Abstract
Accumulating evidence suggests that the passenger strands microRNAs (miRNAs) derived from pre-miRNAs are closely involved in cancer pathogenesis. Analysis of our miRNA expression signature of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed that miR-144-5p (the passenger strand derived from pre-miR-144) was significantly downregulated in LUAD tissues. The aim of this study was to identify therapeutic target molecules controlled by miR-144-5p in LUAD cells. Ectopic expression assays demonstrated that miR-144-5p attenuated LUAD cell aggressiveness, e.g., inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities, and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cells. A total of 18 genes were identified as putative cancer-promoting genes controlled by miR-144-5p in LUAD cells based on our in silico analysis. We focused on a family with sequence similarity 111 member B (FAM111B) and investigated its cancer-promoting functions in LUAD cells. Luciferase reporter assay showed that expression of FAM111B was directly regulated by miR-144-5p in LUAD cells. FAM111B knockdown assays showed that LUAD cells significantly suppressed malignant phenotypes, e.g., inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities, and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cells. Furthermore, we investigated the FAM111B-mediated molecular networks in LUAD cells. Identifying target genes regulated by passenger strands of miRNAs may aid in the discovery of diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for LUAD.
1. Introduction
Cancer is not only one of the most serious life-threatening diseases, but it can also pose a huge burden to society in any country. Lung cancer has the highest incidence and mortality rate of any cancer, with an estimated 2.3 million cases diagnosed and 1.8 million deaths in 2021 [1]. Histologically, lung cancer is divided into two groups: small cell lung cancer (SCLC), which accounts for 15% of lung cancer patients, and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which accounts for 85% of lung cancer patients. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) accounts for approximately 60% of patients with NSCLC [2].
Although surgical resection is a curative treatment for lung cancer patients, many patients have advanced stages of the disease at the time of diagnosis, and their life prognosis is extremely poor, with only 20% of patients surviving 5 years [3]. The prognosis for LUAD patients with advanced stage has been improved significantly with the development of molecular-targeted drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors [4,5].
One of the serious clinical problems among LUAD is brain metastasis. The incidence of this complication is particularly pronounced in LUAD with activating driver gene mutations, e.g., EGFR, ALK, and ROS-1 [6]. Discovery of new therapeutic target molecules is an important research topic to improve the prognosis of LUAD patients.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are single-stranded short non-coding RNAs (19–22 nucleotides in length), and they act as fine controller of gene expression and modulate almost all biological processes, e.g., proliferation, cell cycle control, programmed cell death, differentiation, invasiveness [7,8]. Regulation of miRNAs is essential for maintaining normal cellular function. Accumulating evidence demonstrated that aberrant expressed miRNAs caused to disrupt RNA networks, and these events have been implicated in the development, metastasis, and drug resistance of cancer cells [9,10].
A unique feature of miRNA is that a single miRNA controls a vast number of RNA transcripts in normal and disease cells. Therefore, it is possible to trace the RNA networks controlled by miRNAs within cells starting with a miRNA interest.
Based on the miRNA expression signature of LUAD, we focused on aberrant expressed miRNAs, and to investigate the functional significance and their controlled genes closely involved in the molecular pathogenesis of LUAD [11].
Our RNA-sequence-based signature revealed that some passenger strand miRNAs were significantly downregulated in LUAD tissues [11]. In miRNA biogenesis, two single-stranded miRNAs (the guide strand and the passenger strand) are derived from the miRNA precursor. Previous concepts suggested that only the guide strand of a miRNA actually functions to regulate the miRNA’s target RNAs within the cell. On the other hand, the passenger strand was thought to be degraded within the cell and to be non-functional [12]. Therefore, passenger strands derived from miRNA precursors have been left behind in cancer research and their functions remain poorly understood.
To date, miR-144-3p (the guide strand derived from pre-miR-144) has been shown to be an antitumor miRNA in various types of cancers, including lung cancer. In the analysis of our signature, we focused on miR-144-5p (the passenger strand), because its expression was significantly downregulated in LUAD tissues, and the role of miR-144-5p has not been fully elucidated in LUAD cells. Antitumor roles of miR-144-5p in LUAD cells was confirmed by our functional assays.
Interestingly, a total of 18 cell cycle-related genes (ARHGAP11A, CDC3, CENPF, CENPN, CHEK1, CP, DEPDC1B, ECT2, FAM111B, FAM64A, HELLS, HJURP, KIF11, NCAPG, RALGPS2, SGOL1, SPC24, and TRIP13) were identified as putative miR-144-5p controlled genes, and potential therapeutic targets for this disease. The analysis of the poorly characterized passenger strand of miRNAs may reveal new therapeutic targets for LUAD. Our RNA-sequence-based miRNA expression signatures provide the research field with information about which miRNAs they need to analyze.
2. Results
2.1. Genomics Structure of miR-144-5p and miR-144-3p, and Their Expression in LUAD Clinical Specimens
We previously created the miRNA expression signature of LUAD based on RNA-sequencing [11]. Our signature revealed that both strands of pre-miR-144 (miR-144-5p: the passenger strand and miR-144-3p: the guide strand) were downregulated in LUAD tissues (Figure 1A). Downregulation of both strands of miRNAs in LUAD clinical specimens was confirmed by a large number of cohort data by TCGA datasets (p < 0.001; Figure 1B). Spearman’s rank analysis revealed a positive correlation between the expression levels of miR-144-5p and miR-144-3p (r = 0.882, p < 0.001; Figure 1C).
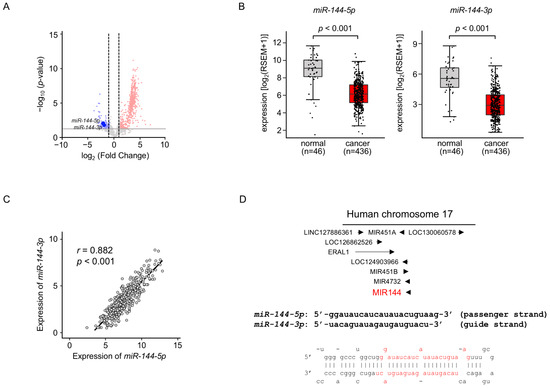
Figure 1.
Expression levels of miR-144-5p and miR-144-3p in LUAD clinical specimens (A) Volcano plot showing the miRNA expression signature obtained through miRNA sequencing (GEO accession number: GSE230229). The log2 fold change (FC) in expression is plotted on the x-axis and the log10 p-value is on the y-axis. The red and blue dots represent the upregulated (log2 FC > 1.0 and p < 0.05) miRNAs and downregulated (log2 FC < −1.0 and p < 0.05), respectively. (B) Validation of miR-144-5p and miR-144-3p expression levels in LUAD clinical specimens. The expression levels of both miRNAs were markedly reduced in cancer tissues. (p < 0.001). (C) Positive correlations (Spearman’s rank test) between the expression levels of miR-144-5p and miR-144-3p in clinical specimens (r = 0.882, p < 0.001). (D) The chromosomal position of pre-miR-144 within the human genome. The mature sequences of miR-144-5p (passenger strand) and miR-144-3p (guide strand) are shown.
Human genome database showed that pre-miR-144 was located on chromosome 17q11.2. Interestingly, four miRNAs (miR-451a, miR-451b, miR-144, and miR-4732) are located in close proximity in this region (Figure 1D). Among these miRNAs, the downregulation of miR-451a was detected in TCGA database analysis.
Our recent studies demonstrated that some passenger strands of miRNAs are closely involved in the molecular pathogenesis of human cancers [13,14]. In this study, we focused on miR-144-5p and investigated its functional role to identify target genes in LUAD cells.
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
2.2. Antitumor Roles of miR-144-5p in LUAD Cells
Antitumor effects of miR-144-5p were assessed by ectopic expression assays using two LUAD cell lines (A549 and H1299). Expression of miR-144-5p inhibited the proliferation of LUAD cells (Figure 2A). Flow cytometry analysis revealed that miR-144-5p expression induced G0/G1 arrest in LUAD cells (Figure 2B). Furthermore, we observed an increase in apoptotic cells by miR-144-5p expression (Figure 2C).
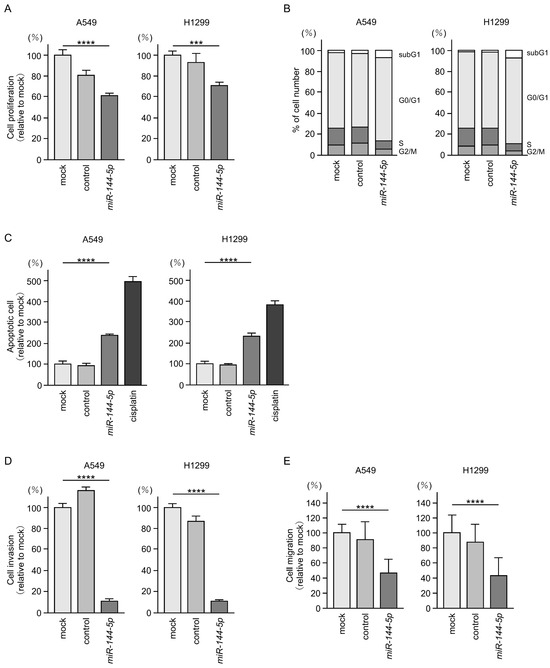
Figure 2.
Antitumor functions of miR-144-5p in LUAD cells (A549 and H1299). (A) Cell proliferation was evaluated using XTT assay. Cancer cell viability was analyzed 72 h after transient transfection of miRNAs. (B) At 72 h after transient transfection with miR-144-5p, cell cycle status evaluated using flow cytometry. (C) At 72 h after transient transfection with miR-144-5p, apoptotic cells was evaluated using flow cytometry with Annexin V-FITC- and PI-PerCP-Cy5-5-A-stained cells. Cisplatin (30 µM) was used as a positive control for induction of apoptosis. (D) At 72 h after seeding miR-144-5p-transfected cells into the chambers, cell invasion was evaluated using Matrigel invasion assays. (E) At 72 h after seeding miR-144-5p transfected cells into the chambers, cell migration assessed using a membrane culture system. ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.
Cancer cell invasion and migration abilities were markedly suppressed after miR-144-5p expression in LUAD cells (Figure 2D,E). Typical images of the invasion and migration assays after miR-144-5p expression are shown in Figure S1.
Our present data strongly suggest that miR-144-5p acts as an antitumor miRNA in LUAD cells.
2.3. Identification of miR-144-5p Controlled Cancer-Promoting Genes in LUAD Cells
The next area of interest is determining which genes are controlled by antitumor miR-144-5p in LUAD cells.
Our strategy for the identification of miR-144-5p controlled genes in LUAD cells is shown in Figure 3. The TargetScanHuman database (release 8.0) revealed that 2076 genes contained miR-144-5p binding sites within their 3′ untranslated regions (UTR). Using the gene expression profile with the GEO database (accession number: GSE19188), we identified 756 genes that were upregulated (log2 fold change > 1.5) in NSCLC tissues compared to normal tissues. Integrating two datasets revealed that a total of 69 genes were identified as putative miR-144-5p controlled genes in LUAD cells (Table 1).
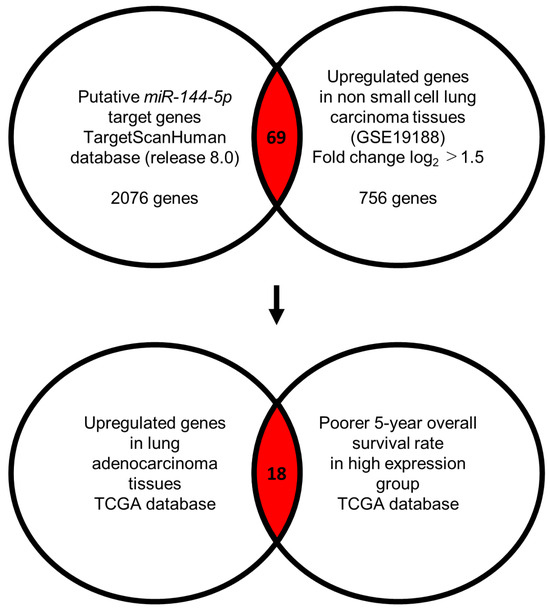
Figure 3.
Flowchart for identification of miR-144-5p targets in LUAD cell. To identify putative targets of miR-144-5p in LUAD cells, we used two datasets: the TargetScanHuman database (release 8.0) and our original mRNA expression profile (Upregulated genes in non-small cell lung carcinoma tissues; GEO accession number: GSE19188). A total of 69 genes were identified as candidate targets of miR-144-5p. Furthermore, we searched for genes that were associated with the prognosis of LUAD patients using two databases: OncoLnc (http://www.oncolnc.org, accessed on 17 May 2024) and GEPIA (http://gepia2.cancer-pku.cn/#analysis, accessed on 17 May 2024). Among the miR-144-5p target genes, 18 genes were upregulated in LUAD tissues, and closely associated with poor prognosis in LUAD patients.

Table 1.
Putative target genes regulated by miR-144-5p in A549 cells.
2.4. Clinical Significance of miR-144-5p Controlled Genes by TCGA-LUAD Analysis
We used the TCGA-LUAD database to confirm the clinical significance of 69 genes potentially controlled by miR-144-5p.
A total of 18 of these target genes (Table 1, Bold) were upregulated in LUAD tissues (n = 499) compared with normal lung tissues (n = 58) (Figure 4A), and closely associated with poor prognosis in LUAD patients (5-year overall survival rate, p < 0.05) (Figure 4B).
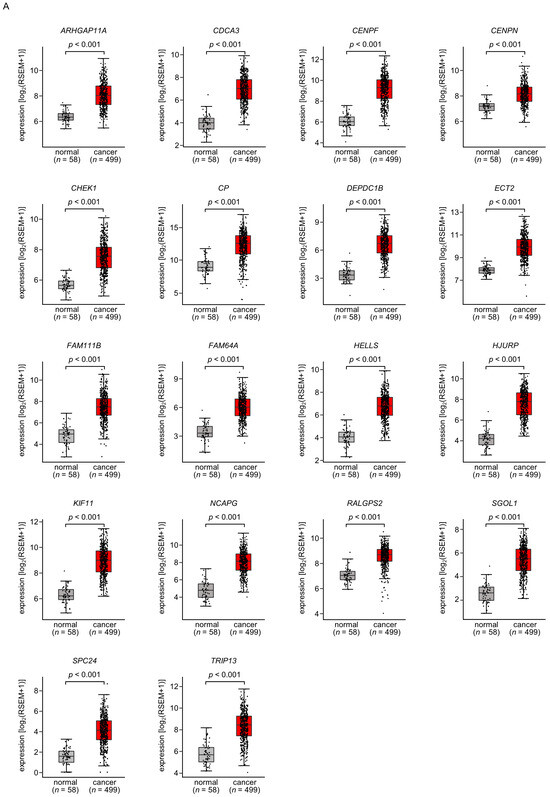
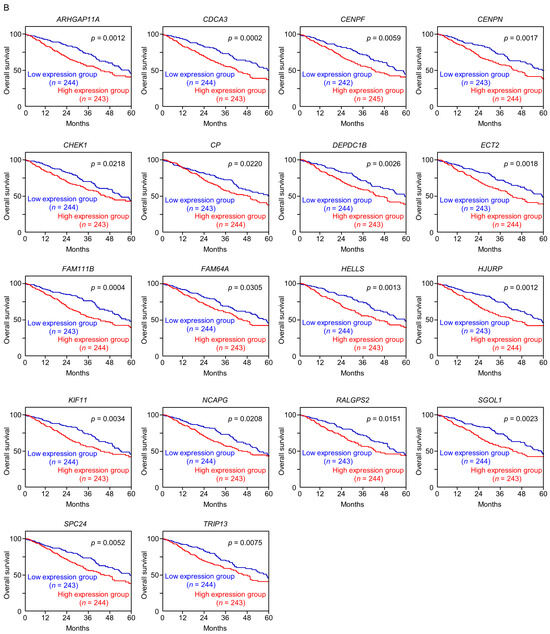
Figure 4.
Expression levels and 5-year overall survival rate of the 18 target genes regulated by miR-144-5p in LUAD (A) The expression levels of the 18 target genes of miR-144-5p (ARHGAP11A, CDCA3, CENPF, CENPN, CHEK1, CP, DEPDC1B, ECT2, FAM111B, FAM64A, HELLS, HJURP, KIF11, NCAPG, RALGPS, SGOL1, SPC24, TRIP13) in LUAD clinical specimens were assessed using the TCGA-LUAD dataset. All genes were upregulated in LUAD tissues (n = 499) compared with normal tissues (n = 58) (p < 0.001). (B) Kaplan–Meier curves of the 5-year overall survival rates based on expression of the 18 target genes (ARHGAP11A, CDCA3, CENPF, CENPN, CHEK1, CP, DEPDC1B, ECT2, FAM111B, FAM64A, HELLS, HJURP, KIF11, NCAPG, RALGPS, SGOL1, SPC24, TRIP13) are shown. Lower expression levels of all 18 genes were significantly associated with poorer overall survival in LUAD patients. The patients (n = 487) were divided into high and low-expression groups based on the median gene expression level. The red and blue lines denote the high and low expression groups, respectively.
Among these genes, the expression of two genes (CDCA3: p = 0.0002 and FAM111B: p = 0.0004) had a significant impact on the prognosis of lung cancer patients. Recently, it has been reported that CDCA3 is regulated by miR-144-5p in lung cancer cells [15]. Therefore, in this analysis, we focused on FAM111B and conducted further analysis.
2.5. Direct Regulation of FAM111B by miR-144-5p in LUAD Cells
Both mRNA and protein expression levels were significantly reduced by ectopic expression of miR-144-5p in LUAD cells (Figure 5A,B). Full-size images of Western blots are shown in Figure S2.
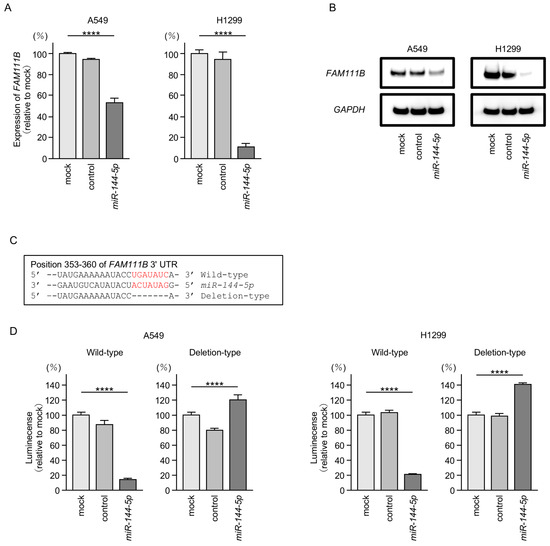
Figure 5.
MiR-144-5p expression directly regulated FAM111B in LUAD cells. (A) Expression level of FAM111B mRNA is markedly reduced by ectopic expression of miR-144-5p in LUAD cells (A549 and H1299). Total RNA was isolated 72 h after miRNA transfection and quantified by real-time PCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (B) Significant reduction of the FAM111B protein level by ectopic expression of miR-144-5p in LUAD cells (A549 and H1299). Proteins were isolated 72 h after miR-144-5p transfection and quantified by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (C) Putative miR-144-5p binding sites in the 3′UTR of the FAM111B gene were detected using the TargetScanHuman database (release 8.0). (D) Dual luciferase reporter assays revealed reduced luminescence activity after co-transfection of miR-144-5p with a vector containing the miR-144-5p binding site (wild-type) in LUAD cells (A549 and H1299). In contrast, no luminescence activity was observed after co-transfection of miR-144-5p with a vector lacking the miR-144-5p binding site (deletion-type) in LUAD cells. ****, p < 0.0001.
Subsequently, we demonstrated, using the luciferase reporter assay, that miR-144-5p directly binds to the 3′UTR of the FAM111B gene. The putative miR-144-5p-binding site on the 3′-UTR of the FAM111B gene is shown in Figure 5C. Luciferase activity was markedly decreased when LUAD cells were co-transfected with miR-144-5p and a vector containing a miR-144-5p-binding sequence (Figure 5D). In contrast, no decrease in luciferase activity was observed when a vector lacking the miR-144-5p-binding sequence was used (Figure 5D). These results indicated that miR-144-5p directly binds to the 3′-UTR of FAM111B and modulates its expression in LUAD cells.
2.6. Functional Significance of FAM111B in LUAD Cells
We investigated the oncogenic function of FAM111B in LUAD cells using siRNA-mediated FAM111B knockdown assays. Both mRNA and protein levels were significantly reduced by two siRNAs (siFAM111B-1 and siFAM111B-2) in LUAD cells (Figure 6A,B). Full-size images of the Western blots are shown in Figure S3.
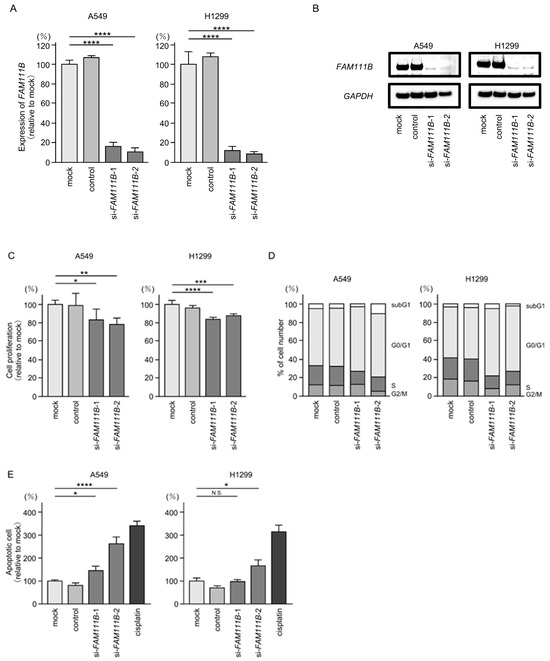
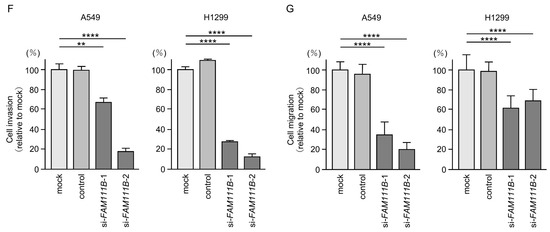
Figure 6.
Effects of knockdown of FAM111B by siRNAs in LUAD cells (A549 and H1299) (A) The inhibitory effects of two different siRNAs targeting FAM111B (siFAM111B-1 and siFAM111B-2) expression were examined. FAM111B- mRNA levels were effectively inhibited by each siRNA in LUAD cells (A549 and H1299). (B) FAM111B protein levels were effectively inhibited by two siRNAs (siFAM111B-1 and siFAM111B-2) in LUAD cells (A549 and H1299). (C) Cell proliferation was evaluated using XTT assays 72 h after siRNA transfection into LUAD cells. (D) At 72 h after transient transfection with siFAM111B-1 and siFAM111B-2, cell cycle status was evaluated using flow cytometry. (E) At 72 h after transient knockdown of FAM111B, apoptotic cells were evaluated using flow cytometry with Annexin V-FITC- and PI-PerCP-Cy5-5-A-stained cells. Cisplatin (30 µM) was used as a positive control for induction of apoptosis. (F) At 72 h after seeding FAM111B-knockdown cells into the chambers, cell invasion assessed using Matrigel invasion assays. (G) At 72 h after seeding FAM111B-knockdown cells into the chambers, cell migration was assessed using a membrane culture system. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001; N.S., not significant.
Cancer cell proliferation was slightly inhibited by siRNAs-transfected LUAD cells. In H1299 cells, there was only a slight effect on cell proliferation (Figure 6C). Moreover, cell cycle arrest (G0/G1 phase), and induced apoptotic cells were detected in siRNAs-transfected LUAD cells (Figure 6D,E). However, there was only a slight increase in apoptotic cells in H1299 cells. Cancer cell invasion and migration abilities were markedly suppressed in siRNAs-transfected LUAD cells (Figure 6F,G). Typical images of invasion and migration assays in siRNAs-transfection LUAD cells are shown in Figure S4.
2.7. Clinical Significance of FAM111B in LUAD Clinical Specimens
To confirm the expression of FAM111B in LUAD clinical specimens, immunostaining was conducted. Stronger immunostaining of the FAM111B protein was observed in cancerous tissues than in normal lung tissues. (Figure 7A). The protein expression of FAM111B was scored, and expression of FAM111B in cancerous tissues was significantly higher than in normal tissues (Figure 7B). The characteristics of patient samples used for immunostaining are shown in Table S1.
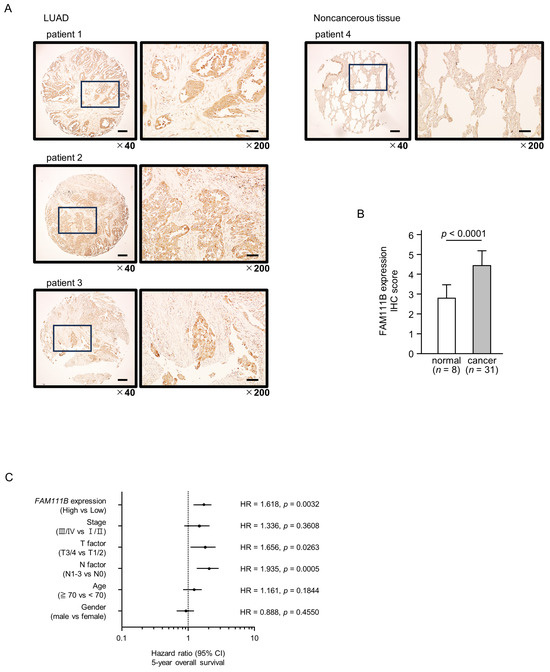
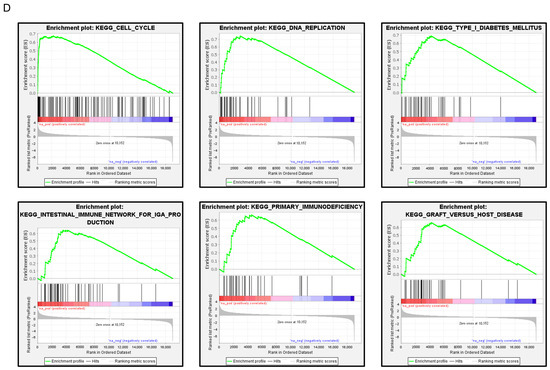
Figure 7.
FAM111B expression and its clinical significance in LUAD. (A) Immunohistochemical staining of FAM111B. (B) Cancer tissues showed strong immunostaining, in contrast to the weak staining observed in noncancerous tissues. The data are means and standard errors of the means. Mann–Whitney U-tests. Scale bar: 200 µm (low magnification); 50 µm (high magnification). (C) Forest plot showing the results of multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis of the 5-year overall survival rate. A significantly lower overall survival rate was observed in patients with high FAM111B expression. The data were sourced from TCGA-LUAD datasets. (D) FAM111B-mediated pathways identified by gene set enrichment analysis. The “cell cycle”, “DNA replication” pathways were enriched in patients with high FAM111B expression.
Multivariate analysis revealed that FAM111B expression is an independent prognostic factor for LUAD, even when accounting for clinical prognostic factors including stage, T-factor, N-factor, age, and gender (Figure 7C). Specifically, higher FAM111B expression correlated with a reduced 5-year overall survival rate.
To identify FAM111B-mediated molecular pathways in LUAD patients, we performed gene set enrichment analysis with TCGA-LUAD data. The “cell cycle”, “DNA replication” pathways were enriched in patients with high FAM111B expression compared to low FAM111B expression (Table 2, Figure 7D).

Table 2.
FAM111B-mediated pathways by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA).
3. Discussion
RNA-sequence based miRNA expression signatures suggest that two types of miRNAs (the guide strands and the passenger strands) derived from miRNA precursors are deeply involved in the molecular pathogenesis of human cancer [16]. Based on previous concepts of miRNA biogenesis, analysis of the guide strands of miRNAs has been prioritized in cancer research. On the other hand, recent research have revealed that some passenger strands of miRNAs also control the expression of target molecules within cells, and dysregulate passenger strands act as oncogenes and tumor-suppressors in cancer cells [16,17]. Exploring the RNA networks controlled by passenger strands might uncover new therapeutic targets for cancer.
In the human genome, miR-144 is located close to miR-451a, miR-451b, and miR-4732 on the chromosome 17q11.2 [18]. Previous studies demonstrated that expression of miR-451a was frequently downregulated in multiple type of cancers, including lung cancers [19,20,21]. Gain-of-function assays showed ectopic expression of miR-451a attenuated malignant phenotypes of lung cancer cells via targeting several oncogenes [22,23]. Recent studies indicated that both strands of miR-4732-5p and miR-4732-3p prevented lung cancer aggressiveness through inhibited TBX15/TNFSF11 axis or PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/Snail pathway [24,25].
Numerous studies have demonstrated that miR-144-3p (the guide strand) has tumor suppressor functions in various types of cancers, including lung cancer [26]. Compared to the analysis of miR-144-3p, miR-144-5p (the passenger strand) has not been fully characterized in cancer cells. Previously, the expression of miR-144-5p enhanced radio sensitivity of NSCLC cells in vitro and mouse xenografts in vivo through targeting activating transcription factor 2 [27]. Recent studies have demonstrated that aberrantly expressed non-coding RNAs or circulating RNAs may be involved in promoting cancer cell malignant transformation by adsorbing tumor-suppressive miRNAs [28,29]. Circular RNA, circRACGAP1 was overexpressed in NSCLC tissues, and its downregulation enhanced the Gefitinib sensitivity of NSCLC cells [30]. CircRACGAP1 was directly regulated by miR-144-5p in NSCLC cells [30].
Apart from our current data, it has been shown that miR-144-5p acted as an antitumor miRNA in lung cancer cells. Taking into account previous reports, it has been shown that suppression of expression of miRNA cluster (miR-451/miR-144/miR-4732) located on chromosomes 17q11.2 had a profound impact on the malignant transformation of lung cancer cells. An important task for the future will be to clarify the molecular mechanisms underlying the expression control of the miRNAs present in this cluster.
Our next challenge is to identify therapeutic targets for LUAD among the molecules regulated by these clustered miRNAs. In this study, a total of 18 genes were identified as LUAD therapeutic targets controlled by miR-144-5p. Among these targets, we have already analyzed three genes (FAM64A; miR-99a target, HELLs; miR-150-3p target, and TRIP13; miR-139-3p target) as oncogenic target molecules regulated by tumor-suppressive miRNAs in lung cancer [13,14,31]. Treatment of DCZ0415 (TRIP13 specific inhibitor) significantly attenuated the malignant transformation of LUAD cells. Moreover, when combined with anticancer drugs (cisplatin and carboplatin), DCZ0415 exerted a synergistic effect in inhibiting cell proliferation [14].
In this study, we focused on FAM111B because its oncogenic roles in LUAD cells are not fully understood. Previous studies have demonstrated that the FAM111B protein contains a trypsin/cysteine protease-like domain at its C-terminus [32]. However, the function of this domain in cells is not fully understood. According to several reports, FAM111B is a poorly characterized protease involved in DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis [32].
Regarding human disease, FAM111B gene mutations have been reported in patients with POIKTMP, a hereditary multisystemic fibrosis disorder. The syndrome is characterized by fibrosis of multiple organs, including the skin and lungs [32]. However, the molecular mechanism by which FAM111B mutations cause POIKTMP remains unknown.
In human cancers, overexpression of FAM111B has been reported in multiple cancer types, e.g., esophageal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, bladder cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer and lung cancer [33,34,35,36,37,38]. Furthermore, functional analysis of FAM111B suggested that aberrant expression of FAM111B had cancer-promoting functions such as promoting the cell cycle progression and inhibition of apoptosis [33,34,35,36,37,38]. Our siRNA-mediated knockdown assays demonstrated that downregulation of FAM111B significantly inhibited cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion abilities, and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and strongly suggested as a cancer-promoting gene in LUAD cells. A Recent study of hepatoma cells showed that silencing FAM111B induced cell cycle arrest (G0/G1), and reduced cell migration and invasion abilities [39]. Importantly, FAM111B reduced the p53 expression level by degrading p53 protein in hepatoma cells [39]. Inactivation of the p53 by FAM111B led to activation of the cyclin D1-CDK4/6 pathway, thereby inducing cell proliferation [39]. In LUAD cells (KRAS-driven LUAD under serum-starvation conditions), FAM111B-knockout cells demonstrated that FAM111B controlled cell cycle progression in a cyclin D1-CDK4-dependent manner by degrading p16 [40]. These reports suggest that FAM111B is involved in cancer cell proliferation by controlling gatekeeper genes in cell cycle regulation.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Analysis of LUAD Clinical Specimens by TCGA Database
Expression of miRNA and miRNA target genes in LUAD tissues assessed using the following databases: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) (https://www.cancer.gov/tcga, accessed on 17 May 2024), Genomic Data Commons Data Portal (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/, accessed on 17 May 2024), and FIREBROWSE (http://firebrowse.org/, accessed on 17 May 2024). Overall survival data were obtained from OncoLnc (http://www.oncolnc.org/) (data downloaded on 17 May 2024) and cBioPortal (https://www.cbioportal.org/, accessed on 17 May 2024).
4.2. Functional Assays of miRNAs and miRNA Target Genes in LUAD Cells
Two LUAD cell lines, A549 and H1299 were used in this study; two cell lines were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA).
The procedures for RNA extraction and qRT-PCR were described in our previous studies [11,14,22].
Functional assays (e.g., proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, migration and invasion) were performed for transient transfection of small RNAs (miRNAs and siRNAs) into LUAD cells. All miRNA precursors were transfected at 10 nM, and all siRNAs were transfected at 5nM into cell lines using Opti-MEM (catalog no.: 31985070, Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and Lipofectamine RNAiMAX (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The analysis procedures have been described in our previous studies [11,14,22].
The reagents used in the experiments are shown in the Table S2.
4.3. Identification of Oncogenic Targets Controlled by miR-144-5p in LUAD Cells
To identify oncogenic targets controlled by miR-144-5p in LUAD, we used TargetScanHuman v8.0 (https://www.targetscan.org/vert_80/, accessed on 24 May 2023), and a gene expression profile from the GEO database (GEO accession number: GSE19188). We used GeneCodis 4 software to infer the molecular functions of the miR-144-5p target genes [41]. Gene set enrichment analysis software was used to infer the molecular pathways controlled by these genes [42,43].
4.4. Plasmid Construction and Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
Vector construction and dual-luciferase reporter assays were performed as described in our previous studies [11,14,22]. The purified plasmid vectors were transfected into LUAD cells using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) at 20 ng/well. The vector insertion sequences are shown in Figure S5, and the reagents used are listed in Table S2.
4.5. Western Blotting and Immunohistochemistry
Western blotting and immunohistochemical analysis were performed according to our previous studies [11,14,22]. The intensity and area of staining were evaluated based on previous reports [44], and immunohistochemical scores were calculated. The antibodies used in the study are listed in Table S2. A list of clinical specimens evaluated by immunohistochemistry is given in Table S1.
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyzes were achieved using R ver. 4.4.0 (R Core Team, Vienna, Austria; https://www.R-project.org/, accessed on 25 April 2024) and GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). The differences between the two groups were analyzed by Student’s t-tests. Multiple group comparison was performed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s tests for post hoc analysis. Survival rates were analyzed by Kaplan–Meier survival curves and the log-rank test.
5. Conclusions
Our miRNA signature and TCGA-LUAD database analysis revealed that miR-144-5p (the passenger strand) was significantly downregulated in LUAD tissues. Ectopic expression of miR-144-5p attenuated the malignant phenotypes of LUAD cells, suggesting that this miRNA acted as an antitumor miRNA in LUAD cells. In total, 18 genes (ARHGAP11A, CDC3, CENPF, CENPN, CHEK1, CP, DEPDC1B, ECT2, FAM111B, FAM64A, HELLS, HJURP, KIF11, NCAPG, RALGPS2, SGOL1, SPC24, and TRIP13) were identified as therapeutic targets by miR-144-5p regulation in LUAD cells. FAM111B was directly regulated by miR-144-5p, and its overexpression facilitated LUAD cell aggressiveness. The involvement of the passenger strand in the molecular pathogenesis of LUAD, and the search for its regulatory genes are effective strategies for discovering therapeutic target for LUAD.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms25189974/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S., K.M. and K.T.; methodology, N.S.; validation, N.S., K.M., K.T. and H.I.; formal analysis, Y.T., T.S., Y.H., H.S., Y.G. and N.K.; investigation, Y.T., T.S., Y.H., H.S., Y.G. and N.K.; resources, Y.G.; data curation, Y.T., T.S. and Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.T., Y.H. and N.S.; visualization, Y.T., Y.H. and N.S.; supervision, N.S.; project administration, N.S., K.M., K.T. and H.I.; funding acquisition, N.S., T.S., H.S. and K.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by KAKENHI; grant numbers 24K12641, 24K11370, 24K11371, and 22K08260.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee on Epidemiological and its related Studies, Sakuragaoka Campus, Kagoshima University (approval no. 210101 eki-kai 2, 31 August 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. These data can be accessed here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE230229 (accessed on 24 May 2024) and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE19188 (accessed on 24 May 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirker, R. Conquering lung cancer: Current status and prospects for the future. Pulmonology 2020, 26, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.C.; Tan, D.S.W. Targeted Therapies for Lung Cancer Patients with Oncogenic Driver Molecular Alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Remon, J.; Hellmann, M.D. First-Line Immunotherapy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, B.D.; Cheung, V.J.; Patel, A.J.; Suki, D.; Rao, G. Epidemiology of metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczyński, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Szyłło, K.; Hogendorf, P. miRNAs in Cancer (Review of Literature). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen, B.M.; Hidayat, H.J.; Salihi, A.; Sabir, D.K.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. MicroRNA: A signature for cancer progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomioka, Y.; Suetsugu, T.; Seki, N.; Tanigawa, K.; Hagihara, Y.; Shinmura, M.; Asai, S.; Kikkawa, N.; Inoue, H.; Mizuno, K. The Molecular Pathogenesis of Tumor-Suppressive miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p Target Genes: GINS4 Facilitates Aggressiveness in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cells 2023, 12, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matranga, C.; Tomari, Y.; Shin, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Zamore, P.D. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 2005, 123, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Tanigawa, K.; Misono, S.; Suetsugu, T.; Sanada, H.; Uchida, A.; Kawano, M.; Machida, K.; Asai, S.; Moriya, S.; et al. Regulation of Oncogenic Targets by Tumor-Suppressive miR-150-3p in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagihara, Y.; Tomioka, Y.; Suetsugu, T.; Shinmura, M.; Misono, S.; Goto, Y.; Kikkawa, N.; Kato, M.; Inoue, H.; Mizuno, K.; et al. Identification of Tumor-Suppressive miR-139-3p-Regulated Genes: TRIP13 as a Therapeutic Target in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Xia, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, K.; Li, C. MiRNA-144-5p down-modulates CDCA3 to regulate proliferation and apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mutat. Res. 2022, 825, 111798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.; Adams, C.M.; Jiang, W.; Greenawalt, E.; Eischen, C.M. Pan-cancer analysis reveals cooperativity of both strands of microRNA that regulate tumorigenesis and patient survival. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Z. microRNA regulation in cancer: One arm or two arms? Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1516–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Zha, X. MicroRNA-144: A novel biological marker and potential therapeutic target in human solid cancers. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 6716–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Sugawara, S.; Okato, A.; Kato, M.; Kojima, S.; Yamazaki, K.; Naya, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Impact of novel oncogenic pathways regulated by antitumor miR-451a in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandres, E.; Bitarte, N.; Arias, F.; Agorreta, J.; Fortes, P.; Agirre, X.; Zarate, R.; Diaz-Gonzalez, J.A.; Ramirez, N.; Sola, J.J.; et al. microRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Tanaka, M.; Yoshida, M.; Umakoshi, M.; Nanjo, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Saito, M.; Kohno, T.; Kuriyama, S.; Konno, H.; et al. The low expression of miR-451 predicts a worse prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer cases. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, A.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Yamada, Y.; Misono, S.; Sanada, H.; Kikkawa, N.; Kumamoto, T.; Suetsugu, T.; Inoue, H. Regulation of KIF2A by Antitumor miR-451a Inhibits Cancer Cell Aggressiveness Features in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Z.X.; Yang, J.S.; Pan, X.; De, W.; Chen, L.B. MicroRNA-451 functions as a tumor suppressor in human non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ras-related protein 14 (RAB14). Oncogene 2011, 30, 2644–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Bai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L. miR-4732-3p prevents lung cancer progression via inhibition of the TBX15/TNFSF11 axis. Epigenomics 2023, 15, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Yin, C. The miR-4732-5p/XPR1 axis suppresses the invasion, metastasis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/Snail pathway. Mol. Omics 2022, 18, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooshkaki, O.; Rezaei, Z.; Rahmati, M.; Vahedi, P.; Derakhshani, A.; Brunetti, O.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Mansoori, B.; Silvestris, N.; Baradaran, B. MiR-144: A New Possible Therapeutic Target and Diagnostic/Prognostic Tool in Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Peng, L.; Hua, S.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Jie, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. miR-144-5p Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells via Targeting ATF2. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5109497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.P.; He, Y.J.; Hou, J.C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, S.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.D.; Hu, J.H.; Zhong, S.L.; et al. The role of circRNAs in cancers. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20170750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qi, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S.; et al. Emerging Epigenetic Regulation of Circular RNAs in Human Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xiong, H.; Xia, Z.K.; Liu, B.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.X.; Hu, C.H.; Liu, P. circRACGAP1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer proliferation by regulating miR-144-5p/CDKL1 signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Tanigawa, K.; Nohata, N.; Misono, S.; Okada, R.; Asai, S.; Moriya, S.; Suetsugu, T.; Inoue, H.; Seki, N. FAM64A: A Novel Oncogenic Target of Lung Adenocarcinoma Regulated by Both Strands of miR-99a (miR-99a-5p and miR-99a-3p). Cells 2020, 9, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arowolo, A.; Malebana, M.; Sunda, F.; Rhoda, C. Proposed Cellular Function of the Human FAM111B Protein and Dysregulation in Fibrosis and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 932167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Xiao, X. Overexpressed FAM111B degrades GSDMA to promote esophageal cancer tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance. Cell Oncol. 2024, 47, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, W.; Cui, Q.; Chen, S. Family with sequence similarity 111 member B contributes to tumor growth and metastasis by mediating cell proliferation, invasion, and EMT via transforming acidic coiled-coil protein 3/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Peng, L.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, M. FAM111B Acts as an Oncogene in Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gu, Y.; Ni, H.; Quan, Q.; Guo, L. Silencing of FAM111B inhibits tumor growth and promotes apoptosis by decreasing AKT activity in ovarian cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, S.; Han, Z.; Jiang, X. YY1-Induced Transcriptional Activation of FAM111B Contributes to the Malignancy of Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, e417–e425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, K.; Huang, J.; Sun, Q.; Shao, C.; Luo, J.; Xu, L.; Shen, Y.; Ren, B. FAM111B, a direct target of p53, promotes the malignant process of lung adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2829–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; He, H.Y.; Fan, Z.H.; Li, C.M.; Gong, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Xiong, H.J.; Xie, C.M.; Bie, P. Silencing of FAM111B inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatoma cells through activating p53 pathway. Dig. Liver Dis. 2023, 55, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, K.; Nojima, S.; Hijiki, S.; Tahara, S.; Ohshima, K.; Matsui, T.; Hori, Y.; Kurashige, M.; Umeda, D.; Kiyokawa, H.; et al. FAM111B enhances proliferation of KRAS-driven lung adenocarcinoma by degrading p16. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2635–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Moreno, A.; López-Domínguez, R.; Villatoro-García, J.A.; Ramirez-Mena, A.; Aparicio-Puerta, E.; Hackenberg, M.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Carmona-Saez, P. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Regulatory Elements. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.L.; Huang, W.G.; Chen, Z.C.; Peng, F.; Zhang, P.F.; Li, M.Y.; Li, F.; Li, J.L.; Li, C.; Yi, H.; et al. Identification of novel nasopharyngeal carcinoma biomarkers by laser capture microdissection and proteomic analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).