TCF7L2 Polymorphism rs7903146 (C/T) and Gestational Diabetes Influence on Obstetric Outcome: A Romanian Case–Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Obstetrical Outcomes
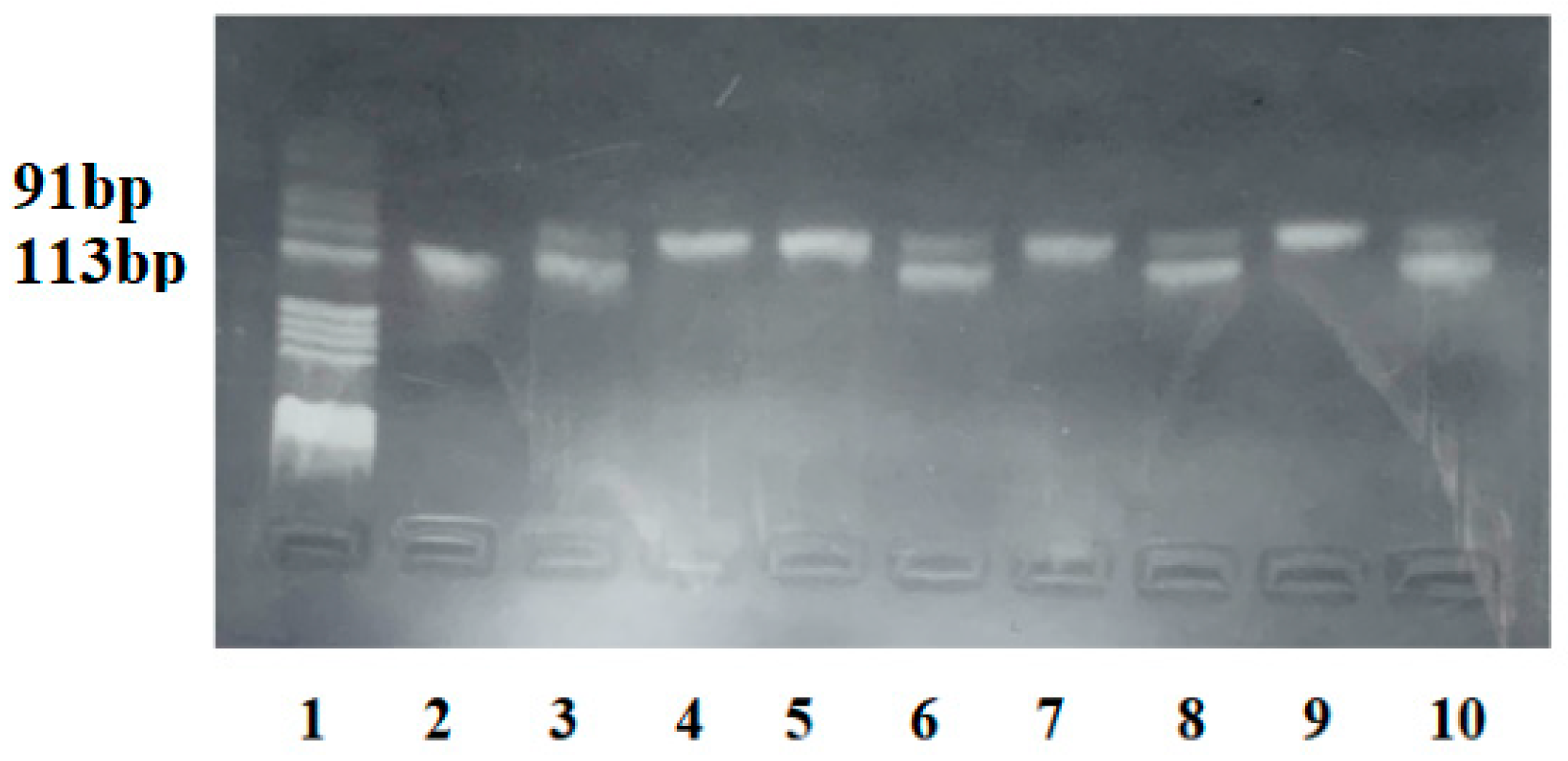
2.2. Genetic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Blood Collection and Biochemical Assays
4.3. rs7903146 (C/T) Polymorphism Genotyping
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metzger, B.E.; Gabbe, S.G.; Persson, B.; Lowe, L.P.; Dyer, A.R.; Oats, J.; Buchanan, T.A. International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, D.S.; Hwee, J.; Shah, B.R.; Booth, G.L.; Bierman, A.S.; Lipscombe, L.L. Trends in incidence of diabetes in pregnancy and serious perinatal outcomes: A large, population-based study in Ontario, Canada, 1996–2010. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.E.; Lowe, L.P.; Dyer, A.R.; Trimble, E.R.; Chaovarindr, U.; Coustan, D.R.; HAPO Study Cooperative Research Group. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pagán, A.; Sabater-Molina, M.; Olza, J.; Prieto-Sánchez, M.T.; Blanco-Carnero, J.E.; Parrilla, J.J.; Gil, Á.; Larqué, E. A gene variant in the transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) is associated with an increased risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2014, 180, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopenko, I.; McCarthy, M.I.; Lindgren, C.M. Type 2 diabetes: New genes, new understanding. Trends Genet. TIG 2008, 24, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.F.A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Reynisdottir, I.; Benediktsson, R.; Manolescu, A.; Sainz, J.; Helgason, A.; Stefansson, H.; Emilsson, V.; Helgadottir, A.; et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. Incretin hormones: Their role in health and disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20 (Suppl. 1), 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villareal, D.T.; Robertson, H.; Bell, G.I.; Patterson, B.W.; Tran, H.; Wice, B.; Polonsky, K.S. TCF7L2 variant rs7903146 affects the risk of type 2 diabetes by modulating incretin action. Diabetes 2010, 59, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potasso, L.; Perakakis, N.; Lamprinou, A.; Polyzou, E.; Kassanos, D.; Peter, A.; Päth, G.; Seufert, J.; Laubner, K. Clinical Impact of the TCF7L2 Gene rs7903146 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Risk Polymorphism in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Impaired Glycemic Control and Increased Need of Insulin Therapy. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabash, A.; Valerio, J.D.; de la Torre, N.G.; Jimenez, I.; Del Valle, L.; Melero, V.; Assaf-Balut, C.; Fuentes, M.; Bordiu, E.; Durán, A.; et al. TCF7L2 rs7903146 polymorphism modulates the association between adherence to a Mediterranean diet and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Metab. Open 2020, 8, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauchi, S.; Meyre, D.; Choquet, H.; Deghmoun, S.; Durand, E.; Gaget, S.; Lecoeur, C.; Froguel, P.; Levy-Marchal, C. TCF7L2 rs7903146 variant does not associate with smallness for gestational age in the French population. BMC Med. Genet. 2007, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kuusisto, J.; Vänttinen, M.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Lindström, J.; Tuomilehto, J.; Uusitupa, M.; Laakso, M. Variants of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene predict conversion to type 2 diabetes in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study and are associated with impaired glucose regulation and impaired insulin secretion. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jin, S. Meta-analysis of association between TCF7L2 polymorphism rs7903146 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasek, D.; Krystynik, O.; Goldmannova, D.; Cibickova, L.; Schovanek, J. Circulating levels of selected adipokines in women with gestational diabetes and type 2 diabetes. J. Appl. Biomed. 2020, 18, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Haslinger, P.; Bancher-Todesca, D.; Leipold, H.; Knöfler, M.; Handisurya, A.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Worda, C. Transcription factor 7-like 2 gene polymorphisms and gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauenborg, J.; Grarup, N.; Damm, P.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Jørgensen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Hansen, T. Common type 2 diabetes risk gene variants associate with gestational diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaat, N.; Lernmark, A.; Karlsson, E.; Ivarsson, S.; Parikh, H.; Berntorp, K.; Groop, L. A variant in the transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene is associated with an increased risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huopio, H.; Cederberg, H.; Vangipurapu, J.; Hakkarainen, H.; Pääkkönen, M.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Heinonen, S.; Laakso, M. Association of risk variants for type 2 diabetes and hyperglycemia with gestational diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Fei, Y.; Ling, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shu, J.; Li, C.; Dong, F. Polymorphisms in TCF7L2 gene are associated with gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese Han population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.C.; Lin, W.T.; Yeh, Y.H.; Wung, S.F. Transcription Factor 7-Like 2 (TCF7L2) rs7903146 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, J.; Mukherjee, R.; Sahu, P.; Datta, C.; Chowdhury, S.; Mandal, D.; Ghosh, A. Association of common variants of TCF7L2 and PCSK2 with gestational diabetes mellitus in West Bengal, India. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2024, 43, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhang, M.; Ren, J.; Jiang, X. Correlation between TCF7L2 and CAPN10 gene polymorphisms and gestational diabetes mellitus in different geographical regions: A meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyssenko, V.; Lupi, R.; Marchetti, P.; Del Guerra, S.; Orho-Melander, M.; Almgren, P.; Sjögren, M.; Ling, C.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Lethagen, A.-L.; et al. Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L. Impaired glucolipid metabolism in gestational diabetes mellitus with T variation of TCF7L2 rs7903146: A case–control study. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2023, 44, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firneisz, G.; Rosta, K.; Al-Aissa, Z.; Hadarits, O.; Harreiter, J.; Nádasdi, Á.; Bancher-Todesca, D.; Németh, L.; Igaz, P.; Rigó, J., Jr.; et al. The MTNR1B rs10830963 Variant in Interaction with Pre-Pregnancy BMI Is a Pharmacogenetic Marker for the Initiation of Antenatal Insulin Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jääskeläinen, T.; Klemetti, M.M. Genetic Risk Factors and Gene-Lifestyle Interactions in Gestational Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freathy, R.M.; Weedon, M.N.; Bennett, A.; Hypponen, E.; Relton, C.L.; Knight, B.; Shields, B.; Parnell, K.S.; Groves, C.J.; Ring, S.M.; et al. Type 2 diabetes TCF7L2 risk genotypes alter birth weight: A study of 24,053 individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, Z.H.; Hughes, L.M.; Khan, S.S. Genetic contributions to risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep. 2023, 17, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, M.; Lin, L. IADPSG criteria for diagnosing gestational diabetes mellitus and predicting adverse pregnancy outcomes. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, P.J.; Kennedy, A.; Sohaey, R.; Byrne, J.L.B.; Oh, K.Y.; Puchalski, M.D. Diagnostic Imaging: Obstetrics, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1034–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Kiliś-Pstrusińska, K.; Zwolińska, D.; Szczepańska, M.; Grzeszczak, W.; Study Group. Is TCF7L2 variant associated with non-diabetic chronic kidney disease progression? Results of a family-based study. Adv. Hyg. Exp. Med. 2014, 68, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GDM a (n = 61) | Non-GDM (n = 55) | p-Value d | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (arithmetic mean ± SD b) | |||
| Maternal age (years) | 31.9 ± 3.88 | 30.53 ± 5.07 | 0.102 |
| BMI c at admission | 31.49 ± 4.58 | 29.06 ± 4.24 | 0.004 |
| Weight gain during pregnancy (kg) | 15.05 ± 5.58 | 15.89 ± 5.24 | 0.418 |
| Gestational age at birth (weeks) | 38.44 ± 1.68 | 39.31 ± 1.17 | 0.002 |
| Family history of diabetes no (%) | 16 (26.2%) | 8 (14.5%) | 0.119 |
| Smoking habit, no (%) | 10 (16.4%) | 2 (3.6%) | 0.021 |
| Parity, no (%) | 0.737 | ||
| Nulliparous | 42 (68.9%) | 39 (70.9%) | |
| Multiparous | 19 (31.1%) | 16 (29.1%) | |
| Delivery route no (%) | 0.581 | ||
| Vaginal | 29 (47.5%) | 29 (52.7%) | |
| C-section | 32 (52.5%) | 26 (47.3%) | |
| APGAR score at 5 min | 1.000 | ||
| ≥7 | 59 (96.7%) | 53 (96.4%) | |
| <7 | 2 (3.3%) | 2 (3.6%) | |
| Birth weight (centiles) | 0.015 | ||
| ≤p10 | 3 (4.9%) | 3 (5.5%) | |
| p10–p90 | 23 (37.7%) | 35 (63.6%) | |
| ≤p90 | 35 (57.4%) | 17 (30.9%) | |
| GDM (N = 61) | Non-GDM (N = 55) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal complications, (%) | |||
| Hypertensive pathology | 12 (19.7%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.002 |
| Premature rupture of membranes | 5 (8.2%) | 0 | 0.059 |
| Preterm birth | 6 (9.8%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.117 |
| Polyhydramnios | 5 (8.2%) | 0 | 0.059 |
| Failure of labor induction | 7 (11.5%) | 0 | 0.014 |
| Shoulder dystocia/soft tissue lacerations | 12 (19.7%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.002 |
| Fetal dystocia | 4 (6.6%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0.367 |
| Fetal complications, (%) | |||
| IUGR | 3 (4.9%) | 3 (5.5%) | 1.000 |
| Macrosomia | 26 (42.6%) | 12 (21.8%) | 0.019 |
| Perinatal asphyxia/acute fetal distress | 0 | 2 (3.6%) | 0.223 |
| TCF7L2 rs7903146 Genotype | Frequencies | p-Value b | OR [95%CI] c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDM a (N = 61) | Non-GDM (N = 55) | |||
| CC, no (%) | 23/61 (37.7%) | 28/55 (50.9%) | 0.074 | 0.58 [0.28–1.22] |
| CT, no (%) | 23/61 (37.7%) | 22/55 (40%) | 0.91 [0.43–1.92] | |
| TT, no (%) | 15/61 (24.6%) | 5/55 (9.1%) | 3.26 [1.10–9.68] | |
| Alleles | ||||
| C allele, no (%) | 69/122 (56.6%) | 78/110 (70.9%) | 0.016 | 0.53 [0.31–0.92] |
| T allele, no (%) | 53/122 (43.3%) | 32/110 (29.1%) | 1.87 [1.09–3.23] | |
| Dominant model | ||||
| CC, no (%) | 23/61 (37.7%) | 28/55 (50.9%) | 0.107 | 0.58 [0.28–1.22] |
| CT+TT, no (%) | 38/61 (62.3%) | 27/55 (49.1%) | 1.71 [0.82–3.59] | |
| Recessive model | ||||
| TT, no (%) | 15/61 (24.6%) | 5/55 (9.1%) | 0.024 | 3.26 [1.10–9.68] |
| CC+CT, no (%) | 46/61 (75.4%) | 50/55 (90.1%) | 0.31 [0.10–0.91] | |
| Co-dominant model | ||||
| CT, no (%) | 23/61 (37.7%) | 22/55 (40%) | 0.475 | 0.91 [0.43–1.92] |
| CC+TT, no (%) | 38/61 (62.3%) | 33/55 (60%) | 1.1 [0.52–2.33] | |
| Homozygote | ||||
| CC, no (%) | 23/38 (60.5%) | 28/33 (84.8%) | 0.021 | 0.27 [0.09–0.87] |
| TT, no (%) | 15/38 (39.5%) | 5/33 (15.2%) | 3.65 [1.15–11.57] | |
| Heterozygote | ||||
| CC, no (%) | 23/48 (50%) | 28/50 (56%) | 0.351 | 0.79 [0.35–1.76] |
| CT, no (%) | 23/48 (40%) | 22/50 (44%) | 1.27 [0.57–2.84] | |
| GDM Type | Insulin-Requiring GDM | Non-Insulin-Requiring GDM | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 5 (22.7%) | 18 (46.2%) | 0.34 (0.11–1.12) |
| CT | 7 (31.8%) | 16 (41%) | 0.67 (0.22–2.02) |
| TT | 10 (45.5%) | 5 (12.8%) | 5.67 (1.61–19.97) |
| p-value | 0.015 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruciat, G.; Florian, A.R.; Chaikh-Sulaiman, M.-S.; Staicu, A.; Caracostea, G.V.; Procopciuc, L.M.; Stamatian, F.; Muresan, D. TCF7L2 Polymorphism rs7903146 (C/T) and Gestational Diabetes Influence on Obstetric Outcome: A Romanian Case–Control Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25074039
Cruciat G, Florian AR, Chaikh-Sulaiman M-S, Staicu A, Caracostea GV, Procopciuc LM, Stamatian F, Muresan D. TCF7L2 Polymorphism rs7903146 (C/T) and Gestational Diabetes Influence on Obstetric Outcome: A Romanian Case–Control Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(7):4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25074039
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruciat, Gheorghe, Andreea Roxana Florian, Mariam-Suzana Chaikh-Sulaiman, Adelina Staicu, Gabriela Valentina Caracostea, Lucia Maria Procopciuc, Florin Stamatian, and Daniel Muresan. 2024. "TCF7L2 Polymorphism rs7903146 (C/T) and Gestational Diabetes Influence on Obstetric Outcome: A Romanian Case–Control Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 7: 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25074039
APA StyleCruciat, G., Florian, A. R., Chaikh-Sulaiman, M.-S., Staicu, A., Caracostea, G. V., Procopciuc, L. M., Stamatian, F., & Muresan, D. (2024). TCF7L2 Polymorphism rs7903146 (C/T) and Gestational Diabetes Influence on Obstetric Outcome: A Romanian Case–Control Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(7), 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25074039







