 b | 7.7 7.9 | 100 102 |
| Ba(II) | BaCl2 | 1000 | 7.3 | 95.6 |
| Br− | NaBr | 2000 c | 7.8 | 101 |
| Ca(II) | Ca(NO3)2 | 750 | 7.7 | 100 |
| Cd(II) | CdCl2 | 100 | 7.4 | 96.2 |
| Cl− | NaCl | 2000 c | 7.3 | 95.2 |
| Cr(III) | Cr2(SO4)3 | 2 a | 8.0 | 104 |
| Cr(VI) | K2CrO4 | 2 | 7.9 | 103 |
| Co(II) | CoSO4·7H2O | 10 | 7.6 | 99.4 |
| Cu(II) | Cu(SO4)2·5H2O | 5 a | 7.6 | 98.6 |
| EDTA2− | Na2EDTA·2H2O | 500 1000 | 7.4 6.8 | 96.2 88.0 |
| F− | NaF | 200 500 | 7.9 8.1 | 102 105 |
| Fe(III) | Fe2(SO4)3 | 5 a | 7.5 | 97.9 |
| HPO42− | Na2HPO4·12H2O | 100 | 7.9 | 103 |
| Li+ | Li2SO4·H2O | 1000 | 8.2 | 107 |
| Mg(II) | MgSO4·7H2O | 2500 c | 7.9 | 103 |
| Mn(II) | MnSO4·H2O | 5 a | 7.3 | 95.6 |
| Ni(II) | NiSO4·7H2O | 1000 c | 7.8 | 102 |
| NO3− | NaNO3 | 2000 c | 7.7 | 99.4 |
| Pb(II) | Pb(NO3)2 | 10 c | 7.9 | 103 |
| Re(VII) | NH4ReO4 | 100 | 8.2 | 106 |
| SO42− | MgSO4·7H2O | 10,000 b | 7.9 | 103 |
| V(V) | NH4VO3 | 2 a | 8.0 | 104 |
| W(VI) | Na2WO4·2H2O | 1 | 8.5 | 111 |
| Zn(II) | ZnSO4·7H2O | 1000 c | 7.9 | 102 |
| # | Certified Mo Content, % | Other Ingredients, % | Mo Found,* % | R, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.96 | 17.7 (W), 4.71 (Co), 4.21 (Cr), 1.58 (V), 0.35 (Mn), 0.18 (Si), 0.081(C), and the balance Fe | 0.964 ± 0.032 | 100.4 |
| 2 | 0.97 | 11.7 (W), 4.09 (Cr), 0.35 (Mn), 0.12 (Ni), 0.10 (Cu), 0.083 (C), 0.22 (Si), and the balance Fe | 0.960 ± 0.040 | 99.0 |
| Bottled Water | Mo(VI) Concentration, ng mL−1 | RSD, % | R, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added | Found c | |||
| Gorna Banya a | 0 | 16.7 ± 1.5 | 9.0 | – |
| 19.2 | 35.8 ± 2.7 | 7.7 | 99.6 | |
| 38.4 | 57.4 ± 4.1 | 7.2 | 106 | |
| 57.6 | 74.1 ± 9.2 | 12.4 | 99.7 | |
| 76.8 | 92.4 ± 5.6 | 6.0 | 98.7 | |
| Devin b | 0 | 21.8 ± 1.8 | 8.9 | – |
| 19.2 | 40.0 ± 3.2 | 8.1 | 94.6 | |
| 38.4 | 62.4 ± 2.2 | 3.6 | 106 | |
| 57.6 | 81.7 ± 1.0 | 1.2 | 104 | |
| 76.8 | 96.0 ± 0.8 | 0.8 | 96.7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Divarova, V.; Gajdošová, A.; Racheva, P.; Gavazov, K. An Ionic Liquid-Assisted Mixed Micelle-Mediated Centrifuge-Less Cloud Point Extraction Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Molybdenum(VI). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104597
Divarova V, Gajdošová A, Racheva P, Gavazov K. An Ionic Liquid-Assisted Mixed Micelle-Mediated Centrifuge-Less Cloud Point Extraction Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Molybdenum(VI). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104597
Chicago/Turabian StyleDivarova, Vidka, Andrea Gajdošová, Petya Racheva, and Kiril Gavazov. 2025. "An Ionic Liquid-Assisted Mixed Micelle-Mediated Centrifuge-Less Cloud Point Extraction Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Molybdenum(VI)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104597
APA StyleDivarova, V., Gajdošová, A., Racheva, P., & Gavazov, K. (2025). An Ionic Liquid-Assisted Mixed Micelle-Mediated Centrifuge-Less Cloud Point Extraction Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Molybdenum(VI). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104597







