The miR-182-5p/GPX4 Pathway Contributes to Sevoflurane-Induced Ototoxicity via Ferroptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
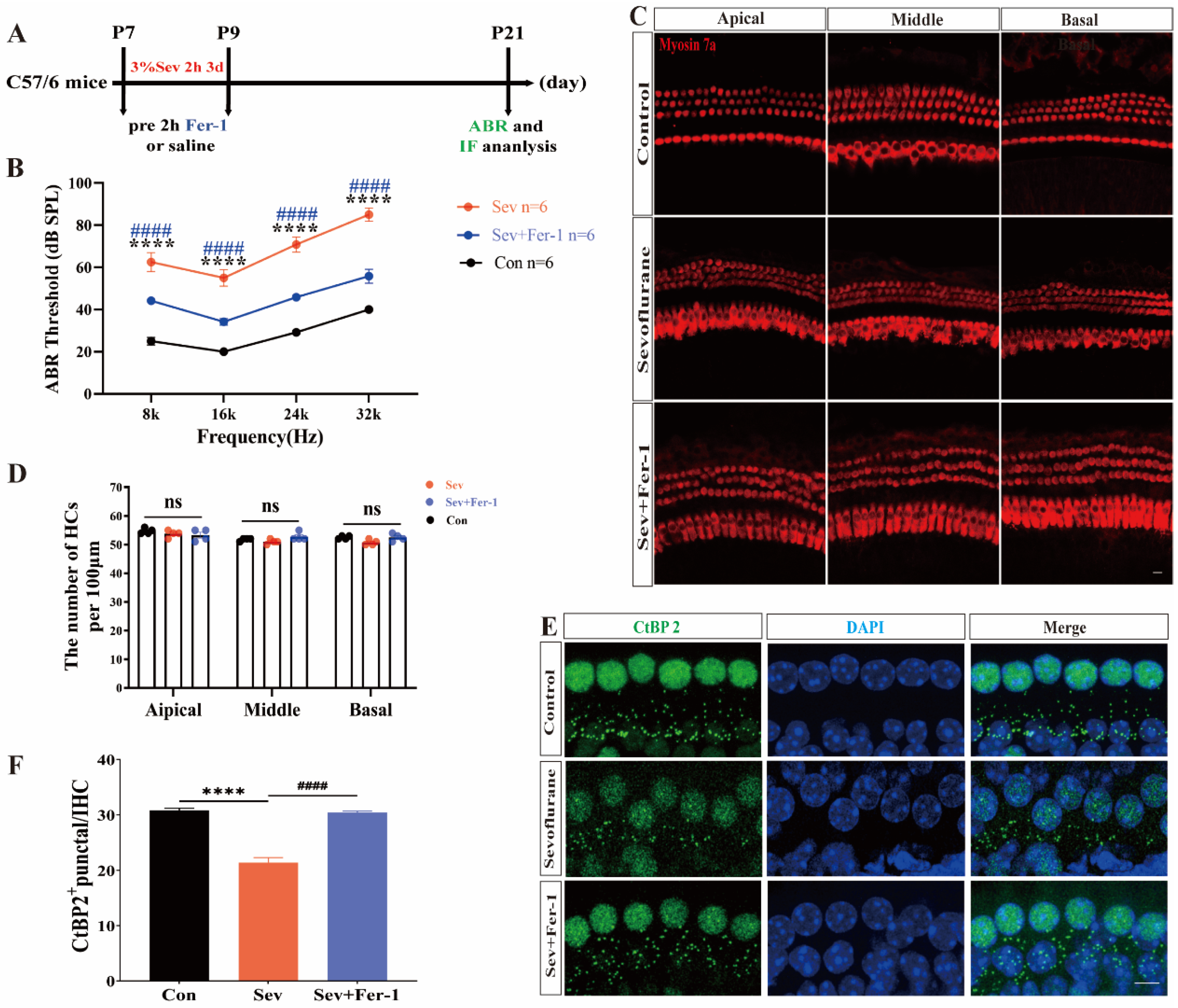
2.1. Fer-1 Attenuated the Ototoxic Effects of Sevoflurane in Mice
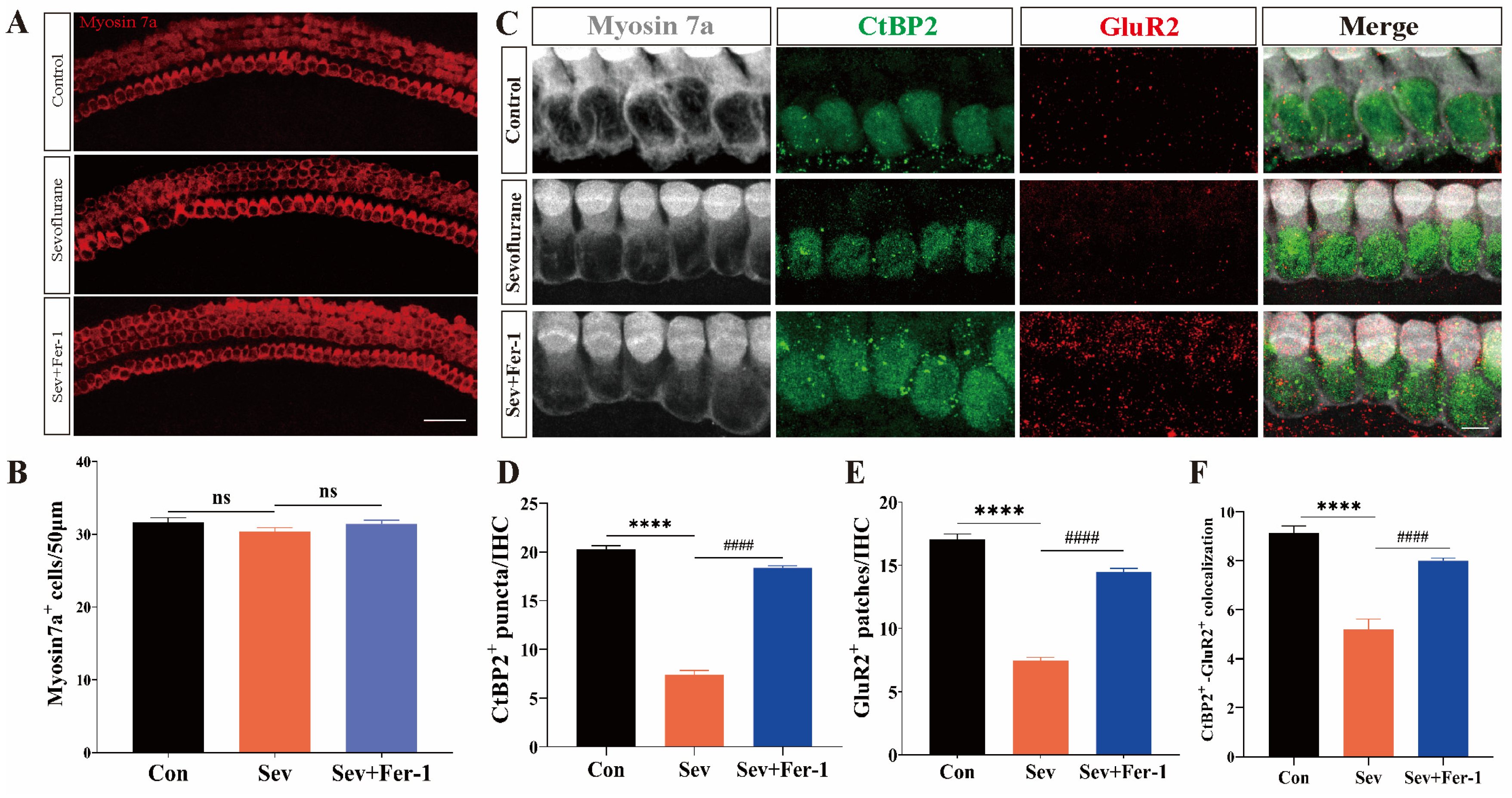
2.2. Fer-1 Attenuated Sevoflurane-Induced Ototoxic Effects in Cochlear Explants
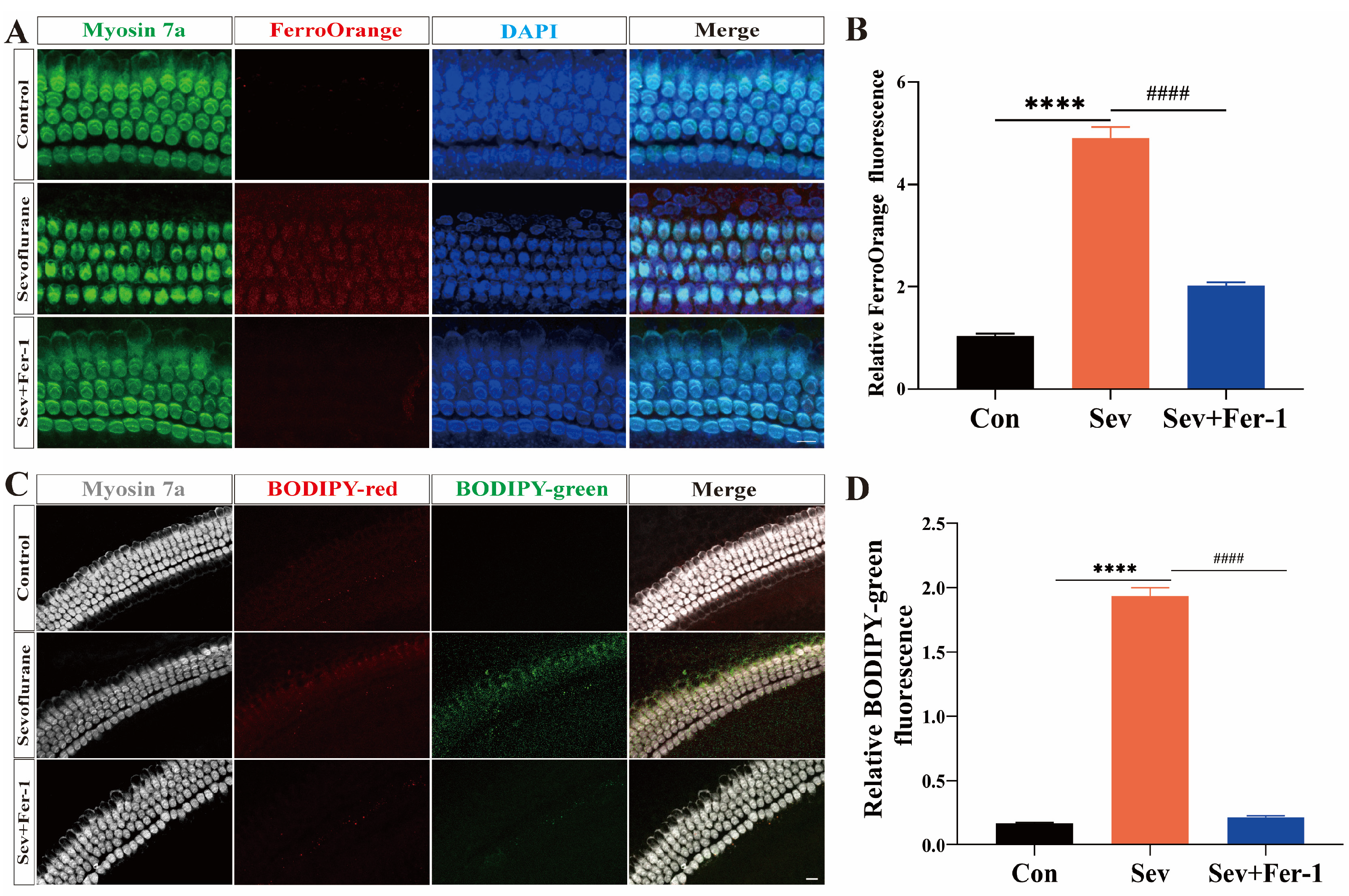
2.3. Sevoflurane-Induced Ferroptosis in Cochlear Explants
2.4. Sevoflurane-Induced Ferroptosis in HEI-OC1 Cells
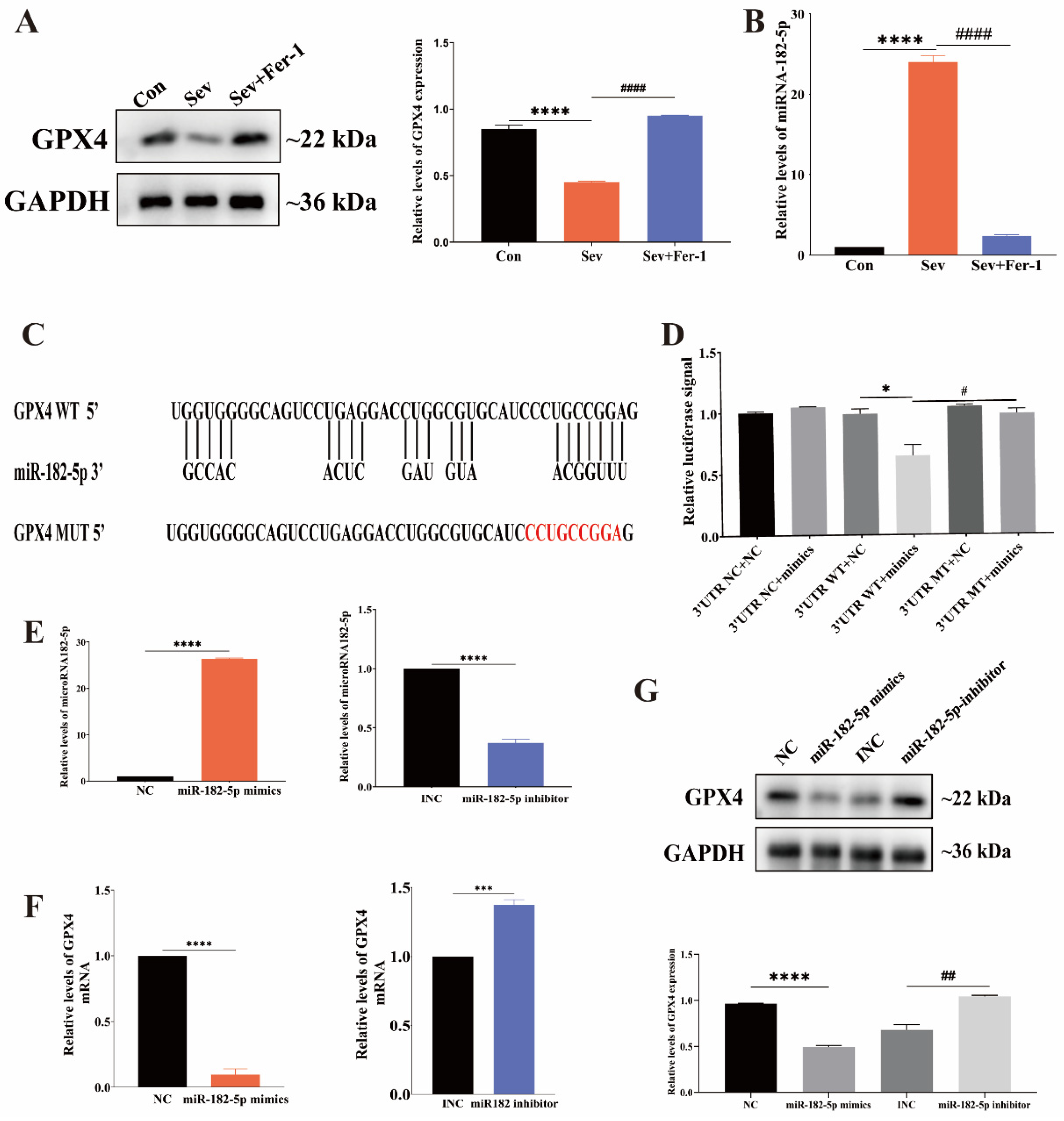
2.5. MiR-182-5p Targeted GPX4 in HEI-OC1 Cells
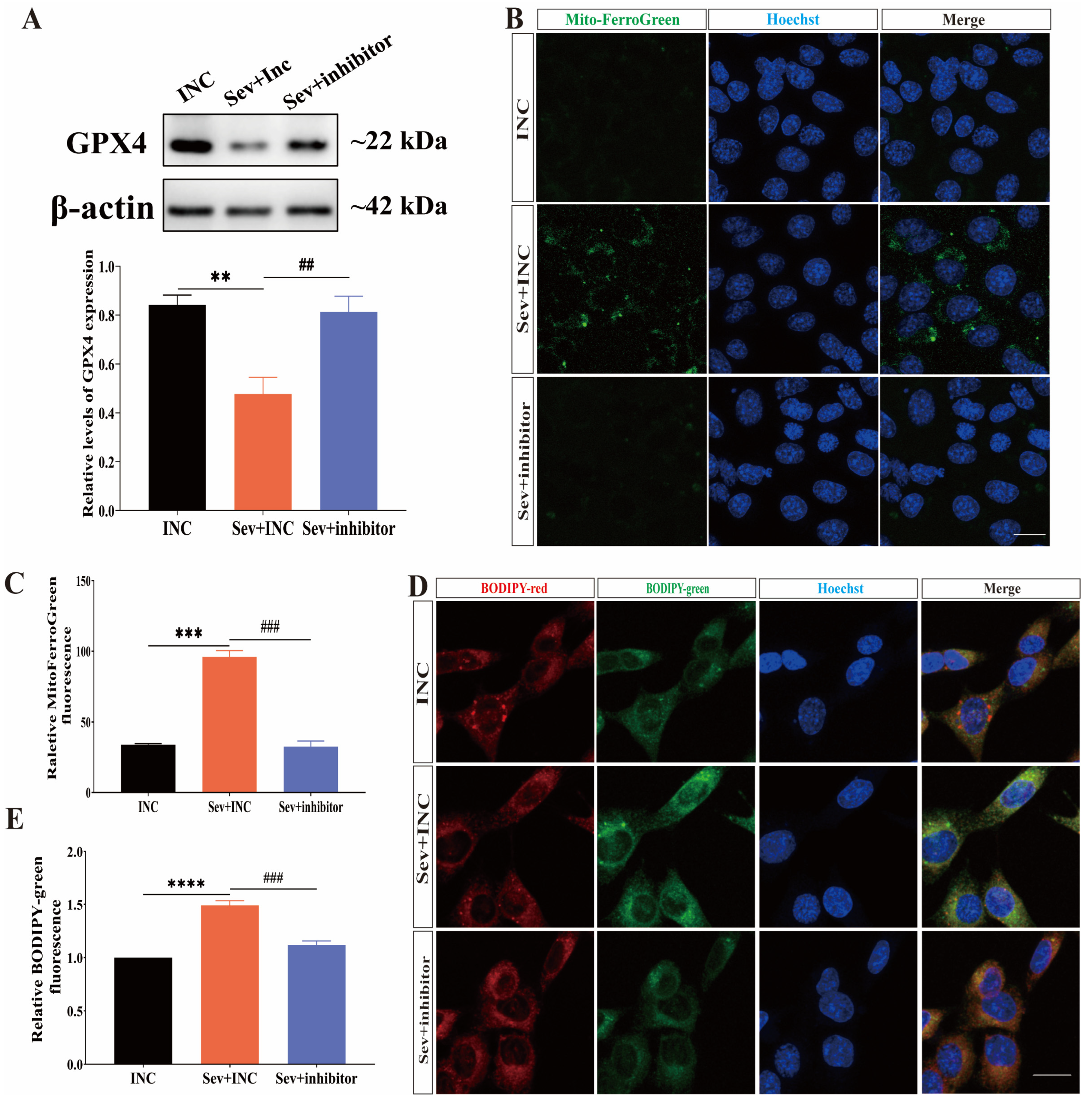
2.6. Inhibition of miR-182-5p Attenuated Sevoflurane-Induced Ferroptosis in HEI-OC1 Cells
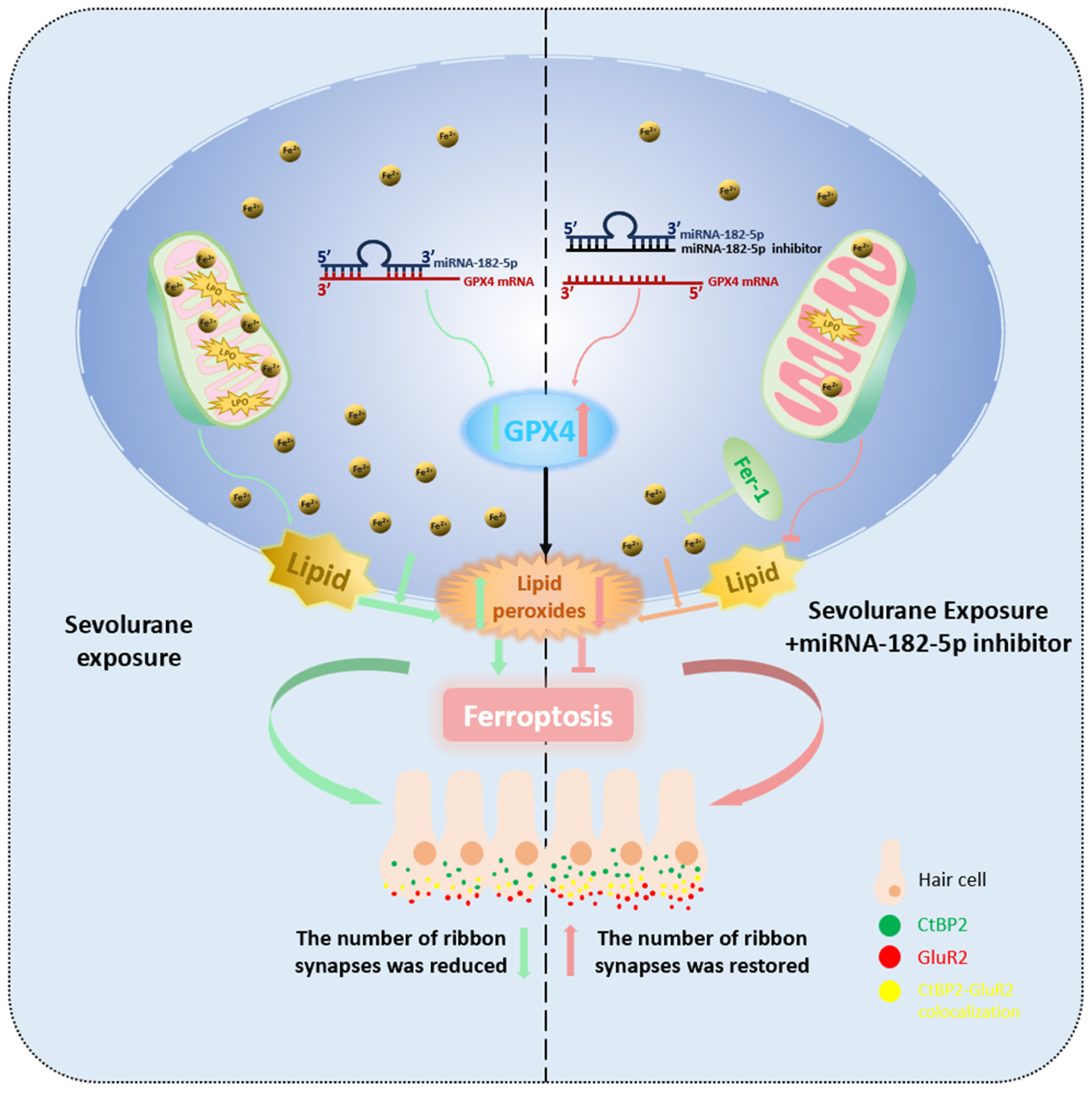
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Anesthesia Treatment
4.2. Cochlear Explant Culture and Treatment
4.3. HEI-OC1 Cell Culture and Treatment
4.4. Acquisition of Mouse Cochlear Basement Membrane
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.6. Cell Viability Test
4.7. Fe2+ Measurement
4.8. ROS Measurement
4.9. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Dual Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
4.12. ABR Test
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, L.S.; Li, G.; Dimaggio, C.; Byrne, M.; Rauh, V.; Brooks-Gunn, J.; Kakavouli, A.; Wood, A. Anesthesia and neurodevelopment in children: Time for an answer? Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.G.; Loepke, A.W. Anesthetics and sedatives: Toxic or protective for the developing brain? Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, C.; Ma, J.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, D.; Chen, C.; Ruan, N.; Su, Y.; Nan, H.; Lian, Q.; Lin, H. Isoflurane and Sevoflurane Induce Cognitive Impairment in Neonatal Rats by Inhibiting Neural Stem Cell Development Through Microglial Activation, Neuroinflammation, and Suppression of VEGFR2 Signaling Pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; Chen, X. Prolonged anesthesia induces neuroinflammation and complement-mediated microglial synaptic elimination involved in neurocognitive dysfunction and anxiety-like behaviors. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Gong, M.; Yan, M.; Zhang, X. Sevoflurane induces endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis in hippocampal neurons of aging rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, N.; Fu, N.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J. Role of GABAA receptor depolarization-mediated VGCC activation in sevoflurane-induced cognitive impairment in neonatal mice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 964227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyott, S.J.; Pavlinkova, G.; Yamoah, E.N.; Fritzsch, B. Harmony in the Molecular Orchestra of Hearing: Developmental Mechanisms from the Ear to the Brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2024, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, M.; Van Dijk, P.; Nunes, I.; Rüttiger, L.; Zimmermann, U. Advances in the neurobiology of hearing disorders: Recent developments regarding the basis of tinnitus and hyperacusis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 111, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhou, X.; Jin, L.; Li, W.; Li, G.-L.; Shen, X. Multiple Sevoflurane Exposures During the Neonatal Period Cause Hearing Impairment and Loss of Hair Cell Ribbon Synapses in Adult Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 945277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pantopoulos, K. Regulation of cellular iron metabolism. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, M.; Huang, Z.-H.; Wang, M.; Sun, W.-Y.; Kurihara, H.; Huang, R.-T.; Wang, R.; Huang, F.; Liang, L.; et al. ALOX5 inhibition protects against dopaminergic neurons undergoing ferroptosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 193, 106779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, M.; Li, M.; Su, Y.; Yan, Z.; Lin, Y.; et al. pH-sensitive molybdenum (Mo)-based polyoxometalate nanoclusters have therapeutic efficacy in inflammatory bowel disease by counteracting ferroptosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 188, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, Z.-B.; Shao, L.; Zhao, Z.-M.; Fan, X.-X.; Sui, X.; Yu, L.-L.; Wang, X.-R.; Zhang, R.-N.; Wang, W.-J.; et al. β-Elemene enhances erlotinib sensitivity through induction of ferroptosis by upregulating lncRNA H19 in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 191, 106739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, F.; Hao, S.; Hou, D.; Zeng, X.; Huang, H.; Sethi, G.; Guo, J.; Duan, C. Low-dose Olaparib improves septic cardiac function by reducing ferroptosis via accelerated mitophagy flux. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 200, 107056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hong, G.; Bi, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; An, Y.; Guo, N.; Dong, F.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Inhibition of Gpx4-mediated Ferroptosis Alleviates Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss in C57BL/6 mice. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 1387–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Chang, X.; Bai, X.; Liu, H.-B.; Chen, X.-B.; Chen, H.-P.; Liu, Y.-H. Activation of Nrf2 inhibits ferroptosis and protects against oxaliplatin-induced ototoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Tang, D.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Han, J.; Hu, B.; Nie, G.; He, Y. Liproxstatin-1 Protects Hair Cell-Like HEI-OC1 Cells and Cochlear Hair Cells against Neomycin Ototoxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1782659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Gu, X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, C.; Yao, G.; Lin, C. Identification and experimental validation of ferroptosis-related gene lactotransferrin in age-related hearing loss. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1309115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gong, H.; Huang, H.; Tuerhong, G.; Xia, H. Participation of Mind Bomb-2 in Sevoflurane Anesthesia Induces Cognitive Impairment in Aged Mice via Modulating Ferroptosis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2399–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, P. Multiple sevoflurane exposures during mid-trimester induce neurotoxicity in the developing brain initiated by 15LO2-Mediated ferroptosis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 2972–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomgren, K.; Zhu, C.; Hallin, U.; Hagberg, H. Mitochondria and ischemic reperfusion damage in the adult and in the developing brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G. Mitochondria-Related Ferroptosis Drives Cognitive Deficits in Neonatal Mice Following Sevoflurane Administration. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 887062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szakats, S.; McAtamney, A.; Cross, H.; Wilson, M.J. Sex-biased gene and microRNA expression in the developing mouse brain is associated with neurodevelopmental functions and neurological phenotypes. Biol. Sex Differ. 2023, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Wang, J. MiR-106a facilitates the sensorineural hearing loss induced by oxidative stress by targeting connexin-43. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 14080–14093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Shu, T.; Peng, H.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, M.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y. LncRNA H19 inhibits oxidative stress injury of cochlear hair cells by regulating miR-653-5p/SIRT1 axis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2022, 54, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krohs, C.; Körber, C.; Ebbers, L.; Altaf, F.; Hollje, G.; Hoppe, S.; Dörflinger, Y.; Prosser, H.M.; Nothwang, H.G. Loss of miR-183/96 Alters Synaptic Strength via Presynaptic and Postsynaptic Mechanisms at a Central Synapse. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 6796–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Liu, P.-S.; Zheng, D.; Xie, X. The interplay of miRNAs and ferroptosis in diseases related to iron overload. Apoptosis 2024, 29, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.-L.; Xie, J.-Q.; Shen, J.-J.; Ying, M.-D.; Chen, X.-Z. Neuron-derived exosomes mediate sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in neonatal mice via transferring lncRNA Gas5 and promoting M1 polarization of microglia. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Niu, Y.; Qiu, L.; Yang, J.; Sun, J.; Xia, J. Melatonin-mediated mitophagy protects against long-term impairments after repeated neonatal sevoflurane exposures. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 125, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Piao, M.; Liu, N.; Gu, W.; Feng, C. Sevoflurane Exposure Induces Neuronal Cell Ferroptosis Initiated by Increase of Intracellular Hydrogen Peroxide in the Developing Brain via ER Stress ATF3 Activation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 61, 2313–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.-S.-Y.; Zhong, W.-J.; Sha, H.-X.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Jin, L.; Duan, J.-X.; Xiong, J.-B.; You, Z.-J.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, C.-X. mtDNA-cGAS-STING axis-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to postoperative cognitive dysfunction induced by sevoflurane in mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 1927–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; He, Y.; Li, H. Inhibition of the HMGB1/RAGE axis protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 784–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.M.; Samir Ellaithy, L.; Abd El-Aziz, N.S.; Mahdy-Abdallah, H.; Adel Helmy, M. Implication of noise exposure on hearing with emphasis to hOGG1 and GPx-1 polymorphisms and HO-1 protein among textile workers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 6176–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Guo, H.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Sun, K.; Shen, Q.-K.; Li, X.-T. Discussion on the Influence of Gpx 4 Target in the Field of Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Chu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, G.; Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Zeng, H.; Huang, J.; Ge, G. Xanthohumol ameliorates drug-induced hepatic ferroptosis via activating Nrf2/xCT/GPX4 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 126, 155458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Tao, F.; Liu, L.; Cheng, R.; Li, N.; Pan, Y. Self-assembled miR-134-5p inhibitor nanoparticles ameliorate experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) via suppressing ferroptosis. Mikrochim. Acta 2023, 190, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, G.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Shao, Y.; Hu, K.; Wu, B.; Zhang, L. miR-129-2-3p mediates LPS-induced macrophage polarization and ferroptosis by targeting the SMAD3-GPX4 axis. Gene 2024, 894, 147962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Luo, L.; Cai, W.; Li, J.; Li, S.; et al. miR-125b-5p in adipose derived stem cells exosome alleviates pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells ferroptosis via Keap1/Nrf2/GPX4 in sepsis lung injury. Redox. Biol. 2023, 62, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Ding, X.; Zheng, J.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Xiang, H.; Dou, M.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, P.; Xue, W. miR-182-5p and miR-378a-3p regulate ferroptosis in I/R-induced renal injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrashkin, K.A.; Izumikawa, M.; Miyazawa, T.; Wang, C.-H.; Crumling, M.A.; Swiderski, D.L.; Beyer, L.A.; Gong, T.-W.L.; Raphael, Y. The fate of outer hair cells after acoustic or ototoxic insults. Hear. Res. 2006, 218, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.M.; Doetzlhofer, A.; Lee, Y.S.; Groves, A.K.; Segil, N. Mammalian cochlear supporting cells can divide and trans-differentiate into hair cells. Nature 2006, 441, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Otero, J.; Xue, H.Z.; Davis, R.L. Reciprocal regulation of presynaptic and postsynaptic proteins in bipolar spiral ganglion neurons by neurotrophins. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 14023–14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xu, F.; Geng, R.; Li, B.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, Q. RNA-seq analysis highlights DNA replication and DNA repair associated with early-onset hearing loss in the cochlea of DBA/2J mice. Life Sci. 2024, 337, 122350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Huang, W.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Sun, J.-Q.; Chai, R. Stem Cell-Based Hair Cell Regeneration and Therapy in the Inner Ear. Neurosci. Bull. 2024, 40, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, L.; Yu, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, G.; Li, W.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, X. The miR-182-5p/GPX4 Pathway Contributes to Sevoflurane-Induced Ototoxicity via Ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126774
Jin L, Yu X, Zhou X, Li G, Li W, He Y, Li H, Shen X. The miR-182-5p/GPX4 Pathway Contributes to Sevoflurane-Induced Ototoxicity via Ferroptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(12):6774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126774
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Lin, Xiaopei Yu, Xuehua Zhou, Gang Li, Wen Li, Yingzi He, Huawei Li, and Xia Shen. 2024. "The miR-182-5p/GPX4 Pathway Contributes to Sevoflurane-Induced Ototoxicity via Ferroptosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 12: 6774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126774
APA StyleJin, L., Yu, X., Zhou, X., Li, G., Li, W., He, Y., Li, H., & Shen, X. (2024). The miR-182-5p/GPX4 Pathway Contributes to Sevoflurane-Induced Ototoxicity via Ferroptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(12), 6774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126774




