SRSF3 and HNRNPH1 Regulate Radiation-Induced Alternative Splicing of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Elevated Levels of PRMT5-ISO5 Improve the Poor Prognosis of HCC
2.2. IR induces PRMT5-ISO5 Transcript Levels by Changing the Levels of SRSF3 and HNRNPH1
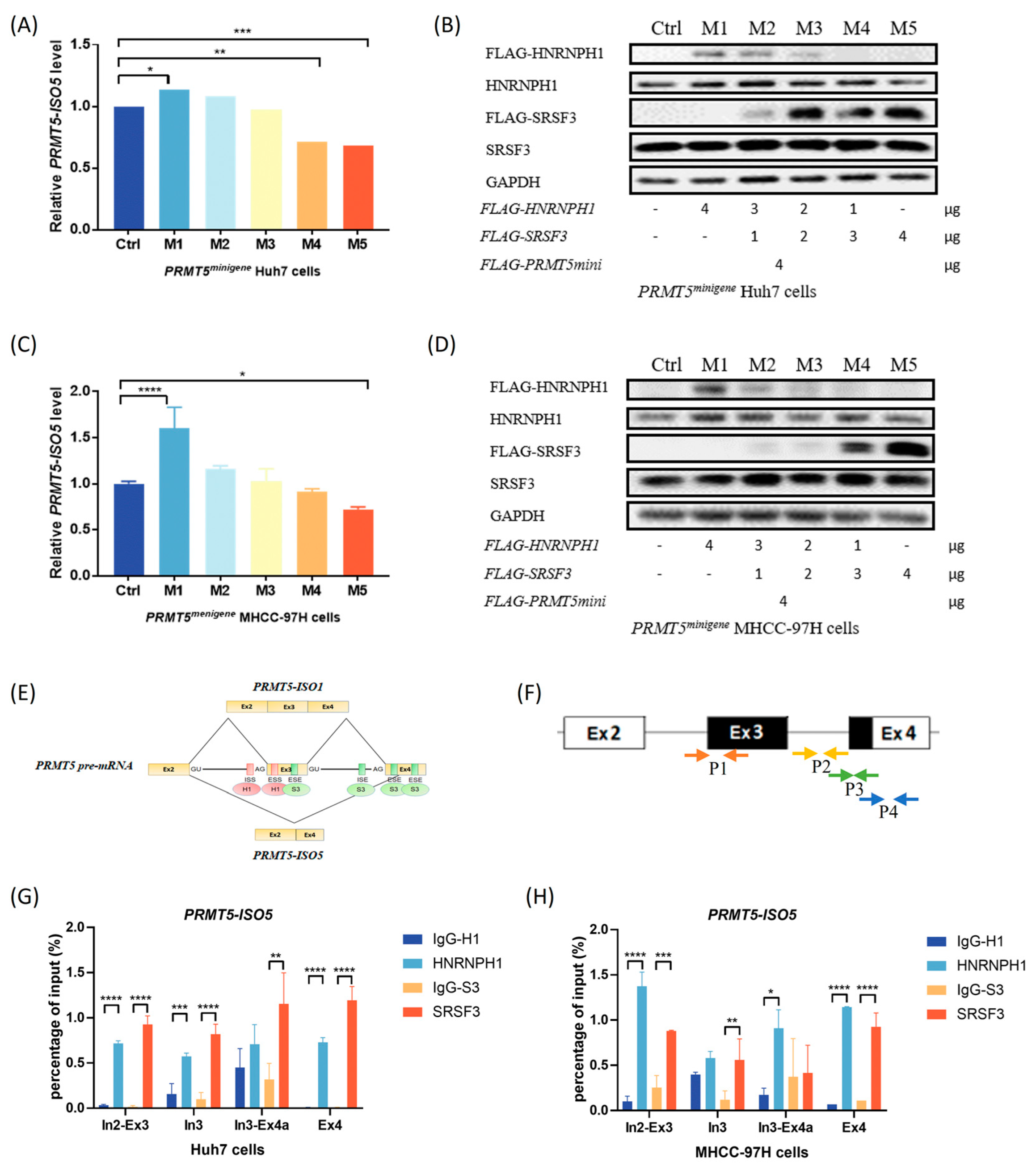
2.3. The Antagonistic Interaction of SRSF3 and HNRNPH1 Depends on Their Competitive Binding with PRMT5
2.4. Elevated Levels of PRMT5-ISO5 Suppress Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth
2.5. Liver-Specific Knockout of Prmt5 Inhibits Hepatocarcinogenesis
3. Discussion
3.1. IR Induces the Generation of the PRMT5-ISO5 Transcript Which Improves the Poor Prognosis of HCC Patients
3.2. SRSF3 and HNRNPH1 Play Opposite Roles in Regulating PRMT5 AS Induced by IR, Which Depends on Their Competitive Binding Abilities
3.3. IR Induces the Elevated Level of PRMT5-ISO5 Which Increases Cell Radiosensitivity, Resulting in a Therapeutic Effect on Xenograft Tumors
3.4. Liver-Specific Knockout of Prmt5 Inhibits Hepatocarcinogenesis
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. IR Treatment
4.4. Plasmid Construction and siRNAs
4.5. Cell Transfection
4.6. Generation of PRMT5 Knockout Clones
4.7. Colony Formation Assay
4.8. Reverse Transcription-Quantitative PCR and Western Blotting
4.9. RNA Immunoprecipitation
4.10. Xenograft Model and Treatments
4.11. Hydrodynamic Tail-Vein Injection and Prmt5 Conditional Knockout Experiments
4.12. Tumor Growth and Histochemistry Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Qin, S. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Opportunities and Challenges. Oncologist 2019, 24 (Suppl. S1), S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, J.; He, W.; Li, H.; Piao, J.; Xu, H.; Duan, X. Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an effective and safe treatment for small hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; Lou, L.; Tian, M.; Lu, G.; Tian, J.; Chen, X. MAPK4 deletion enhances radiation effects and triggers synergistic lethality with simultaneous PARP1 inhibition in cervical cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Zhao, X.; Shi, X.; Hu, Y.; Qu, F.; Zhang, X. Radiation induces NORAD expression to promote ESCC radiotherapy resistance via EEPD1/ATR/Chk1 signalling and by inhibiting pri-miR-199a1 processing and the exosomal transfer of miR-199a-5p. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, S.; He, X. Transcriptome-Wide Analysis Reveals the Landscape of Aberrant Alternative Splicing Events in Liver Cancer. Hepatology 2019, 69, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, S.; Sun, L.; Cai, J.; et al. Myelocytomatosis-Protein Arginine N-Methyltransferase 5 Axis Defines the Tumorigenesis and Immune Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1932–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wen, C.; Jiang, H.; Ma, S.; Liu, X. Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 Functions via Interacting Proteins. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 725301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Xie, J. Evolutionary Emergence of a Novel Splice Variant with an Opposite Effect on the Cell Cycle. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 2203–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owens, J.L.; Beketova, E.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q.; Pawar, J.S.; Asberry, A.M.; Yang, J.; Deng, X.; Elzey, B.D.; Ratliff, T.L.; et al. Targeting Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 Suppresses Radiation-induced Neuroendocrine Differentiation and Sensitizes Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, F.; Giulietti, M.; Burini, A.B.; Principato, G. SpliceAid 2: A database of human splicing factors expression data and RNA target motifs. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the Human Tissue-specific Expression by Genome-wide Integration of Transcriptomics and Antibody-based Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahba, A.; Ryan, M.C.; Shankavaram, U.T.; Camphausen, K.; Tofilon, P.J. Radiation-induced alternative transcripts as detected in total and polysome-bound mRNA. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.E.; Alcedo, K.P.; Kim, H.J.; Snider, N.T. Alternative Splicing in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020, 10, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavian, N.; Cheung, V. SRSF1 Is a Mediator of Radiation-Induced Alternative Splicing in B-Lymphocytes. Blood 2016, 128, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullà, A.; Hideshima, T.; Bianchi, G.; Fulciniti, M.; Samur, M.K.; Qi, J.; Tai, Y.-T.; Harada, T.; Morelli, E.; Amodio, N.; et al. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 has prognostic relevance and is a druggable target in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 32, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrold, J.; Davies, C.C. PRMTs and Arginine Methylation: Cancer’s Best-Kept Secret? Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 993–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ronai, Z.A. PRMT5 function and targeting in cancer. Cell Stress 2020, 4, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Xiao, K.; Ye, Y.; Liang, H.; Chen, M.; Luo, J.; Qin, Z. High PRMT5 expression is associated with poor overall survival and tumor progression in bladder cancer. Aging 2020, 12, 8728–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfil, A.R.; Al-Saleem, J.; Howard, C.M.; Mates, J.M.; Kwiek, J.J.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Green, P.L. PRMT5 Is Upregulated in HTLV-1-Mediated T-Cell Transformation and Selective Inhibition Alters Viral Gene Expression and Infected Cell Survival. Viruses 2015, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kędzierska, H.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. Splicing factors of SR and hnRNP families as regulators of apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 396, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, S.; Chen, D.; Chen, B.; Yu, T.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Q.; Yao, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, Z.; et al. Transcriptomic analyses of RNA-binding proteins revealeIF3cpromotes cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sokół, E.; Kędzierska, H.; Czubaty, A.; Rybicka, B.; Rodzik, K.; Tański, Z.; Bogusławska, J.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. microRNA-mediated regulation of splicing factors SRSF1, SRSF2 and hnRNP A1 in context of their alternatively spliced 3′UTRs. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 363, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gao, F.; He, M.; Ding, X.F.; Wong, A.M.; Sze, S.C.; Yu, A.C.; Sun, T.; Chan, A.W.; Wang, X.; et al. Long-Read RNA Sequencing Identifies Alternative Splice Variants in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Tumor-Specific Isoforms. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Sun, B.; Qi, Y.; Ji, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, J.; Wang, T.; et al. SRSF1 inhibits autophagy through regulating Bcl-x splicing and interacting with PIK3C3 in lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, F.; Cheng, S.; Xu, Y.; Deng, H.; Gu, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, M.; et al. DDX17-regulated alternative splicing that produced an oncogenic isoform of PXN-AS1 to promote HCC metastasis. Hepatology 2021, 75, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettouh, H.; Fartoux, L.; Aoudjehane, L.; Wendum, D.; Clapéron, A.; Chrétien, Y.; Rey, C.; Scatton, O.; Soubrane, O.; Conti, F.; et al. Mitogenic Insulin Receptor-A Is Overexpressed in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma due to EGFR-Mediated Dysregulation of RNA Splicing Factors. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3974–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Qian, X.; Peng, L.-X.; Jiang, Y.; Hawke, D.H.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Cote, G.; Wang, H.; et al. A splicing switch from ketohexokinase-C to ketohexokinase-A drives hepatocellular carcinoma formation. Nature 2016, 18, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamazaki, T.; Liu, L.; Conlon, E.G.; Manley, J.L. Burkitt lymphoma-related TCF3 mutations alter TCF3 alternative splicing by disrupting hnRNPH1 binding. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiani, D.; Bok, J.; Massignani, E.; Wu, L.; Tabaglio, T.; Ippolito, M.R.; Cuomo, A.; Ozbek, U.; Zorgati, H.; Ghoshdastider, U.; et al. Proteomics profiling of arginine methylation defines PRMT5 substrate specificity. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaat8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautrey, H.; Jackson, C.; Dittrich, A.-L.; Browell, D.; Lennard, T.; Tyson-Capper, A. SRSF3 and hnRNP H1 regulate a splicing hotspot of HER2 in breast cancer cells. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbo, C.; Orrù, S.; Salvatore, F. SRp20: An overview of its role in human diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 436, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Horikawa, I.; Ajiro, M.; Robles, A.I.; Fujita, K.; Mondal, A.M.; Stauffer, J.K.; Zheng, Z.-M.; Harris, C.C. Downregulation of splicing factor SRSF3 induces p53β, an alternatively spliced isoform of p53 that promotes cellular senescence. Oncogene 2012, 32, 2792–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Karagoz, E.; Liang, B.; Song, X.; Shang, R.; Evert, K.; Xu, M.; Che, L.; Evert, M.; et al. Axis inhibition protein 1 (Axin1) Deletion–Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis Requires Intact β-Catenin but Not Notch Cascade in Mice. Hepatology 2019, 70, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xia, X.; Hu, J.; Fowlkes, N.W.; Li, S. WSX1 act as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating neoplastic PD-L1 expression. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvisi, D.F.; Wang, C.; Ho, C.; Ladu, S.; Lee, S.A.; Mattu, S.; Destefanis, G.; Delogu, S.; Zimmermann, A.; Ericsson, J. Increased Lipogenesis, Induced by AKT-mTORC1-RPS6 Signaling, Promotes Development of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1071–1083.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, T.-W.; Yevsa, T.; Woller, N.; Hoenicke, L.; Wuestefeld, T.; Dauch, D.; Hohmeyer, A.; Gereke, M.; Rudalska, R.; Potapova, A.; et al. Senescence surveillance of pre-malignant hepatocytes limits liver cancer development. Nature 2011, 479, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Xu, E.; Zhao, Y.; Singh, S.; Li, X.; Couchy, G.; Chen, X.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Chikina, M.; Monga, S.P. Modeling a human hepatocellular carcinoma subset in mice through coexpression of met and point-mutant β-catenin. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1587–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudalska, R.; Dauch, D.; Longerich, T.; McJunkin, K.; Wuestefeld, T.; Kang, T.-W.; Hohmeyer, A.; Pesic, M.; Leibold, J.; von Thun, A.; et al. In vivo RNAi screening identifies a mechanism of sorafenib resistance in liver cancer. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Tseng, T.-C.; Soong, R.-S.; Peng, C.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Huang, S.-F.; Chuang, T.-H.; Kao, J.-H.; Huang, L.-R. A novel spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma mouse model for studying T-cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Yue, F.; Chen, X.; Narayanan, N.; Qiu, J.; Syed, S.A.; Imbalzano, A.N.; Deng, M.; Yu, P.; Hu, C.; et al. Protein Arginine Methyltransferase PRMT5 Regulates Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Biogenesis in White Adipose Tissues. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 202002602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Tamiya, H.; Tocci, S.; Ronai, Z.A. PRMT5 control of cGAS/STING and NLRC5 pathways defines melanoma response to antitumor immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsson, V.; Gibbs, D.L.; Brown, S.D.; Wolf, D.; Bortone, D.S.; Ou Yang, T.-H.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Gao, G.F.; Plaisier, C.L.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. The Immune Landscape of Cancer. Immunity 2018, 48, 812–830.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bamodu, O.A.; Chang, H.-L.; Ong, J.-R.; Lee, W.-H.; Yeh, C.-T.; Tsai, J.-T. Elevated PDK1 Expression Drives PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Promotes Radiation-Resistant and Dedifferentiated Phenotype of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2020, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, X.-O.; Rozen, E.J.; Sun, X.; Sallis, B.; Verdejo-Torres, O.; Wigglesworth, K.; Moon, D.; Huang, T.; Cavaretta, J.P.; et al. PRMT5 activates AKT via methylation to promote tumor metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Xue, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, M.; Li, G.; Feng, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, S. Screening of Prognostic Biomarkers for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Primary Liver Cancer. Dose-Response 2022, 20, 15593258221097589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Zhang, M.; Litchfield, D.; Wang, L.; Kung, S.; Xie, J. Differential expression, distinct localization and opposite effect on Golgi structure and cell differentiation by a novel splice variant of human PRMT5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015, 1853, 2444–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazim, M.; Masuda, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Nasrin, F.; Takeda, J.I.; Ohe, K.; Ohkawara, B.; Ito, M.; Ohno, K. Competitive regu-lation of alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation by hnRNP H and CstF64 determines acetylcholinesterase isoforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Crutchley, J.; Zhang, D.; Owzar, K.; Kastan, M.B. Identification of a DNA Damage-Induced Alternative Splicing Pathway That Regulates p53 and Cellular Senescence Markers. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, D.; Gakhar, G.; Madgwick, D.; Hurt, A.; Takemoto, D.; Nguyen, T.A. A novel role of gap junction connexin46 protein to protect breast tumors from hypoxia. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 127, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mátés, L.; Chuah, M.K.L.; Belay, E.; Jerchow, B.; Manoj, N.; Acosta-Sanchez, A.; Grzela, D.; Schmitt, A.; Becker, K.; Matrai, J.; et al. Molecular evolution of a novel hyperactive Sleeping Beauty transposase enables robust stable gene transfer in vertebrates. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, S.M.; Decker, S.A.; Larson, J.D.; Ericson, K.; Forster, C.; Gallardo, J.L.; Long, C.; Demorest, Z.L.; Zamora, E.A.; Low, W.C.; et al. De novo Induction of Genetically Engineered Brain Tumors in Mice Using Plasmid DNA. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, C.; Tian, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, T.; Chen, H.; Dai, J.; Liang, Z.; Ma, S.; Liu, X. SRSF3 and HNRNPH1 Regulate Radiation-Induced Alternative Splicing of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314832
Wen C, Tian Z, Li L, Chen T, Chen H, Dai J, Liang Z, Ma S, Liu X. SRSF3 and HNRNPH1 Regulate Radiation-Induced Alternative Splicing of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314832
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Chaowei, Zhujun Tian, Lan Li, Tongke Chen, Huajian Chen, Jichen Dai, Zhenzhen Liang, Shumei Ma, and Xiaodong Liu. 2022. "SRSF3 and HNRNPH1 Regulate Radiation-Induced Alternative Splicing of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314832
APA StyleWen, C., Tian, Z., Li, L., Chen, T., Chen, H., Dai, J., Liang, Z., Ma, S., & Liu, X. (2022). SRSF3 and HNRNPH1 Regulate Radiation-Induced Alternative Splicing of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314832




