PPIA-coExp: Discovering Context-Specific Biomarkers Based on Protein–Protein Interactions, Co-Expression Networks, and Expression Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Performance Evaluation of PPIA-coExp in ENCODE and TCGA-BRCA Database
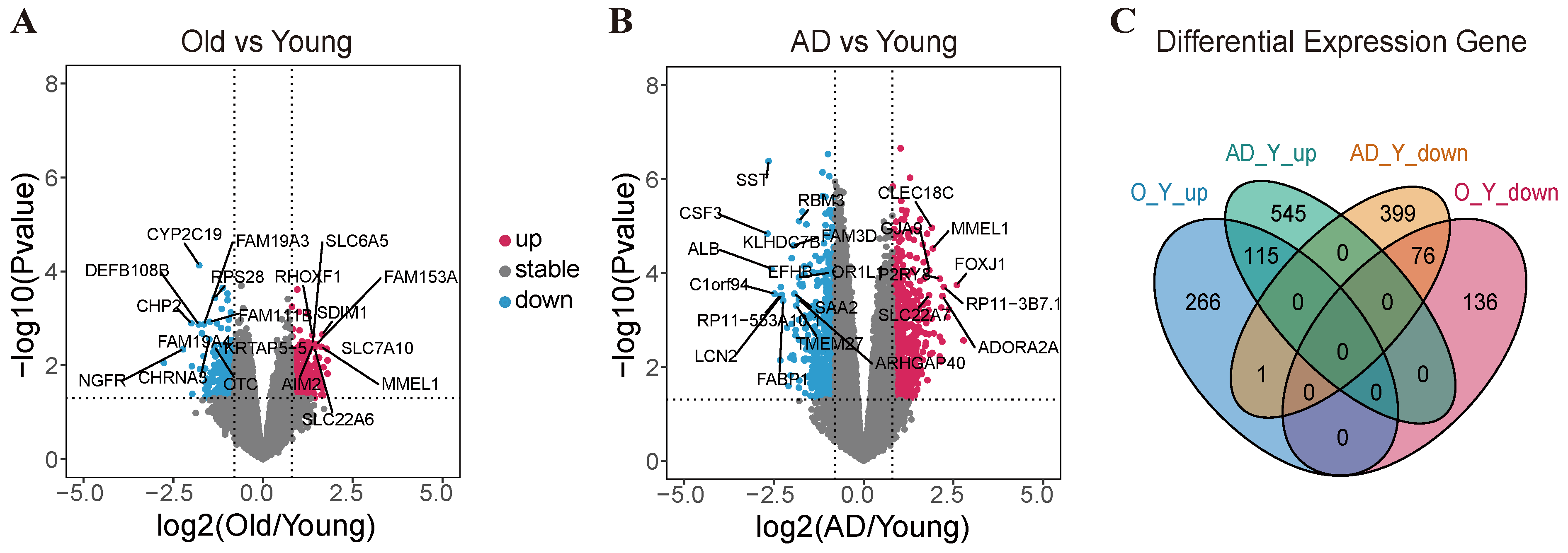
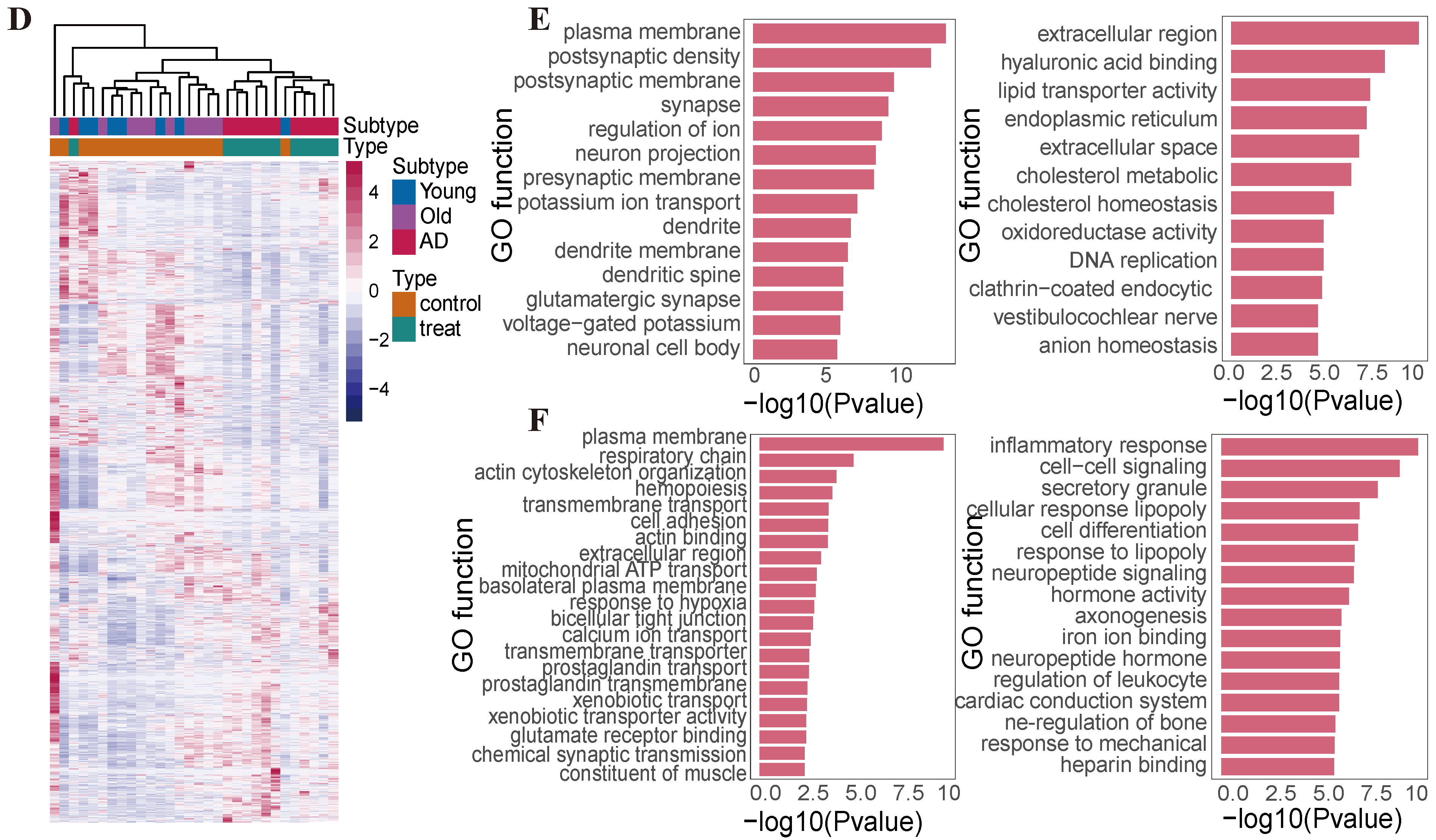
2.2. Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals the Differentially Expressed Genes Between Human Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease
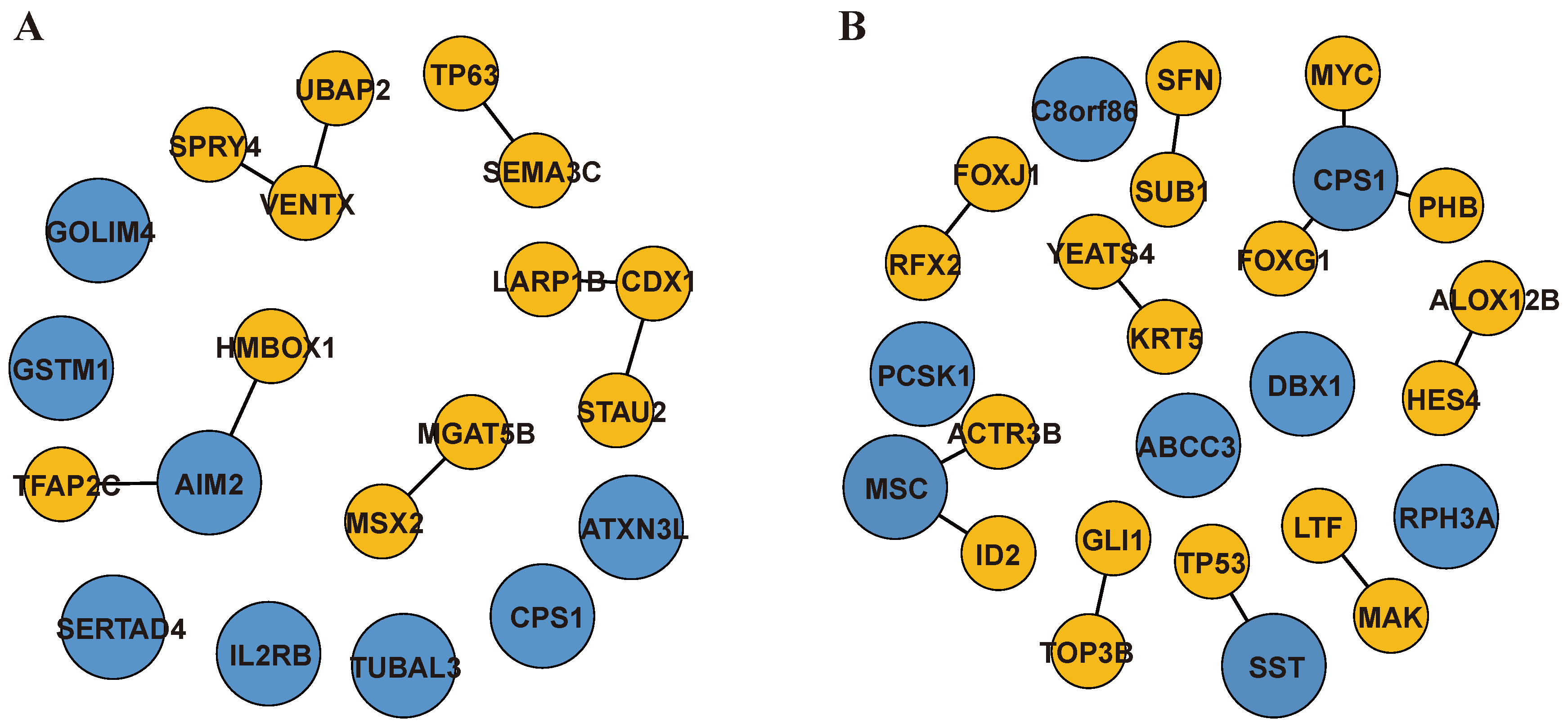
2.3. Genome-Wide Optimization Model for TF-Biomarkers and DEG-Biomarkers Identification
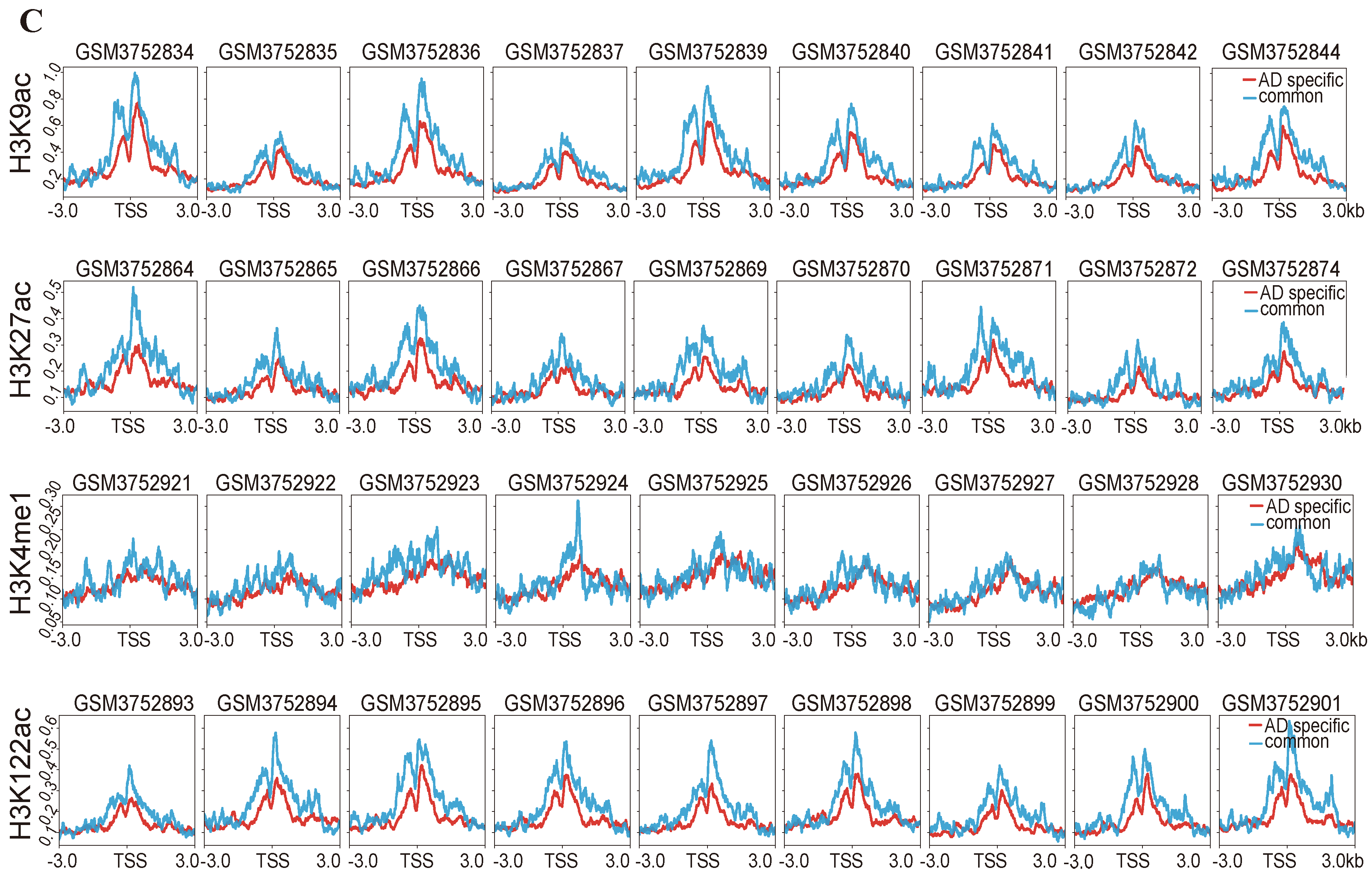
2.4. Difference in Histone Modification Distribution in the Younger, Old, and AD Groups
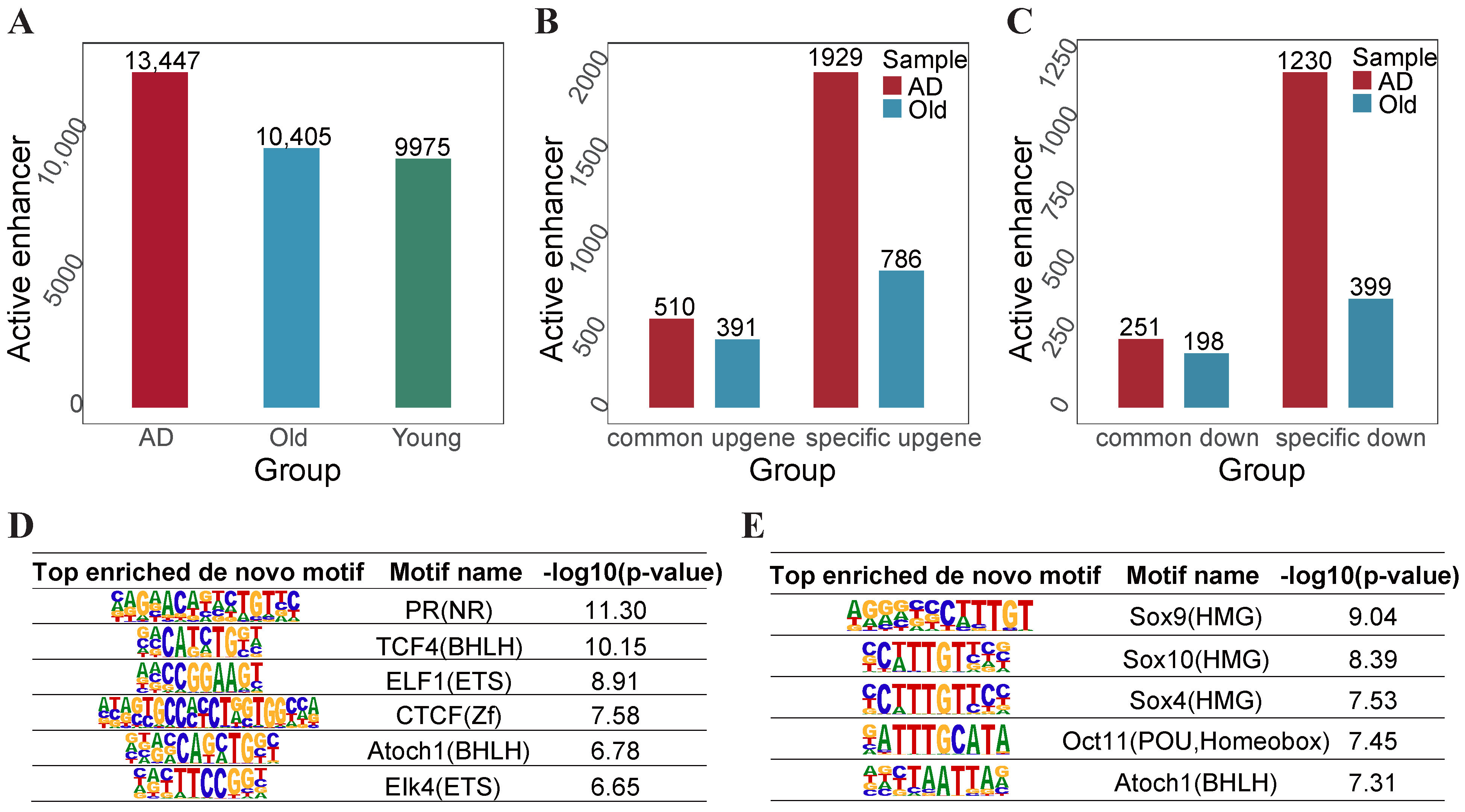
2.5. AD-Specific and Old-Specific Active Enhancers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
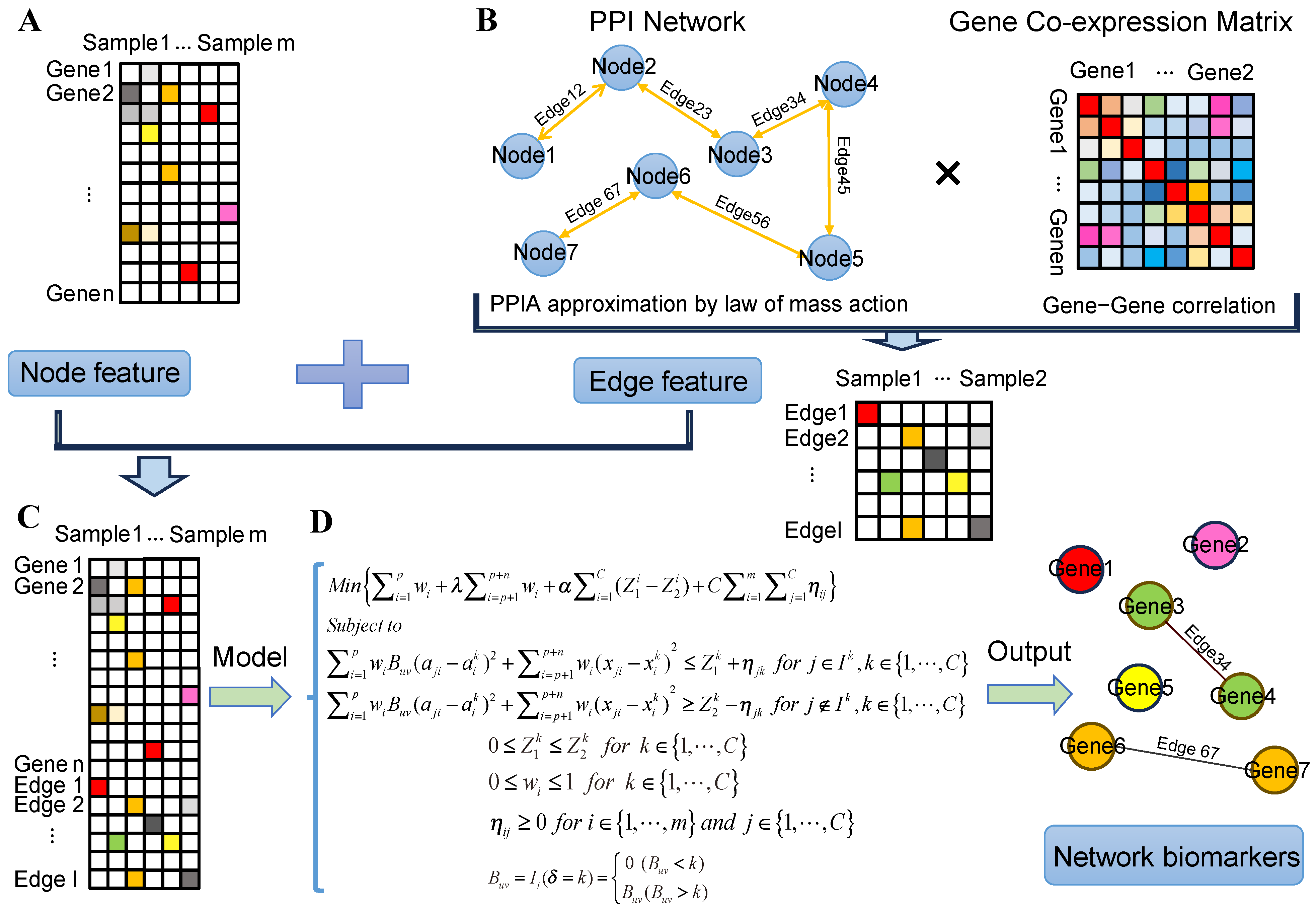
4.1. Estimating the Protein–Protein Interaction Affinity by the Law of Mass Action
4.2. Construct Context-Specific Gene Co-Expression Networks
4.3. Overview of the PPIA-coExp
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
4.5. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
4.6. Differentially Expressed Genes and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.7. The Histone Modification Levels Flanking the Transcription Start Site (TSS)
4.8. Enhancer Annotation and Motif Enrichment
4.9. Hierarchical Clustering
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPIA-coExp | protein–protein interaction affinity–co-expression network |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| PPIA | protein–protein interaction affinity |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| PCC | Pearson correlation coefficient |
| BioGRID | Biological General Repository for Interaction Datasets |
| Sensitivity | |
| Specificity | |
| Accuracy | |
| RNA-Seq | RNA sequencing |
| TPM | transcripts per million |
| GSEA | gene set enrichment analysis |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| HMs | histone modifications |
| TSS | transcription start site |
| TFs | transcription factors |
References
- Hirata, T.; Arai, Y.; Yuasa, S.; Abe, Y.; Takayama, M.; Sasaki, T.; Kunitomi, A.; Inagaki, H.; Endo, M.; Morinaga, J.; et al. Associations of cardiovascular biomarkers and plasma albumin with exceptional survival to the highest ages. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaman, Y.A.R.; Embaye, K.S.; Huang, F.; Li, L.; Zhu, F.; Wang, J.-Z.; Liu, R.; Feng, J.; Wang, X. Biomarkers used in Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 74, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Mohan, A.; Guleria, R. Biomarkers in cancer screening, research and detection: Present and future: A review. Biomarkers 2006, 11, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hédou, J.; Marić, I.; Bellan, G.; Einhaus, J.; Gaudillière, D.K.; Ladant, F.-X.; Verdonk, F.; Stelzer, I.; Feyaerts, D.; Tsai, A.; et al. Stabl: Sparse and reliable biomarker discovery in predictive modeling of high-dimensional omic data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paplomatas, P.; Krokidis, M.G.; Vlamos, P.; Vrahatis, A.G. An ensemble feature selection approach for analysis and modeling of transcriptome data in Alzheimer’s disease. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lin, J.; Zack, D.J.; Qian, J. Computational analysis of tissue-specific combinatorial gene regulation: Predicting interaction between transcription factors in human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4925–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.-S.; Jin, Q. ellipsoidFN: A tool for identifying a heterogeneous set of cancer biomarkers based on gene expressions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Z.-Y. An integrative framework for protein interaction network and methylation data to discover epigenetic modules. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L. EdgeMarker: Identifying differentially correlated molecule pairs as edge-biomarkers. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 362, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, S.; Vosa, U.; van der Graaf, A.; Franke, L.; de Magalhaes, J.P. Gene co-expression analysis for functional classification and gene-disease predictions. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Gao, C.; Duren, Z.; Wang, Y. GuidingNet: Revealing transcriptional cofactor and predicting binding for DNA methyltransferase by network regularization. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Kim, Y.; Gewirtz, A.D.H.; Jo, B.; Gao, C.; McDowell, I.C.; Engelhardt, B.; Battle, A. Co-expression networks reveal the tissue-specific regulation of transcription and splicing. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1843–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eimer, W.A.; Kumar, D.K.V.; Shanmugam, N.K.N.; Rodriguez, A.S.; Mitchell, T.; Washicosky, K.J.; György, B.; Breakefield, X.; Tanzi, R.; Moir, R.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease-associated β-amyloid is rapidly seeded by herpesviridae to protect against brain infection. Neuron 2018, 99, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, R.; Zeisel, J.; Bennett, K. World Alzheimer Report 2020. Available online: https://www.alzint.org/resource/world-alzheimer-report-2020/ (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Tellechea, P.; Pujol, N.; Esteve-Belloch, P.; Echeveste, B.; García-Eulate, M.R.; Arbizu, J.; Riverol, M. Early- and late-onset Alzheimer disease: Are they the same entity? Neurol. (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 33, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Kong, J.; Hu, P. Computational drug repurposing for Alzheimer’s disease using risk genes from GWAS and single-cell RNA sequencing studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 617537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seath, P.; Macedo-Orrego, L.E.; Velayudhan, L. Clinical characteristics of early-onset versus late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Shah, P.P.; Nativio, R.; Berger, S.L. Epigenetic mechanisms of longevity and aging. Cell 2016, 166, 822–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Teschendorff, A.E. Epigenetic and genetic deregulation in cancer target distinct signaling pathway domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klein, H.-U.; McCabe, C.; Gjoneska, E.; Sullivan, S.E.; Kaskow, B.J.; Tang, A.; Smith, R.; Xu, J.; Pfenning, A.; Bernstein, B.; et al. Epigenome-wide study uncovers large-scale changes in histone acetylation driven by tau pathology in the aging and Alzheimer human brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Y.; Bai, H. M6A RNA methylation modification and tumor immune microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 9, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-Q.; Hao, Y.-D.; La, T.; Li, Q.-Z. Inferring the Functional Effect of Gene-body H3K79me2 Signals in Normal Samples on Gene Expression Changes: A Potential Susceptibility Marker in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Curr. Bioinform. 2023, 18, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chomiak, A.A.; Hong, Y.; Lowe, C.C.; Kopsidas, C.A.; Chan, W.-C.; Andrade, J.; Pan, H.; Zhou, X.; Monuki, E.S.; et al. Histone H2A ubiquitination resulting from Brap loss of function connects multiple aging hallmarks and accelerates neurodegeneration. iScience 2022, 25, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Stetson, L.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Models of epigenetic age capture patterns of DNA methylation in glioma associated with molecular subtype, survival, and recurrence. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nativio, R.; Donahue, G.; Berson, A.; Lan, Y.; Amlie-Wolf, A.; Tuzer, F.; Toledo, J.; Gosai, S.; Gregory, B.; Torres, C.; et al. Dysregulation of the epigenetic landscape of normal aging in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, S. BCseq: Accurate single cell RNA-seq quantification with bias correction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zhang, P.-J.; Wen, X.-Y.; Chen, L.; Tian, Y.-P.; Wang, Y. A novel mixed integer programming for multi-biomarker panel identification by distinguishing malignant from benign colorectal tumors. Methods 2015, 83, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Mu, H.; Zhao, H. HMBOX1, a member of the homeobox family: Current research progress. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 48, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchanathan, R.; Ramalingam, V.; Liu, H.; Choubey, D. Human prostate epithelial cells activate the AIM2 inflammasome upon cellular senescence: Role of POP3 protein in aging-related prostatic inflammation. Life 2021, 11, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, S.-F.; Yun, Q.; Liu, W.-J.; Zhai, H.-R.; Shi, H.-Z.; Xie, L.-G.; Qian, J.-J.; Zhao, C.-J.; Zhang, W.-N. FOXG1 as a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease with a particular focus on cell cycle regulation. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 86, 1255–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.; Somvanshi, R.K.; Kumar, U. Somatostatin Maintains Permeability and Integrity of Blood-Brain Barrier in β-Amyloid Induced Toxicity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, F.; Dündar, F.; Diehl, S.; Grüning, B.A.; Manke, T. deepTools: A flexible platform for exploring deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W187–W191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.-W.; Zhao, F.; Qian, X.-Y.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Zhao, J.; Su, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.; Miao, J.; et al. Identification of a small molecule preventing BMSC senescence in vitro by improving intracellular homeostasis via ANXA7 and Hmbox1. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 56722–56730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Seo, J.S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Ha, K.-T.; Choi, B.T.; Shin, Y.-I.; Yun, Y.J.; Shin, H.K. AIM2 inflammasome contributes to brain injury and chronic post-stroke cognitive impairment in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.; Yan, B.Q.; Wang, H.; Negm, L.; Sackmann, C.; Verkuyl, C.; Rezai-Stevens, V.; Eid, S.; Vediya, N.; Sato, C.; et al. Somatostatin slows Aβ plaque deposition in aged APP NL-F/NL-F mice by blocking Aβ aggregation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Wang, L.; Hu, P.; Hu, L. Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions Using Sequence and Network Information via Variational Graph Autoencoder. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2023, 20, 3182–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waage, P.; Gulberg, C.M. Studies concerning affinity. J. Chem. Educ. 1986, 63, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, C.; Rube, H.T.; Kribelbauer, J.F.; Crocker, J.; Loker, R.E.; Martini, G.D.; Laptenko, O.; Freed-Pastor, W.; Prives, C.; Stern, D.; et al. Accurate and sensitive quantification of protein-DNA binding affinity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3692–E3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traxler, L.; Herdy, J.R.; Stefanoni, D.; Eichhorner, S.; Pelucchi, S.; Szücs, A.; Santagostino, A.; Kim, Y.; Agarwal, R.; Schlachetzki, J.; et al. Warburg-like metabolic transformation underlies neuronal degeneration in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1248–1263.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Han, Z.; Wang, T.; Shao, W.; Xiang, S.; Salama, P.; Rizkalla, M.; Huang, K.; Zhang, J. TSUNAMI: Translational Bioinformatics Tool Suite for Network Analysis and Mining. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Meyer, C.A.; Eeckhoute, J.; Johnson, D.S.; Bernstein, B.E.; Nusbaum, C.; Myers, R.; Brown, M.; Li, W.; et al. Model-based Analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; He, Q.-Y. ChIPseeker: An R/Bioconductor package for ChIP peak annotation, comparison and visualization. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2382–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
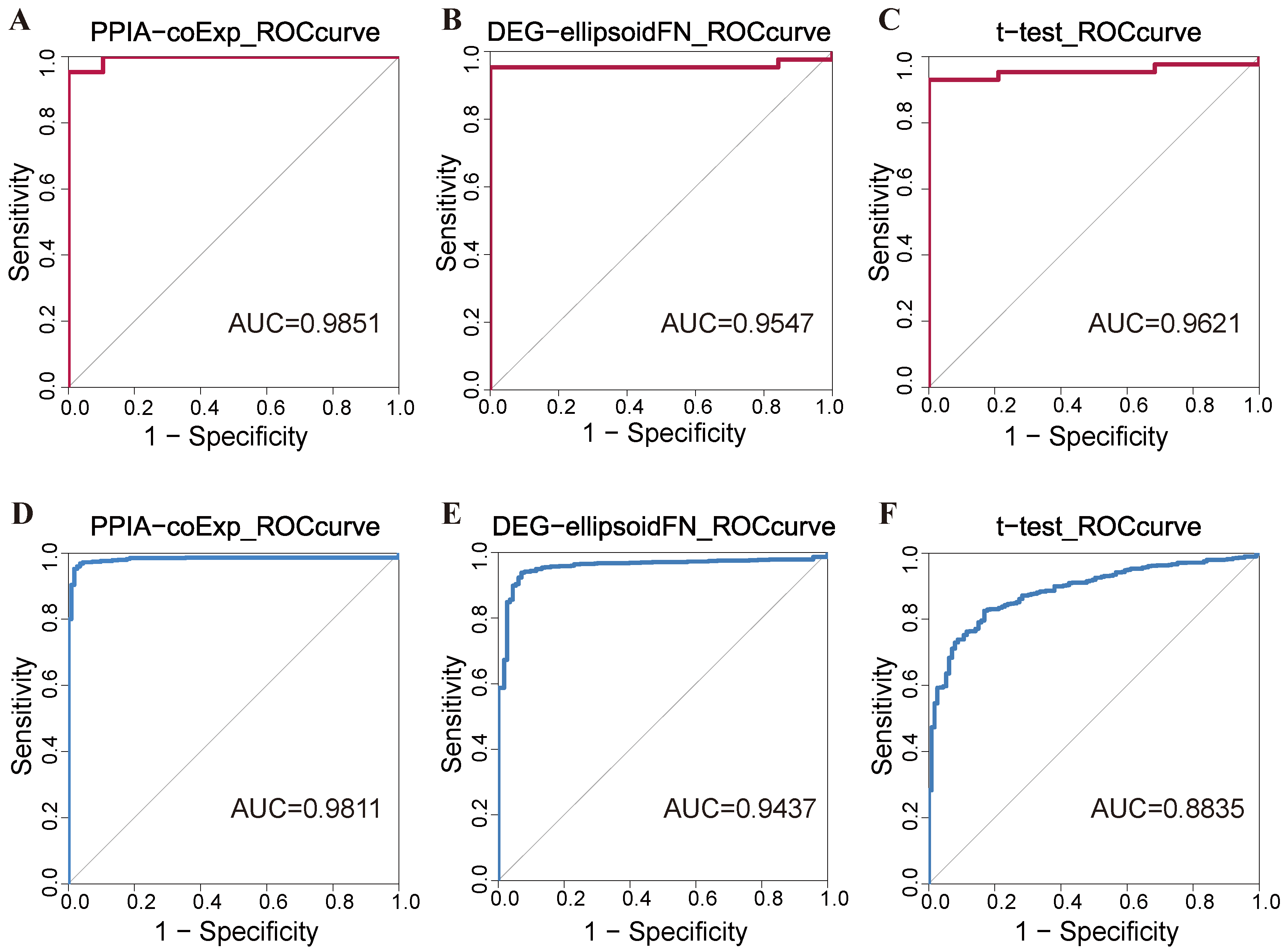

| Model | Sn | Sp | ACC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene-node | 0.7895 | 0.9535 | 0.9032 | 0.9547 |
| t-test | 0.8947 | 0.9302 | 0.9194 | 0.9621 |
| PPIA-coExp | 0.9474 | 0.9535 | 0.9516 | 0.9851 |
| Model | Sn | Sp | ACC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene-node | 0.9027 | 0.9425 | 0.9326 | 0.9437 |
| t-test | 0.4124 | 0.9737 | 0.8765 | 0.8835 |
| PPIA-coExp | 0.8850 | 0.9762 | 0.9650 | 0.9811 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, D.; Fan, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y. PPIA-coExp: Discovering Context-Specific Biomarkers Based on Protein–Protein Interactions, Co-Expression Networks, and Expression Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312608
Yan D, Fan Z, Li Q, Chen Y. PPIA-coExp: Discovering Context-Specific Biomarkers Based on Protein–Protein Interactions, Co-Expression Networks, and Expression Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312608
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Dongsheng, Zhiyu Fan, Qianzhong Li, and Yingli Chen. 2024. "PPIA-coExp: Discovering Context-Specific Biomarkers Based on Protein–Protein Interactions, Co-Expression Networks, and Expression Data" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312608
APA StyleYan, D., Fan, Z., Li, Q., & Chen, Y. (2024). PPIA-coExp: Discovering Context-Specific Biomarkers Based on Protein–Protein Interactions, Co-Expression Networks, and Expression Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312608





