Staphylococcus aureus Co-Infection in COVID-19 Patients: Virulence Genes and Their Influence on Respiratory Epithelial Cells in Light of Risk of Severe Secondary Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Presence of Toxin and Adhesin Genes
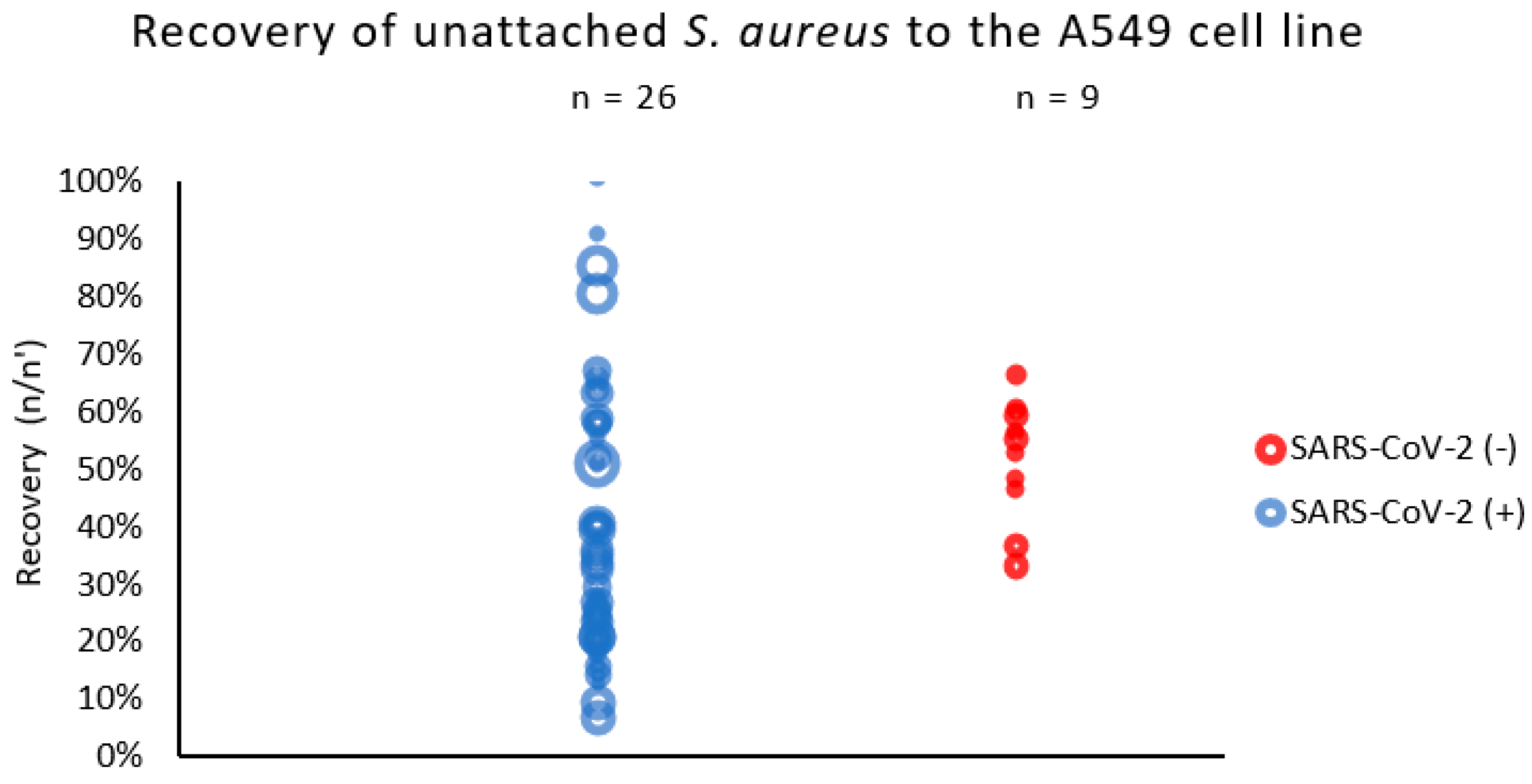
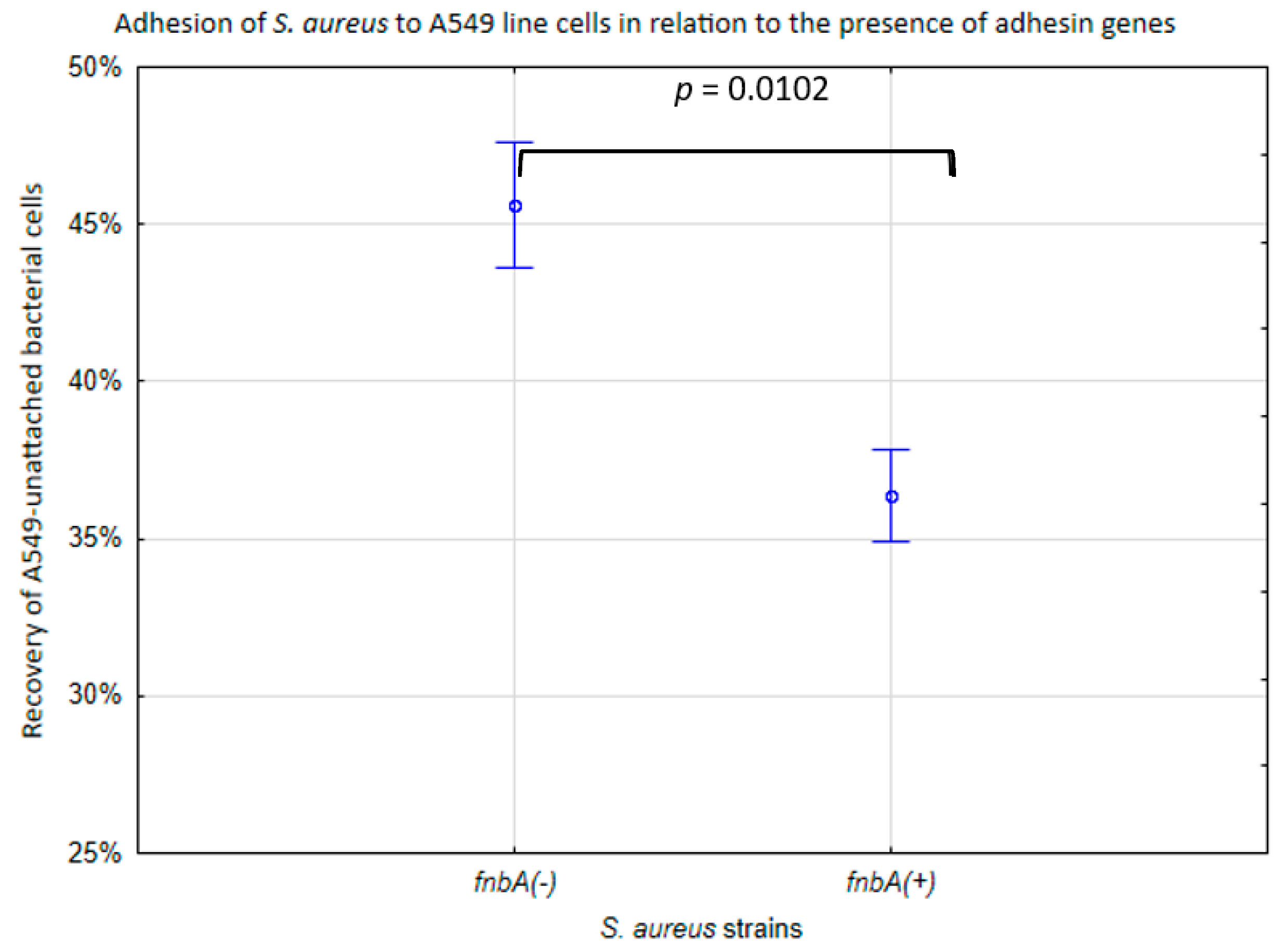
2.2. The Adhesion of S. aureus Strains to the Pulmonary Epithelial Cells (A549 Line)
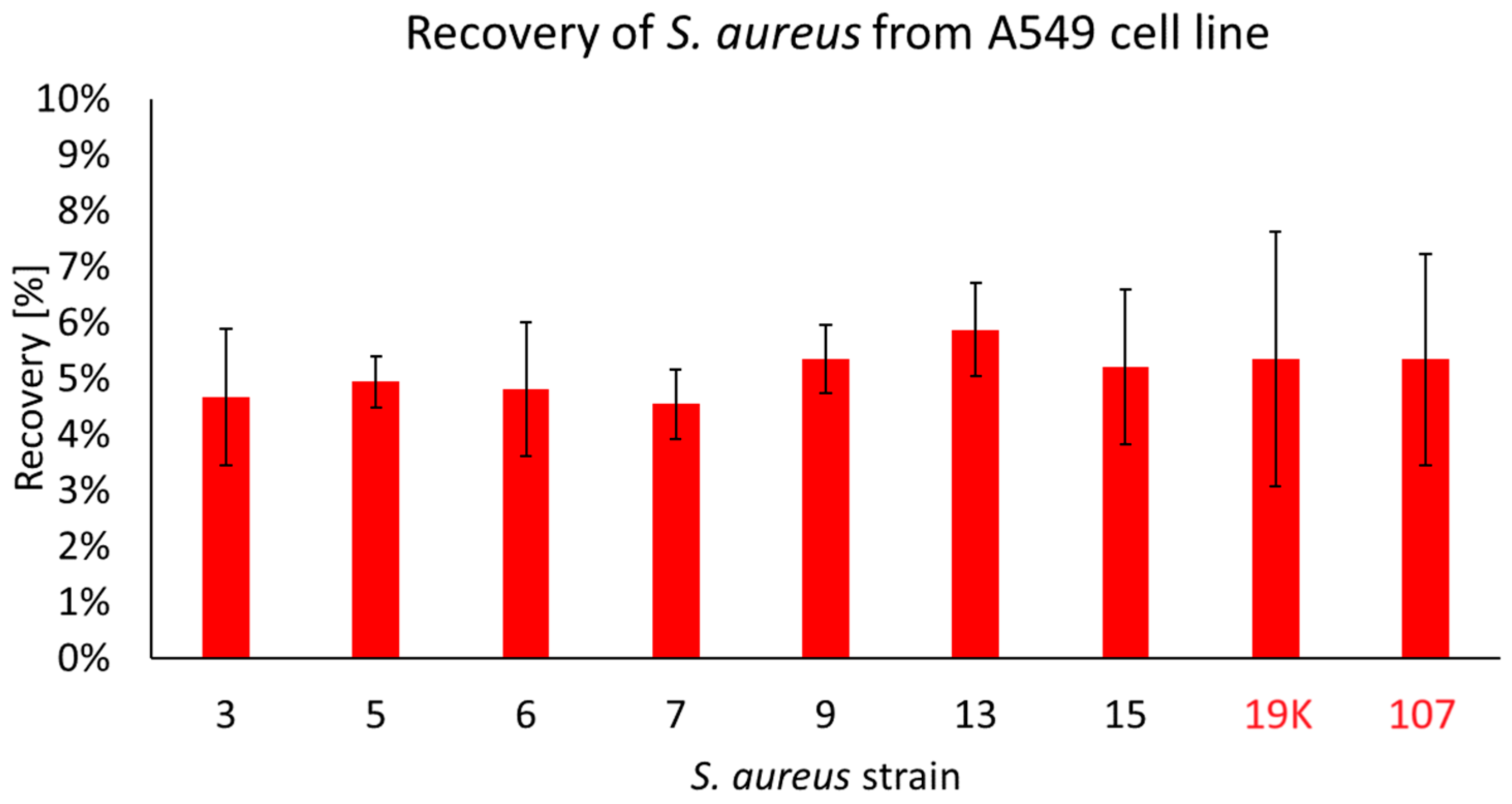
2.3. The Penetration of S. aureus Strains into the Pulmonary Epithelial Cells
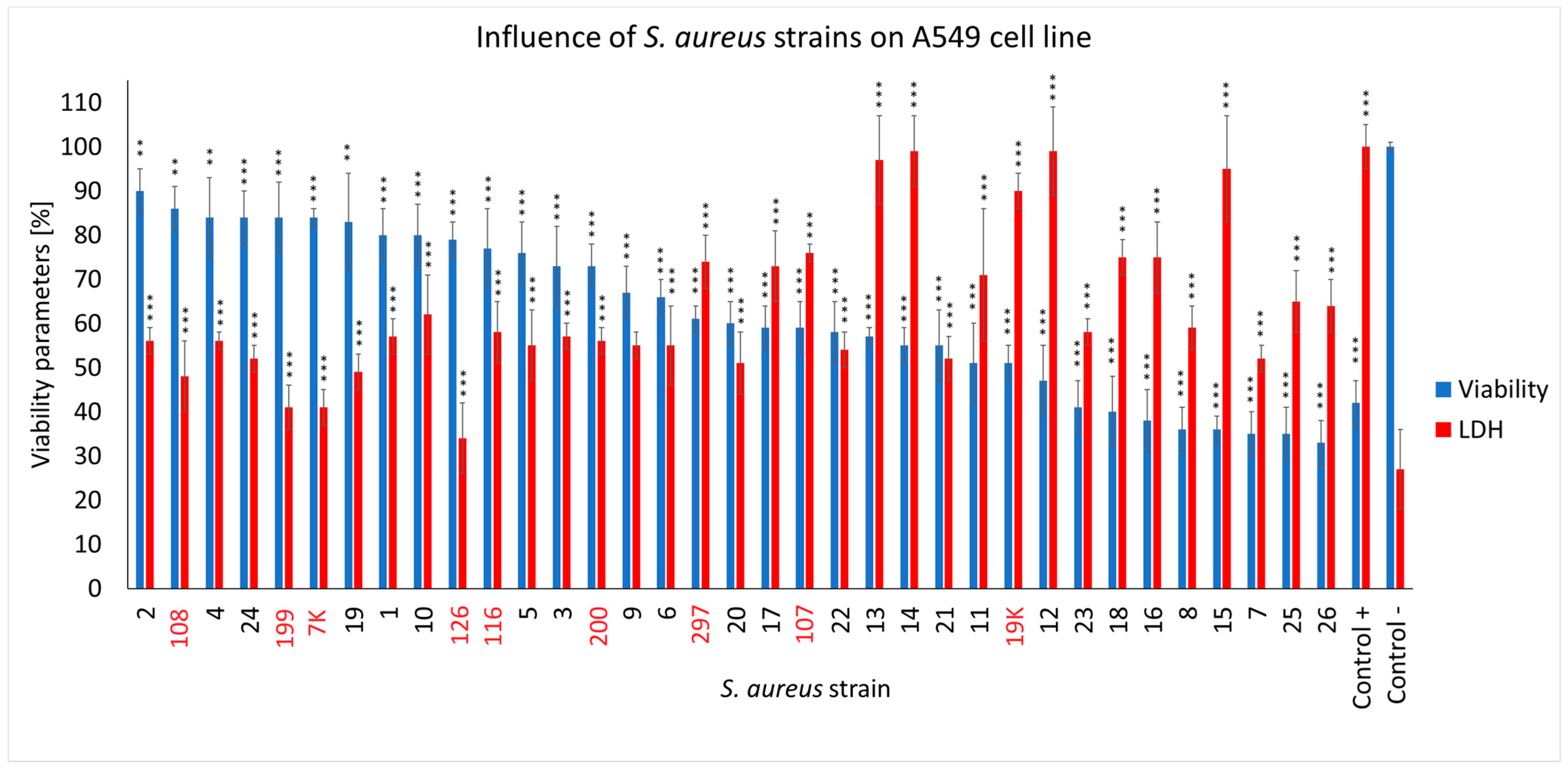
2.4. The Effect of S. aureus Strains on the Viability of Respiratory Epithelial Cells (A549 Line) and Their Membrane Integrity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strain Collection and Identification
4.2. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
4.3. Bacterial DNA Isolation
4.4. Screening for the Presence of Toxin and Adhesin Genes
4.5. The Adhesion of the S. aureus Strains to the Pulmonary Epithelial Cells
4.6. The Penetration of S. aureus Strains into the Pulmonary Epithelial Cells
4.7. The Neutral Red Viability Assay
4.8. The Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joseph, C.; Togawa, Y.; Shindo, N. Bacterial and Viral Infections Associated with Influenza. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 7, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, M.E.; McLoughlin, R.M. Staphylococcus aureus and Influenza A Virus: Partners in Coinfection. mBio 2016, 7, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgogna, T.R.; Hisey, B.; Heitmann, E.; Obar, J.J.; Meissner, N.; Voyich, J.M. Secondary Bacterial Pneumonia by Staphylococcus aureus Following Influenza a Infection Is SaeR/S Dependent. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgene, M.F.; Botelho-Nevers, E.; Grattard, F.; Pillet, S.; Berthelot, P.; Pozzetto, B.; Verhoeven, P.O. Staphylococcus aureus Colonization and Non-Influenza Respiratory Viruses: Interactions and Synergism Mechanisms. Virulence 2018, 9, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, J.A.; Dupper, A.C.; Malik, Y.; Gavioli, E.M.; Banga, J.; Berbel Caban, A.; Nadkarni, D.; Obla, A.; Vasa, C.V.; Mazo, D.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia in Patients Infected with COVID-19: A Case Series. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitmann, L.; Monard, C.; Dauwalder, O.; Simon, M.; Argaud, L. Early Bacterial Co-Infection in ARDS Related to COVID-19. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalbert, J.R.; Varshney, K.; Tobin, R.; Pajaro, R. Clinical Outcomes in Patients Co-Infected with COVID-19 and Staphylococcus Aureus: A Scoping Review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluytmans, J.; van Belkum, A.; Verbrugh, H. Nasal Carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: Epidemiology, Underlying Mechanisms, and Associated Risks. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuter, J.; Hatcher, V.B.; Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus Binding to Human Nasal Mucin. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Eiff, C.; Becker, K.; Machka, K.; Stammer, H.; Peters, G. Nasal Carriage as a Source of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowy Franklin, D. Staphylococcus aureus Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Belkum, A.; Melles, D.C.; Nouwen, J.; van Leeuwen, W.B.; van Wamel, W.; Vos, M.C.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Verbrugh, H.A. Co-Evolutionary Aspects of Human Colonisation and Infection by Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.P.; Cornforth, D.M.; Mideo, N. Evolution of Virulence in Opportunistic Pathogens: Generalism, Plasticity, and Control. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Ganesh, V.K.; Höök, M. Adhesion, Invasion and Evasion: The Many Functions of the Surface Proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintarak, S.; Whawell, S.A.; Speight, P.M.; Packer, S.; Nair, S.P. Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by Human Keratinocytes. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 5668–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speziale, P.; Pietrocola, G. The Multivalent Role of Fibronectin-Binding Proteins A and B (FnBPA and FnBPB) of Staphylococcus aureus in Host Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, S.J.; Moore, C.E.; Justice, A.; Kantzanou, M.; Story, L.; Mackie, K.; O’Neill, G.; Day, N.P.J. Virulent Combinations of Adhesin and Toxin Genes in Natural Populations of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4987–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Löffler, B. Staphylococcus aureus Dynamically Adapts Global Regulators and Virulence Factor Expression in the Course from Acute to Chronic Infection. Curr. Genet. 2016, 62, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraunholz, M.; Sinha, B. Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus: Live-in and Let Die. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus aureus Toxins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mempel, M.; Lina, G.; Hojka, M.; Schnopp, C.; Seidl, H.-P.; Schäfer, T.; Ring, J.; Vandenesch, F.; Abeck, D. High Prevalence of Superantigens Associated with the Egc Locus in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Patients with Atopic Eczema. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 22, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lina, G.; Piémont, Y.; Godail-Gamot, F.; Bes, M.; Peter, M.-O.; Gauduchon, V.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J. Involvement of Panton-Valentine Leukocidin—Producing Staphylococcus aureus in Primary Skin Infections and Pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, Y.; Issartel, B.; Vanhems, P.; Fournet, J.-C.; Lina, G.; Bes, M.; Vandenesch, F.; Piémont, Y.; Brousse, N.; Floret, D.; et al. Association between Staphylococcus aureus Strains Carrying Gene for Panton-Valentine Leukocidin and Highly Lethal Necrotising Pneumonia in Young Immunocompetent Patients. Lancet 2002, 359, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.K.; Yarwood, J.M.; Schlievert, P.M. Toxic Shock Syndrome and Bacterial Superantigens: An Update. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Medina, E.; Hussain, M.; Völker, W.; Heitmann, V.; Niemann, S.; Holzinger, D.; Roth, J.; Proctor, R.A.; Becker, K.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Phenotype Switching: An Effective Bacterial Strategy to Escape Host Immune Response and Establish a Chronic Infection. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Geraci, J.; Löffler, B. Staphylococcus aureus Regulator Sigma B Is Important to Develop Chronic Infections in Hematogenous Murine Osteomyelitis Model. Pathogens 2017, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alouf, J.E.; Müller-Alouf, H. Staphylococcal and Streptococcal Superantigens: Molecular, Biological and Clinical Aspects. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 292, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzembowski, T.; Piechowicz, L.; Bronk, M.; Pałubicka, A.; Naumiuk, Ł. Changes in the Protein Profile in Staphylococcal Strains from Patients Infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2023, 72, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechowicz, L.; Garbacz, K.; Galiński, J. Staphylococcus aureus of Phage Type 187 Isolated from People Occurred to Be a Genes Carrier of Eneterotoxin C and Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2008, 211, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, K.; Piechowicz, L.; Mroczkowska, A. Distribution of Toxin Genes among Different Spa Types and Phage Types of Animal Staphylococcus aureus. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaźmierczak, N.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Piechowicz, L. Biofilm Formation and Prevalence of Biofilm-Related Genes among Clinical Strains of Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krut, O.; Utermöhlen, O.; Schlossherr, X.; Krönke, M. Strain-Specific Association of Cytotoxic Activity and Virulence of Clinical Staphylococcus aureus Isolates. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2716–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Qatouseh, L.F.; Chinni, S.V.; Seggewiß, J.; Proctor, R.A.; Brosius, J.; Rozhdestvensky, T.S.; Peters, G.; von Eiff, C.; Becker, K. Identification of Differentially Expressed Small Non-Protein-Coding RNAs in Staphylococcus aureus Displaying Both the Normal and the Small-Colony Variant Phenotype. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Pöllath, C.; Siegmund, A.; Deinhardt-Emmer, S.; Hoerr, V.; Svensson, C.-M.; Thilo Figge, M.; Monecke, S.; Löffler, B. Clinical S. Aureus Isolates Vary in Their Virulence to Promote Adaptation to the Host. Toxins 2019, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziewanowska, K.; Patti, J.M.; Deobald, C.F.; Bayles, K.W.; Trumble, W.R.; Bohach, G.A. Fibronectin Binding Protein and Host Cell Tyrosine Kinase Are Required for Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4673–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionin, B.; Hammamieh, R.; Shupp, J.W.; Das, R.; Pontzer, C.H.; Jett, M. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B Causes Differential Expression of Rnd3 and RhoA in Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells While Inducing Actin Stress Fiber Assembly and Apoptosis. Microb. Pathog. 2008, 45, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, D.S.; Soria, J.A.; Gaviglio, E.A.; Garcia-Keller, C.; Cancela, L.M.; Rodriguez-Galan, M.C.; Wang, J.M.; Iribarren, P. Toll-like Receptor 2 Ligands Promote Microglial Cell Death by Inducing Autophagy. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitur, K.; Wachtel, S.; Brown, A.; Wickersham, M.; Paulino, F.; Peñaloza, H.F.; Soong, G.; Bueno, S.; Parker, D.; Prince, A. Necroptosis Promotes Staphylococcus aureus Clearance by Inhibiting Excessive Inflammatory Signaling. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe, Y.M.; Bedoui, S.; Stinear, T.P.; Hachani, A. Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus and Host Cell Death Pathways. Cell. Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.; Borges, A.; Simões, M. Staphylococcus aureus Toxins and Their Molecular Activity in Infectious Diseases. Toxins 2018, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Y.-A.; Haefliger, J.-A.; Piroth, L.; François, P.; Widmer, E.; Entenza, J.M.; Sinha, B.; Herrmann, M.; Francioli, P.; Vaudaux, P.; et al. Fibrinogen and Fibronectin Binding Cooperate for Valve Infection and Invasion in Staphylococcus aureus Experimental Endocarditis. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzoni, C.; Kelley, W.L. Staphylococcus aureus: New Evidence for Intracellular Persistence. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz-Linek, U.; Werner, J.M.; Pickford, A.R.; Gurusiddappa, S.; Kim, J.H.; Pilka, E.S.; Briggs, J.A.G.; Gough, T.S.; Höök, M.; Campbell, I.D.; et al. Pathogenic Bacteria Attach to Human Fibronectin through a Tandem β-Zipper. Nature 2003, 423, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, A.; Fraunholz, M.J. In or out: Phagosomal Escape of Staphylococcus aureus. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinka, J.; Hachmeister, M.; Geraci, J.; Sordelli, D.; Hansen, U.; Niemann, S.; Oetermann, S.; Peters, G.; Löffler, B.; Tuchscherr, L. Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Chronic Osteomyelitis Are Characterized by High Host Cell Invasion and Intracellular Adaptation, but Still Induce Inflammation. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morens, D.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Fauci, A.S. Predominant Role of Bacterial Pneumonia as a Cause of Death in Pandemic Influenza: Implications for Pandemic Influenza Preparedness. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullers, J.A. The Co-Pathogenesis of Influenza Viruses with Bacteria in the Lung. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Rénia, L.; MacAry, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The Trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, Inflammation and Intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Goodarzi, P.; Asadi, M.; Soltani, A.; Aljanabi, H.A.A.; Jeda, A.S.; Dashtbin, S.; Jalalifar, S.; Mohammadzadeh, R.; Teimoori, A.; et al. Bacterial Co-Infections with SARS-CoV-2. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 2097–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vidal, C.; Sanjuan, G.; Moreno-García, E.; Puerta-Alcalde, P.; Garcia-Pouton, N.; Chumbita, M.; Fernandez-Pittol, M.; Pitart, C.; Inciarte, A.; Bodro, M.; et al. Incidence of Co-Infections and Superinfections in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, Z.; Knoop, B.T.; Dofferhoff, A.S.M.; Blaauw, M.J.T.; Janssen, N.A.; van Apeldoorn, M.; Kerckhoffs, A.P.M.; van de Maat, J.S.; Hoogerwerf, J.J.; ten Oever, J. Few Bacterial Co-Infections but Frequent Empiric Antibiotic Use in the Early Phase of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Results from a Multicentre Retrospective Cohort Study in The Netherlands. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.; Troise, O.; Donaldson, H.; Mughal, N.; Moore, L.S.P. Bacterial and Fungal Coinfection among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study in a UK Secondary-Care Setting. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westblade, L.F.; Simon, M.S.; Satlin, M.J. Bacterial Coinfections in Coronavirus Disease 2019. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deinhardt-Emmer, S.; Haupt, K.F.; Garcia-Moreno, M.; Geraci, J.; Forstner, C.; Pletz, M.; Ehrhardt, C.; Löffler, B. Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia: Preceding Influenza Infection Paves the Way for Low-Virulent Strains. Toxins 2019, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łubowska, N.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Kosznik-Kwaśnicka, K.; Zauszkiewicz-Pawlak, A.; Węgrzyn, A.; Dołęgowska, B.; Piechowicz, L. Characterization of the Three New Kayviruses and Their Lytic Activity Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piechowicz, L.; Garbacz, K. Poultry-Like pA+ Biotype of Staphylococcus aureus CC346/084 Clone in Human Population. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarzembowski, T.; Jóźwik, A.; Wiśniewska, K.; Witkowski, J. Flow Cytometry Approach Study of Enterococcus faecalis Vancomycin Resistance by Detection of Vancomycin@FL Binding to the Bacterial Cells. Curr Microbiol 2010, 61, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daca, A.; Gołębiewska, J.; Bronk, M.; Jarzembowski, T. Changes of Urine Isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Biofilm Affect Monocytes’ Response. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, M.; Wang, G.; Johnson, W.M. Multiplex PCR for Detection of Genes for Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins, Exfoliative Toxins, Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin 1, and Methicillin Resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzembowski, T.; Jóźwik, A.; Wiśniewska, K.; Witkowski, J.; Jarzembowski, T.; Jóźwik, A.; Wiśniewska, K.; Witkowski, J. Single Cell Level Survey on Heterogenic Glycopeptide and β-Lactams Resistance. In Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria—A Continuous Challenge in the New Millennium; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0472-8. [Google Scholar]
- Peyrusson, F.; Varet, H.; Nguyen, T.K.; Legendre, R.; Sismeiro, O.; Coppée, J.-Y.; Wolz, C.; Tenson, T.; Van Bambeke, F. Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus Persisters upon Antibiotic Exposure. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanenkov, V.V.; Felici, F.; Menon, A.G. Uptake and Intracellular Fate of Phage Display Vectors in Mammalian Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1999, 1448, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Ramachandran, A.; Thanki, A.M.; Vukusic, F.B.I.; Barylski, J.; Clokie, M.R.J. Bacteriophages Are More Virulent to Bacteria with Human Cells than They Are in Bacterial Culture; Insights from HT-29 Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repetto, G.; del Peso, A.; Zurita, J.L. Neutral Red Uptake Assay for the Estimation of Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosznik-Kwaśnicka, K.; Stasiłojć, M.; Stasiłojć, G.; Kaźmierczak, N.; Piechowicz, L. The Influence of Bacteriophages on the Metabolic Condition of Human Fibroblasts in Light of the Safety of Phage Therapy in Staphylococcal Skin Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Virulence Gene * | COVID-19 Strains n = 26 (%) | Non-COVID-19 Strains n = 21 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesin genes | ||
| fnbA | 21 (80.8) | 21 (100) |
| fnbB | 26 (100) ** | 7 (33.3) |
| Toxin genes | ||
| tst | 2 (7.7) | 0 |
| sea | 0 | 4 (19.0) *** |
| seb | 0 | 1 (4.8) |
| sec | 1 (3.8) | 0 |
| sed | 0 | 0 |
| pvl | 0 | 1 (4.8) |
| eta | 0 | 0 |
| etb | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piechowicz, L.; Kosznik-Kwaśnicka, K.; Jarzembowski, T.; Daca, A.; Necel, A.; Bonawenturczak, A.; Werbowy, O.; Stasiłojć, M.; Pałubicka, A. Staphylococcus aureus Co-Infection in COVID-19 Patients: Virulence Genes and Their Influence on Respiratory Epithelial Cells in Light of Risk of Severe Secondary Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251810050
Piechowicz L, Kosznik-Kwaśnicka K, Jarzembowski T, Daca A, Necel A, Bonawenturczak A, Werbowy O, Stasiłojć M, Pałubicka A. Staphylococcus aureus Co-Infection in COVID-19 Patients: Virulence Genes and Their Influence on Respiratory Epithelial Cells in Light of Risk of Severe Secondary Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(18):10050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251810050
Chicago/Turabian StylePiechowicz, Lidia, Katarzyna Kosznik-Kwaśnicka, Tomasz Jarzembowski, Agnieszka Daca, Agnieszka Necel, Ada Bonawenturczak, Olesia Werbowy, Małgorzata Stasiłojć, and Anna Pałubicka. 2024. "Staphylococcus aureus Co-Infection in COVID-19 Patients: Virulence Genes and Their Influence on Respiratory Epithelial Cells in Light of Risk of Severe Secondary Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 18: 10050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251810050
APA StylePiechowicz, L., Kosznik-Kwaśnicka, K., Jarzembowski, T., Daca, A., Necel, A., Bonawenturczak, A., Werbowy, O., Stasiłojć, M., & Pałubicka, A. (2024). Staphylococcus aureus Co-Infection in COVID-19 Patients: Virulence Genes and Their Influence on Respiratory Epithelial Cells in Light of Risk of Severe Secondary Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(18), 10050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251810050







