Circular Sponge against miR-21 Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin against Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
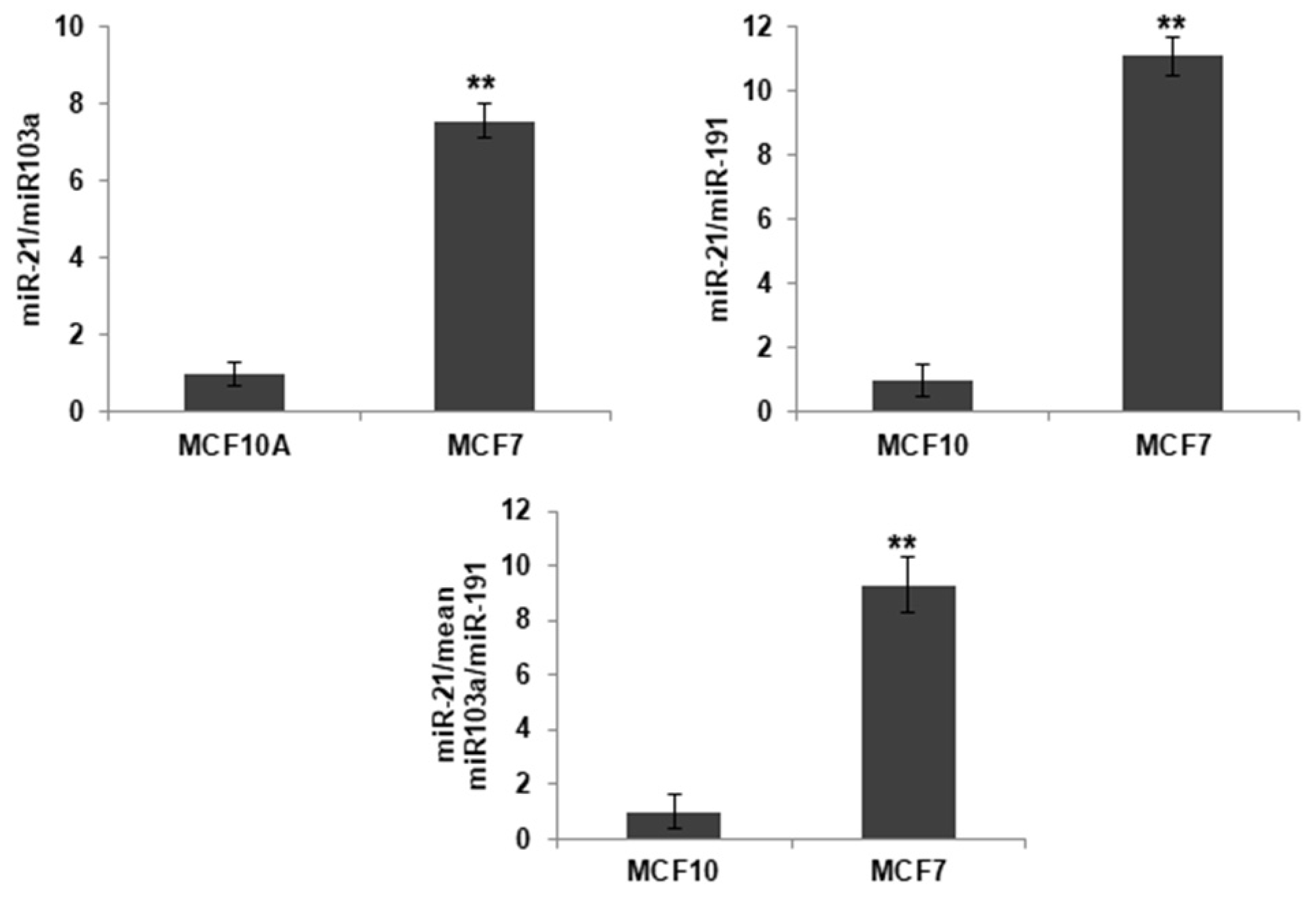
2.1. MiR-21 Differential Expression in Breast Cancer Cells
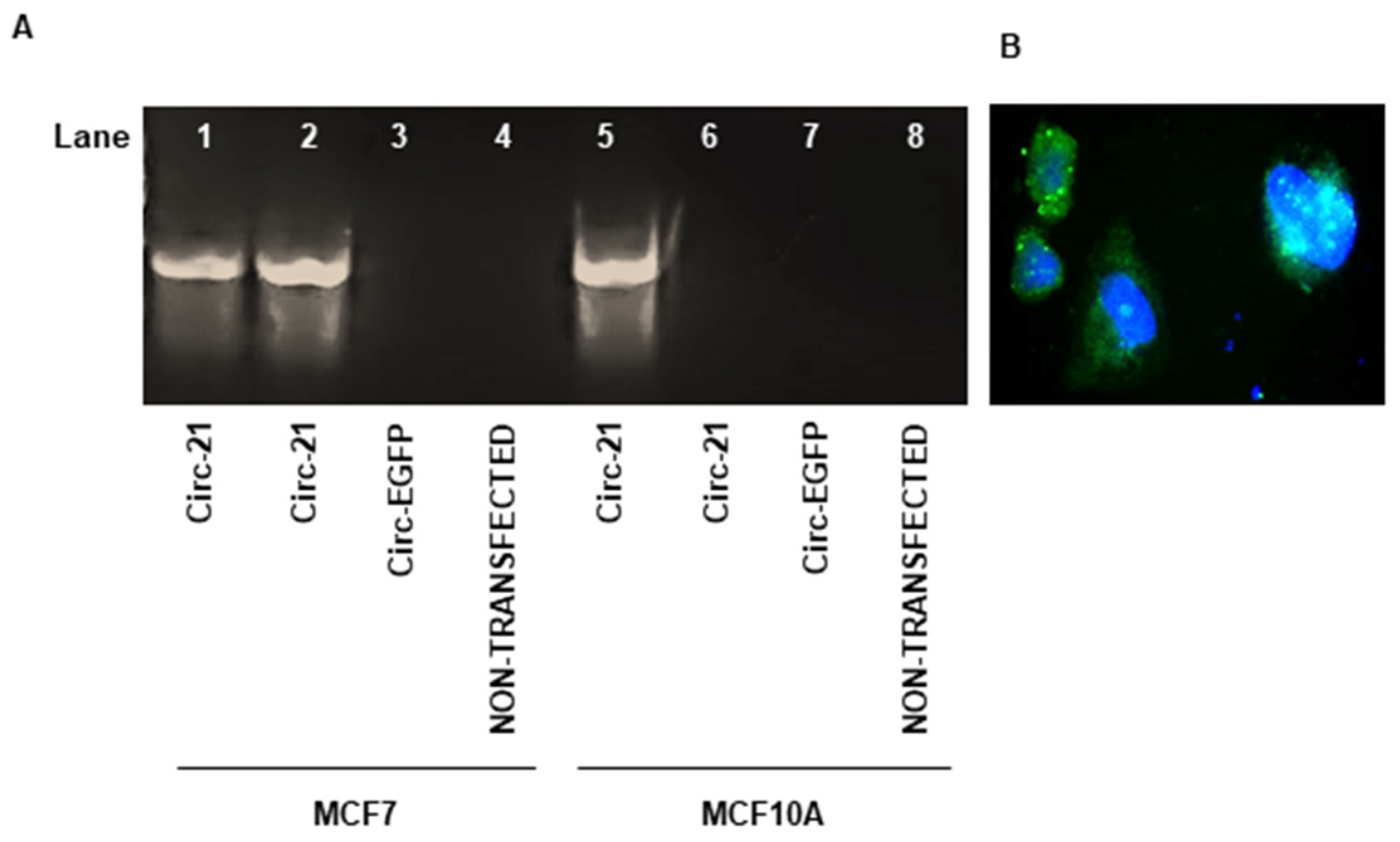
2.2. Detection of Correct Expression of the Circular Sponge
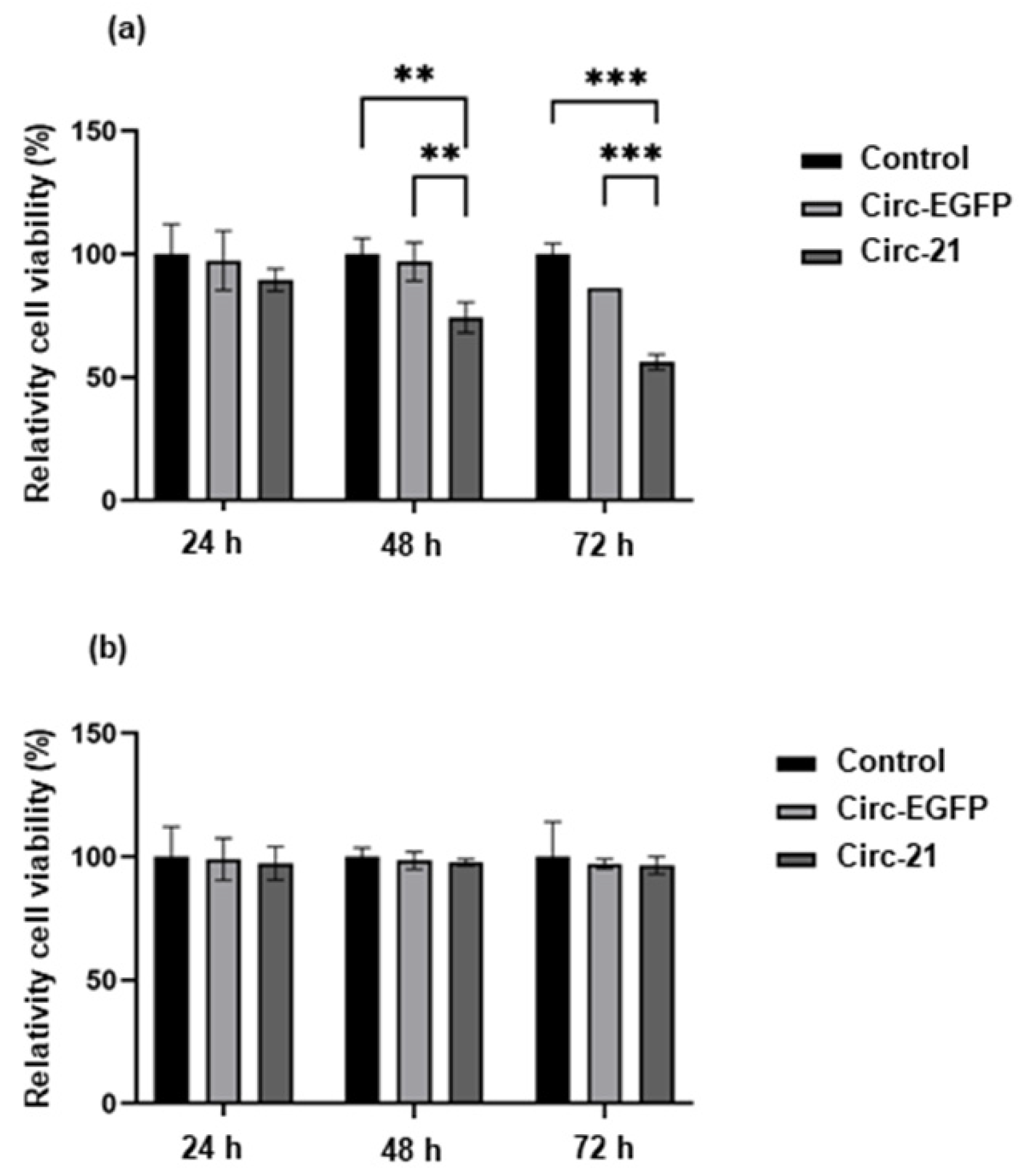
2.3. The Circ-21 Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth
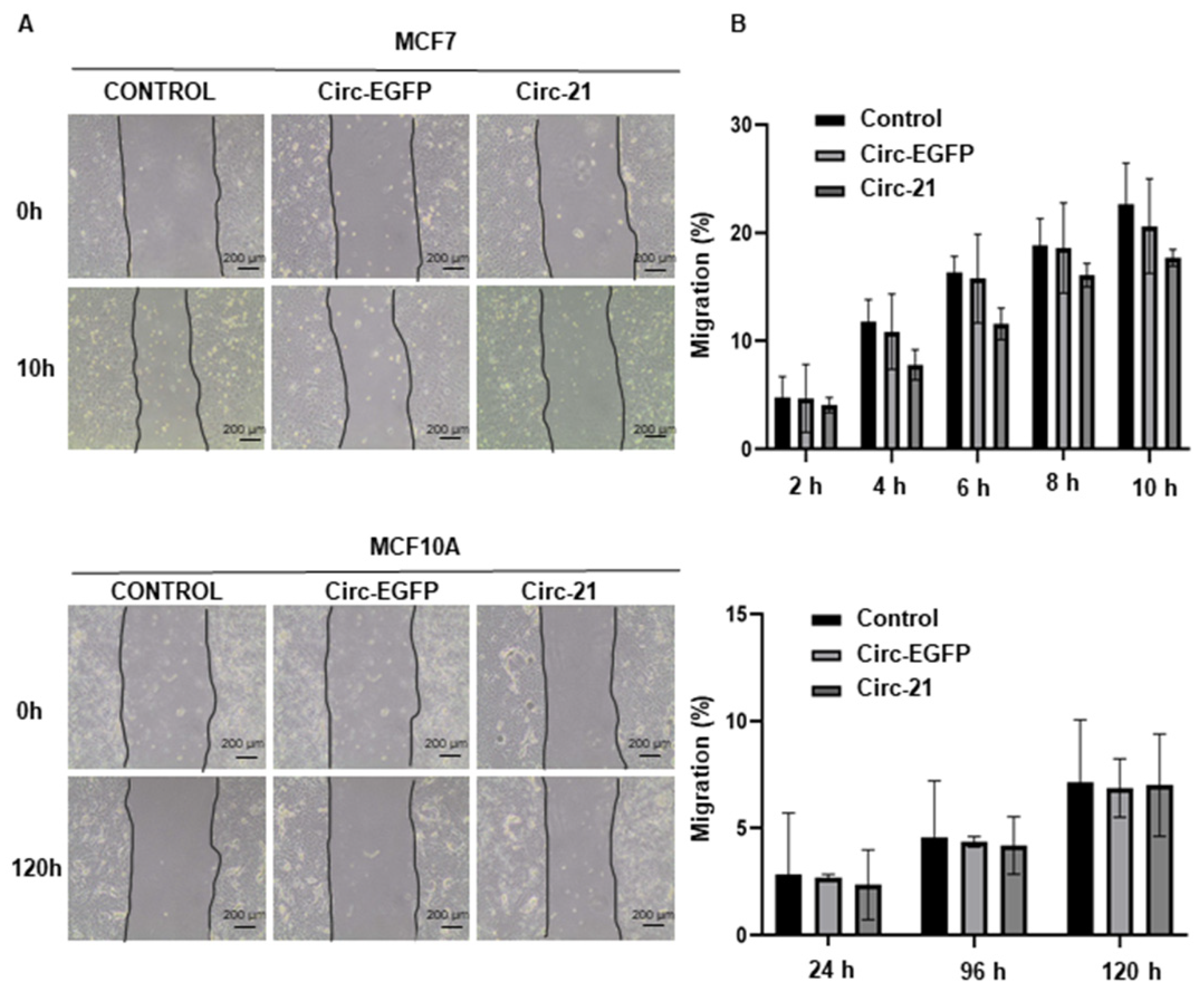
2.4. The Cir-21 Decreases Breast Cancer Cell Migration
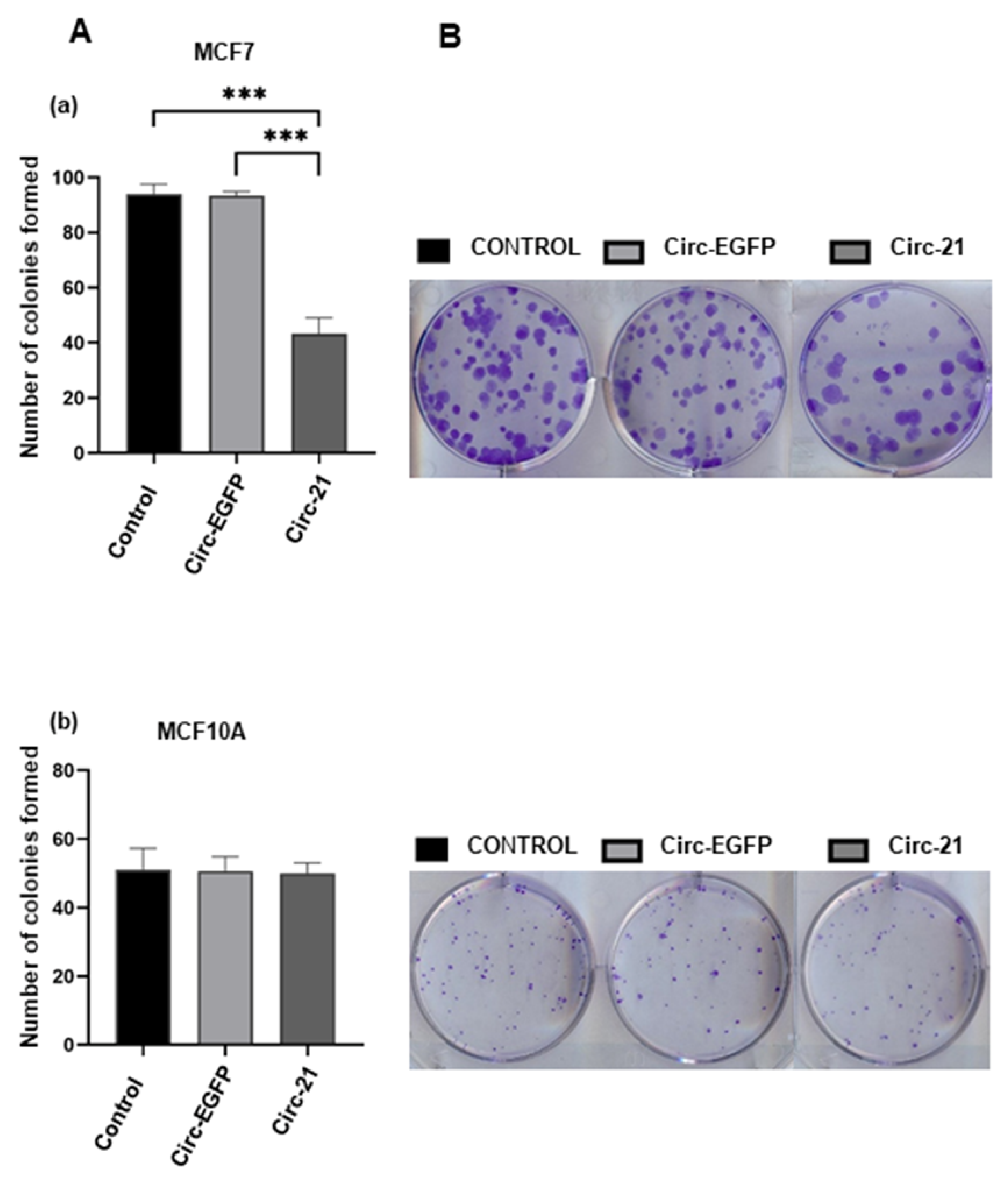
2.5. Effect of the Circ-21 in Cell Colony Formation
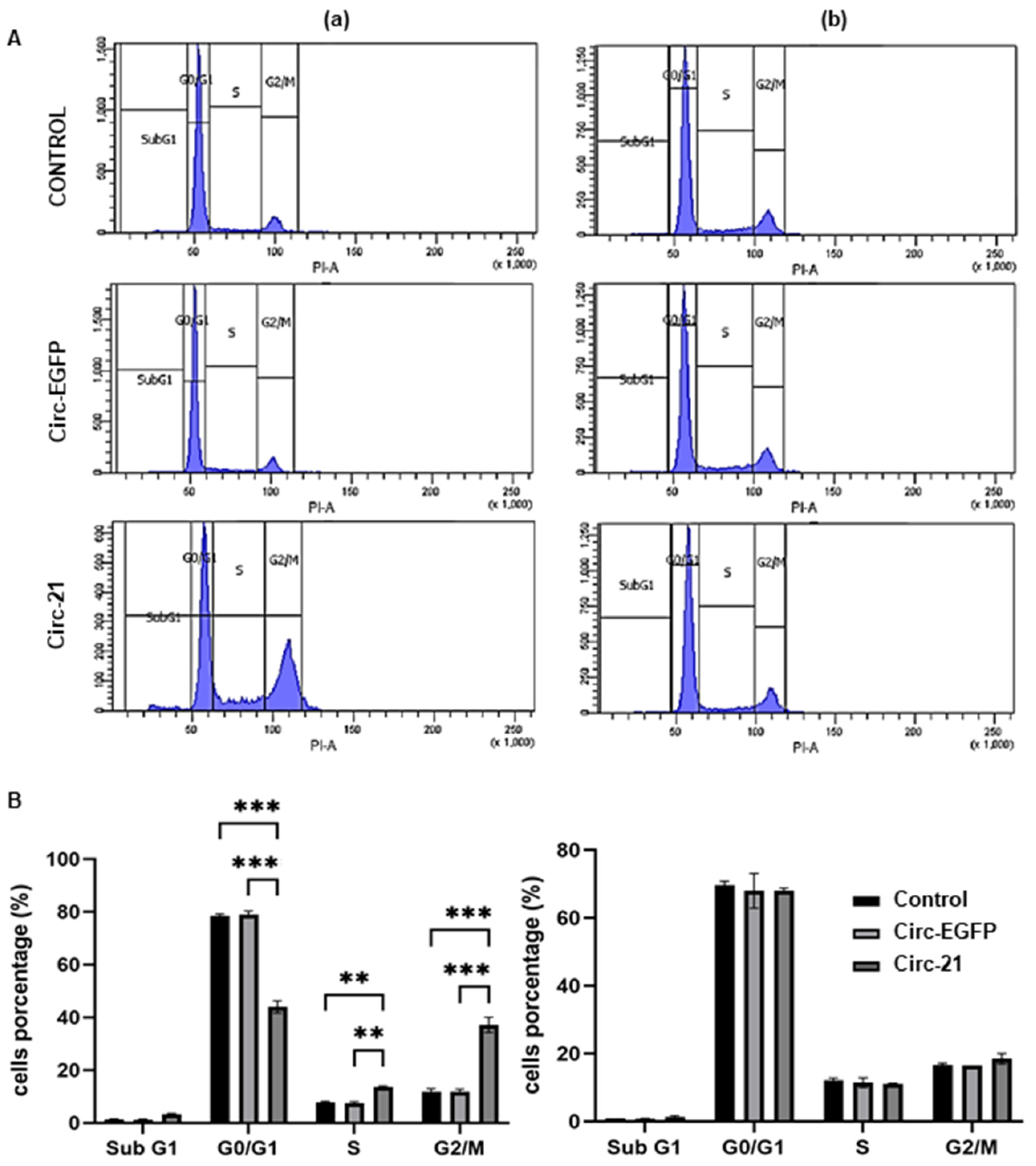
2.6. The Circ-21 Leads to Cell Cycle Arrest
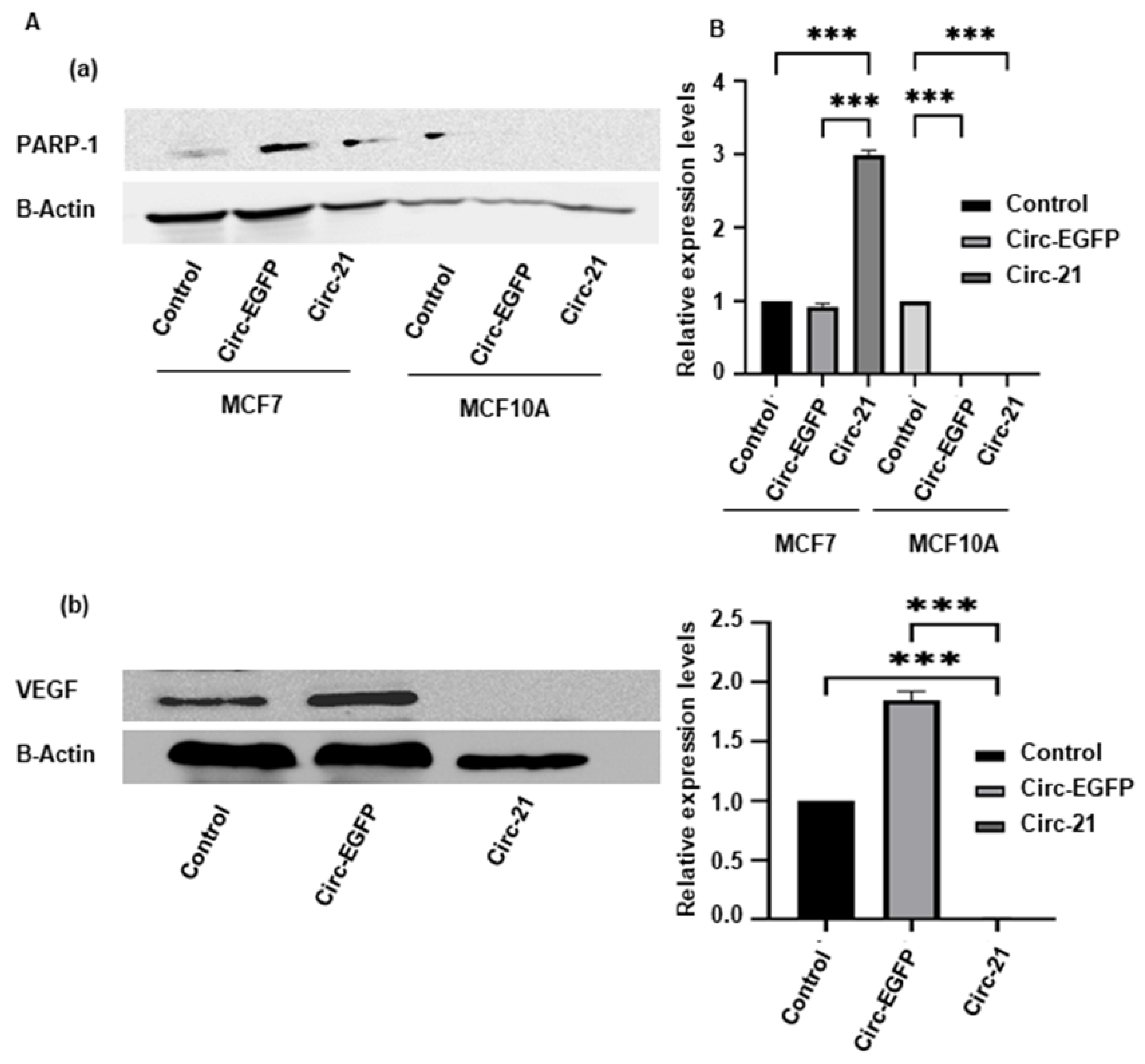
2.7. Western Blot
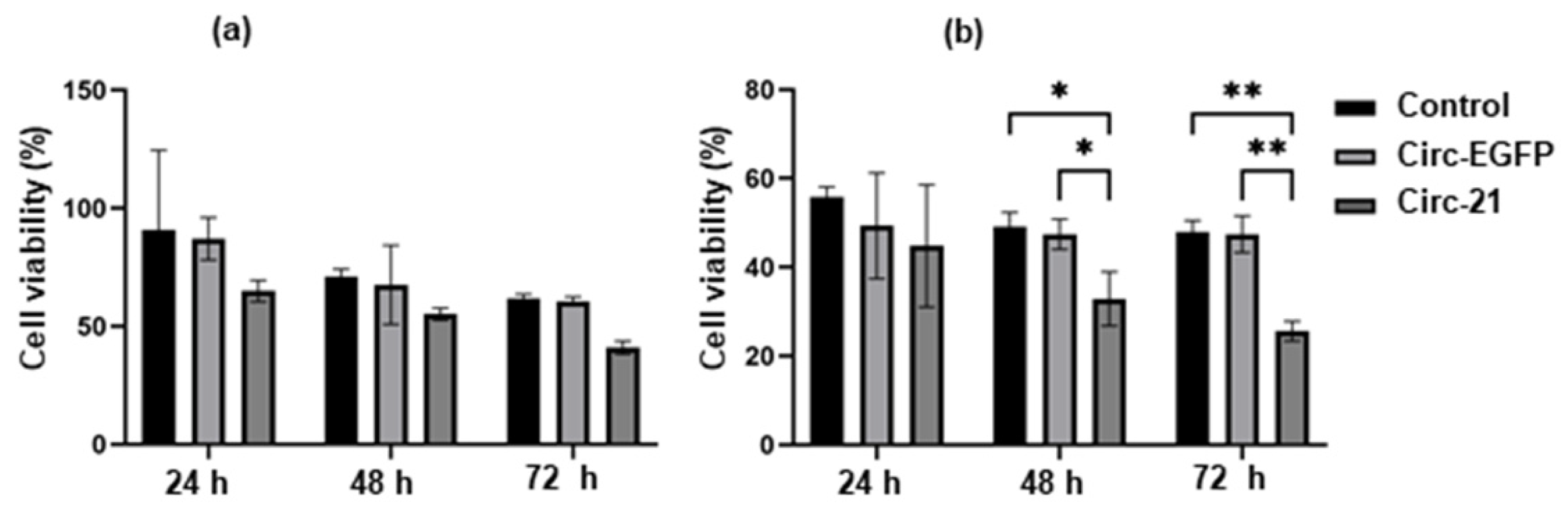
2.8. Combined the Circ-21-Doxorubicin Therapy Induced Growth Disturbance on Breast Cancer Cells
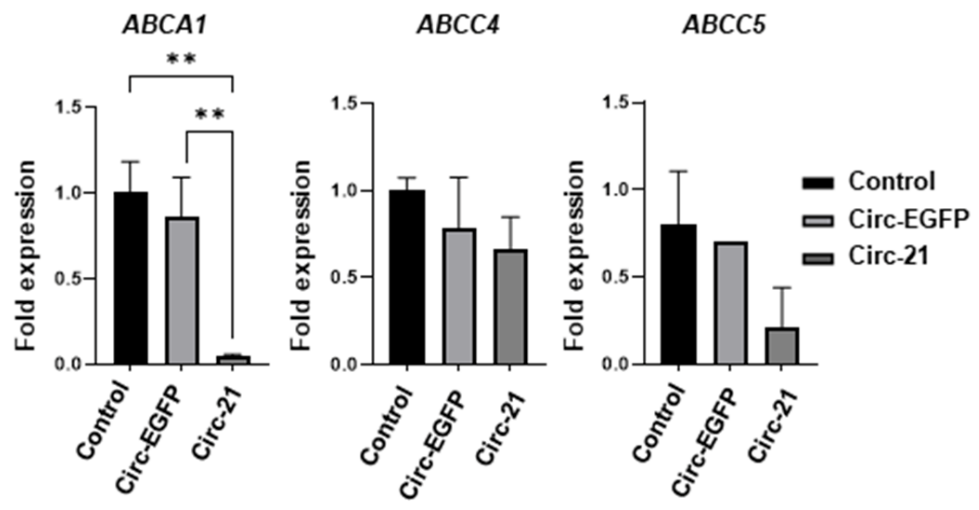
2.9. Resitance Gene
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. miR-21 Expression Levels
4.3. Sponge Expression Vector
4.4. Transfection of Cells
4.5. Detection of the Circ-21 Expression
4.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.7. Wound Healing Assay
4.8. Colony Formation
4.9. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Combined Treatment
4.12. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Houghton, S.C.; Hankinson, S.E. Cancer progress and priorities: Breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 822–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soe, Z.C.; Kwon, J.B.; Thapa, R.K.; Ou, W.; Nguyen, H.T.; Gautam, M.; Oh, K.T.; Choi, H.G.; Ku, S.K.; Yong, C.S.; et al. Transferrin-conjugated polymeric nanoparticle for receptor-mediated delivery of doxorubicin in doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebigil, C.G.; Désaubry, L. Updates in anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Hassan, M.I.; Gupta, D.; Dwivedi, N.; Islam, A. Design and evaluation of pyrimidine derivatives as potent inhibitors of ABCG2, a breast cancer resistance protein. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, P.; Deng, M.; Huang, C.; Hu, T.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, M.; Hamon, Y.; Chimini, G. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Lauschke, V.M. Ethnogeographic and inter-individual variability of human ABC transporters. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 623–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobo-Albavera, L.; Domínguez-Pérez, M.; Medina-Leyte, D.J.; González-Garrido, A.; Villarreal-Molina, T. Molecular sciences the role of the ATP-binding cassette A1 (ABCA1) in human disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Di, D.; Chen, F. Expression of LXR β, ABCA1 and ABCG1 in human triple negative breast cancer tissues. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, F.G.; Shabir, K.; Brown, J.E.; Bill, R.M.; Rothnie, A.J. Roles of ABCC1 and ABCC4 in proliferation and migration of breast cancer cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russel, F.G.M.; Koenderink, J.B.; Masereeuw, R. Multidrug Resistance Protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4): A versatile efflux transporter for drugs and signalling molecules. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, F.; Chen, X.; Dong, L.-F.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Long, J.-P. A systemic analysis on pemetrexed in treating patients with breast cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 4567–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Janke, L.J.; Yang, J.J.; Evans, W.E.; Schuetz, J.D.; Relling, M.V. Differential effects of thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) and multidrug resistance-associated protein gene 4 (MRP4) on mercaptopurine toxicity. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Yin, Y.; Chen, T.; Chen, J.; Ge, M.; Lu, Y.; Xie, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y. Development of liposomal pemetrexed for enhanced therapy against multidrug resistance mediated by ABCC5 in breast cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourskaia, A.A.; Amir, E.; Dong, Z.; Tiedemann, K.; Cory, S.; Omeroglu, A.; Bertos, N.; Ouellet, V.; Clemons, M.; Scheffer, G.L.; et al. ABCC5 supports osteoclast formation and promotes breast cancer metastasis to bone. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wan, Y.; Yao, Y. MiRNA-21 promotes proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells through targeting PTEN. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Hagedorn, C.H.; Cullen, B.R. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as MRNAs. RNA 2004, 10, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, J.; Ni, X.; Castanares, M.; Liu, M.M.; Esopi, D.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Rodriguez, R.; Mendell, J.T.; Lupold, S.E. A novel source for miR-21 expression through the alternative polyadenylation of VMP1 gene transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 6821–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Min, M.; Zou, L.; Shen, P.; Zhu, Y. The clinical role of MicroRNA-21 as a promising biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Lin, T.; Pang, Q.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Tai, M.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Y.; Mao, P. Extracellular miRNA-21 as a novel biomarker in glioma: Evidence from meta-analysis, clinical validation and experimental investigations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, M.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, X.; Han, L.; Wang, G.; Jia, Z.; Pu, P.; Kang, C.; Yao, Z. Downregulation of miR-21 enhances chemotherapeutic effect of taxol in breast carcinoma cells. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 9, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mattos-Arruda, L.; Bottai, G.; Nuciforo, P.G.; di Tommaso, L.; Giovannetti, E.; Peg, V.; Losurdo, A.; Pérez-Garcia, J.; Masci, G.; Corsi, F. MicroRNA-21 links epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inflammatory signals to confer resistance to neoadjuvant trastuzumab and chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, Y.; Ma, H. Combined aspirin and apatinib treatment suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5409–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, G. Downregulation of MiR-21 inhibits the malignant phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting VHL. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, P.; Xiao, X.; Hu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Q. MicroRNA-21 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration of human bronchial epithelial cells by targeting poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerase-1 and activating PI3K/AKT signaling. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 26, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, S.; Wu, D.; Qian, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Q. MiR-21 modulates proliferation and apoptosis of human airway smooth muscle cells by regulating autophagy via PARP-1/AMPK/MTOR signalling pathway. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2022, 301, 103891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-X.; Lu, B.-B.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Z.-X.; Yin, Y.-M. MicroRNA-21 modulates chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by targeting PTEN. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, K.K.; Kjems, J.; Hansen, T.B. Circular RNAs: Identification, biogenesis and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, A.R.; Perazzoli, G.; Cabeza, L.; Mesas, C.; Quiñonero, F.; García-Pinel, B.; Vélez, C. Novel microRNA sponges to specifically modulate gene expression in colon cancer cells. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2020, 30, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama, A.R.; Quiñonero, F.; Mesas, C.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J. Synthetic circular miR-21 sponge as tool for lung cancer treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentze, M.W.; Preiss, T. Circular RNAs: Splicing’s enigma variations. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obi, P.; Chen, Y.G. The design and synthesis of circular RNAs. Methods 2021, 196, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadder, N.J.; Giridhar, K.V.; Baffy, N.; Riegert-Johnson, D.; Couch, F.J. Hereditary cancer syndromes—A primer on diagnosis and management: Part 1: Breast-ovarian cancer syndromes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.X.; Wu, Q.N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Liao, D.Z.; Hou, J.H.; Fu, J.; Zeng, M.S.; Yun, J.P.; Wu, Q.L. Knockdown of miR-21 in human breast cancer cell lines inhibits proliferation, in vitro migration and in vivotumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tan, Z.; Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, T.; Zheng, C.; Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, S. MicroRNA-21 promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting LZTFL1. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Dreyfuss, G.; Eddy, S.R.; Griffiths-Jones, S.A.M.; Marshall, M. A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 2003, 9, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karedath, T.; Al-Dasim, F.M.; Ahmed, I.; Al-Qurashi, A.; Raza, A.; Andrews, S.S.; Ahmed, A.A.; Ali Mohamoud, Y.; Dermime, S.; Malek, J.A. Regulation of circular RNA CircNFATC3 in cancer cells alters proliferation, migration, and oxidative phosphorylation. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 595156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Leng, K.; Ji, D.; Qu, L.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Increased expression of circular RNA Circ_0005230 indicates dismal prognosis in breast cancer and regulates cell proliferation and invasion via MiR-618/CBX8 Signal pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1710–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.U.; Jing, W.; Luo, P.; Qiu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, M.; Liang, C.; Yu, M.; Tu, J. The circular RNA Hsa_circ_0001445 regulates the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma and may serve as a diagnostic biomarker. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 3073467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, S.; Luo, P.; Zhou, H.; Jing, W.; Liang, C.; Tu, J. Down-regulation of Hsa_circ_0001649 in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts a poor prognosis. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 22, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Fan, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, W. Maspin inhibits MCF 7 cell invasion and proliferation by downregulating MiR 21 and increasing the expression of its target genes. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chu, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. MiR-21 promotes cell migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting KLF5. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yuan, M.; Xian, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, D.; Cheng, Y. Promotion of ovarian cancer cell invasion, migration and colony formation by the miR 21/Wnt/CD44v6 pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.; Nie, Y.-J. Exploration of the regulatory effect of miR-21 on breast cancer cell line proliferation and invasion as well as the downstream target genes. Asian. Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, C.; Li, H. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro tumor-suppressive effect of anti-miR-21-equipped RNA nanoparticles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 558, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Dong, Z.; Yang, L.; Gong, Z. MiR-21 induces cell cycle at S phase and modulates cell proliferation by down-regulating HMSH2 in lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magura, J.; Moodley, R.; Mackraj, I. The effect of hesperidin and luteolin isolated from Eriocephalus Africanus on apoptosis, cell cycle and miRNA expression in MCF-7. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Tian, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X. MiRNA oligonucleotide and sponge for miRNA-21 inhibition mediated by PEI-PLL in breast cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 2015, 25, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Song, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z. DNA nanosponge for adsorption and clearance of intracellular miR-21 and enhanced antitumor chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 46604–46613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Yeom, C.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, S.; Lee, E.; Park, M.J.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, S.B.; Chang, S. Simultaneous inhibition of multiple oncogenic miRNAs by a multi-potent microRNA sponge. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.-N.; Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Deng, J.-L.; Li, Z.-X.; Zhu, Y.-S. LncRNA H19 is a major mediator of doxorubicin chemoresistance in breast cancer cells through a Cullin4A-MDR1 pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, S.; Wu, K.; Bai, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Ye, Q.; Xu, F.; Sun, H. Human drug efflux transporter ABCC5 confers acquired resistance to pemetrexed in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, F.; Dong, H.; Jia, X.; Guo, W.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Ju, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y. Functionalized graphene oxide mediated adriamycin delivery and miR-21 gene silencing to overcome tumor multidrug resistance in vitro. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grada, A.; Otero-Vinas, M.; Prieto-Castrillo, F.; Obagi, Z.; Falanga, V. Research techniques made simple: Analysis of collective cell migration using the wound healing assay. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, e11–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rama, A.R.; Lara, P.; Mesas, C.; Quiñonero, F.; Vélez, C.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J. Circular Sponge against miR-21 Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin against Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314803
Rama AR, Lara P, Mesas C, Quiñonero F, Vélez C, Melguizo C, Prados J. Circular Sponge against miR-21 Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin against Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314803
Chicago/Turabian StyleRama, Ana R., Patricia Lara, Cristina Mesas, Francisco Quiñonero, Celia Vélez, Consolación Melguizo, and Jose Prados. 2022. "Circular Sponge against miR-21 Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin against Breast Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314803
APA StyleRama, A. R., Lara, P., Mesas, C., Quiñonero, F., Vélez, C., Melguizo, C., & Prados, J. (2022). Circular Sponge against miR-21 Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin against Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314803





