NAD+ Anabolism Disturbance Causes Glomerular Mesangial Cell Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
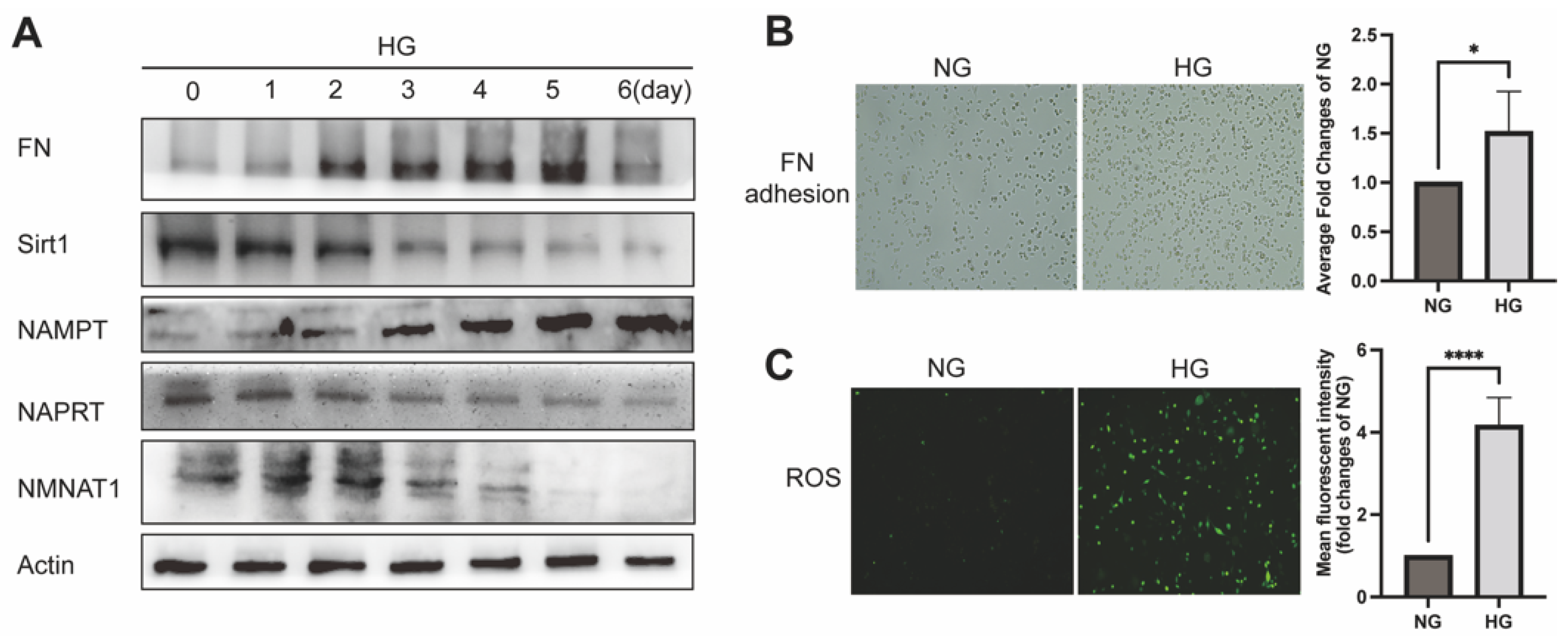
2.1. NAD+-Related Metabolic Enzymes Alters in High Glucose Conditionally Injuried Mesangial Cells
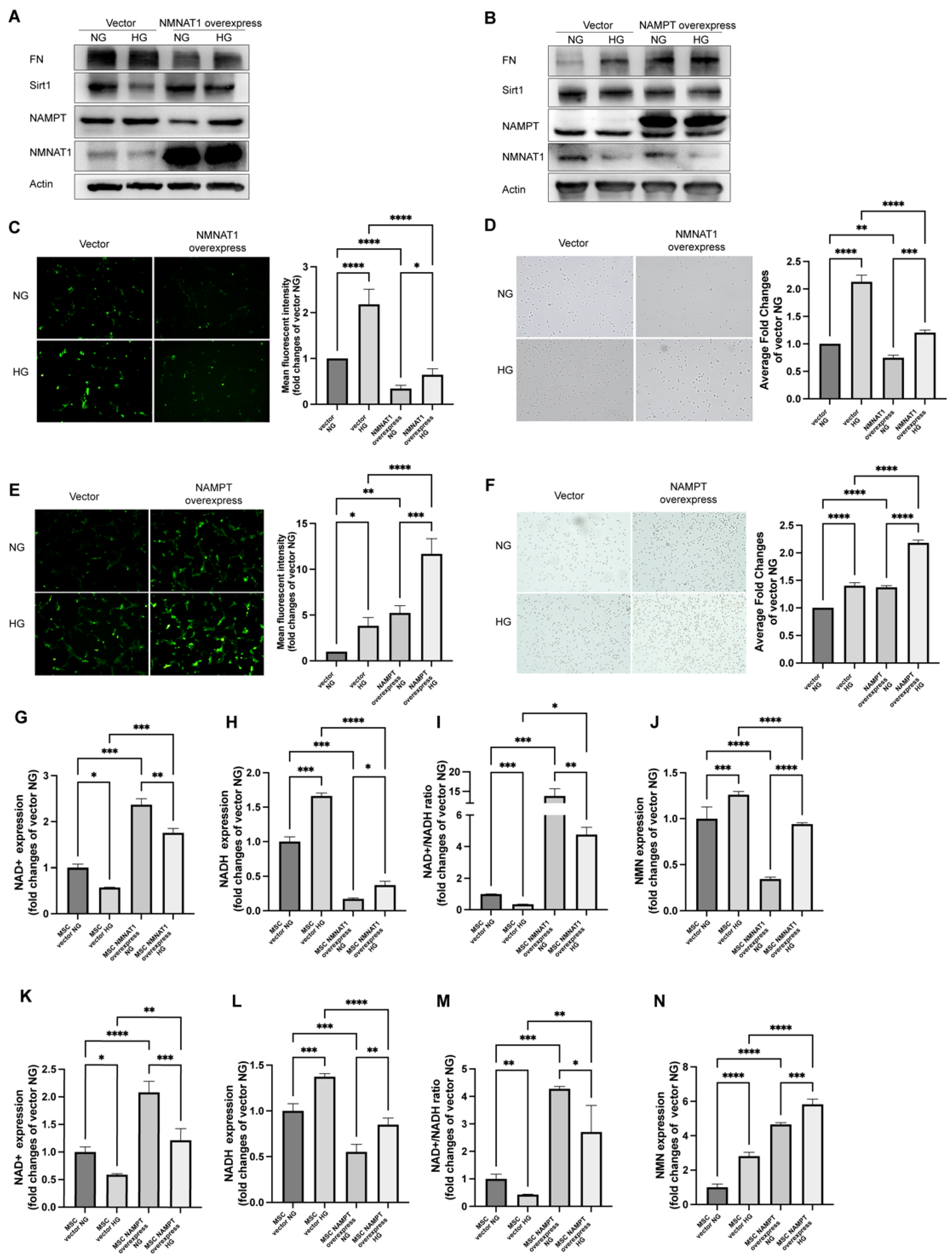
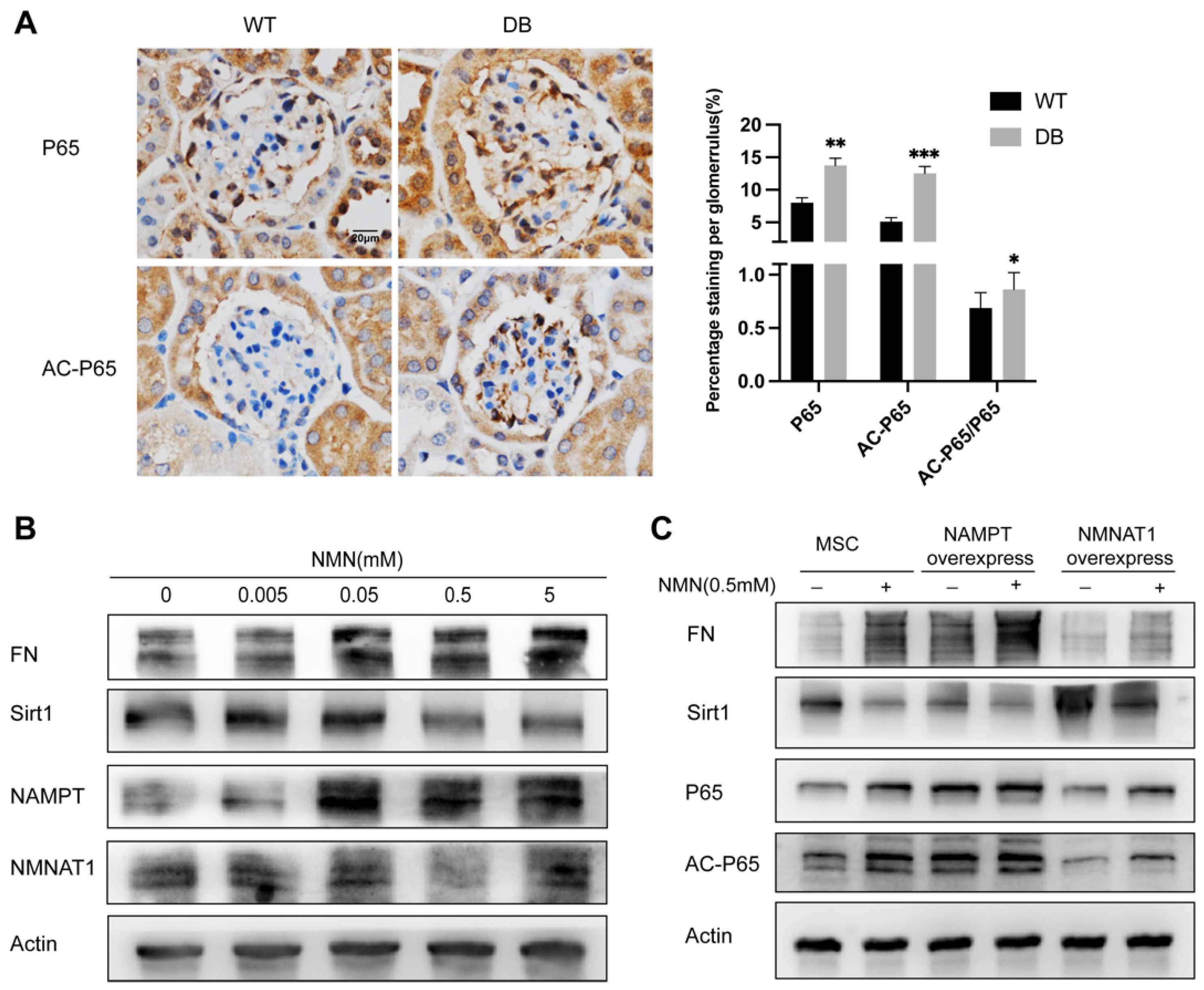
2.2. NMN Level Parallels Mesangial Cell Injury When NMNAT1 or NAMPT Overexpressed
2.3. FK866 and Quercetin Alleviates NAD+ Anabolism Disturbance in HG-Injured MSC
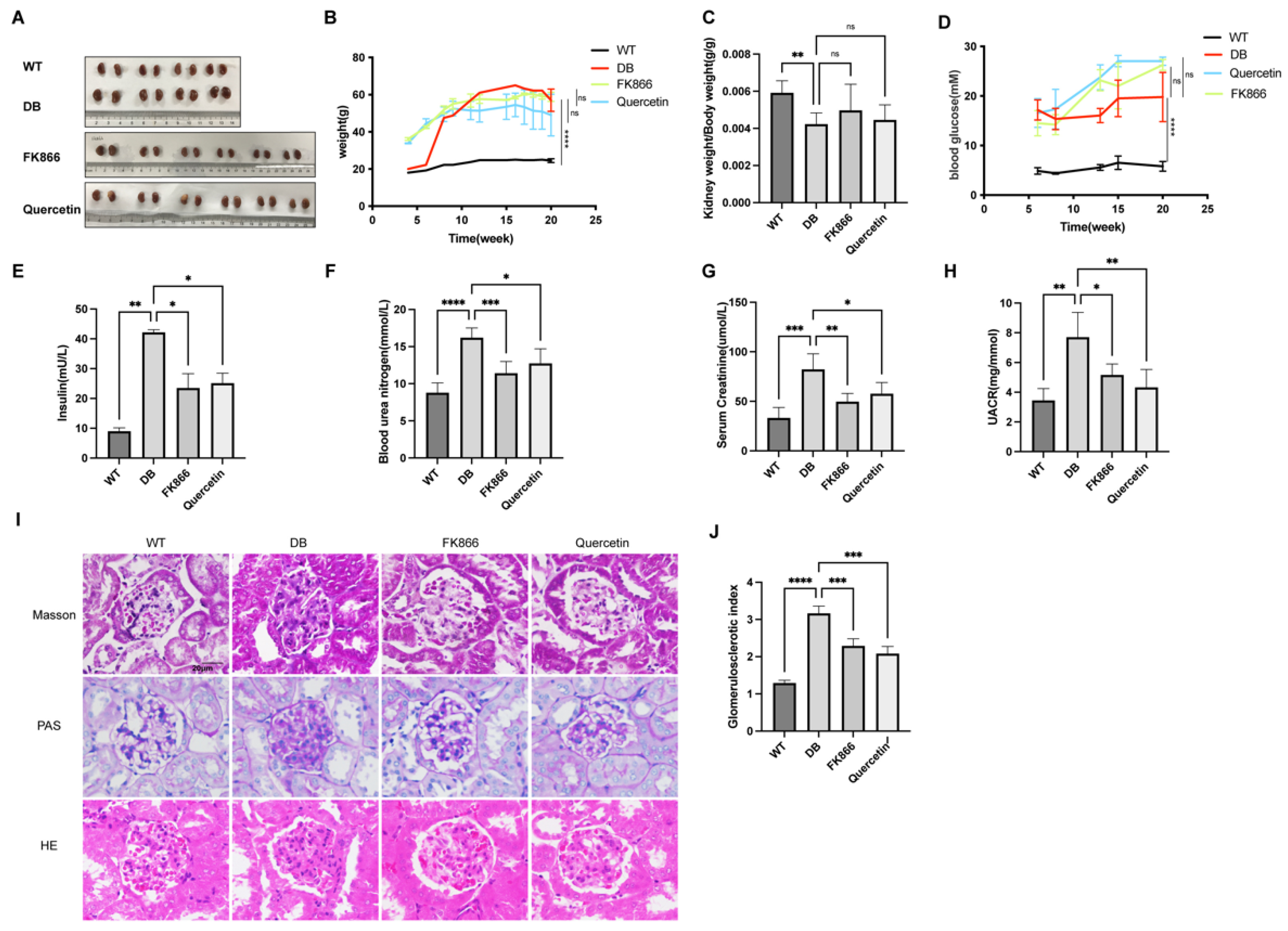
2.4. FK866 and Quercetin Improves Insulin Resistance and Kidney Function in db/db DN Mice
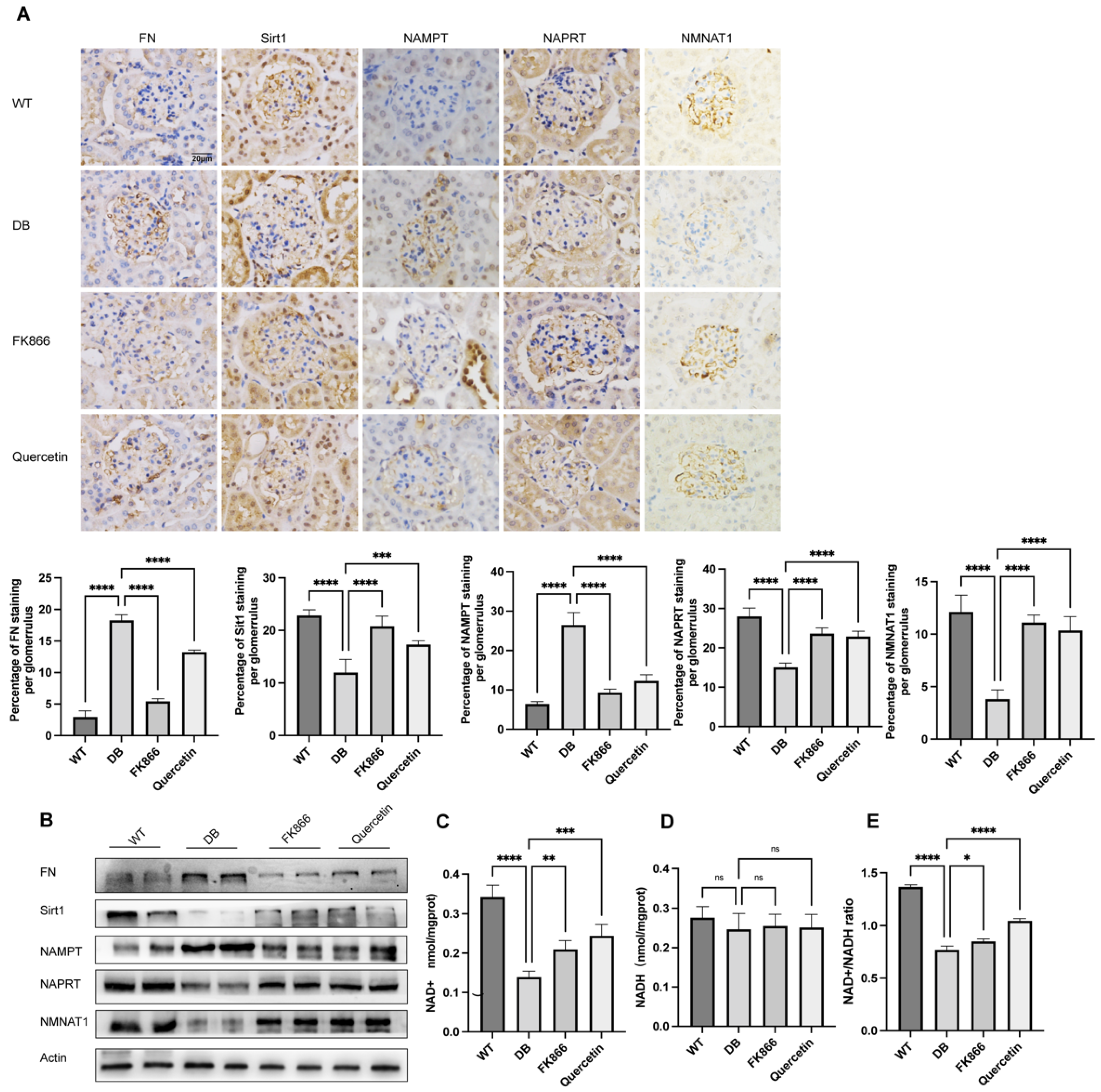
2.5. FK866 and Quercetin Lessens NAD+ Anabolism Disturbance and FN Overproduction in db/db DN Mice
2.6. NMN Accumulation Causes Changes in Sirt1/NF-κB P65/FN Associated with DN
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement and Diagnosis
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.3. Animal Studies
4.4. Western Blot
4.5. Histology and Immunohistochemistry Analysis
4.6. Transfection of Lentivirus
4.7. MSC Damage Detection
4.7.1. Intracellular ROS Determination
4.7.2. Cell Attachment Assay
4.8. Metabolite Collection and LCMS
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| DN | Diabetic nephropathy |
| MSC | Mesangial cells |
| HMSC | Human mesangial cells |
| Sirt1 | Sirtuin1 |
| NAD | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NMN | Nicotinamide mononucleotide |
| NAMPT | Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase |
| NAM | Nicotinamide |
| NMNAT | Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| LCMS | Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry |
| FN | Fibronectin |
| NG | Normal glucose |
| HG | High glucose |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer solution |
| WT | Wild type |
| DCFH-DA | 2,7-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| AC-P65 | Acetyl-nuclear factor-κB P65 |
| HE | Hematoxylin–eosin |
| PAS | Periodic Acid–Schiff stain |
| PARP | Poly ADP-ribose polymerase |
References
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembillo, G.; Ingrasciotta, Y.; Crisafulli, S.; Luxi, N.; Siligato, R.; Santoro, D.; Trifirò, G. Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: From Pathophysiology to Pharmacological Aspects with a Focus on Therapeutic Inertia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, G. New insights into the pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy: From haemodynamics to molecular pathology. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 34, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornberg, A.; Pricer, W.E., Jr. On the structure of triphosphopyridine nucleotide. J. Biol. Chem. 1950, 186, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.C. Mitochondria and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, A.; Kulikova, V.; Ziegler, M. The human NAD metabolome: Functions, metabolism and compartmentalization. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 50, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorin, Y.; Block, K.; Hernandez, J.; Bhandari, B.; Wagner, B.; Barnes, J.L.; Abboud, H.E. Nox4 NAD(P)H oxidase mediates hypertrophy and fibronectin expression in the diabetic kidney. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 39616–39626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Wakino, S.; Simic, P.; Sakamaki, Y.; Minakuchi, H.; Fujimura, K.; Hosoya, K.; Komatsu, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Kanda, T.; et al. Renal tubular Sirt1 attenuates diabetic albuminuria by epigenetically suppressing Claudin-1 overexpression in podocytes. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, S.; Kitada, M.; Kanasaki, K.; Maegawa, H.; Koya, D. Anti-aging molecule, Sirt1: A novel therapeutic target for diabetic nephropathy. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, S.; Koya, D.; Uzu, T.; Maegawa, H. Role of nutrient-sensing signals in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 315494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tervaert, T.W.; Mooyaart, A.L.; Amann, K.; Cohen, A.H.; Cook, H.T.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Ferrario, F.; Fogo, A.B.; Haas, M.; de Heer, E.; et al. Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Chen, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; He, Y. Preventive effect of Shenkang injection against high glucose-induced senescence of renal tubular cells. Front. Med. 2019, 13, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Sunq, A.; Roth, R.A.; Hou, J. Inducible Expression of Claudin-1 in Glomerular Podocytes Generates Aberrant Tight Junctions and Proteinuria through Slit Diaphragm Destabilization. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kida, Y.; Zullo, J.A.; Goligorsky, M.S. Endothelial sirtuin 1 inactivation enhances capillary rarefaction and fibrosis following kidney injury through Notch activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Lv, C.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q. Mir-217 promotes inflammation and fibrosis in high glucose cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells via Sirt1/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, C.; Feldmann, M. NF-κB as a target for modulating inflammatory responses. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 5735–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhong, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Jim, B.; Zhou, M.M.; Chuang, P.Y.; He, J.C. Role of transcription factor acetylation in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2440–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hu, T.; Wei, R.; Cai, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Qiao, W.; Feng, L. Endogenous Nampt upregulation is associated with diabetic nephropathy inflammatory-fibrosis through the NF-κB p65 and Sirt1 pathway; NMN alleviates diabetic nephropathy inflammatory-fibrosis by inhibiting endogenous Nampt. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4181–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Takagi, S.; Nitta, K.; Kitada, M.; Srivastava, S.P.; Takagaki, Y.; Kanasaki, K.; Koya, D. Renal protective effects of empagliflozin via inhibition of EMT and aberrant glycolysis in proximal tubules. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e129034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.; Fu, B.; Bai, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, L.; Cui, J.; Cui, S.; Wei, R.; Chen, X.; Cai, G. NAD blocks high glucose induced mesangial hypertrophy via activation of the sirtuins-AMPK-mTOR pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 27, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Martin, A.; Ucero, A.C.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Santamaria, B.; Picatoste, B.; Carrasco, S.; Lorenzo, O.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. Endogenous NAMPT dampens chemokine expression and apoptotic responses in stressed tubular cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camp, S.M.; Ceco, E.; Evenoski, C.L.; Danilov, S.M.; Zhou, T.; Chiang, E.T.; Moreno-Vinasco, L.; Mapes, B.; Zhao, J.; Gursoy, G.; et al. Unique Toll-Like Receptor 4 Activation by NAMPT/PBEF Induces NFκB Signaling and Inflammatory Lung Injury. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, I.; Hasegawa, K.; Sakamaki, Y.; Muraoka, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kusahana, E.; Ono, T.; Kanda, T.; Tokuyama, H.; Wakino, S.; et al. Pre-emptive Short-term Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Treatment in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Mao, X.; DiAntonio, A.; Milbrandt, J. NMNAT1 inhibits axon degeneration via blockade of SARM1-mediated NAD(+) depletion. Elife 2016, 5, e19749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, J.C.; Banal, C.; Chow, B.S.; Cooper, M.E.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K. Diabetes and Kidney Disease: Role of Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 657–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Tu, X.; Wu, R. Vascular endothelial dysfunction, a major mediator in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandl, G.; Wolfrum, C. Hemostasis, endothelial stress, inflammation, and the metabolic syndrome. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, M.; Nascimento-Ferreira, I.; Orsomando, G.; Mori, V.; Gilley, J.; Brown, R.; Janeckova, L.; Vargas, M.E.; Worrell, L.A.; Loreto, A.; et al. A rise in NAD precursor nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) after injury promotes axon degeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Kakita, H.; Kubota, S.; Sene, A.; Lee, T.J.; Ban, N.; Dong, Z.; Lin, J.B.; Boye, S.L.; DiAntonio, A.; et al. SARM1 depletion rescues NMNAT1-dependent photoreceptor cell death and retinal degeneration. Elife 2020, 9, e62027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Xie, X.J.; Li, W.H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, T.; Li, S.L.; Lu, J.G.; Zhang, L.; et al. A Cell-Permeant Mimetic of NMN Activates SARM1 to Produce Cyclic ADP-Ribose and Induce Non-apoptotic Cell Death. iScience 2019, 15, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, M.A.; Rooney, T.M.; Pandya, J.D.; Wishart, T.M.; Gillingwater, T.H.; Geddes, J.W.; Sullivan, P.G.; Freeman, M.R. WldS prevents axon degeneration through increased mitochondrial flux and enhanced mitochondrial Ca2+ buffering. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, S.A.; Martinez, N.W.; Yoo, S.; Jara, J.S.; Zamorano, S.; Hetz, C.; Twiss, J.L.; Alvarez, J.; Court, F.A. Axonal degeneration is mediated by the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Dai, J.; Niu, M.; Li, B.; Chen, C.; Jiang, M.; Wu, Z.; Bao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; et al. Inhibition of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase protects against acute pancreatitis via modulating macrophage polarization and its related metabolites. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xing, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; et al. NAP1L2 drives mesenchymal stem cell senescence and suppresses osteogenic differentiation. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakino, S.; Hasegawa, K.; Itoh, H. Sirtuin and metabolic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, H. NAD+ Anabolism Disturbance Causes Glomerular Mesangial Cell Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073458
Li X, Li Y, Li F, Chen Q, Zhao Z, Liu X, Zhang N, Li H. NAD+ Anabolism Disturbance Causes Glomerular Mesangial Cell Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(7):3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073458
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xue, Yankun Li, Fengxia Li, Qi Chen, Zhonghua Zhao, Xueguang Liu, Nong Zhang, and Hui Li. 2022. "NAD+ Anabolism Disturbance Causes Glomerular Mesangial Cell Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 7: 3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073458
APA StyleLi, X., Li, Y., Li, F., Chen, Q., Zhao, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, N., & Li, H. (2022). NAD+ Anabolism Disturbance Causes Glomerular Mesangial Cell Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), 3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073458




