Copper Overload Increased Rat Striatal Levels of Both Dopamine and Its Main Metabolite Homovanillic Acid in Extracellular Fluid
Abstract
1. Introduction
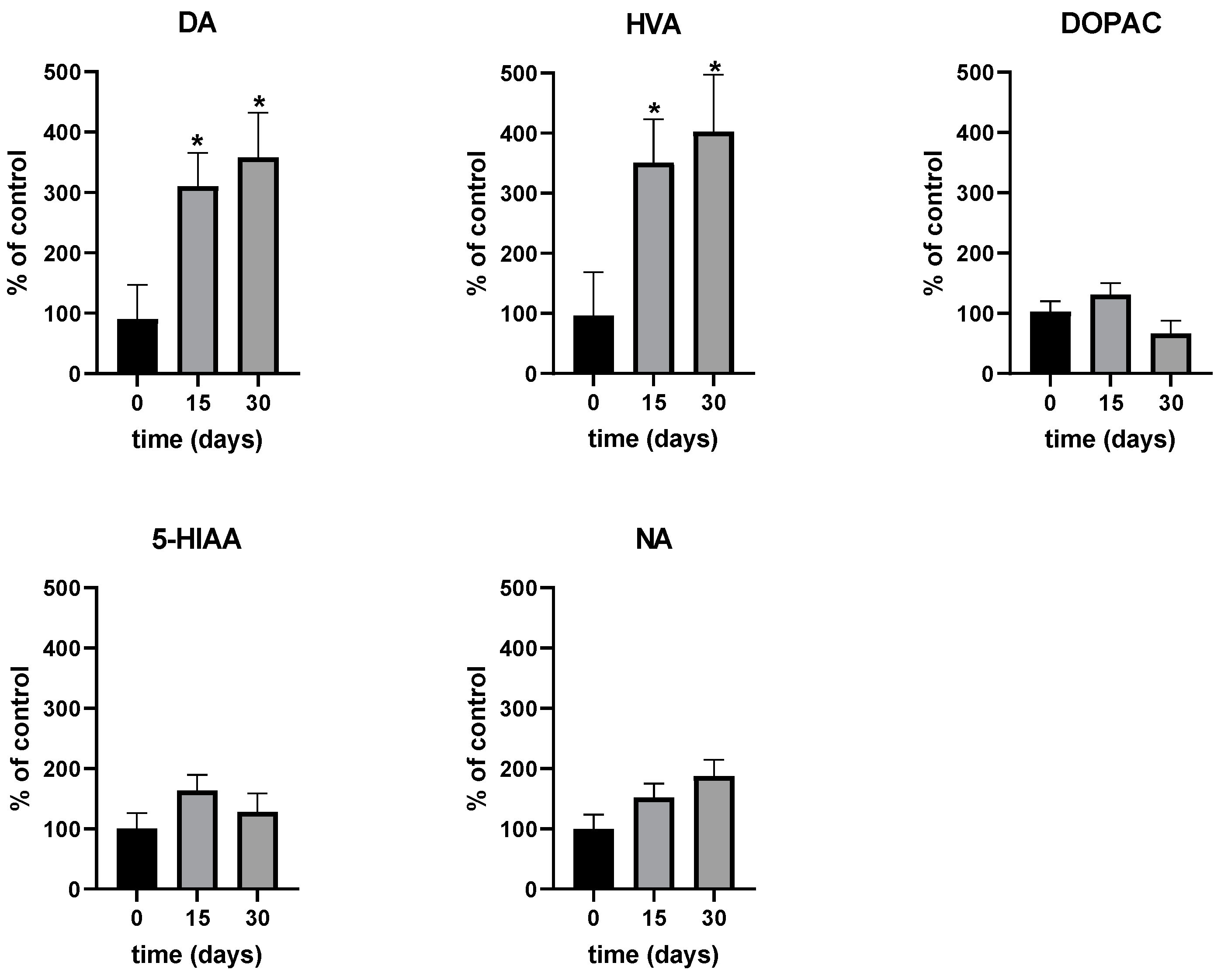
2. Results
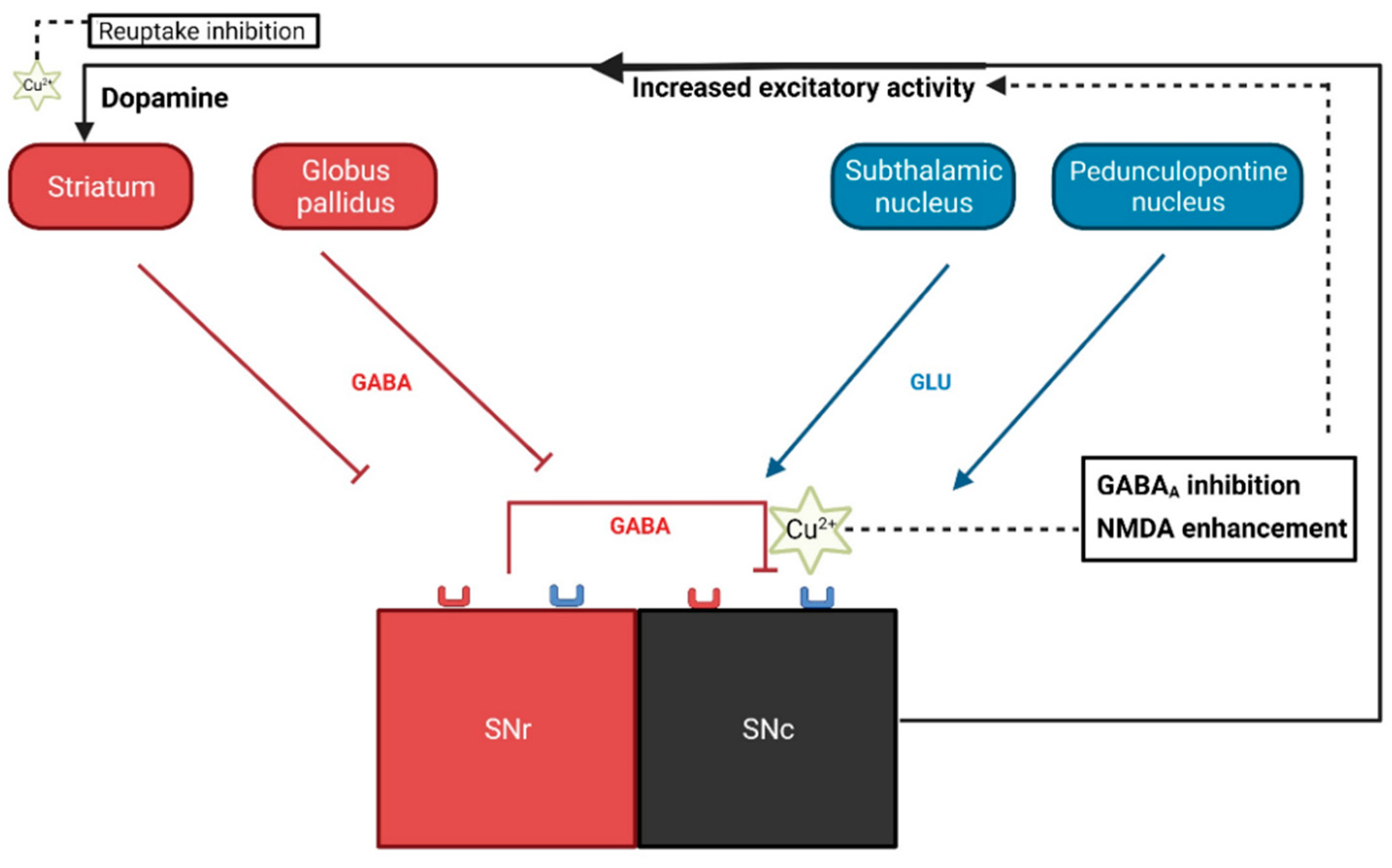
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rat Treatment
4.2. Microdialysis Procedure
4.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dusek, P.; Roos, P.M.; Litwin, T.; Schneider, S.A.; Flaten, T.P.; Aaseth, J. The neurotoxicity of iron, copper and manganese in Parkinson’s and Wilson’s diseases. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 31, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruces-Sande, A.; Isabel Rodriguez-Perez, A.; Herbello-Hermelo, P.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Mendez-Alvarez, E.; Luis Labandeira-Garcia, J.; Soto-Otero, R. Copper Increases Brain Oxidative Stress and Enhances the Ability of 6-Hydroxydopamine to Cause Dopaminergic Degeneration in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Prasad, R. Recent Discoveries on the Functions of Astrocytes in the Copper Homeostasis of the Brain: A Brief Update. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 26, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambrosi, N.; Rossi, L. Copper at synapse: Release, binding and modulation of neurotransmission. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 90, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, C.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Gavazzo, P. Multiple effects of copper on NMDA receptor currents. Brain Res. 2014, 1542, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharonova, I.N.; Vorobjev, V.S.; Haas, H.L. Interaction between copper and zinc at GABAA receptors in acutely isolated cerebellar Purkinje cells of the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, T.P.; Houston, C.M.; Brickley, S.G. Copper block of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the mature cerebellum and striatum. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 13431–13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Mayer, F.P.; Hasenhuetl, P.S.; Burtscher, V.; Schicker, K.; Sitte, H.H.; Freissmuth, M.; Sandtner, W. Occupancy of the zinc-binding site by transition metals decreases the substrate affinity of the human dopamine transporter by an allosteric mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4235–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwin, T.; Dusek, P.; Szafrański, T.; Dzieżyc, K.; Członkowska, A.; Rybakowski, J.K. Psychiatric manifestations in Wilson’s disease: Possibilities and difficulties for treatment. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 8, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnacka, B.; Szeszkowski, W.; Buettner, J.; Golebiowski, M.; Gromadzka, G.; Czlonkowska, A. Heterozygous carriers for Wilson’s disease-magnetic spectroscopy changes in the brain. Metab. Brain Dis. 2009, 24, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squitti, R.; Simonelli, I.; Ventriglia, M.; Siotto, M.; Pasqualetti, P.; Rembach, A.; Doecke, J.; Bush, A.I. Meta-analysis of serum non-ceruloplasmin copper in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 38, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Meana, J.J.; O’Connor, W.T.; Goiny, M.; Reid, M.S.; Ungerstedt, U. Neuronal dependence of extracellular dopamine, acetylcholine, glutamate, aspartate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) measured simultaneously from rat neostriatum using in vivo microdialysis: Reciprocal interactions. Amino Acids 1992, 2, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Tepper, J.M. Basal ganglia control of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2009, 73, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, M.; Westerink, B.H. The role of GABA receptors in the control of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons: Dual-probe microdialysis study in awake rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 219, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorell, J.M.; Johnson, C.C.; Rybicki, B.A.; Peterson, E.L.; Kortsha, G.X.; Brown, G.G.; Richardson, R.J. Occupational exposure to manganese, copper, lead, iron, mercury and zinc and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 1999, 20, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeon, B.; Kim, J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, K.; Chang, Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, M. Dopamine transporter imaging with [123I]-β-CIT demonstrates presynaptic nigrostriatal dopaminergic damage in Wilson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 65, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Sierrra-Paredes, G.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Effect of chronic treatment with angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonists on striatal dopamine levels in normal rats and in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease treated with L-DOPA. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruces-Sande, A.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Sierra-Paredes, G.; Vázquez-Agra, N.; Hermida-Ameijeiras, Á.; Pose-Reino, A.; Méndez-Álvarez, E.; Soto-Otero, R. Copper Overload Increased Rat Striatal Levels of Both Dopamine and Its Main Metabolite Homovanillic Acid in Extracellular Fluid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158309
Cruces-Sande A, Garrido-Gil P, Sierra-Paredes G, Vázquez-Agra N, Hermida-Ameijeiras Á, Pose-Reino A, Méndez-Álvarez E, Soto-Otero R. Copper Overload Increased Rat Striatal Levels of Both Dopamine and Its Main Metabolite Homovanillic Acid in Extracellular Fluid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158309
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruces-Sande, Antón, Pablo Garrido-Gil, Germán Sierra-Paredes, Néstor Vázquez-Agra, Álvaro Hermida-Ameijeiras, Antonio Pose-Reino, Estefanía Méndez-Álvarez, and Ramón Soto-Otero. 2024. "Copper Overload Increased Rat Striatal Levels of Both Dopamine and Its Main Metabolite Homovanillic Acid in Extracellular Fluid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158309
APA StyleCruces-Sande, A., Garrido-Gil, P., Sierra-Paredes, G., Vázquez-Agra, N., Hermida-Ameijeiras, Á., Pose-Reino, A., Méndez-Álvarez, E., & Soto-Otero, R. (2024). Copper Overload Increased Rat Striatal Levels of Both Dopamine and Its Main Metabolite Homovanillic Acid in Extracellular Fluid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158309







