Comparative Analysis of the Effects of Maternal Hypoxia and Placental Ischemia on HIF1-Dependent Metabolism and the Glucocorticoid System in the Embryonic and Newborn Rat Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
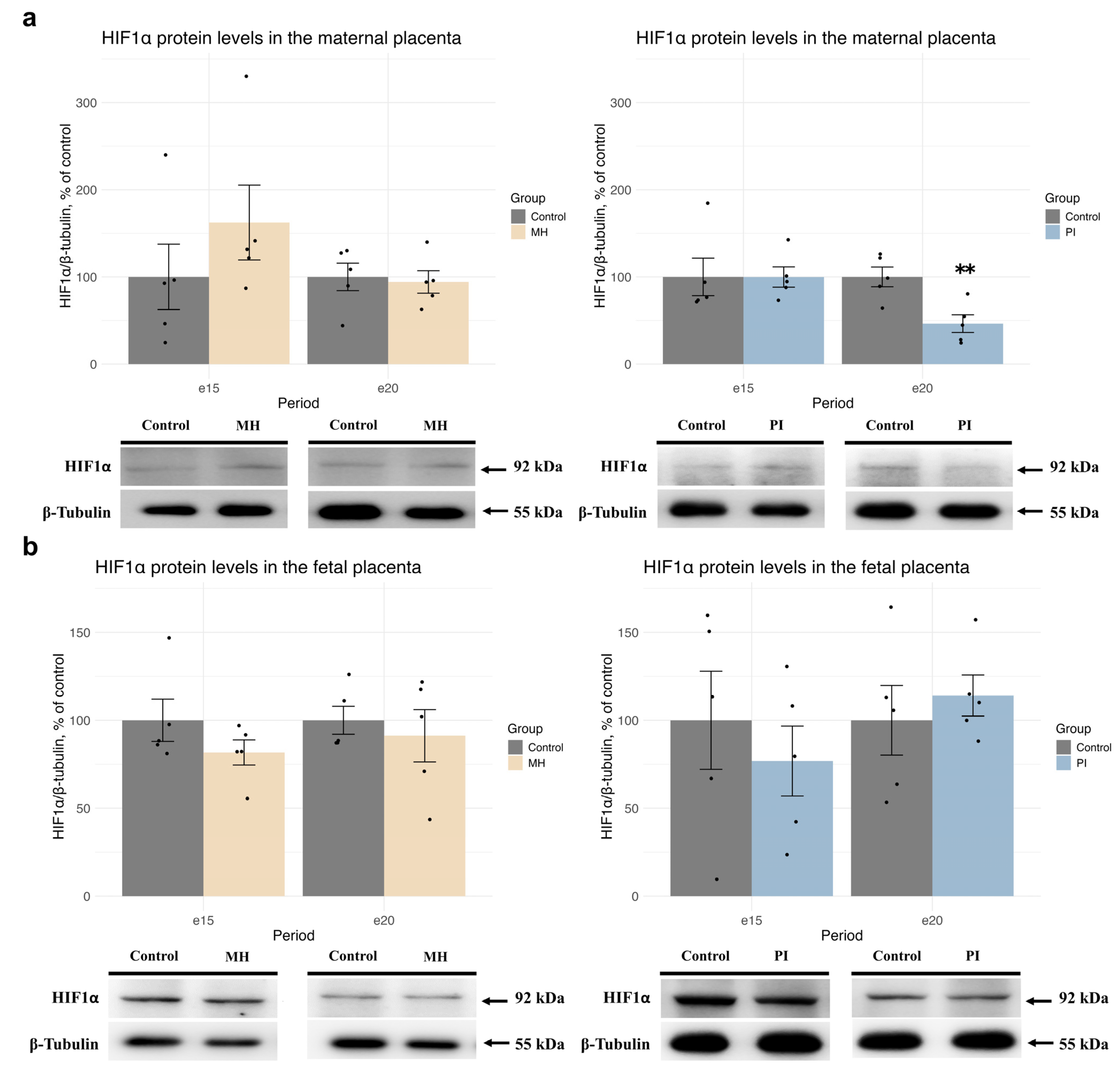
2.1. Expression of HIF1α and Glucocorticoid Receptors, Glucocorticoid-Dependent Transcription, and Corticosterone Metabolism in Maternal and Fetal Placenta During MH or PI
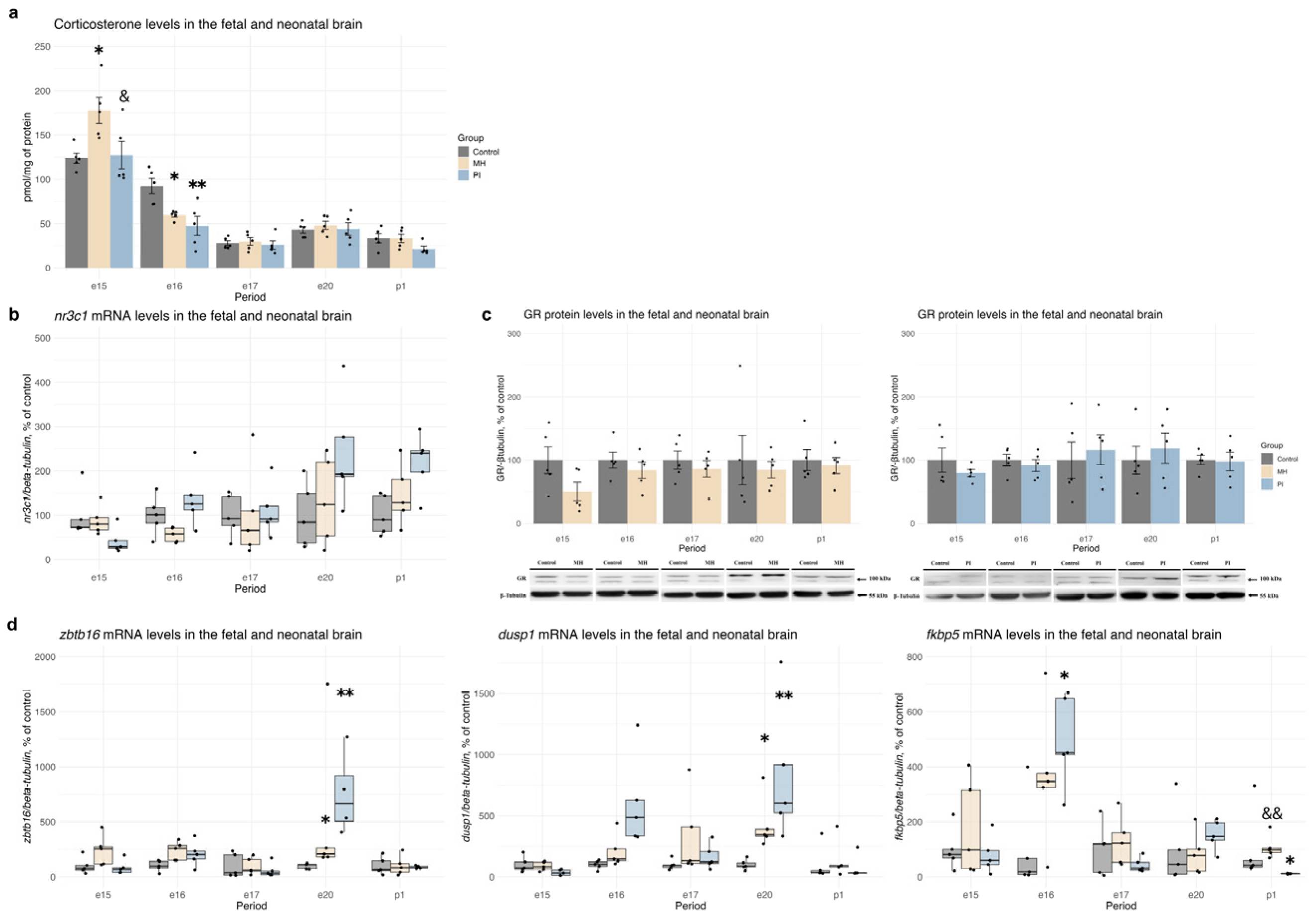
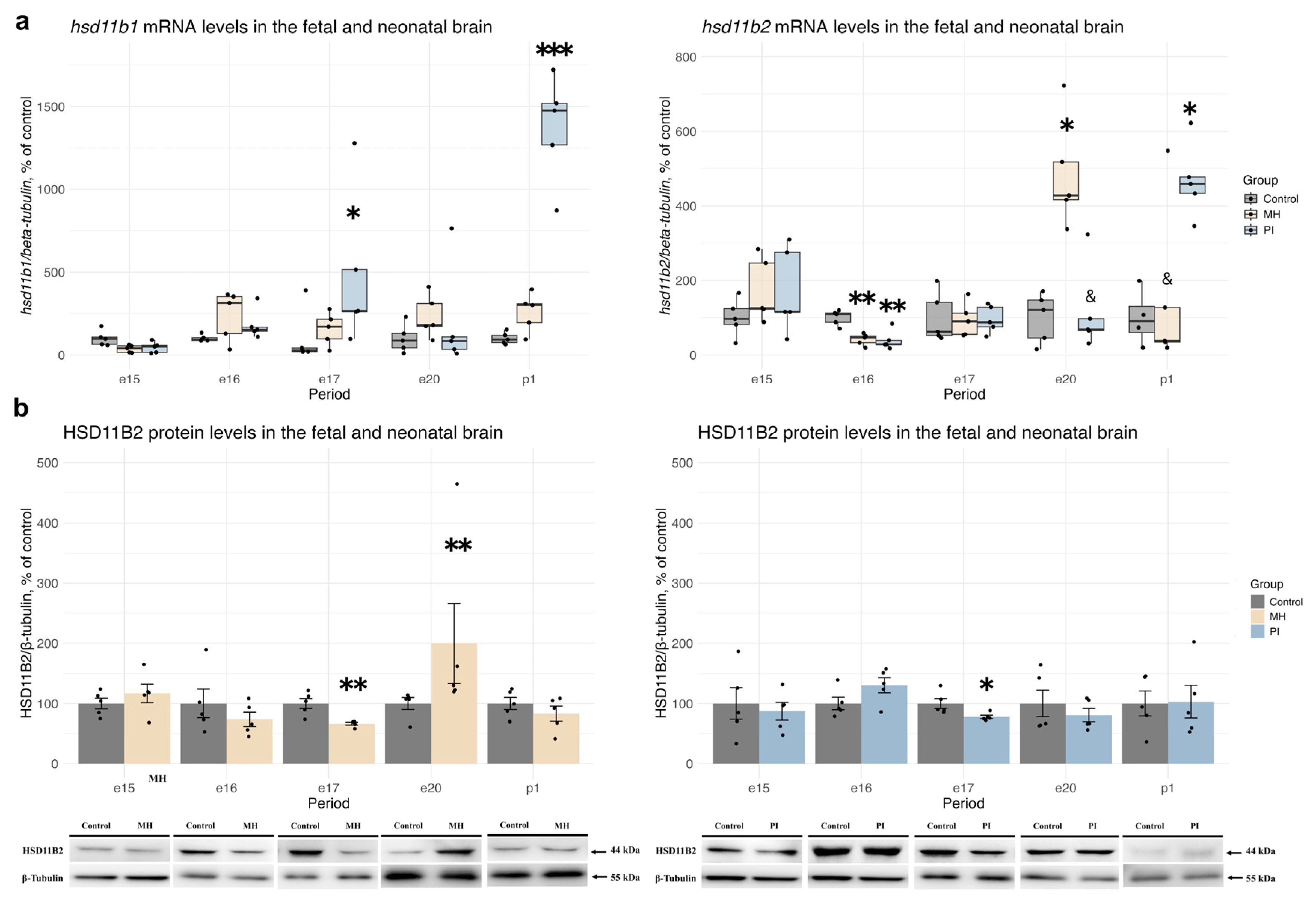
2.2. Activity of the Glucocorticoid System in Brain Development During MH or PI
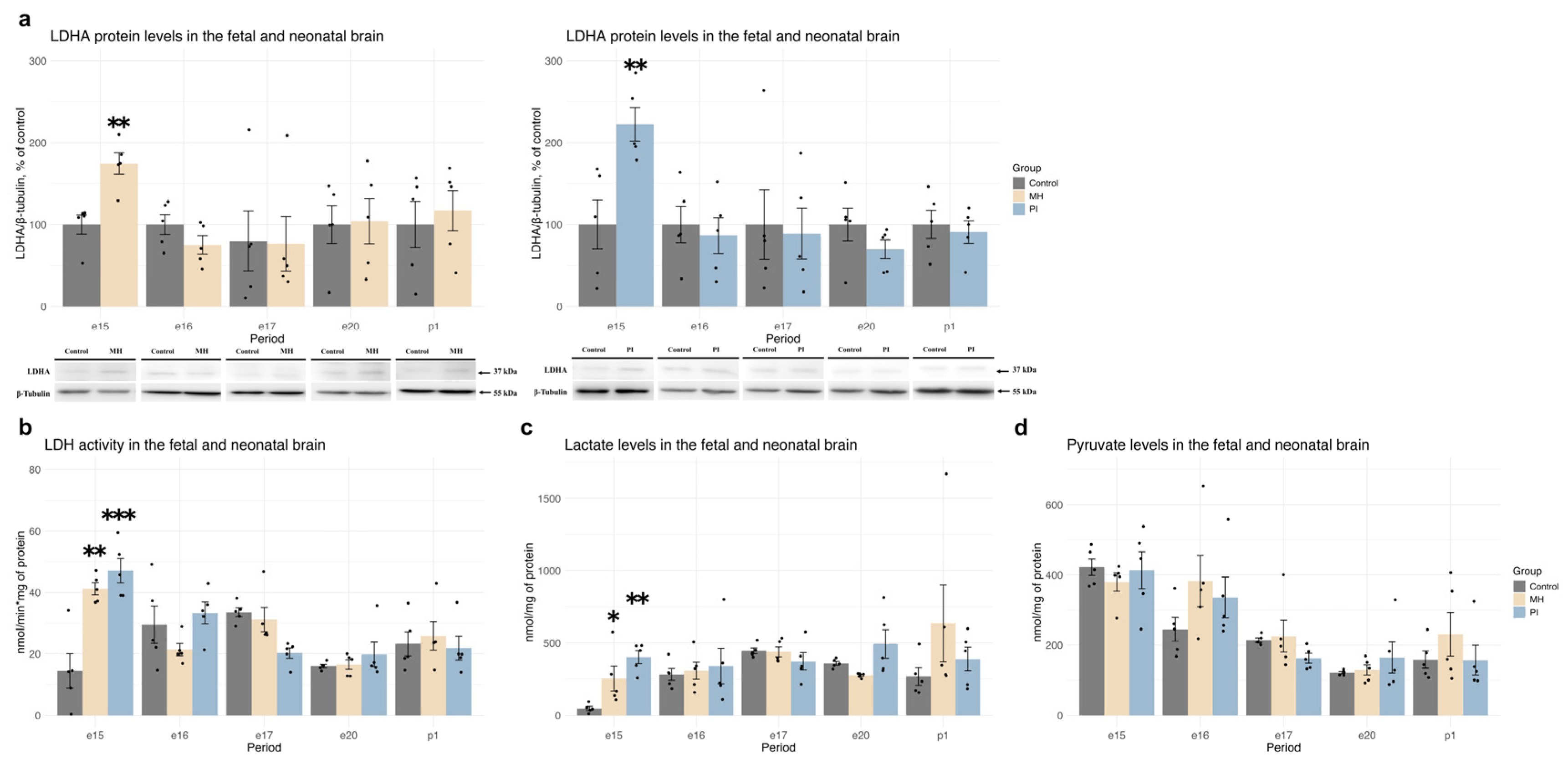
2.3. Expression of HIF1α, HIF1-Dependent Transcription, and Anaerobic Glycolysis Activity in Brain Development During MH or PI
2.4. Activity of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Redox State in Brain Development During MH or PI
3. Discussion
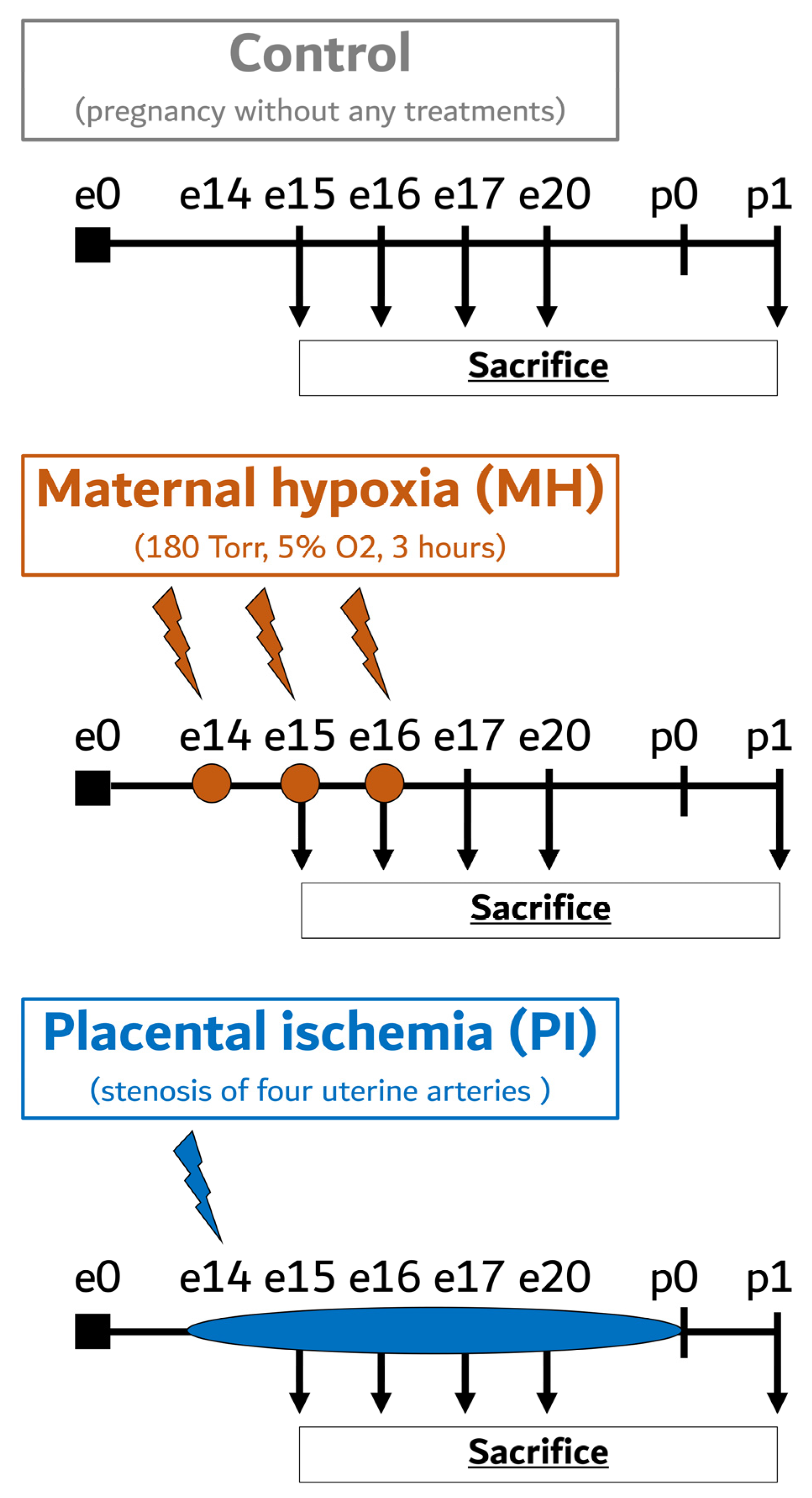
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Maternal Hypoxia
4.3. Placental Ischemia
4.4. Sample Preparation
4.5. ELISA Analysis of Corticosterone Levels
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Quantitative RT PCR
4.8. Measurement of Lactate Dehydrogenase Activity
4.9. Measurement of Lactate Levels
4.10. Measurement of Pyruvate Levels
4.11. Measurement of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Activity
4.12. Measurement of NADPH Levels
4.13. Measurement of Reduced Glutathione Levels
4.14. Measurement of Malonic Dialdehyde Levels
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Semenza, G.L. Oxygen sensing, homeostasis, and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, M. Effects of Prenatal Hypoxia on Nervous System Development and Related Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 755554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucci, S.J.; Hagberg, H. Hypoxia-ischemia in the immature brain. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 3149–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Oxygen sensing, hypoxia-inducible factors, and disease pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinand, P.; Roffe, C. Hypoxia after stroke: A review of experimental and clinical evidence. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2016, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.S.; Chiu, W.T.; Hsu, P.L.; Lin, S.C.; Peng, I.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Tsai, S.J. Pathophysiological implications of hypoxia in human diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, H.; Huleihel, M. The effect of prenatal hypoxia on brain development: Short- and long-term consequences demonstrated in rodent models. Dev. Sci. 2006, 9, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.R.; Bale, T.L.; Epperson, C.N. Prenatal programming of mental illness: Current understanding of relationship and mechanisms. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2015, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensch, T.K. Critical period regulation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 27, 549–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A. Living with the past: Evolution, development, and patterns of disease. Science 2004, 305, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratilov, V.A.; Vetrovoy, O.V.; Tyulkova, E.I. Prenatal Hypoxia Affects Nicotine Consumption and Withdrawal in Adult Rats via Impairment of the Glutamate System in the Brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 4550–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.; Reichenberg, A.; Kolevzon, A. Prenatal and perinatal metabolic risk factors for autism: A review and integration of findings from population-based studies. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalivaeva, N.N.; Turner, A.J.; Zhuravin, I.A. Role of Prenatal Hypoxia in Brain Development, Cognitive Functions, and Neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzeszczak, K.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Malinowski, W.; Ziętek, P.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. Oxidative Stress in Pregnancy. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piešová, M.; Mach, M. Impact of perinatal hypoxia on the developing brain. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüsken, E.; Appel, S.; Saschin, L.; Kuiper-Makris, C.; Oberholz, L.; Schömig, C.; Tauscher, A.; Dötsch, J.; Kribs, A.; Alejandre Alcazar, M.A.; et al. Intrauterine Growth Restriction: Need to Improve Diagnostic Accuracy and Evidence for a Key Role of Oxidative Stress in Neonatal and Long-Term Sequelae. Cells 2024, 13, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rodriguez, P.J.; Xiong, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Fetal hypoxia increases vulnerability of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats: Role of glucocorticoid receptors. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 65, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda, A.B.; Pessoa, A.J.r.; Castillo, R.L.; Figueroa, C.A.; Pulgar, V.M.; Farías, J.G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the hypoxic tissue: Role of HIF-1 and ROS. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2013, 31, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, I.A.; Hewitson, T.D. Hypoxia in tissue repair and fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, L. Epigenetic mechanisms in developmental programming of adult disease. Drug. Discov. Today 2011, 16, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Coq, J.O.; Ogawa, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ohshima, M. A Rat Model of Mild Intrauterine Hypoperfusion with Microcoil Stenosis. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, e56723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrovoy, O.; Tyulkova, E.; Stratilov, V.; Baranova, K.; Nimiritsky, P.; Makarevich, P.; Rybnikova, E. Long-Term Effects of Prenatal Severe Hypoxia on Central and Peripheral Components of the Glucocorticoid System in Rats. Dev. Neurosci. 2020, 42, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrovoy, O.; Stratilov, V.; Nimiritsky, P.; Makarevich, P.; Tyulkova, E. Prenatal Hypoxia Induces Premature Aging Accompanied by Impaired Function of the Glutamatergic System in Rat Hippocampus. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, A.; Arloth, J.; Pütz, B.; Weber, P.; Klengel, T.; Mehta, D.; Gonik, M.; Rex-Haffner, M.; Rubel, J.; Uhr, M.; et al. Dexamethasone stimulated gene expression in peripheral blood is a sensitive marker for glucocorticoid receptor resistance in depressed patients. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benediktsson, R.; Calder, A.A.; Edwards, C.R.; Seckl, J.R. Placental 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: A key regulator of fetal glucocorticoid exposure. Clin. Endocrinol. 1997, 46, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J. The developmental origins of adult disease. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 588S–595S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolini, E.; Fowden, A.; Coan, P.; Sandovici, I.; Smith, P.; Dean, W.; Burton, G.; Tycko, B.; Reik, W.; Sibley, C.; et al. Regulation of placental efficiency for nutrient transport by imprinted genes. Placenta 2006, 27, S98–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, D.Q.; Manning, S.E.; Hillier, A.; Anderson, S.L.; Nordgren, R.E.; Walters, S.E.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Cooley, W.C.; Gaelic, S.E.; Bauman, M.L. Timing of prenatal stressors and autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2005, 35, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattani, M.T.; Hindmarch, P.C.; Fisher, D.A. Endocrinology of fetal development. Williams Textb. Endocrinol. 1998, 834–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busada, J.T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid Action During Development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 125, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odaka, H.; Adachi, N.; Numakawa, T. Impact of glucocorticoid on neurogenesis. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurinczuk, J.J.; White-Koning, M.; Badawi, N. Epidemiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, A.; Cui, X.; Luan, W.; Ali, A.A.; Pertile, R.A.; Alexander, S.A.; Eyles, D.W. Prenatal hypoxia alters the early ontogeny of dopamine neurons. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camm, E.J.; Cross, C.M.; Kane, A.D.; Tarry-Adkins, J.L.; Ozanne, S.E.; Giussani, D.A. Maternal antioxidant treatment protects adult offspring against memory loss and hippocampal atrophy in a rodent model of developmental hypoxia. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Grauw, T.J.; Myers, R.E.; Scott, W.J. Fetal growth retardation in rats from different levels of hypoxia. Neonatology 1986, 49, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckl, J.R.; Holmes, M.C. Mechanisms of disease: Glucocorticoids, their placental metabolism and fetal ‘programming’ of adult pathophysiology. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 3, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierans, S.J.; Taylor, C.T. Regulation of glycolysis by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF): Implications for cellular physiology. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrovoy, O.; Stratilov, V.; Potapova, S.; Tyulkova, E. Oxidative stress accompanies HIF1-dependent impairment of glucose metabolism in the hippocampus of adult rats survived prenatal severe hypoxia. Dev. Neurosci. 2023, 46, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrovoy, O.; Sarieva, K.; Lomert, E.; Nimiritsky, P.; Eschenko, N.; Galkina, O.; Lyanguzov, A.; Tyulkova, E.; Rybnikova, E. Pharmacological HIF1 Inhibition Eliminates Downregulation of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Prevents Neuronal Apoptosis in Rat Hippocampus Caused by Severe Hypoxia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrovoy, O.V.; Nimiritsky, P.P.; Tyulkova, E.I.; Rybnikova, E.A. Transcription factor HIF1 negatively regulates the content of glucose-6phosphate dehydrogenase in HEK293T cells. Cell Tissue Biol. 2021, 15, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratilov, V.; Potapova, S.; Safarova, D.; Tyulkova, E.; Vetrovoy, O. Prenatal Hypoxia Triggers a Glucocorticoid-Associated Depressive-like Phenotype in Adult Rats, Accompanied by Reduced Anxiety in Response to Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrovoy, O.; Stratilov, V.; Lomert, E.; Tyulkova, E. Prenatal Hypoxia-Induced Adverse Reaction to Mild Stress is Associated with Depressive-Like Changes in the Glucocorticoid System of Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 48, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderhaeghen, T.; Timmermans, S.; Watts, D.; Paakinaho, V.; Eggermont, M.; Vandewalle, J.; Wallaeys, C.; Van Wyngene, L.; Van Looveren, K.; Nuyttens, L.; et al. Reprogramming of glucocorticoid receptor function by hypoxia. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e53083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettori, A.; Greenald, D.; Wilson, G.K.; Peron, M.; Facchinello, N.; Markham, E.; Sinnakaruppan, M.; Matthews, L.C.; McKeating, J.A.; Argenton, F.; et al. Glucocorticoids promote Von Hippel Lindau degradation and HIF-1α stabilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9948–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, D.; Santhakumar, K.; Markham, E.; Li, N.; Storbeck, K.H.; Krone, N.; Cunliffe, V.T.; van Eeden, F.J. Bidirectional crosstalk between Hypoxia-Inducible Factor and glucocorticoid signalling in zebrafish larvae. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhaeghen, T.; Beyaert, R.; Libert, C. Bidirectional Crosstalk Between Hypoxia Inducible Factors and Glucocorticoid Signalling in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 684085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, S.; Calcaterra, V.; Pelizzo, G.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Prenatal Hypoxia and Placental Oxidative Stress: Insights from Animal Models to Clinical Evidences. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, L. Epigenetic Programming of Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy in Response to Fetal Hypoxia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 124, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaney, M.J.; Szyf, M. Maternal Care as a Model for Experience-Dependent Chromatin Plasticity? Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Lei, J.; Xu, T.; Zhao, M.; Cai, H.; Qiu, J.; Gao, Q. Effects of Prenatal Hypoxia on Placental Glucocorticoid Barrier: Mechanistic Insight from Experiments in Rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2022, 110, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratilov, V.; Vetrovoy, O.; Potapova, S.; Tyulkova, E. The Prenatal Hypoxic Pathology Associated with Maternal Stress Predisposes to Dysregulated Expression of the chrna7 Gene and the Subsequent Development of Nicotine Addiction in Adult Offspring. Neuroendocrinology 2024, 114, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybnikova, E.; Nalivaeva, N. Glucocorticoid-Dependent Mechanisms of Brain Tolerance to Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Tsiarli, M.; Rudine, A.; Kendall, N.; O Pratt, M.; Krall, R.; Thiels, E.; DeFranco, D.B.; Monaghan, A.P. Antenatal Dexamethasone Exposure Differentially Affects Distinct Cortical Neural Progenitor Cells and Triggers Long-Term Changes in Murine Cerebral Architecture and Behavior. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abul, M.; Al-Bader, M.D.; Mouihate, A. Prenatal Activation of Glucocorticoid Receptors Induces Memory Impairment in a Sex-Dependent Manner: Role of Cyclooxygenase-2. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 3767–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enayati, M.; Mosaferi, B.; Homberg, J.R.; Mendes Diniz, D.; Salari, A.-A. Prenatal Maternal Stress Alters Depression-Related Symptoms in a Strain- and Sex-Dependent Manner in Rodent Offspring. Life Sci. 2020, 251, 117597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, M.; Coq, J.-O.; Otani, K.; Hattori, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Sato, Y.; Harada-Shiba, M.; Ihara, M.; Tsuji, M. Mild Intrauterine Hypoperfusion Reproduces Neurodevelopmental Disorders Observed in Prematurity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, J.P.; Alexander, B.T.; Llinas, M.T.; Bennett, W.A.; Khalil, R.A. Pathophysiology of preeclampsia: Linking placental ischemia/hypoxia with microvascular dysfunction. Microcirculation 2002, 9, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMarca, B.; Amaral, L.M.; Harmon, A.C.; Cornelius, D.C.; Faulkner, J.L.; Cunningham, M.W., Jr. Placental Ischemia and Resultant Phenotype in Animal Models of Preeclampsia. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2016, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckl, J. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and the brain: Not (yet) lost in translation. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 295, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyakanchuk, A.A.; Balázs, Z.; Nashev, L.G.; Amrein, K.E.; Odermatt, A. 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 reductase activity is dependent on a high ratio of NADPH/NADP+ and is stimulated by extracellular glucose. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 301, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, S.; Almeida, A.; Bolaños, J.P. Antioxidant and bioenergetic coupling between neurons and astrocytes. Biochem. J. 2012, 443, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, E.A.; Stewart, P.M. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: Unexpected connections. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 14, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas, L.E.; Carnero, A. NAD+ metabolism, stemness, the immune response, and cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS. Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene | Primers Sequences (5′–3′) | Annealing T (°C) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| beta-tubulin | Forward TAGAGGAGATGCTACTTA Reverse AATGGTGATAATACTGTTAA | 58 | 147 |
| dusp1 | Forward ACCAGTATTAACCATTCC Reverse TTCGTTCTTCTATGAGTAG | 57 | 115 |
| fkbp5 | Forward ATCTGCCACTTATTATGTAA Reverse AGTCAAGGAGTTCAATCT | 57 | 106 |
| g6pd | Forward AAGATGATGACCAAGAAG Reverse TTGTATCTGTTGCCATAG | 56 | 80 |
| glut1 | Forward AATATGTGGAGCAACTGT Reverse TAGGTGAAGATGAAGAAGAG | 56 | 79 |
| nr3c1 | Forward ATCATACAGACAATCAAG Reverse TACTCTTCATAGGATACC | 58 | 156 |
| hk1 | Forward CTGGACTGTGGAATCTTG Reverse AGTAAGGAGGCTACATCAT | 56 | 80 |
| hif1α | Forward CCATTCCTCATCCATCAA Reverse CCATCAACTCAGTAATCCT | 56 | 114 |
| hsd11b1 | Forward CCTCTGATTGCTTCCTAC Reverse TTGGTCATCAAGTGTTCT | 57 | 83 |
| hsd11b2 | Forward CCTATGGTGAAGACTACA Reverse AATGATGGCATCTACAAC | 57 | 98 |
| ldha | Forward CGAGAGCATAATGAAGAAC Reverse TCCTTGATTCCATAGAGAC | 56 | 75 |
| mct4 | Forward CCTATATTGCCAATCCTCCAT Reverse TGTCTATCTCTGCCTTCTCA | 57 | 75 |
| pdk1 | Forward TACTCAACCAGCACTCTT Reverse GCATTCTCATAGCCATCTT | 57 | 121 |
| pfkb3 | Forward ATCTATGAGTGAGTGTCT Reverse ATGGTAATAGTGAGTATGC | 56 | 84 |
| zbtb16 | Forward GATGAAGACATACGGATG Reverse TGAATGAGCCAGTAAATG | 57 | 82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vetrovoy, O.; Potapova, S.; Stratilov, V.; Tyulkova, E. Comparative Analysis of the Effects of Maternal Hypoxia and Placental Ischemia on HIF1-Dependent Metabolism and the Glucocorticoid System in the Embryonic and Newborn Rat Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413342
Vetrovoy O, Potapova S, Stratilov V, Tyulkova E. Comparative Analysis of the Effects of Maternal Hypoxia and Placental Ischemia on HIF1-Dependent Metabolism and the Glucocorticoid System in the Embryonic and Newborn Rat Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413342
Chicago/Turabian StyleVetrovoy, Oleg, Sofiya Potapova, Viktor Stratilov, and Ekaterina Tyulkova. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of the Effects of Maternal Hypoxia and Placental Ischemia on HIF1-Dependent Metabolism and the Glucocorticoid System in the Embryonic and Newborn Rat Brain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413342
APA StyleVetrovoy, O., Potapova, S., Stratilov, V., & Tyulkova, E. (2024). Comparative Analysis of the Effects of Maternal Hypoxia and Placental Ischemia on HIF1-Dependent Metabolism and the Glucocorticoid System in the Embryonic and Newborn Rat Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413342






