Comparative Analysis of Six Complete Plastomes of Tripterospermum spp.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Plastome
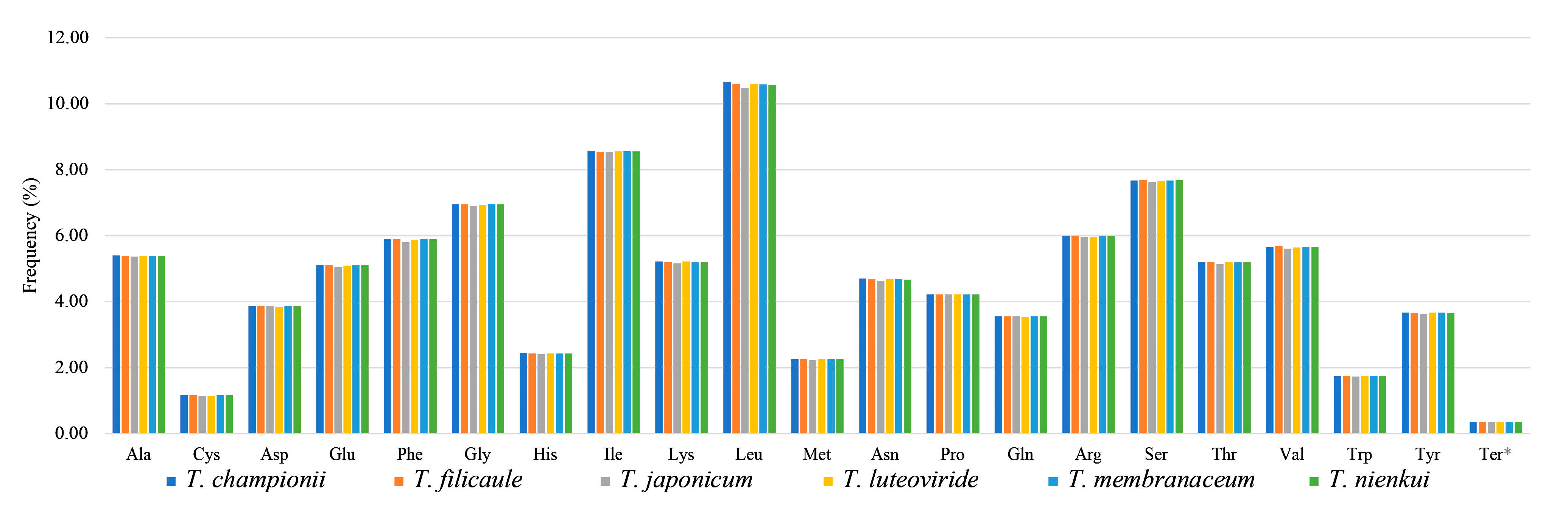
2.2. Codon Usage Analysis
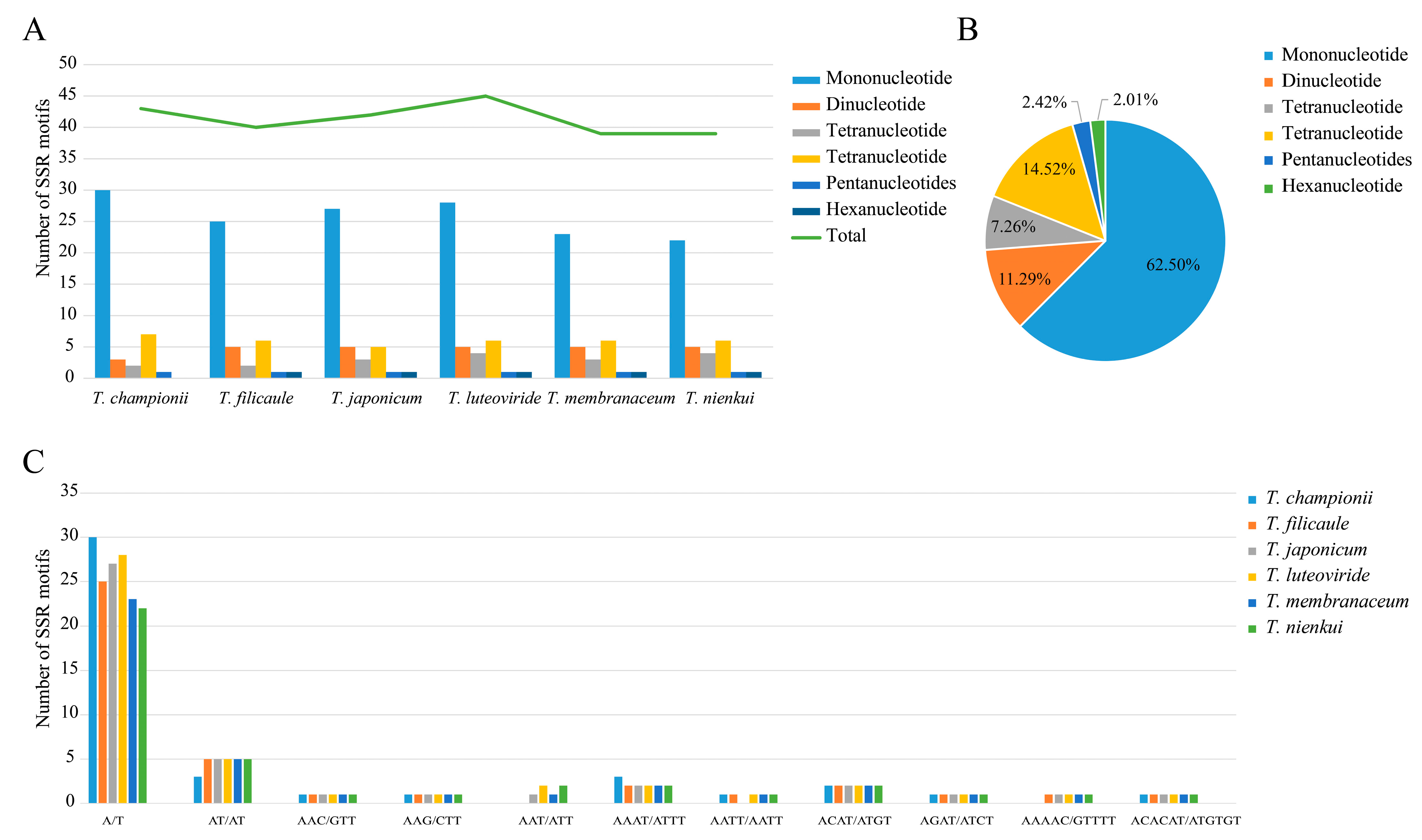
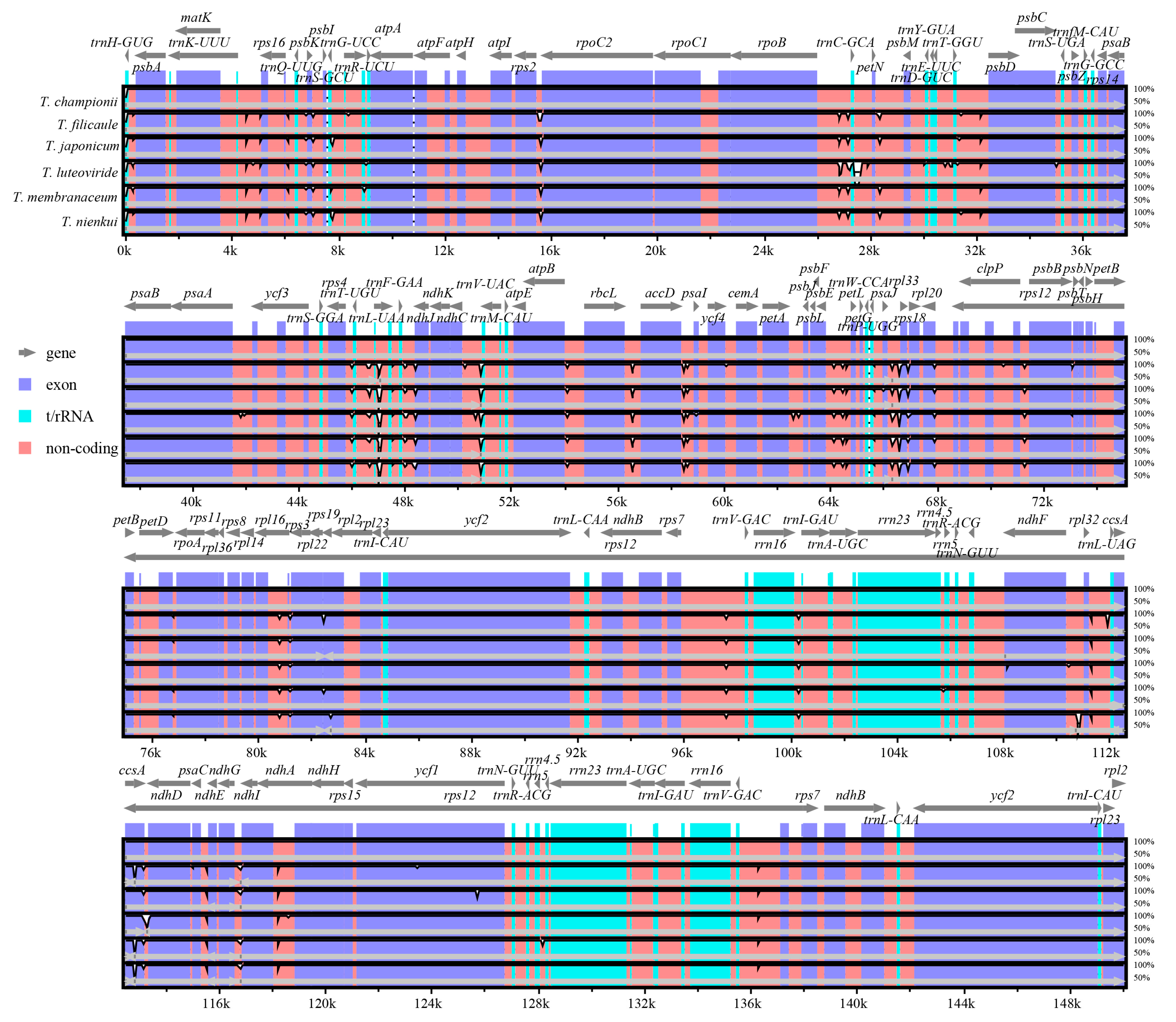
2.3. Repeat Sequence Analysis
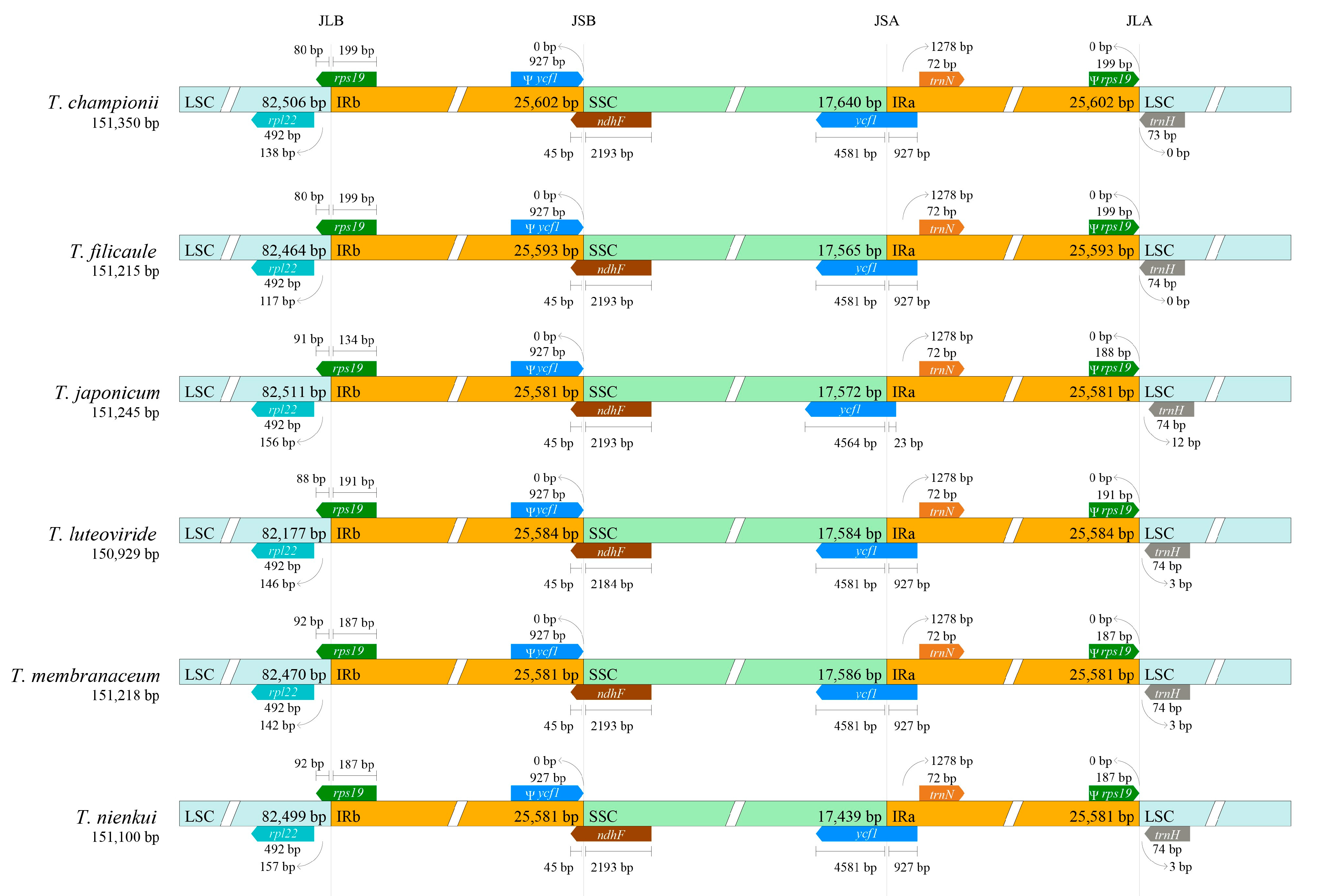
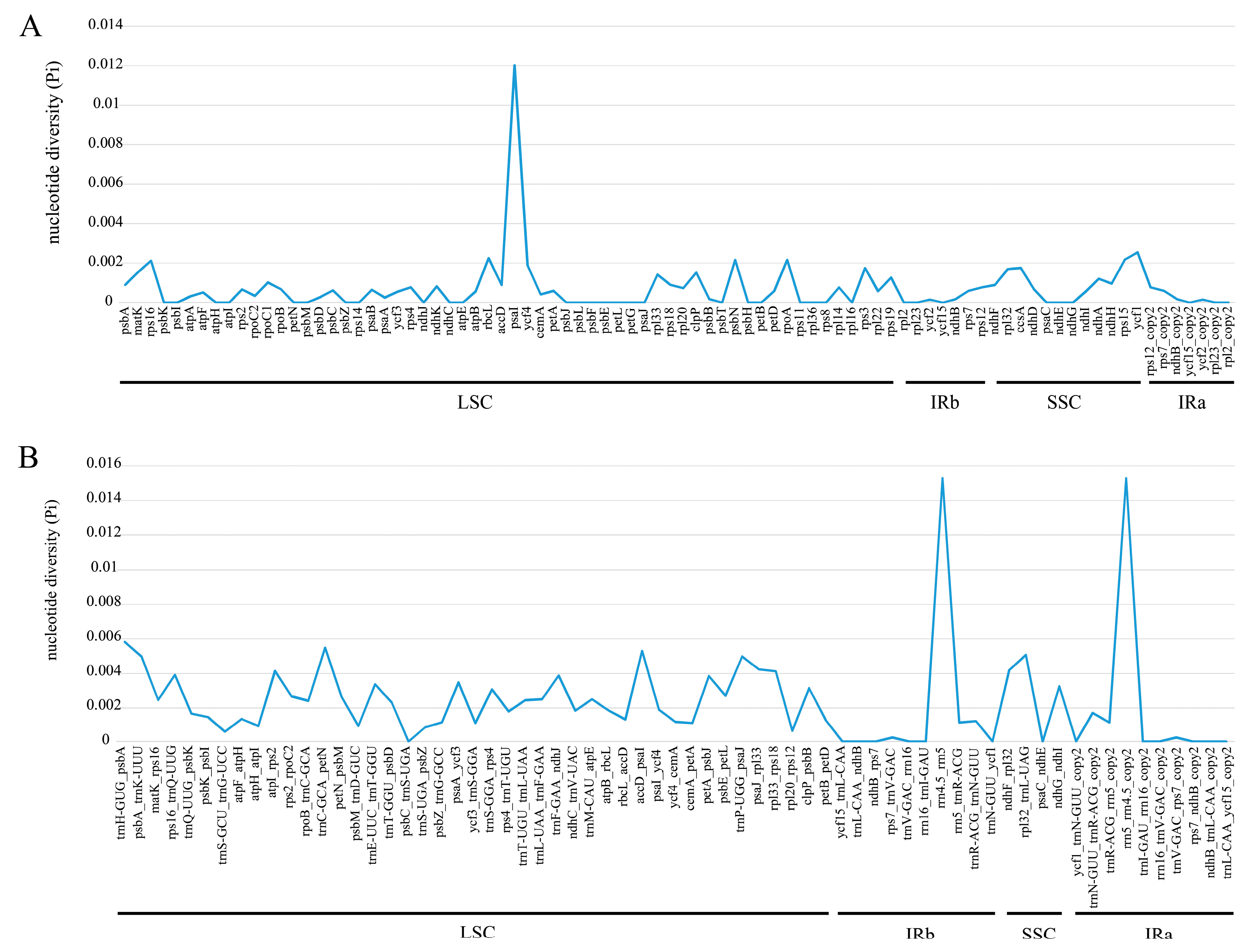
2.4. Sequence Divergence Analysis
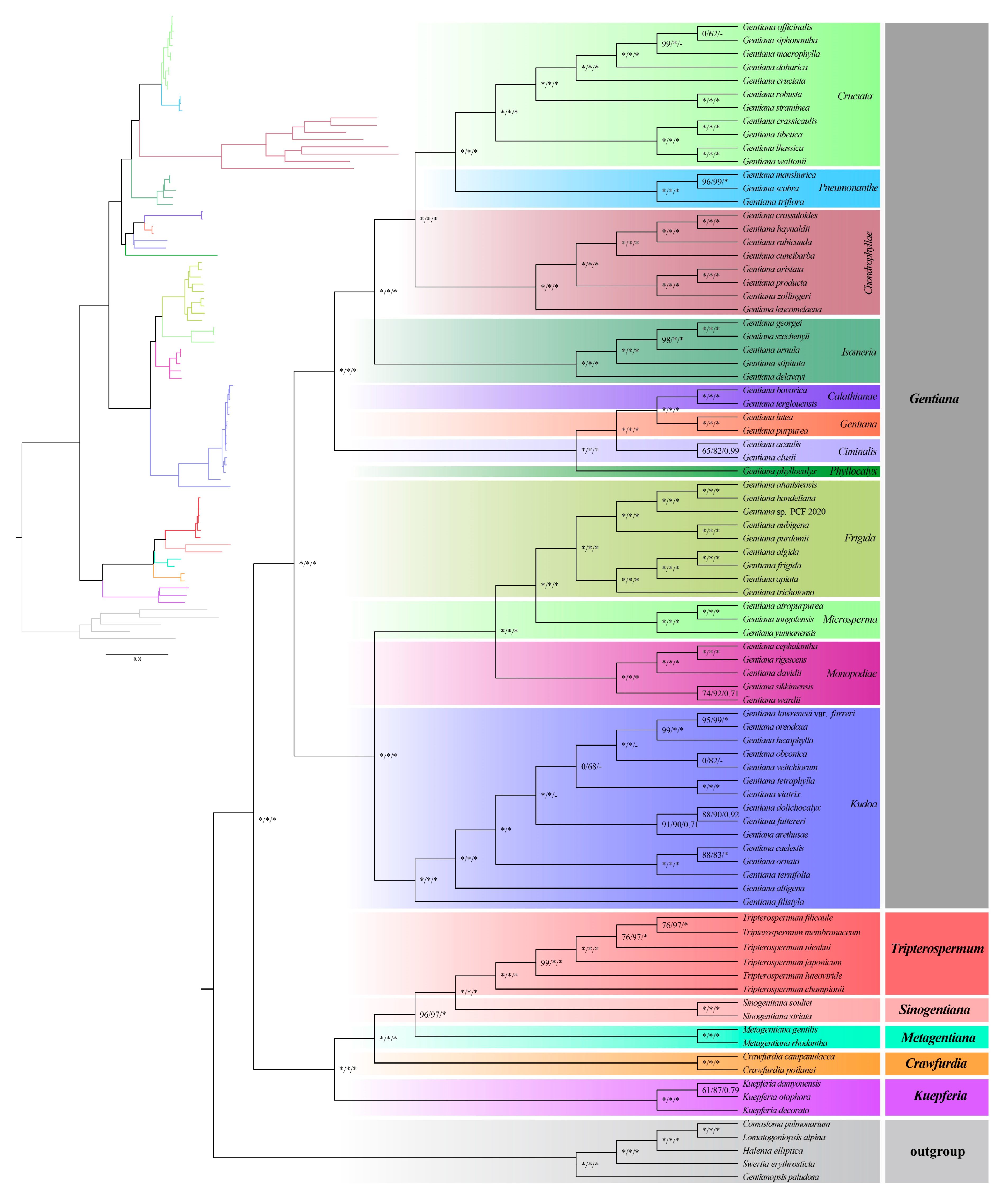
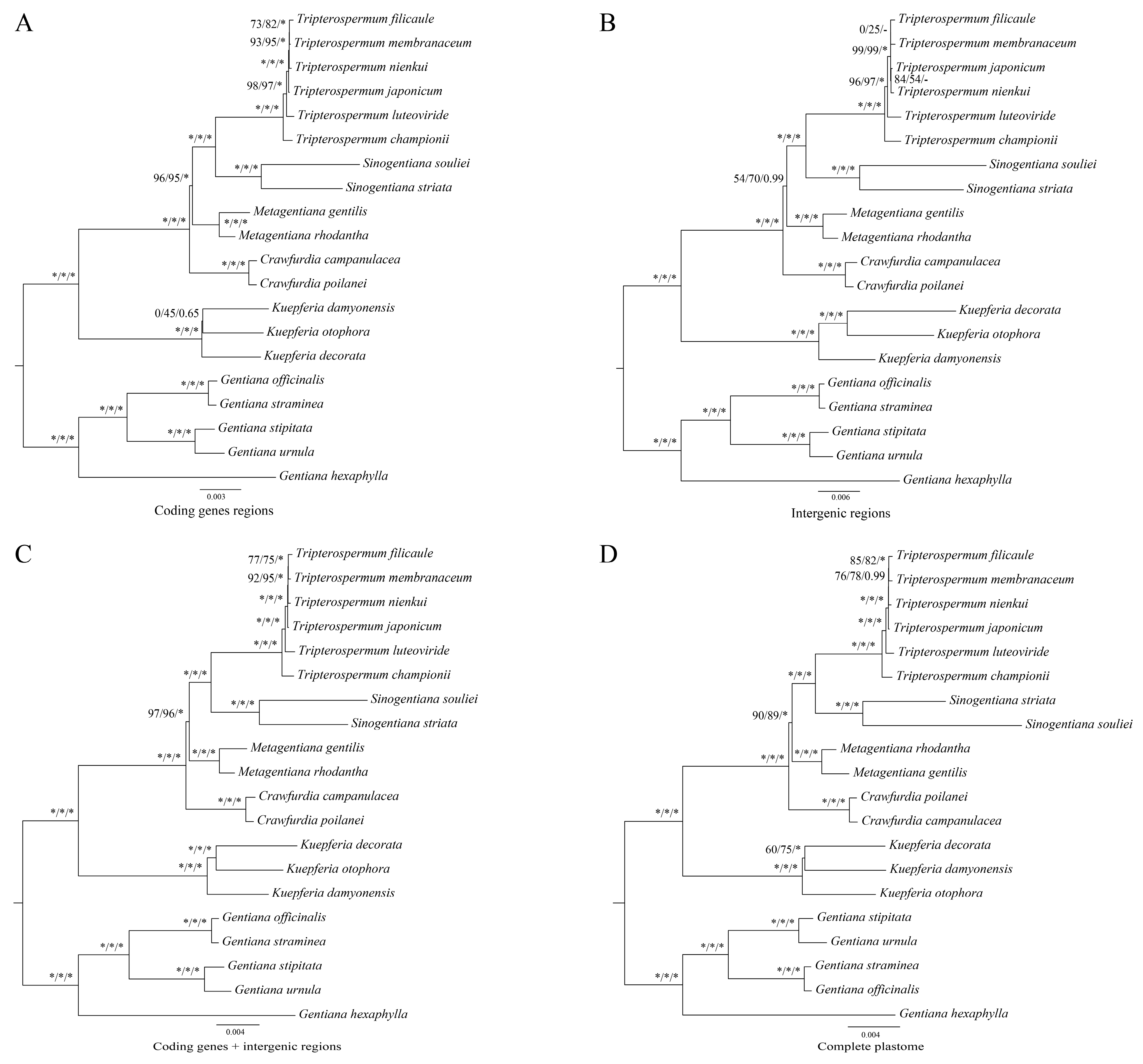
2.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Discussion
3.1. Variation of Plastome Sequences
3.2. Codon Usage and Repeat Sequence Analysis
3.3. Sequence Divergence Analysis and Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Sequencing
4.2. Plastome Assembly and Annotation
4.3. Plastome Structure Comparisons and Sequence Divergence Analysis
4.4. Repeat Sequence and Codon Usage Analysis
4.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murata, J. Synopsis of Tripterospermum (Gentianaceae). Journal of the Faculty of Science; Section III: Botany; University of Tokyo: Bunkyo City, Japan, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- POWO. Plants of the World Online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2023. Available online: http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Ho, T.N.; Pringle, J.S. Gentianaceae. In Flora of China; Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanic Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1995; Volume 16, p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-H.; Lin, J.-Y.; Lin, C.-N.; Hsu, S.-Y. Inhibition of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme by tetrahydroxyxanthones isolated from Tripterospermum lanceolatum. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.-F.; Raung, S.-L.; Tsao, L.-T.; Lin, C.-N.; Wang, J.-P. Examination of the inhibitory effect of norathyriol in formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced respiratory burst in rat neutrophils. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, H.; Kijima, K. An iridoid gentiobioside, a benzophenone glucoside and acylated flavone C-glycosides from Tripterospermum japonicum (Sieb. et Zucc.) Maxim. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, K.C.; Ma, C.H.; Ye, G.; Fan, M.S.; Huang, C.G. Two new secoiridoid glycosides from Tripterospermum chinense. Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-J.; Ye, G. Flavonoids and xanthones from Tripterospermum chinense. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2008, 44, 514–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, C.-J.; Wei, Y.-L.; Si, J.-G.; Fu, L.; Dong, J.-X.; Zou, Z.-M. The novel indole glucoalkaloid and secoiridoid glucoside from Tripterospermum chinense. Phytochem. Lett. 2020, 35, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, A.; Yuan, Y.-M.; Küpfer, P.; Alvarez, N. Phylogeny of subtribe Gentianinae (Gentianaceae): Biogeographic inferences despite limitations in temporal calibration points. Taxon 2010, 59, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, A.; Matuszak, S.; Sun, H.; Liu, E.; Yuan, Y.-M.; Muellner-Riehl, A.N. Two new genera of Gentianinae (Gentianaceae): Sinogentiana and Kuepferia supported by molecular phylogenetic evidence. Taxon 2014, 63, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, C.L. Tripterospermum. Bijdrangen tot de Flora van Nederlandsch Indië; Lands Drukkerij: Batavia, Indonesia, 1826; p. 849. [Google Scholar]
- Wallich, N. Tentanien Florae Napalensis Illustratae, Part 2; Asiatic Lithographicae Press: Serampore/Calcutta, India, 1826; pp. 37–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.N.; Chen, S.L.; Liu, S.W. Metagentiana, a new genus of Gentianaceae1. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 2002, 43, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, C.B. Gentianaceae. In The Flora of British India; Hooker, J.D., Ed.; Reeve: London, UK, 1885; Volume 4, pp. 93–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ridley, H.N. Gentianaceae. In The Flora of the Malay Peninsula; L. Reeve & Co.: London, UK, 1923; Volume 2, pp. 432–437. [Google Scholar]
- Ubolcholaket, A. Gentianaceae. In Flora of Thailand; Smitinand, T., Larsen, K., Eds.; Chutima Press: Bangkok, Thailand, 1987; Volume 5, pp. 72–92. [Google Scholar]
- Marquand, C.V.B. New Asiatic Gentians: II. Bull. Misc. Inf. R. Bot. Gard. Kew 1931, 1931, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquand, C.V.B. The gentians of China. Bull. Misc. Inf. R. Bot. Gard. Kew 1937, 1937, 134–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xia, T.A.O.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, S. Molecular systematics and biogeography of Crawfurdia, Metagentiana and Tripterospermum (Gentianaceae) based on nuclear ribosomal and plastid DNA sequences. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Chen, S.-L.; Xia, T.; Wang, Y.-J. Phylogeny of Metagentiana and related genera (Gentianaceae) inferred from nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences. J. Syst. Evol. 2005, 43, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszak, S.; Muellner-Riehl, A.N.; Sun, H.; Favre, A. Dispersal routes between biodiversity hotspots in Asia: The case of the mountain genus Tripterospermum (Gentianinae, Gentianaceae) and its close relatives. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, A.; Ray, S.; Roy, A. Molecular markers in phylogenetic studies-a review. J. Phylogenetics Evol. Biol. 2014, 2, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Clegg, M.T.; Gaut, B.S.; Learn, G.H., Jr.; Morton, B.R. Rates and patterns of chloroplast DNA evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6795–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.-D.; Liu, D.-K.; Xu, S.-W.; Zhou, C.-Y.; Gao, X.-Y.; Zeng, M.-Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.-L.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Z. Plastid phylogenomics improves resolution of phylogenetic relationship in the Cheirostylis and Goodyera clades of Goodyerinae (Orchidoideae, Orchidaceae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2021, 164, 107269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, U.; Dong, W.L.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, R.N.; Shahzad, K.; Ma, X.F.; Li, Z.H. Comparative plastid genomics of Pinus species: Insights into sequence variations and phylogenetic relationships. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 58, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.K.; Ruhlman, T.A. Plastid genomes of seed plants. Genom. Chloroplasts Mitochondria 2012, 35, 103–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, X. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of species in Gentiana section Cruciata (Gentianaceae) and the development of authentication markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Landis, J.B.; Lv, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, N.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Deng, T. Plastome phylogenomic study of Gentianeae (Gentianaceae): Widespread gene tree discordance and its association with evolutionary rate heterogeneity of plastid genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.C.; Sun, S.S.; Twyford, A.D.; Li, B.B.; Zhou, R.Q.; Chen, S.L.; Gao, Q.B.; Favre, A. Lineage-specific plastid degradation in subtribe Gentianinae (Gentianaceae). Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 3286–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Xia, M.; Chi, X.; Khan, G.; Chen, S.; Zhang, F. Plastome sequencing reveals phylogenetic relationships among Comastoma and related taxa (Gentianaceae) from the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 16034–16046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-J.; Cheng, C.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Wu, C.-L.; Su, T.-M.; Chaw, S.-M. Dynamics and evolution of the inverted repeat-large single copy junctions in the chloroplast genomes of monocots. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.-D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, C.-Y.; Zeng, M.-Y.; Gao, X.-Y.; Li, M.-H.; Liu, Z.-J.; Chen, S.-P. Comparative Analysis of Plastomes in Elsholtzieae: Phylogenetic Relationships and Potential Molecular Markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quax, T.E.F.; Claassens, N.J.; Söll, D.; van der Oost, J. Codon bias as a means to fine-tune gene expression. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Cowe, E.; Higgins, D.G.; Shields, D.C.; Wolfe, K.H.; Wright, F. Codon usage patterns in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable within-species diversity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 8207–8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, D.E. The use of chloroplast DNA polymorphism in studies of gene flow in plants. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaal, B.A.; Hayworth, D.A.; Olsen, K.M.; Rauscher, J.T.; Smith, W.A. Phylogeographic studies in plants: Problems and prospects. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provan, J.; Powell, W.; Hollingsworth, P.M. Chloroplast microsatellites: New tools for studies in plant ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, G.J.; McNicoll, J.; Ramsay, G.; Meyer, R.C.; De Jong, W.S. Polymorphic simple sequence repeat markers in chloroplast genomes of Solanaceous plants. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 99, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; McCouch, S.R. Microsatellites and microsynteny in the chloroplast genomes of Oryza and eight other Gramineae species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 100, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumley, T.W.; Palmer, J.D.; Mower, J.P.; Fourcade, H.M.; Calie, P.J.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Pelargonium × hortorum: Organization and evolution of the largest and most highly rearranged chloroplast genome of land plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.-J.; Moore, M.J.; Li, D.-Z.; Yi, T.-S. PGA: A software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3. 1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.C.E.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32 (Suppl. S2), W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peden, J.F. Analysis of Codon Usage. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, J.A.A. MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author, Volume 2. In Evolutionary Biology Centre; Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
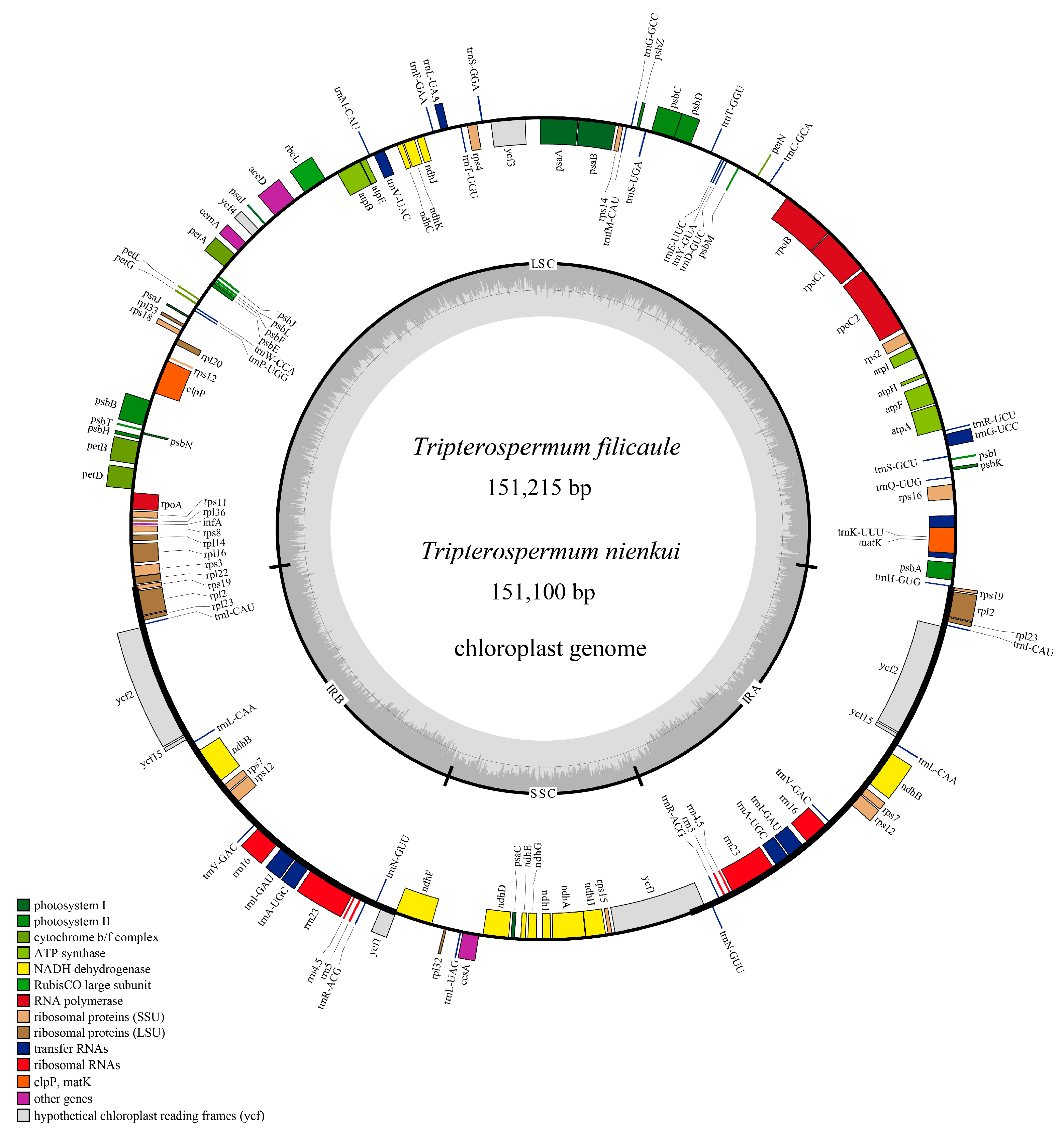
| Category of Genes | Group | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Photosystem I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| Photosystem II | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| Large subunit of rubisco | rbcL | |
| Cytochrome b/f complex | petA, petB *, petD *, petG, petL, petN | |
| ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF *, atpH, atpI | |
| NADH dehydrogenase | ndhA *, ndhB * (*2), ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK | |
| Self-replication-related genes | Ribosomal RNA | rrn4.5 (*2), rrn5 (*2), rrn16 (*2), rrn23 (*2) |
| Transfer RNA | trnA-UGC * (*2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnfM-CAU, trnG-GCC, trnG-UCC *, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU (*2), trnI-GAU * (*2), trnK-UUU *, trnL-CAA (*2), trnL-UAA *, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU (*2), trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG (*2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC (*2), trnV-UAC *, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA | |
| RNA polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1 *, rpoC2 | |
| Small subunit of ribosomal proteins | rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7 (*2), rps8, rps11, rps12 ** (*2), rps14, rps15, rps16 *, rps18, Ψrps19, rps19 | |
| Large subunit of ribosomal proteins | rpl2 * (*2), rpl14, rpl16 *, rpl20, rpl22, rpl23 (*2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 | |
| Other genes | Protease | clpP ** |
| Maturase | matK | |
| Envelop membrane protein | cemA | |
| Acetyl-CoA-carboxylase | accD | |
| Translation initiation factor | ΨinfA | |
| C-type cytochrome synthesis | ccsA | |
| Genes with unknown function | Hypothetical chloroplast reading frames | Ψycf1, ycf1, ycf2 (*2), ycf3 **, ycf4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, X.-D.; Lin, W.-J.; Fu, H.-H.; Lin, Y.-Z.; Shen, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.-J.; Li, M.-H.; Chen, S.-P. Comparative Analysis of Six Complete Plastomes of Tripterospermum spp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052534
Tu X-D, Lin W-J, Fu H-H, Lin Y-Z, Shen J, Chen S, Liu Z-J, Li M-H, Chen S-P. Comparative Analysis of Six Complete Plastomes of Tripterospermum spp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052534
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Xiong-De, Wen-Jun Lin, Hou-Hua Fu, Yi-Zhe Lin, Jun Shen, Shuai Chen, Zhong-Jian Liu, Ming-He Li, and Shi-Pin Chen. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of Six Complete Plastomes of Tripterospermum spp." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052534
APA StyleTu, X.-D., Lin, W.-J., Fu, H.-H., Lin, Y.-Z., Shen, J., Chen, S., Liu, Z.-J., Li, M.-H., & Chen, S.-P. (2024). Comparative Analysis of Six Complete Plastomes of Tripterospermum spp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052534








