A Transcriptome Analysis of mRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NGS Transcriptome Analysis of Transcripts
2.2. Functional and Pathway Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Selection
4.2. RNA Extraction
4.3. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
4.4. Functional and Pathways Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Lau, L.M.; Breteler, M.M. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. Neurol. 2006, 5, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, J.M.; De Jager, P.L.; Feany, M.B. Parkinson’s disease: Genetics and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Meng, L.; Wan, C.M.; Liu, Z.H.; Liao, W.H.; Yan, X.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Tang, B.S.; Guo, J.F. Identifying the presence of Parkinson’s disease using low-frequency fluctuations in BOLD signals. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 645, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twelves, D.; Perkins, K.S.; Counsell, C. Systematic review of incidence studies of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2003, 18, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savica, R.; Grossardt, B.R.; Bower, J.H.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Rocca, W.A. Incidence and pathology of synucleinopathies and tauopathies related to parkinsonism. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pringsheim, T.; Jette, N.; Frolkis, A.; Steeves, T.D. The prevalence of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2014, 29, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Constantinescu, R.; Thompson, J.P.; Biglan, K.M.; Holloway, R.G.; Kieburtz, K.; Marshall, F.J.; Ravina, B.M.; Schifitto, G.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology 2007, 68, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Rub, U.; Bratzke, H.; Del Tredici, K. Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 318, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, D.; Moreau, C.; Dujardin, K.; Cabantchik, I.; Defebvre, L.; Bordet, R. New pharmacological options for treating advanced Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, 1640–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winklhofer, K.F.; Haass, C. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.Y.; Lang, A.E. The nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease--an overview. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2010, 25, S123–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.D.; Neumiller, J.J.; Setter, S.M.; Dobbins, E.K. Clinical review of treatment options for select nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Am. J. Geriatr. Pharmacother. 2010, 8, 294–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Arico, D.; Lanuzza, B.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Tripodi, M.; Giardina, F.; Bella, R.; Puligheddu, M.; Pennisi, G.; Ferri, R.; et al. Facilitatory/inhibitory intracortical imbalance in REM sleep behavior disorder: Early electrophysiological marker of neurodegeneration? Sleep 2020, 43, zsz242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, F.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Ferri, R.; Pennisi, G.; Nicoletti, A.; Zappia, M.; Bella, R.; Pennisi, M. Clinical and Electrophysiological Hints to TMS in De Novo Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.D.; Ge, Y. Alterations of miRNAs reveal a dysregulated molecular regulatory network in Parkinson’s disease striatum. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 629, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Bai, L.; Qin, C. Long noncoding RNAs in neurodevelopment and Parkinson’s disease. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2019, 2, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenoglio, C.; Ridolfi, E.; Galimberti, D.; Scarpini, E. An emerging role for long non-coding RNA dysregulation in neurological disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20427–20442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batista, P.J.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteller, M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, X. Long Non-coding RNA in Neuronal Development and Neurological Disorders. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.W.; Luo, T.; Zou, S.S.; Wu, A.S. The Role of Long Noncoding RNAs in Central Nervous System and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, Z.; Zheng, D.; Qing, H. Regulatory Roles of Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Central Nervous System and Associated Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, P.; Ratti, A.; Venturin, M. The Long Non-Coding RNAs in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Novel Mechanisms of Pathogenesis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahariya, S.; Paddibhatla, I.; Kumar, S.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Pallepati, A.; Gutti, R.K. Long non-coding RNA: Classification, biogenesis and functions in blood cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.B.; Mattick, J.S. Long noncoding RNAs in cell biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutschner, T.; Diederichs, S. The hallmarks of cancer: A long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xin, C.; Liu, J. Long Non-coding RNAs in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, R.C.; Brilot, F. Autoimmune basal ganglia disorders. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.C.; Huang, W.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Shen, C.H.; Chou, Y.C.; Lin, C.L.; Lin, K.T.; Kao, C.H. Inverse Association of Parkinson Disease with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nationwide Population-based Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentzos, M.; Rombos, A. The role of IL-15 in central nervous system disorders. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 125, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, J.J., Jr.; Probstel, A.K.; Zamvil, S.S. B cells in autoimmune and neurodegenerative central nervous system diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 728–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajares, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Manda, G.; Bosca, L.; Cuadrado, A. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, T.H.; Zabetian, C.P.; Tenesa, A.; Laederach, A.; Montimurro, J.; Yearout, D.; Kay, D.M.; Doheny, K.F.; Paschall, J.; Pugh, E.; et al. Common genetic variation in the HLA region is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbach, J.A.; Norman, P.J.; Creary, L.E.; Damotte, V.; Montero-Martin, G.; Caillier, S.; Anderson, K.M.; Misra, M.K.; Nemat-Gorgani, N.; Osoegawa, K.; et al. A specific amino acid motif of HLA-DRB1 mediates risk and interacts with smoking history in Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7419–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulzer, D.; Alcalay, R.N.; Garretti, F.; Cote, L.; Kanter, E.; Agin-Liebes, J.; Liong, C.; McMurtrey, C.; Hildebrand, W.H.; Mao, X.; et al. T cells from patients with Parkinson’s disease recognize alpha-synuclein peptides. Nature 2017, 546, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brochard, V.; Combadiere, B.; Prigent, A.; Laouar, Y.; Perrin, A.; Beray-Berthat, V.; Bonduelle, O.; Alvarez-Fischer, D.; Callebert, J.; Launay, J.M.; et al. Infiltration of CD4+ lymphocytes into the brain contributes to neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.A.; Kannarkat, G.T.; Cintron, A.F.; Butkovich, L.M.; Fraser, K.B.; Chang, J.; Grigoryan, N.; Factor, S.A.; West, A.B.; Boss, J.M.; et al. LRRK2 levels in immune cells are increased in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinson’s Dis. 2017, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, T.; Lee, T.H. Cellular Mechanisms of Melatonin: Insight from Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.X.; Sainz, R.M.; Alatorre-Jimenez, M.; Qin, L. Melatonin as an antioxidant: Under promises but over delivers. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, F.; Li, W.A.; Geng, X.; Li, C.; Meng, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; Yu, F. A review of sleep disorders and melatonin. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, L.M.; Amara, A.W.; Videnovic, A. A systematic review of the literature on disorders of sleep and wakefulness in Parkinson’s disease from 2005 to 2015. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 35, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakhaki, R.D.; Ostadmohammadi, V.; Kouchaki, E.; Aghadavod, E.; Bahmani, F.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Reiter, R.J.; Mansournia, M.A.; Asemi, Z. Melatonin supplementation and the effects on clinical and metabolic status in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 195, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, C.A.; Carvalhedo de Bruin, P.F.; Lopes, L.A.; Magalhaes, M.C.; de Lourdes Seabra, M.; de Bruin, V.M. Effect of exogenous melatonin on sleep and motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Neurol. 2007, 254, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, M.; Park, S.; Jang, W.; Park, J.; Oh, E.; Cho, J.W.; Kim, J.S.; Youn, J. Prolonged-release melatonin in Parkinson’s disease patients with a poor sleep quality: A randomized trial. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2020, 75, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Lara, D.L.; Gonzalez-Enriquez, G.V.; Torres-Mendoza, B.M.; Gonzalez-Usigli, H.; Cardenas-Bedoya, J.; Macias-Islas, M.A.; de la Rosa, A.C.; Jimenez-Delgado, A.; Pacheco-Moises, F.; Cruz-Serrano, J.A.; et al. Effect of melatonin administration on the PER1 and BMAL1 clock genes in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Louis, E.K.; Boeve, A.R.; Boeve, B.F. REM Sleep Behavior Disorder in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2017, 32, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilat, M.; Coeytaux Jackson, A.; Marshall, N.S.; Hammond, D.; Mullins, A.E.; Hall, J.M.; Fang, B.A.M.; Yee, B.J.; Wong, K.K.H.; Grunstein, R.R.; et al. Melatonin for rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson’s disease: A randomised controlled trial. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2020, 35, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunz, D.; Mahlberg, R. A two-part, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of exogenous melatonin in REM sleep behaviour disorder. J. Sleep Res. 2010, 19, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.; Maes, M. Gut Dysbiosis Dysregulates Central and Systemic Homeostasis via Suboptimal Mitochondrial Function: Assessment, Treatment and Classification Implications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogavero, M.P.; Silvani, A.; DelRosso, L.M.; Salemi, M.; Ferri, R. Focus on the Complex Interconnection between Cancer, Narcolepsy and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Possible Case of Orexin-Dependent Inverse Comorbidity. Cancers 2021, 13, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Reiter, R.J.; Alipoor, R.; Dadgostar, E.; Kouchaki, E.; Asemi, Z. Melatonin and Parkinson Disease: Current Status and Future Perspectives for Molecular Mechanisms. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, D.M.; Economides, A.N.; Rojas, E.; Lamb, T.M.; Nunez, L.; Jones, P.; Lp, N.Y.; Espinosa, R., 3rd; Brannan, C.I.; Gilbert, D.J.; et al. Identification of mammalian noggin and its expression in the adult nervous system. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6077–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nan, H.; Zhou, L.; Liang, W.; Meng, J.; Lin, K.; Li, M.; Hou, J.; Wang, L. Epigenetically associated CCL20 upregulation correlates with esophageal cancer progression and immune disorder. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 228, 153683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarsheth, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Zou, W. Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Du, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Zha, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Weng, C.; Fang, X.; et al. CCR9 Promotes Migration and Invasion of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inamo, J.; Suzuki, K.; Takeshita, M.; Kassai, Y.; Takiguchi, M.; Kurisu, R.; Okuzono, Y.; Tasaki, S.; Yoshimura, A.; Takeuchi, T. Identification of novel genes associated with dysregulation of B cells in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhong, M. Transcriptional profiling of long-intergenic noncoding RNAs in lung squamous cell carcinoma and its value in diagnosis and prognosis. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.X.; Zheng, H.; Deng, X.F.; Zhou, D.; Dai, J.G. Status of the Parkinson’s disease gene family expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zuo, Z.; Lu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, A.; Liu, X. Silencing of PINK1 represses cell growth, migration and induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Murata, H.; Sakaguchi, M.; Kataoka, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nasu, Y.; Kumon, H.; Huh, N.H. Partial sensitization of human bladder cancer cells to a gene-therapeutic adenovirus carrying REIC/Dkk-3 by downregulation of BRPK/PINK1. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, P.; Vatrano, S.; Cannarella, R.; Calogero, A.E.; Marchese, G.; Ravo, M.; Fraggetta, F.; Pepe, L.; Pennisi, M.; Romano, C.; et al. A study of gene expression by RNA-seq in patients with prostate cancer and in patients with Parkinson disease: An example of inverse comorbidity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 7627–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xun, N.; Wu, J.G. Long non-coding RNA FGF14-AS2 represses proliferation, migration, invasion, and induces apoptosis in breast cancer by sponging miR-205-5p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 6971–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, M.; Cosentino, F.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Giurato, G.; Borgione, E.; Marchese, G.; Santa Paola, S.; Lanuzza, B.; et al. mRNA expression profiling of mitochondrial subunits in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddine, M.A.; Li, Y.J.; van der Walt, J.M.; Walters, R.; Jewett, R.M.; Xu, H.; Wang, T.; Walter, J.W.; Scott, B.L.; Hulette, C.; et al. Genomic convergence to identify candidate genes for Parkinson disease: SAGE analysis of the substantia nigra. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2005, 20, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annesley, S.J.; Lay, S.T.; De Piazza, S.W.; Sanislav, O.; Hammersley, E.; Allan, C.Y.; Francione, L.M.; Bui, M.Q.; Chen, Z.P.; Ngoei, K.R.; et al. Immortalized Parkinson’s disease lymphocytes have enhanced mitochondrial respiratory activity. Dis. Models Mech. 2016, 9, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gezen-Ak, D.; Alaylioglu, M.; Genc, G.; Sengul, B.; Keskin, E.; Sordu, P.; Gulec, Z.E.K.; Apaydin, H.; Bayram-Gurel, C.; Ulutin, T.; et al. Altered Transcriptional Profile of Mitochondrial DNA-Encoded OXPHOS Subunits, Mitochondria Quality Control Genes, and Intracellular ATP Levels in Blood Samples of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2020, 74, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Gallardo, E.; Iceta, R.; Iglesias, E.; Montoya, J.; Ruiz-Pesini, E. OXPHOS toxicogenomics and Parkinson’s disease. Mutat. Res. 2011, 728, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, W.D., Jr.; Parks, J.K.; Swerdlow, R.H. Complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease frontal cortex. Brain Res. 2008, 1189, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, W.D., Jr.; Parks, J.K. Mitochondrial ND5 mutations in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosel, S.; Grasbon-Frodl, E.M.; Mautsch, U.; Egensperger, R.; von Eitzen, U.; Frishman, D.; Hofmann, S.; Gerbitz, K.D.; Mehraein, P.; Graeber, M.B. Novel mutations of mitochondrial complex I in pathologically proven Parkinson disease. Neurogenetics 1998, 1, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulua, A.C.; Simon, A.; Maddipati, R.; Pelletier, M.; Park, H.; Kim, K.Y.; Sack, M.N.; Kastner, D.L.; Siegel, R.M. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote production of proinflammatory cytokines and are elevated in TNFR1-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.P.; Brodsky, I.E.; Rahner, C.; Woo, D.K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Walsh, M.C.; Choi, Y.; Shadel, G.S.; Ghosh, S. TLR signalling augments macrophage bactericidal activity through mitochondrial ROS. Nature 2011, 472, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supinski, G.S.; Schroder, E.A.; Callahan, L.A. Mitochondria and Critical Illness. Chest 2020, 157, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angajala, A.; Lim, S.; Phillips, J.B.; Kim, J.H.; Yates, C.; You, Z.; Tan, M. Diverse Roles of Mitochondria in Immune Responses: Novel Insights into Immuno-Metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsche, M.; Konig, I.R.; Delcambre, S.; Petrucci, S.; Balck, A.; Bruggemann, N.; Zimprich, A.; Wasner, K.; Pereira, S.L.; Avenali, M.; et al. Mitochondrial damage-associated inflammation highlights biomarkers in PRKN/PINK1 parkinsonism. Brain A J. Neurol. 2020, 143, 3041–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, S.; Benito-Leon, J.; Pena-Bautista, C.; Baquero, M.; Chafer-Pericas, C. Recent Evidence in Epigenomics and Proteomics Biomarkers for Early and Minimally Invasive Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1273–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, M.; Marchese, G.; Cordella, A.; Cannarella, R.; Barone, C.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Calogero, A.E.; Romano, C. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 expression in patients with Down syndrome. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Liao, Y. Subread/Rsubread Users Guide; The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research: Melbourne, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, A.D.; Thurston, M.J.; Machhi, J.; Olson, K.E.; Namminga, K.L.; Gendelman, H.E.; Mosley, R.L. Immunotherapy for Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 137, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Kordower, J.H. Immunotherapy in Parkinson’s disease: Current status and future directions. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 132, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, J.A. Inverse association between cancer and neurodegenerative disease: Review of the epidemiologic and biological evidence. Biogerontology 2014, 15, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fores-Martos, J.; Boullosa, C.; Rodrigo-Dominguez, D.; Sanchez-Valle, J.; Suay-Garcia, B.; Climent, J.; Falco, A.; Valencia, A.; Puig-Butille, J.A.; Puig, S.; et al. Transcriptomic and Genetic Associations between Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
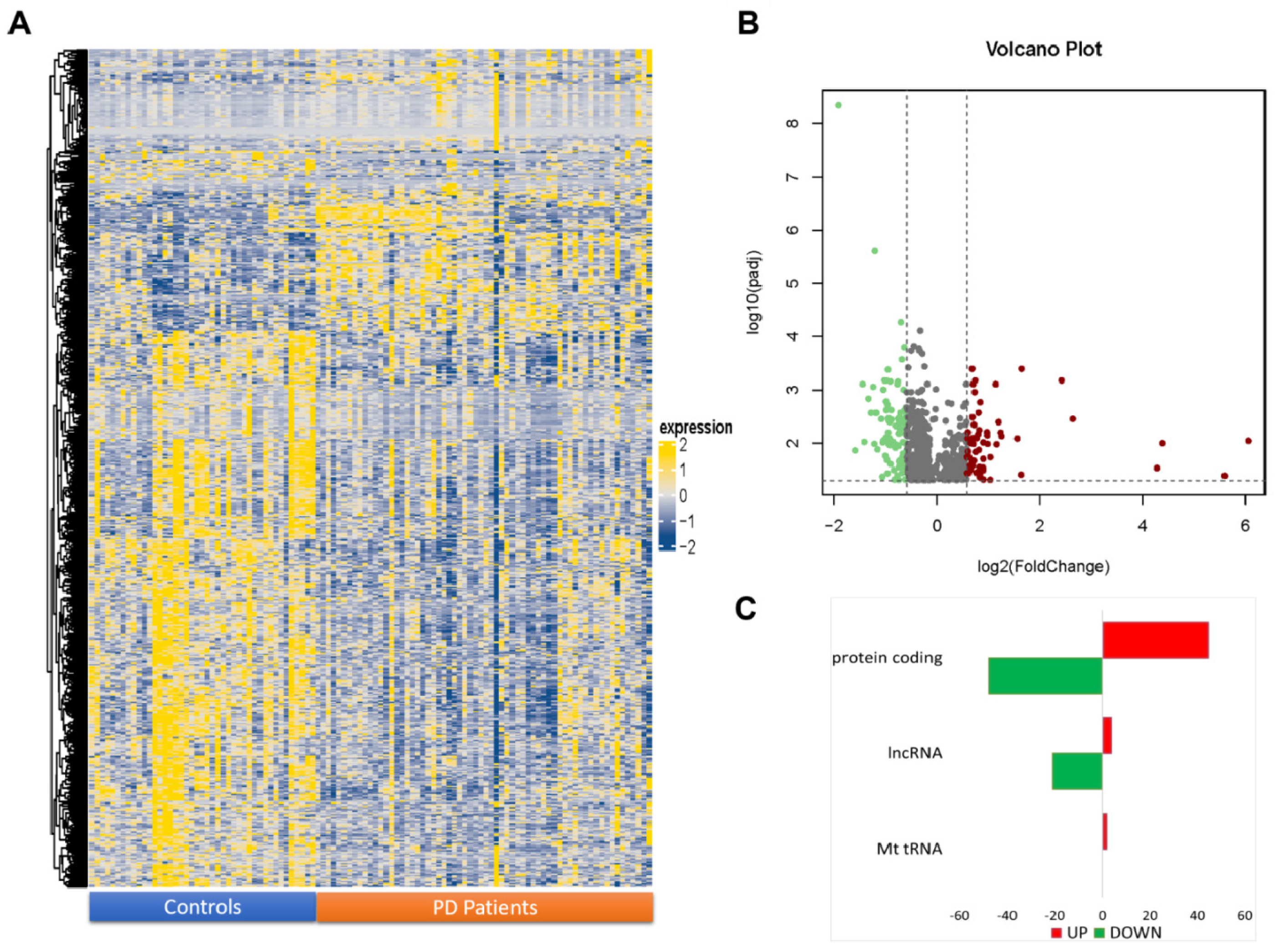
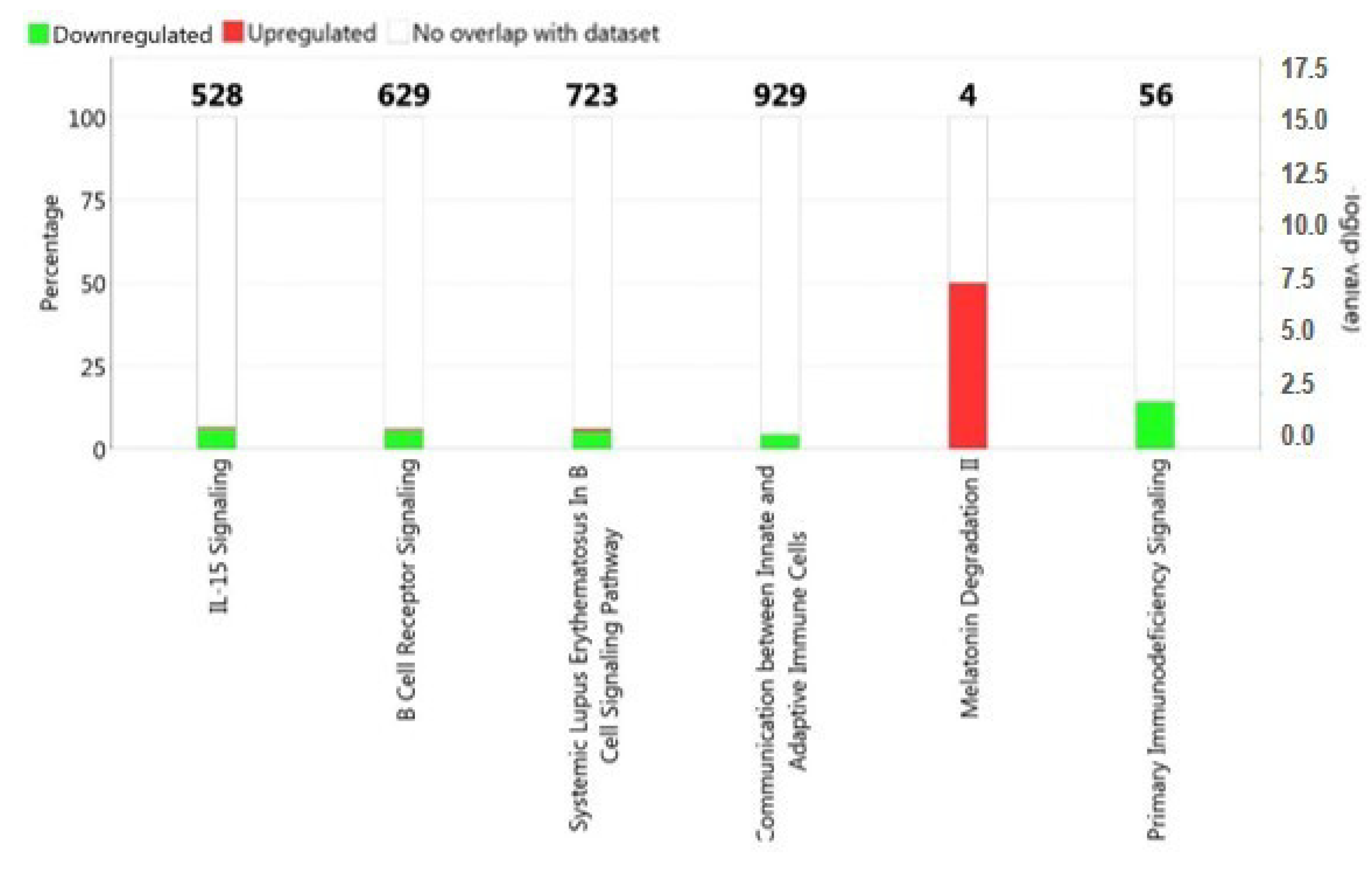
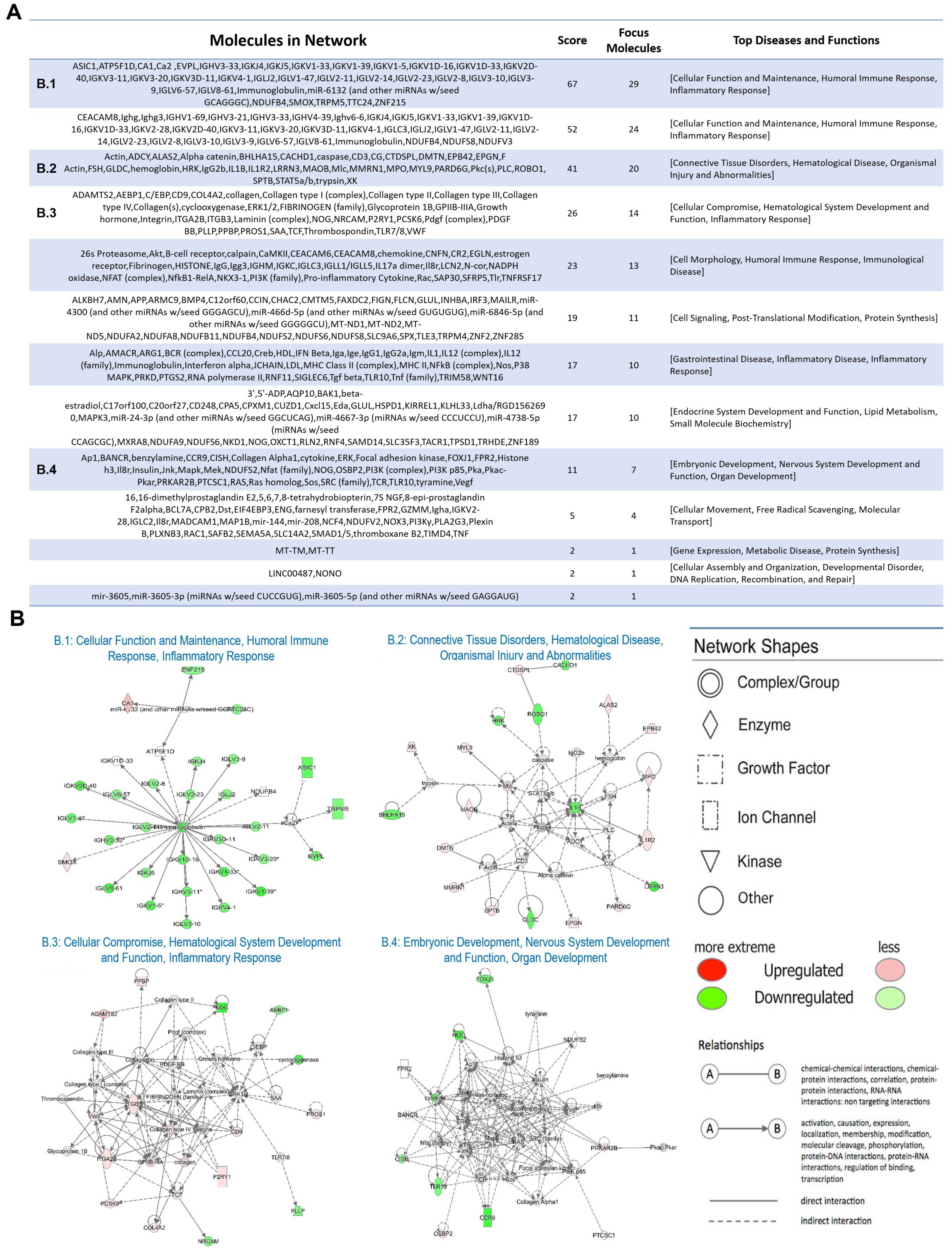

| RNA | Fold Change | Type | RNA | Fold Change | Type | RNA | Fold Change | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOG | −3.75 | pr_coding | EVPL | −1.89 | pr_coding | AC009237.14 | −1.60 | lncRNA |
| CCL20 | −3.02 | pr_coding | ROBO1 | −1.89 | pr_coding | ZNF2 | −1.58 | pr_coding |
| LRRN3 | −2.73 | pr_coding | ZNF285 | −1.87 | pr_coding | AL442128.2 | −1.58 | lncRNA |
| TNFRSF17 | −2.36 | pr_coding | FOXJ1 | −1.87 | pr_coding | KLHL33 | −1.58 | pr_coding |
| CCR9 | −2.31 | pr_coding | AC010331.1 | −1.79 | lncRNA | LIMD1-AS1 | −1.57 | lncRNA |
| PTGS2 | −2.22 | pr_coding | SFRP5 | −1.77 | pr_coding | CHAC2 | −1.56 | pr_coding |
| MXRA8 | −2.11 | pr_coding | NKX3-1 | −1.77 | pr_coding | C12orf60 | −1.56 | pr_coding |
| IL1B | −2.08 | pr_coding | LINC02848 | −1.75 | lncRNA | TRPM5 | −1.56 | pr_coding |
| GLDC | −2.06 | pr_coding | WNT16 | −1.71 | pr_coding | AL034550.2 | −1.56 | lncRNA |
| CD248 | −2.05 | pr_coding | LEF1-AS1 | −1.70 | lncRNA | AEBP1 | −1.55 | pr_coding |
| HRK | −2.03 | pr_coding | LINC02132 | −1.70 | lncRNA | AC103563.7 | −1.55 | lncRNA |
| BHLHA15 | −1.99 | pr_coding | C17orf100 | −1.69 | pr_coding | ZNF215 | −1.54 | pr_coding |
| AL132996.1 | −1.98 | lncRNA | CR2 | −1.67 | pr_coding | CISH | −1.53 | pr_coding |
| MAILR | −1.98 | lncRNA | IGLL5 | −1.67 | pr_coding | IL6R-AS1 | −1.52 | lncRNA |
| LINC00487 | −1.96 | lncRNA | NRCAM | −1.67 | pr_coding | BCL7A | −1.52 | pr_coding |
| CPA5 | −1.94 | pr_coding | TLR10 | −1.65 | pr_coding | SLC35F3 | −1.52 | pr_coding |
| CACHD1 | −1.94 | pr_coding | AC009123.1 | −1.65 | lncRNA | MIR4458HG | −1.52 | lncRNA |
| LINC02295 | −1.93 | lncRNA | PLLP | −1.64 | pr_coding | SIGLEC6 | −1.52 | pr_coding |
| JCHAIN | −1.93 | pr_coding | MIR3142HG | −1.64 | lncRNA | ZNF667-AS1 | −1.51 | lncRNA |
| FGF14-AS2 | −1.91 | lncRNA | TTC24 | −1.62 | pr_coding | AMACR | −1.51 | pr_coding |
| AC097634.1 | −1.91 | lncRNA | RNF157-AS1 | −1.62 | lncRNA | CNFN | −1.50 | pr_coding |
| ASIC1 | −1.90 | pr_coding | AMN | −1.61 | pr_coding |
| RNA | Fold Change | Type | RNA | Fold Change | Type | RNA | Fold Change | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT-TW | 66.69 | MT_tRNA | OSBP2 | 1.87 | pr_coding | SPTB | 1.64 | pr_coding |
| MT-TT | 48.33 | MT_tRNA | ARG1 | 1.87 | pr_coding | SMOX | 1.63 | pr_coding |
| MT-ND5 | 20.89 | pr_coding | CEACAM6 | 1.87 | pr_coding | P2RY1 | 1.63 | pr_coding |
| CA1 | 6.24 | pr_coding | LCN2 | 1.86 | pr_coding | MPO | 1.62 | pr_coding |
| ADAMTS2 | 5.36 | pr_coding | COL4A2 | 1.82 | pr_coding | VWF | 1.61 | pr_coding |
| PPBP | 3.11 | pr_coding | RNF11 | 1.79 | pr_coding | AC132872.2 | 1.61 | lncRNA |
| IL1R2 | 2.95 | pr_coding | TRHDE | 1.78 | pr_coding | CTDSPL | 1.60 | pr_coding |
| MAP1B | 2.39 | pr_coding | SAMD14 | 1.76 | pr_coding | PLXNB3 | 1.59 | pr_coding |
| CEACAM8 | 2.36 | pr_coding | PROS1 | 1.76 | pr_coding | CD9 | 1.58 | pr_coding |
| ITGB3 | 2.24 | pr_coding | XK | 1.75 | pr_coding | SPX | 1.58 | pr_coding |
| ITGA2B | 2.21 | pr_coding | ALAS2 | 1.70 | pr_coding | TRIM58 | 1.56 | pr_coding |
| MAOB | 2.05 | pr_coding | LINC02701 | 1.68 | lncRNA | MMRN1 | 1.54 | pr_coding |
| FIGN | 2.05 | pr_coding | SAP30 | 1.67 | pr_coding | PARD6G | 1.53 | pr_coding |
| EPGN | 1.98 | pr_coding | DMTN | 1.66 | pr_coding | FAXDC2 | 1.53 | pr_coding |
| AQP10 | 1.97 | pr_coding | PCSK6 | 1.65 | pr_coding | AC093849.4 | 1.52 | lncRNA |
| MYL9 | 1.96 | pr_coding | CMTM5 | 1.65 | pr_coding | CRYZL2P-SEC16B | 1.51 | lncRNA |
| EPB42 | 1.87 | pr_coding | PRKAR2B | 1.64 | pr_coding |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salemi, M.; Lanza, G.; Mogavero, M.P.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Borgione, E.; Iorio, R.; Ventola, G.M.; Marchese, G.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Ravo, M.; et al. A Transcriptome Analysis of mRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031535
Salemi M, Lanza G, Mogavero MP, Cosentino FII, Borgione E, Iorio R, Ventola GM, Marchese G, Salluzzo MG, Ravo M, et al. A Transcriptome Analysis of mRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031535
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalemi, Michele, Giuseppe Lanza, Maria Paola Mogavero, Filomena I. I. Cosentino, Eugenia Borgione, Roberta Iorio, Giovanna Maria Ventola, Giovanna Marchese, Maria Grazia Salluzzo, Maria Ravo, and et al. 2022. "A Transcriptome Analysis of mRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031535
APA StyleSalemi, M., Lanza, G., Mogavero, M. P., Cosentino, F. I. I., Borgione, E., Iorio, R., Ventola, G. M., Marchese, G., Salluzzo, M. G., Ravo, M., & Ferri, R. (2022). A Transcriptome Analysis of mRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031535







