Functional Involvement of Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription in the Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus
Abstract
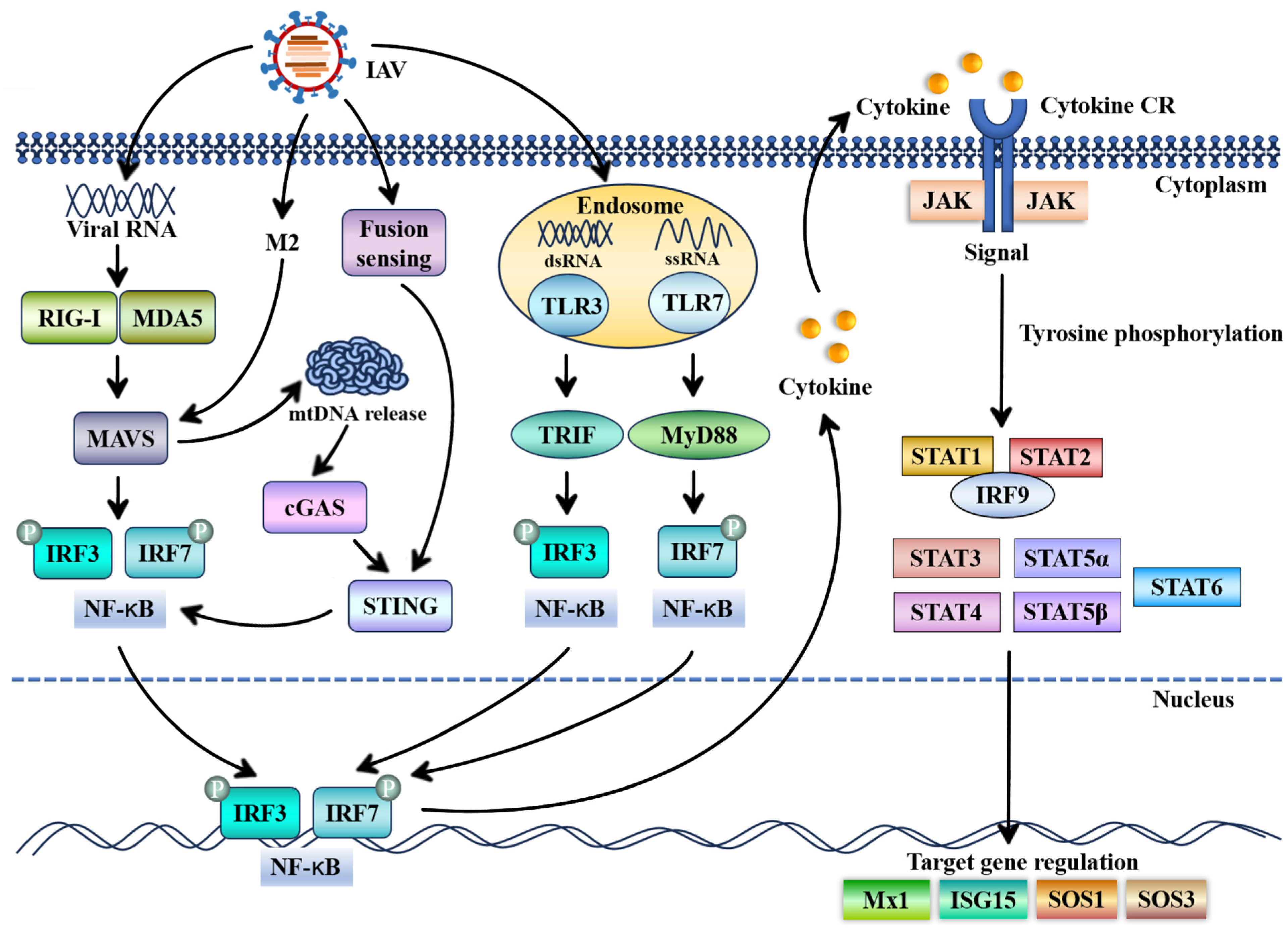
1. Introduction
2. The STAT Protein Family
2.1. Chromosomal Localization and Structure of STAT Proteins
2.2. STAT Proteins’ Induction in Different Bird Species
2.3. Biological Processes Involving STAT Proteins
3. Antiviral Roles of STAT Proteins and Their Underlying Mechanisms in Influenza A Virus Infection
3.1. Regulatory Roles of STAT1 and STAT2 During Influenza A Virus Infection
3.2. Functional Involvement of STAT3 in Regulation of Influenza A Virus Infection
3.3. Important Roles of STAT4 During Influenza A Virus Infection
3.4. Roles of STAT5 in Influenza A Virus Infection
3.5. Regulatory Roles of STAT6 Against Influenza A Virus Infection
| STATs | Effect on Influenza Virus | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAT1/STAT2 | Type I IFN inhibited IAV replication | STAT1 or STAT2 is phosphorylated during IAV infection and STAT1-STAT2 heterodimers are formed by modulation of type I IFN | [39,41,42] |
| ISGs inhibited IAV replication | STAT1 and STAT2 promote the expression of key ISGs | [43,44,49] | |
| STAT3 | Type I IFN inhibited IAV replication | STAT3 is upregulated in IAV-infected cells by modulation of type I IFN | [71,74] |
| ISGs inhibited IAV replication | Phosphorylated STAT3 promoted the production of early ISGs, such as MX1, OASL1, and OAS3 | [75] | |
| STAT4 | IFN-γ inhibited IAV replication | STAT4 triggers CD4Th cells to produce IFN-γ, leading to anti-influenza virus effects | [83,84] |
| STAT5 | Immune response inhibited IAV replication | STAT5 modulates immune response to IAV infection by transduction of IL-2 | [85,87] |
| STAT6 | Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines inhibited IAV replication | STAT6 is upregulated and exerts antiviral effects on inflammatory cytokines and chemokines | [95,98,99] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loh, C.Y.; Arya, A.; Naema, A.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Looi, C.Y. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STATs) Proteins in Cancer and Inflammation: Functions and Therapeutic Implication. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Bian, Q.; Rong, D.; Wang, L.; Song, J.; Huang, H.S.; Zeng, J.; Mei, J.; Wang, P.Y. JAK/STAT pathway: Extracellular signals, diseases, immunity, and therapeutic regimens. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1110765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Hu, X. Signaling by STATs. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xue, C.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J. LiL: Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Autoimmune disorders and cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayesh, M.E.H.; Kohara, M.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K. Recent Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of the Toll-like Receptor Response to Influenza Virus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, A.; Abdelwhab, E.M.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Pleschka, S. Zoonotic Potential of Influenza A Viruses: A Comprehensive Overview. Viruses 2018, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajao, D.S.; Vincent, A.L.; Perez, D.R. Adaptation of Human Influenza Viruses to Swine. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, F.; Xie, Z.; Li, M.; Xie, Z.; Luo, S.; Xie, L. Roles and functions of IAV proteins in host immune evasion. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1323560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F. Research progress on the nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) of influenza a virus. Virulence 2024, 15, 2359470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puigdevall, L.; Michiels, C.; Stewardson, C.; Dumoutier, L. JAK/STAT: Why choose a classical or an alternative pathway when you can have both? J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Cheon, H.; Kanno, Y.; Gadina, M.; Sartorelli, V.; Horvath, C.M.; Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Stark, G.R.; O’Shea, J.J. The JAK-STAT pathway at 30: Much learned, much more to do. Cell 2022, 185, 3857–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, K.L.; Brockwell, N.K.; Parker, B.S. JAK-STAT Signaling: A Double-Edged Sword of Immune Regulation and Cancer Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchipudi, S.V.; Tellabati, M.; Sebastian, S.; Londt, B.Z.; Jansen, C.; Vervelde, L.; Brookes, S.M.; Brown, I.H.; Dunham, S.P.; Chang, K.C. Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus infection in chickens but not ducks is associated with elevated host immune and pro-inflammatory responses. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, P.; Mishra, A.; Deka, R.P.; Pinto, S.M.; Subbannayya, Y.; Sood, R.; Prasad, T.S.K.; Raut, A.A. Proteomics Analysis of Duck Lung Tissues in Response to Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, H.; Wilhelmi, S.; Rajavel, A.; Boelhauve, M.; Wittmann, M.; Ramzan, F.; Schmitt, A.O.; Gültas, M. Comparative Investigation of Coincident Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Underlying Avian Influenza Viruses in Chickens and Ducks. Biology 2023, 12, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.L.; Manore, S.G.; Doheny, D.L.; Lo, H.W. STAT family of transcription factors in breast cancer: Pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 3, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomeo, M.; Cavalli, A.; Cascio, A. STAT1 and Its Crucial Role in the Control of Viral Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, C.E.; Deng, S.; Ong, M.S.; Yap, C.T. Involvement of STAT5 in Oncogenesis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, G.; Zhou, Y. Innate Immune Sensing of Influenza A Virus. Viruses 2020, 12, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, C.K.; Rahbek, S.H.; Gad, H.H.; Bak, R.O.; Jakobsen, M.R.; Jiang, Z.; Hansen, A.L.; Jensen, S.K.; Sun, C.; Thomsen, M.K.; et al. Influenza A virus targets a cGAS-independent STING pathway that controls enveloped RNA viruses. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, M.; Koshiba, T.; Ichinohe, T. Influenza A virus M2 protein triggers mitochondrial DNA-mediated antiviral immune responses. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.; Iwasaki, A. Type I and Type III Interferons—Induction, Signaling, Evasion, and Application to Combat COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, P.; Xu, X.; Deng, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ma, H.; Wei, D.; Sun, S. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, H.; Stark, G.R. Unphosphorylated STAT1 prolongs the expression of interferon-induced immune regulatory genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9373–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testoni, B.; Völlenkle, C.; Guerrieri, F.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S.; Blandino, G.; Levrero, M. Chromatin dynamics of gene activation and repression in response to interferon alpha (IFN(alpha)) reveal new roles for phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of the transcription factor STAT2. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20217–20227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, Y.; Okada, S. Inborn errors of STAT1 immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 72, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, I.; Fagard, R. STAT1 and pathogens, not a friendly relationship. Biochimie 2010, 92, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; An, H.J.; Cho, E.S.; Kang, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Cho, Y.Y. Stat2 stability regulation: An intersection between immunity and carcinogenesis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canar, J.; Darling, K.; Dadey, R.; Gamero, A.M. The duality of STAT2 mediated type I interferon signaling in the tumor microenvironment and chemoresistance. Cytokine 2023, 161, 156081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergholz, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Ramseier, M.; Prakadan, S.; Wang, W.; Fang, R.; Kabraji, S.; Zhou, Q.; Gray, G.K.; et al. PI3Kβ controls immune evasion in PTEN-deficient breast tumours. Nature 2023, 617, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, T.; Dai, W.; Qiu, N.; Xu, M.; Qiao, Y.; Ke, L.; Zhao, J.; et al. TMEM25 inhibits monomeric EGFR-mediated STAT3 activation in basal state to suppress triple-negative breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siersbæk, R.; Scabia, V.; Nagarajan, S.; Chernukhin, I.; Papachristou, E.K.; Broome, R.; Johnston, S.J.; Joosten, S.E.P.; Green, A.R.; Kumar, S.; et al. IL6/STAT3 Signaling Hijacks Estrogen Receptor α Enhancers to Drive Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 412–423.e419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lopez McDonald, M.C.; Kim, C.; Ma, M.; Pan, Z.T.; Kaufmann, C.; Frank, D.A. The complementary roles of STAT3 and STAT1 in cancer biology: Insights into tumor pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1265818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrpouya-Bahrami, P.; Moriarty, A.K.; De Melo, P.; Keeter, W.C.; Alakhras, N.S.; Nelson, A.S.; Hoover, M.; Barrios, M.S.; Nadler, J.L.; Serezani, C.H.; et al. STAT4 is expressed in neutrophils and promotes antimicrobial immunity. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e141326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Mai, H.; Peng, J.; Zhou, B.; Hou, J.; Jiang, D. STAT4: An immunoregulator contributing to diverse human diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Murphy, J.J. STAT5 in Cancer and Immunity. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.; Shin, H.Y. Genomic Mutations of the STAT5 Transcription Factor Are Associated with Human Cancer and Immune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. STAT6: Its role in interleukin 4-mediated biological functions. J. Mol. Med. 1997, 75, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo-Olarte, R.D.; Rivera-Rugeles, A.; Nava-Lira, E.; Sánchez-Barrera, Á.; Ledesma-Soto, Y.; Saavedra, R.; Armas-López, L.; Terrazas, L.I.; Ávila-Moreno, F.; Leon-Cabrera, S. STAT6 controls the stability and suppressive function of regulatory T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2250128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathiou, G.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Ferrand, E.; Dumollard, J.M.; Peoc’h, M. STAT6: A review of a signaling pathway implicated in various diseases with a special emphasis in its usefulness in pathology. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 223, 153477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escaffre, O.; Juelich, T.L.; Neef, N.; Massey, S.; Smith, J.; Brasel, T.; Smith, J.K.; Kalveram, B.; Zhang, L.; Perez, D.; et al. STAT-1 Knockout Mice as a Model for Wild-Type Sudan Virus (SUDV). Viruses 2021, 13, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, B.; Shen, C.; Zhang, T.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Shi, X.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; et al. MGF360-9L Is a Major Virulence Factor Associated with the African Swine Fever Virus by Antagonizing the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. mBio 2022, 13, e0233021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trammell, C.E.; Ramirez, G.; Sanchez-Vargas, I.; St Clair, L.A.; Ratnayake, O.C.; Luckhart, S.; Perera, R.; Goodman, A.G. Coupled small molecules target RNA interference and JAK/STAT signaling to reduce Zika virus infection in Aedes aegypti. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.D.; Young, H.A. IFN-γ: A cytokine at the right time, is in the right place. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 43, 101280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesev, E.V.; LeDesma, R.A.; Ploss, A. Decoding type I and III interferon signalling during viral infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.R.; Moseley, G.W. The Dynamic Interface of Viruses with STATs. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00856-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanunza, E.; Carletti, F.; Quartu, M.; Grandi, N.; Ermellino, L.; Milia, J.; Corona, A.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Ippolito, G.; Tramontano, E. Zika virus NS2A inhibits interferon signaling by degradation of STAT1 and STAT2. Virulence 2021, 12, 1580–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Deng, F.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Ning, Y.J. Heartland virus antagonizes type I and III interferon antiviral signaling by inhibiting phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT2 and STAT1. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 9503–9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; You, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pei, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, M.; Chen, J. Tick-borne encephalitis virus NS4A ubiquitination antagonizes type I interferon-stimulated STAT1/2 signalling pathway. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Qiao, C.; Miao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, H. Ubiquitination network in the type I IFN-induced antiviral signaling pathway. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2350384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Bao, L.; Li, F.; Liu, B.; Wu, X.; Hu, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. H1N1 influenza virus dose dependent induction of dysregulated innate immune responses and STAT1/3 activation are associated with pulmonary immunopathological damage. Virulence 2022, 13, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ling, Y.; Zhou, K.; Han, M.; Wang, X.; Yue, M.; Li, Y. Influenza A virus inhibits TET2 expression by endoribonuclease PA-X to attenuate type I interferon signaling and promote viral replication. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liao, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Rothman, P.B.; Gao, G.F.; et al. Critical role of Syk-dependent STAT1 activation in innate antiviral immunity. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Xiao, M.; Yang, B.; Rai, K.R.; Maarouf, M.; Guo, G.; Chen, J.L. Syk Facilitates Influenza A Virus Replication by Restraining Innate Immunity at the Late Stage of Viral Infection. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0020022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.R.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Maarouf, M.; Li, Y.; Xiao, M.; Liao, Y.; et al. Robust expression of p27Kip1 induced by viral infection is critical for antiviral innate immunity. Cell Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, B.; Xiao, M.; Li, Y.; Liao, Y.; Rai, K.R.; Zhao, Z.; Ouyang, J.; et al. RDUR, a lncRNA, Promotes Innate Antiviral Responses and Provides Feedback Control of NF-κB Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 672165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.R.; Liao, Y.; Cai, M.; Qiu, H.; Wen, F.; Peng, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Guo, G.; Chi, X.; et al. MIR155HG Plays a Bivalent Role in Regulating Innate Antiviral Immunity by Encoding Long Noncoding RNA-155 and microRNA-155-5p. mBio 2022, 13, e0251022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarouf, M.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Rai, K.R.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Xiao, M.; Chen, J.L. Identification of lncRNA-155 encoded by MIR155HG as a novel regulator of innate immunity against influenza A virus infection. Cell Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, C.M.; Dhume, K.; Prokop, E.; Strutt, T.M.; McKinstry, K.K. STAT1 Controls the Functionality of Influenza-Primed CD4 T Cells but Therapeutic STAT4 Engagement Maximizes Their Antiviral Impact. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinesco, N.J.; Srikanth, S.; De Vito, L.; Moras, C.; Ramasubramanian, V.; Chinnappan, B.; Hartwick, S.; Schwab, K.E.; Wu, Y.; Gopal, R. STAT1 regulates neutrophil gelatinase B-associated lipocalin induction in influenza-induced myocarditis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.J.; Lin, K.M.; Chen, S.J.; Ku, C.C.; Huang, C.W.; Huang, C.H.; Gale, M., Jr.; Tsai, C.H. Type I Interferon Orchestrates Demand-Adapted Monopoiesis during Influenza A Virus Infection via STAT1-Mediated Upregulation of Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor Expression. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0010223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Rai, K.R.; Zhou, W.; Wang, S.; Chi, X.; Guo, G.; Chen, J.L.; Liu, S. Initial activation of STAT2 induced by IAV infection is critical for innate antiviral immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 960544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, R.; Lee, B.; McHugh, K.J.; Rich, H.E.; Ramanan, K.; Mandalapu, S.; Clay, M.E.; Seger, P.J.; Enelow, R.I.; Manni, M.L.; et al. STAT2 Signaling Regulates Macrophage Phenotype During Influenza and Bacterial Super-Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucciol, G.; Moens, L.; Ogishi, M.; Rinchai, D.; Matuozzo, D.; Momenilandi, M.; Kerrouche, N.; Cale, C.M.; Treffeisen, E.R.; Al Salamah, M.; et al. Human inherited complete STAT2 deficiency underlies inflammatory viral diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, E.K.; Schmolke, M.; Wolff, T.; Viemann, D.; Roth, J.; Bode, J.G.; Ludwig, S. Influenza A virus inhibits type I IFN signaling via NF-kappaB-dependent induction of SOCS-3 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothlichet, J.; Chignard, M.; Si-Tahar, M. Cutting edge: Innate immune response triggered by influenza A virus is negatively regulated by SOCS1 and SOCS3 through a RIG-I/IFNAR1-dependent pathway. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2034–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, Q.; Xu, N.; Xie, Y.; Chen, S.; Qin, T.; Peng, D. Influenza a virus antagonizes type I and type II interferon responses via SOCS1-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of JAK1. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Dong, Y.; Bian, Y.; Xu, N.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Du, Y.; Qin, T.; Chen, S.; Peng, D.; et al. The influenza virus PB2 protein evades antiviral innate immunity by inhibiting JAK1/STAT signalling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.; Röpke, C. Suppressors of cytokine signalling: SOCS. Apmis 2002, 110, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Chi, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Gao, G.F.; Chen, J.L. Suppression of interferon lambda signaling by SOCS-1 results in their excessive production during influenza virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Chen, L.; Gu, S.; Ye, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, S. Inducible Guanylate-Binding Protein 7 Facilitates Influenza A Virus Replication by Suppressing Innate Immunity via NF-κB and JAK-STAT Signaling Pathways. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, F.; Zou, Z.; Bi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Shang, D.; Yan, Y.; Ju, X.; et al. Avian influenza viruses suppress innate immunity by inducing trans-transcriptional readthrough via SSU72. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczyk, K.; Nowicka, H.; Kostyrko, K.; Antonczyk, A.; Wesoly, J.; Bluyssen, H.A. The unique role of STAT2 in constitutive and IFN-induced transcription and antiviral responses. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2016, 29, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, N.; Melki, I.; Jing, H.; Habib, T.; Huang, S.S.Y.; Danielson, J.; Kula, T.; Drutman, S.; Belkaya, S.; Rattina, V.; et al. Life-threatening influenza pneumonitis in a child with inherited IRF9 deficiency. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2567–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnking, K.; Klemm, C.; Löffler, B.; Niemann, S.; van Krüchten, A.; Peters, G.; Ludwig, S.; Ehrhardt, C. Super-infection with Staphylococcus aureus inhibits influenza virus-induced type I IFN signalling through impaired STAT1-STAT2 dimerization. Cell Microbiol. 2015, 17, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Song, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Gao, Q.; Xu, Q.; et al. Single-Cell Sequencing of Peripheral Mononuclear Cells Reveals Distinct Immune Response Landscapes of COVID-19 and Influenza Patients. Immunity 2020, 53, 685–696.e683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca Suarez, A.A.; Van Renne, N.; Baumert, T.F.; Lupberger, J. Viral manipulation of STAT3: Evade, exploit, and injure. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namkoong, H.; Ishii, M.; Fujii, H.; Yagi, K.; Asami, T.; Asakura, T.; Suzuki, S.; Hegab, A.E.; Kamata, H.; Tasaka, S.; et al. Clarithromycin expands CD11b+Gr-1+ cells via the STAT3/Bv8 axis to ameliorate lethal endotoxic shock and post-influenza bacterial pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahony, R.; Gargan, S.; Roberts, K.L.; Bourke, N.; Keating, S.E.; Bowie, A.G.; O’Farrelly, C.; Stevenson, N.J. A novel anti-viral role for STAT3 in IFN-α signalling responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, M.; Gu, R.; Hong, J.; Yang, Z.; Chi, X.; Guo, G.; et al. STAT3 regulates antiviral immunity by suppressing excessive interferon signaling. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yan, R.; Chen, B.; Pan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.L. Influenza Virus-Induced Robust Expression of SOCS3 Contributes to Excessive Production of IL-6. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chong, H.C.; Ng, S.Y.; Kwok, K.W.; Teo, Z.; Tan, E.H.P.; Choo, C.C.; Seet, J.E.; Choi, H.W.; Buist, M.L.; et al. Angiopoietin-like 4 Increases Pulmonary Tissue Leakiness and Damage during Influenza Pneumonia. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalem, M.; Dabous, E.; Awad, A.M.; Alalem, N.; Guirgis, A.A.; El-Masry, S.; Khalil, H. Influenza a virus regulates interferon signaling and its associated genes; MxA and STAT3 by cellular miR-141 to ensure viral replication. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. MicroRNA-4485 ameliorates severe influenza pneumonia via inhibition of the STAT3/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othumpangat, S.; Beezhold, D.H.; Umbright, C.M.; Noti, J.D. Influenza Virus-Induced Novel miRNAs Regulate the STAT Pathway. Viruses 2021, 13, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzelli, A.A.; McWilliams, I.L.; Shin, B.; Bryars, M.T.; Harrington, L.E. Intrinsic STAT4 Expression Controls Effector CD4 T Cell Migration and Th17 Pathogenicity. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Gu, J.; Wang, R.; Lee, S.; Shan, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, X. TIGIT reverses IFN-α-promoted Th1-like Tregs via in-sequence effects dependent on STAT4. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Nakayamada, S.; Kubo, S.; Sakata, K.; Yamagata, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Kitanaga, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tanaka, Y. Expansion of T follicular helper-T helper 1 like cells through epigenetic regulation by signal transducer and activator of transcription factors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, A.; Rodrigo, E.; Wolfe, T.; Bot, S.; Von Herrath, M.G. Infection-triggered regulatory mechanisms override the role of STAT 4 in control of the immune response to influenza virus antigens. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5794–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Scott, J.M.; Kakarla, T.; Duriancik, D.M.; Choi, S.; Cho, C.; Lee, T.; Park, H.; French, A.R.; Beli, E.; et al. Activation mechanisms of natural killer cells during influenza virus infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury, M.; Vazquez-Mateo, C.; Hernandez-Escalante, J.; Dooms, H. Partial STAT5 signaling is sufficient for CD4(+) T cell priming but not memory formation. Cytokine 2022, 150, 155770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarino, A.V.; Laurence, A.D.; Davis, F.P.; Nivelo, L.; Brooks, S.R.; Sun, H.W.; Jiang, K.; Afzali, B.; Frasca, D.; Hennighausen, L.; et al. A central role for STAT5 in the transcriptional programing of T helper cell metabolism. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabl9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuazon, J.A.; Read, K.A.; Sreekumar, B.K.; Roettger, J.E.; Yaeger, M.J.; Varikuti, S.; Pokhrel, S.; Jones, D.M.; Warren, R.T.; Powell, M.D.; et al. Eos Promotes TH2 Differentiation by Interacting with and Propagating the Activity of STAT5. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahil, Z.; Leylek, R.; Schürch, C.M.; Chen, H.; Bjornson-Hooper, Z.; Christensen, S.R.; Gherardini, P.F.; Bhate, S.S.; Spitzer, M.H.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; et al. Landscape of coordinated immune responses to H1N1 challenge in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5800–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlwain, D.R.; Chen, H.; Rahil, Z.; Bidoki, N.H.; Jiang, S.; Bjornson, Z.; Kolhatkar, N.S.; Martinez, C.J.; Gaudillière, B.; Hedou, J.; et al. Human influenza virus challenge identifies cellular correlates of protection for oral vaccination. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1828–1837.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Abe, J.I.; Chau, K.M.; Wang, Y.; Vu, H.T.; Reddy Velatooru, L.; Gulraiz, F.; Imanishi, M.; Samanthapudi, V.S.K.; Nguyen, M.T.H.; et al. MAGI1 inhibits interferon signaling to promote influenza A infection. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 791143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Zha, B. The roles of STAT6 in regulating B cell fate, activation, and function. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 233, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.C.; Jackson, D.J.; Maltby, S.; Walton, R.P.; Ching, Y.M.; Glanville, N.; Singanayagam, A.; Brewins, J.J.; Clarke, D.; Hirsman, A.G.; et al. Rhinovirus-induced CCL17 and CCL22 in Asthma Exacerbations and Differential Regulation by STAT6. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STAT6 Gain-of-Function International Consortium. Human germline gain-of-function in STAT6: From severe allergic disease to lymphoma and beyond. Trends Immunol. 2024, 45, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.W.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhao, C.Q.; Xue, S.J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.Z.; Xu, J.F.; Su, X. Vagal-α7nAChR signaling is required for lung anti-inflammatory responses and arginase 1 expression during an influenza infection. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Sun, L. Cyclosporine A Regulates Influenza A Virus-induced Macrophages Polarization and Inflammatory Responses by Targeting Cyclophilin A. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 861292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, A.; Antão, A.V.; Dietschmann, A.; Radtke, D.; Tenbusch, M.; Voehringer, D. STAT6-induced production of mucus and resistin-like molecules in lung Club cells does not protect against helminth or influenza A virus infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2024, 54, e2350558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeler, S.P.; Agapov, E.V.; Hinojosa, M.E.; Letvin, A.N.; Wu, K.; Holtzman, M.J. Influenza A Virus Infection Causes Chronic Lung Disease Linked to Sites of Active Viral RNA Remnants. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2354–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, A.C.; Hilmer, K.M.; Zickovich, J.M.; Obar, J.J. Inflammatory response of mast cells during influenza A virus infection is mediated by active infection and RIG-I signaling. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4676–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, N.; Maisner, A. Nipah Virus Impairs Autocrine IFN Signaling by Sequestering STAT1 and STAT2 into Inclusion Bodies. Viruses 2023, 15, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yi, Z. NS5-independent Ablation of STAT2 by Zika virus to antagonize interferon signalling. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Qiu, F.; Gu, R.; Xu, E. Functional Involvement of Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription in the Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413589
Liu S, Qiu F, Gu R, Xu E. Functional Involvement of Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription in the Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413589
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shasha, Feng Qiu, Rongrong Gu, and Erying Xu. 2024. "Functional Involvement of Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription in the Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413589
APA StyleLiu, S., Qiu, F., Gu, R., & Xu, E. (2024). Functional Involvement of Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription in the Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413589




