Biomimetic Diatom Biosilica and Its Potential for Biomedical Applications and Prospects: A Review
Abstract
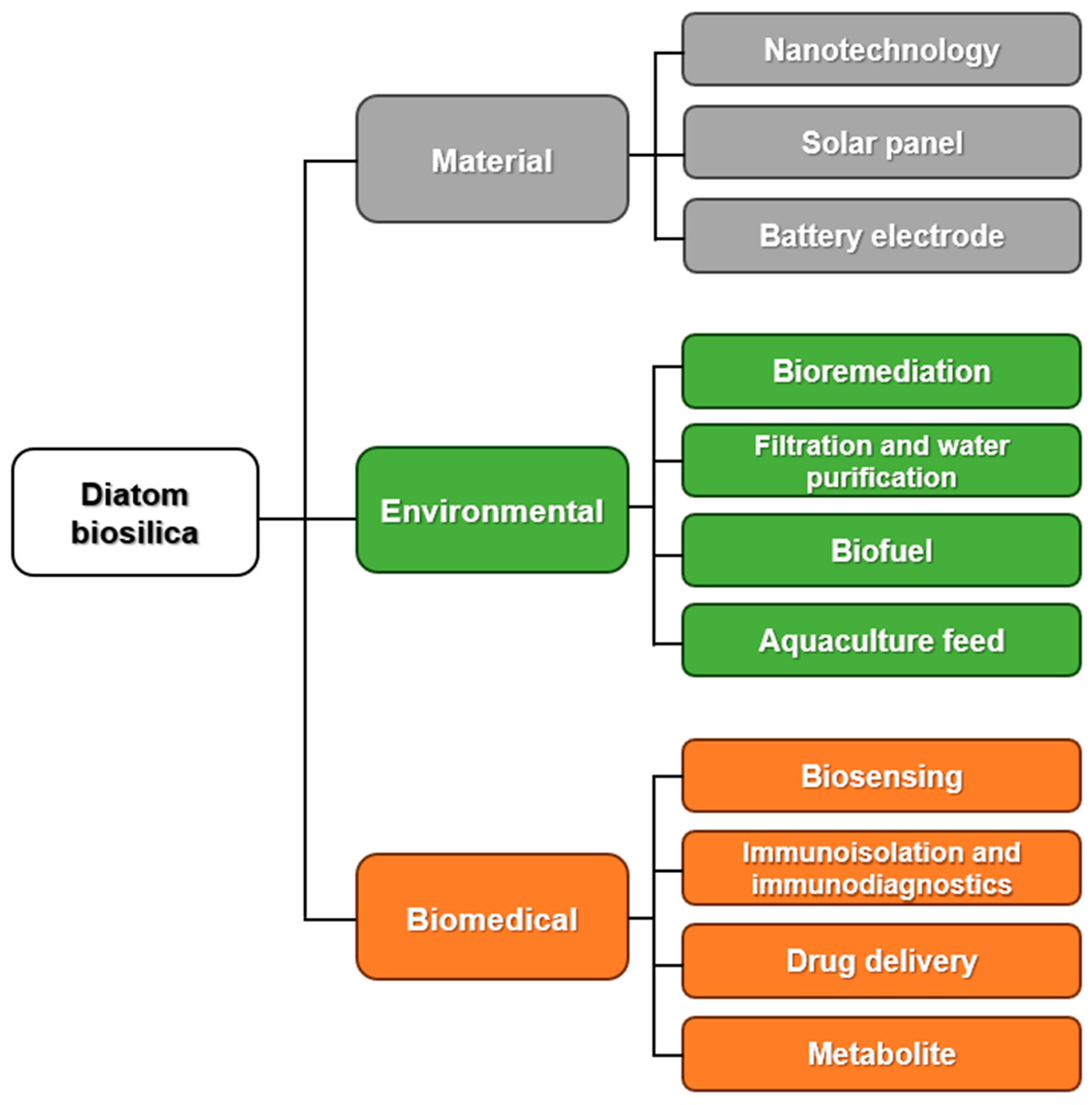
1. Introduction
2. Silicon Uptake and Frustule Formation
3. Diatom Biosilica: Structure, Purification, and Surface Modification
3.1. Unique 3D Structure of Diatoms
3.2. Purification of Raw Diatom Biosilica
3.3. Surface Modification of Diatom Biosilica
4. Biomedical Applications of Diatom Biosilica
4.1. Bone Regeneration
| Application | Type | Function | Type of Functionalization | Loading Material | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite | Diatom (Thalassiosira weissflogii) | Osteoactive material | Bisphosphonates | - | [60] |
| Diatomite | Polyelectrolyte scaffold | Chitosan/Na-carboxymethylcellulose | - | [61] | |
| Diatomite | Chitosan membrane | - | - | [63] | |
| Diatomite | PHBV-PCL fibrous scaffold | - | Pullulan | [62] | |
| Diatomite | Chitosan composites | - | - | [64] | |
| Diatomite | Silk fibroin | - | - | [65] | |
| Diatomite | Collagen/chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite | - | - | [66] | |
| Material loading | Diatomite | Chitosan composite | Polyethyleneimine | BMP-2 | [67] |
| PHBV-PCL fibrous scaffold | - | Melatonin | [68] | ||
| Diatomite scaffold | - | Copper | [69] | ||
| Biocoating | Diatomite | Magnesium implants | - | ZrO2 particle | [70,71] |
| Ceramic coating | - | - | [72] |
4.2. Wound Healing
| Application | Type | Function | Form | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wound healing | Diatomite | Promoting bioactivity of wound dressings for tissue regeneration | Scaffolds | [78] |
| Diatom (Cyclotella cryptica sp.) | Biocompatibility, sustained drug release, non-adherence, and antibacterial activity with hemostatic properties | Hydrogel | [79] | |
| Silica nanoparticles (Diatom) | Accelerates diabetic wound healing | Hydrogel | [82] | |
| Wound healing and hemostasis | Diatomite | Stops bleeding | Scaffolds | [83] |
| Biocompatibility and hemostasis | Diatomite | New hemostatic substance | Particles | [84] |
| Diatomite | Hemostatic material with non-toxic side effects and rapid coagulation promotion | Particles | [85] | |
| Hemostasis | Diatomite | Fast hemostasis with controlled porous structure | Aerogel | [86] |
| Diatom (Thalassiosira weissflogii, Thalassiosira sp., Cyclotella cryptica) | Hemostasis and rapid blood clotting | Frustum | [87] | |
| Diatom (Cyclotella cryptica sp.) | Improves hemostasis efficiency | Frustule | [88] | |
| Diatomite | Hemostatic and antibacterial material | Spheres | [89] | |
| Mechanical properties and hemostasis | Diatomite | Low-cost, high-efficiency, and rapid hemostasis material | Sponge | [90] |
| Antibacterial, hemostatic, and osteogenic | Diatomite | Bio-multifunctional sponge after tooth extraction | Sponge | [91] |
| Antibacterial | Diatomite | Antibacterial activity | Membrane | [92] |
| Diatom (C. cryptica) | Healing of infected wounds, and suppressing inflammation, collagen, and angiogenesis | Particles | [81] |
4.3. Drug Delivery Systems
4.4. Other Applications
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Halsey, K.H.; Boss, E.; Karp-Boss, L.; Milligan, A.J.; Peers, G. Thoughts on the evolution and ecological niche of diatoms. Ecol. Monogr. 2021, 91, e01457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.G.; Vanormelingen, P. An inordinate fondness? The number, distributions, and origins of diatom species. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2013, 60, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiry, M.D. How Many Species of Algae Are There? J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.G. The species concept in diatoms. Phycologia 1999, 38, 437–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tréguer, P.; Bowler, C.; Moriceau, B.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Gehlen, M.; Aumont, O.; Bittner, L.; Dugdale, R.; Finkel, Z.; Iudicone, D.; et al. Influence of diatom diversity on the ocean biological carbon pump. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, M.; Doktycz, M.J.; Allison, D.P. Application of AFM in understanding biomineral formation in diatoms. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2008, 456, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuluaga-Astudillo, D.; Ruge, J.C.; Camacho-Tauta, J.; Reyes-Ortiz, O.; Caicedo-Hormaza, B. Diatomaceous Soils and Advances in Geotechnical Engineering—Part I. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losic, D.; Rosengarten, G.; Mitchell, J.G.; Voelcker, N.H. Pore architecture of diatom frustules: Potential nanostructured membranes for molecular and particle separations. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2006, 6, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.T.; Wu, B.Y.; Lyu, S.; Li, T.; Han, H.; Li, D.D.; Wang, J.K.; Zhang, J.T.; Lu, X.; Sun, D.Z. Improving the thermal energy storage capability of diatom-based biomass/polyethylene glycol composites phase change materials by artificial culture methods. Sol. Energy Mat. Sol. Cells 2021, 219, 110797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, N.; Berne, C.; Spain, J.; Kröger, N. Silica immobilization of an enzyme through genetic engineering of the diatom. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1843–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terracciano, M.; De Stefano, L.; Rea, I. Diatoms Green Nanotechnology for Biosilica-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Simon, D.P.; Diaz-Garza, A.M.; Fantino, E.; Messaabi, A.; Meddeb-Mouelhi, F.; Germain, H.; Desgagné-Penix, I. Diatoms Biotechnology: Various Industrial Applications for a Greener Tomorrow. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 636613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardo, A.; Orefice, I.; Balzano, S.; Barra, L.; Romano, G. Mini-Review: Potential of Diatom-Derived Silica for Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delasoie, J.; Zobi, F. Natural Diatom Biosilica as Microshuttles in Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontano, C.; Chianese, G.; Terracciano, M.; de Stefano, L.; Rea, I. Nanostructured Biosilica of Diatoms: From Water World to Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, S.; Kumeria, T.; Aw, M.S.; Losic, D. Diatom Silica for Biomedical Applications: Recent Progress and Advances. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1800552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payares, L.M.A.; Púa, L.D.G.; Pareja, L.A.D.; Méndez, S.C.P.; Méndez, V.N.P. Microalgae Applications to Bone Repairing Processes: A Review. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 2991–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Schröder, H.C.; Feng, Q.L.; Draenert, F.; Müller, W.E.G. The Deep-Sea Natural Products, Biogenic Polyphosphate (Bio-PolyP) and Biogenic Silica (Bio-Silica), as Biomimetic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: Fabrication of a Morphogenetically-Active Polymer. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 718–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowska, W.; Sprynskyy, M.; Wojtczak, I.; Dabek, P.; Witkowski, A.; Buszewski, B. “Outsourcing” Diatoms in Fabrication of Metal-Doped 3D Biosilica. Materials 2020, 13, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulichová, J.; Urbánková, P. Symmetric and Asymmetric Components of Shape Variation in the Diatom Genus (Bacillariophyta). Symmetry 2020, 12, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Y.; Lundholm, N.; Ellegaard, M. Effects of abiotic factors on the nanostructure of diatom frustules-ranges and variability. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5889–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losic, D.; Pillar, R.J.; Dilger, T.; Mitchell, J.G.; Voelcker, N.H. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) characterisation of the porous silica nanostructure of two centric diatoms. J. Porous Mat. 2007, 14, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, N.; Sumper, M.; Kröger, N. Biosilica formation in diatoms: Characterization of native silaffin-2 and its role in silica morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12075–12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabravolski, S.A.; Isayenkov, S.V. Evolution of the Membrane Transport Protein Domain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröger, N.; Lorenz, S.; Brunner, E.; Sumper, M. Self-assembly of highly phosphorylated silaffins and their function in biosilica morphogenesis. Science 2002, 298, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowler, C.; De Martino, A.; Falciatore, A. Diatom cell division in an environmental context. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, N.; Deutzmann, R.; Sumper, M. Polycationic peptides from diatom biosilica that direct silica nanosphere formation. Science 1999, 286, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumper, M.; Kröger, N. Silica formation in diatoms:: The function of long-chain polyamines and silaffins. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthappa, U.T.; Brahmkhatri, V.; Sriram, G.; Jung, H.Y.; Yu, J.X.; Kurkuri, N.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Altalhi, T.; Neelgund, G.M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Nature engineered diatom biosilica as drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2018, 281, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gutu, T.; Gale, D.K.; Jiao, J.; Rorrer, G.L.; Chang, C.H. Self-Assembly of Nanostructured Diatom Microshells into Patterned Arrays Assisted by Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Deposition and Inkjet Printing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4178–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losic, D.; Mitchell, J.G.; Lal, R.; Voelcker, N.H. Rapid fabrication of micro- and nanoscale patterns by replica molding from diatom biosilica. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, K.M.; Rogers, T.N.; Altan, B.S.; Hackney, S.A.; Hamm, C. Engineering and medical applications of diatoms. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, M. Diatoms, Biomineralization Processes, and Genomics. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4855–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, D.K.; Gutu, T.; Jiao, J.; Chang, C.H.; Rorrer, G.L. Photoluminescence Detection of Biomolecules by Antibody-Functionalized Diatom Biosilica. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, N.L.; Thaxton, C.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Control of nanoparticle assembly by using DNA-modified diatom templates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5500–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, E.M.; Pickering, R.A.; Shoji, K.; Hossain, M.I.; Glover, T.G.; Krause, J.W.; Tang, Y.Z. Effect of cleaning methods on the dissolution of diatom frustules. Mar. Chem. 2020, 224, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Dutta, A.; Kapoor, N.; Kumar, A.; Tiwari, A. Envisaging marine diatom as a “SMART” drug delivery system for insoluble drugs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 68, 102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Li, T.; Sha, L.Y.; Chen, F.F.; Li, M.N.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Li, D.D.; Sun, D.Z. Comparative of diatom frustules, diatomite, and silica particles for constructing self-healing superhydrophobic materials with capacity for thermal energy storage. Appl. Energy 2023, 332, 120482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.J.; Shen, Z.; Shen, X.Z. Dual-functional calcium alginate hydrogel beads for disinfection control and removal of dyes in water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Sun, N.F.; Liu, X.D.; Chen, Z.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Hu, T.H.; Xue, X.B.; Zhang, S.L.; Sheetah, G.; Xie, Y. Diatomite-Based Adsorbent Decorated with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for the Removal of Hazardous Metal Ions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 8958–8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoy, M.; Gultepe, E.; Pandey, S.; Khashab, M.A.; Gracias, D.H. Silane surface modification for improved bioadhesion of esophageal stents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Ichinose, T.; Hirose, Y.; Kuroda, R.; Mayama, S. Diatom Cells Grown and Baked on a Functionalized Mica Surface. J. Biol. Phys. 2008, 34, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettieri, S.; Setaro, A.; De Stefano, L.; De Stefano, M.; Maddalena, P. The gas-detection properties of light-emitting diatoms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, L.; Rendina, I.; De Stefano, M.; Bismuto, A.; Maddalena, P. Marine diatoms as optical chemical sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 233902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Cai, J.; Pan, J.F.; Chen, M.L.; Li, A.B.; Jiang, Y.G. Biosilica structures obtained from Nitzschia, Ditylum, Skeletonema, and Coscinodiscus diatom by a filtration-aided acid cleaning method. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 95, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delalat, B.; Sheppard, V.C.; Ghaemi, S.R.; Rao, S.; Prestidge, C.A.; McPhee, G.; Rogers, M.L.; Donoghue, J.F.; Pillay, V.; Johns, T.G.; et al. Targeted drug delivery using genetically engineered diatom biosilica. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.R.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J.J. Preparation and characteristics of biosilica derived from marine diatom biomass of Nitzschia closterium and Thalassiosira. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2017, 35, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.H.; Shin, J.W.; Ki, M.R.; Pack, S.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles on biosilica diatomite: Well-dispersed particle formation and reusability. Process. Biochem. 2023, 125, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Min, K.H.; Kanth, B.K.; Jang, E.K.; Pack, S.P. Production of TiO-deposited Diatoms and Their Applications for Photo-catalytic Degradation of Aqueous Pollutants. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2020, 25, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losic, D.; Yu, Y.; Aw, M.S.; Simovic, S.; Thierry, B.; Addai-Mensah, J. Surface functionalisation of diatoms with dopamine modified iron-oxide nanoparticles: Toward magnetically guided drug microcarriers with biologically derived morphologies. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6323–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Pack, S.P. Biomimetic and bioinspired silicifications: Recent advances for biomaterial design and applications. Acta Biomater. 2021, 120, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Son, R.G.; Park, K.S.; Pack, S.P. Oriented multivalent silaffin-affinity immobilization of recombinant lipase on diatom surface: Reliable loading and high performance of biocatalyst. Colloids Surface B 2022, 219, 112830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phogat, S.; Saxena, A.; Kapoor, N.; Aggarwal, C.; Tiwari, A. Diatom mediated smart drug delivery system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.D.H.; Bonani, W.; Speranza, G.; Sglavo, V.; Ceccato, R.; Maniglio, D.; Motta, A.; Migliaresi, C. Processing and characterization of diatom nanoparticles and microparticles as potential source of silicon for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2016, 59, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Buchanan, F.; Ford, L.; Julius, M.; Walsh, P.J. A comparison of the degradation behaviour of 3D printed PDLGA scaffolds incorporating bioglass or biosilica. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2021, 120, 111755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoda, A.; Borkiewicz, L.; Rivero-Müller, A.; Alam, P. Sintered nanoporous biosilica diatom frustules as high efficiency cell-growth and bone-mineralisation platforms. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Essien, E.R.; Adesalu, A.T.; Julius, M.L. Bioactive glass 45S5 from diatom biosilica. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Dev. 2017, 2, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, A.; FitzGerald, V.; Pignotti, E.; Knowles, J.C.; Sen, T.; Bruce, I.J. Preparation and characterisation of porous silica and silica/titania monoliths for potential use in bone replacement. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 156, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicco, S.R.; Vona, D.; De Giglio, E.; Cometa, S.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M.; Palumbo, F.; Ragni, R.; Farinola, G.M. Chemically Modified Diatoms Biosilica for Bone Cell Growth with Combined Drug-Delivery and Antioxidant Properties. Chempluschem 2015, 80, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicco, S.R.; Vona, D.; Leone, G.; De Giglio, E.; Bonifacio, M.A.; Cometa, S.; Fiore, S.; Palumbo, F.; Ragni, R.; Farinola, G.M. Functionalization of diatom biosilica with sodium alendronate as osteoactive material. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 104, 109897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburaci, S.; Kimna, C.; Tihminlioglu, F. Bioactive diatomite and POSS silica cage reinforced chitosan/Na-carboxymethyl cellulose polyelectrolyte scaffolds for hard tissue regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 100, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgic, A.D.; Atila, D.; Karatas, A.; Tezcaner, A.; Keskin, D. Diatom shell incorporated PHBV/PCL-pullulan co-electrospun scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 100, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburaci, S.; Tihminlioglu, F. Diatomite reinforced chitosan composite membrane as potential scaffold for guided bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 80, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburaci, S.; Tihminlioglu, F. Biosilica incorporated 3D porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 91, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.D.H.; Liaudanskaya, V.; Bonani, W.; Migliaresi, C.; Motta, A. Enhancing bioactive properties of silk fibroin with diatom particles for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gönenmis, D.E.; Özcan, Y. Preparation of Diatom-Doped Bio-Nanocomposite Materials for Bone Tissue Scaffolds. Mater. Res. 2022, 25, e20220234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Ren, W.J.; Hou, R.X.; Liu, H.F.; Li, R.; Du, S.J.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.Y. PEI-modified diatomite/chitosan composites as bone tissue engineering scaffold for sustained release of BMP-2. J. Biomater. Sci.-Polym. Ed. 2021, 32, 1337–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgic, A.D.; Atila, D.; Tezcaner, A.; Gürses, S.; Keskin, D. Diatom silica frustules-doped fibers for controlled release of melatonin for bone regeneration. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 186, 111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, W.X.; Wu, G.S.; Hu, Y.Z.; Li, S.H.; Gao, X.R.; Chen, X.G.; Ji, Q.X. Copper-deposited diatom-biosilica enhanced osteogenic potential in periodontal ligament stem cells and rat cranium. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2023, 111, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedelnikova, M.B.; Kashin, A.D.; Uvarkin, P.V.; Tolmachev, A.I.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Ugodchikova, A.V.; Luginin, N.A.; Bakina, O.V. Porous Biocoatings Based on Diatomite with Incorporated ZrO Particles for Biodegradable Magnesium Implants. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashin, A.D.; Sedelnikova, M.B.; Chebodaeva, V.V.; Uvarkin, P.V.; Luginin, N.A.; Dvilis, E.S.; Kazmina, O.V.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Khlusov, I.A.; Miller, A.A.; et al. Diatomite-based ceramic biocoating for magnesium implants. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 28059–28071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Liu, Q.B. Effects of Diatomite Contents on Microstructure, Microhardness, Bioactivity and Biocompatibility of Gradient Bioceramic Coating Prepared by Laser Cladding. Metals 2022, 12, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velnar, T.; Bailey, T.; Smrkoli, V. The Wound Healing Process: An Overview of the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 1528–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ren, Z.W.; Zhang, X.W.; Wei, D.X. Advances in modified hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels for skin wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 3393–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmady, A.R.; Razmjooee, K.; Saber-Samandari, S.; Toghraie, D. Fabrication of chitosan-gelatin films incorporated with thymol-loaded alginate microparticles for controlled drug delivery, antibacterial activity and wound healing: In-vitro and In-vivo studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.L.; Li, Y.S.; Yu, K.M.; Chen, Z.Y.; Shen, Y.; Zha, B.S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Q.Q.; Zhao, H. Effects of silver foam combined with Dermlin wound healing dressing on inflammation and quality of life in patients with diabetic lower limb ulcers. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, S.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Ghaee, A.; Soleimani, N. Carboxymethyl cellulose-human hair keratin hydrogel with controlled clindamycin release as antibacterial wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Gao, G.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, D.W. 3D Cell Printing of Perfusable Vascularized Human Skin Equivalent Composed of Epidermis, Dermis, and Hypodermis for Better Structural Recapitulation of Native Skin. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozan, H.E.; Wu, G.S.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Li, Q.F.; Sharaf, M.; Chen, X.G. The complex hydrogel based on diatom biosilica and hydroxybutyl chitosan for wound healing. Colloids Surface B 2022, 216, 112523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.J.; Li, J.; Shao, K.; Su, C.; Bi, S.C.; Mu, Y.Z.; Zhang, K.C.; Cao, Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, X.G.; et al. A composite sponge based on alkylated chitosan and diatom-biosilica for rapid hemostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Mu, Y.Z.; Qin, D.; Sun, X.J.; Su, C.; Chen, T.T.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, X.G.; Feng, C. Copper deposited diatom-biosilica with enhanced photothermal and photodynamic performance for infected wound therapy. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 2140–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Lee, H.; Han, G.; Kang, M.; Park, S.; Kim, D.E.; Lee, M.; Kim, M.J.; Na, Y.; Oh, S.; et al. 3D-Printed Functional Hydrogel by DNA-Induced Biomineralization for Accelerated Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintop, I.; Tatli, M.; Soyer, Z.; Yay, A.H.; Örtürk, A.; Karakükçü, Ç. A novel hemostatic scaffold material and the importance of scaffold formation on ending hemorrhage: An experimental rat study. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2020, 26, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.Z.; Fu, Y.M.; Li, J.; Shao, K.; Pang, J.H.; Su, C.; Cai, Y.B.; Sun, X.J.; Cong, X.; Chen, X.G.; et al. Thrombin immobilized polydopamine-diatom biosilica for effective hemorrhage control. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4952–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Jiang, C.Q.; Sun, X.J.; Cao, Z.; Mu, Y.Z.; Cong, X.; Qiu, K.J.; Lin, J.W.; Chen, X.G.; Feng, C. Diatomite hemostatic particles with hierarchical porous structure for rapid and effective hemostasis. Colloids Surface B 2022, 219, 112809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, X.J.; Zhang, K.C.; Yang, G.N.; Mu, Y.Z.; Su, C.; Pang, J.H.; Chen, T.T.; Chen, X.G.; Feng, C. Chitosan/Diatom-Biosilica Aerogel with Controlled Porous Structure for Rapid Hemostasis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 2000951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Pan, K.H.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B.H.; Wang, Y.A.; Feng, C.; Han, J.C. Influence of the physicochemical characteristics of diatom frustules on hemorrhage control. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, R.H.; Pan, K.H.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, R.B.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C.X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Enhancement of hemostatic properties of Cyclotella cryptica frustule through genetic manipulation. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.T.; Fang, Y.; Liang, X.Q.; Huang, C.S.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yu, J.P.; Wang, J.R.; Zhao, G.H. Yeast cell templated porous hollow silica spheres for rapid hemostasis accompanied by antibacterial action. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 3104–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ma, Z.F.; Guan, X.H.; Xiang, Z.H.; Ke, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xin, Z.R.; Shi, Q.; Yin, J.H. Facile fabrication of diatomite-based sponge with high biocompatibility and rapid hemostasis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.J.; Kong, X.W.; Wang, S.N.; Lu, J.L.; Liu, F.Y.; Lu, S.L.; Qi, H.Z.; Zhou, Q.H. Root-shaped antibacterial alginate sponges with enhanced hemostasis and osteogenesis for the prevention of dry socket. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.J.; Yao, G.Y.; Sun, Z.M.; Wang, B.; Yu, C.H.; Zheng, S.L. Fabrication of a novel antibacterial TPU nanofiber membrane containing Cu-loaded zeolite and its antibacterial activity toward Escherichia coli. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 11682–11693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cebral, R.; Peng, G.J.; Reys, L.L.; Silva, S.S.; Oliveira, J.M.; Chen, J.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Dual delivery of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs from chitosan/diatomaceous earth composite membranes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Seo, Y.; Kwon, D.; Kang, S.; Yu, J.; Park, H.; Lee, S.D.; Lee, T. Recent Progress in Diatom Biosilica: A Natural Nanoporous Silica Material as Sustained Release Carrier. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Sun, C.; Huang, Z.; Qjn, F.; Xu, H.L.; Shen, W. Fabrication of Functionalized Porous Silica Nanocapsules with a Hollow Structure for High Performance of Toluene Adsorption-Desorption. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5805–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terracciano, M.; Napolitano, M.; De Stefano, L.; De Luca, A.C.; Rea, I. Gold decorated porous biosilica nanodevices for advanced medicine. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 235601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Managò, S.; Migliaccio, N.; Terracciano, M.; Napolitano, M.; Martucci, N.M.; De Stefano, L.; Rendina, I.; De Luca, A.C.; Lamberti, A.; Rea, I. Internalization kinetics and cytoplasmic localization of functionalized diatomite nanoparticles in cancer cells by Raman imaging. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaharudin, N.S.; Isa, E.D.M.; Ahmad, H.; Rahman, M.B.A.; Jumbri, K. Functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles templated by pyridinium ionic liquid for hydrophilic and hydrophobic drug release application. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Bansal, K.K.; Verma, A.; Yadav, N.; Thakur, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Rosenholm, J.M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Emerging Colloidal Nano Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhas, N.; Parekh, K.; Pandey, A.; Kudarha, R.; Mutalik, S.; Mehta, T. Two dimensional carbon based nanocomposites as multimodal therapeutic and diagnostic platform: A biomedical and toxicological perspective. J. Control. Release 2019, 308, 130–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhali, S.; Jain, R.; Malik, A.; Sharma, S.; Raliya, R. Cultivation of Navicula sp. on rice straw hydrolysate for the production of biogenic silica. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Marella, T.K.; Singh, P.K.; Tiwari, A. Indoor mass cultivation of marine diatoms for biodiesel production using induction plasma synthesized nanosilica. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Véliz, D.S.; Alam, C.; Nietzel, T.; Wyborski, R.; Rivero-Müller, A.; Alam, P. Diatom-inspired skeletonisation of insulin—Mechanistic insights into crystallisation and extracellular bioactivity. Colloids Surface B 2015, 133, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, Z.G. Bio-inspired encapsulation and functionalization of living cells with artificial shells. Colloids Surface B 2014, 113, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamoorthy, P.; Anandhan, S.; Prabu, V.A. Natural nanoporous silica frustules from marine diatom as a biocarrier for drug delivery. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, M.S.; Simovic, S.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Losic, D. Silica microcapsules from diatoms as new carrier for delivery of therapeutics. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthappa, U.T.; Kigga, M.; Sriram, G.; Ajeya, K.V.; Jung, H.Y.; Neelgund, G.M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Facile green synthetic approach of bio inspired polydopamine coated diatoms as a drug vehicle for controlled drug release and active catalyst for dye degradation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 288, 109572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delasoie, J.; Rossier, J.; Haeni, L.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Zobi, F. Slow-targeted release of a ruthenium anticancer agent from vitamin B12 functionalized marine diatom microalgae. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 17221–17232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.N.; Lee, J.; Go, T.W.; Rajabi-Abhari, A.; Mahato, M.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Oh, I.K. Skin-attachable and biofriendly chitosan-diatom triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi-Abhari, A.; Lee, J.; Tabassian, R.; Kim, J.N.; Lee, H.; Oh, I.K. Antagonistically Functionalized Diatom Biosilica for Bio-Triboelectric Generators. Small 2022, 18, e2107638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi-Abhari, A.; Kim, J.N.; Lee, J.; Tabassian, R.; Mahato, M.; Youn, H.J.; Lee, H.; Oh, I.K. Diatom Bio-Silica and Cellulose Nanofibril for Bio-Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Breath Monitoring Masks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, M.; Fernández-Marín, R.; Robles, E.; Labidi, J.; Yilmaz, B.A.; Nefzi, H. Understanding the effects of copolymerized cellulose nanofibers and diatomite nanocomposite on blend chitosan films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyuz, L.; Kaya, M.; Koc, B.; Mujtaba, M.; Ilk, S.; Labidi, J.; Salaberria, A.M.; Cakmak, Y.S.; Yildiz, A. Diatomite as a novel composite ingredient for chitosan film with enhanced physicochemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javalkote, V.S.; Pandey, A.P.; Puranik, P.R.; Deshmukh, P.K. Magnetically responsive siliceous frustules for efficient chemotherapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 50, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, M.H.; Wu, Z.Y.; Chen, G.W.; Lee, C.C.; Lee, Z.H.; Yuan, W.T.; Lin, S.M.; Lin, H.M. Diatom-derived mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with fucoidan for enhanced chemo-photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Saxena, A.; Tyagi, R.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Tiwari, A. Biomass valorization of agriculture wastewater grown freshwater diatom Nitzschia sp. for metabolites, antibacterial activity, and biofertilizer. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 377, 128976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Huang, L.; Ji, P.Y.; Chen, C.P.; Li, X.S.; Gao, Y.H.; Liang, J.R. Using a mixture of wastewater and seawater as the growth medium for wastewater treatment and lipid production by the marine diatom. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, M.N.; Bi, Y.; Qiang, Y.; Xue, H.L.; Yang, L.; Feng, L.D.; Pu, L.M.; Long, H.T.; Prusky, D. Electrostatic adsorption and removal mechanism of ochratoxin A in wine via a positively charged nano-MgO microporous ceramic membrane. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marella, T.K.; Saxena, A.; Tiwari, A. Diatom mediated heavy metal remediation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123068. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffryes, C.; Agathos, S.N.; Rorrer, G. Biogenic nanomaterials from photosynthetic microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Mishra, B.; Tiwari, A. Mass cultivation of marine diatoms using local salts and its impact on growth and productivity. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 352, 127128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.N. Potential use of silica-rich biochar for the formulation of adaptively controlled release fertilizers: A mini review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Advantages | Limitations | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baking | High temperature (calcination) | Reduction in use of hazardous chemicals | Possible alteration of pore size and possible post-treatments with acid solutions | [42] |
| Oxidation | H2SO4 | High efficiency in organic matter removal | Hazardous chemical use, dissolution of thin frustules, and time-consuming post treatments | [43,44] |
| H2SO4 + PTFE filters | Reduction in amount of acid required | Unsuitable for thin frustules | [45] | |
| HNO3 | High efficiency in organic matter removal | High temperature treatments needed to increase efficiency | [44] | |
| Piranha solution (H2SO4 + H2O2) | High efficiency in organic matter removal | Time-consuming Post-treatments | [46] | |
| H2O2 | Less dangerous than use of strong acids | Long incubation, and high temperature post-treatments needed to increase efficiency | [36] | |
| HCl | High purity of frustules | Possible frustule erosion depending on acid strength | [47] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, K.H.; Kim, D.H.; Youn, S.; Pack, S.P. Biomimetic Diatom Biosilica and Its Potential for Biomedical Applications and Prospects: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042023
Min KH, Kim DH, Youn S, Pack SP. Biomimetic Diatom Biosilica and Its Potential for Biomedical Applications and Prospects: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(4):2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042023
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Ki Ha, Dong Hyun Kim, Sol Youn, and Seung Pil Pack. 2024. "Biomimetic Diatom Biosilica and Its Potential for Biomedical Applications and Prospects: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 4: 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042023
APA StyleMin, K. H., Kim, D. H., Youn, S., & Pack, S. P. (2024). Biomimetic Diatom Biosilica and Its Potential for Biomedical Applications and Prospects: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(4), 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042023






