Methoprene-Tolerant (Met) Acts as Methyl Farnesoate Receptor to Regulate Larva Metamorphosis in Mud Crab, Scylla paramamosain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
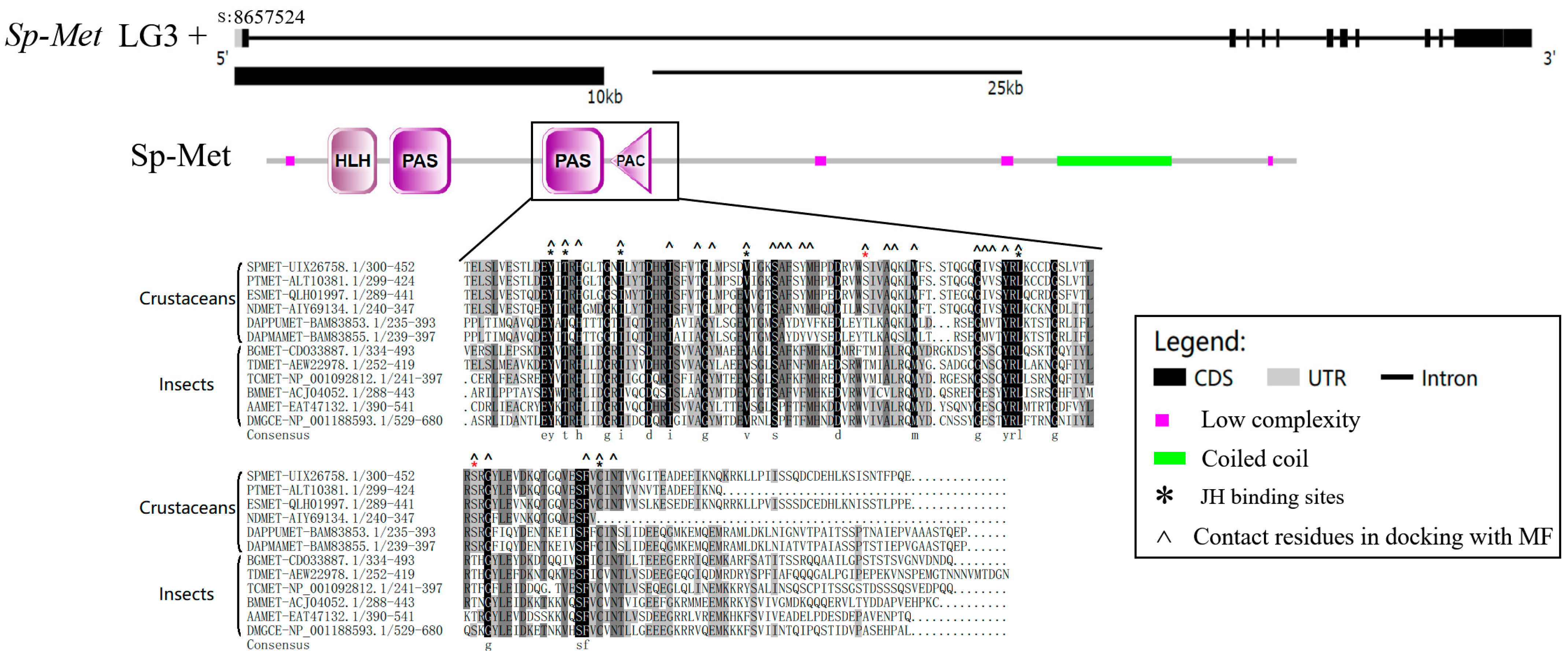
2.1. Characters of Sp-Met Sequence
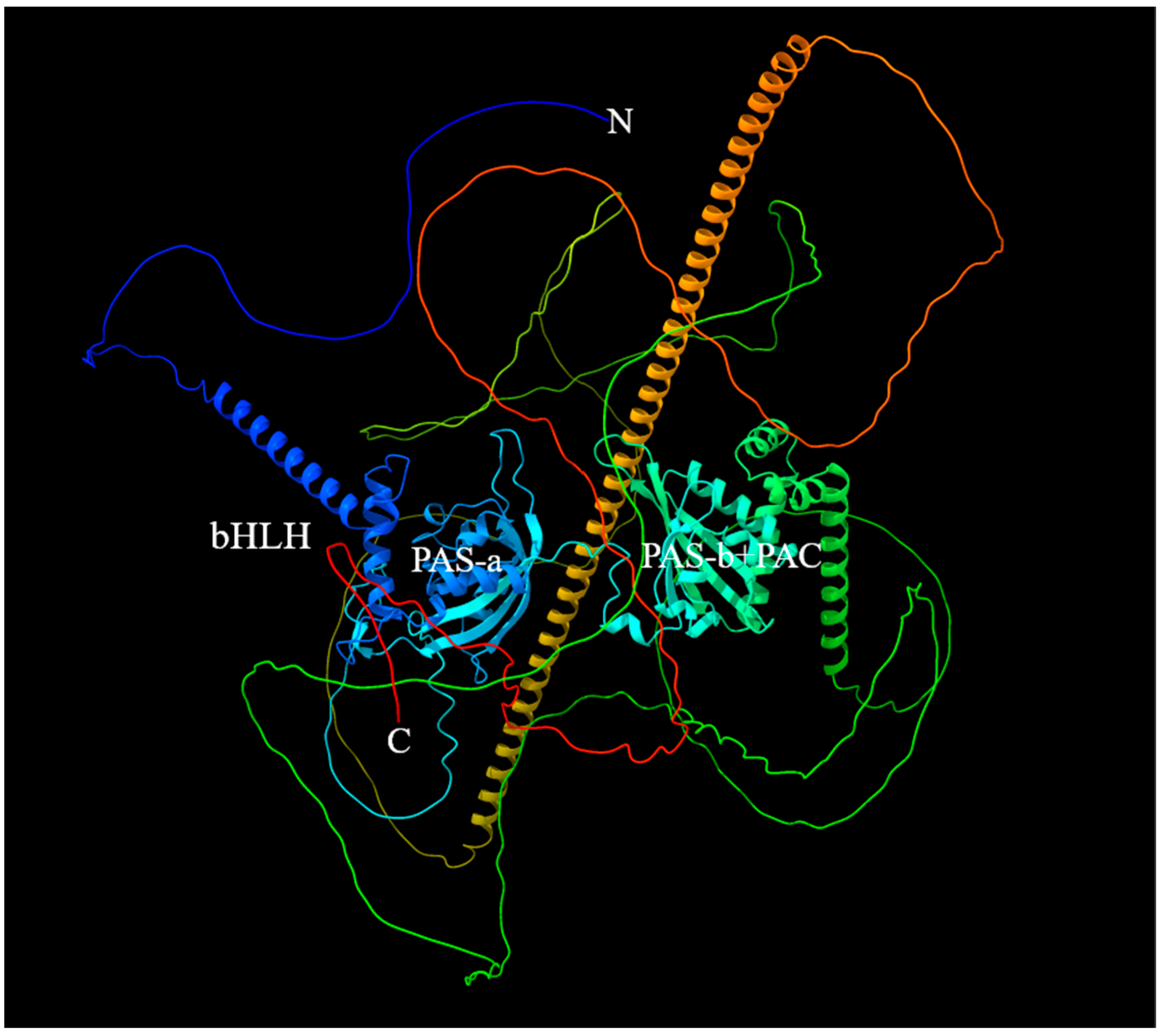
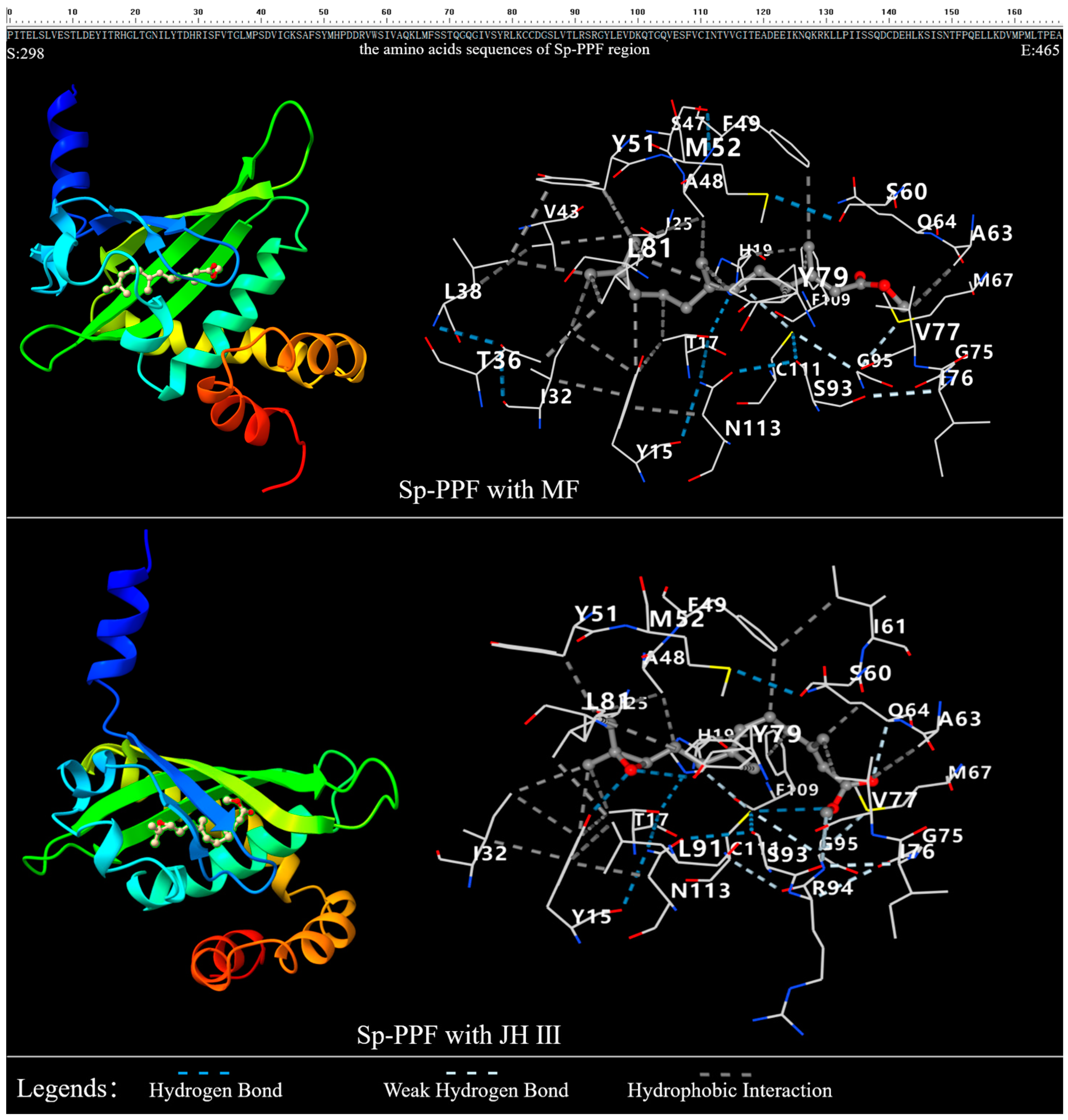
2.2. The 3D Structure of Sp-Met and Binding Analysis with JHs
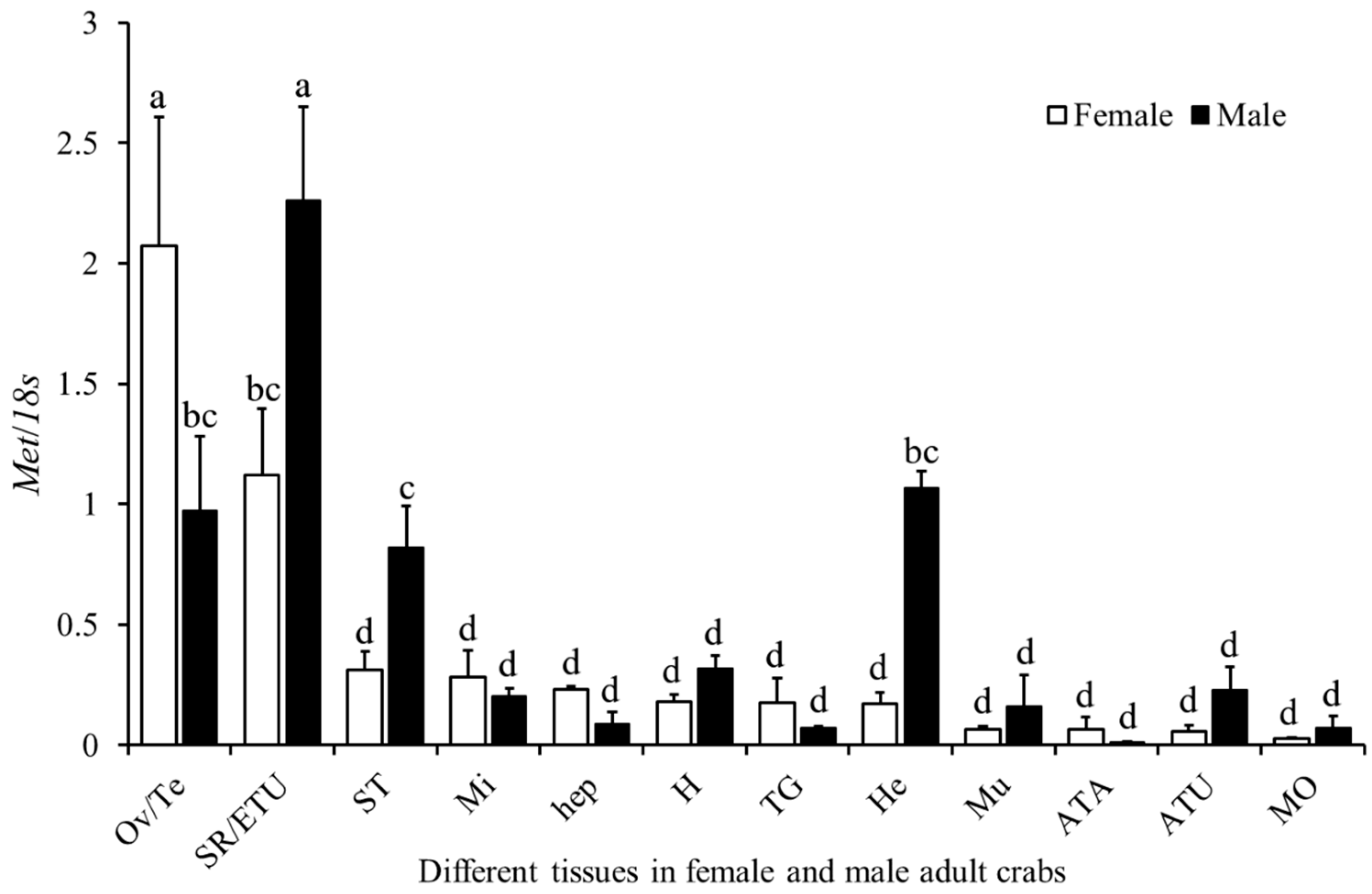
2.3. Expression Profile of Sp-Met in Adult Male and Female Crabs
2.4. Spatial Expression of Sp-Met and Sp-Kr-h1 During the Larval Development
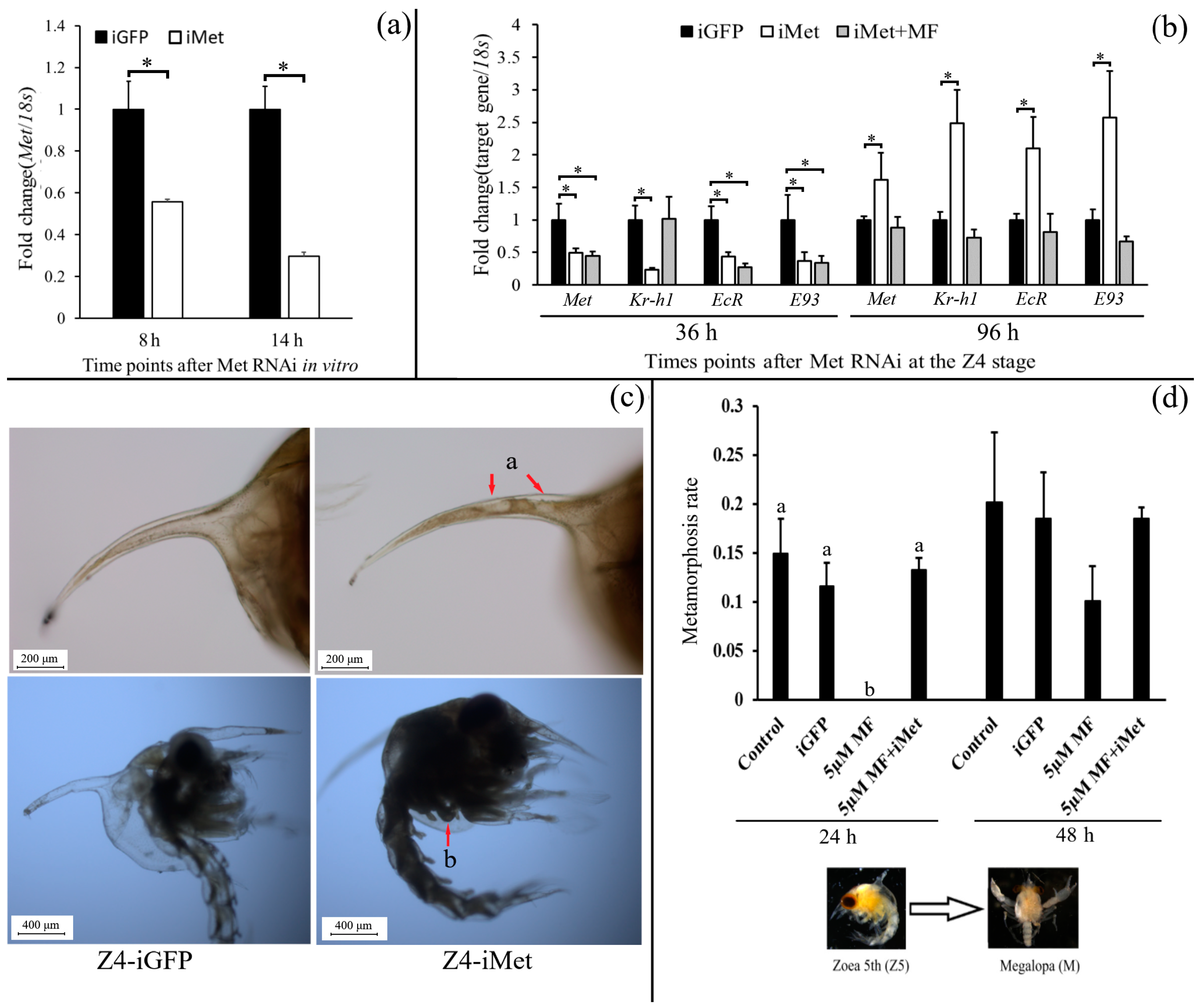
2.5. Function Studies of Sp-Met During Larval Metamorphosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Samples Collection
4.3. Sequence Analysis of Sp-Met
4.4. Docking Analysis Between Met and MF
4.5. Expression Analysis
4.6. Function Study of Sp-Met During Larval Metamorphosis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farhadi, A.; Zhao, Q.; Tan, K. The Molecular Mechanism of Embryonic Development in Decapod Crustaceans. Rev. Aquac. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L. Effect of Methyl Farnesoate and Farnesoic Acid During 5th Zoea and Megalopa Metamorphosis in The Mud Crab Scylla Paramamosain estampador, 1950 (Decapoda, Brachyura, Portunidae). Crustaceana 2021, 94, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jia, Q.Q.; Li, S. Juvenile hormone signaling—A mini review. Insect Sci. 2019, 26, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrovsky, E.B. Hormonal cross talk in insect development. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2005, 16, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laufer, H.; Borst, D.; Baker, F.C.; Reuter, C.C.; Tsai, L.W.; Schooley, D.A.; Carrasco, C.; Sinkus, M. Identification of a juvenile hormone-like compound in a crustacean. Science 1987, 235, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, U.; Takac, P.; Laufer, H.; Sagi, A. Effect of Methyl Farnesoate on Late Larval Development and Metamorphosis in the Prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Decapoda, Palaemonidae): A Juvenoid-like Effect? Biol. Bull. 1998, 195, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.A.; Clare, A.S.; Rees, H.H.; Prescott, M.C.; Wainwright, G.; Thorndyke, M.C. Identification of methyl farnesoate in the cypris larva of the barnacle, Balanus amphitrite, and its role as a juvenile hormone. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 30, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, D.W.; Laufer, H.; Landau, M.; Chang, E.S.; Hertz, W.A.; Baker, F.C.; Schooley, D.A. Methyl farnesoate and its role in crustacean reproduction and development. Insect Biochem. 1987, 17, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, H.; Toyota, K.; Hirakawa, I.; Ogino, Y.; Miyagawa, S.; Oda, S.; Tatarazako, N.; Miura, T.; Colbourne, J.K.; Iguchi, T. A mutation in the receptor Methoprene-tolerant alters juvenile hormone response in insects and crustaceans. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, H.; Watanabe, M.; Araki, M.; Ogino, Y.; Miyagawa, S.; Iguchi, T. Juvenile hormone-independent function of Krüppel homolog 1 in early development of water flea Daphnia pulex. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 93, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, D. Role of Kruppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) in methyl farnesoate-mediated vitellogenesis in the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Gene 2018, 679, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, T.; Jiang, H.; Huang, J.; Huang, M.; Xu, R.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, H.; Su, S. Effects of methyl farnesoate on Krüppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) during vitellogenesis in the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 224, 106653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, S. Juvenile Hormone Studies in Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 785320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Sheng, Z.; Sui, Y.; Palli, S.R. Steroid Receptor Co-activator Is Required for Juvenile Hormone Signal Transduction through a bHLH-PAS Transcription Factor, Methoprene Tolerant. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8437–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, P.; Wiley, J.D.; Ojani, R.; Bevan, D.R.; Li, J.; Zhu, J. A steroid receptor coactivator acts as the DNA-binding partner of the methoprene-tolerant protein in regulating juvenile hormone response genes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 394, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wen, D.; Jia, Q.; Cui, C.; Wang, J.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S. Heat Shock Protein 83 (Hsp83) Facilitates Methoprene-tolerant (Met) Nuclear Import to Modulate Juvenile Hormone Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27874–27885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Dong, W.; Li, S.; Wu, R. Nucleoporin Nup358 facilitates nuclear import of Methoprene-tolerant (Met) in an importin β- and Hsp83-dependent manner. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 81, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayukawa, T.; Minakuchi, C.; Namiki, T.; Togawa, T.; Yoshiyama, M.; Kamimura, M.; Mita, K.; Imanishi, S.; Kiuchi, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of juvenile hormone-mediated induction of Kruppel homolog 1, a repressor of insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11729–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, M.A.; He, Q.; Wen, D.; Zyaan, O.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Baumann, A.A.; Joseph, J.; Wilson, T.G.; Li, S.; et al. Drosophila Met and Gce are partially redundant in transducing juvenile hormone action. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dai, F.; Guo, E.; Li, K.; Ma, L.; Tian, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S. 20-Hydroxyecdysone (20E) Primary Response Gene E93 Modulates 20E Signaling to Promote Bombyx Larval-Pupal Metamorphosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27370–27383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayukawa, T.; Nagamine, K.; Ito, Y.; Nishita, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Shinoda, T. Kruppel homolog 1 inhibits insect metamorphosis via direct transcriptional repression of Broad-complex, a pupal specifier gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 291, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayukawa, T.; Jouraku, A.; Ito, Y.; Shinoda, T. Molecular mechanism underlying juvenile hormone-mediated repression of precocious larval-adult metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Ge, W.; Feng, Q.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S. Antagonistic actions of juvenile hormone and 20-hydroxyecdysone within the ring gland determine developmental transitions in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopova, B.; Jindra, M. Juvenile hormone resistance gene Methoprene-tolerant controls entry into metamorphosis in the beetle Tribolium castaneum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10488–10493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindra, M.; Palli, S.R.; Riddiford, L.M. The Juvenile Hormone Signaling Pathway in Insect Development. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, S.R. Juvenile hormone receptor Methoprene tolerant: Functions and applications. Vitam. Horm. 2023, 123, 619–644. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.-X.; Cao, Y. CB-Dock2: Improved protein–ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W159–W164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.-P.; Iwema, T.; Epa, V.C.; Takaki, K.; Rynes, J.; Jindra, M. Ligand-binding properties of a juvenile hormone receptor, Methoprene-tolerant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 21128–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponting, C.P.; Aravind, L. PAS: A multifunctional domain family comes to light. Curr. Biol. 1997, 7, R674–R677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T. Juvenile hormone as a physiological regulator mediating phenotypic plasticity in pancrustaceans. Dev. Growth Differ. 2018, 61, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddiford, L.M. Juvenile hormone action: A 2007 perspective. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, T.T.; Shin, S.W.; Dou, W.; Roy, S.; Zhao, B.; Hou, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Zou, Z.; Girke, T.; Raikhel, A.S. Hairy and Groucho mediate the action of juvenile hormone receptor Methoprene-tolerant in gene repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E735–E743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Peng, H.J.; Zhu, J. Juvenile hormone-activated phospholipase C pathway enhances transcriptional activation by the methoprene-tolerant protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1871–E1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirth, C.K.; Tang, H.Y.; Makohon-Moore, S.C.; Salhadar, S.; Gokhale, R.H.; Warner, R.D.; Koyama, T.; Riddiford, L.M.; Shingleton, A.W. Juvenile hormone regulates body size and perturbs insulin signaling in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7018–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Saha, T.T.; Roy, S.; Shin, S.W.; Backman, T.W.H.; Girke, T.; White, K.P.; Raikhel, A.S. Juvenile hormone and its receptor, methoprene-tolerant, control the dynamics of mosquito gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2173–E2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, T.; Han, Y.; Huang, M.; Jiang, H.; Huang, J.; Tao, M.; Xu, R.; Xie, Q.; Su, S. Potential role of Methoprene-tolerant (Met) in methyl farnesoate-mediated vitellogenesis in the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 252, 110524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolonko, M.; Bystranowska, D.; Taube, M.; Kozak, M.; Bostock, M.; Popowicz, G.; Ożyhar, A.; Greb-Markiewicz, B. The intrinsically disordered region of GCE protein adopts a more fixed structure by interacting with the LBD of the nuclear receptor FTZ-F1. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2020, 18, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakaley, E.K.M.; Wang, H.Y.; LeBlanc, G.A. Agonist-mediated assembly of the crustacean methyl farnesoate receptor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Fu, Y.; Chen, W.; Ma, L. Identification and Evolution Analysis of the Complete Methyl Farnesoate Biosynthesis and Related Pathway Genes in the Mud Crab, Scylla paramamosain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Tuo, P.; Xu, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Zhu, D. Molecular Characterization of the Cytochrome P450 Epoxidase (CYP15) in the Swimming Crab Portunus trituberculatus and Its Putative Roles in Methyl Farnesoate Metabolism. Biol. Bull. 2022, 242, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Rivera-Perez, C.; Abdou, M.; Jia, Q.; He, Q.; Liu, X.; Zyaan, O.; Xu, J.; Bendena, W.G.; Tobe, S.S.; et al. Methyl Farnesoate Plays a Dual Role in Regulating Drosophila Metamorphosis. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Xie, X.; Tao, T.; Jiang, Q.; Shao, J.; Zhu, D. Molecular characterization of methoprene-tolerant gene (Met) in the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus: Its putative role in methyl farnesoate-mediated vitellogenin transcriptional activation. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 174, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijbels, M.; Lenaerts, C.; Broeck, J.V.; Marchal, E. Juvenile Hormone receptor Met is essential for ovarian maturation in the Desert Locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherasse, S.; Dacquin, P.; Aron, S. Mating triggers an up-regulation of vitellogenin and defensin in ant queens. J. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 205, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyota, K.; Yamane, F.; Ohira, T. Impacts of Methyl Farnesoate and 20-Hydroxyecdysone on Larval Mortality and Metamorphosis in the Kuruma Prawn Marsupenaeus japonicus. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketomi, T.; Motono, M.; Miyawaki, M. On the biological function of the mandibular gland of decapod crustacea. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 1989, 13, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Q.-J.; Fu, S.-G.; Xu, X.-J.; He, J.-T. A new and practical application of JH antagonist KK-42 to promoting growth of shrimp Penaeus schmitti. Aquaculture 2007, 270, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzner, F.; Meth, R.; Krüger, C.; Nischik, E.; Eiler, S.; Sombke, A.; Torres, G.; Harzsch, S. An atlas of larval organogenesis in the European shore crab Carcinus maenas L. (Decapoda, Brachyura, Portunidae). Front. Zool. 2018, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Ye, H.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Zeng, C. Ecdysone receptor in the mud crab Scylla paramamosain: A possible role in promoting ovarian development. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 224, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Wen, D.; He, Q.; Wang, S.; Shao, W.; Jiang, R.J.; An, S.; Sun, Y.; et al. Juvenile hormone counteracts the bHLH-PAS transcription factors MET and GCE to prevent caspase-dependent programmed cell death in Drosophila. Development 2009, 136, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z.; Yang, M.-H.; Chen, W.; Li, Q.; Cui, M.; Jiang, K.; et al. A chromosome-level genome of the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain Estampador) provides insights into the evolution of chemical and light perception in this crustacean. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 1299–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for structure building and analysis. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabo, F.; Le, D.; Fengying, Z.; Lingbo, M.; Mengdi, Z.; Dan, Z.; Manman, S.; Yan, P.; Zhenguo, Q.; Keji, J. Identification of suitable reference genes of Scylla paramamosain for gene expression profiling in various tissues and under vibrio challenge. Crustaceana 2018, 91, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar]

| PPF of Sp-Met | Docking with MF | Docking with JH III | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vina Score (kcal/mol) | Cavity Volume (Å3) | Vina Score (kcal/mol) | Cavity Volume (Å3) | |
| Wild type | −7.2 | 189 | −7.2 | 189 |
| T333A | −7.5 | 220 | −7.8 | 220 |
| L335Y | −7.6 | 633 | −7.8 | 633 |
| Y348F | −7.0 | 200 | −7.5 | 228 |
| S357V | −7.2 | 637 | −7.7 | 637 |
| Q361L | −7.7 | 574 | −8.1 | 574 |
| V374S | −7.3 | 205 | −7.6 | 488 |
| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Met-F | CTCGTCCGAAGTTTGTTGCTG | PCR |
| Met-R | GATTGCCACAGAAAGGGCAGT | PCR |
| Sp-Met-RTF | GAACTGTGACTCGGATGGGG | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-Met-RTR | GACAACCCTCACGAAGCTGA | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-Kr-h1-RTF | GGGGACAAAAGGTGAGGCAT | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-Kr-h1-RTR | TTTGTCTCTCACAGCACGCA | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-18S-RTF | GGGGTTTGCAATTGTCTCCC | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-18S-RTR | GGTGTGTACAAAGGGCAGGG | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-EcR-RTF | AGCAGCCCGGTTCTATGATG | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-EcR-RTR | TCCCAAGCCAGCAAACTCAT | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-E93-RTF | CAAGAAGCTGGTGGAGCAGA | Real time-PCR |
| Sp-E93-RTR | TTCGCCTCCTCGTCAGAAAC | Real time-PCR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Wang, W.; Jin, X.; Liu, Z.; Luo, M.; Fu, Y.; Zhan, T.; Ma, K.; Zhang, F.; Ma, L. Methoprene-Tolerant (Met) Acts as Methyl Farnesoate Receptor to Regulate Larva Metamorphosis in Mud Crab, Scylla paramamosain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312746
Zhao M, Wang W, Jin X, Liu Z, Luo M, Fu Y, Zhan T, Ma K, Zhang F, Ma L. Methoprene-Tolerant (Met) Acts as Methyl Farnesoate Receptor to Regulate Larva Metamorphosis in Mud Crab, Scylla paramamosain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312746
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ming, Wei Wang, Xin Jin, Zhiqiang Liu, Minghao Luo, Yin Fu, Tianyong Zhan, Keyi Ma, Fengying Zhang, and Lingbo Ma. 2024. "Methoprene-Tolerant (Met) Acts as Methyl Farnesoate Receptor to Regulate Larva Metamorphosis in Mud Crab, Scylla paramamosain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312746
APA StyleZhao, M., Wang, W., Jin, X., Liu, Z., Luo, M., Fu, Y., Zhan, T., Ma, K., Zhang, F., & Ma, L. (2024). Methoprene-Tolerant (Met) Acts as Methyl Farnesoate Receptor to Regulate Larva Metamorphosis in Mud Crab, Scylla paramamosain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312746






