Brassinosteroid Signaling Dynamics: Ubiquitination-Dependent Regulation of Core Signaling Components
Abstract
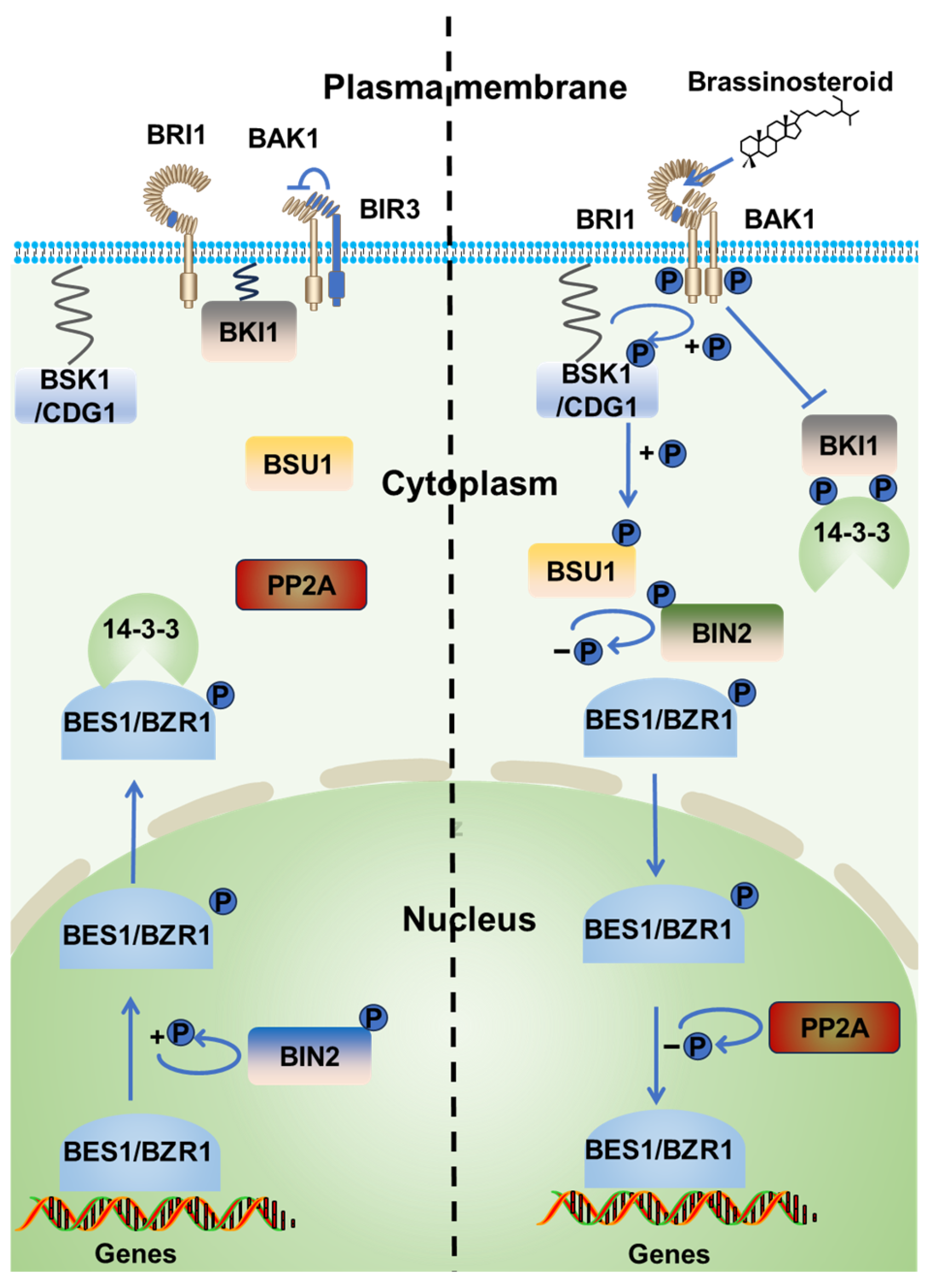
:1. Introduction
2. BRI1 Regulation by Ubiquitination
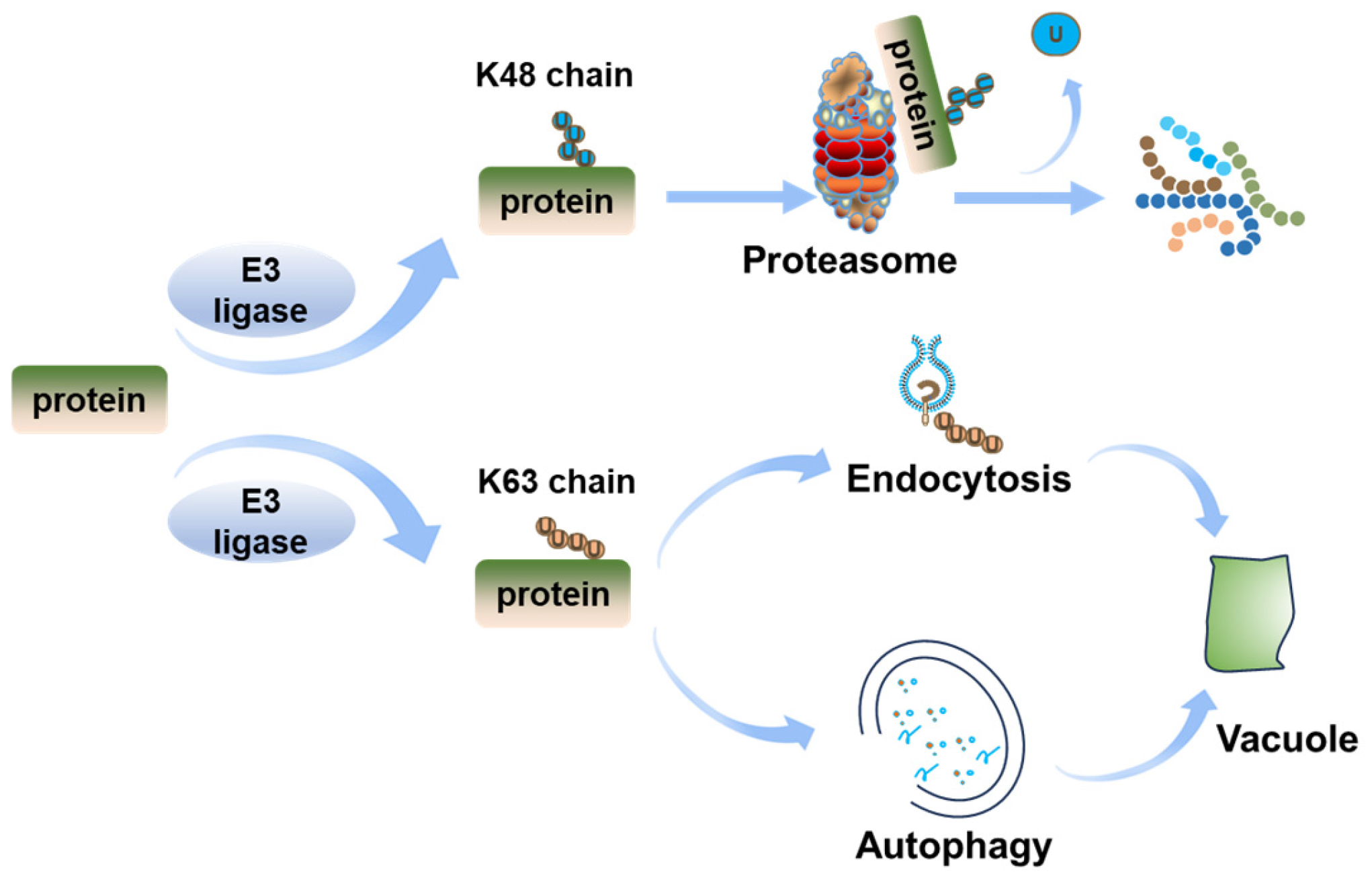
2.1. Ubiquitination Regulates BRI1 Endocytosis and Degradation
2.2. Ubiquitination Regulates BRI1 Degradation by UPS
3. BIN2 Regulation by Ubiquitination
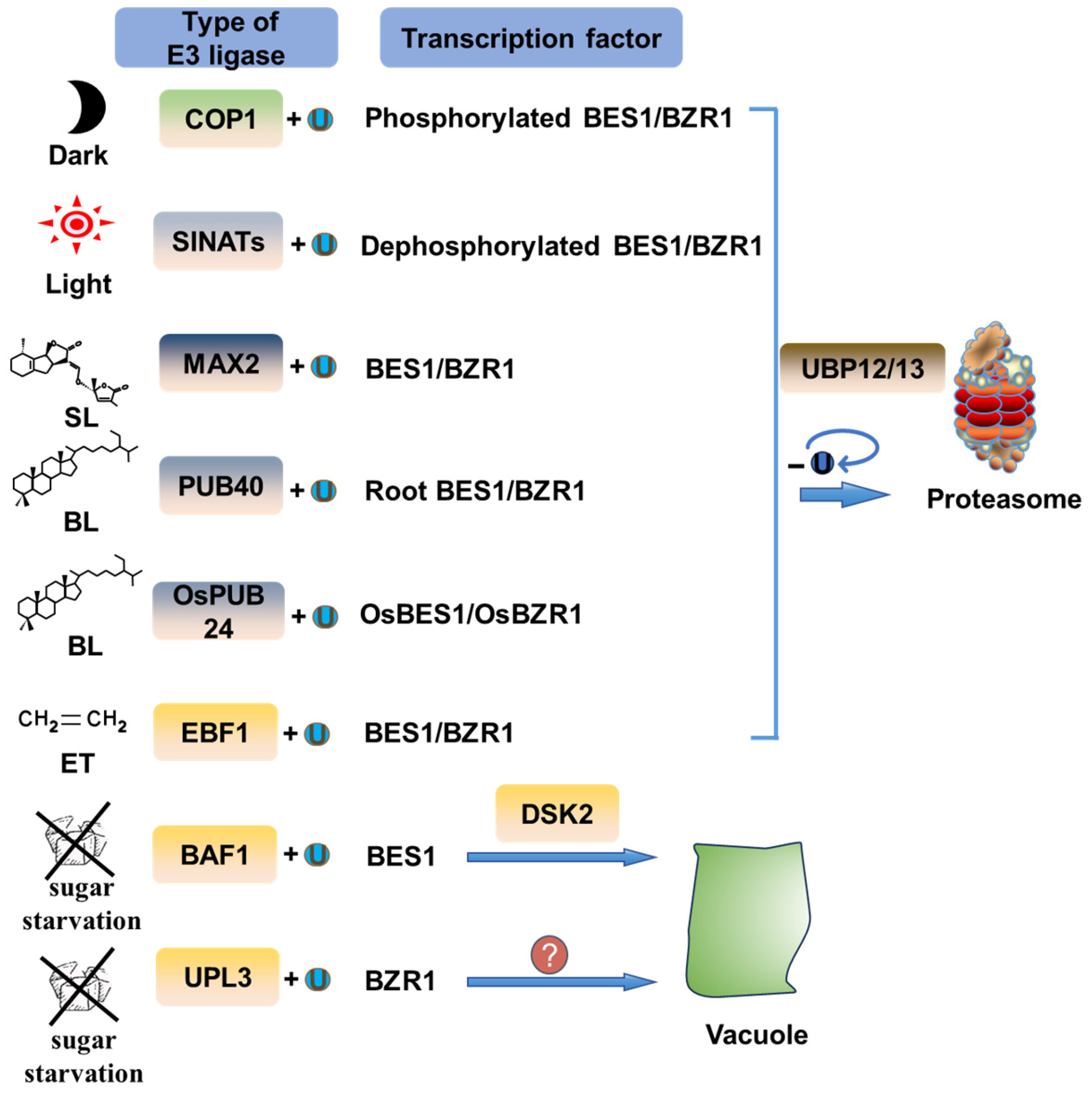
4. BES1/BZR1 Regulation by Ubiquitination
4.1. Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of BES1/BZR1 by the Proteasome Pathway
4.2. Ubiquitination-Mediated Degradation of BES1/BZR1 via Autophagy
5. Ubiquitination Regulation of Other BR Signal Transduction Components
6. Conclusions and Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALIX | apoptosis-linked gene 2-interacting protein X |
| APC/C | Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome |
| ATG8 | autophagy-related 8 |
| BAF1 | BES1-ASSOCIATED F-BOX 1 |
| BAK1 | BRI1-Associated Receptor Kinase 1 |
| BES1 | bri1-EMS suppressor 1 |
| BIK1 | Botrytis-Induced Kinase 1 |
| BIL4 | Brassinazole-Insensitive-Long hypocotyl 4 |
| BIN2 | Brassinosteroid-Insensitive 2 |
| BKI1 | BRI1 Kinase Inhibitor 1 |
| BOP1 | Blade On-Petiole-1 |
| BRC1 | Branched 1 |
| BRFP1 | BRASSINOSTEROID F-BOX Protein 1 |
| BRI1 | Brassinosteroid-Insensitive 1 |
| BRs | Brassinosteroids |
| BSKs | BR Signaling Kinases |
| BSL1-3 | BSU1-like proteins 1–3 |
| BSU1 | bri1 suppressor 1 |
| BZR1 | Brassinazole-Resistant 1 |
| CDG | Constitutive Differential Growth |
| CIE | clathrin-independent endocytosis |
| CLASP | cytoplasmic linker protein-associated protein |
| CME | clathrin-mediated endocytosis |
| COP1/SPA1 | Constitutively Photomorphogenic 1/Suppressor of phyA-105 |
| CRLs | cullin-RING ligases |
| CUL1 | Cullin 1 |
| DGS1 | grain size 1 |
| DSK2 | Dominant Suppressor Of Kar 2 |
| DUBs | Deubiquitinating enzymes |
| EBF1 | Ethylene-Insensitive 3 Binding F-BOX Protein 1 |
| EIN3 | Ethylene-Insensitive 3 |
| ENTH | Epsin N-Terminal Homology |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERAD | ER-associated degradation |
| ESCRT | endosomal sorting complex required for transport |
| HECT | E6AP carboxyl terminus |
| KIB1 | Kink suppressed in bzr1-1D 1 |
| LRR | leucine-rich repeat |
| MAX2 | More Axillary Growth Locus 2 |
| MVB | multivesicular bodies |
| PIF3 | Photoperiod-Interactive Factor 3 |
| PM | plasma membrane |
| PP2A | protein phosphatase 2A |
| PPKLs | protein phosphatases with kelch-like |
| RGLG1 | RING-domain ligase 1 |
| RHA3A | RING-H2 Finger A3A |
| RING | Really Interesting New Gene |
| RLCKs | receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases |
| RZF1 | Ring Zinc finger 1 |
| SGD1 | small grain and dwarf 1 |
| SINATs | Seven-IN-Absentia of Arabidopsis thaliana |
| SL | strigolactone |
| TGN/EE | trans-Golgi network/early endosome |
| TOR | target of rapamycin |
| TPC | TPLATE complex |
| TUD1 | Taihu Dwarf1 |
| UPL3 | Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase 3 |
| UPS | ubiquitin–proteasome system |
| WSB1 | WD repeat and SOCS box-containing protein 1 |
References
- Clouse, S.D.; Sasse, J.M. Brassinosteroids: Essential regulators of plant growth and development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1998, 49, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Bai, M.-Y.; Oh, E.; Zhu, J.-Y. Brassinosteroid signaling network and regulation of photomorphogenesis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 701–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.-N.; Jin, J.-Q.; Wang, X.-L. The mechanisms of brassinosteroids’ action: From signal transduction to plant development. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, F.; Naeem, M.; Zulfiqar, B.; Akram, A.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Raheel, M.; Shabbir, R.N.; Hussain, R.A.; Anwar, I.; Aurangzaib, M. Understanding brassinosteroid-regulated mechanisms to improve stress tolerance in plants: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15959–15975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-F.; Lu, J.; Yu, J.-W.; Zhang, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, Q.-Q. The brassinosteroid-regulated transcription factors BZR1/BES1 function as a coordinator in multisignal-regulated plant growth. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2018, 1861, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manghwar, H.; Hussain, A.; Ali, Q.; Liu, F. Brassinosteroids (BRs) Role in Plant Development and Coping with Different Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Shen, B.; Li, W.; Liu, L.; Li, J. Post-translational Regulation of BRI1-EMS Suppressor 1 and Brassinazole-Resistant 1. Plant Cell Physiol. 2024, 65, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chory, J. A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell 1997, 90, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Li, J. BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, J.; Lease, K.A.; Doke, J.T.; Tax, F.E.; Walker, J.C. BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kota, U.; He, K.; Blackburn, K.; Li, J.; Goshe, M.B.; Huber, S.C.; Clouse, S.D. Sequential transphosphorylation of the BRI1/BAK1 receptor kinase complex impacts early events in brassinosteroid signaling. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chory, J. Brassinosteroids regulate dissociation of BKI1, a negative regulator of BRI1 signaling, from the plasma membrane. Science 2006, 313, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Tang, J.; Hu, Z.; Chai, C.; Zhou, B.; Chai, J. Structure reveals that BAK1 as a co-receptor recognizes the BRI1-bound brassinolide. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Kim, T.-W.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Sun, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wang, R.; Burlingame, A.L.; Wang, Z.-Y. BSKs mediate signal transduction from the receptor kinase BRI1 in Arabidopsis. Science 2008, 321, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-W.; Guan, S.; Burlingame, A.L.; Wang, Z.-Y. The CDG1 kinase mediates brassinosteroid signal transduction from BRI1 receptor kinase to BSU1 phosphatase and GSK3-like kinase BIN2. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-W.; Guan, S.; Sun, Y.; Deng, Z.; Tang, W.; Shang, J.-X.; Sun, Y.; Burlingame, A.L.; Wang, Z.-Y. Brassinosteroid signal transduction from cell-surface receptor kinases to nuclear transcription factors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Mora-Garcia, S.; Li, J.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J. BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell 2002, 109, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nam, K.H. Regulation of brassinosteroid signaling by a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase. Science 2002, 295, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yuan, M.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Kim, T.-W.; Zhou, H.-W.; Deng, Z.; Gampala, S.S. PP2A activates brassinosteroid-responsive gene expression and plant growth by dephosphorylating BZR1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-X.; Gendron, J.M.; Sun, Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Gendron, N.; Sun, C.Q.; Wang, Z.-Y. BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 2005, 307, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Vafeados, D.; Tao, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J. A new class of transcription factors mediates brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Cell 2005, 120, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranjo-Arcos, M.; Srivastava, M.; Deligne, F.; Bhagat, P.K.; Mansi, M.; Sadanandom, A.; Vert, G. SUMO/deSUMOylation of the BRI1 brassinosteroid receptor modulates plant growth responses to temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2217255120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, P.; Ma, X.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Mishev, K.; Lu, D.; Kumar, R.; Vanhoutte, I. Regulation of Arabidopsis brassinosteroid receptor BRI1 endocytosis and degradation by plant U-box PUB12/PUB13-mediated ubiquitination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1906–E1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierstra, R.D. The ubiquitin–26S proteasome system at the nexus of plant biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffner, M.; Nuber, U.; Huibregtse, J.M. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1–E2–E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. Nature 1995, 373, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A.; Varshavsky, A. The ubiquitin system. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Parry, G.; Estelle, M. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and plant development. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3181–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Scalf, M.; Smith, L.M.; Vierstra, R.D. Advanced proteomic analyses yield a deep catalog of ubiquitylation targets in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1523–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, D. Recognition and processing of ubiquitin-protein conjugates by the proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 477–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Bennett, E.J.; Huttlin, E.L.; Guo, A.; Li, J.; Possemato, A.; Sowa, M.E.; Rad, R.; Rush, J.; Comb, M.J. Systematic and quantitative assessment of the ubiquitin-modified proteome. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.A.; Beli, P.; Weinert, B.T.; Nielsen, M.L.; Cox, J.; Mann, M.; Choudhary, C. A proteome-wide, quantitative survey of in vivo ubiquitylation sites reveals widespread regulatory roles. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M111.013284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnowski, L.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Brzywczy, J.; Piecho-Kabacik, M.; Krčkova, Z.; Martinec, J.; Wawrzynska, A.; Sirko, A. A selective autophagy cargo receptor NBR1 modulates abscisic acid signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, T.M.; Brennan, B.; Yang, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Bassham, D.C.; Walley, J.; Yin, Y. Selective autophagy of BES1 mediated by DSK2 balances plant growth and survival. Dev. Cell 2017, 41, 33–46. e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komander, D.; Clague, M.J.; Urbé, S. Breaking the chains: Structure and function of the deubiquitinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.; Nagel, M.-K.; Isono, E. Measuring the DUB activity of Arabidopsis deubiquitylating enzymes. In Plant Proteostasis: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, B.; Deligne, F.; Brillada, C.; Dünser, K.; Ditengou, F.A.; Turek, I.; Allahham, A.; Grujic, N.; Dagdas, Y.; Ott, T. K63-linked ubiquitin chains are a global signal for endocytosis and contribute to selective autophagy in plants. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 1337–1345. e1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Takagi, J.; Claus, L.A.N.; Zhang, C.; Yasuda, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Yamaguchi, J.; Shan, L.; Russinova, E.; Sato, T. Deubiquitinating enzymes UBP12 and UBP13 stabilize the brassinosteroid receptor BRI1. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e53354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.-J.; Lin, W.-H.; Fu, F.-F.; Xu, Z.-H.; Xue, H.-W. Receptor-like protein ELT1 promotes brassinosteroid signaling through interacting with and suppressing the endocytosis-mediated degradation of receptor BRI1. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1182–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Duan, P.; Yan, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Zheng, L.; Chai, T.; Xu, R. An endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation–related E2–E3 enzyme pair controls grain size and weight through the brassinosteroid signaling pathway in rice. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1076–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Sui, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhi, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. An E2-E3 pair contributes to seed size control in grain crops. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grones, P.; De Meyer, A.; Pleskot, R.; Mylle, E.; Kraus, M.; Vandorpe, M.; Yperman, K.; Eeckhout, D.; Dragwidge, J.M.; Jiang, Q. The endocytic TPLATE complex internalizes ubiquitinated plasma membrane cargo. Nat. Plants 2022, 8, 1467–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona-López, X.; Cuyas, L.; Marín, E.; Rajulu, C.; Irigoyen, M.L.; Gil, E.; Puga, M.I.; Bligny, R.; Nussaume, L.; Geldner, N. ESCRT-III-associated protein ALIX mediates high-affinity phosphate transporter trafficking to maintain phosphate homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2560–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagami, A.; Saito, C.; Nakazawa, M.; Fujioka, S.; Uemura, T.; Matsui, M.; Sakuta, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Osada, H.; Nakano, A. Evolutionarily conserved BIL4 suppresses the degradation of brassinosteroid receptor BRI1 and regulates cell elongation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, D.-M.; Yang, H.; Oh, E.; Bi, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.-Y. The F-box protein KIB1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced inactivation and degradation of GSK3-like kinases in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 648–657.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yin, W.; Niu, M.; Meng, W.; Dong, N.; Liu, J. The U-box ubiquitin ligase TUD1 promotes brassinosteroid-induced GSK2 degradation in rice. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.J. Putative E3 ligases as candidates controlling BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 2 (BIN2) kinase in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 14, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhu, W.; Jia, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, X. Strigolactone/MAX2-induced degradation of brassinosteroid transcriptional effector BES1 regulates shoot branching. Dev. Cell 2013, 27, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Han, C.; Bai, M.; Fan, M. EBF1 negatively regulates brassinosteroid-induced apical hook development and cell elongation through promoting BZR1 degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, C.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, T.-W. Plant U-Box40 mediates degradation of the brassinosteroid-responsive transcription factor BZR1 in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.J.; Cui, L.H.; Oh, T.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, W.T. OsBZR1 turnover mediated by OsSK22-regulated U-box E3 ligase OsPUB24 in rice BR response. Plant J. 2019, 99, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Jeong, Y.J.; Corvalan, C.; Fujioka, S.; Cho, S.; Park, T.; Choe, S. Darkness and gulliver2/phy B mutation decrease the abundance of phosphorylated BZR1 to activate brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2014, 77, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, C.; Cai, Z.; Hu, Y.; Nolan, T.; Yu, F.; Yin, Y.; Xie, Q.; Tang, G.; Wang, X. SINAT E3 ligases control the light-mediated stability of the brassinosteroid-activated transcription factor BES1 in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2017, 41, 47–58. e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Jeong, J.S.; Zhou, Y.; Mustafa, N.F.B.; Chua, N.-H. Deubiquitination of BES1 by UBP12/UBP13 promotes brassinosteroid signaling and plant growth. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Yang, F.; Yao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Lin, H.; Guo, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, D. The deubiquitinating enzymes UBP12 and UBP13 positively regulate recovery after carbon starvation by modulating BES1 stability in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 4516–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.e.; Han, Q.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, T.; Han, J.; Zhou, H.; Lin, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, D. Sumoylation of BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR 1 (BES1) by the SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 negatively regulates brassinosteroids signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Nolan, T.M.; Clark, N.M.; Jiang, H.; Montes-Serey, C.; Guo, H.; Bassham, D.C.; Walley, J.W.; Yin, Y. The F-box E3 ubiquitin ligase BAF1 mediates the degradation of the brassinosteroid-activated transcription factor BES1 through selective autophagy in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 3532–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gonzalez, E.; Grismer, T.; Xu, S.-L.; Wang, Z.-Y. UPL3 Promotes BZR1 Degradation, Growth Arrest, and Seedling Survival under Starvation Stress in Arabidopsis. bioRxiv 2023, 2023, 562997. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nguyen, T.; Park, C.-R.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.S. BES1/BZR1 Homolog 3 cooperates with E3 ligase AtRZF1 to regulate osmotic stress and brassinosteroid responses in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 636–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Patil, S.B.; Fang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, M. The Arabidopsis U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase PUB30 negatively regulates salt tolerance by facilitating BRI1 kinase inhibitor 1 (BKI1) degradation. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 2831–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, J.; Cao, B.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Dong, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W. Reducing brassinosteroid signalling enhances grain yield in semi-dwarf wheat. Nature 2023, 617, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Grubb, L.E.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Li, L.; Gao, C.; Ma, M.; Feng, F.; Li, M.; Li, L. A regulatory module controlling homeostasis of a plant immune kinase. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 493–504. e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, H.; Chen, S.; Wong, K.B.; Xia, Y. Arabidopsis PUB2 and PUB4 connect signaling components of pattern-triggered immunity. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 2249–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Claus, L.A.; Leslie, M.E.; Tao, K.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Li, B.; Zhou, J.; Savatin, D.V. Ligand-induced monoubiquitination of BIK1 regulates plant immunity. Nature 2020, 581, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.; Chen, K.; Han, Y.; Wang, R.; Zou, Y.; Du, M.; Lu, D. BIK1 protein homeostasis is maintained by the interplay of different ubiquitin ligases in immune signaling. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldner, N.; Hyman, D.L.; Wang, X.; Schumacher, K.; Chory, J. Endosomal signaling of plant steroid receptor kinase BRI1. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, N.G.; Di Rubbo, S.; Mylle, E.; Van den Begin, J.; Schneider-Pizoń, J.; Hniliková, J.; Šíša, M.; Buyst, D.; Vilarrasa-Blasi, J.; Szatmári, A.-M. Fluorescent castasterone reveals BRI1 signaling from the plasma membrane. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.-H.; Liu, J.-Z.; Jin, H.; Lin, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.-X.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Huang, H.; Qi, Y.-J. Warm temperatures induce transgenerational epigenetic release of RNA silencing by inhibiting siRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9171–9176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Lu, W.; Huang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Mao, J.; Li, J. NcBRI1 positively regulate vascular development and promote biomass production in Neolamarckia cadamba. Plant Sci. 2025, 352, 112352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, B.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. PtBRI1. 2 promotes shoot growth and wood formation through a brassinosteroid-mediated PtBZR1-PtWNDs module in poplar. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 6350–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, J.M.; Haguenauer-Tsapis, R. Ubiquitin lys63 is involved in ubiquitination of a yeast plasma membrane protein. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5847–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.; Dohmann, E.; Cayrel, A.; Johnson, A.; Fischer, W.; Pojer, F.; Satiat-Jeunemaître, B.; Jaillais, Y.; Chory, J.; Geldner, N. Internalization and vacuolar targeting of the brassinosteroid hormone receptor BRI1 are regulated by ubiquitination. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubus Claus, L.A.; Liu, D.; Hohmann, U.; Vukašinović, N.; Pleskot, R.; Liu, J.; Schiffner, A.; Jaillais, Y.; Wu, G.; Wolf, S. BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1 internalization can occur independent of ligand binding. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bücherl, C.A.; van Esse, G.W.; Kruis, A.; Luchtenberg, J.; Westphal, A.H.; Aker, J.; van Hoek, A.; Albrecht, C.; Borst, J.W.; de Vries, S.C. Visualization of BRI1 and BAK1 (SERK3) membrane receptor heterooligomers during brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 1911–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, S.; Montiel-Jorda, A.; Cayrel, A.; Huguet, S.; Roux, C.P.-L.; Ljung, K.; Vert, G. Brassinosteroid signaling -dependent root responses to prolonged elevated ambient temperature. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez Valencia, J.; Goodman, K.; Otegui, M.S. Endocytosis and endosomal trafficking in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 309–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rubbo, S.; Irani, N.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Xu, Z.-Y.; Gadeyne, A.; Dejonghe, W.; Vanhoutte, I.; Persiau, G.; Eeckhout, D.; Simon, S. The clathrin adaptor complex AP-2 mediates endocytosis of brassinosteroid insensitive1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2986–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, P.; Wan, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, Q.; Mettbach, U.; Baluška, F.; Šamaj, J.; Fang, X.; Lucas, W.J. A membrane microdomain-associated protein, Arabidopsis Flot1, is involved in a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway and is required for seedling development. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; De Camilli, P. The association of epsin with ubiquitinated cargo along the endocytic pathway is negatively regulated by its interaction with clathrin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2766–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, C.E.; Mohney, R.P.; Miller, S.L.; Hanes, R.N.; O’Bryan, J.P. The ubiquitin-interacting motifs target the endocytic adaptor protein epsin for ubiquitination. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Lee, M.H.; Song, K.; Ahn, G.; Lee, J.; Hwang, I. The A/ENTH domain-containing protein AtECA4 is an adaptor protein involved in cargo recycling from the trans-Golgi network/early endosome to the plasma membrane. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 568–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouhar, J.; Sauer, M. Helping hands for budding prospects: ENTH/ANTH/VHS accessory proteins in endocytosis, vacuolar transport, and secretion. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 4232–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yperman, K.; Wang, J.; Eeckhout, D.; Winkler, J.; Vu, L.D.; Vandorpe, M.; Grones, P.; Mylle, E.; Kraus, M.; Merceron, R.; et al. Molecular architecture of the endocytic TPLATE complex. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.; Halat, L.S.; Khan, D.; Jancowski, S.; Ambrose, C.; Belmonte, M.F.; Wasteneys, G.O. The microtubule-associated protein CLASP sustains cell proliferation through a brassinosteroid signaling negative feedback loop. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2718–2729. e2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isono, E.; Kalinowska, K. ESCRT-dependent degradation of ubiquitylated plasma membrane proteins in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 40, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, A.; Grones, P.; Van Damme, D. How will I recognize you? Insights into endocytic cargo recognition in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2023, 75, 102429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, K.; Nagel, M.-K.; Goodman, K.; Cuyas, L.; Anzenberger, F.; Alkofer, A.; Paz-Ares, J.; Braun, P.; Rubio, V.; Otegui, M.S. Arabidopsis ALIX is required for the endosomal localization of the deubiquitinating enzyme AMSH3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5543–E5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.D.; Brodsky, J.L.; McCracken, A.A. Proteasome-dependent endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation: An unconventional route to a familiar fate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13797–13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhang, A.-S.; Worthen, C.; Knutson, M.D.; Enns, C.A. An iron-regulated and glycosylation-dependent proteasomal degradation pathway for the plasma membrane metal transporter ZIP14. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9175–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, F.; Tsuchiya, H.; Saeki, Y.; Tanaka, K. K63 ubiquitylation triggers proteasomal degradation by seeding branched ubiquitin chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1401–E1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Jin, H.; Tzfira, T.; Li, J. Multiple mechanism–mediated retention of a defective brassinosteroid receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 3418–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, C.; Ali, K.; Zheng, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, G.; Li, W.; Zheng, B. A non-redundant function of MNS5: A class I α-1, 2 mannosidase, in the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of misfolded glycoproteins. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 873688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubuki, S.; Saito, Y.; Tomioka, M.; Ito, H.; Kawashima, S. Differential inhibition of calpain and proteasome activities by peptidyl aldehydes of di-leucine and tri-leucine. J. Biochem. 1996, 119, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Lin, B.; Wu, Y.; Tang, S.; Xie, Q. Arabidopsis Ubiquitin Conjugase UBC32 Is an ERAD Component That Functions in Brassinosteroid-Mediated Salt Stress Tolerance. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Printsev, I.; Curiel, D.; Carraway, K.L. Membrane protein quantity control at the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Membr. Biol. 2017, 250, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-X.; Gendron, J.M.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.-Y. The GSK3-like kinase BIN2 phosphorylates and destabilizes BZR1, a positive regulator of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10185–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vert, G.; Chory, J. Downstream nuclear events in brassinosteroid signalling. Nature 2006, 441, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Peng, P.; Schmitz, R.J.; Decker, A.D.; Tax, F.E.; Li, J. Two putative BIN2 substrates are nuclear components of brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Regulation of the Arabidopsis GSK3-like kinase BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 2 through proteasome-mediated protein degradation. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; Du, L.; Yin, Y.; Qian, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chu, C. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2562–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroski, M.D.; Deshaies, R.J. Function and regulation of cullin–RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, D.-G. Characterization of BRASSINOSTEROID F-BOX proteins BRFPs that regulate BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 2 kinase. J. Plant Biol. 2022, 65, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.-J.; Li, J.; Zhu, D.; Deng, X.W. Noncanonical role of Arabidopsis COP1/SPA complex in repressing BIN2-mediated PIF3 phosphorylation and degradation in darkness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3539–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komander, D.; Rape, M. The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolkiewicz, K.; Gruszka, D. Glycogen synthase kinases in model and crop plants–From negative regulators of brassinosteroid signaling to multifaceted hubs of various signaling pathways and modulators of plant reproduction and yield. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 939487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, S.; Broda, M.; Abbas, Z.; Vaneechoutte, D.; Belt, K.; Säll, T.; Vandepoele, K.; Van Aken, O. Neofunctionalization of mitochondrial proteins and incorporation into signaling networks in plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, P.; Tang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Tang, H. Rice qGL3/OsPPKL1 functions with the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK3 to modulate brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augello, G.; Emma, M.R.; Cusimano, A.; Azzolina, A.; Montalto, G.; McCubrey, J.A.; Cervello, M. The role of GSK-3 in cancer immunotherapy: GSK-3 inhibitors as a new frontier in cancer treatment. Cells 2020, 9, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronkov, A.; Krauss, S. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and small molecule inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 634–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Tao, Y.; Che, G.; Yun, Y.; Ren, M.; Liu, Y. WSB1, as an E3 ligase, restrains myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury by activating β-catenin signaling via promoting GSK3β ubiquitination. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Chen, S. Exogenous application of low-concentration sugar enhances brassinosteroid signaling for skotomorphogenesis by promoting BIN2 degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, D. Exploring the brassinosteroid signaling in monocots reveals novel components of the pathway and implications for plant breeding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Liu, M.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Tang, W. Nucleocytoplasmic trafficking and turnover mechanisms of BRASSINAZOLE RESISTANT 1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101838118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, X. Regulation of shoot branching by strigolactones and brassinosteroids: Conserved and specific functions of Arabidopsis BES1 and rice BZR1. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potuschak, T.; Lechner, E.; Parmentier, Y.; Yanagisawa, S.; Grava, S.; Koncz, C.; Genschik, P. EIN3-dependent regulation of plant ethylene hormone signaling by two Arabidopsis F box proteins: EBF1 and EBF2. Cell 2003, 115, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Jin, Y.; Wang, M.; Jin, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, M.; Jin, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhu, Y. Genome-wide analysis of SINA family in plants and their phylogenetic relationships. DNA Seq. 2008, 19, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.C.; Bianchimano, L.; Oh, J.; Montepaone, S.R.; Tarkowská, D.; Minguet, E.G.; Schön, J.; Hourquet, M.G.; Flugel, T.; Blazquez, M.A. Organ-specific COP1 control of BES1 stability adjusts plant growth patterns under shade or warmth. Dev. Cell 2022, 57, 2009–2025.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Komatsu, T.; Yamagami, A.; Nakazawa, M.; Matsui, M.; Kawaide, H.; Natsume, M.; Osada, H.; Asami, T.; Nakano, T. Formation and dissociation of the BSS1 protein complex regulates plant development via brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Holmlund, M.; Lorrain, S.; Norberg, M.; Bako, L.; Fankhauser, C.; Nilsson, O. BLADE-ON-PETIOLE proteins act in an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex to regulate PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 4 abundance. Elife 2017, 6, e26759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Orosa-Puente, B.; Campanaro, A.; Zhang, C.; Sadanandom, A. SUMO conjugation to BZR1 enables brassinosteroid signaling to integrate environmental cues to shape plant growth. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 1410–1423.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.S.; Raffeiner, M.; Zeng, Y.; Üstün, S.; Dagdas, Y. Autophagy in Plant Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2025, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bassham, D.C. TOR is a negative regulator of autophagy in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, M.E.; Florencio, F.J.; Crespo, J.L. Inhibition of target of rapamycin signaling and stress activate autophagy in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 1874–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melino, G.; Cecconi, F.; Pelicci, P.G.; Mak, T.W.; Bernassola, F. Emerging roles of HECT-type E3 ubiquitin ligases in autophagy regulation. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 2033–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, T.M.; Vukašinović, N.; Liu, D.; Russinova, E.; Yin, Y. Brassinosteroids: Multidimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Li, J. Regulation of three key kinases of brassinosteroid signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhou, J.-M. Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases: Central players in plant receptor kinase–mediated signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Lu, D.; Gao, X.; Jiang, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; Mengiste, T.; He, P.; Shan, L. Inverse modulation of plant immune and brassinosteroid signaling pathways by the receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase BIK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12114–12119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Wu, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, L.; He, P. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, BIK1, associates with a flagellin receptor complex to initiate plant innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves Dias, M.; Soleimani, F.; Monaghan, J. Activation and turnover of the plant immune signaling kinase BIK1: A fine balance. Essays Biochem. 2022, 66, 207–218. [Google Scholar]

| Functional Classification | Name | Gene ID | Protein Family | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRI1 de/ubiquitination | UBC35 | AT1G78870 | UBC | [36] |
| UBC36 | AT1G16890 | UBC | [36] | |
| PUB12 | AT2G28830 | U-BOX | [23] | |
| PUB13 | AT3G46510 | U-BOX | [23] | |
| UBP12 | AT5G06600 | DUB | [37] | |
| UBP13 | AT3G11910 | DUB | [37] | |
| OsELT1 | Os02g58390 | RLK | [38] | |
| OsSMG3 | Os03g03080 | UBC | [39] | |
| OsDGS1 | Os03g07069 | RING | [39] | |
| SiUBC32 | Seita.9G428900 | UBC | [40] | |
| SiSGD1 | Seita.9G123200 | RING | [40] | |
| TASH3 | AT2G07360 | T-PLATE complex | [41] | |
| AMSH3 | AT1G15130 | DUB | [42] | |
| BIL4 | AT3G63310 | [43] | ||
| BIN2/OsGSK2 ubiquitination | KIB1 | AT4G12810 | F-BOX | [44] |
| OsTUD1 | Os03g13010 | U-BOX | [45] | |
| BRFP1 | AT2G45100 | F-BOX | [46] | |
| BRFP2 | AT3G09360 | F-BOX | [46] | |
| BES1/BZR1 de/ubiquitination | MAX2 | AT2G42620 | F-BOX | [47] |
| EBF1 | AT2G25490 | F-BOX | [48] | |
| PUB40 | AT5G40140 | U-BOX | [49] | |
| OsPUB24 | Os03g06571 | U-BOX | [50] | |
| COP1 | AT2G32950 | RING | [51] | |
| SINATs | AT3G58040 | RING | [52] | |
| UBP12 | AT5G06600 | DUB | [53,54] | |
| UBP13 | AT3G11910 | DUB | [53,54] | |
| SIZ1 | AT5G60410 | SUMO E3 ligase | [55] | |
| DSK2 | AT2G17200 | Autophagy receptor | [33] | |
| BAF1 | AT1G76920 | F-BOX | [56] | |
| UPL3 | AT4G38600 | HECT | [57] | |
| BEH3 ubiquitination | RZF1 | AT3G56580 | RING | [58] |
| BKI1 ubiquitination | PUB30 | AT3G49810 | U-BOX | [59] |
| TaZnF-B | TraesCS4B02G042900 | RING | [60] | |
| BIK1 ubiquitination | PUB25 | AT3G19380 | U-BOX | [61] |
| PUB26 | AT1G49780 | U-BOX | [61] | |
| PUB2 | AT5G67340 | U-BOX | [62] | |
| PUB4 | AT2G23140 | U-BOX | [62] | |
| RHA3A | AT2G17450 | RING | [63] | |
| RHA3B | AT4G35480 | RING | [63] | |
| RGLG1 | AT3G01650 | RING | [64] | |
| RGLG2 | AT5G14420 | RING | [64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, J. Brassinosteroid Signaling Dynamics: Ubiquitination-Dependent Regulation of Core Signaling Components. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104502
Qiu R, Zhou Y, Mao J. Brassinosteroid Signaling Dynamics: Ubiquitination-Dependent Regulation of Core Signaling Components. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104502
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Riguang, Yan Zhou, and Juan Mao. 2025. "Brassinosteroid Signaling Dynamics: Ubiquitination-Dependent Regulation of Core Signaling Components" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104502
APA StyleQiu, R., Zhou, Y., & Mao, J. (2025). Brassinosteroid Signaling Dynamics: Ubiquitination-Dependent Regulation of Core Signaling Components. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104502





