Interleukin Profiling in Atopic Dermatitis and Chronic Nodular Prurigo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Recruitment and Testing of Chemically Induced Hyperknesis
4.2. Gene Expression Analysis
4.3. Data Analysis and Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaowattanapanit, S.; Wongjirattikarn, R.; Chaisuriya, N.; Ungarreevittaya, P.; Poosekeaw, P.; Winaikosol, K.; Choonhakarn, C.; Julanon, N.; Salao, K. Increased IL-31 expression in serum and tissue protein in prurigo nodularis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2022, 13, 20406223221112561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Hacini-Rachinel, F.; Fogel, P.; Rousseau, F.; Xing, X.; Patrick, M.T.; Billi, A.C.; Berthier, C.C.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Lazzari, A.; et al. Transcriptomic characterization of prurigo nodularis and the therapeutic response to nemolizumab. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonowska, J.; Gleń, J.; Roman Nowicki Nowicki, R.; Trzeciak, M. New Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis—New Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcovich, S.; Maurelli, M.; Gisondi, P.; Peris, K.; Yosipovitch, G.; Girolomoni, G. Pruritus as a distinctive feature of type 2 inflammation. Vaccines 2021, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Li, Y.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Steinhoff, M.; Chen, W.; Wang, J. Th2 modulation of transient receptor potential channels: An unmet therapeutic intervention for atopic dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, C.; Del Duca, E.; Guttman-Yassky, E. The IL-4, IL-13 and IL-31 pathways in atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, P.G.; Jolin, H.E.; Smith, P.; Emson, C.L.; Townsend, M.J.; Fallon, R.; Smith, P.; McKenzie, A.N. IL-4 induces characteristic Th2 responses even in the combined absence of IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13. Immunity 2002, 17, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, E.B.; Sivaprasad, U. Th2 Cytokines and Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 2, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Bieber, T.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Beck, L.A.; Blauvelt, A.; Cork, M.J.; Silverberg, J.I.; Deleuran, M.; Kataoka, Y.; Lacour, J.P.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Dupilumab versus Placebo in Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2335–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulzii, D.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Nakahara, T.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, K.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Furue, M. Scratching Counteracts IL-13 Signaling by Upregulating the Decoy Receptor IL-13Rα2 in Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuhara, K.; Nunomura, S.; Nanri, Y.; Ono, J.; Takai, M.; Kawaguchi, A. Periostin: An emerging biomarker for allergic diseases. Allergy 2019, 74, 2116–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfi, F. The impact of mast cells in neuroimmunology and cancer. Eur. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2023, 12, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, Y.H.; Egawa, G.; Honda, T.; Kabashima, K. Mast cells in type 2 skin inflammation: Maintenance and function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2250359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogatzki-Zahn, E.M.; Pereira, M.P.; Cremer, A.; Zeidler, C.; Dreyer, T.; Riepe, C.; Wempe, C.; Lotts, T.; Segelcke, D.; Ringkamp, M.; et al. Peripheral Sensitization and Loss of Descending Inhibition Is a Hallmark of Chronic Pruritus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 203–211.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agelopoulos, K.; Renkhold, L.; Wiegmann, H.; Dugas, M.; Süer, A.; Zeidler, C.; Schmelz, M.; Pereira, M.P.; Ständer, S. Transcriptomic, Epigenomic, and Neuroanatomic Signatures Differ in Chronic Prurigo, Atopic Dermatitis, and Brachioradial Pruritus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 264–272.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campion, M.; Leila Smith Smith, L.; Gatault, S.; Métais, C.; Buddenkotte, J.; Steinhoff, M. Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 evoke scratching behaviour in mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Castillo, J.M.; Das, M.; Strakosha, M.; McGurk, A.; Artru, E.; Kam, C.; Alasharee, M.; Wesemann, D.R.; Tomura, M.; Karasuyama, H.; et al. IL-4 acts on skin derived dendritic cells to promote the Th2 response to cutaneous sensitization and the development of allergic skin inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, M.; Ulzii, D.; Nakahara, T.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, K.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Kido-Nakahara, M. Implications of IL-13Rα2 in atopic skin inflammation. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Lu, Z.; Steinhoff, M.; Li, Y.; Buhl, T.; Fischer, M.; Chen, W.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, R.; Yan, X.; et al. Innate immune regulates cutaneous sensory IL-13 receptor alpha 2 to promote atopic dermatitis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 98, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umehara, Y.; Kiatsurayanon, C.; Trujillo-Paez, J.V.; Chieosilapatham, P.; Peng, G.; Yue, H.; Nguyen, H.L.T.; Song, P.; Okumura, K.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Intractable Itch in Atopic Dermatitis: Causes and Treatments. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Andersen, H.H.; Akiyama, T.; Nattkemper, L.A.; van Laarhoven, A.; Elberling, J.; Yosipovitch, G.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Alloknesis and hyperknesis-mechanisms, assessment methodology, and clinical implications of itch sensitization. Pain 2018, 159, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yosipovitch, G.; Berger, T.; Fassett, M.S. Neuroimmune interactions in chronic itch of atopic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Agelopoulos, K.; Pereira, M.P.; Wiegmann, H.; Ständer, S. Cutaneous neuroimmune crosstalk in pruritus. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bury, J.; Zirwas, M. Unexpected Clinical Lessons Learned From IL-4 and IL-13 Blockade. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1007–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, M.R.; Miron, Y.; Chen, F.; Miller, P.E.; Zhang, A.; Korotzer, A.; Richman, D.; Bryce, P.J. Type 2 cytokines sensitize human sensory neurons to itch-associated stimuli. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1258823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liao, V.; Cornman, H.L.; Ma, E.; Kwatra, S.G. Prurigo nodularis: New insights into pathogenesis and novel therapeutics. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 190, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature Selection with the Boruta Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
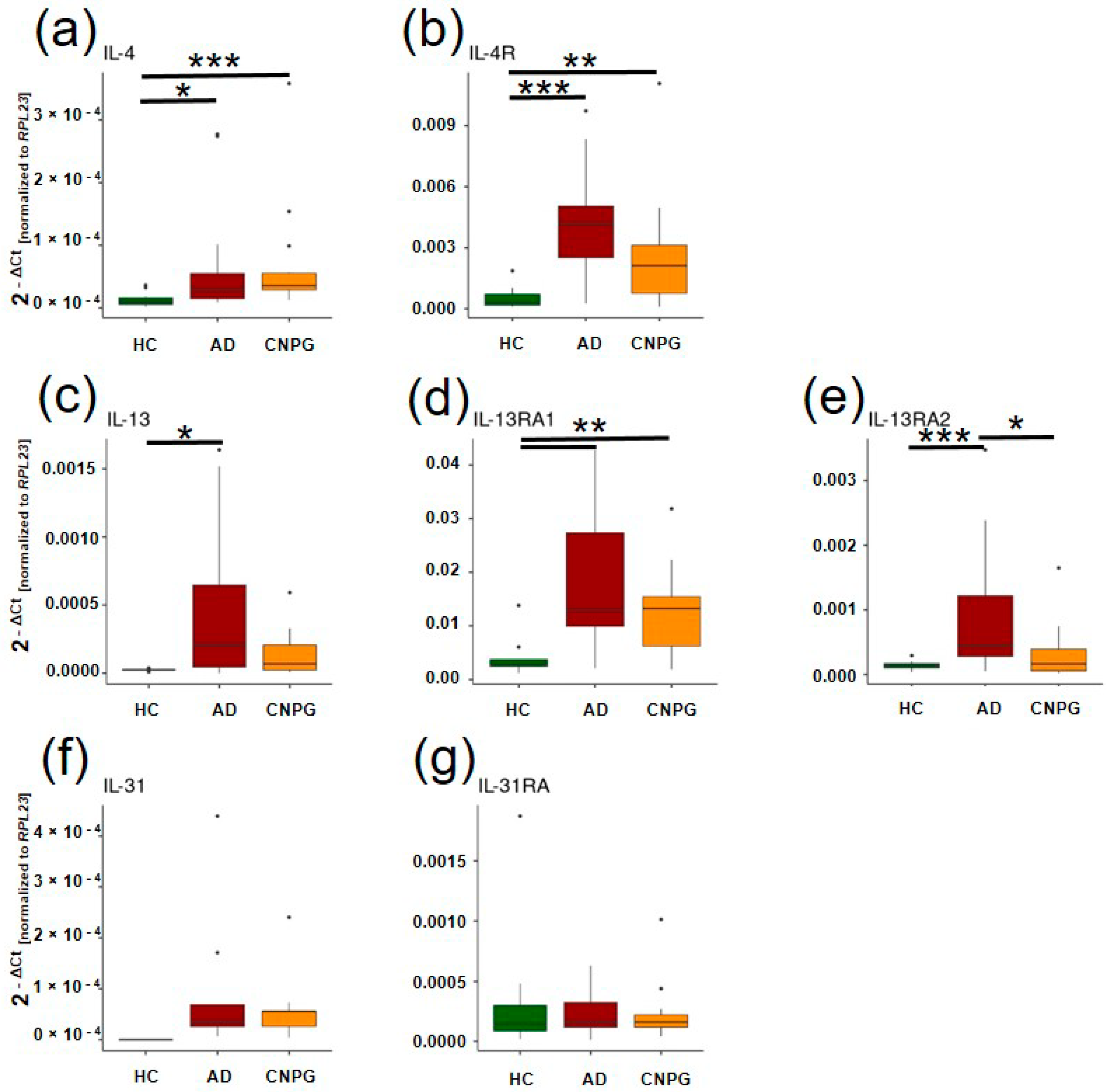
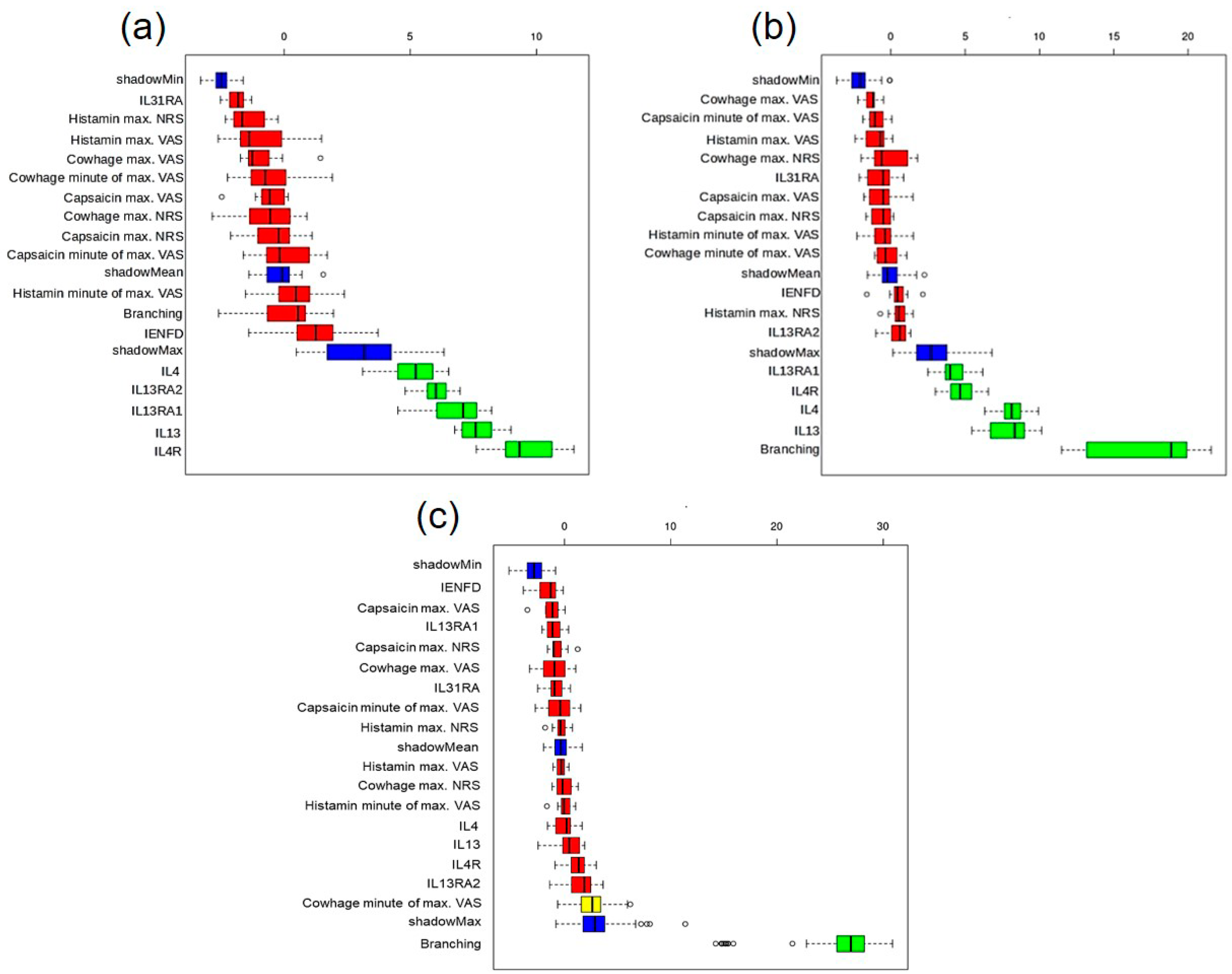
| Diagnosis | Sex (m/f) | Mean Age [min/max] | Median VAS Last 4 Weeks [IQR] | Median Pruritus Duration in Month [IQR] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atopic dermatitis | 8/9 | 50.06 [21; 71] | 7 [5; 8] | 133.35 [70.98; 281.19] |
| Chronic nodular prurigo | 3/11 | 56.5 [37; 76] | 5 [2.5; 7] | 101.11 [63.71; 183.88] |
| Healthy controls | 6/4 | 49.3 [23; 66] | NA | NA |
| Gene | Name | Amplicon Length (bp) | Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL4 | Hs00174122_m1 interleukin 4 TaqMan Assay | 70 | Thermo Fisher Scientific |
| IL13 | Hs00174379_m1 interleukin 13 TaqMan Assay | 82 | Thermo Fisher Scientific |
| IL4R | Hs00166237_m1 interleukin 4 receptor TaqMan Assay | 70 | Thermo Fisher Scientific |
| IL13RA1 | Hs00609817_m1 interleukin 13 receptor subunit alpha 1 TaqMan Assay | 147 | Thermo Fisher Scientific |
| IL13RA2 | Hs00152924_m1 interleukin 13 receptor subunit alpha 2 TaqMan Assay | 83 | Thermo Fisher Scientific |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiegmann, H.; Renkhold, L.; Zeidler, C.; Agelopoulos, K.; Ständer, S. Interleukin Profiling in Atopic Dermatitis and Chronic Nodular Prurigo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158445
Wiegmann H, Renkhold L, Zeidler C, Agelopoulos K, Ständer S. Interleukin Profiling in Atopic Dermatitis and Chronic Nodular Prurigo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158445
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiegmann, Henning, Lina Renkhold, Claudia Zeidler, Konstantin Agelopoulos, and Sonja Ständer. 2024. "Interleukin Profiling in Atopic Dermatitis and Chronic Nodular Prurigo" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158445
APA StyleWiegmann, H., Renkhold, L., Zeidler, C., Agelopoulos, K., & Ständer, S. (2024). Interleukin Profiling in Atopic Dermatitis and Chronic Nodular Prurigo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158445






