A Decision Tree Model Using Urine Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers for Predicting Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Females
Abstract
1. Introduction
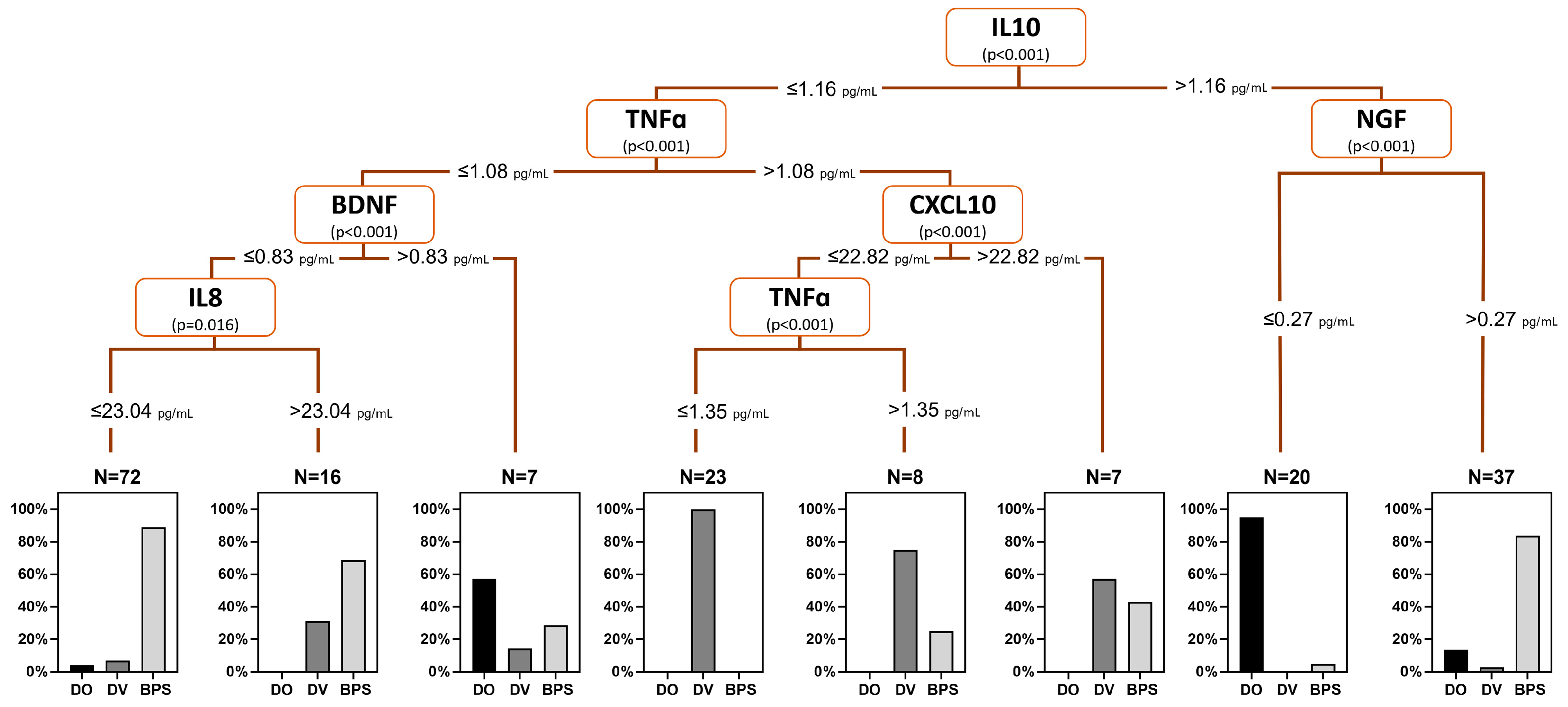
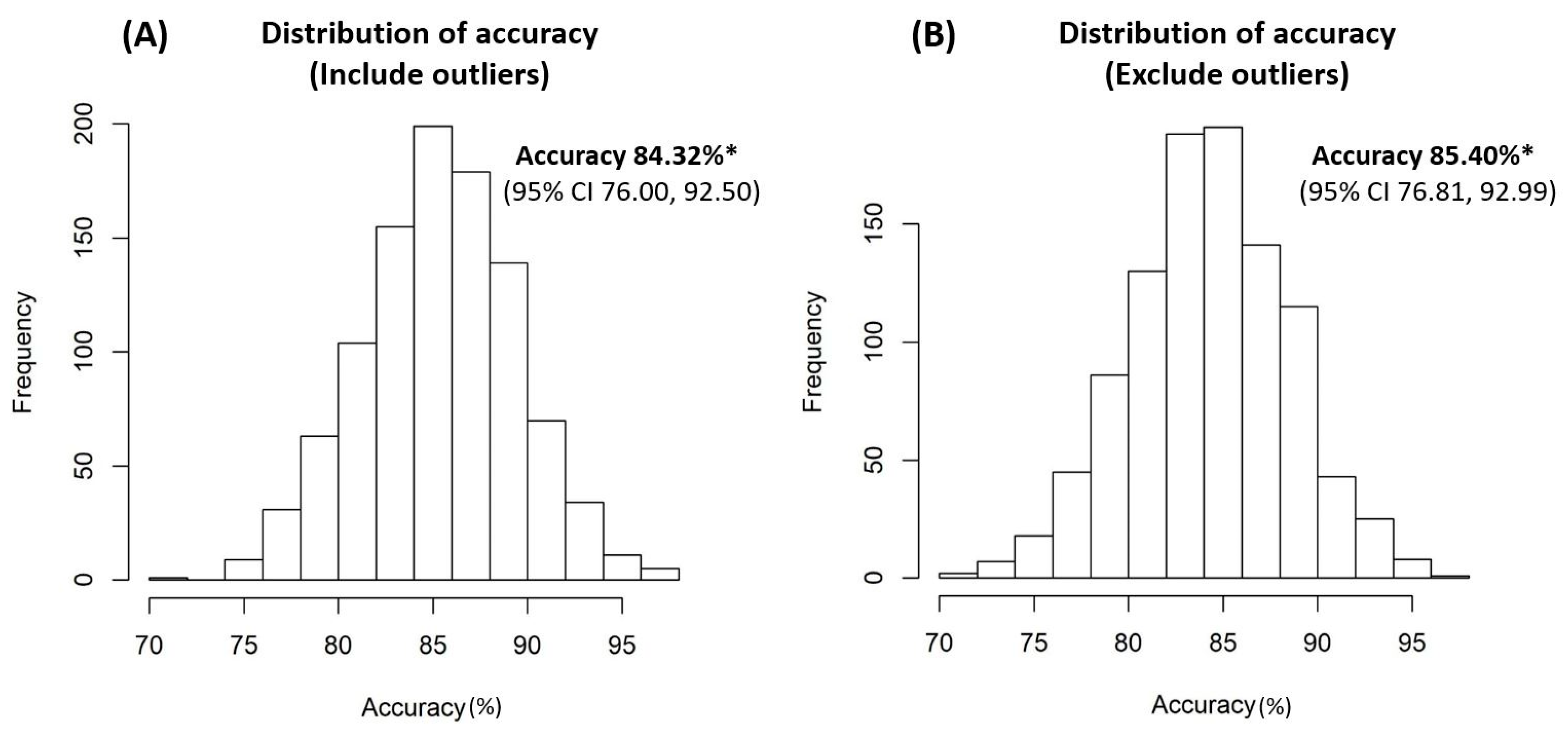
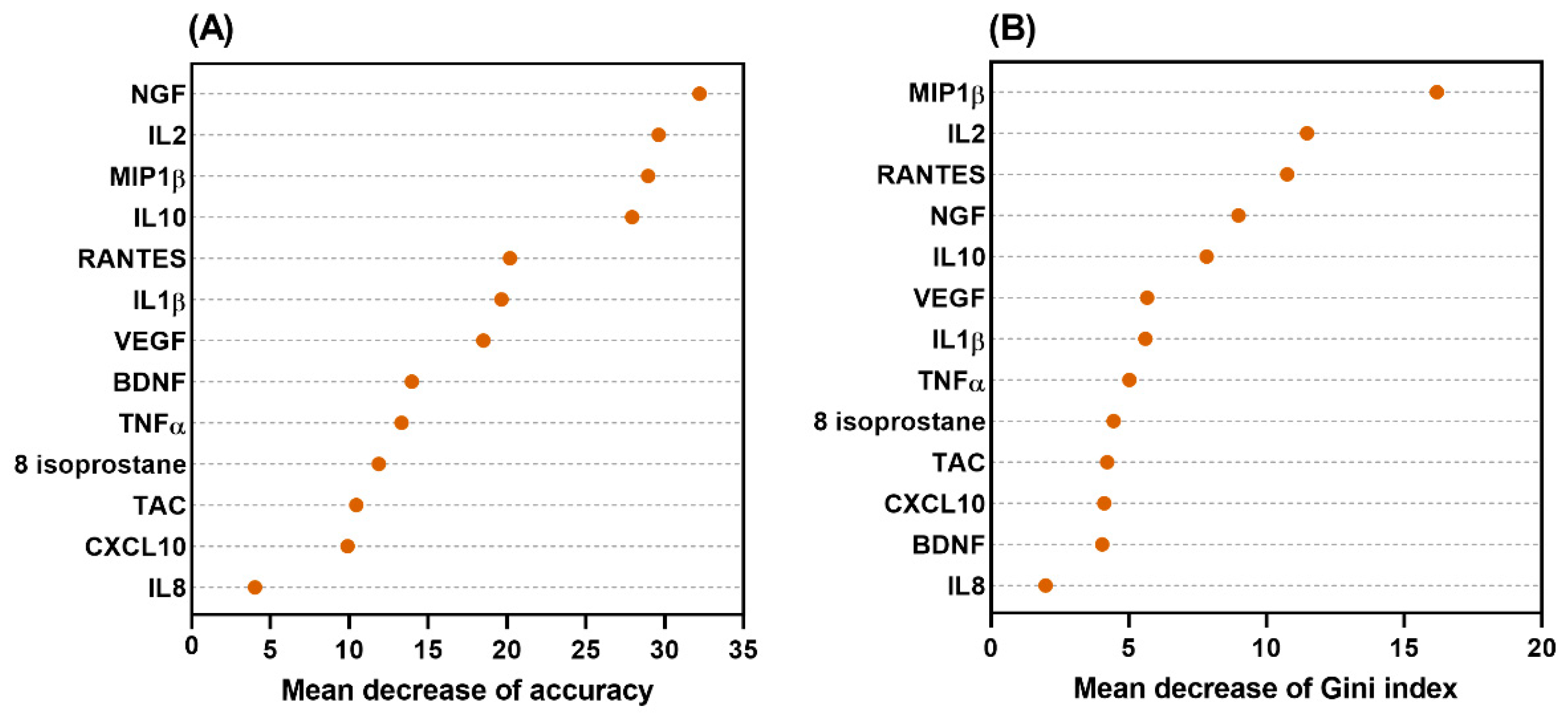
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Investigation of Clinical Characteristics
4.2. Assessment of Urine Biomarker Levels
4.3. Quantification of Inflammatory Cytokines
4.4. Quantification of Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)
4.5. Quantification of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Establishment of the Decision Tree Model
4.8. Internal Validation of the Decision-Tree Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irwin, D.E.; Milsom, I.; Hunskaar, S.; Reilly, K.; Kopp, Z.; Herschorn, S.; Coyne, K.; Kelleher, C.; Hampel, C.; Artibani, W.; et al. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: Results of the EPIC study. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 1306–1314; discussion 1314–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.P.; Chuang, Y.C.; Sumarsono, B.; Chang, H.C. The prevalence and bother of lower urinary tract symptoms in men and women aged 40 years or over in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118 Pt 1, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C. Clinical symptoms are not reliable in the diagnosis of lower urinary tract dysfunction in women. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2012, 111, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.M.; Lin, H.H.; Kuo, H.C. Videourodynamic Studies of Women with Voiding Dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Chen, S.F.; Kuo, H.C. Role of videourodynamic study in precision diagnosis and treatment for lower urinary tract dysfunction. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020, 32, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, N.Y.; Helfand, B.T.; Andreev, V.P.; Kowalski, J.T.; Bradley, M.S.; Lai, H.H.; Berger, M.B.; Mueller, M.G.; Bickhaus, J.A.; Packiam, V.T.; et al. Biomarkers Implicated in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Systematic Review and Pathway Analyses. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shie, J.H.; Kuo, H.C. Higher levels of cell apoptosis and abnormal E-cadherin expression in the urothelium are associated with inflammation in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. BJU Int. 2011, 108 Pt 2, E136–E141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Kuo, H.C. Urothelial Dysfunction and Chronic Inflammation in Diabetic Patients with Overactive Bladder. Low. Urin. Tract. Symptoms 2017, 9, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Lee, C.L.; Kuo, H.C. Urothelial Dysfunction, Suburothelial Inflammation and Altered Sensory Protein Expression in Men with Bladder Outlet Obstruction and Various Bladder Dysfunctions: Correlation with Urodynamics. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Imai, A.; Tanaka, T.; Hagiwara, K.; Konishi, S.; Okita, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Tobisawa, Y.; Yoneyama, T.; et al. Relationship between oxidative stress and lower urinary tract symptoms: Results from a community health survey in Japan. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiya, M.; Andersson, K.E.; Yamaguchi, O. Chronic bladder ischemia and oxidative stress: New pharmacotherapeutic targets for lower urinary tract symptoms. Int. J. Urol. 2015, 22, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes-Lopes, T.; Cruz, F. Urinary Biomarkers in Overactive Bladder: Revisiting the Evidence in 2019. Eur Urol Focus 2019, 5, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Matsuo, T.; Mitsunari, K.; Asai, A.; Ohba, K.; Sakai, H. A Review of Oxidative Stress and Urinary Dysfunction Caused by Bladder Outlet Obstruction and Treatments Using Antioxidants. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Urine biomarkers in ESSIC type 2 interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and overactive bladder with developing a novel diagnostic algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Ho, H.C.; Hsu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Diagnostic and prognostic value of urine biomarkers among women with dysfunctional voiding. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng-Rogenski, S.; Liebert, M. Interleukin-8 is essential for normal urothelial cell survival. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009, 297, F816–F821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Dubey, S.; Varney, M.L.; Dave, B.J.; Singh, R.K. IL-8 directly enhanced endothelial cell survival, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinases production and regulated angiogenesis. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3369–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiya, M.; Sagawa, K.; Yazaki, J.; Takahashi, N.; Kushida, N.; Haga, N.; Aikawa, K.; Matsui, T.; Oka, M.; Fukui, T.; et al. Increased bladder activity is associated with elevated oxidative stress markers and proinflammatory cytokines in a rat model of atherosclerosis-induced chronic bladder ischemia. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2012, 31, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochodnicky, P.; Cruz, C.D.; Yoshimura, N.; Cruz, F. Neurotrophins as regulators of urinary bladder function. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2012, 9, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haylen, B.T.; de Ridder, D.; Freeman, R.M.; Swift, S.E.; Berghmans, B.; Lee, J.; Monga, A.; Petri, E.; Rizk, D.E.; Sand, P.K.; et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2010, 29, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Merwe, J.P.; Nordling, J.; Bouchelouche, P.; Bouchelouche, K.; Cervigni, M.; Daha, L.K.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Irwin, P.; et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: An ESSIC proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Urine cytokines as biomarkers for diagnosing interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and mapping its clinical characteristics. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2020, 318, F1391–F1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.F.; Jiang, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Urinary biomarkers in patients with detrusor underactivity with and without bladder function recovery. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hothorn, T.; Hornik, K.; Zeileis, A. Unbiased Recursive Partitioning: A Conditional Inference Framework. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2006, 15, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, C.; Boulesteix, A.-L.; Zeileis, A.; Hothorn, T. Bias in random forest variable importance measures: Illustrations, sources and a solution. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.C.; Glavis-Bloom, J.; Modi, P.; Nasrin, S.; Rege, S.; Chu, C.; Schmid, C.H.; Alam, N.H. Empirically Derived Dehydration Scoring and Decision Tree Models for Children With Diarrhea: Assessment and Internal Validation in a Prospective Cohort Study in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Glob. Health Sci. Pract. 2015, 3, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr.; Lee, K.L.; Mark, D.B. Multivariable prognostic models: Issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat. Med. 1996, 15, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Altman, D.G.; Moons, K.G. Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): The TRIPOD statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| DO (n = 31) | DV (n = 45) | BPS (n = 114) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 63.9 ± 9.0 | 53.2 ± 14.2 | 54.6 ± 12.4 | <0.001 |
| IPSS-V | 3.9 ± 4.4 | 9.1 ± 7.2 | NA | 0.001 |
| IPSS-S | 7.5 ± 3.5 | 6.0 ± 4.0 | NA | 0.122 |
| IPSS | 11.4 ± 5.8 | 15.1 ± 9.9 | NA | 0.083 |
| OABSS | 9.4 ± 3.2 | NA | NA | |
| OSS | NA | NA | 20.6 ± 7.9 | |
| VAS | NA | NA | 4.2 ± 2.6 | |
| MBC | NA | NA | 717.8 ± 179.1 | |
| Glomerulation grade | NA | NA | 1.1 ± 0.9 | |
| VUDS | ||||
| FSF | 108.7 ± 48.6 | 125.2 ± 55.2 | 131.1 ± 59.9 | 0.124 |
| CBC | 286.3 ± 134.7 | 278.8 ± 134.3 | 251.6 ± 137.8 | 0.321 |
| Pdet | 18.0 ± 11.0 | 47.8 ± 42.7 | 22.3 ± 17.6 | <0.001 |
| Qmax | 16.1 ± 7.3 | 10.6 ± 6.8 | 10.3 ± 6.4 | <0.001 |
| cQmax | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| Vol | 272.1 ± 134 | 228.7 ± 115.8 | 211.9 ± 117.1 | 0.049 |
| PVR | 14.7 ± 40.8 | 56.4 ± 66 | 50.8 ± 102.8 | 0.093 |
| VE | 0.95 ± 0.11 | 0.80 ± 0.23 | 0.82 ± 0.27 | 0.017 |
| Urine Biomarkers * | 1. DO n = 31 | 2. DV n = 45 | 3. BPS n = 114 | p-Value | Post Hoc Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 0.61 ± 0.54 (1) | 1.16 ± 1.4 (1) | 0.64 ± 0.49 (3) | 0.001 | 1, 3 < 2 |
| IL-2 | 0.74 ± 0.19 (0) | 0.28 ± 0.22 (0) | 0.76 ± 0.18 (0) | <0.001 | 2 < 1, 3 |
| IL-6 | 2.05 ± 2.62 (1) | 2.14 ± 5.16 (2) | 1.72 ± 1.53 (2) | 0.674 | |
| IL-8 | 20.67 ± 34.38 (1) | 30.96 ± 63.85 (1) | 14.17 ± 15.83 (2) | 0.016 | 3 < 2 |
| IL-10 | 1.54 ± 0.51 (1) | 0.99 ± 0.11 (2) | 1.07 ± 0.34 (2) | <0.001 | 2, 3 < 1 |
| Eotaxin | 6.04 ± 5.74 (1) | 5.78 ± 7.3 (1) | 8.62 ± 6.98 (3) | 0.031 | 2 < 3 |
| CXCL10 | 30.25 ± 45.83 (2) | 10.64 ± 20.03 (1) | 44.72 ± 58.44 (2) | <0.001 | 2 < 3 |
| MCP-1 | 326.29 ± 304.61 (1) | 196.09 ± 378.98 (1) | 282.14 ± 242.36 (4) | 0.128 | |
| MIP-1β | 3.66 ± 3.03 (1) | 1.36 ± 4.02 (1) | 3.16 ± 2.09 (3) | <0.001 | 2 < 1, 3 |
| RANTES | 8.81 ± 6.36 (0) | 4.21 ± 7.82 (1) | 9.33 ± 6.99 (2) | <0.001 | 2 < 1, 3 |
| TNFα | 0.87 ± 0.40 (1) | 1.21 ± 0.33 (2) | 0.78 ± 0.42 (2) | <0.001 | 1, 3 < 2 |
| VEGF | 14.63 ± 5.96 (0) | 5.56 ± 4.91 (1) | 14.41 ± 6.81 (1) | <0.001 | 2 < 1, 3 |
| NGF | 0.26 ± 0.07 (0) | 0.21 ± 0.05 (1) | 0.37 ± 0.17 (4) | <0.001 | 1, 2 < 3 |
| BDNF | 0.60 ± 0.22 (0) | 0.63 ± 0.15 (0) | 0.50 ± 0.17 (3) | <0.001 | 3 < 2 |
| PGE2 | 261.77 ± 174.5 (0) | 217.57 ± 186.73 (1) | 239.40 ± 167.73 (3) | 0.550 | |
| 8-isoprostane | 32.53 ± 29.78 (0) | 12.89 ± 14.70 (1) | 39.09 ± 29.58 (2) | <0.001 | 2 < 1, 3 |
| TAC | 1558.76 ± 1358.87 (0) | 604.35 ± 420.40 (2) | 1657.94 ± 1189.74 (3) | <0.001 | 2 < 1, 3 |
| 8-OHdG | 26.00 ± 17.68 (0) | 32.42 ± 19.44 (0) | 33.18 ± 17.92 (0) | 0.150 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.-H.; Jhang, J.-F.; Wang, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Kuo, H.-C. A Decision Tree Model Using Urine Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers for Predicting Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Females. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312857
Jiang Y-H, Jhang J-F, Wang J-H, Wu Y-H, Kuo H-C. A Decision Tree Model Using Urine Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers for Predicting Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Females. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312857
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yuan-Hong, Jia-Fong Jhang, Jen-Hung Wang, Ya-Hui Wu, and Hann-Chorng Kuo. 2024. "A Decision Tree Model Using Urine Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers for Predicting Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Females" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312857
APA StyleJiang, Y.-H., Jhang, J.-F., Wang, J.-H., Wu, Y.-H., & Kuo, H.-C. (2024). A Decision Tree Model Using Urine Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers for Predicting Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Females. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312857







