Lactobacillus brevis GKJOY Supplementation Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Reproductive Dysfunction in Male Rats with Polystyrene Microplastics-Induced Reproductive Toxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
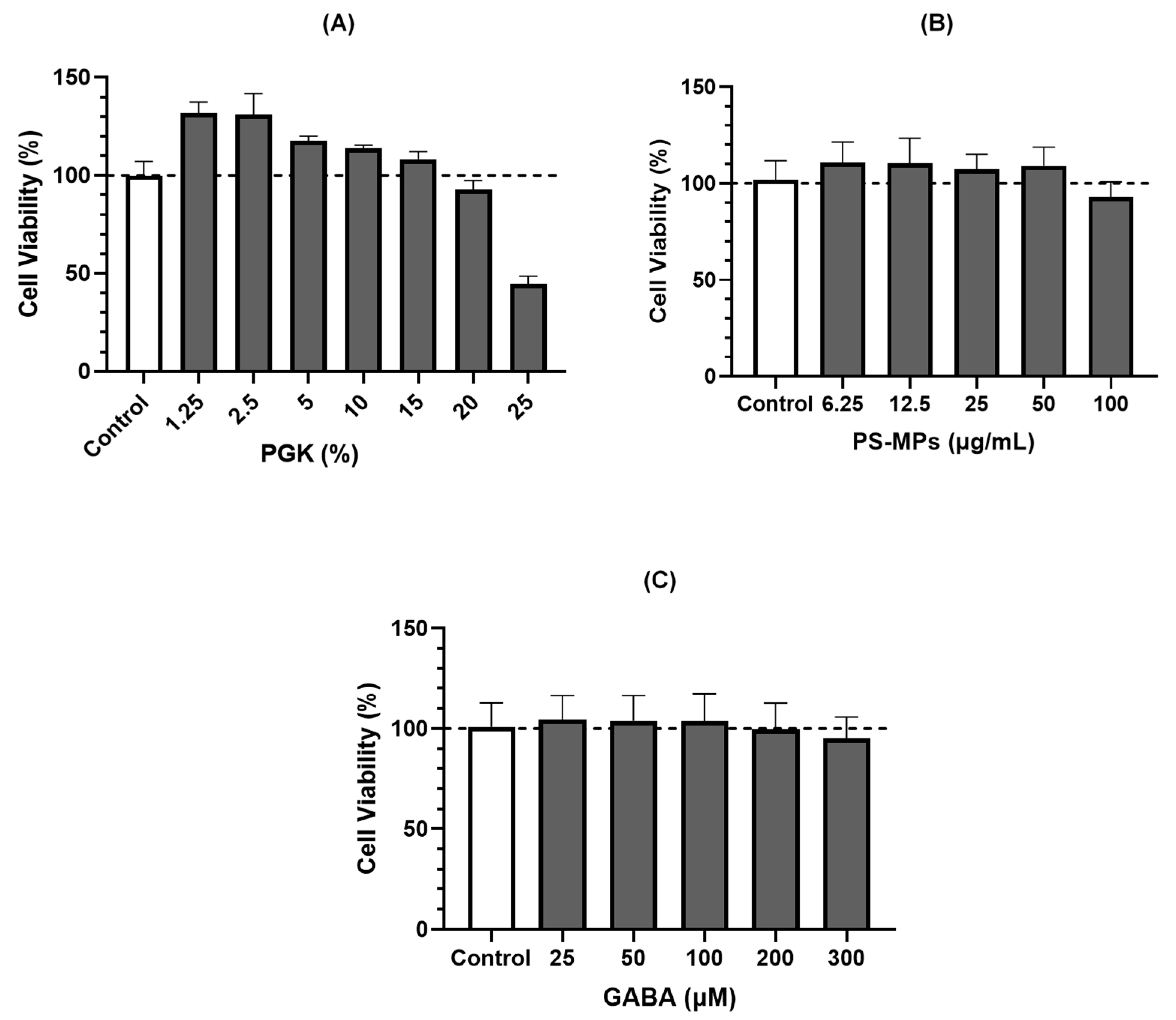
2.1. Leydig Cell (LC540) Viability
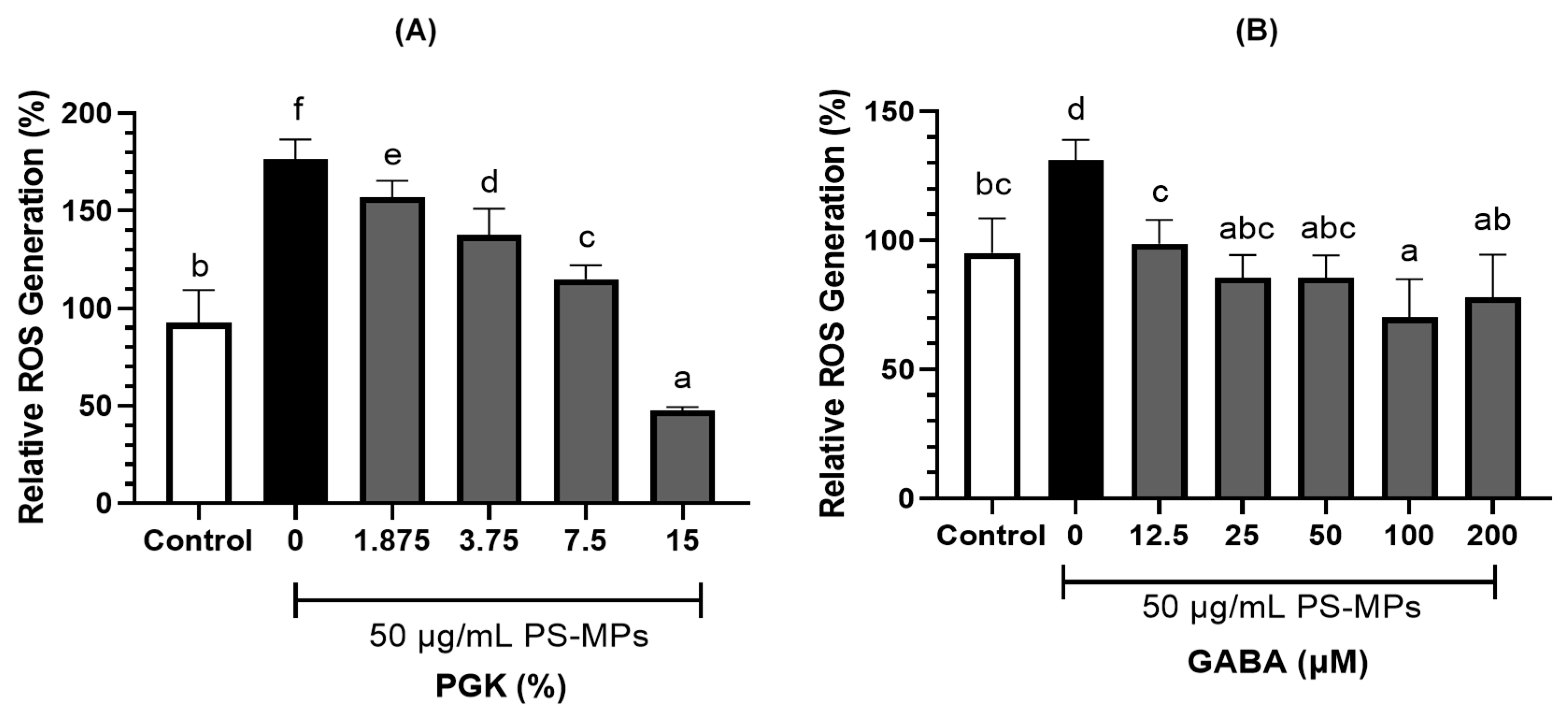
2.2. Reactive Oxygen Species Production in LC540 Cells
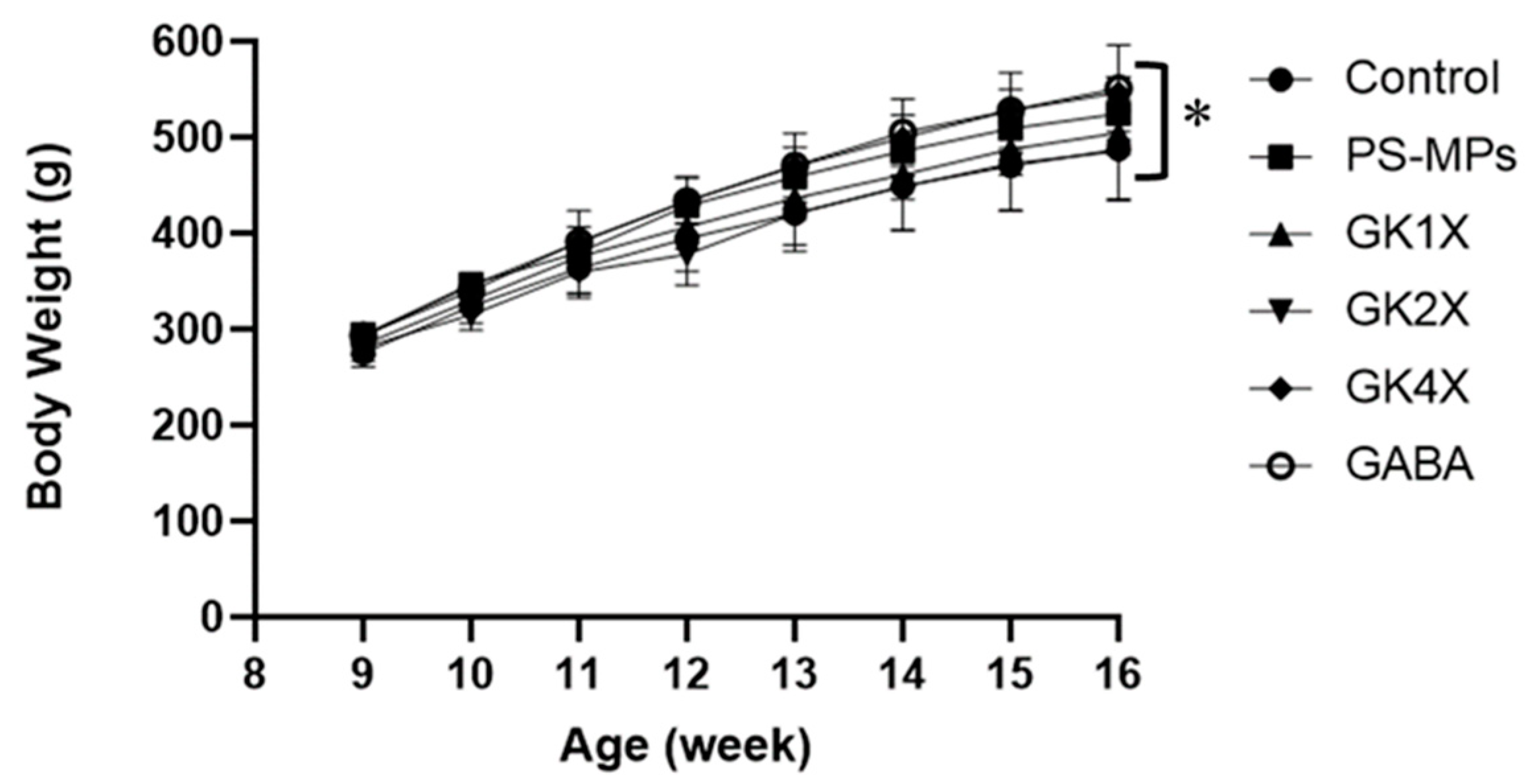
2.3. Rats’ Body Weight and Organ Weight
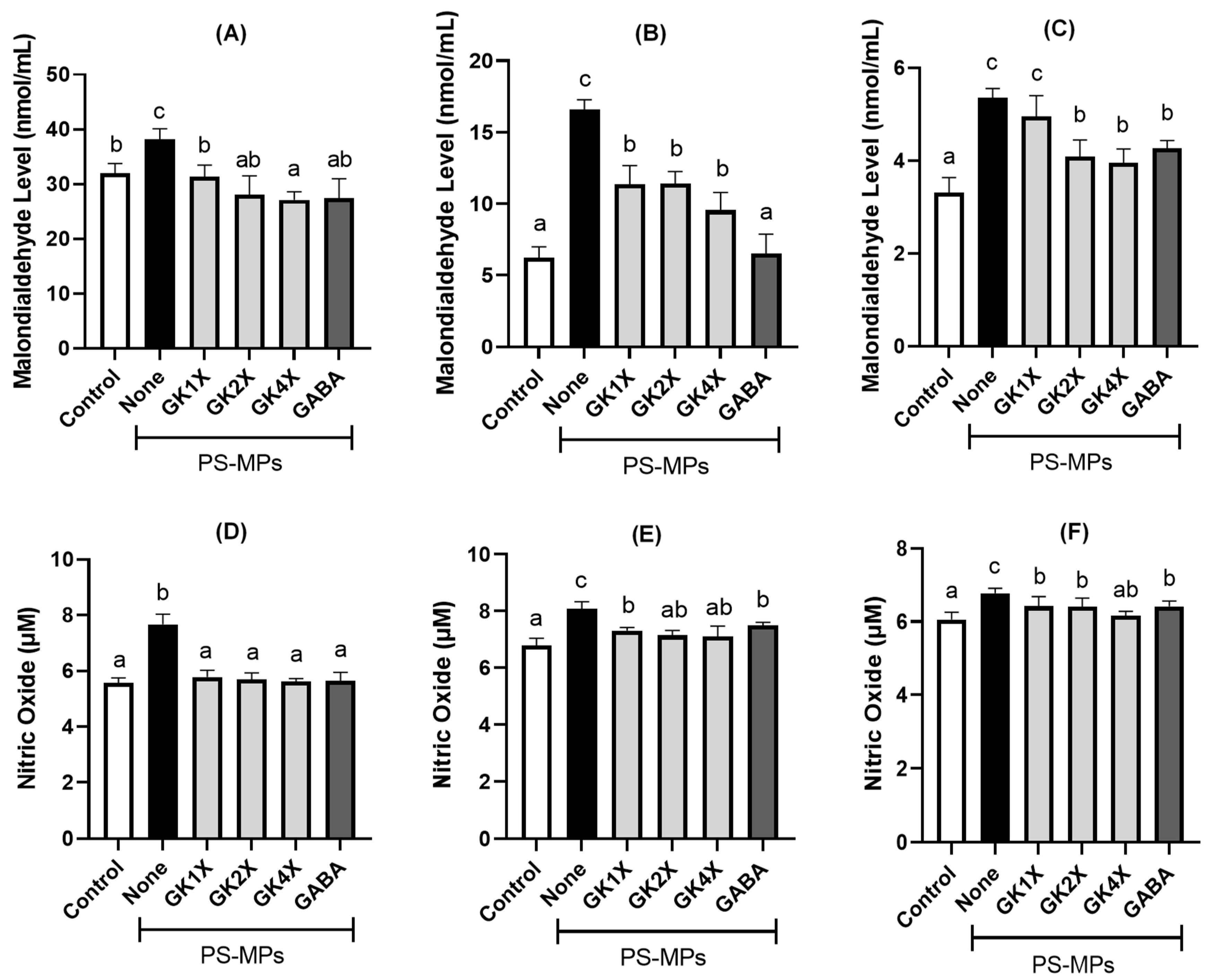
2.4. Malondialdehyde and Nitric Oxide Concentrations
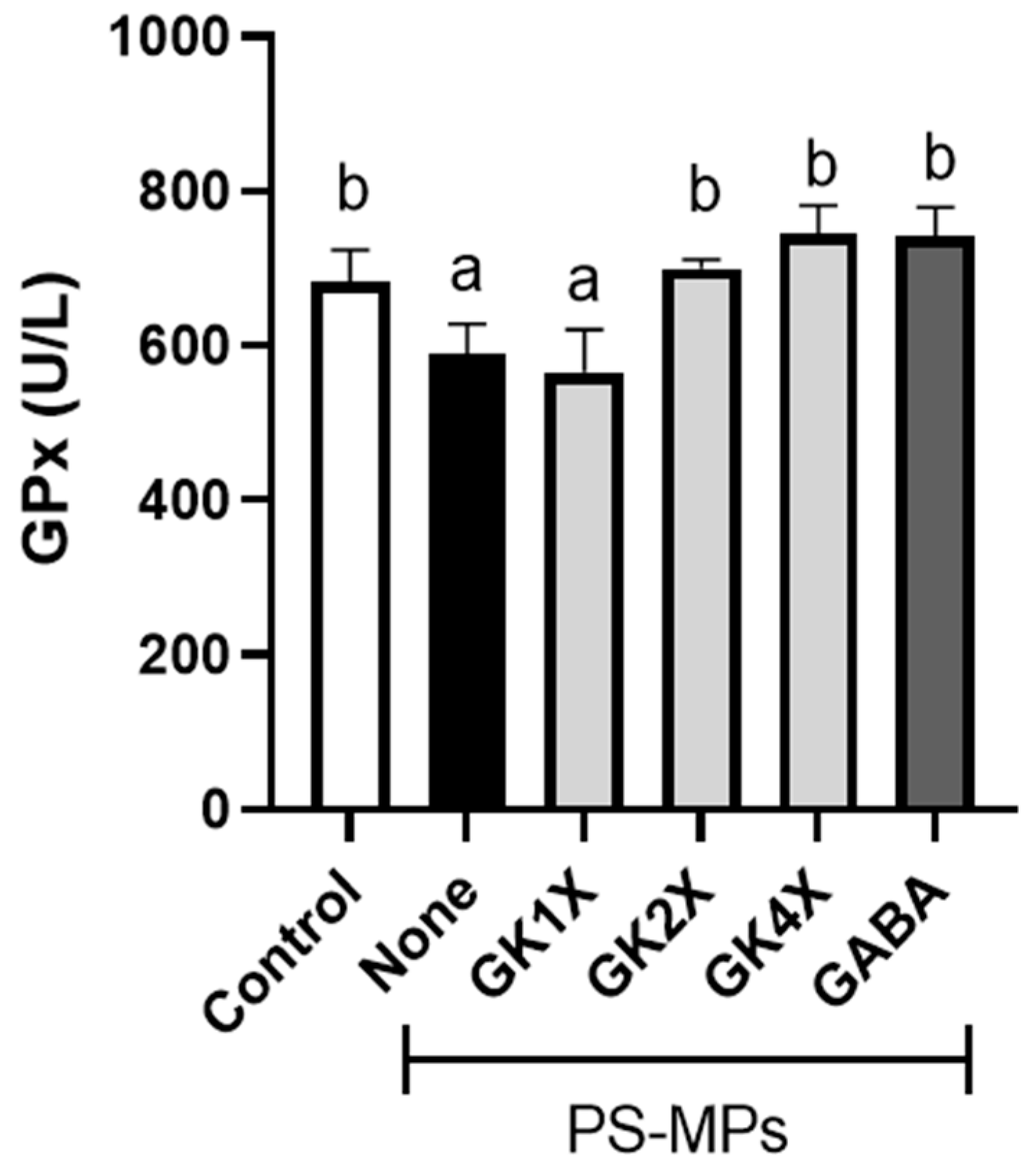
2.5. Glutathione Peroxidase Activity
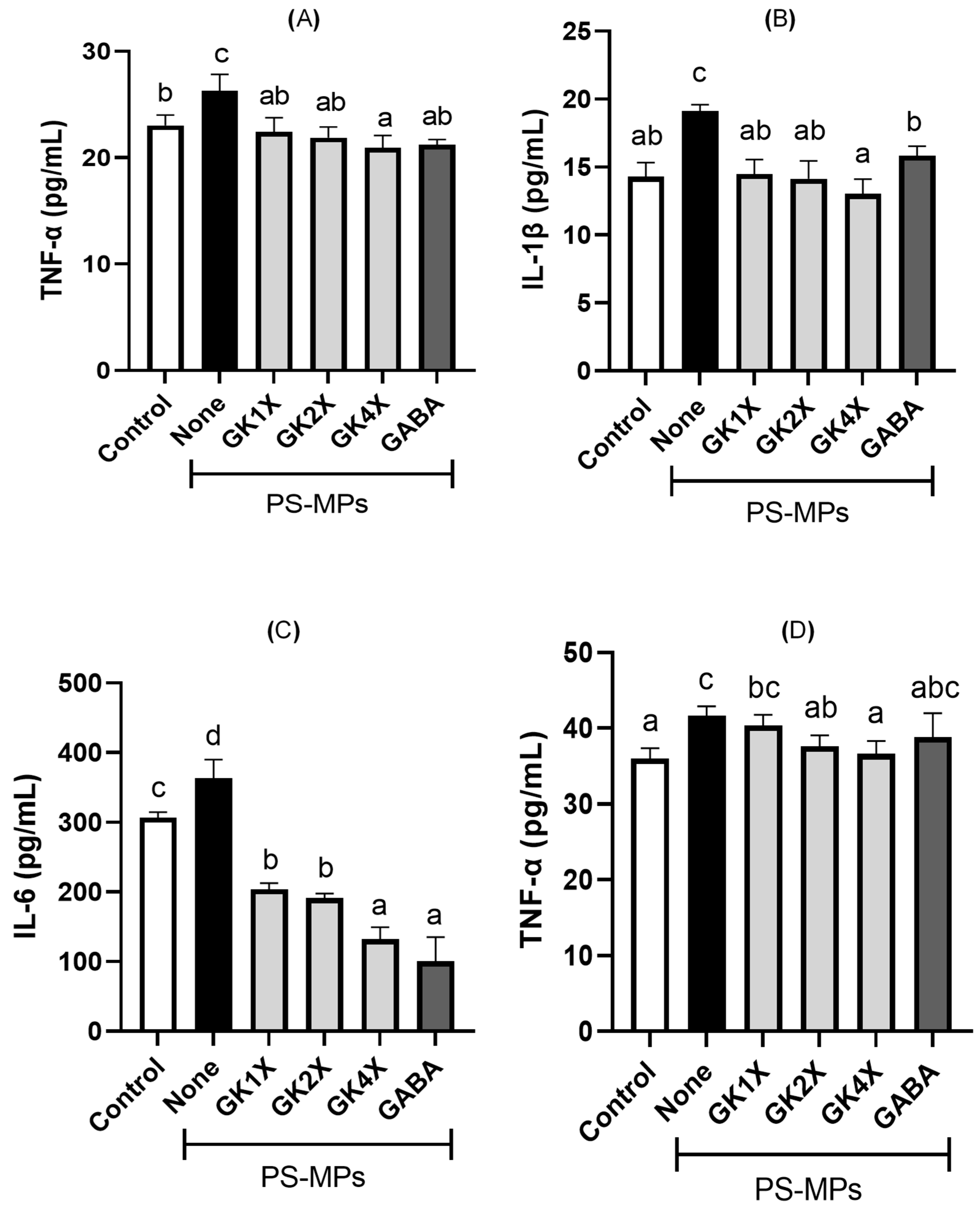
2.6. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expressions
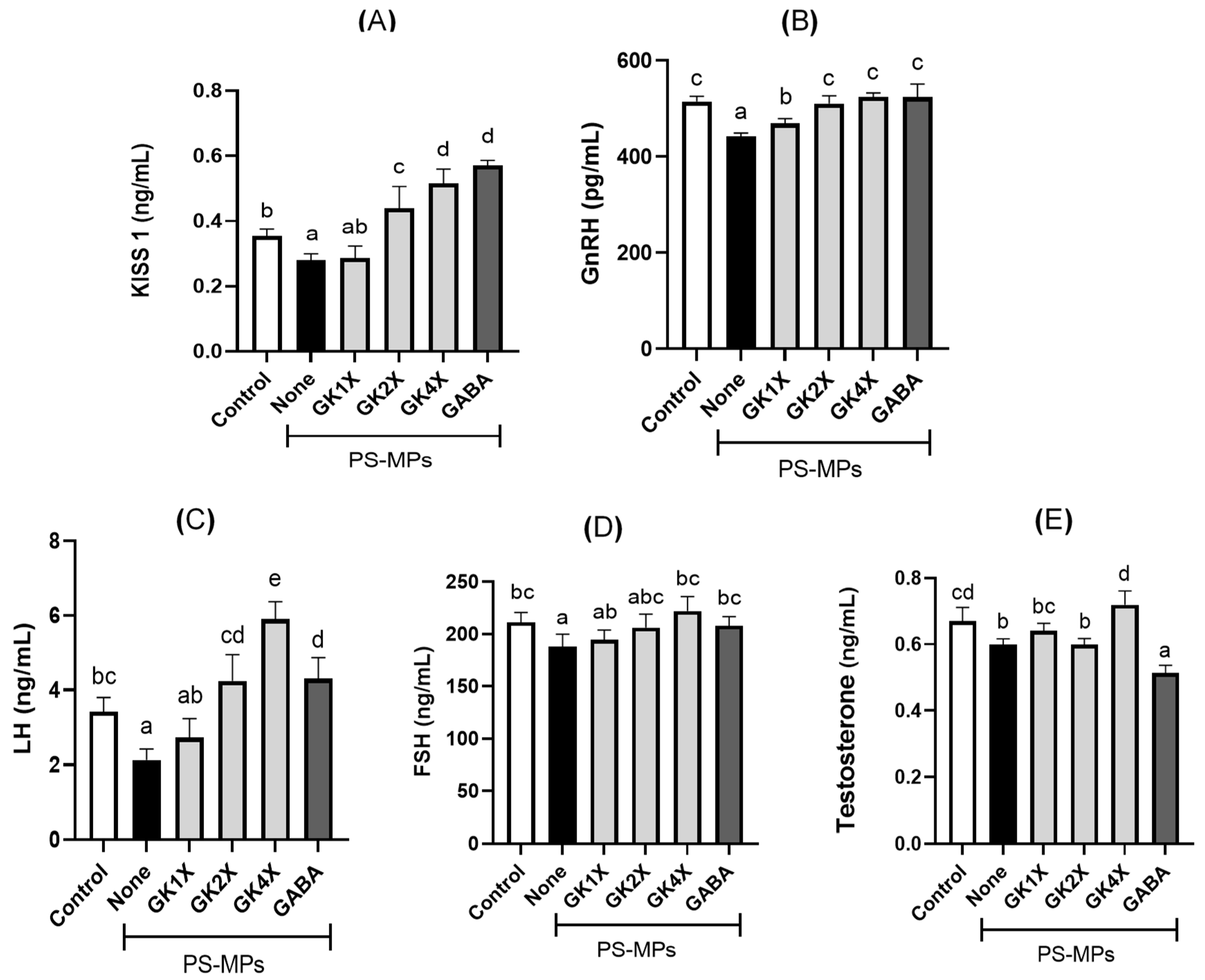
2.7. Kisspeptin and Reproductive Hormone Levels
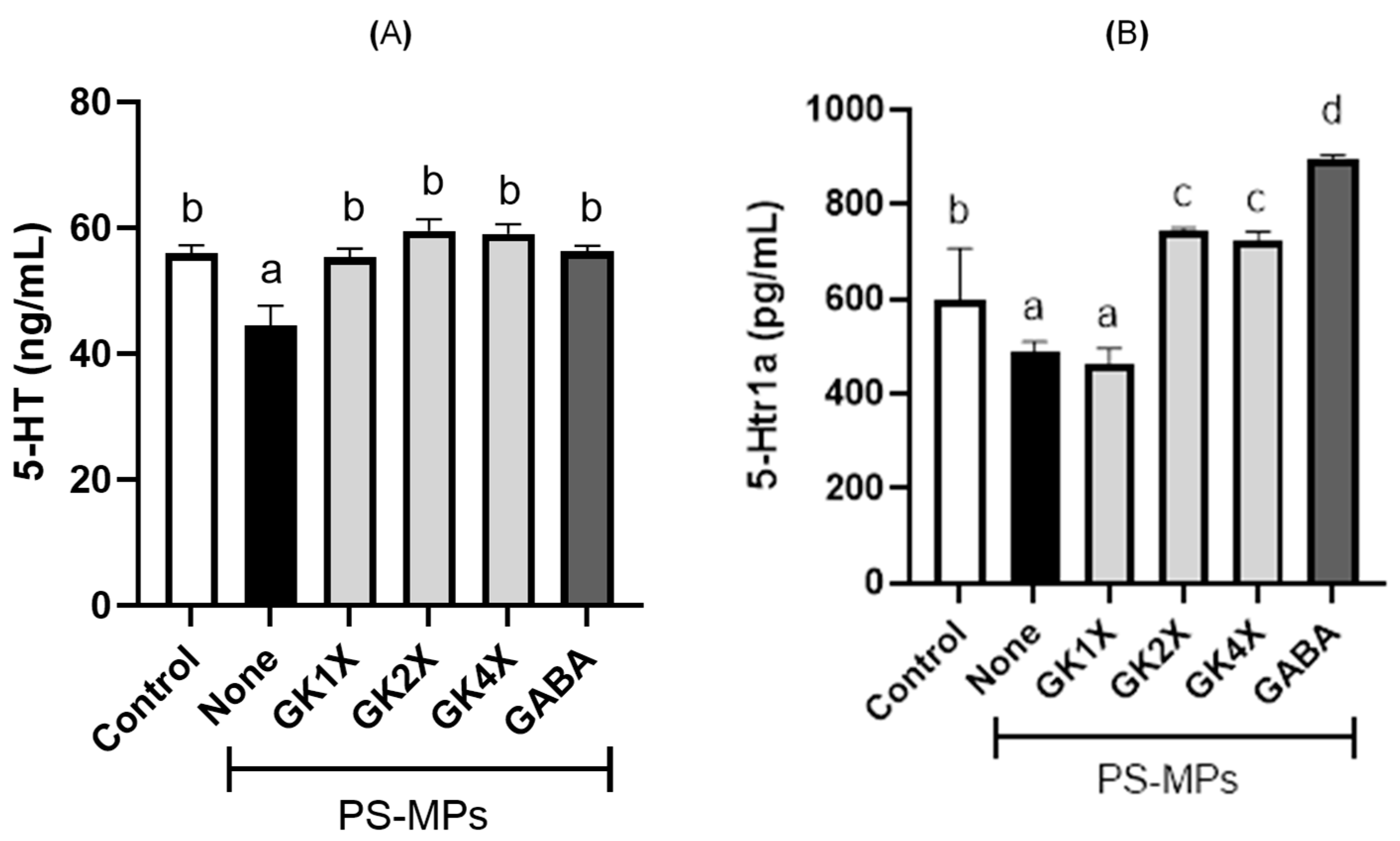
2.8. 5-Hydroxytryptamine and 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 1A Expression
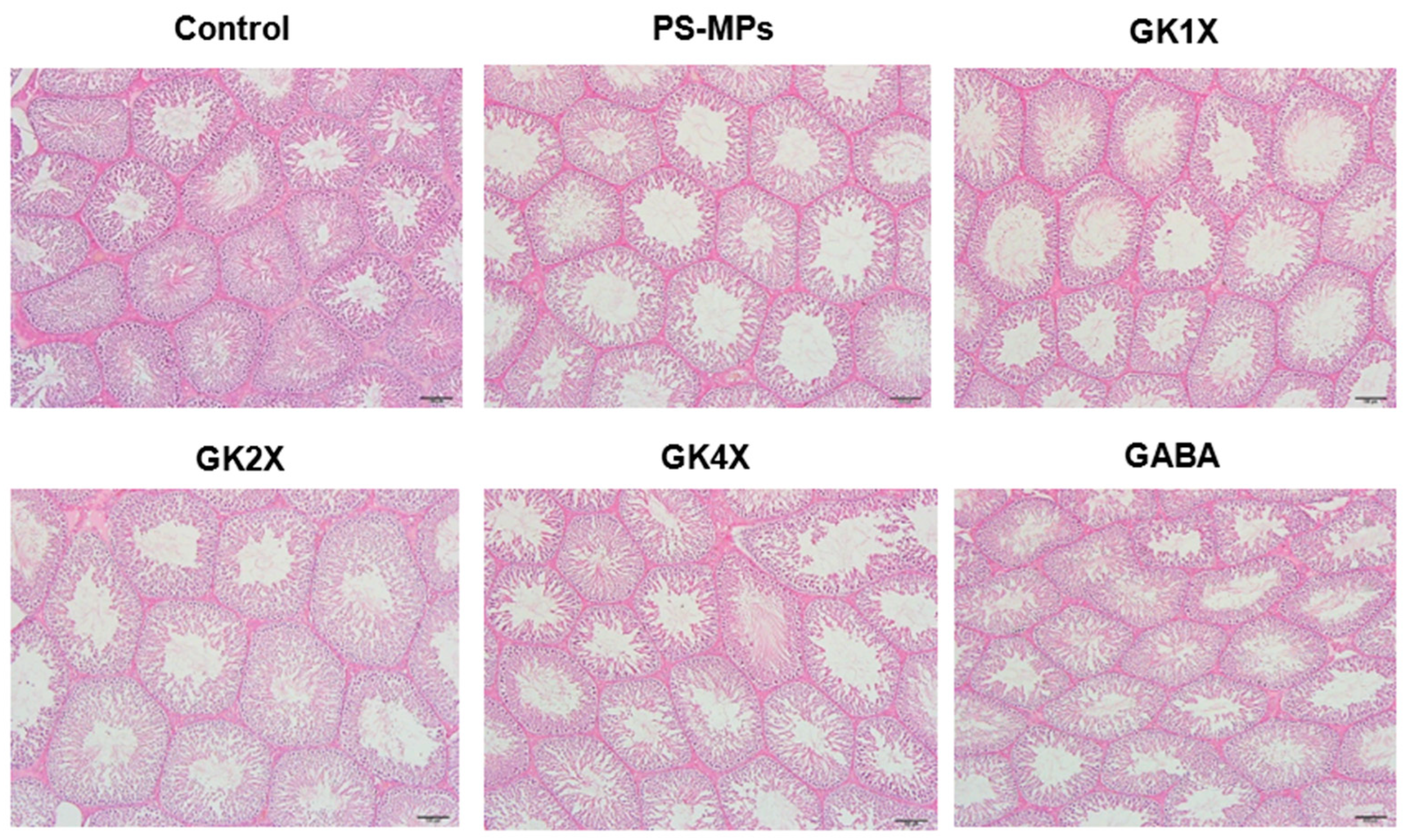
2.9. Testis Histopathology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Polystyrene Microplastics (PS-MPs) Solution Preparation
4.3. Preparation of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Solution
4.4. Cell-Free Supernatant Postbiotic Preparation
4.5. Leydig Cell Line (LC540) Study
4.5.1. Cell Viability Assay
4.5.2. Reactive Oxygen Species Assay
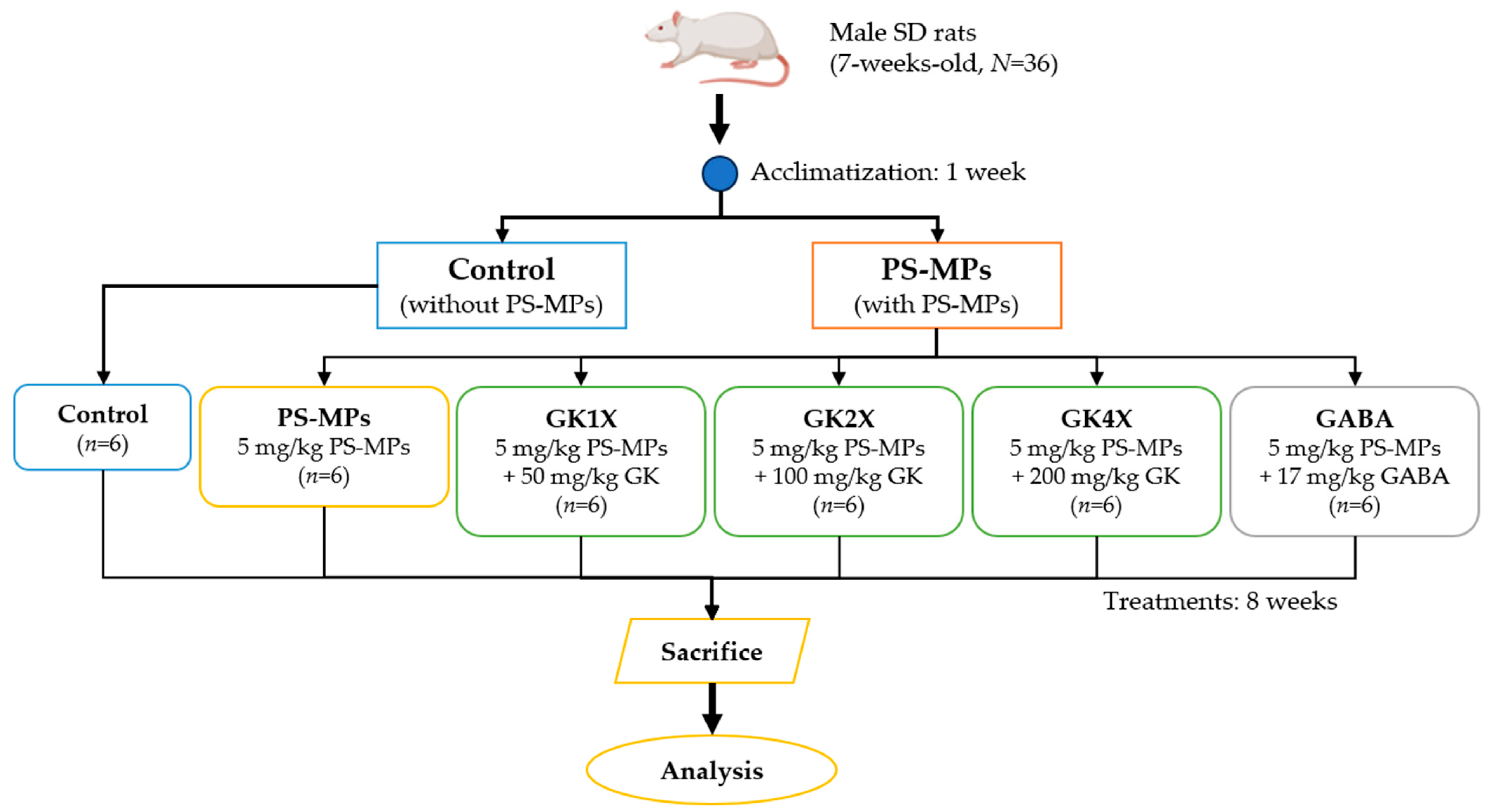
4.6. Animal Study
4.6.1. Animal Treatment
4.6.2. Blood Sample Collection
4.6.3. Tissue Homogenized Preparation
4.6.4. Testis Histopathology Analysis
4.6.5. Malondialdehyde and Nitric Oxide Assay
4.6.6. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, Kisspeptin, and Reproductive Hormones Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| 5-Htr1a | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A |
| FSH | Follicle-stimulating hormone |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| GK | Lactobacillus brevis GKJOY powder |
| GK1X | A low dose of L. brevis GKJOY (50 mg/kg) |
| GK2X | A medium dose of L. brevis GKJOY (100 mg/kg) |
| GK4X | A high dose of L. brevis GKJOY (200 mg/kg) |
| GnRH | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PGK | Postbiotic metabolites of Lactobacillus brevis GKJOY |
| PS-MPs | Polystyrene microplastics |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Wang, W.; Guan, J.; Feng, Y.; Nie, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Fu, F. Polystyrene microplastics induced nephrotoxicity associated with oxidative stress, inflammation, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in juvenile rats. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1059660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziani, K.; Ioniță-Mîndrican, C.-B.; Mititelu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Negrei, C.; Moroșan, E.; Drăgănescu, D.; Preda, O.-T. Microplastics: A real global threat for environment and food safety: A state of the art review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, M.; Stucchi, M.; Ambrosini, R.; Romano, A. A global perspective on microplastic bioaccumulation in marine organisms. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Najam, S.; Hamza, A.; Azmat, R.; Ashraf, A.; Unuofin, J.O.; Lebelo, S.L.; Simal-Gandara, J. Pinostrobin alleviates testicular and spermatological damage induced by polystyrene microplastics in adult albino rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Bang, J.; Kim, T.; Oh, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Hong, J. In vitro chemical and physical toxicities of polystyrene microfragments in human-derived cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-S.; Amarakoon, D.; Wei, C.-i.; Choi, K.Y.; Smolensky, D.; Lee, S.-H. Adverse effect of polystyrene microplastics (ps-mps) on tube formation and viability of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-W.; Chu, C.-W.; Huang, C.-C.; Chia, Z.-C.; Wang, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-H. Polystyrene microplastics induce hepatic lipid metabolism and energy disorder by upregulating the nr4a1-ampk signaling pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 369, 125850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, C.; Niu, W.; Han, S.; Qin, M.; Tian, Z.; Zuo, W.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Polystyrene microplastics promote intestinal colonization of Aeromonas veronii through inducing intestinal microbiota dysbiosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, D.; Guo, M.; Mu, M.; Liu, Y.; Nie, X.; Li, B.; Li, J.; et al. A comparative review of microplastics and nanoplastics: Toxicity hazards on digestive, reproductive and nervous system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Deng, T.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 mapk signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangene, S.; Morovvati, H.; Anbara, H.; Hye Khan, M.A.; Goorani, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause reproductive toxicity in male mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 194, 115083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yan, M.; Pan, C.; Liu, Z.; Sha, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, L.; Pan, M.; Li, D.; Han, X.; et al. Chronic exposure to polystyrene microplastics induced male reproductive toxicity and decreased testosterone levels via the lh-mediated lhr/camp/pka/star pathway. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, B.; Liu, T.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z. Probiotics improve polystyrene microplastics-induced male reproductive toxicity in mice by alleviating inflammatory response. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Reproductive toxicity of polystyrene microplastics: In vivo experimental study on testicular toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, T.; Negi, R.; Sharma, B.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.; Rai, A.K.; Shreaz, S.; Rustagi, S.; Chaudhary, N.; Kaur, T.; et al. Next generation probiotics for human health: An emerging perspective. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anee, I.J.; Alam, S.; Begum, R.A.; Shahjahan, R.M.; Khandaker, A.M. The role of probiotics on animal health and nutrition. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2021, 82, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maretti, C.; Cavallini, G. The association of a probiotic with a prebiotic (flortec, bracco) to improve the quality/quantity of spermatozoa in infertile patients with idiopathic oligoasthenoteratospermia: A pilot study. Andrology 2017, 5, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helli, B.; Kavianpour, M.; Ghaedi, E.; Dadfar, M.; Haghighian, H.K. Probiotic effects on sperm parameters, oxidative stress index, inflammatory factors and sex hormones in infertile men. Hum. Fertil. 2020, 25, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureen, S.; Hussain, T.; Noureen, A.; Altyar, A.E. Effect of Lactobacillus brevis (mg000874) on antioxidant-related gene expression of the liver and kidney in d-galactose-induced oxidative stress mice model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 84099–84109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarce, D.G.; Riesco, M.F.; Martínez-Vázquez, J.M.; Robles, V. Diet supplemented with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory probiotics improves sperm quality after only one spermatogenic cycle in zebrafish model. Nutrients 2019, 11, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodke, H.; Jogdand, S. Role of probiotics in human health. Cureus 2022, 14, e31313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, E.; Corr, S.C. Lactobacillus spp. For gastrointestinal health: Current and future perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 840245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, T.M.; Patterson, E.; Wall, R.; O’Sullivan, O.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Influence of gaba and gaba-producing Lactobacillus brevis dpc 6108 on the development of diabetes in a streptozotocin rat model. Benef. Microbes 2016, 7, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Fanti, V.; Rodriguez-Sobstel, C.; Gibson, G.; Wijeyesekera, A.; Karatzas, K.-A.; Chakrabarti, B. Gamma aminobutyric acid production by commercially available probiotic strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.Y.; Lin, H.-T.V.; Tsai, G.J. Gamma-aminobutyric acid production in black soybean milk by Lactobacillus brevis fpa 3709 and the antidepressant effect of the fermented product on a forced swimming rat model. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.J.; Ghosh, S.; Islam, R.; Sarkar, S.; Saha, T. Dietary supplementation of Lactobacillus brevis sad ameliorates high-fat diet-induced hyperglycemia and associated metabolic issues in swiss albino mice. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2024, 11, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, G.L.T.D.; Manalo, R.A.M.; Ko, S.K.K.; Arollado, E.C.; Samaniego, A.A. Lactobacillus brevis biotech 1766 attenuates oxidative stress and histopathological changes following aluminum poisoning in icr mice. Acta Medica Philipp. 2023, 58, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahiminejad, A.; Sepahi, A.A.; Yadegar, A.; Meyfour, A. Pasteurized form of a potential probiotic Lactobacillus brevis ibrc-m10790 exerts anti-inflammatory effects on inflammatory bowel disease in vitro. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.-Y.; Sudirman, S.; Wei, E.-Y.; Kong, Z.-L.; Hwang, D.-F. Fucoidan from Cladosiphon okamuranus enhances antioxidant activity and prevents reproductive dysfunction in polystyrene microplastic-induced male rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visalli, G.; Facciolà, A.; Pruiti Ciarello, M.; De Marco, G.; Maisano, M.; Di Pietro, A. Acute and sub-chronic effects of microplastics (3 and 10 µm) on the human intestinal cells ht-29. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadac-Czapska, K.; Ośko, J.; Knez, E.; Grembecka, M. Microplastics and oxidative stress—Current problems and prospects. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmaa, L.; Al Mehdi, K.; Khadija, A.; Jawad, L.; Rachida, R. Effects of exposure to micro/nanoplastics of polystyrene on neuronal oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and anxiety-like behavior in mice: A systematic review. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I.; Lushchak, O. Interplay between reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in living organisms. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 349, 109680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walke, G.; Gaurkar, S.S.; Prasad, R.; Lohakare, T.; Wanjari, M. The impact of oxidative stress on male reproductive function: Exploring the role of antioxidant supplementation. Cureus 2023, 15, e42583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; DeJi; Li, B.; Huang, X. Recent perspective of Lactobacillus in reducing oxidative stress to prevent disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, T.; Cui, J.; Ye, H.; Zhou, C.; Ye, L.; Zhou, L. Polystyrene microplastics trigger colonic inflammation in rats via the tlr4/nf-κb/cox-2 pathway and modulation of intestinal microbiota. Toxicology 2025, 513, 154090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomichova, O.; Oliveira, P.F.; Bernardino, R.L. Exploring the interplay between inflammation and male fertility. FEBS J. 2024, 2024, 17366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Probiotic Lactobacillus casei zhang reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production and hepatic inflammation in a rat model of acute liver failure. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 55, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Yu, C.; Zhao, H.; Huang, D. The role of kisspeptin in the control of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and reproduction. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 925206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, S.-J.; Jang, W.J.; Lee, E.-W. Protective effects of the postbiotic Levilactobacillus brevis bk3 against h2o2-induced oxidative damage in skin cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Gong, L.Z.; Xu, J.X. Antioxidative activity and protective effect of probiotics against high-fat diet-induced sperm damage in rats. Animal 2013, 7, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunzi, E.; Pariano, M.; Costantini, C.; Garaci, E.; Puccetti, P.; Romani, L. Host–microbe serotonin metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 36, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadzoi, K.M.; Yang, J.; Siroky, M.B. Neural regulation of sexual function in men. World J. Clin. Urol. 2013, 2, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbiydzenyuy, N.E.; Joanna Hemmings, S.M.; Shabangu, T.W.; Qulu-Appiah, L. Exploring the influence of stress on aggressive behavior and sexual function: Role of neuromodulator pathways and epigenetics. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, N.; Lei, Z.; Hou, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. Polystyrene microplastics induce blood–testis barrier disruption regulated by the mapk-nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47921–47931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Je, H.-W.; Lee, S.; Choi, W.; Min, T.; Kim, K.-W.; Bai, S.C. Evaluation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (gaba) as a functional feed ingredient on growth performance, immune enhancement, and disease resistance in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) under high stocking density. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, S.; Umezu, K.; Takamori, H.; Hiradate, Y.; Hara, K.; Tanemura, K. Exogenous gamma-aminobutyric acid addition enhances porcine sperm acrosome reaction. Anim. Sci. J. 2022, 93, e13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Vazquez, C.I.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Chiu, M.-H.; Chen, C.-S.; Ni, C.-W.; Gong, G.-C.; Quigg, A.; Santschi, P.H.; Chin, W.-C. Nano- and microplastics trigger secretion of protein-rich extracellular polymeric substances from phytoplankton. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y. Protective effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid against oxidative stress by inducing phase ii enzymes in c2c12 myoblast cells. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, L.-O.; Foo, H.L.; Loh, T.C.; Mohammed Alitheen, N.B.; Yeap, S.K.; Abdul Mutalib, N.E.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Yusoff, K. Postbiotic metabolites produced by Lactobacillus plantarum strains exert selective cytotoxicity effects on cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudirman, S.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Johnson, A.; Tsou, D.; Kong, Z.-L. Amelioration effects of nanoencapsulated triterpenoids from petri dish-cultured Antrodia cinnamomea on reproductive function of diabetic male rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5059–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbrecht, I.; Horn, S.; Giesy, J.P.; Pieters, R. A method to determine reactive oxygen species production in intestinal and liver cell cultures using the 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate assay. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudirman, S.; Su, C.-Y.; Tsou, D.; Lee, M.-C.; Kong, Z.-L. Hippocampus kuda protein hydrolysate improves male reproductive dysfunction in diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVMA. 2000 report of the avma panel on euthanasia. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 669–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudirman, S.; Chang, H.-W.; Chen, C.-K.; Kong, Z.-L. A dietary polysaccharide from Eucheuma cottonii downregulates proinflammatory cytokines and ameliorates osteoarthritis-associated cartilage degradation in obese rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5697–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudirman, S.; Hwang, Y.-Y.; Su, C.-H.; Lu, T.-Y.; Kuo, H.-P.; Hwang, D.-F.; Kong, Z.-L. Blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) water extract ameliorates intestinal immune response in high-fat diet–streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 9357–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelali, A.; Al-Bader, M.; Kilarkaje, N. Effects of trans-resveratrol on hyperglycemia-induced abnormal spermatogenesis, DNA damage and alterations in poly (adp-ribose) polymerase signaling in rat testis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 311, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.-C.; Su, Y.-T.; Lu, M.-C.; Chou, Y.; Ho, T.-Y. Determination of nitrate in natural waters by vanadium reduction and the griess assay: Reassessment and optimization. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Organs (% of Body Weight) | Control | PS-MPs | GK1X | GK2X | GK4X | GABA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | 3.69 ± 0.32 | 3.84 ± 0.39 | 3.62 ± 0.37 | 3.73 ± 0.38 | 3.97 ± 0.50 | 3.82 ± 0.53 |
| Spleen | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.03 |
| Kidney | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 0.84 ± 0.05 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 0.76 ± 0.30 | 0.84 ± 0.11 | 0.88 ± 0.04 |
| Abdominal adipose | 1.61 ± 0.44 | 1.38 ± 0.27 | 1.61 ± 0.26 | 1.20 ± 0.32 | 1.39 ± 0.27 | 1.44 ± 0.32 |
| Testis | 0.71 ± 0.08 | 0.68 ± 0.07 | 0.76 ± 0.05 | 0.74 ± 0.07 | 0.70 ± 0.09 | 0.64 ± 0.06 |
| Epididymal adipose | 1.33 ± 0.26 | 1.09 ± 0.33 | 1.36 ± 0.27 | 1.11 ± 0.50 | 1.44 ± 0.14 | 1.34 ± 0.33 |
| Parameters | Control | PS-MPs | GK1X | GK2X | GK4X | GABA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness of the epithelium (μm) | 114.00 ± 7.77 c | 62.19 ± 14.08 a | 71.77 ± 10.45 a | 107.65 ± 10.32 c | 104.93 ± 5.76 bc | 91.05 ± 4.41 b |
| Area of seminiferous lumen/tubules (%) | 3.28 ± 0.45 a | 31.57 ± 2.69 e | 23.63 ± 1.54 d | 10.85 ± 1.42 c | 7.73 ± 1.02 b | 12.89 ± 1.48 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, Y.-Y.; Sudirman, S.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Kong, F.; Hwang, D.-F.; Kong, Z.-L. Lactobacillus brevis GKJOY Supplementation Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Reproductive Dysfunction in Male Rats with Polystyrene Microplastics-Induced Reproductive Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104533
Hwang Y-Y, Sudirman S, Hsu Y-C, Chen C-C, Kong F, Hwang D-F, Kong Z-L. Lactobacillus brevis GKJOY Supplementation Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Reproductive Dysfunction in Male Rats with Polystyrene Microplastics-Induced Reproductive Toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104533
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Yi-Yuh, Sabri Sudirman, Yu-Chen Hsu, Chin-Chu Chen, Fanbin Kong, Deng-Fwu Hwang, and Zwe-Ling Kong. 2025. "Lactobacillus brevis GKJOY Supplementation Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Reproductive Dysfunction in Male Rats with Polystyrene Microplastics-Induced Reproductive Toxicity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104533
APA StyleHwang, Y.-Y., Sudirman, S., Hsu, Y.-C., Chen, C.-C., Kong, F., Hwang, D.-F., & Kong, Z.-L. (2025). Lactobacillus brevis GKJOY Supplementation Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Reproductive Dysfunction in Male Rats with Polystyrene Microplastics-Induced Reproductive Toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104533


_Kim.png)





