Role of IL-27 in COVID-19: A Thin Line between Protection and Disease Promotion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Interleukin 27 Conformation and Its Biological Function in Immunity
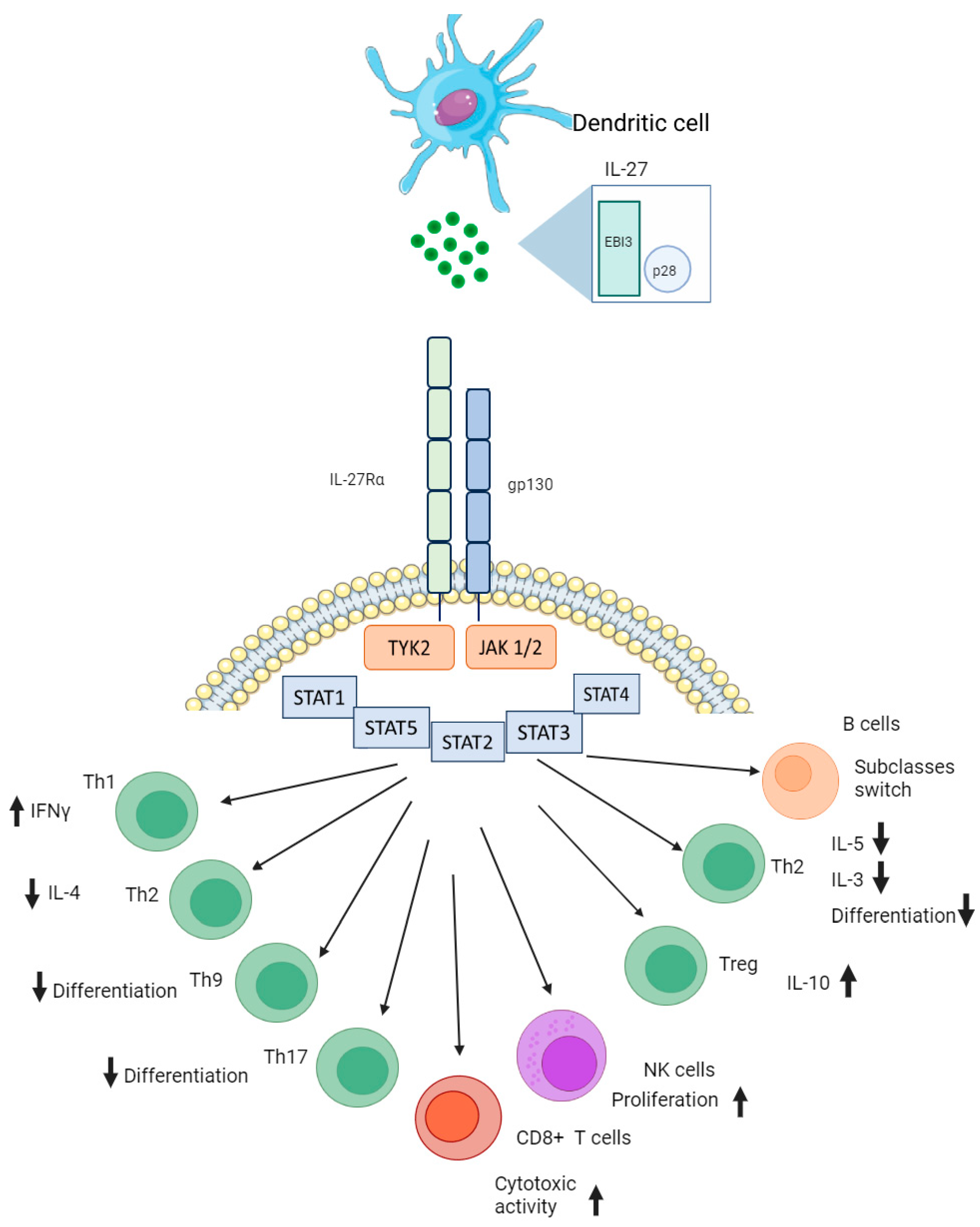
3. Interleukin 27 in Infectious Pathology
4. Interleukin 27 in COVID-19
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filip, R.; Gheorghita Puscaselu, R.; Anchidin-Norocel, L.; Dimian, M.; Savage, W.K. Global Challenges to Public Health Care Systems during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of Pandemic Measures and Problems. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanna, F.; Maglio, M.; Landini, P.; Fini, M. Body Localization of ACE-2: On the Trail of the Keyhole of SARS-CoV-2. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 594495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boechat, J.L.; Chora, I.; Morais, A.; Delgado, L. The Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 Immunopathology—Current Perspectives. Pulmonology 2021, 27, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligong, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, M.; Jiang, J.; Yin, H.; Dauphars, D.J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; He, Y. Preventing Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokine to Target in a Raging Storm? Front. Cell Dev. Bio. 2020, 8, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.; Qin, L.; Puah, S.H. COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): Clinical Features and Differences from Typical Pre-COVID-19 ARDS. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 213, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Immunoregulatory Functions of the IL-12 Family of Cytokines in Antiviral Systems. Viruses 2019, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Huang, A.; Nie, J.; Tan, J.; Xing, S.; Qu, Y.; Jiang, K. IL-35 Regulates the Function of Immune Cells in Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 683332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastelein, R.A.; Hunter, C.A.; Cua, D.J. Discovery and Biology of IL-23 and IL-27: Related but Functionally Distinct Regulators of Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devergne, O.; Hummel, M.; Koeppen, H.; Le Beau, M.; Nathanson, E. A Novel Interleukin-12 P40-Related Protein Induced by Latent Epstein-barr Virus Infection in B Lymphocytes. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflanz, S.; Timans, J.C.; Cheung, J.; Rosales, R.; Kanzler, H.; Gilbert, J.M.; Hibbert, L.; Churakova, T.; Travis, M.; Vaisberg, E. IL-27, a Heterodimeric Cytokine Composed of EBI3 and P28 Protein, Induces Proliferation of Naive CD4+ T Cells. Immunity 2002, 16, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Lv, Z.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, H.; Yin, N.; Qi, H. The Dual Role of IL-27 in CD4+ T Cells. Immunity 2021, 138, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Fyfe, P.K.; Gardner, S.; Wilmes, S.; Bubeck, D.; Moraga, I. Structural Insights into the Assembly and Activation of the IL-27 Signaling Complex. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e55450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Kim, D.; Feige, M.J. IL-30† (IL-27A): A Familiar Stranger in Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, Y.; Kondo, T.; Xiao, S.; Yosef, N.; Gaublomme, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, C. Protein C Receptor (PROCR) Is a Negative Regulator of Th17 Pathogenicity. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 213, 2489–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, H.; de Santos, B.B.; França da Silva, F.A.; Cordeiro Santos, M.L.; Braga de Souza, J.C.; Macêdo Lopes Correia, L.W.; Lopes, T. Relationship between Th17 Immune Response and Cancer. World. J Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mchedlidze, T.; Kindermann, M.; Neves, A.T.; Voehringer, D.; Neurath, M.F.; Wirtz, S. IL-27 Suppresses Type 2 Immune Responses In Vivo via Direct Effects on Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 9, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Ma, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Han, J.; Wu, X.; Lei, L.; Yin, Z. Dendritic Cell-derived IL-27 P28 Regulates T Cell Program in Pathogenicity and Alleviates Acute Graft-versus-host Disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Valentin-Torres, A.; Dvorina, N.; Jang, E.; Nagarajavel, V. Treg-specific Il-27rα Deletion Uncovers a Key Role for IL-27 in Treg Function to Control Autoimmunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10190–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, C.J.; Uwadiae, F.I.; Swieboda, D.; Harker, J.A. Early IL-6 Signalling Promotes IL-27 Dependent Maturation of Regulatory T Cells in the Lungs and Resolution of Viral Immunopathology. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourko, O.; Seaver, K.; Odoardi, N.; Basta, S.; Gee, K. IL-27, IL-30, and IL-35: A Cytokine Triumvirate in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Masters, E.A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Muthukrishnan, G. Interleukin-27 and Its Diverse Effects on Bacterial Infections. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Rajasekaran, K.; Nanbakhsh, A.; Gorski, J.; Thakar, M.S.; Malarkannan, S. IL-27 promotes NK cell effector functions via Maf-Nrf2 pathway during influenza infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwirner, N.W.; Zwirner, N.W.; Ziblat, A. Regulation of NK Cell Activation and Effector Functions by the IL-12 Family of Cytokines: The Case of IL-27. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Chiba, Y.; Furusawa, J.-I.; Xu, M.; Tsunoda, R.; Higuchi, K.; Mizoguchi, I. Potential Clinical Application of Interleukin-27 as an Antitumor Agent. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Dilger, P.; Bird, C.; Wadhwa, M. IL-27 Promotes Proliferation of Human Leukemic Cell Lines through the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway and Suppresses Sensitivity to Chemotherapeutic Drugs. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, D.; Hahn, C.; Brüne, B.; Roberts, E.; Weigert, A. Apoptotic Tumor Cells Induce IL-27 Release from Human Dcs to Activate Treg Cells That Express CD69 and Attenuate Cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batten, M.; Li, J.; Yi, S.; Kljavin, N.M.; Danilenko, D.M.; Lucas, S.; Lee, J.; de Sauvage, F.J.; Ghilardi, N. Interleukin 27 Limits Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Suppressing the Development of Interleukin 17–producing T Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meka, R.; Venkatesha, S.; Dudics, S.; Acharya, B.; Moudgil, K. Il-27-induced Modulation of Autoimmunity and Its Therapeutic Potential. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, N.; Mizoguchi, I.; Okumura, M.; Chiba, Y.; Xu, M.; Shimizu, M.; Matsui, M.; Mizuguchi, J.; Yoshimoto, T. A Pivotal Role for Interleukin-27 in CD8+ T Cell Functions and Generation of Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 605483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.; Ghilardi, N.; Li, J.; de Sauvage, F.J. IL-27 Regulates IL-12 Responsiveness of Naive CD4+ T Cells through Stat1-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2003, 100, 15047–15052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Yasuda, K.; Mizuguchi, J.; Nakanishi, K. IL-27 Suppresses Th2 Cell Development and Th2 Cytokines Production from Polarized Th2 Cells: A Novel Therapeutic Way for Th2-mediated Allergic Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4415–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, R.; Yaneva, T.; Beauseigle, D.; El-Khoury, L.; Arbour, N. IL-27 Increases the Proliferation and Effector Functions of Human Naïve CD8+ T Lymphocytes and Promotes Their Development into Tc1 Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zak, J.; Pratumchai, I.; Shaabani, N.; Vartabedian, V.; Nguyen, N.; Wu, T.; Xiao, C.; Teijaro, J. IL-27 promotes the expansion of self-renewing CD8+ T cells in persistent viral infection. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1791–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, J.; Visperas, A.; Sanogo, Y.O.; Bechtel, J.J.; Dvorina, N.; Kim, S.; Jang, E. An Il-27/lag3 Axis Enhances Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cell–Suppressive Function and Therapeutic Efficacy. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.R.; Lindsell, C.J.; Lahni, P.; Hart, K.W.; Gibot, S. Interleukin 27 as a Sepsis Diagnostic Biomarker in Critically Ill Adults. Shock 2013, 40, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Du, W.; Jiang, H.; Ai, Q.; Feng, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J. Multiplex Cytokine Profiling Identifies Interleukin-27 as a Novel Biomarker for Neonatal Early Onset Sepsis. Shock 2017, 47, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; He, M.; Wu, Z. IL-27 Is Elevated in Sepsis with Acute Hepatic Injury and Promotes Hepatic Damage and Inflammation in the CLP Model. Cytokine 2020, 127, 154936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtz, S.; Tubbe, I.; Galle, P.R.; Schild, H.; Birkenbach, M.; Blumberg, R.S.; Neurath, M.F. Protection from Lethal Septic Peritonitis by Neutralizing the Biological Function of Interleukin 27. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, L.; Berrens, Z.; Stenson, E.K.; Zackoff, M.; Danziger-Isakov, L.; Lahni, P.; Wong, H.R. Interleukin-27 as a Candidate Diagnostic Biomarker for Bacterial Infection in Immunocompromised Pediatric Patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.R.; Wong, H.R.; Liu, K.D.; Kangelaris, K.N.; Lahni, P.; Calfee, C.S. Performance of Interleukin-27 as a Sepsis Diagnostic Biomarker in Critically Ill Adults. J. Crit. Care 2014, 29, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Chen, F.; Zhao, T.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y. The Interleukin-27 -964A>G Polymorphism Enhances Sepsis-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Confers Susceptibility to the Development of Sepsis. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skouras, V.; Magkouta, S.; Psallidas, I.; Tsilioni, I.; Maragozidis, P.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Kalomenidis, I. Interleukin-27 Improves the Ability of Adenosine Deaminase to Rule Out Tuberculous Pleural Effusion Regardless of Pleural Tuberculosis Prevalence. Infect Dis. 2015, 47, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Xu, F.; Huang, S.; Xiang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Ren, G. IL-27 Is Elevated in Patients with COPD and Patients with Pulmonary TB and Induces Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells to Produce CXCL10. Chest 2012, 141, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollnick, H.; Barber, J.; Wilkinson, R.J.; Newton, S.M.; Garg, A. IL-27 Inhibits Anti-mycobacterium Tuberculosis Innate Immune Activity of Primary Human Macrophages. Tuberculosis 2023, 139, 102326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Huang, C.; Yan, J.-M.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, X.-L.; Pan, Q. Accumulation of EBI3 Induced by Virulent Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Inhibits Apoptosis in Murine Macrophages. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, ftz007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Dutta, R.K.; Khan, M.A.; Ishaq, M.; Sharma, K.; Malhotra, H.; Majumdar, S. IL-27 Inhibits Ifn-γ Induced Autophagy by Concomitant Induction of JAK/PI3 K/akt/mtor Cascade and Up-Regulation of Mcl-1 in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis H37rv Infected Macrophages. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 55, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.; Yang, S.; Niu, W.; Tan, L.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Tang, Y.; Sun, L.; Pang, G.; Qiao, S. IL-27/IL-27R Mediates Protective Immunity Against Chlamydial Infection by Suppressing Excessive Th17 Responses and Reducing Neutrophil Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 2160–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.M.; Robinson, K.M.; Lee, B.; Scheller, E.V.; Mandalapu, S.; Enelow, R.I.; Kolls, J.K.; Alcorn, J.F. The Role of IL-27 in Susceptibility to Post-Influenza Staphylococcus Aureus Pneumonia. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.D.M.; Liu, F.D.M.; Kenngott, E.E.; Schröter, M.F.; Kühl, A.A.; Jennrich, S.; Watzlawick, R.; Hoffmann, U.; Wolff, T.; Norley, S. Timed Action of IL-27 Protects from Immunopathology While Preserving Defense in Influenza. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yao, S.; Huang, S.; Wright, J.; Braciale, T.J.; Sun, J. Type I IFN Signaling Facilitates the Development of Il-10-producing Effector CD8+ T Cells During Murine Influenza Virus Infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 2778–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamichi, T.; Yang, J.; Huang, D.-W.; Brann, T.W.; Fullmer, B.; Adelsberger, J.W.; Lempicki, R.A.; Baseler, M.; Lane, H.C. IL-27, a Novel Anti-hiv Cytokine, Activates Multiple Interferon-Inducible Genes in Macrophages. AIDS 2008, 22, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Xiao, S.; He, B.; He, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, L.-W.; He, M.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y. The Role of IL-27 and Its Receptor in the Pathogenesis of HIV/AIDS and Anti-viral Immune Response. Curr. HIV Res. 2017, 15, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harker, J.A.; Dolgoter, A.; Zuniga, E.I. Cell-intrinsic IL-27 and Gp130 Cytokine Receptor Signaling Regulates Virus-specific CD4+ T Cell Responses and Viral Control During Chronic Infection. Immunity 2013, 39, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes de Oca, M.; de Labastida Rivera, F.; Winterford, C.; Frame, T.C.M.; Ng, S.S.; Amante, F.H.; Edwards, C.L.; Bukali, L.; Wang, Y.; Uzonna, J.E.; et al. IL-27 Signalling Regulates Glycolysis in Th1 Cells to Limit Immunopathology During Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, N.A.; Kumar, R.; Gautam, S.; Nylén, S.; Singh, O.P.; Sundar, S.; Sacks, D.B. IL-27 and IL-21 Are Associated with T Cell IL-10 Responses in Human Visceral Leishmaniasis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3977–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsentieva, N.A.; Liubimova, N.E.; Batsunov, O.K.; Korobova, Z.R.; Stanevich, O.V.; Lebedeva, A.A.; Vorobyov, E.A.; Vorobyova, S.V.; Kulikov, A.N.; Lioznov, D.A. Plasma Cytokines in Patients with COVID-19 during Acute Phase of the Disease and Following Complete Recovery. Med. Immunol. 2021, 23, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, B.; Najafizadeh, M.; Motedayyen, H.; ArefNezhad, R. Predicting Roles of IL-27 and IL-32 in Determining the Severity and Outcome of COVID-19. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2022, 36, 03946320221145827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingler, J.; Lambert, G.S.; Bandres, J.C.; Emami-Gorizi, R.; Nádas, A.; Oguntuyo, K.Y.; Amanat, F.; Bermudez-Gonzalez, M.; Gleason, C.; Kleiner, G. Immune Profiles to Distinguish Hospitalized versus Ambulatory COVID-19 Cases in Older Patients. iScience 2022, 25, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laatifi, M.; Douzi, S.; Ezzine, H.; Naya, A.; Bouklouze, A.; Zaid, Y.; Naciri, M. Explanatory Predictive Model for COVID-19 Severity Risk Employing Machine Learning, Shapley Addition, and LIME. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-López, J.F.; Urcuqui-Inchima, S. Antiviral Response and Immunopathogenesis of Interleukin 27 in COVID-19. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsentieva, N.A.; Liubimova, N.E.; Batsunov, O.K.; Korobova, Z.R.; Kuznetsova, R.N.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Stanevich, O.V.; Lebedeva, A.A.; Vorobyev, E.A.; Vorobieva, S.V. Predictive Value of Specific Cytokines for Lethal COVID-19 Outcome. Infect. Immunol. 2022, 12, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, Q.; Lin, S.; Shen, N.; Yin, Y.; Cao, J. I L-27 Is Elevated in Acute Lung Injury and Mediates Inflammation. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, X.M.; Cao, P.; Zhang, C.; Feng, C.M.; Zheng, L.; Xu, D.X.; Fu, L.; Zhao, H. Serum IL-27 Predicts the Severity and Prognosis in Patients with Community-acquired Pneumonia: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korobova, Z.R.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Liubimova, N.E.; Batsunov, O.K.; Dedkov, V.G.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Sharova, A.A.; Adish, Z.; Chernykh, E.I.; Kaschenko, V.A.; et al. Cytokine Profiling in Different SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Korobova, Z.R.; Isakov, D.V.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Batsunov, O.K.; Khamitova, I.V.; Kuznetsova, R.N.; Savin, T.V.; Akisheva, T.V.; et al. Heterogenous CD8+ T Cell Maturation and ‘Polarization’ in Acute and Convalescent COVID-19 Patients. Viruses 2022, 14, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Year of Publication | Authors | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Arsentieva N.A. et al. | Increase in IL-27 levels in acute COVID-19 patients vs. healthy donors (p < 0.0001); decrease in IL-27 concentrations in convalescents when compared to healthy donors (p = 0.0015). | [56] |
| 2022 | Arsentieva N.A. et al. | IL-27 showed a statistically significant increase in concentrations in COVID-19 acute patients when compared to healthy donors (p < 0.001 for non-survivors and p < 0.05 for survivors). | [61] |
| 2022 | Korobova Z.R. et al. | IL-27 was one of the four biological markers showing statistically significant changes in concentrations in the blood plasma of patients infected with different variants of SARS-CoV-2 (p < 0.001). | [64] |
| 2022 | Kudryavtsev I.V. et al. | The correlation between Tc17 cells of central memory and TEMRA cells and serum IL-27 levels was negative in patients with acute COVID-19, a tendency not observed in convalescent or healthy donors. | [65] |
| 2022 | Zamani B. et al. | IL-27, along with IL-32 and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), was highlighted as one of the markers of severe COVID-19 and lethal outcomes. | [57] |
| 2022 | Klingler J. et al. | In patients with higher demographic risk factors (i.e., male, black/Hispanic descent, and median age over 63 years old), IL-27 was suggested as one of the factors to prove the need for hospitalization. | [58] |
| 2023 | Laatifi M. et al. | The COVID-19 prognosis was based on machine learning and included several cytokines, including IL-27, along with IL-9, IL-12p40, and MCP-3, to play the role of markers for non-severe COVID-19. | [60] |
| 2023 | Valdés-López and Urcuqui-Inchima | IL-27 triggers a strong pro-inflammatory and antiviral reaction that relies on STAT1 without requiring IFN in COVID-19-derived PBMCs and monocytes, which is linked to a severe clinical outcome of COVID-19. This effect is also seen in macrophages that have been stimulated by S protein. | [62] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korobova, Z.R.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Santoni, A.; Totolian, A.A. Role of IL-27 in COVID-19: A Thin Line between Protection and Disease Promotion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147953
Korobova ZR, Arsentieva NA, Santoni A, Totolian AA. Role of IL-27 in COVID-19: A Thin Line between Protection and Disease Promotion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(14):7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147953
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorobova, Zoia R., Natalia A. Arsentieva, Angela Santoni, and Areg A. Totolian. 2024. "Role of IL-27 in COVID-19: A Thin Line between Protection and Disease Promotion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 14: 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147953
APA StyleKorobova, Z. R., Arsentieva, N. A., Santoni, A., & Totolian, A. A. (2024). Role of IL-27 in COVID-19: A Thin Line between Protection and Disease Promotion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(14), 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147953







