Chemical, In Cellulo, and In Silico Characterization of the Aminocholine Analogs of VG
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Druglikeness of the Synthesized Compounds
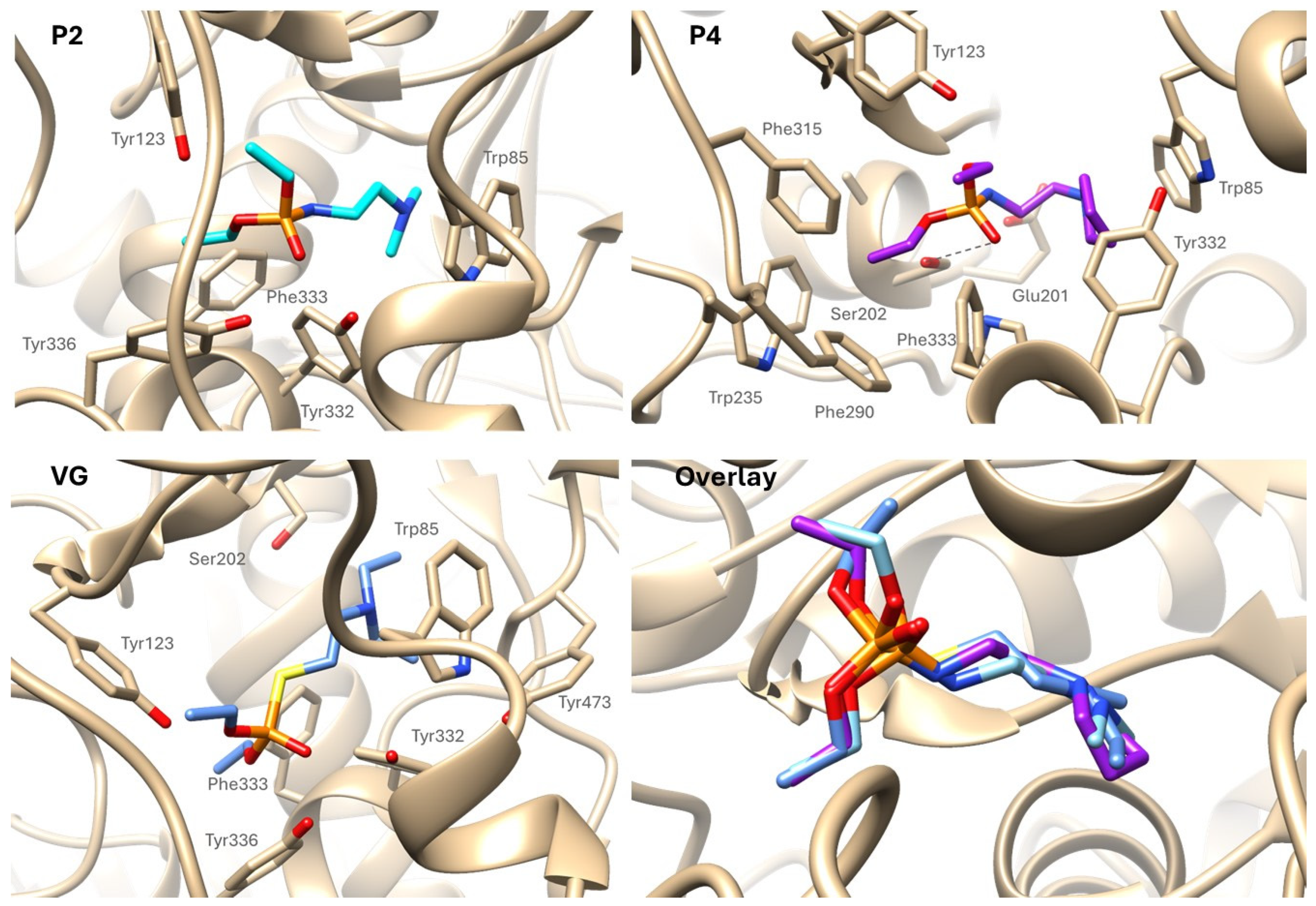
2.3. Molecular Docking
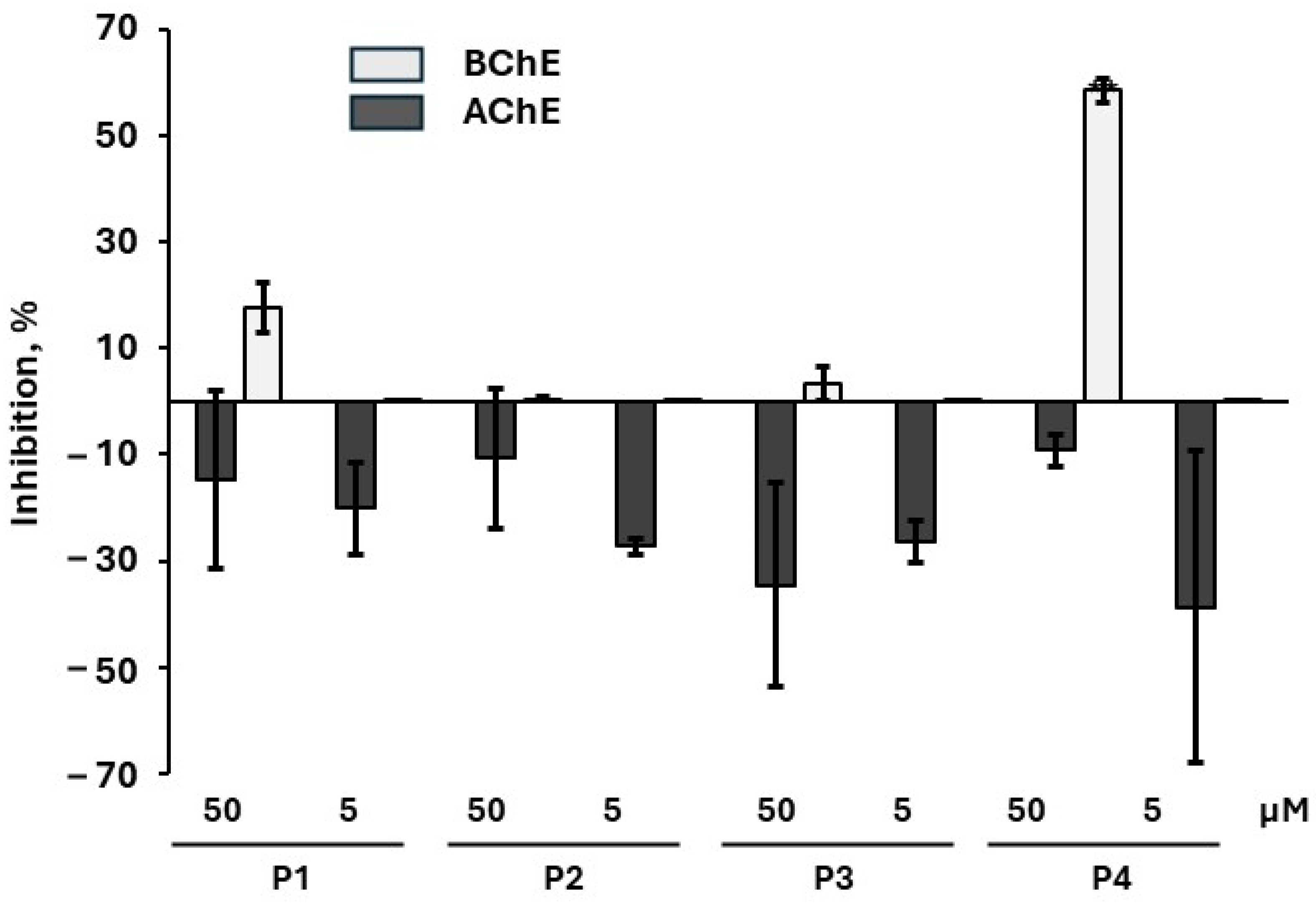
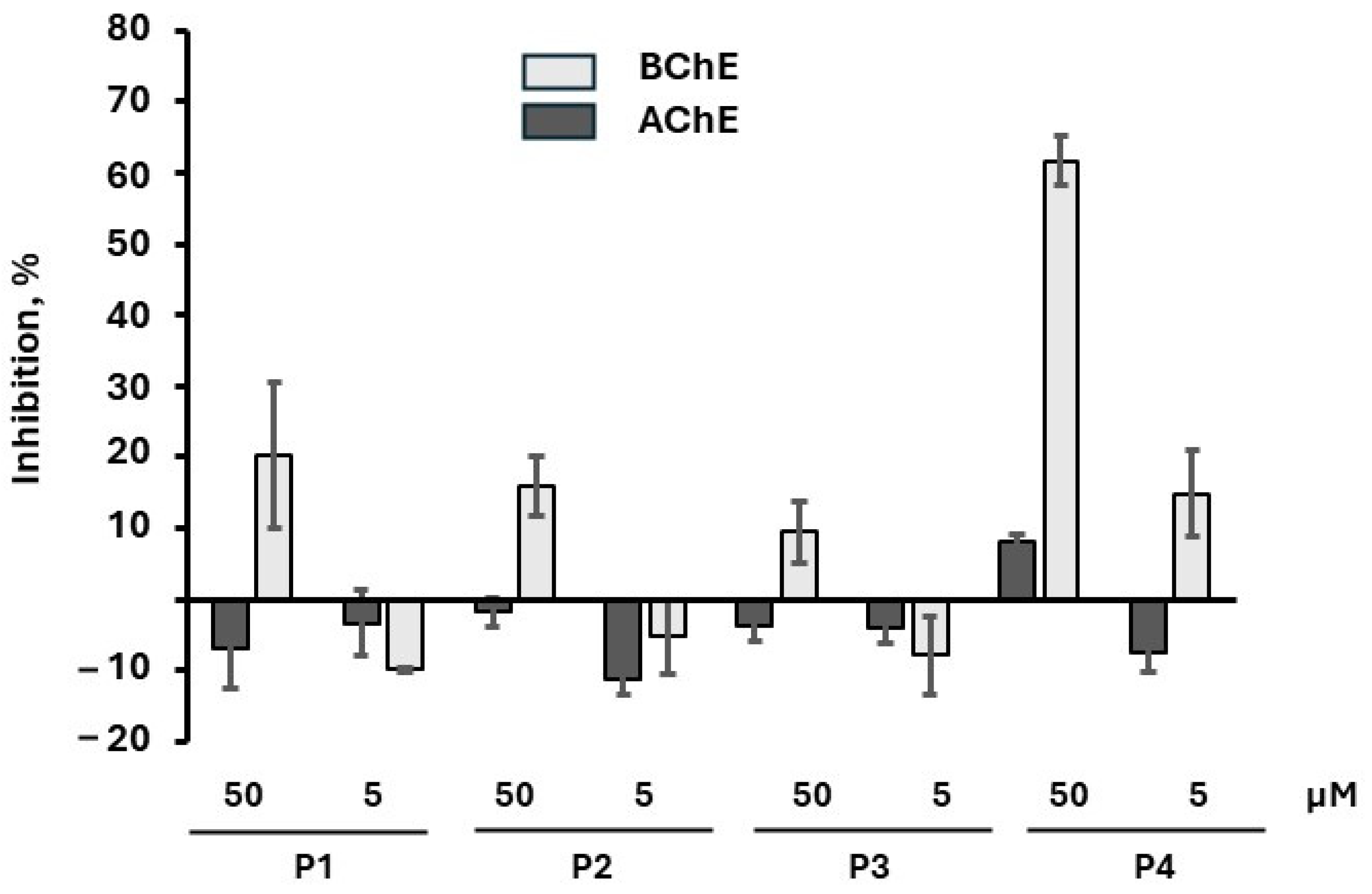
2.4. Inhibition of AChE Activity
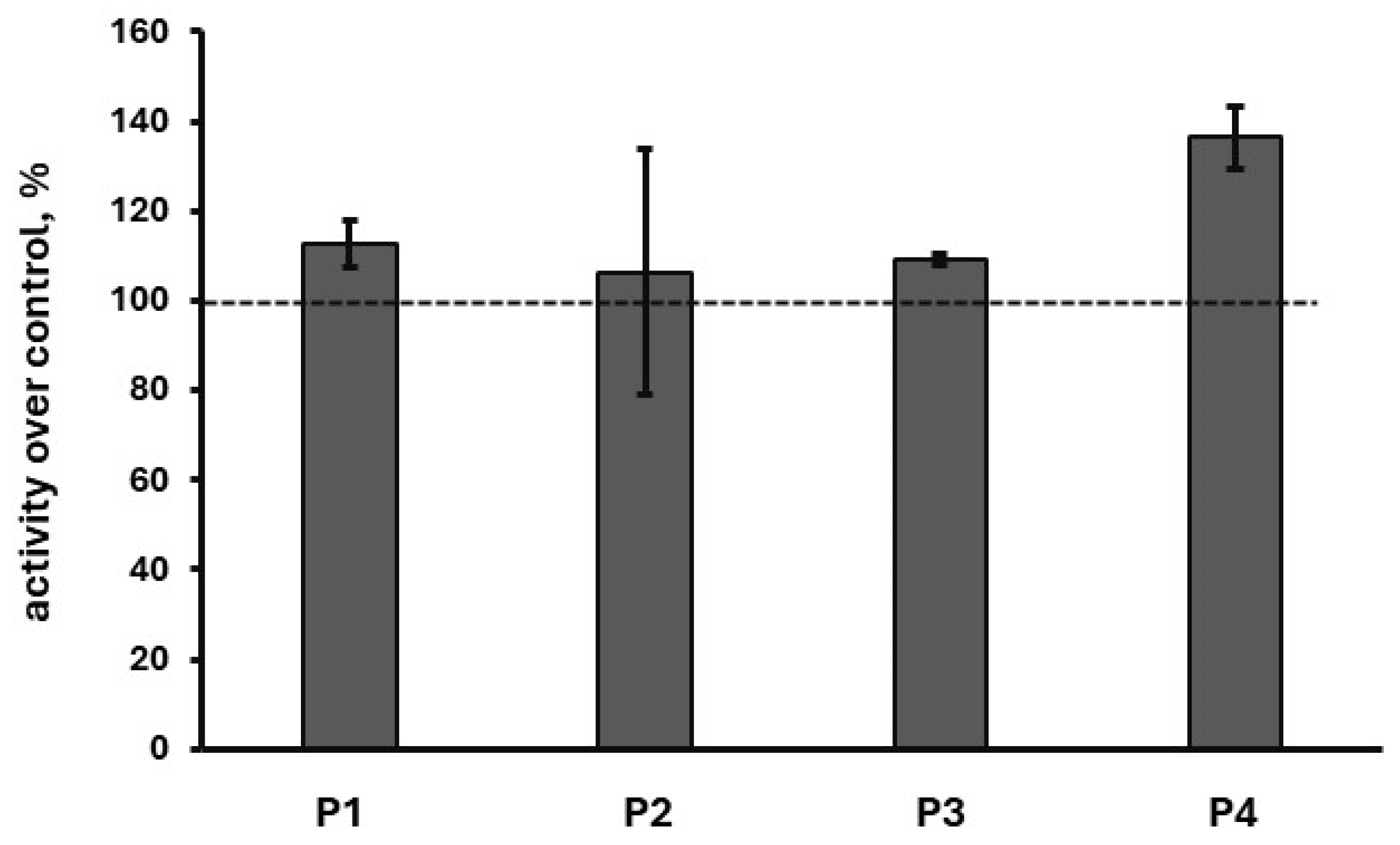
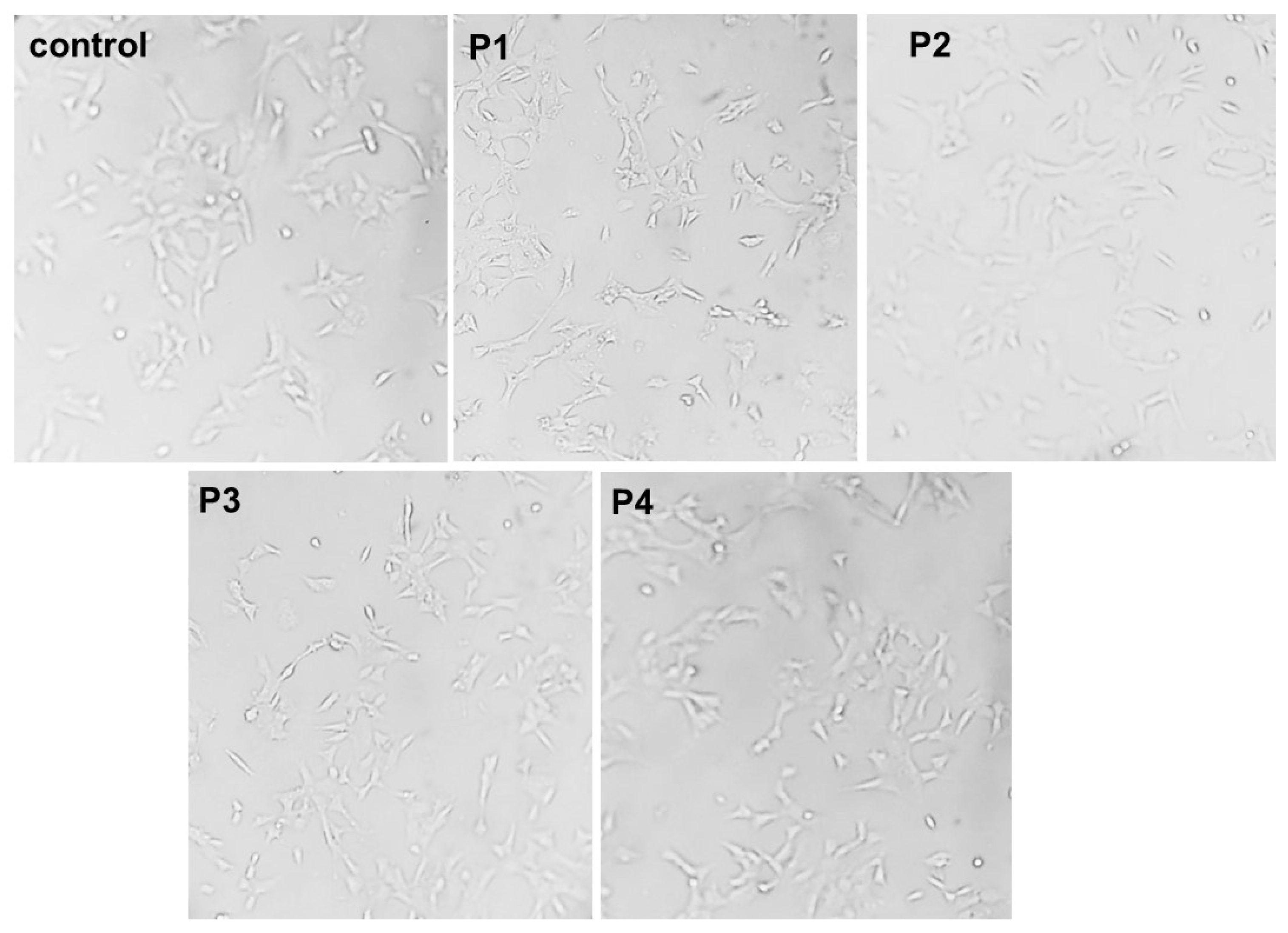
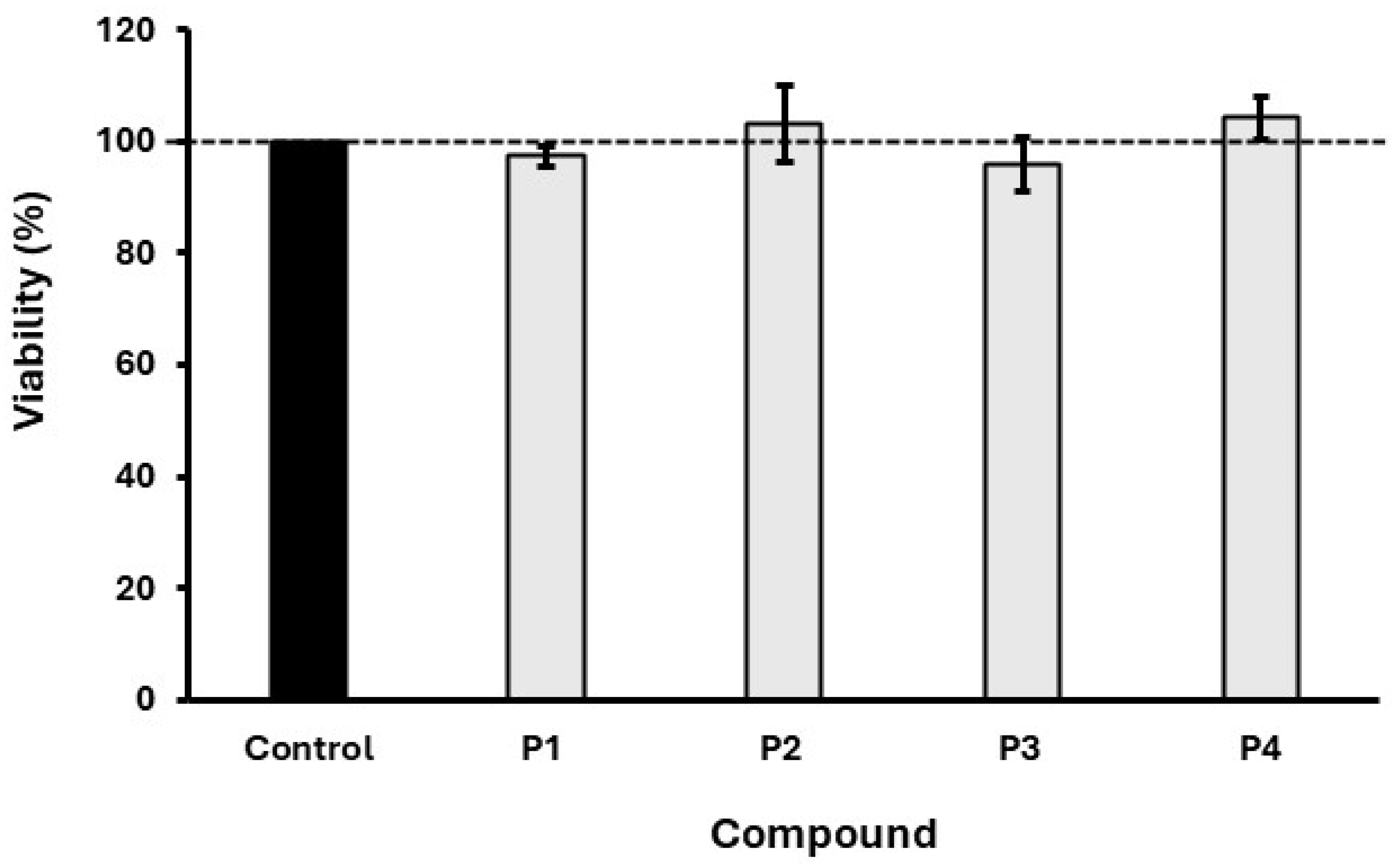
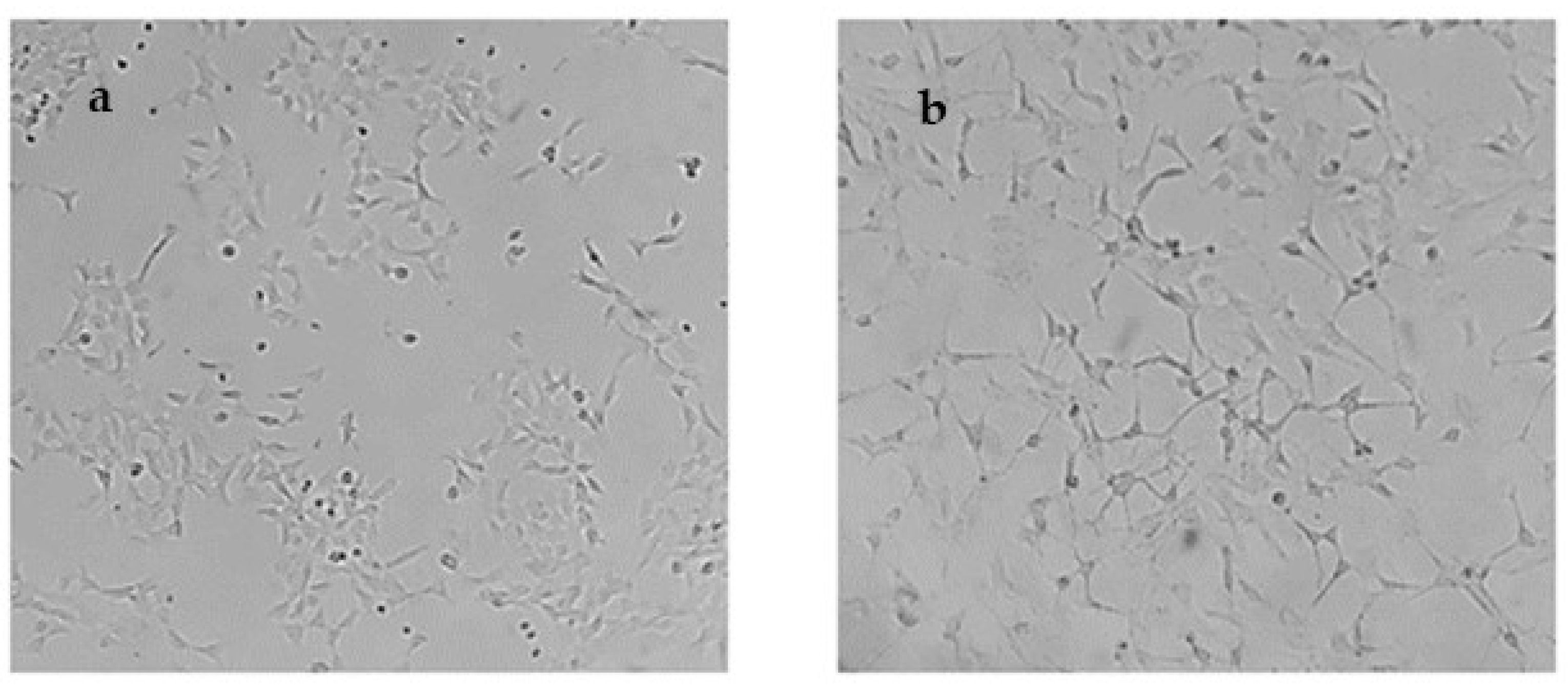
2.5. In Cellulo Assessment of the Compounds in SH-SY5Y Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. General Synthesis
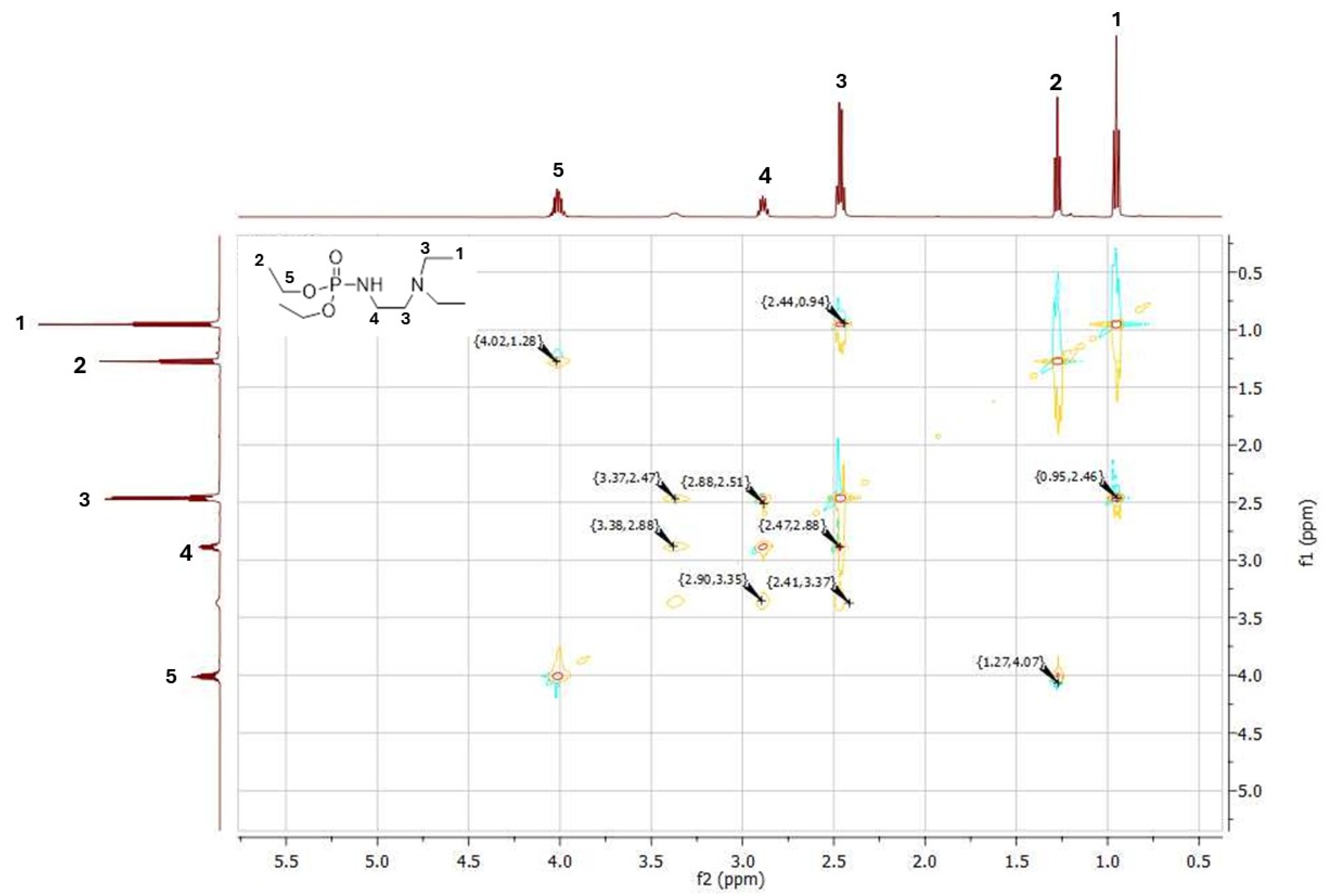
4.3. NMR Spectroscopy
4.4. Purified AChE Activity
4.5. Cell Line and Differentiation
4.6. Determination of AChE and Butyrylcholinesterase Activity in SH-SY5Y Cells
4.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4.8. In Silico Druglikeness Prediction
4.9. Experimental Protocol for Molecular Docking
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pampalakis, G.; Kostoudi, S. Chemical, physical, and toxicological properties of V-agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroniadou-Anderjaska, V.; Apland, J.P.; Figueiredo, T.H.; De Araujo Furtado, M.; Braga, M.F. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (nerve agents) as weapons of mass destruction: History, mechanism of action, and medical countermeasures. Neuropharmacology 2020, 181, 108298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerfeldt, S.; Fagerlind, L. Selenophosphorus compounds as powerful cholinesterase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 1967, 10, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquilonius, S.M.; Fredriksson, T.; Sundwall, A. Studies on phosphorylated thiocholine and choline derivatives I. General toxicology and pharmacology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1964, 6, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajgar, J. Chapter 4: Organophosphates and nerve agents. In Nerve Agents Poisoning and Its Treatment in Schematic Figures and Tables; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Vayron, P.; Renard, P.Y.; Taran, F.; Créminon, C.; Frobert, Y.; Grassi, J.; Mioskowski, C. Toward antibody-catalyzed hydrolysis of organophosphorus poisons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7058–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Mulay, S.V.; Kim, Y.; Jorayev, P.; Churchill, D.G. Nerve agent simulant diethyl chlorophosphate detection using a cyclization reaction approach with high stokes shift system. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Manna, A.; Paul, S. Rapid ‘naked eye’ response of DCP, a nerve agent simulant: From molecules to low-cost devices for both liquid and vapour phase detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 21984–21988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, S.; Jukič, M.; Bren, U. Molecular filters in medicinal chemistry. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muegge, I.; Heald, S.L.; Brittelli, D. Simple selection criteria for drug-like chemical matter. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMENT properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W5–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasteel, E.E.J.; Nijmeijer, S.M.; Darney, K.; Lautz, L.S.; Dorne, J.L.C.M.; Kramer, N.I.; Westerink, R.H.S. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in electric eel and human donor blood: An in vitro approach to investigate interspecies differences and human variability in toxicodynamics. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 4055–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, S.F.A.; Kitagawa, D.A.S.; Rodrigues, R.B.; Bernardo, L.B.; da Silva, T.N.; dos Santos, W.V.; Correa, A.B.A.; de Almeida, J.S.F.D.; França, T.C.C.; Kuča, K.; et al. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of neutral aryloximes as reactivators of Electrophorus eel acetylcholinesterase inhibited by NEMP, a VX surrogate. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 309, 108682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Singh, R.; Shivhare, S.; Divya; Kumar, D.; Gutti, G.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.K. Improved machine learning scoring functions for identification of Electrophorus electricus’s acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Mol. Divers. 2022, 26, 1455–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, U. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkrabkova, L.; Muckova, L.; Hrabinova, M.; Sorf, A.; Kobrlova, T.; Jost, P.; Bezdekova, D.; Korabecny, J.; Jun, D.; Soukup, O. Differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells as a model for evaluation of nerve agent-associated neurotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalevich, J.; Langford, D. Considerations for the use of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells in neurobiology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1078, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, D.G.; Beckloff, G.N. Pharmacology of two tetracovalent organophosphorus compounds and their optical isomers. J. Med. Pharm. Chem. 1959, 1, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Huchthausen, J.; Schlichting, R.; Scholz, S.; Henneberger, L.; Escher, B.I. Validation of an SH-SY5Y cell-based acetylcholinesterase inhibition assay for water quality assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 3046–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Suarez, L.; Awabdh, S.A.; Coumoul, X.; Chauvet, C. The SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line, a relevant in vitro cell model for investigating neurotoxicology in human: Focus on organic pollutants. Neurotoxicology 2022, 92, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoff, M.A.; Unger, C.C.; Bützer, P.; Metzulat, M.; Klapötke, T.M.; Karaghiosoff, K.L. Bioactivity and toxicological study of Amiton and related isomers. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2019, 194, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, N.H.; Utsuki, T.; Ingram, D.K.; Wagn, Y.; Pepeu, G.; Scali, C.; Yu, O.S.; Mamczarz, J.; Holloway, H.W.; Giordano, T.; et al. Selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibition elevates brain acetylcholine, augments learning and lowers Azlheimer β-amyloid peptide in rodent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17213–17218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerschmidt, F.; Hanbauer, M. Transformation of arylmethylamines into α-aminophosphonic acids via metalated phosphoramidates: Rearrangement of partly configurationally stable N-phosphorylated α-aminocarbanions. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 6121–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohanka, M.; Hrabinova, M.; Kuca, K.; Simonato, J.P. Assessment of acetylcholinesterase activity using indoxylacetate and comparison with the standard Ellman’s method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2631–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chainoglou, E.; Siskos, A.; Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Hybridization of curcumin analogues with cinnamic acid derivatives as multi-target agents against Alzheimer’s disease target. Molecules 2020, 25, 4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liargkova, T.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Koukoulitsa, C.; Voulgari, E.; Avgoustakis, C. Simple chalcones and bis-chalcones ethers as possible pleiotropic agents. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.M.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Prot. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W174–W181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachon, F.; Carletti, E.; Ronco, C.; Trovaslet, M.; Nicolet, Y.; Jean, L.; Renard, P.Y. Crystal structures of human cholinesterases in complex with huprine W and tacrine: Elements of specificity for anti-Alzheimer’s drugs targeting acetyl- and butyryl-cholinesterase. Biochem. J. 2013, 453, 393–399. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterases in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, J.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.; Simmerling, C. Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.; Case, D. ANTECHAMBER: An accessory software package for molecular mechanical calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2000, 222, U403. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, R.; Villarreal, M.A. Vinardo: A Scoring Function Based on AutodockVina Improves Scoring, Docking, and Virtual Screening. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, D.; Baumgartner, M.; Camacho, C. Lessons Learned in Empirical Scoring with smina from the CSAR 2011 Benchmarking Exercise. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, J.L.; Rizzuti, B.; Jiménez-Alesanco, A.; Abián, O.; Velázquez-Campoy, A.; Iovanna, J.L. The paralogue of the intrinsically disordered nuclear protein 1 has a nuclear localization sequence that binds to human importin α3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhiuzzi, M.A.; Ioele, G.; De Luca, M.; Rizzuti, B.; Scordamaglia, D.; Lappano, R.; Maggiolini, M.; Garofalo, A.; Grande, F. Dissecting CYP1A2 activation by arylalkanoic acid prodrugs toward the development of anti-inflammatory agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chainoglou, E.; Siskos, A.; Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Hybridization of curcumin analogues with cinnamic acid derivatives as multi-target agents against Alzheimer’s disease targets. Molecules 2020, 25, 4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lensink, M.F.; Mendez, R.; Wodak, S.J. Docking and scoring protein complexes: CAPRI 3rd edition. Proteins 2007, 69, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostoudi, S.; Iatridis, N.; Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Pampalakis, G. Synthesis and biological evaluation of V-type nerve agent mimics. In Proceedings of the 23rd Panhellenic Chemistry Conference, Athens, Greece., 25–28 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kostoudi, S.; Angelis, G.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Pampalakis, G. Design, synthesis of a new class of organophosphate acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for pharmacological applications. In Proceedings of the 19th Hellenic Symposium on Medicinal Chemistry (HSMC-19), Patras, Greece, 9–11 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
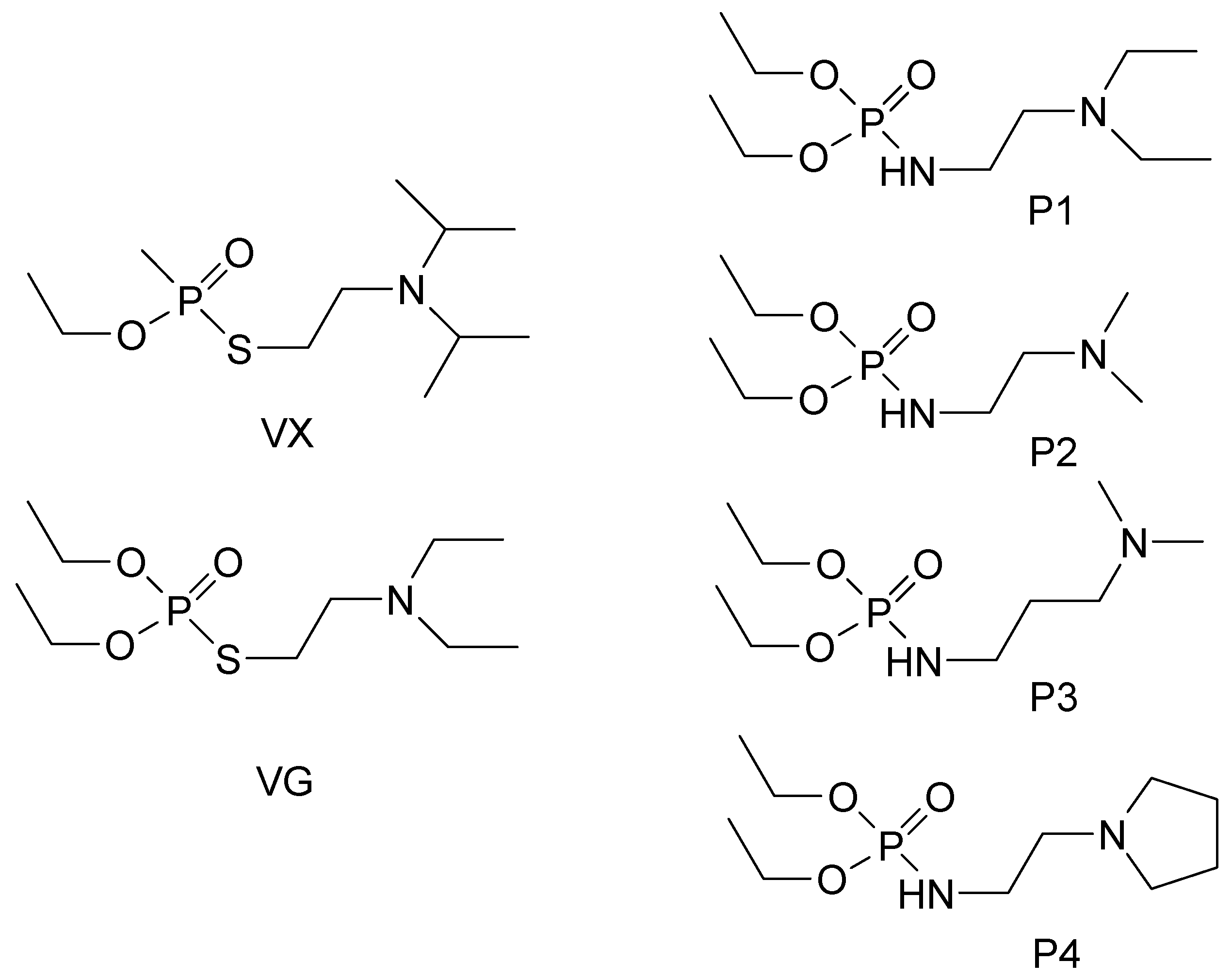
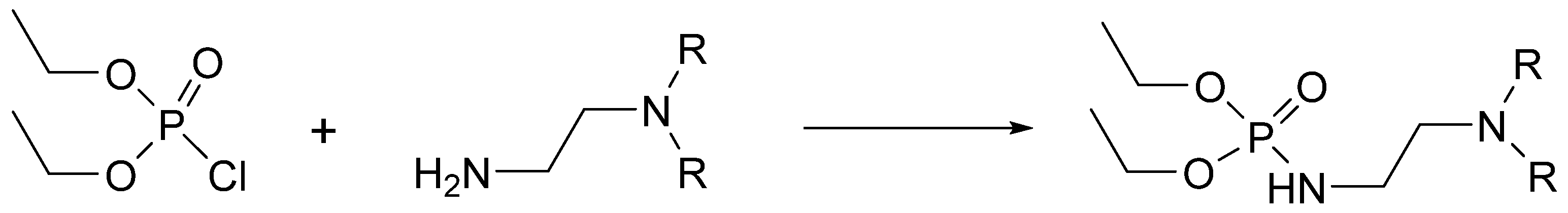
| Compound P1 | Compound P2 | Compound P3 | Compound P4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADMET lab2 | Swiss ADME | pkCSM | ADMET lab2 | Swiss ADME | pkCSM | ADMET lab2 | Swiss ADME | pkCSM | ADMET lab2 | Swiss ADME | pkCSM | |
| H-acceptor | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| H-donors | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Rotatable bonds | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Fraction sp3 (sp3 hybridized C/total C) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||
| Van der Waals volume | 249.708 | 215.116 | 232.412 | 241.151 | ||||||||
| TPSA | 50.8 | 60.61 | 99.080 | 50.8 | 60.61 | 86.350 | 50.8 | 60.61 | 92.715 | 50.8 | 60.61 | 98.074 |
| Molecular refractivity (MR) | 66.72 | 57.10 | 61.91 | 68.52 | ||||||||
| LogPo/w | 0.51 | 1.35 | 2.0989 | −0.318 | 0.71 | 1.3187 | −0.089 | 1.05 | 1.7088 | 0.137 | 1.10 | 1.8529 |
| LogD (LogPo/w at pH 7.4) | 0.052 | −0.619 | −0.782 | 0.188 | ||||||||
| LogS (mol·L−1) (solubility) | 0.42 | −1.21 −1.59 −2.75 | −1.903 | 0.856 | −0.71 −0.83 −1.94 | −1.372 | 0.841 | −0.96 −1.21 −2.35 | −1.22 | 0.429 | −1.18 −1.34 −2.27 | −2.062 |
| Blood–brain barrier penetration | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
| Gastrointestinal penetration | High | High | High | High | ||||||||
| Caco-2 permeability (cm∙s−1) * | −4.646 | −5.273 | −5.331 | −4.935 | ||||||||
| Skin penetration (cm∙s−1) | 7.31 | 6.79 ** | −7.66 | 6.89 | −7.49 | 6.82 | −7.47 | 6.88 | ||||
| Fu (%) | 87.794 | 90.969 | 91.329 | 88.762 | ||||||||
| VD (L kg−1) | 0.813 | 1.151 | 1.268 | 0.960 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostoudi, S.; Iatridis, N.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Pontiki, E.; Pampalakis, G. Chemical, In Cellulo, and In Silico Characterization of the Aminocholine Analogs of VG. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312656
Kostoudi S, Iatridis N, Hadjipavlou-Litina D, Pontiki E, Pampalakis G. Chemical, In Cellulo, and In Silico Characterization of the Aminocholine Analogs of VG. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312656
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostoudi, Stavroula, Nikolaos Iatridis, Dimitra Hadjipavlou-Litina, Eleni Pontiki, and Georgios Pampalakis. 2024. "Chemical, In Cellulo, and In Silico Characterization of the Aminocholine Analogs of VG" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312656
APA StyleKostoudi, S., Iatridis, N., Hadjipavlou-Litina, D., Pontiki, E., & Pampalakis, G. (2024). Chemical, In Cellulo, and In Silico Characterization of the Aminocholine Analogs of VG. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312656






