Pheromone-Binding Protein 1 Performs a Dual Function for Intra- and Intersexual Signaling in a Moth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization of OBP Genes
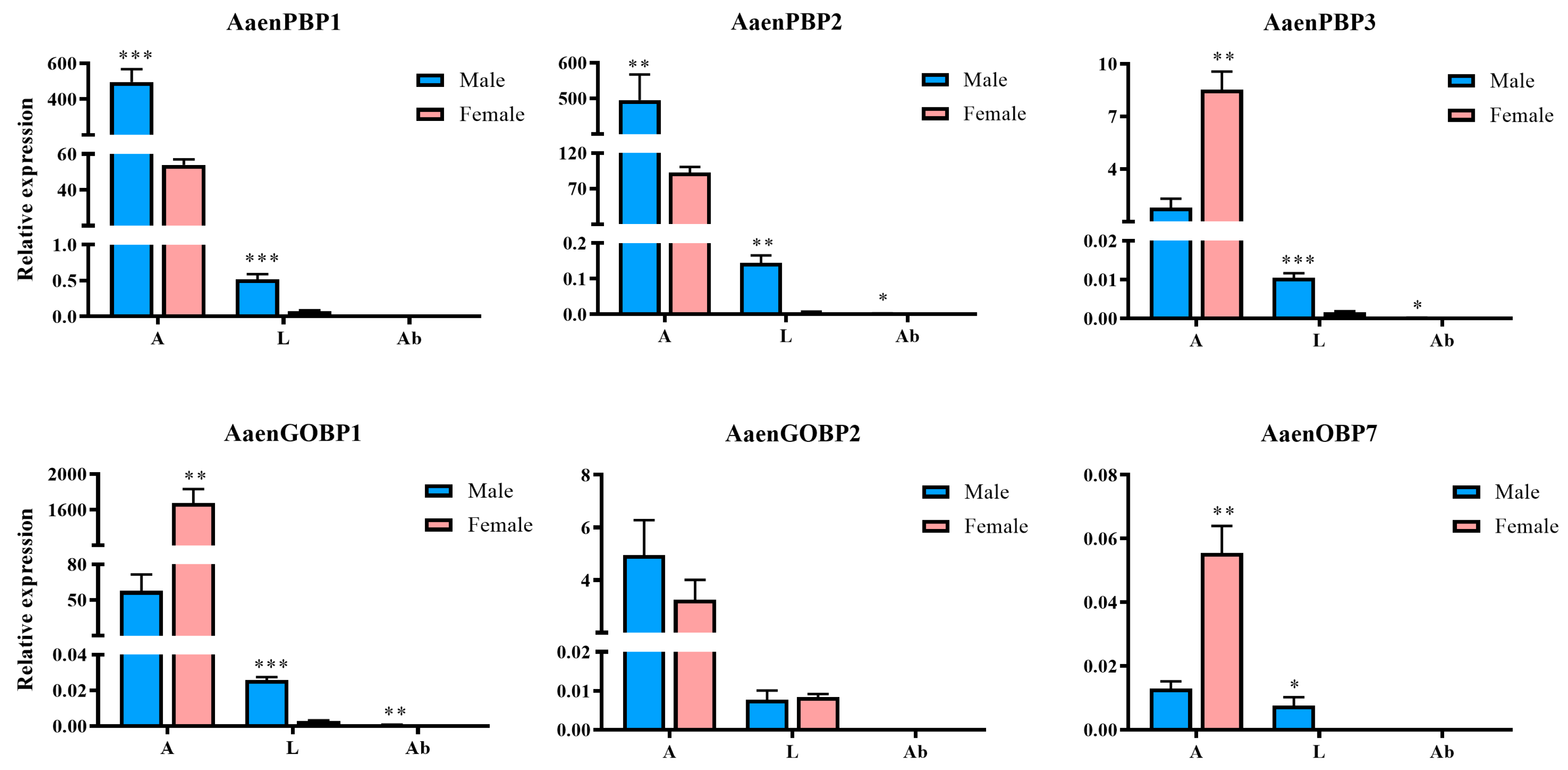
2.2. Expression Profiles of A. aeneociliella OBPs
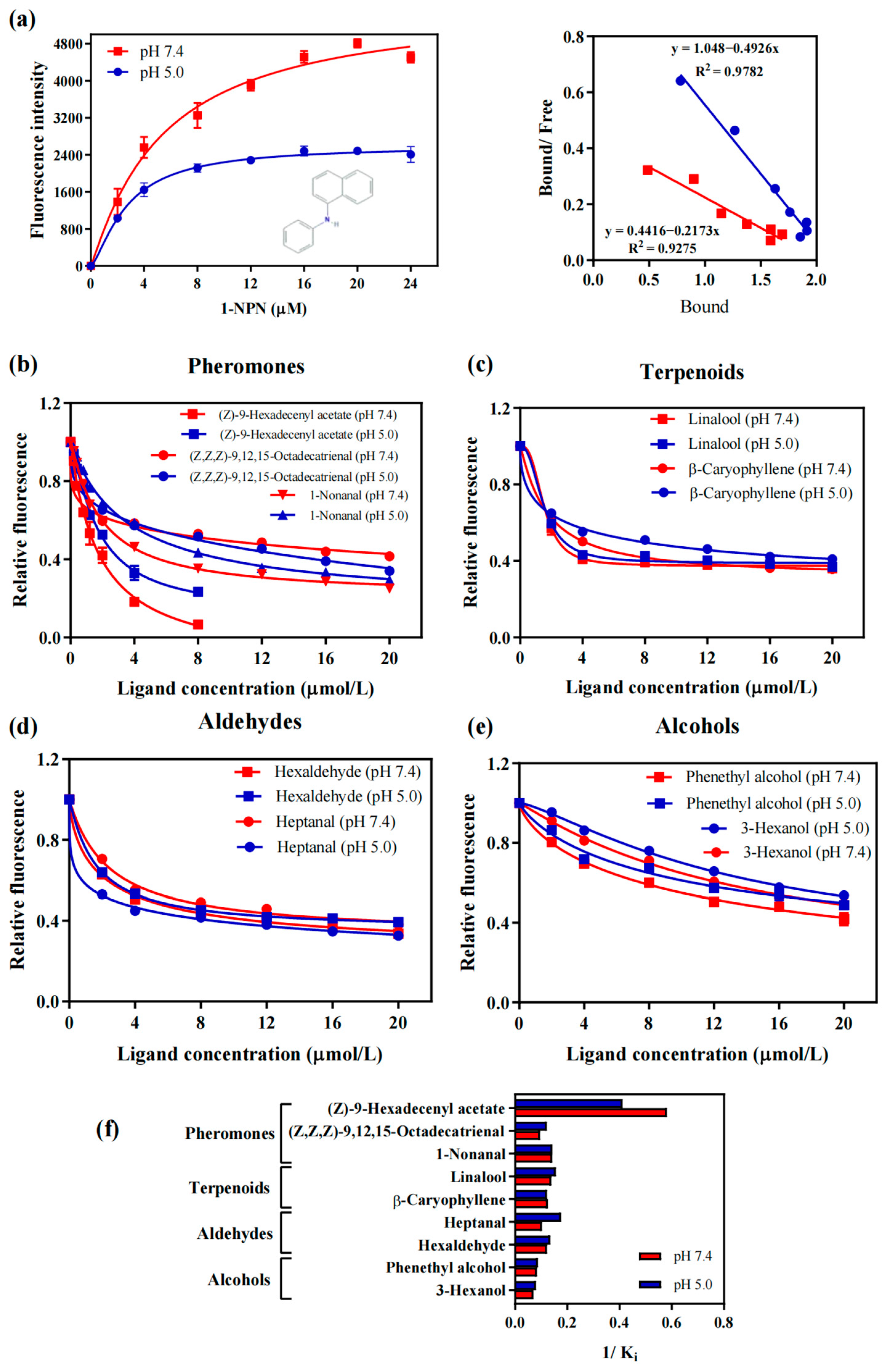
2.3. Binding Assays of Female and Male Pheromones to AaenPBP1
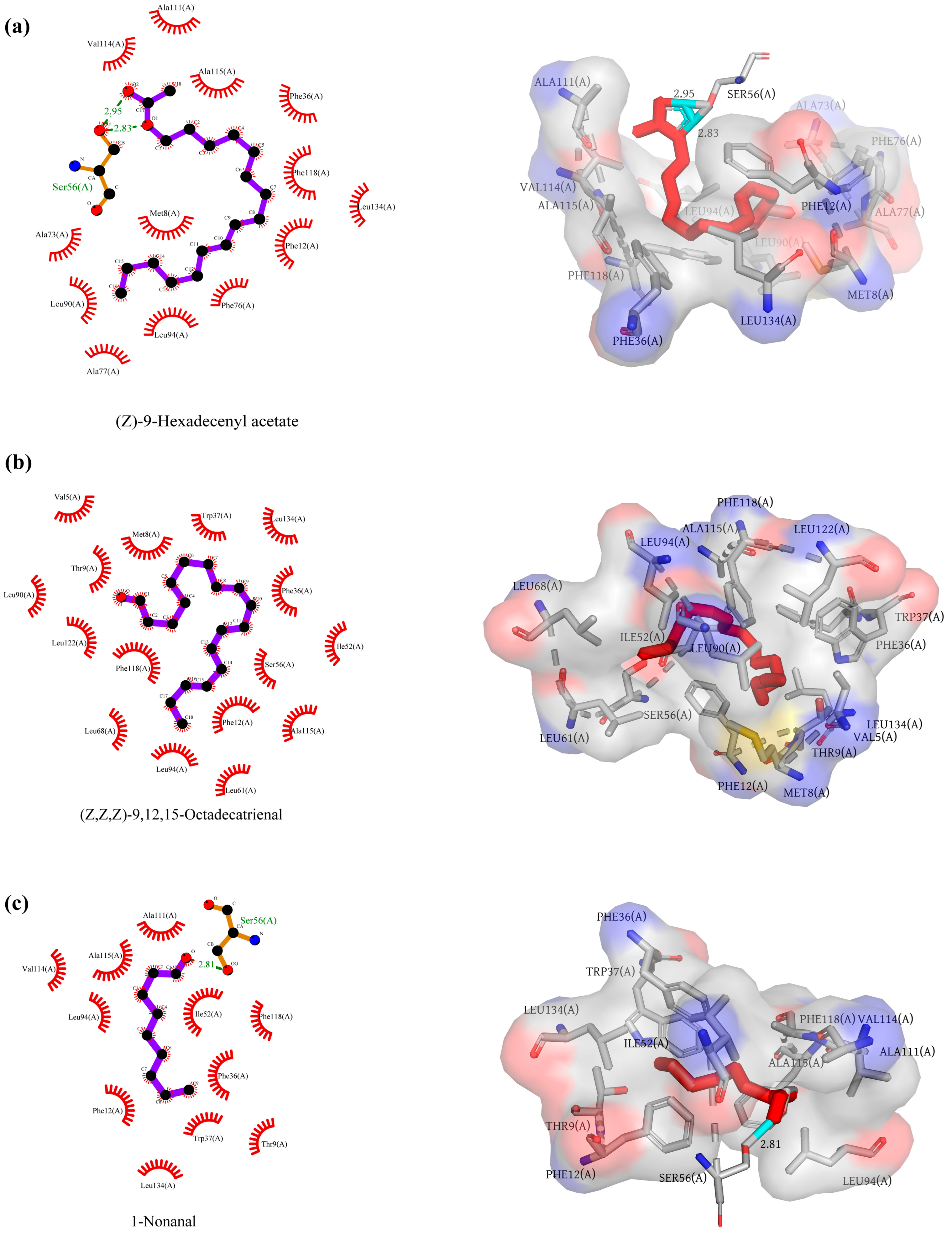
2.4. Molecular Docking of AaenPBP1 to Agriphila aeneociliella Sex Pheromones
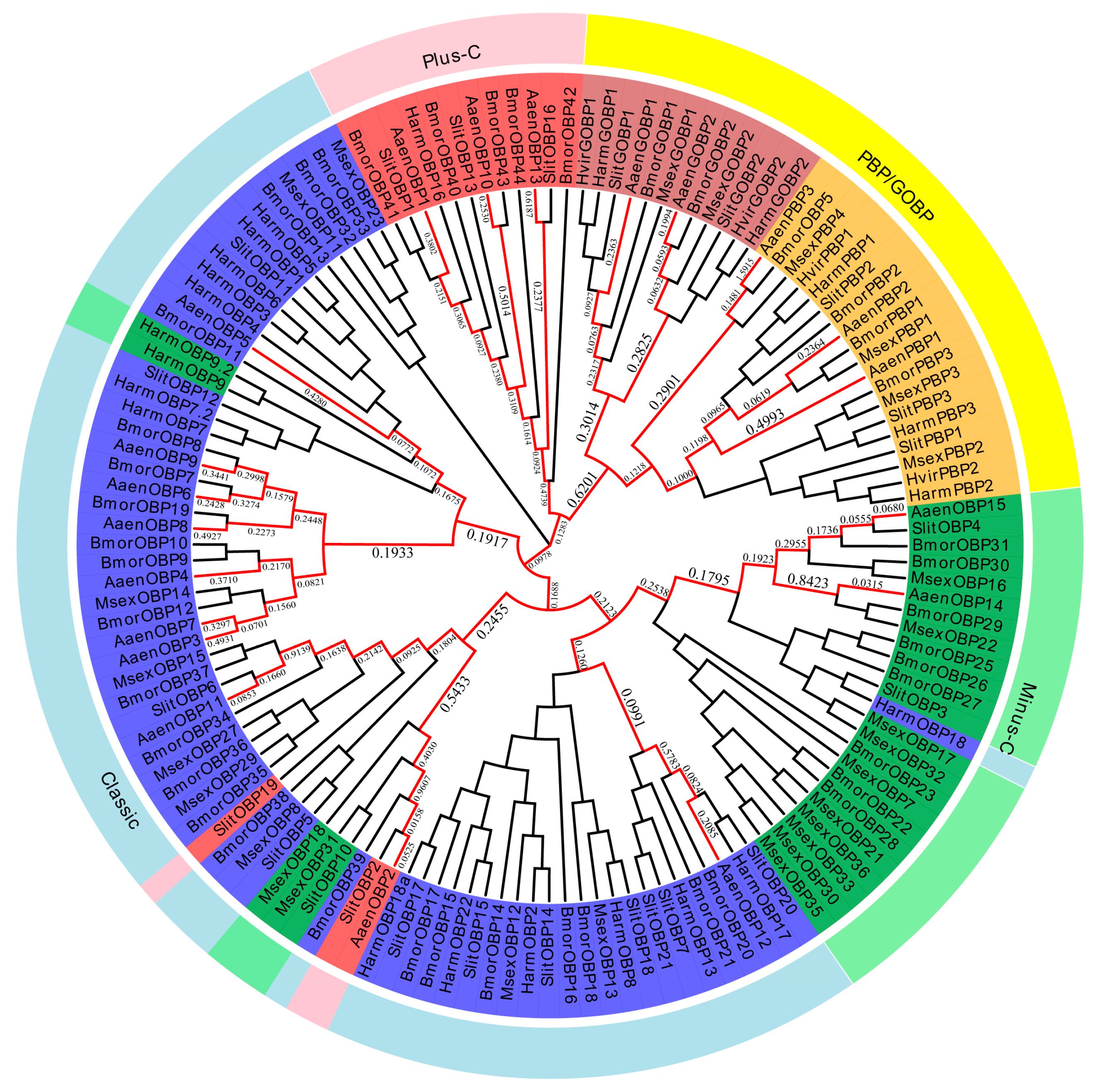
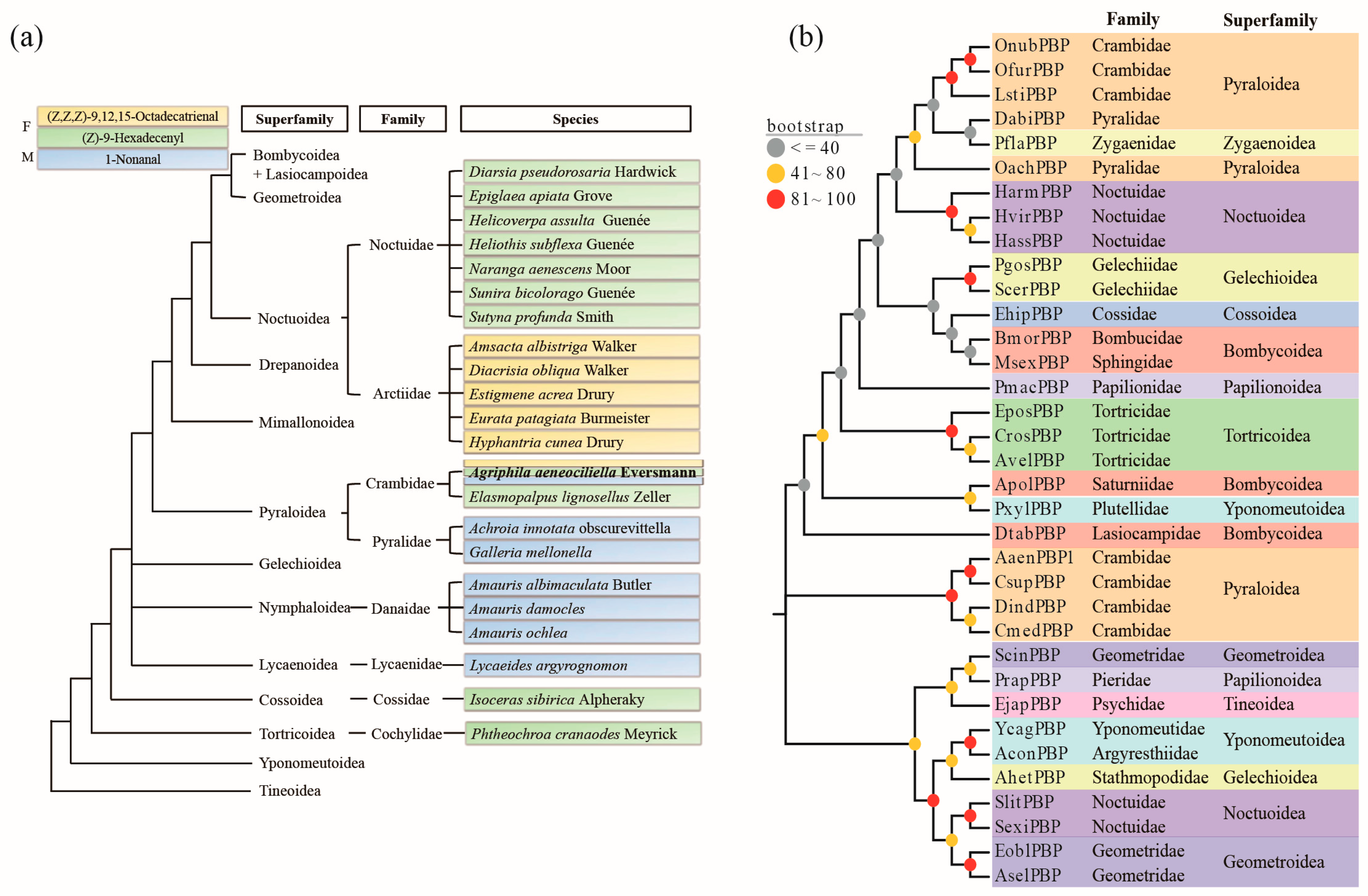
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Rearing
4.2. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Illumina Sequencing
4.3. Gene Identification and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.4. Tissue Expression Profile Analysis
4.5. Preparation of Recombinant Pheromone-Binding Protein 1
4.6. Fluorescence Binding Assay
4.7. Homology Modeling and Molecular Docking
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gadenne, C.; Barrozo, R.B.; Anton, S. Plasticity in Insect Olfaction: To Smell or Not to Smell? Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassau, S.; Krieger, J. The role of SNMPs in insect olfaction. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 383, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.L.; Li, B.L.; Chen, Y.X.; Li, G.W.; Wu, J.X. Functional analysis of the odorant receptor coreceptor in odor detection in Grapholita molesta (lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 108, e21837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelofs, W.L.; Liu, W.; Hao, G.; Jiao, H.; Rooney, A.P.; Linn, C.E. Evolution of moth sex pheromones via ancestral genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13621–13626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, A.T.; Dekker, T.; Heckel, D.G. The Genetic Basis of Pheromone Evolution in Moths. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroumpa, F.A.; Groot, A.T.; Dekker, T.; Heckel, D.G. Genetic mapping of male pheromone response in the European corn borer identifies candidate genes regulating neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6401–E6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, J.; Krieger, J. Insect Pheromone Receptors—Key Elements in Sensing Intraspecific Chemical Signals. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Ando, N.; Haupt, S.S.; Mitsuno, H.; Daimon, T.; Kanzaki, R. Pheromone binding protein is involved in temporal olfactory resolution in the silkmoth. iScience 2021, 24, 103334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Honda, H. Identification and possible functions of the hairpencil scent of the yellow peach moth, Conogethes punctiferalis (Guenee) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1999, 34, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, K.; Shorey, H.H.; Gaston, L.K. Competition Among Courting Male Moths: Male-to-Male Inhibitory Pheromone. Science 1978, 202, 644–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.G.; Riddiford, L.M. Pheromone binding and inactivation by moth antennae. Nature 1981, 293, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, D.P.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q.Y.; Xiang, Z.H. The odorant binding protein gene family from the genome of silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Yang, F.; Liu, H.; Qiao, G.H.; Zhang, A.H.; Wang, S.N. The Female-Biased General Odorant Binding Protein 2 of Semiothisa cinerearia Displays Binding Affinity for Biologically Active Host Plant Volatiles. Biology 2024, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräter, F.; Xu, W.; Leal, W.; Grubmüller, H. Pheromone Discrimination by the Pheromone-Binding Protein of Bombyx mori. Structure 2006, 14, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Xie, M.; Di, Z.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Kong, X.; Lin, L.; Su, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, F.; et al. PBP1 plays key roles in sex pheromone reception of the fall armyworm. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Danoon, O.; Mazumder, S.; Chaudhary, B.P.; Nukala, V.; Bishop, B.; Cahoon, G.; Mohanty, S. Structural and Functional Characterization of European Corn Borer, Ostrinia nubilalis, Pheromone Binding Protein 3. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14013–14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T.; Namiki, S.; Kanzaki, R. Molecular and neural mechanisms of sex pheromone reception and processing in the silkmoth Bombyx mori. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Daimon, T.; Mitsuno, H.; Fujii, T.; Matsuyama, S.; Sezutsu, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Kanzaki, R. In vivo functional characterisation of pheromone binding protein-1 in the silkmoth, Bombyx mori. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, B.; Zheng, X.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y. Temperature-dependent demography of Agriphila aeneociliella (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), a new insect pest of wheat in China. Agric. For. Entomol. 2016, 18, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.D.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, Y. Pheromones emitted by both female and male moths regulate coordination between the sexes for Agriphila aeneociliella (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Insect Sci. 2023, 30, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitter, C.; Davis, D.R.; Cummings, M.P. Phylogeny and Evolution of Lepidoptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond chemoreception: Diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovinella, I.; Dani, F.R.; Niccolini, A.; Sagona, S.; Michelucci, E.; Gazzano, A.; Turillazzi, S.; Felicioli, A.; Pelosi, P. Differential expression of odorant-binding proteins in the mandibular glands of the honey bee according to caste and age. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damberger, F.; Nikonova, L.; Horst, R.; Peng, G.; Leal, W.S.; Wüthrich, K. NMR characterization of a pH-dependent equilibrium between two folded solution conformations of the pheromone-binding protein from Bombyx mori. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlager, C.; Leal, W.S.; Clardy, J. Coil-to-helix transition and ligand release of Bombyx mori pheromone-binding protein. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, W.S.; Chen, A.M.; Ishida, Y.; Chiang, V.P.; Erickson, M.L.; Morgan, T.I.; Tsuruda, J.M. Kinetics and molecular properties of pheromone binding and release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5386–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, L.; Antonczak, S.; Jacquin-Joly, E.; Cabrol-Bass, D.; Golebiowski, J. Deciphering the selectivity of Bombyx mori pheromone binding protein for bombykol over bombykal: A theoretical approach. Chemphyschem 2008, 9, 2785–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, H.; Fujii, T. Chemical Divergences in the Sex Pheromone Communication Systems in Moths. In Insect Sex Pheromone Research and Beyond: From Molecules to Robots; Ishikawa, Y., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyota, R.; Arakawa, M.; Yamakawa, R.; Yasmin, A.; Ando, T. Biosynthetic pathways of the sex pheromone components and substrate selectivity of the oxidation enzymes working in pheromone glands of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, M.R.; Elgar, M.A. The evolution of pheromone diversity. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, H.E.H. The Recognition Concept of Species. In Species and Speciation; Vrba, E., Ed.; Transvaal Museum Monograph No. 4. Pretoria; 1985. Available online: https://philpapers.org/rec/PATTRC (accessed on 27 October 2024).
- Marshall, J.L.; Arnold, M.L.; Howard, D.J. Reinforcement: The road not taken. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.-H. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanacci, V.; Krieger, J.; Bette, S.; Sturgis, J.N.; Lartigue, A.; Cambillau, C.; Breer, H.; Tegoni, M. Revisiting the specificity of Mamestra brassicae and Antheraea polyphemus pheromone-binding proteins with a fluorescence binding assay. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20078–20084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, R.; Jain, A.N. Surflex-Dock: Docking benchmarks and real-world application. J. Comput. Aid. Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple Ligand-Protein Interaction Diagrams for Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | ORF (aa) | Signal Peptide | Blastx Annotation | Acc. Number | Score | E-Value | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AaenPBP1 | 166 | 1–23 | Pheromone-binding protein 1 [Chilo suppressalis] | ADK66921.1 | 250 | 2 × e−82 | 71% |
| AaenPBP2 | 3’miss | ND | Pheromone-binding protein 2 [C. suppressalis] | ACJ07123.1 | 150 | 2 × e−44 | 77% |
| AaenPBP3 | 60 | ND | Pheromone-binding protein 3 [C. suppressalis] | ADL09140.1 | 93.6 | 2 × e−22 | 77% |
| AaenGOBP1 | 140 | ND | General odorant-binding protein 1 [C. suppressalis] | ACJ07126.1 | 240 | 5 × e−79 | 80% |
| AaenGOBP2 | 163 | 1–21 | General odorant-binding protein 2 [C. suppressalis] | ACJ07120.1 | 279 | 4 × e−94 | 81% |
| AaenOBP1 | 212 | 1–39 | Odorant-binding protein 4 [C. suppressalis] | ANZ73034.1 | 229 | 2 × e−73 | 54% |
| AaenOBP2 | 184 | 1–22 | Odorant-binding protein 18 [Conogethes punctiferalis] | QEE82717.1 | 368 | 1 × e−128 | 96% |
| AaenOBP3 | 153 | 1–19 | Odorant-binding protein 25 [C. suppressalis] | ANC68513.1 | 201 | 9 × e−63 | 67% |
| AaenOBP4 | 153 | 1–23 | Odorant-binding protein 13 [Cnaphalocrocis medinalis] | ALT31643.1 | 235 | 7 × e−77 | 74% |
| AaenOBP5 | 150 | 1–20 | Odorant-binding protein [C. suppressalis] | AGM38610.1 | 167 | 3 × e−50 | 61% |
| AaenOBP6 | 149 | 1–19 | Odorant-binding protein 22, partial [C. suppressalis] | ANC68510.1 | 191 | 7 × e−59 | 66% |
| AaenOBP7 | 148 | 1–20 | Odorant-binding protein 29, partial [C. suppressalis] | ANC68517.1 | 213 | 2 × e−68 | 73% |
| AaenOBP8 | 147 | 1–18 | Odorant-binding protein, partial [C. punctiferalis] | APG32537.1 | 149 | 2 × e−43 | 51% |
| AaenOBP9 | 147 | 1–20 | General odorant-binding protein 28a [Helicoverpa armigera] | XP_021194660.1 | 166 | 1 × e−49 | 53% |
| AaenOBP10 | 146 | 1–17 | Odorant-binding protein 4 [C. suppressalis] | AGK24580.1 | 264 | 1 × e−88 | 82% |
| AaenOBP11 | 3’miss | 1–21 | Odorant-binding protein 40 [Dendrolimus punctatus] | ARO70199.1 | 157 | 3 × e−47 | 68% |
| AaenOBP12 | 136 | 1–21 | Odorant-binding protein [C. suppressalis] | AGM38607.1 | 236 | 3 × e−78 | 85% |
| AaenOBP13 | 163 | 1–16 | Odorant-binding protein OBP47 [Lobesia botrana] | AXF48744.1 | 89.7 | 2 × e−19 | 37% |
| AaenOBP14 | 156 | 1–18 | Odorant-binding protein 9 [C. pinicolalis] | QEE82708.1 | 247 | 1 × e−81 | 83% |
| AaenOBP15 | 133 | 1–16 | Odorant-binding protein 2 [C. suppressalis] | AGK24578.1 | 254 | 3 × e−85 | 94% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M.; Francis, F.; Liu, Y. Pheromone-Binding Protein 1 Performs a Dual Function for Intra- and Intersexual Signaling in a Moth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313125
Zhan Y, Zhang J, Xu M, Francis F, Liu Y. Pheromone-Binding Protein 1 Performs a Dual Function for Intra- and Intersexual Signaling in a Moth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):13125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313125
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Yidi, Jiahui Zhang, Mengxian Xu, Frederic Francis, and Yong Liu. 2024. "Pheromone-Binding Protein 1 Performs a Dual Function for Intra- and Intersexual Signaling in a Moth" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 13125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313125
APA StyleZhan, Y., Zhang, J., Xu, M., Francis, F., & Liu, Y. (2024). Pheromone-Binding Protein 1 Performs a Dual Function for Intra- and Intersexual Signaling in a Moth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 13125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313125






