A PLGA/Silk Fibroin Nanofibre Membrane Loaded with Natural Flavonoid Compounds Extracted from Green Cocoons for Wound Healing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
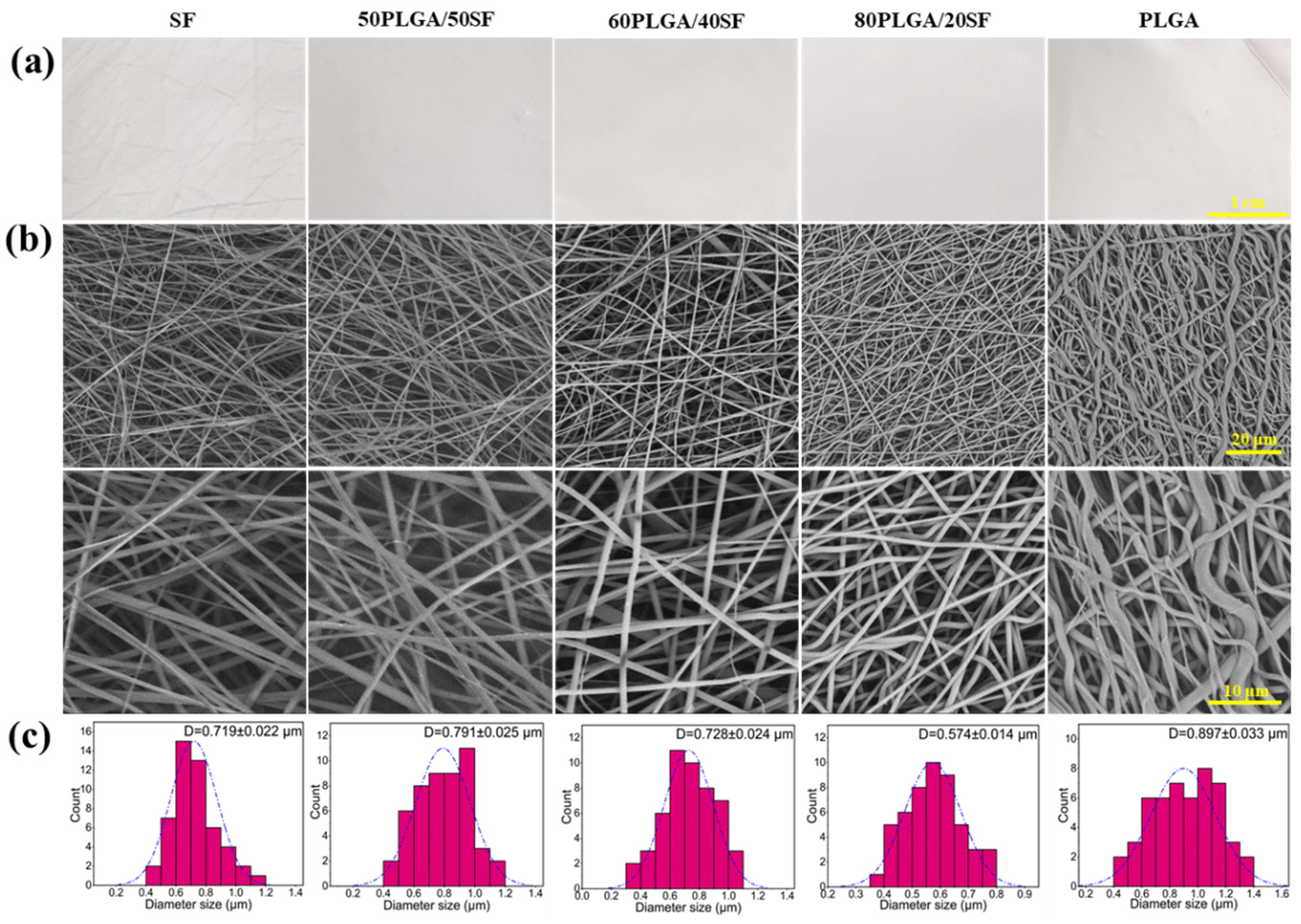
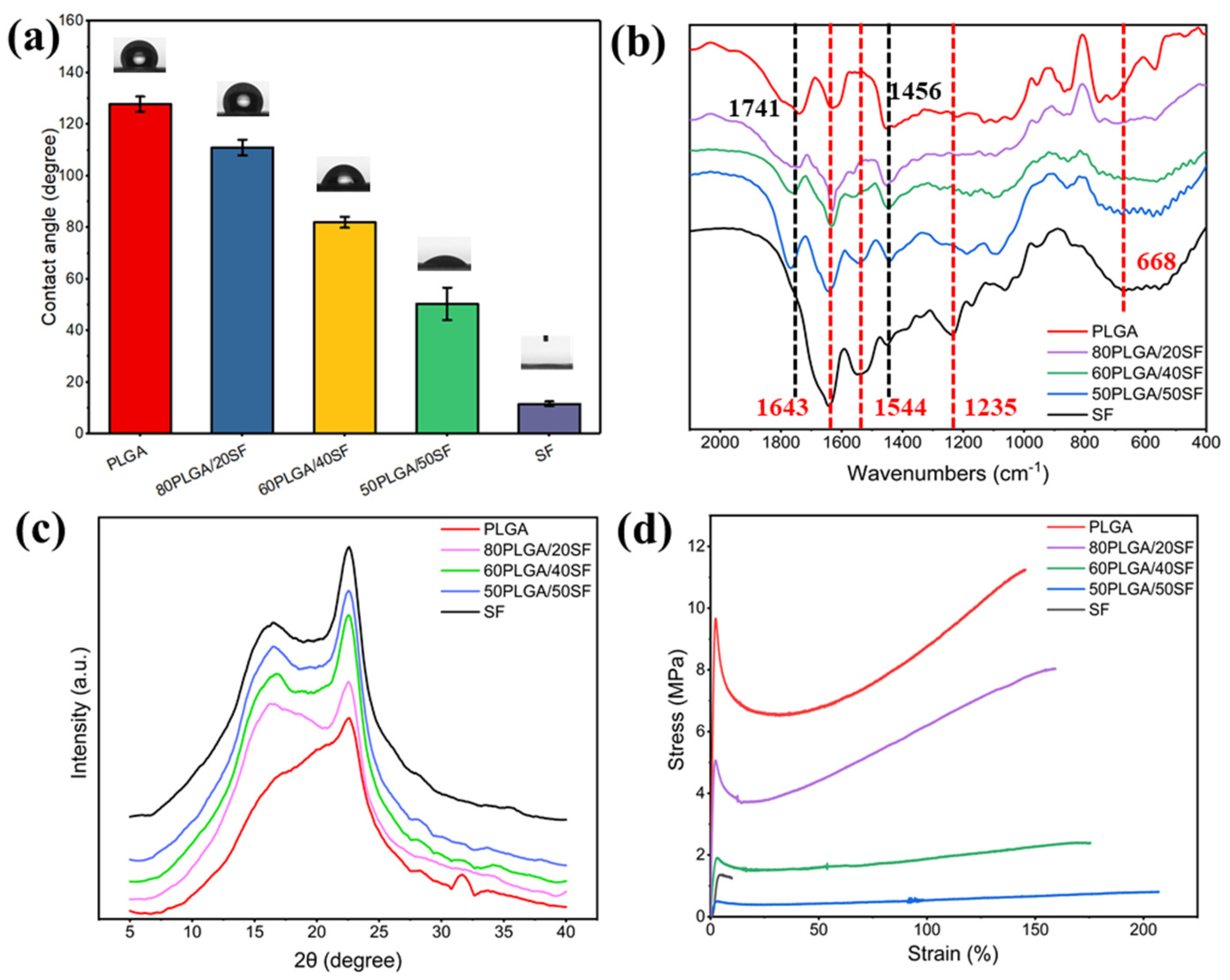
2.1. Characterization of PLGA/SF Nanofibre Membranes
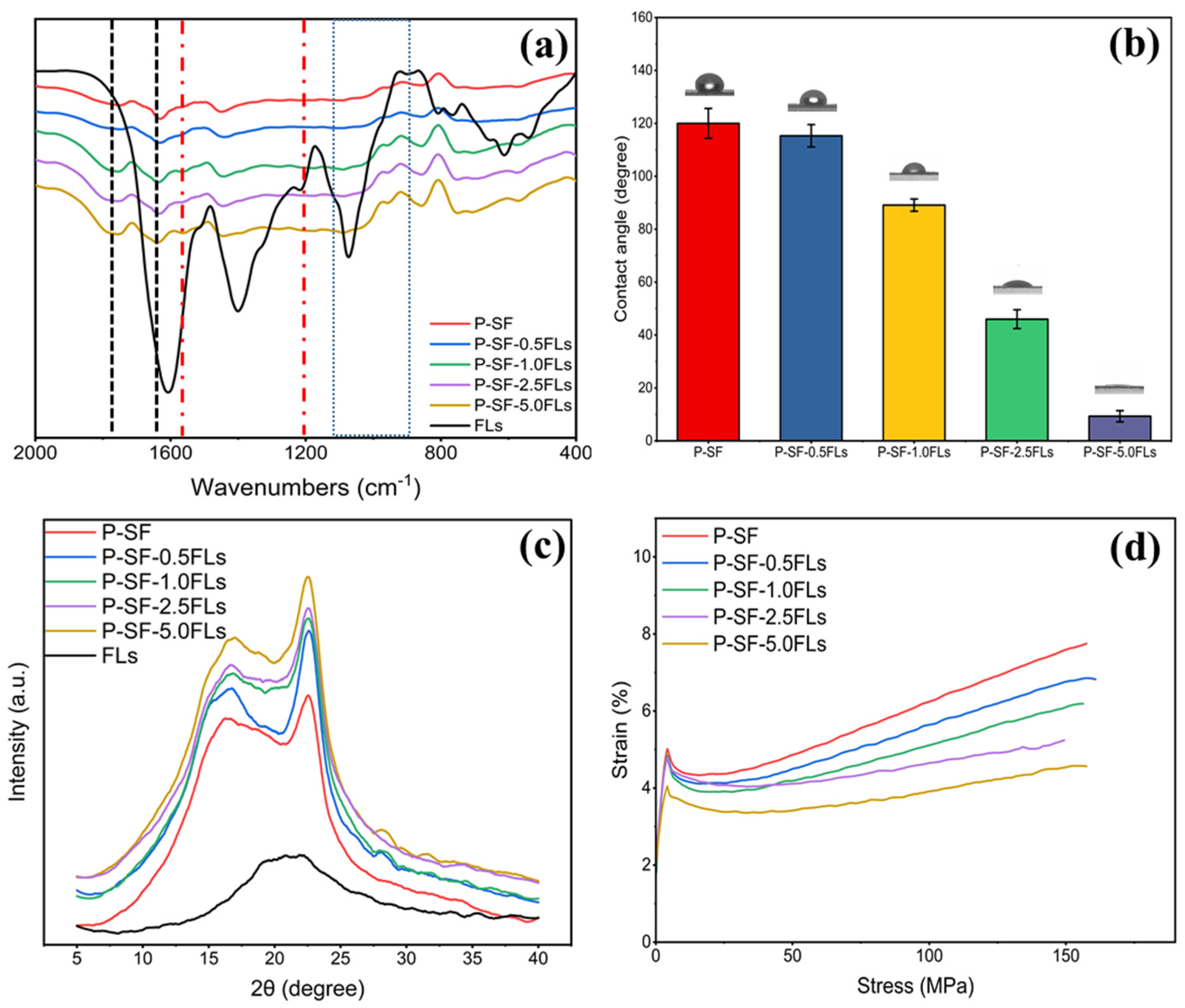
2.2. Fabrication and Characterization of FL-Loaded P-SF Nanofibre Membranes
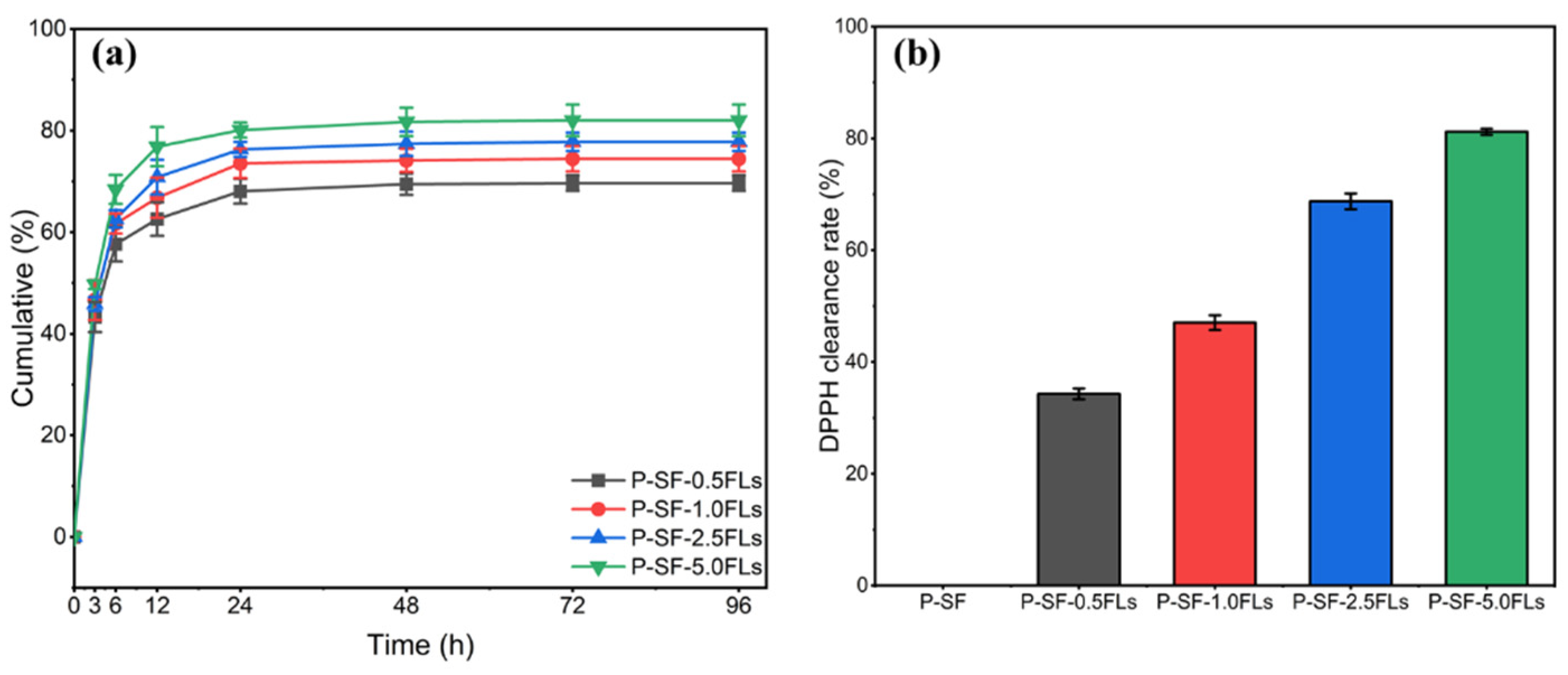
2.3. Release of FLs from FL-Loaded P-SF Membranes
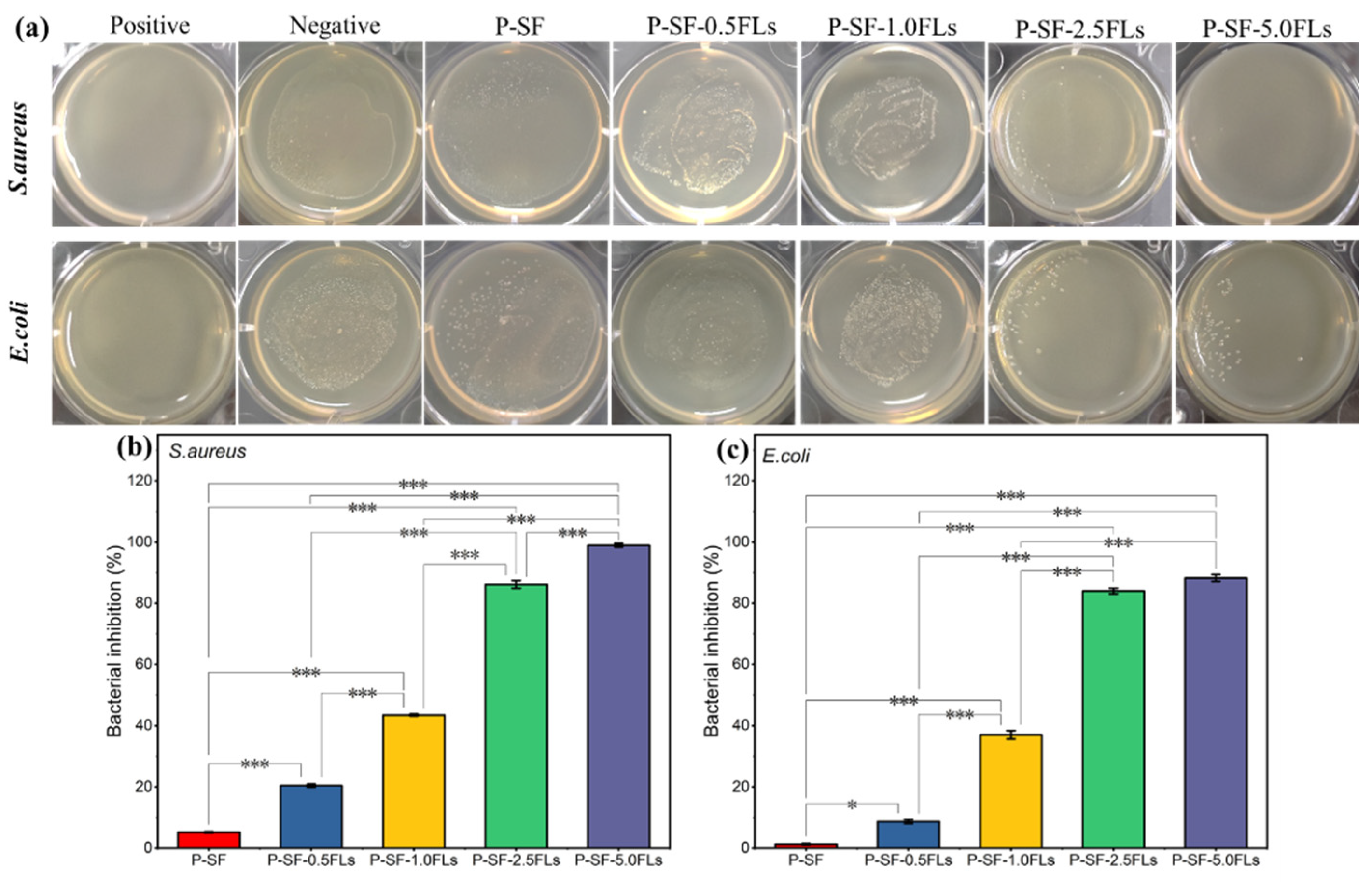
2.4. Anti-Oxidation and Antibacterial Properties of the P-SF-nFL Nanofibre Membranes
2.5. Biocompatibility of the P-SF-nFLs Nanofibre Membranes
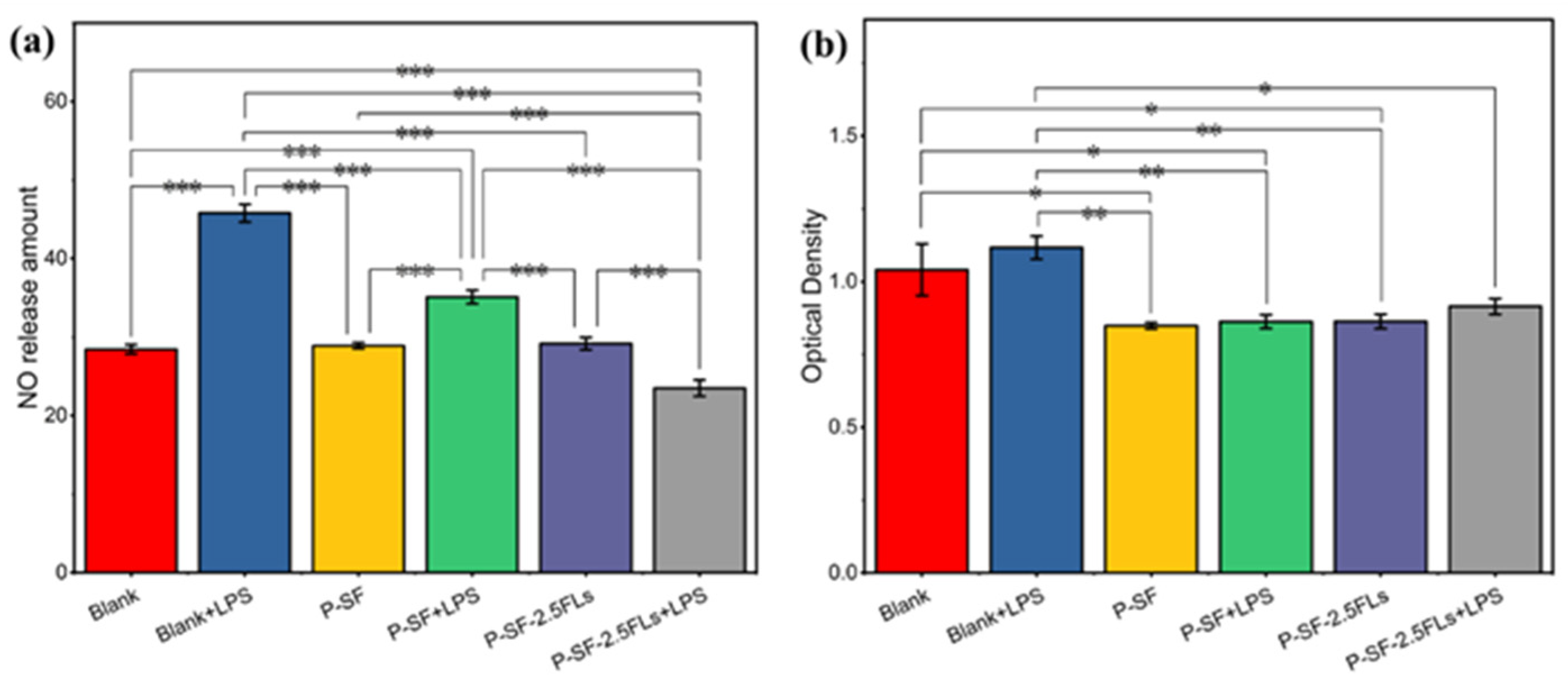
2.6. Anti-Inflammatory Analysis of P-SF-nFLs Nanofibre Membranes
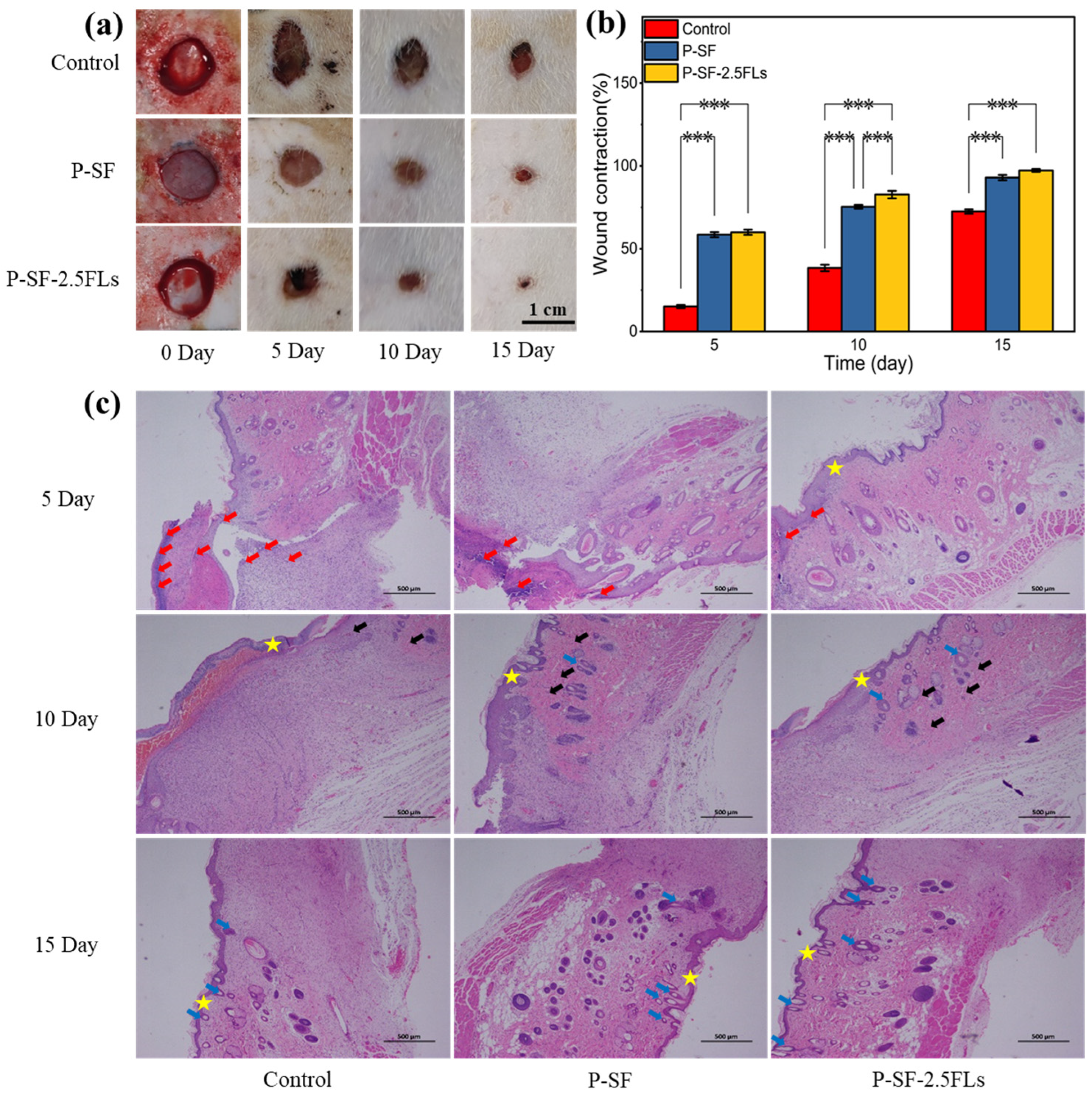
2.7. In Vivo Wound Healing and Histological Analysis
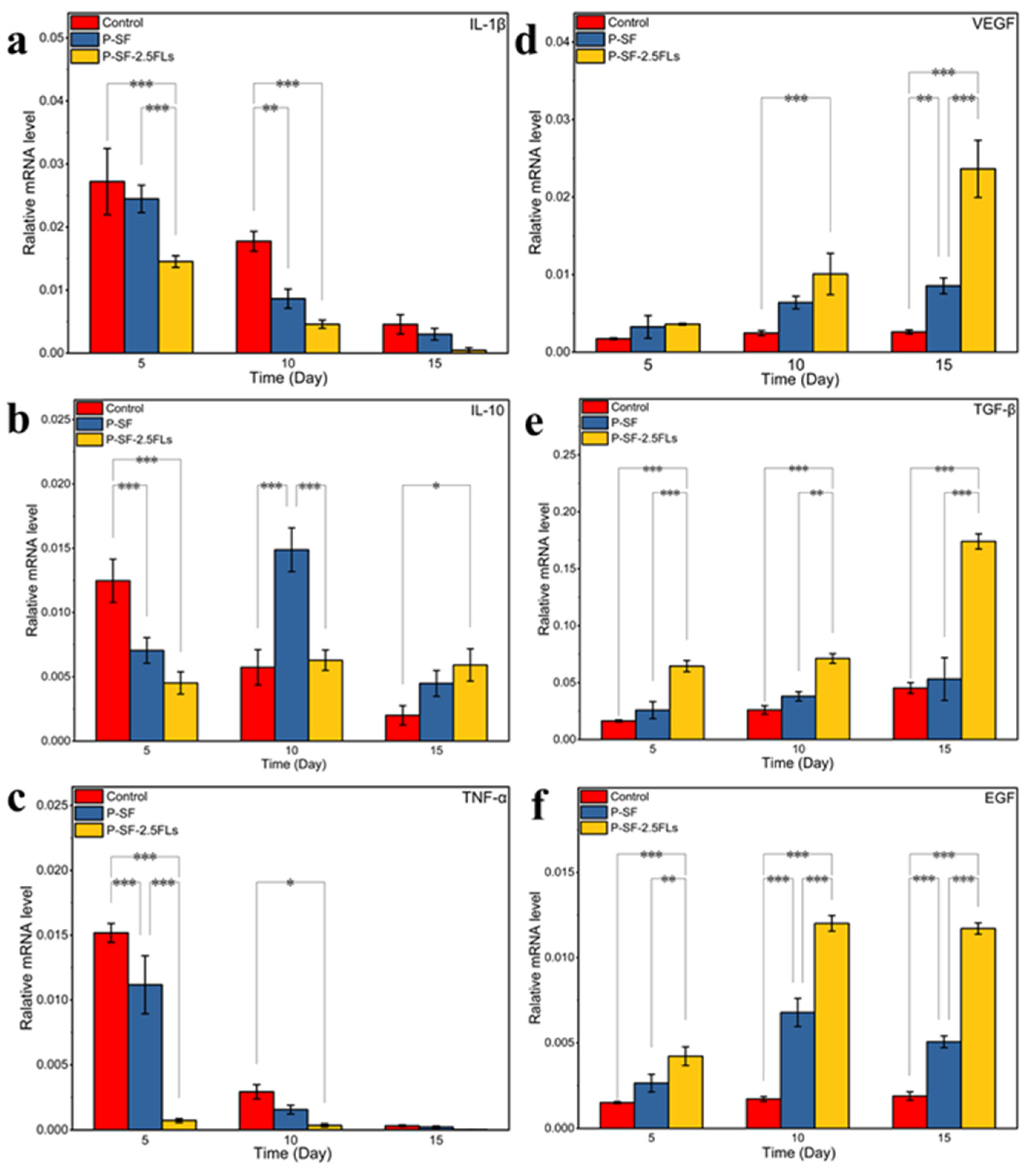
2.8. Effect of FLs on Expression of Genes Involved in Wound Healing
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Extraction of Flavonoids and Preparation of Regenerated Silk Fibroin
3.3. Fabrication of PLGA/SF-nFL Nanofibre Membranes
3.4. Characterization of Composite Nanofibre Membranes
3.5. In Vitro Release of FLs from FL-Loaded Membranes
3.6. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of the Nanofibre Membranes
3.7. In Vitro Biocompatibility of PLGA/SF-nFL Membranes
3.8. Anti-Inflammatory Testing of PLGA/SF-nFL Membranes
3.9. In Vivo Wound Healing with Nanofibre Membranes
3.10. Histological Analysis
3.11. Real-Time qPCR Examination
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spicer, C.D. Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: The importance of polymer choice. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 184–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macneil, S. Progress and opportunities for tissue-engineered skin. Nature 2007, 445, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, J.M.; Sorg, H. Wound repair and regeneration. Eur. Surg. Res. 2012, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Chouhan, D.; Mandal, B.B. Tissue engineered skin and wound healing: Current strategies and future directions. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 3455–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinno, H.; Prakash, S. Complements and the wound healing cascade: An updated review. Plast. Surg. Int. 2013, 2013, 146764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Baker, A.B. Biomaterials and nanotherapeutics for enhancing skin wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandara, A.A.; Mustoe, T.A. Oxygen in wound healing-more than a nutrient. World J. Surg. 2004, 28, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarato, G.; Bertorelli, R.; Athanassiou, A. Borrowing from nature: Biopolymers and biocomposites as smart wound care materials. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2018, 6, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivya, S.; Padma, V.V.; Santhini, E. Wound dressings—A review. Biomedicine 2015, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yang, J.; O’Connor, D.M.; Zhu, C.; Huo, D.; Boulis, N.M.; Xia, Y. Differentiation of bone marrow stem cells into schwann cells for the promotion of neurite outgrowth on electrospun fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12299–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Russell, S.J.; Long, Y.-Z. Advances in portable electrospinning devices for in situ delivery of personalized wound care. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19166–19178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoen, B.; Avrahami, R.; Baruch, L.; Efraim, Y.; Goldfracht, I.; Elul, O.; Machluf, M. Electrospun extracellular matrix: Paving the way to tailor-made natural scaffolds for cardiac tissue regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, R.; Sun, Z.; Su, W.; Pan, G.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, J.; Cui, W. Flexible bipolar nanofibrous membranes for improving gradient microstructure in tendon-to-bone healing. Acta Biomater. 2017, 61, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Yang, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Yu, D.G. A nanofiber-based drug depot with high drug loading for sustained release. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2020, 583, 119397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Pisignano, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospun nanofibers: Maneuvering the migration and differentiation of stem cells with electrospun nanofibers. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Bao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Dai, F.; Li, Z. Electrospun PLGA/SF/artemisinin composite nanofibrous membranes for wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, W.; Tan, G. Silk fibroin combined with electrospinning as a promising strategy for tissue regeneration. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, 2200380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, H.; Long, J.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Jia, Q.; Teng, B.; Tang, T. Osteogenic magnesium incorporated into PLGA/TCP porous scaffold by 3D printing for repairing challenging bone defect. Biomaterials 2019, 197, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Yang, F.; Seyednejad, H.; Chen, Z.; Hennink, W.E.; Anderson, J.M.; van der Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Jansen, J.A. Biocompatibility and degradation characteristics of PLGA-based electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds with nanoapatite incorporation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6604–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariraj, G.; Somashekar, T.H. Influence of cooking and adjustment treatments on reeling and quality characteristics of raw silk. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2004, 29, 207–217. [Google Scholar]
- Daimon, T.; Hirayama, C.; Kanai, M.; Ruike, Y.; Meng, Y.; Kosegawa, E.; Nakamura, M.; Tsujimoto, G.; Katsuma, S.; Shimada, T. The silkworm Green b locus encodes a quercetin 5-O-glucosyltransferase that produces green cocoons with UV-shielding properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11471–11476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfirio, D.A.; Ferreira, R.d.Q.; Malagutti, A.R.; Agostini Valle, E.M. Electrochemical study of the increased antioxidant capacity of flavonoids through complexation with iron(II) ions. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 141, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Xia, X.; Guan, Y.; Yi, H.; Lai, S.; Sun, Y.; Cao, S. Antimicrobial quantitative relationship and mechanism of plant flavonoids to gram-positive bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhao, J.G.; Wei, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.Q. The renal protection of flavonoid-rich ethanolic extract from silkworm green cocoon involves in inhibiting TNF-α-p38 MAP kinase signalling pathway in type 2 diabetic mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.H.; Shao, Z.M.; Tang, D.Q.; Lu, Q.; Chen, X.; Yin, X.X.; Wu, J.; Chen, H. Preventive effects of rutin on the development of experimental diabetic nephropathy in rat. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjaneyulu, M.; Chopra, K. Quercetin, an anti-oxidant bioflavonoid, attenuates diabetic nephropathy in rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 31, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Shang, L.; Chai, R.; Zhao, Y. Natural polymer-derived bioscaffolds for peripheral nerve regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umuhoza, D.; Yang, F.; Long, D.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, A. Strategies for tuning the biodegradation of silk fibroin-based materials for tissue engineering applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1290–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.R.; Kaplan, D.L. Biomedical applications of chemically-modified silk fibroin. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6443–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, K.H.; Fan, C.Y.; Mo, X.M.; Ruan, H.J.; Li, F.F. Aligned natural–synthetic polyblend nanofibers for peripheral nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joodaki, H.; Panzer, M.B. Skin mechanical properties and modeling: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2018, 232, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Xu, F. Cambridge CB PZ, UK, Mechanical properties of skin: A review. Adv. Mech. 2008, 38, 393–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Li, B.; Qiao, M.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Advances on the in vivo and in vitro glycosylations of flavonoids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6587–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordon, S.; Poplonski, J.; Huszcza, E. Microbial glycosylation of flavonoids. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, P.I.; Aguiar-Ricardo, A.; Correia, I.J. Asymmetric membranes as ideal wound dressings: An overview on production methods, structure, properties and performance relationship. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buie, T.W.; Whitely, M.; Mccune, J.; Lan, Z.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Comparative efficacy of resorbable fiber wraps loaded with gentamicin sulfate or gallium maltolate in the treatment of osteomyelitis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2021, 109, 2255–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Ullah, S.; Khan, M.Q.; Hashmi, M.; Kim, I.S. Manuka honey incorporated cellulose acetate nanofibrous mats: Fabrication and in vitro evaluation as a potential wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, Q.V.; Pham Cam, N.; Nguyen Minh, T.; Nguyen Tien, T.; Phan, C.-T.D.; Mechler, A. Antioxidant motifs in flavonoids: O-H versus C-H bond dissociation. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 8935–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, D.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Mendonça, A.G.; Correia, I.J. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, F.; Khameneh, B.; Iranshahi, M.; Iranshahy, M. Antibacterial activity of flavonoids and their structure-activity relationship: An update review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, W.; Tang, F.; Chen, X.; Ren, L. Antibacterial activities of flavonoids: Structure-activity relationship and mechanism. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as potential anti-inflammatory molecules: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Selvaraj, B.; Yoo, K.Y.; Ko, S.-H. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agents. Int. J. Oral Biol. 2020, 45, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzani, O.; Boutin, H.; Chuquet, J.; Rothwell, N. Potential mechanisms of interleukin-1 involvement in cerebral ischaemia. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 100, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklin, M.J.H.; Weith, A.; Duff, G.W. A physical map of the region encompassing the human interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genes. Genomics 1994, 19, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, N.N.; Polverini, P.J.; Koch, A.E.; Volin, M.V.; Gamelli, R.L.; Dipietro, L.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor mediates angiogenic activity during the proliferative phase of wound healing. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.E.; Chen, L.; Mohan, R.R.; Liang, Q.; Liu, J. Expression of HGF, KGF, EGF and receptor messenger RNAs following corneal epithelial wounding. Exp. Eye Res. 1999, 68, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Dai, F. Silk fibroin/polycaprolactone nanofibrous membranes loaded with natural Manuka honey for potential wound healing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e51686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, J.; An, E.; Lu, B.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, K.; Liang, S.; Hu, H.; Han, M.; et al. Deciphering the genetic basis of silkworm cocoon colors provides new insights into biological coloration and phenotypic diversification. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Du, K.; Yan, F.; Li, Y. Microwave-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat germ albumin to prepare polypeptides and influence on physical and chemical properties. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample Name | Concentration of PLGA (wt%) | Concentration of SF (wt%) | Concentration of FLs (mg/g to Dry Matter) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF | - | 10 | - |
| 50PLGA/50SF | 5 | 5 | - |
| 60PLGA/40SF | 6 | 4 | - |
| 80PLGA/20SF | 8 | 2 | - |
| PLGA | 10 | - | - |
| 80PLGA/20SF/nFLs | 8 | 2 | 3, 6, 15, 30 |
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | CCTTCCGTGTTCCTACCCC | ACCAGGAAATGAGCTTGACA |
| IL-1β | AACAAACCCTGCAGTGGT TCG | AGCTGCTTCAGACACTTGCAC |
| IL-10 | CCATCATGCCTGGCT CAG CAC | TGTACTGGCCCCTGCTGATCC |
| TNF-α | GAAGCTCCCTCAGCGAGGACA | TTGGGCCAGTGAGTGAAAGGG |
| VEGF | GAGACCCTGGTGGACATCTT | GATCCGCATGATCTGCATAGG |
| TGF-β | AACAATTCCTGGCGTTACCTT | TGTATTCCGTCTCCTTGGTTC |
| EGF | GCCACGGTTACATTCACTCC | CCAAATCGCCTTCTCTTTCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Dai, F. A PLGA/Silk Fibroin Nanofibre Membrane Loaded with Natural Flavonoid Compounds Extracted from Green Cocoons for Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179263
Chen X, Liu J, Lu Y, Liu H, Cheng L, Li Z, Dai F. A PLGA/Silk Fibroin Nanofibre Membrane Loaded with Natural Flavonoid Compounds Extracted from Green Cocoons for Wound Healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179263
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiang, Jiaqi Liu, Yaru Lu, Huijun Liu, Lan Cheng, Zhi Li, and Fangyin Dai. 2024. "A PLGA/Silk Fibroin Nanofibre Membrane Loaded with Natural Flavonoid Compounds Extracted from Green Cocoons for Wound Healing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179263
APA StyleChen, X., Liu, J., Lu, Y., Liu, H., Cheng, L., Li, Z., & Dai, F. (2024). A PLGA/Silk Fibroin Nanofibre Membrane Loaded with Natural Flavonoid Compounds Extracted from Green Cocoons for Wound Healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179263







